Submitted:
03 November 2023
Posted:
07 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setting
2.2. Calculation of δ15N
2.3. Enzime Activities Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Biomass Production
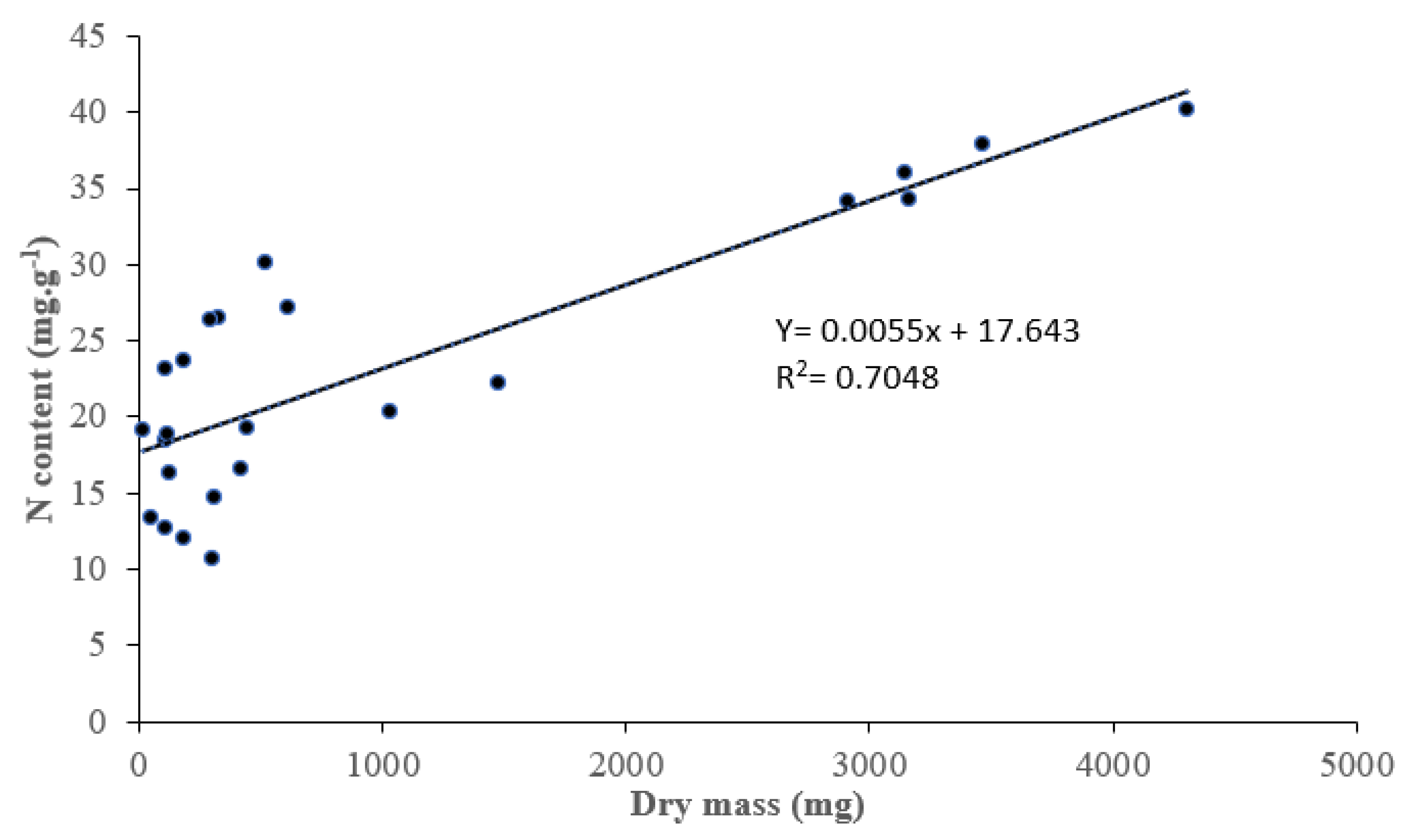
