Submitted:
07 November 2023
Posted:
07 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Modeling of Operating System for a Mobile Robot
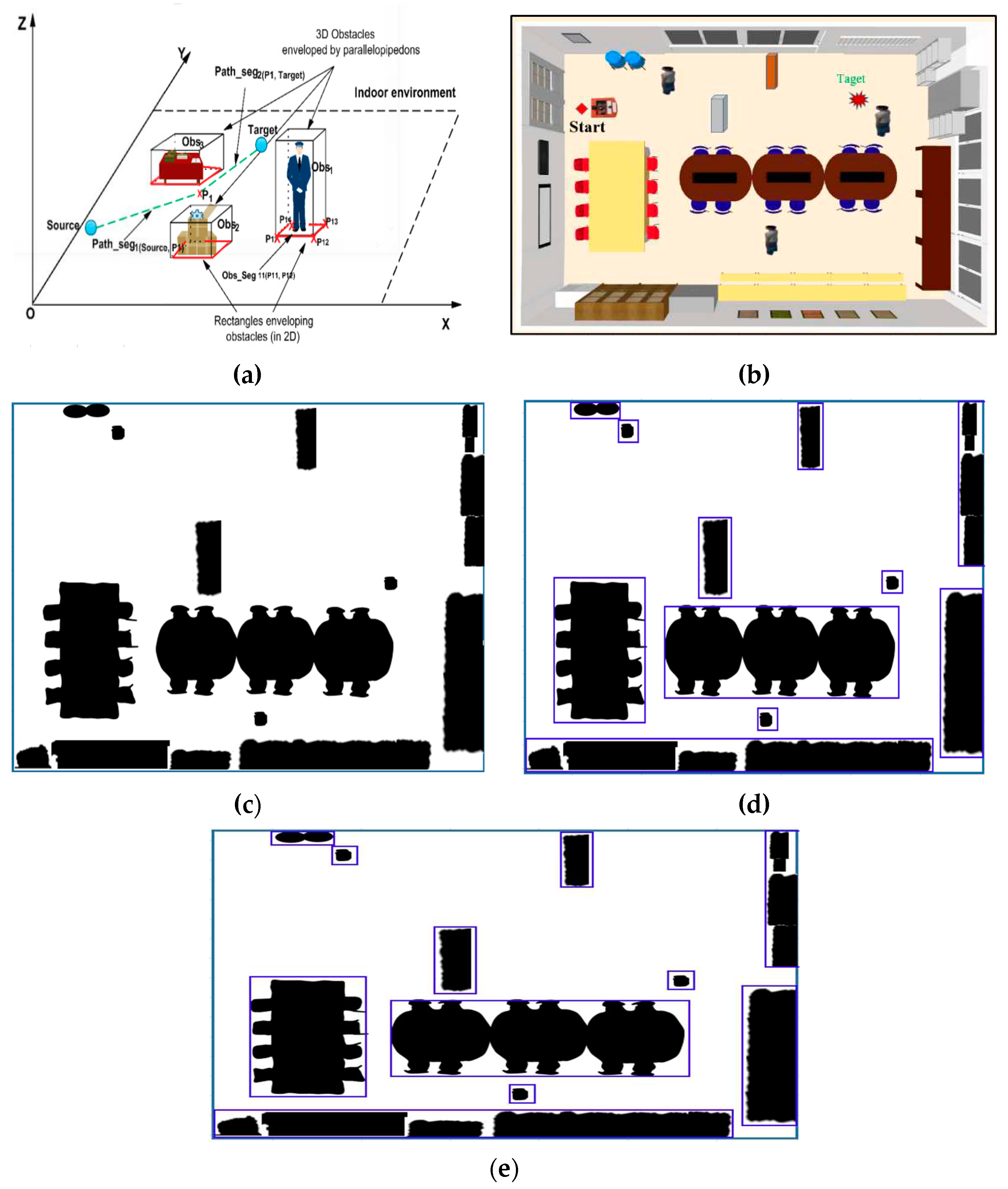
2.1. Obstacle Modeling in Mobile Robot Operating enviroment
2.2. Mathetical Model
- : fragment index generated by the node and + 1.
- : index of the obstacle in the navigation environment.
- : indices of the point that defines an obstacle.
- r(r∊{1…4}): index of segment r from the rectangle approximating the mobile robot.
- : index of the segment t that defines the rectangle of an obstacle.
- node of the path.
- obstacle.
- segment of the path defined by two nodes .
- segment of obstacle defined by two points ().
- CurrentPos: current location of the robot.
- segment of the rectangle approximating the robot.