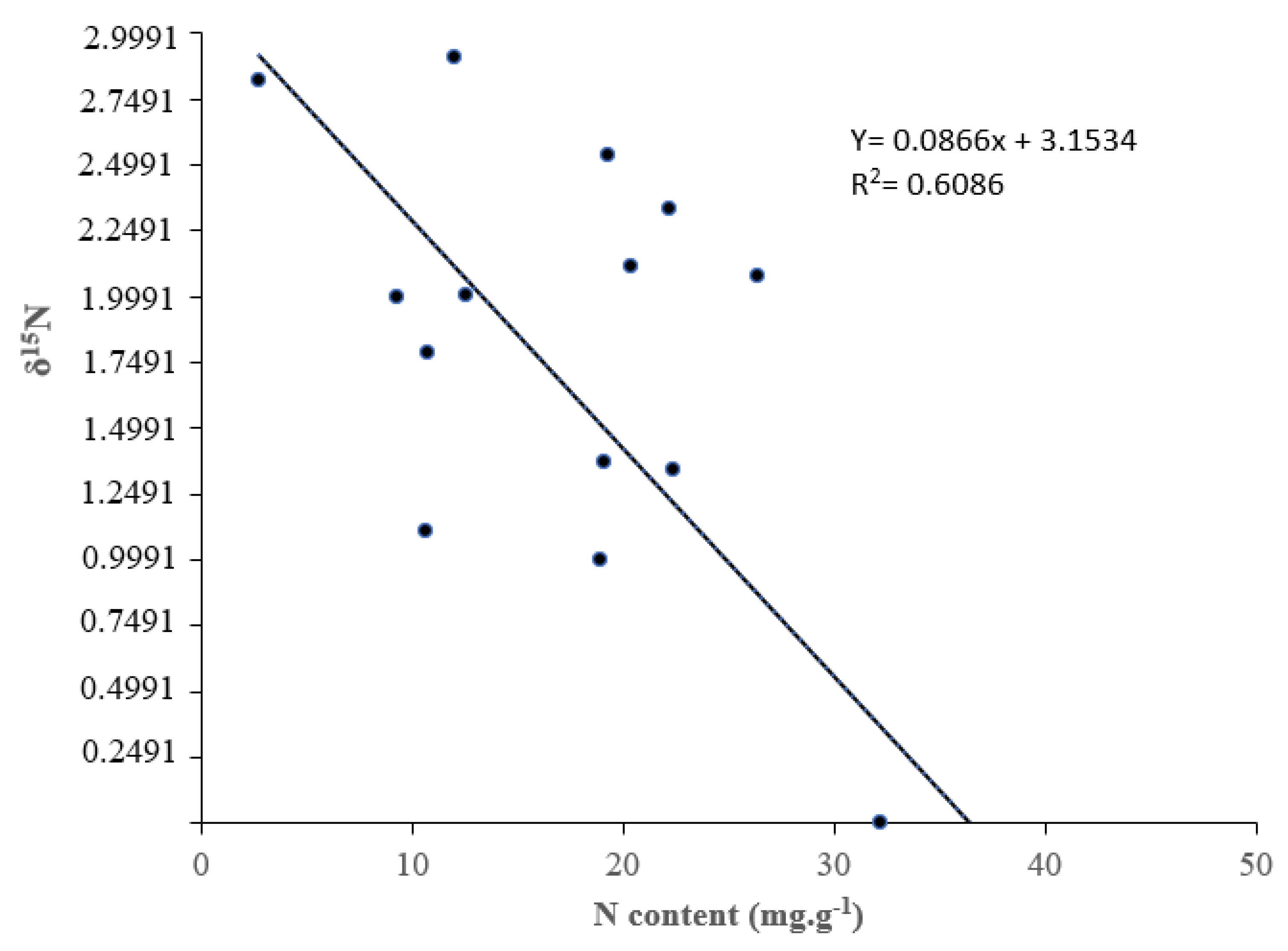
3.2. Nitrogen Concentrantions and Rhizobia Symbiotic Efficiency
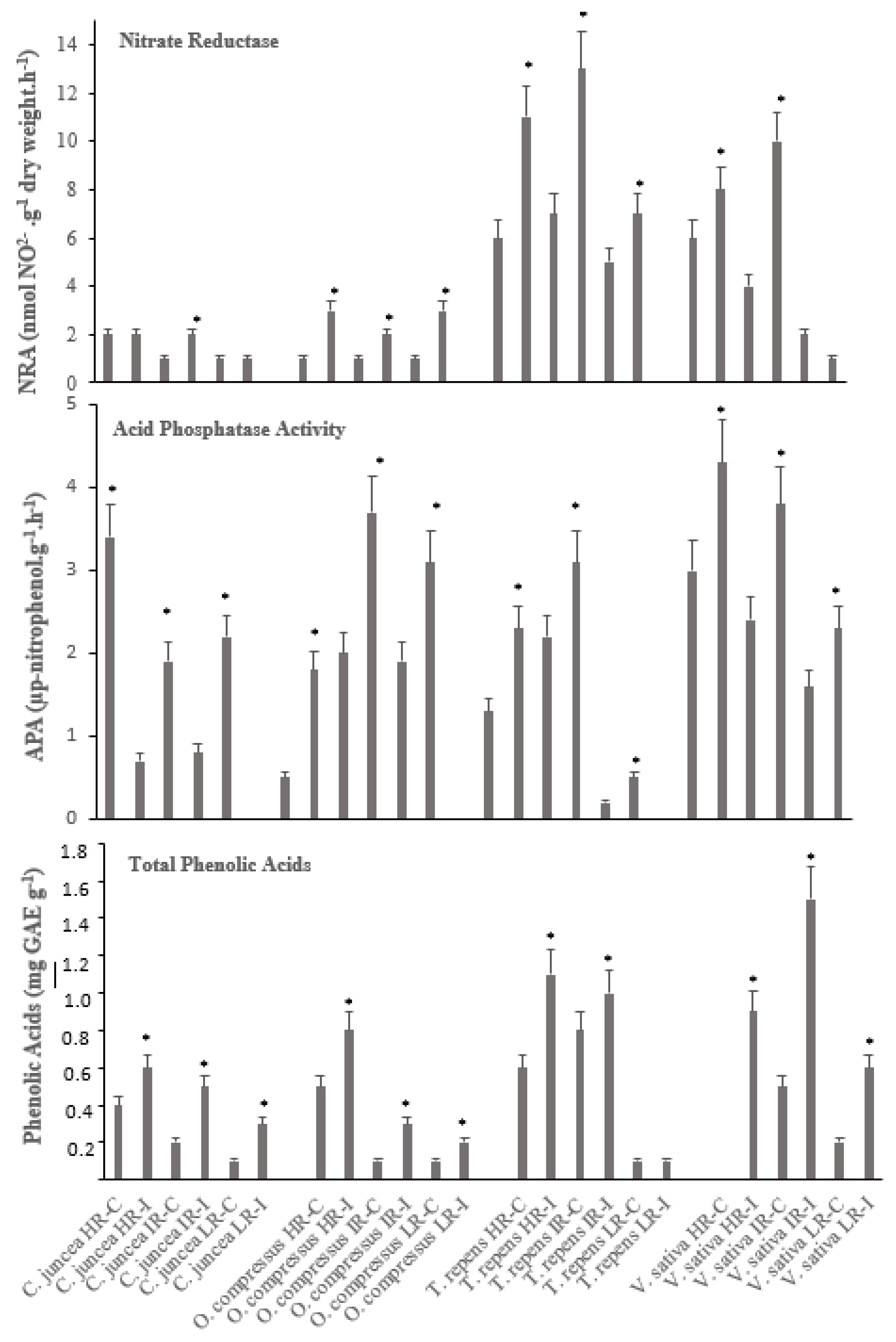
3.3. Enzymatic Activities
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kloepper, J. W.; & Ryu, C. M. J. Sustainable agriculture: The emerging role of rhizosphere bacteria. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2006, 4, 866–879. [Google Scholar]
- Taiz, L.; Zeiger, E.; Moller, I.M.; Murphy, A. (2017) Plant Physiology and Development. 6th Edition, Artmed, Porto Alegre, 858 p.