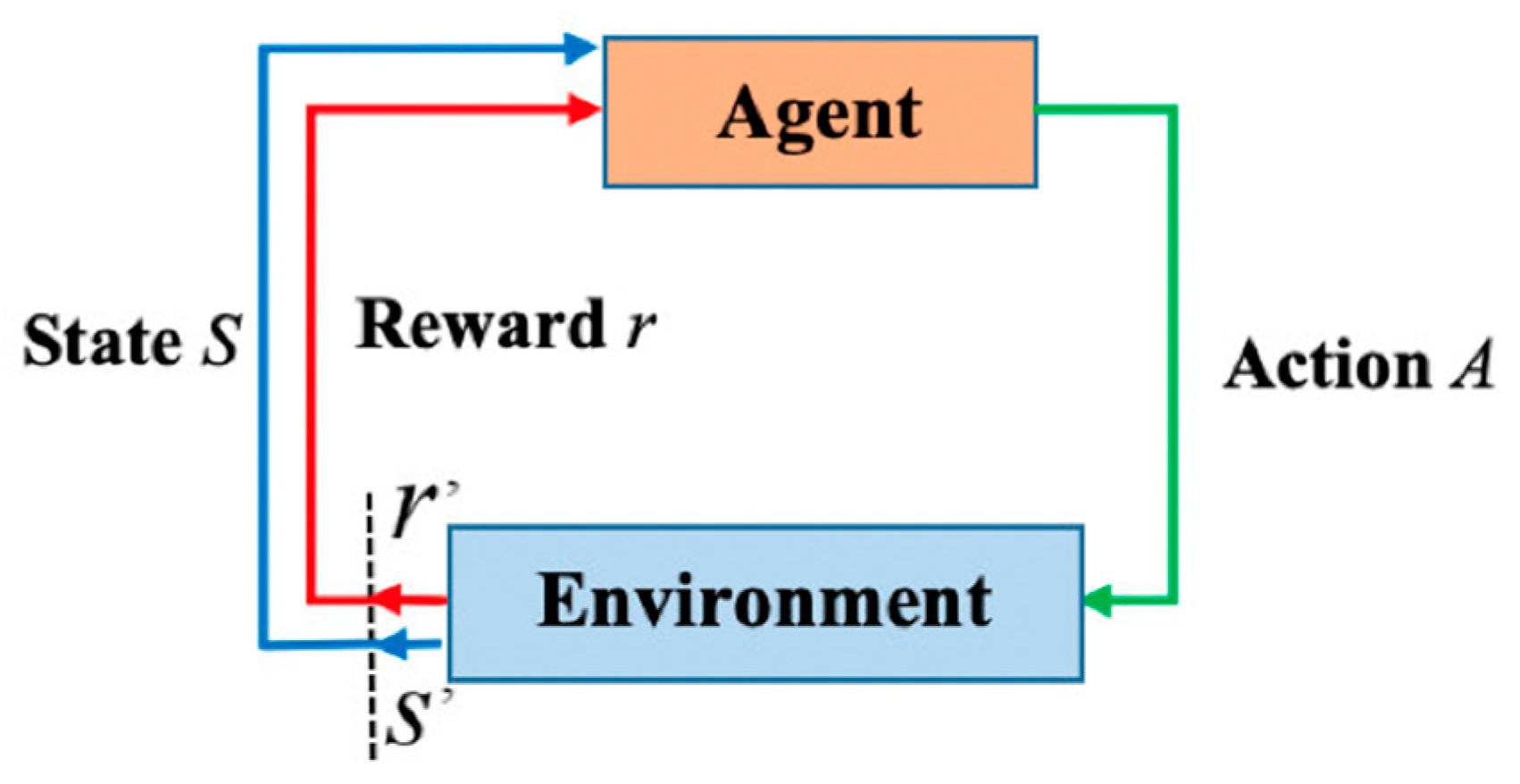
3. Deep Q-Learning and Q-Learning Alorithms in Path Planing for Mobile Robots
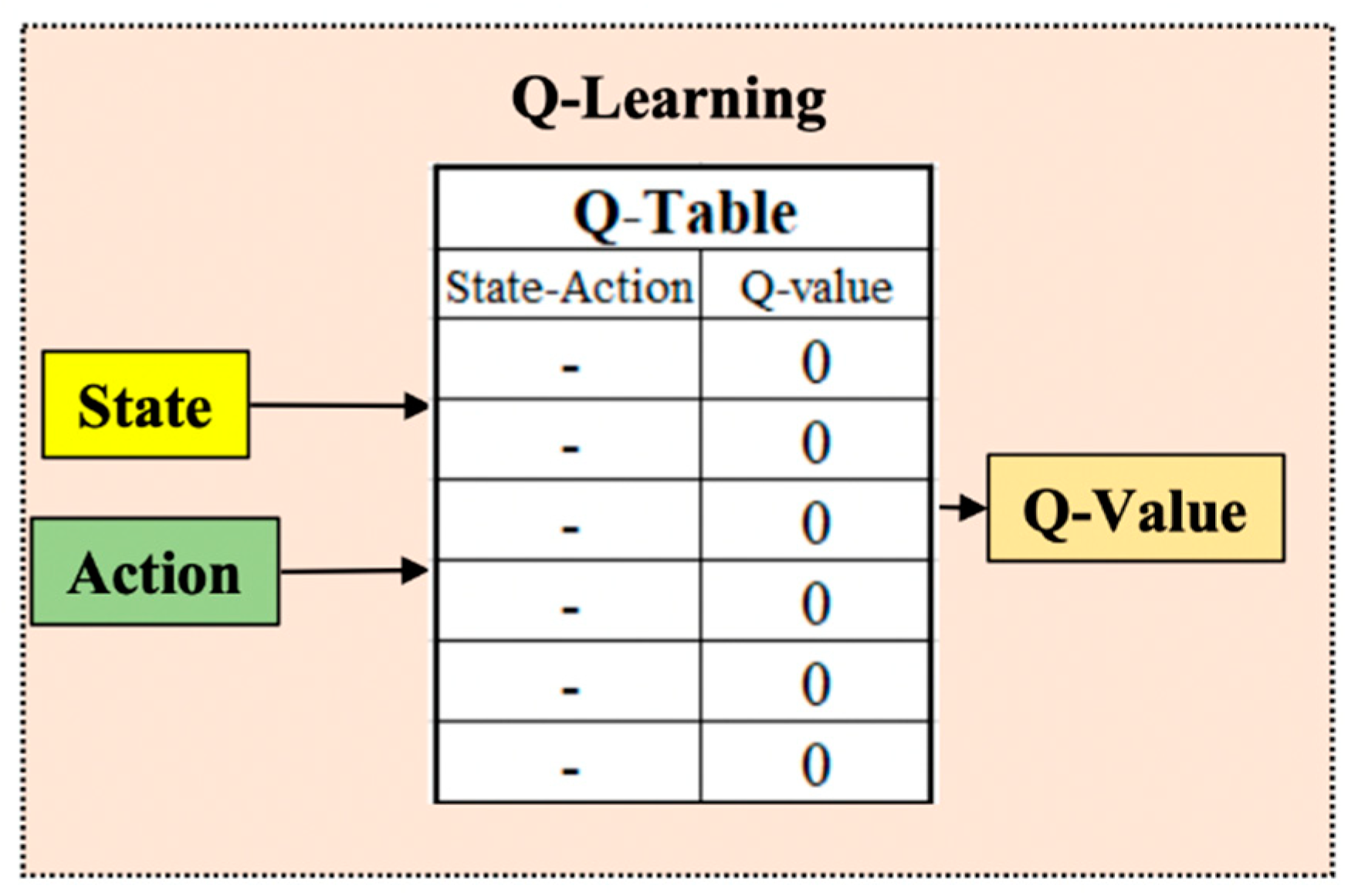
3.1. Q-Leaning
| Algorithm 1: Classical Q-Learning algorithm begin Initialization: |
|
, (states and 𝒎 actions) for (each episode):
end-while end-for end |
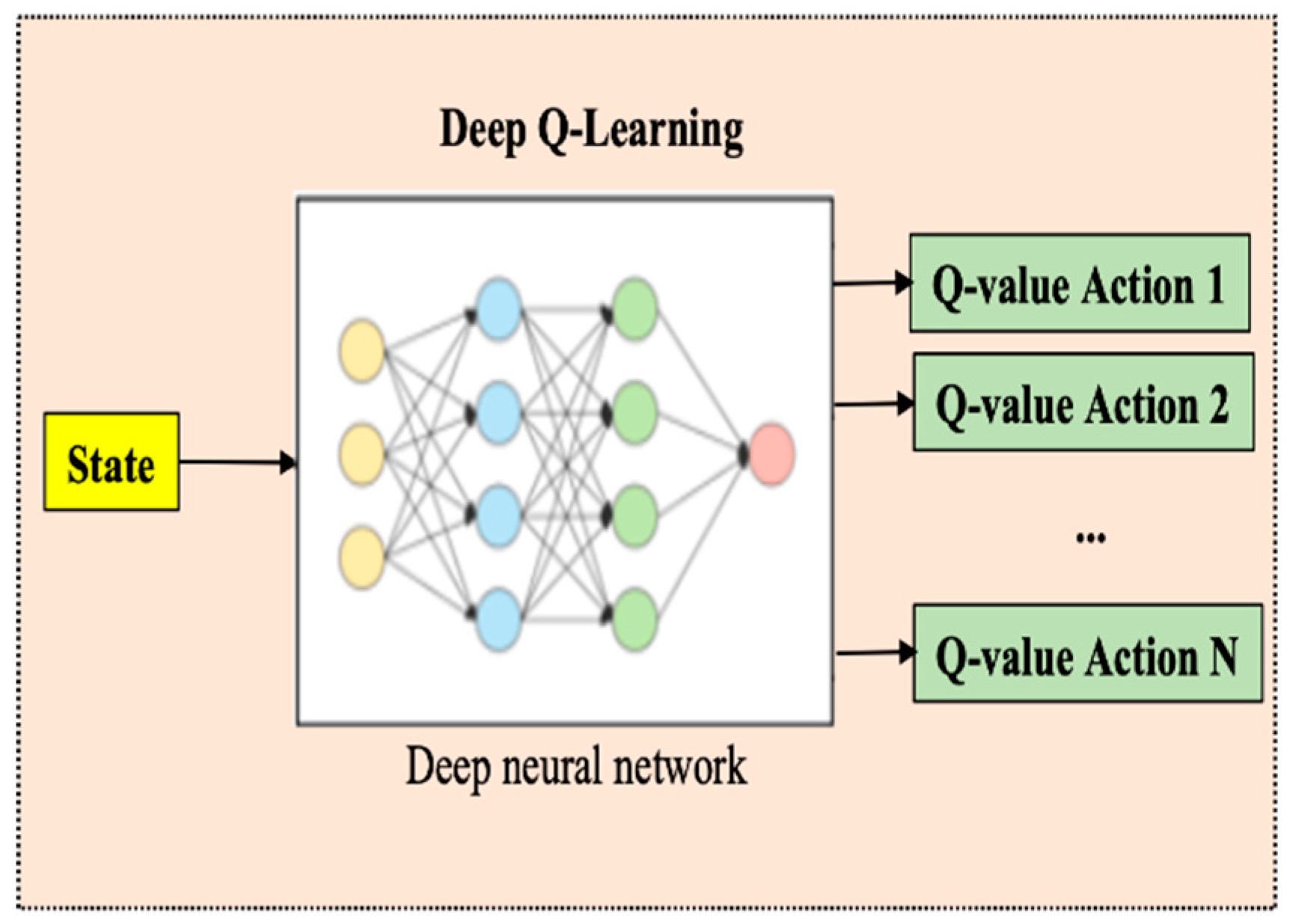
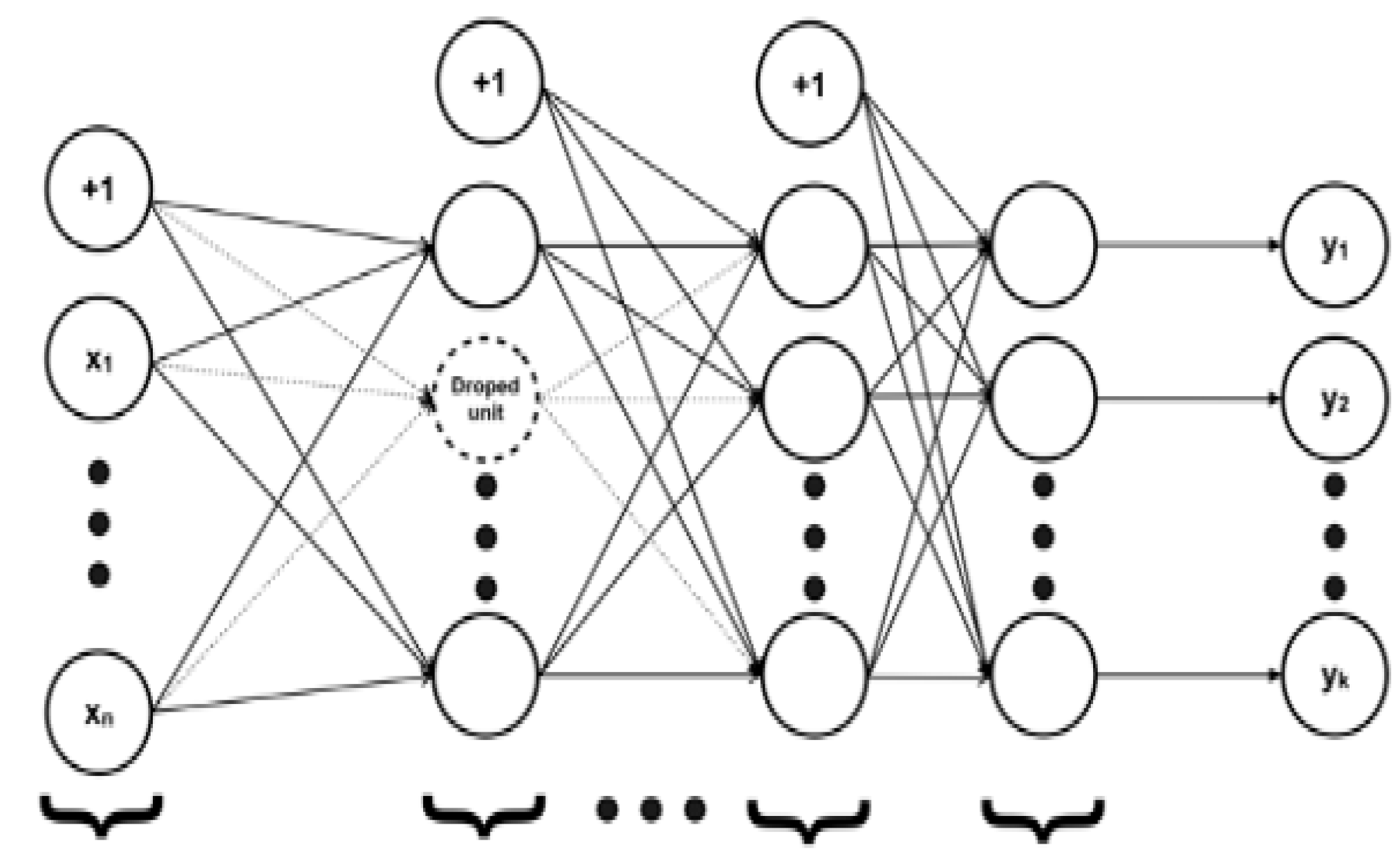
3.2. Deep Q-Leaning
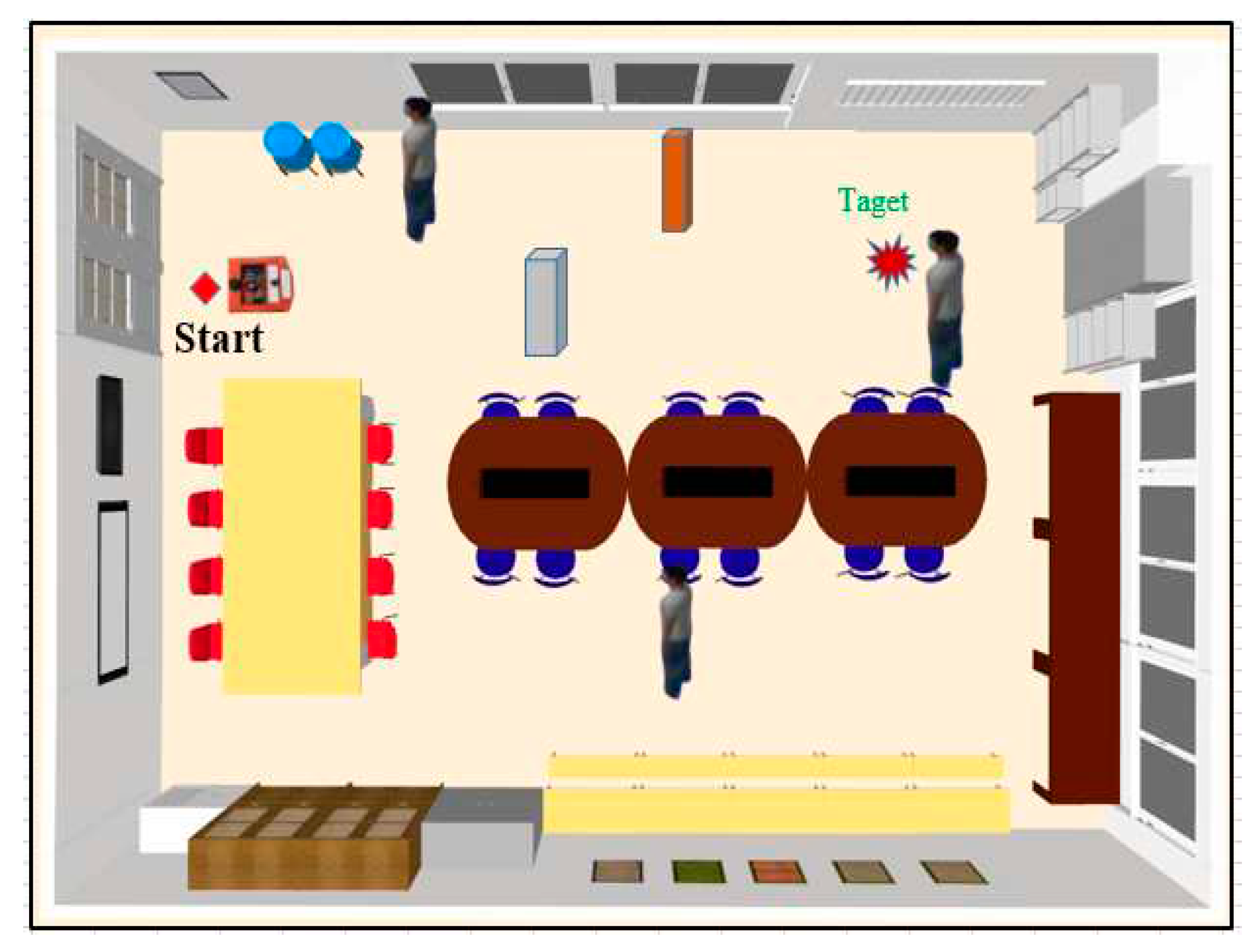
4. Simulation and Experimental Results
4.1. Set Status for a Mobile Robot
4.2. Set Action for a Mobile Robot