- Gazolla-Neto, A.; Aumonde, T. Z.; Pedó, T.; Olsen, D. Ação de níveis de luminosidade sobre o crescimento de plantas de maria-pretinha (Solanum americanum Mill). 2013; 11. [Google Scholar]
- De Lara-Del Rey, I.A.; Pérez-Fernández, M.A. Regulatory Effect of Light and Rhizobial Inoculation on the Root Architecture and Plant Performance of Pasture Legumes. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Martín, M. A.; Sauer, P. V.; Kirst, H.; Sutter, M.; Bína, D.; Greber, B. J.; Nogales, E.; Polívka, T.; Kerfeld, C. A. Structures of a Phycobilisome in Light-Harvesting and Photoprotected States. Nature 2022, 609, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsanius, B.; Karlsson, M.; Rosberg, A.; Dorais, M.; Naznin, M.; Khalil, S.; Bergstrand, K.-J. Light and Microbial Lifestyle: The Impact of Light Quality on Plant–Microbe Interactions in Horticultural Production Systems—A Review. Horticulturae 2019, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Domanski, G. Carbon Input by Plants into the Soil. Review. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2000, 163, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badri, D. V.; Vivanco, J. M. Regulation and Function of Root Exudates. Plant Cell & Environment 2009, 32, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haichar, F. E. Z.; Santaella, C.; Heulin, T.; Achouak, W. Root Exudates Mediated Interactions Belowground. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2014, 77, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bais, H. P.; Weir, T. L.; Perry, L. G.; Gilroy, S.; Vivanco, J. M. THE ROLE OF ROOT EXUDATES IN RHIZOSPHERE INTERACTIONS WITH PLANTS AND OTHER ORGANISMS. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 233–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, T. M.; Klem, K.; Urban, O.; Jansen, M. A. K. Re-interpreting plant morphological responses to UV-B radiation. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2015; 38, 856–866. [Google Scholar]
- Bloom, A. J.; Chapin III, F. S.; & Mooney, H. A. (1985). Resource limitation in plants an economic analogy. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 1985, 16, 363–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milla, R.; Reich, P. B.; & Castro-Díez, P. Tri-trophic interactions in the context of climate change: Effects of psyllid herbivory on nitrogen acquisition and resource allocation in a fast-growing herb. Oikos 2008, 117, 1865–1877. [Google Scholar]
- Lambers, H.; Raven, J.; Shaver, G.; Smith, S. Plant Nutrient-Acquisition Strategies Change with Soil Age. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 2008, 23, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, R. P.; Finzi, A. C.; Bernhardt, E. S. Enhanced Root Exudation Induces Microbial Feedbacks to N Cycling in a Pine Forest under Long-term CO 2 Fumigation. Ecology Letters 2011, 14, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S. M.; Chakraborty, D.; Dey, S. Phenolic Acids Act as Signaling Molecules in Plant-Microbe Symbioses. Plant Signaling & Behavior 2010, 5, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainard, L. D.; Klironomos, J. N.; Hart, M. M. Differential Effect of Sample Preservation Methods on Plant and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal DNA. Journal of Microbiological Methods 2010, 82, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambers, H.; Mougel, C.; Jaillard, B.; Hinsinger, P. Plant-Microbe-Soil Interactions in the Rhizosphere: An Evolutionary Perspective. Plant Soil 2009, 321, 83–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A. Adaptation of Plants to High-Light Environments. Plant Ecology 2019, 214, 215–231. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, C. Shade as a Driver of Plant Adaptations to Low-Light Environments. Environmental Biology 2020, 145, 1611–1621. [Google Scholar]
- Lachica M., Aguilar A., Yánez J. Análisis foliar. Métodos utilizados en la Estación Experimental del Zaidín CSIC (II). An. Edaf. Agrobiol. 1973, 32, 1033–1047.