4.3. Set Up Reward for a Mobile Robot
4.4. Parameter Setting for the Controller
| 6000(s) | Time step of 1 cycle | |
| 0.99 | The discount factor | |
| Learning speed | ||
| 1.0 | Probability of choosing a random action | |
| 0.99 | Reduction rate of epsilon. When a cycle ends epsilon decreases | |
| 0.05 | Minimum stats of epsilon | |
| Batch size | sixty-four | Activate a group of training templates |
| Train start | Sixty -four | Start of input training |
| Memory | Memory size |
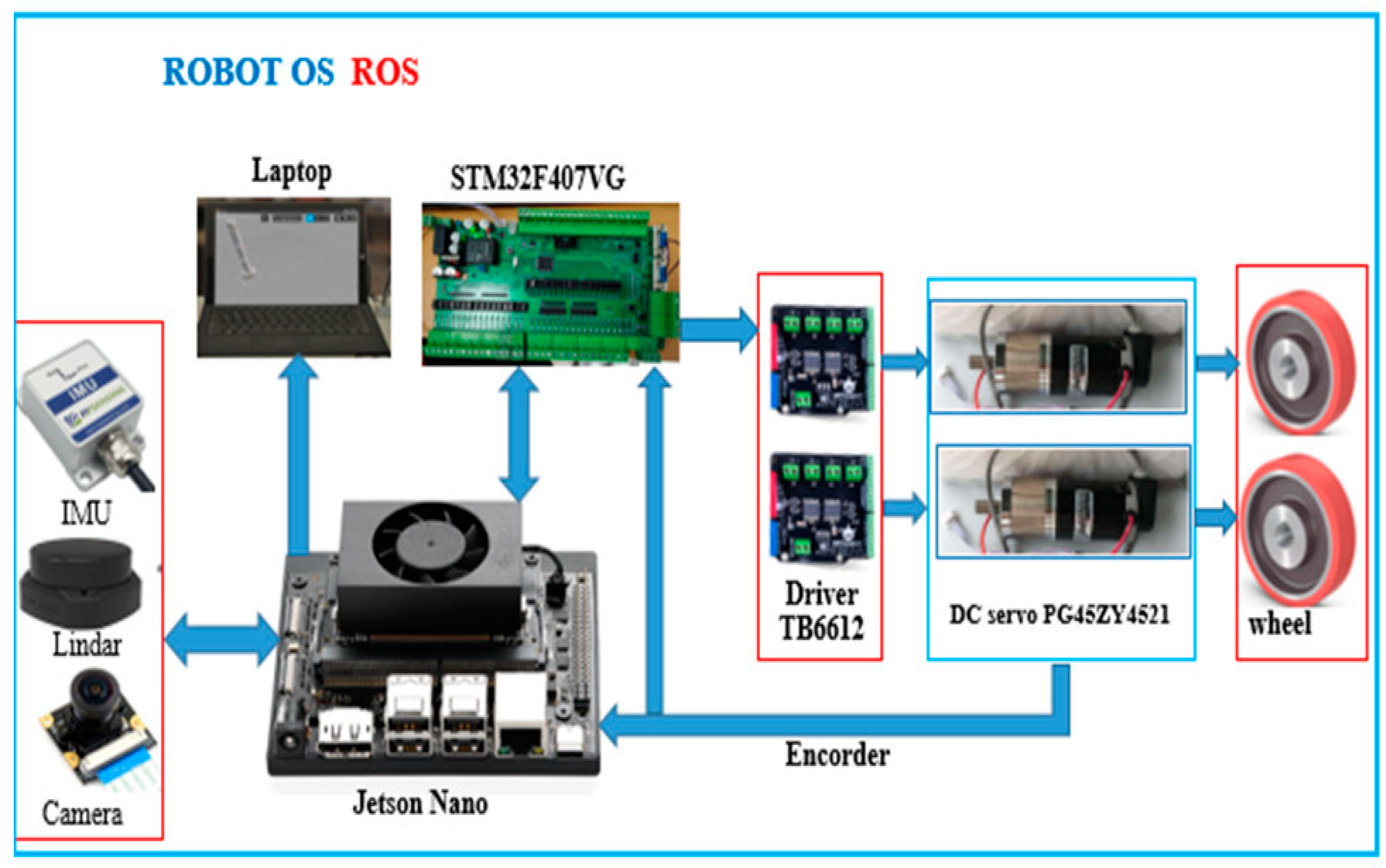
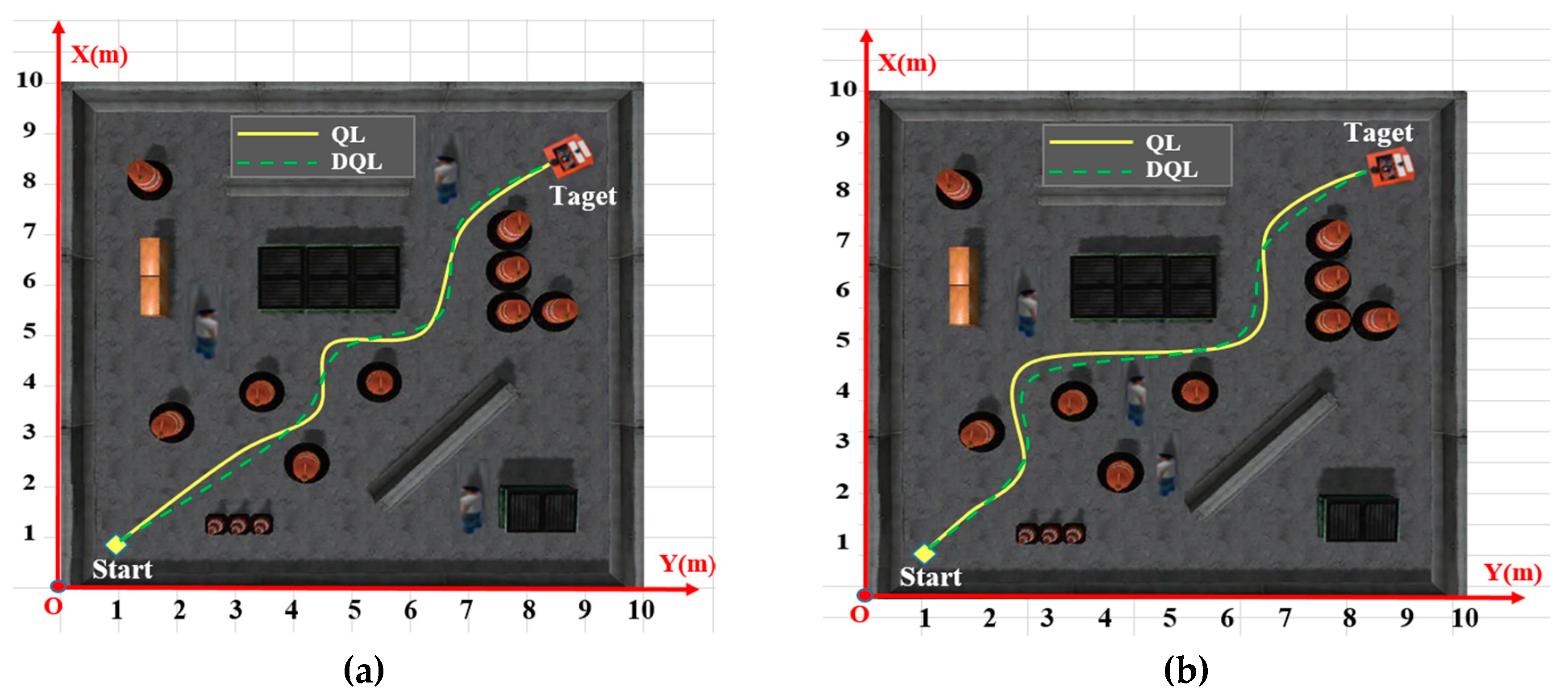
4.5. Simulation Results on ROS-GAZEBO
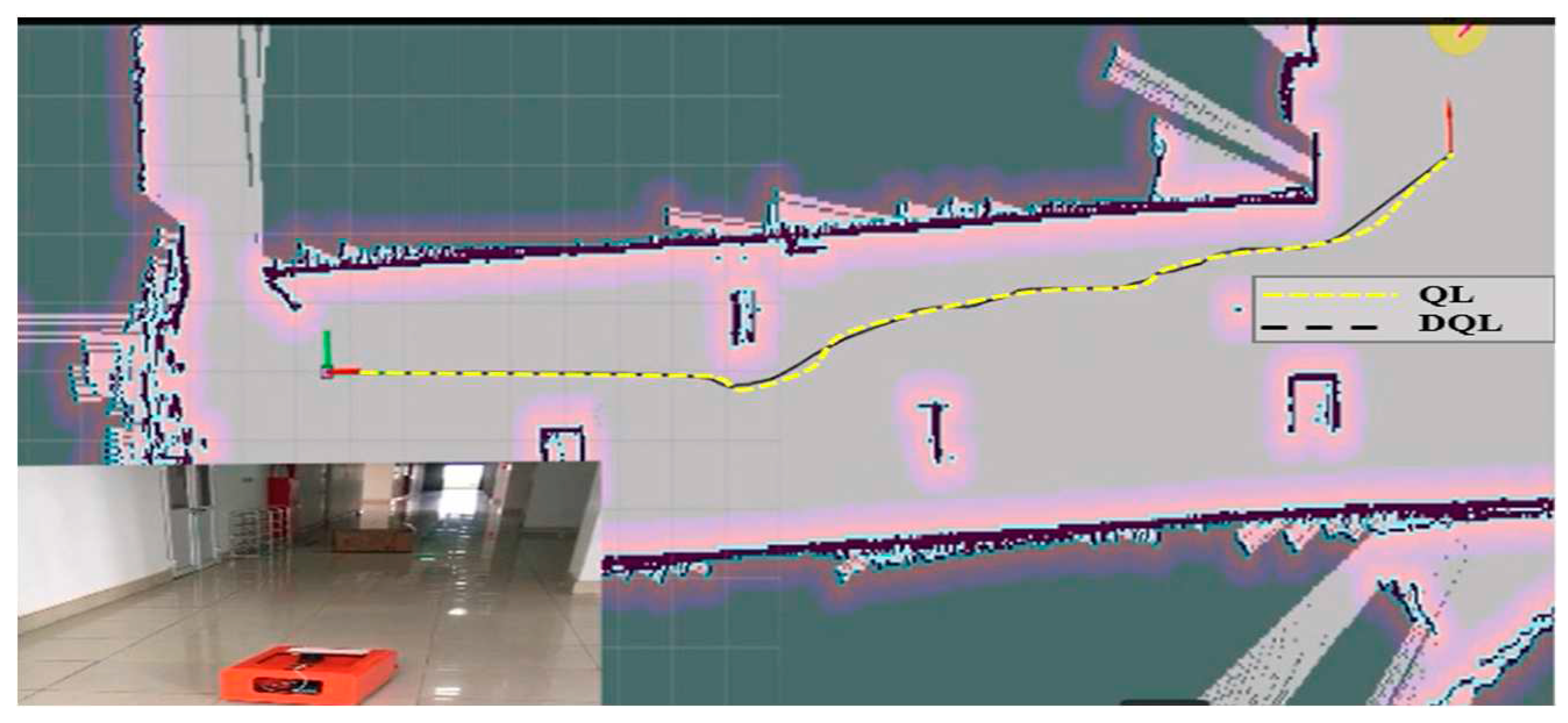
4.6. Experiment Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Path planning generator for autonomous mobile robots. Robots Auton Syst, 2012, 60: 651–656.
- Chaari I, Koubaa A, Trigui S, et al. SmartPATH: an efficient hybrid ACO-GA algorithm for solving the global path planning problem of mobile robots. Int J Adv Robot Syst, 2014, 11: 399-412.
- MS Gharajeh and HB Jond, ''An intelligent approach for autonomous mobile robot’s path planning based on adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system,'' Ain Shams Eng. J. May 2021. [CrossRef]
- MS Gharajeh and HB Jond, ''An intelligent approach for autonomous mobile robot’s path planning based on adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system,'' Ain Shams Eng. J. May 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. Zhang, L. C. Zhang, L. Zhou, Y. Li, and Y. Fan, ''A dynamic path planning method for social robots in the home environment,'' Electronics, vol. 9, no. 7, p. 1173, Jul. 2020.
- X. Yingqi, S. X. Yingqi, S. Wei, Z. Wen, L. Jingqiao, L. Qinhui, and S. Han, ''A real-time' dynamic path planning method combining artificial potential field method and biased target RRT algorithm,'' J. Phys., Conf. Ser, vol. 1905, no. first, May 2021, Art. no. 012015.
- B. Yang, J. B. Yang, J. Yan, Z. Cai, Z. Ding, D. Li, Y. Cao, and L. Guo, ''A novel heuristic emergency path planning method based on vector grid map,'' ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf, vol. 10, no. 6, p. 370, May 2021.
- S. Xiao, X. S. Xiao, X. Tan, and J. Wang, ''A simulated annealing algorithm and grid map-based UAV coverage path planning method for 3D reconstruction,'' Electronics vol. 10, no. 7, p. 853, Apr. 2021.
- T. Lin, ''A path planning method for mobile robot based on A and antcolony algorithms,'' J. Innov. Soc. Sci. Res.vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 157-162, 2020.
- Jianming Guo; Liang Liu; Qing Liu; Yongyu Qu, “An Improvement of D* Algorithm for Mobile Robot Path Planning in Partial Unknown Environment” Print ISBN: 978-0-7695-3804-4. [CrossRef]
- Lai, X. , Wu, D., Wu, D., Li, JH and Yu, H. (2023), "Enhanced DWA algorithm for local path planning of mobile robot", Industrial Robot, Vol. 50 No. 1, pp. 186 194. [CrossRef]
- C. Zong, X. Han, D. Zhang, Y. Liu, W. Zhao, and M. Sun, ''Research on local path planning based on improved RRT algorithm,'' Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng, vol. 235, no. 8, pp. 2086–2100, Mar. 2021.
- Tsai, C.C.; Huang, H.C.; Chan, C.K. Parallel elite genetic algorithm and its application to global path planning for autonomous robot navigation. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 2011, 58, 4813–4821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saska M, Macaˇs M, Pˇreuˇcil L, et al. Robot path planning using particle swarm optimization of Ferguson splines. Print: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA). New York: IEEE Press, 2006. 833–839.
- 9 Raja P, Pugazhenthi S. On-line path planning for mobile robots in dynamic environments. Neural Netw World, 2012, 22: 67–83.
- Than Thi Thuong and Vo Thanh Ha, Adaptive Control For Mobile Robots Based On Inteligent Controller, Journal of Applied Science and Engineering, Vol. 27, No 5, Page 2481-2487.
- Than Thi Thuong, Vo Thanh Ha, and Le Ngoc Truc, Intelligent Control for Mobile Robots Based on Fuzzy Logic Controller, The International Conference on Intelligent Systems & Networks, ICISN 2023: Intelligent Systems and Networks pp 566–573.
- Chen, X.; Kong, Y.; Fang, X.; et al. A fast two-stage ACO algorithm for robotic path planning. Neural Computer Appl 2013, 22, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcaru, C.; Precup, R.E.; Iercan, D.; et al. Optimal robot path planning using gravitational search algorithm. Int J Artif Intell 2013, 10, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Duan, H.B. Path planning of unmanned aerial vehicle based on improved gravitational search algorithm. Sci China Technol Sci 2012, 55, 2712–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.B.; Qiao, P.X. Pigeon-inspired optimization: a new swarm intelligence optimizer for air robot path planning. Int J Intell Comput Cybern 2014, 7, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J. , Wang, Q., He, C., Jaffrès-Runser, K., Xu, Y., Li, Z., & Xu, Y. (2019). QMR: Q-learning based Multiobjective optimization Routing protocol for Flying Ad Hoc Networks. Computer Communications.
- Low, ES, Ong, P., & Cheah, KC (2019). Solving the optimal path planning of a mobile robot using improved Qlearning. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 115, 143-161.
- Luviano, D. , & Yu, W. (2017). Continuous-time path planning for multi-agents with fuzzy reinforcement learning. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 33(1), 491-501.
- Qu, C.; Gai, W.; Zhong, M.; Zhang, J. A novel reinforcement learning based gray wolf optimizer algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) path planning. Applied Soft Computing 2020, 89, 106099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, CJ, & Dayan, P. (1992). Q-learning. Machine learning, 8(3-4), 279-292.
- Jaradat, MAK, Al-Rousan, M., & Quadan, L. (2011). Reinforcement based mobile robot navigation in dynamic environment. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 27(1), 135-149.
- Ganapathy, V. , Yun, SC, & Joe, HK (2009, July). Neural Q-learning controller for mobile robot. In 2009 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (pp. 863-868).
- Oh, CH, Nakashima, T., & Ishibuchi, H. (1998, May). Initialization of Q-values by fuzzy rules for hastening Qlearning. In 1998 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks Proceedings. IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence (Cat. No. 98CH36227) (Vol. 3, pp. 2051-2056). IEEE.
- Jiang, J. , & Xin, J. (2019). Path planning of a mobile robot in a free-space environment using Q-learning. Progress in Artificial Intelligence, 8(1), 133-142.
- ] Wang, YH, Li, THS, & Lin, CJ (2013). Backward Q-learning: The combination of Sarsa algorithm and Qlearning. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 26(9), 2184-2193.
- Das, PK, Mandhata, SC, Behera, HS, & Patro, SN (2012). An improved Q-learning algorithm for pathplanning of a mobile robot. International Journal of Computer Applications, 51(9).
- Goswami, I. , Das, PK, Konar, A., & Janarthanan, R. (2010, December). Extended Q-learning algorithm for pathplanning of a mobile robot. In Asia-Pacific Conference on Simulated Evolution and Learning (pp. 379-383). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
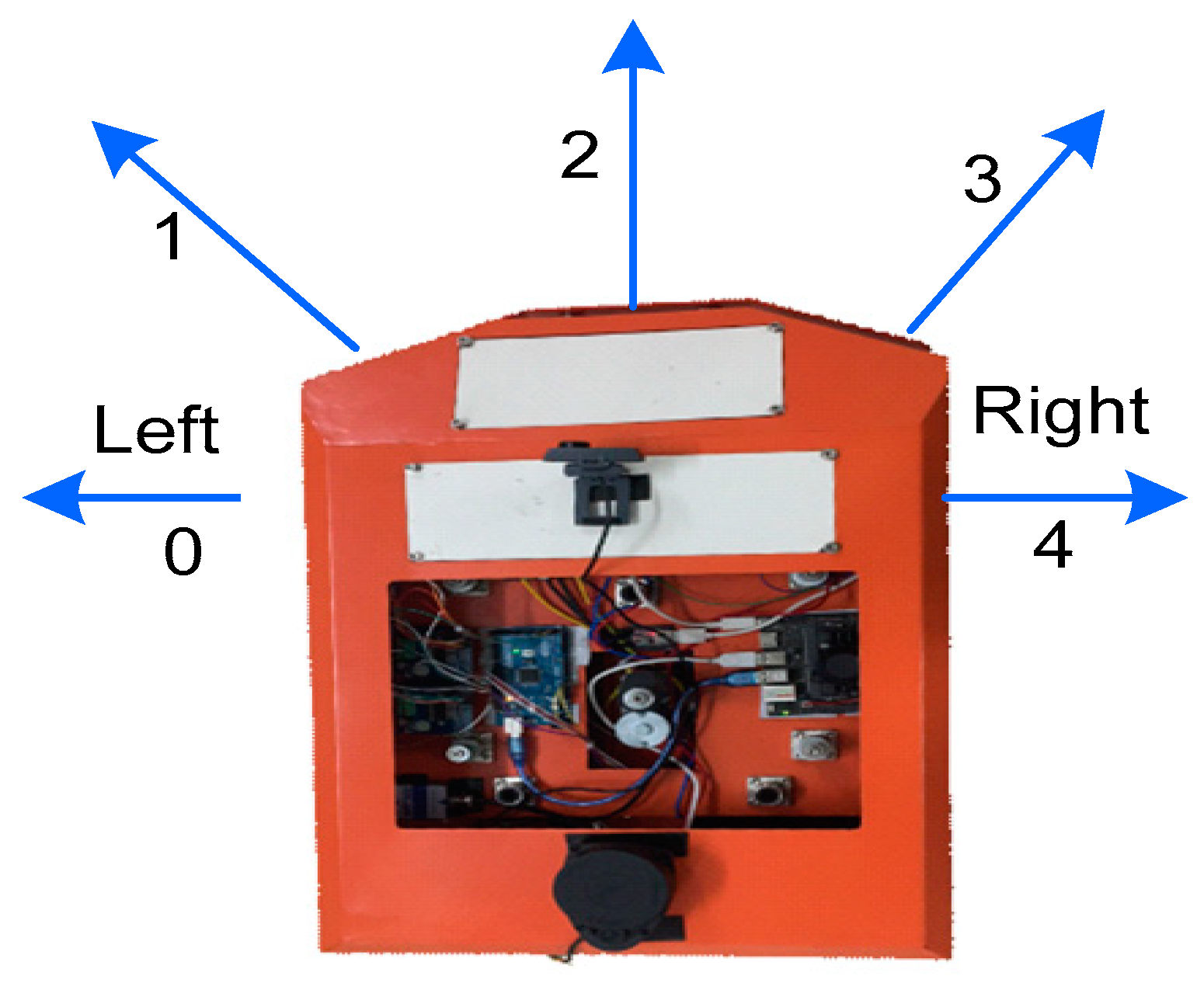



| Action | Angular velocity |
|---|---|
| 0 | -1.5 |
| 1 | -0.75 |
| 2 | 0 |
| 3 | 0.75 |
| 4 | 1.5 |
| No | Algorithm | Case 1 | Case 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance (m) | Run time(s) | Distance (m) | Run time(s) | ||
| 1 | QL | 17.758 | 12.314 | 18.416 | 14.637 |
| 2 | DQL | 17.129 | 7.927 | 17.235 | 8.324 |
| No | Algorithm | Case 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distance (m) | Run time(s) | ||
| 1 | QL | 6.271 | 72.132 |
| DQL | 5.753 | 47.853 | |
| 2 | QL | 6.314 | 74.097 |
| DQL | 5.958 | 51.845 | |
| 3 | QL | 6.264 | 72.124 |
| DQL | 5.386 | 45.734 | |
| Case 2 | |||
| Distance (m) | Run time(s) | ||
| 1 | QL | 20.123 | 57.372 |
| DQL | 21.235 | 32.735 | |
| 2 | QL | 20.123 | 57.375 |
| DQL | 21.235 | 33.738 | |
| 3 | QL | 20.123 | 57.379 |
| DQL | 19.235 | 30.735 | |
| Case 3 | |||
| Distance (m) | Run time(s) | ||
| 1 | QL | 27.682 | 92.132 |
| DQL | 25.638 | 87.867 | |
| 2 | QL | 27.682 | 92.132 |
| DQL | 25.638 | 87.656 | |
| 3 | QL | 27.682 | 92.132 |
| DQL | 26.338 | 60.853 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