- Bouat, A. , Crouzet C. Notes techniques sur un appareil semiautomatique de clorage de l’azote et de certains composes volatiles. Ann. Agric. 1965, 16, 107–118. [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar, G.D.; Ehleringer, J.R.; Hubick, K.T. Carbon isotope discrimination and photosynthesis. Annual Review of Physiology Plant and Molecular Biology 1989, 40, 503–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer. G.; Kohl, D.H. N2-fixation in field settings: Estimations based on natural 15N abundance. Functional Plant Biology 1986, 13, 699–756. [Google Scholar]
- Langelaan, J. G.; Troelstra, S. R. Growth, Chemical Composition, and Nitrate Reductase Activity of Rumex Species in Relation to Form and Level of N Supply. Plant Soil 1992, 145, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streeter, J. G. Acid and alkaline phosphatase activities in roots of legumes. Plant Physiology 1985, 77, 610–614. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, V. L.; Orthofer, R.; & Lamuela-Raventós, R. M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of Folin-Ciocalteu reagent. Methods in Enzymology 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar]
- IBM SPSS Software. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/analytics/spss-statistics-software (accessed on 1 Nov 2023).
- Liu, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; & Li, X. Light intensity and rhizobial inoculation affect root morphology and exudation in soybean (Glycine max L.). Journal of Plant Physiology, 2021; 259, 153333.
- Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; &; Wang, Y. Light intensity-dependent effects of rhizobial inoculation on growth, photosynthesis, and nitrogen metabolism in soybean (Glycine max L.). Frontiers in Plant Science 2022, 13, 873180. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; & Zhang, F. Light intensity and rhizobial inoculation affect the growth, photosynthesis, and nitrogen metabolism of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2022; 21, 617–628. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, Y.; & Li, X. Light intensity affects the rhizosphere microbiome composition and nitrogen fixation in soybean-rhizobia symbiosis. Frontiers in Microbiology 2021, 12, 746538. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Han, J.; Sun, J.; &; Gao, Q. Light intensity affects the growth, physiological traits, and root exudates of soybean plants (Glycine max L.) inoculated with rhizobia. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2020; 152, 129–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Cui, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; & Zhang, F. Rhizobial inoculation enhances the tolerance of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) to salt stress under different light conditions. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023; 14, 1063596.
- Hussain, H. A.; Farooq, M.; Ashraf, M.; & Khan, M. I. R. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of drought tolerance in legumes: A review. Agronomy 2020, 10, 695. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.; Ali, S.; Hameed, A.; Farooq, M.; & Iqbal, N. Role of nitrate reductase activity in drought tolerance of legumes: A review. Plants 2022, 11, 348. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; & Yang, J. Nitrate reductase and its regulation in plants under abiotic stress. Frontiers in Plant Science 2022, 13, 858372. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Lu, L.; Chen, X.; &; Li, Z. Acid phosphatase activity and physiological responses of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) to salt stress and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus inoculation. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2022, 29, 43338–43353. [Google Scholar]
- Güsewell, S. N : P Ratios in Terrestrial Plants: Variation and Functional Significance. New Phytologist 2004, 164, 243–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapin, F. S. ; III, & Bloom, A. J. Phosphate absorption: A major component of nutrient acquisition for some wild plant communities. Oecologia 1981, 51, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Míguez-Montero, M.A.; Valentine, A.; Pérez-Fernández, M.A. Regulatory Effect of Phosphorus and Nitrogen on Nodulation and Plant Performance of Leguminous Shrubs. AoB Plants 2019, 12, plz047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Ma, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; &; Li, X. Rhizobial inoculation enhances the tolerance of soybean (Glycine max L.) to high light stress through modulating the antioxidant system and nitrogen metabolism. Frontiers in Plant Science 2021, 12, 657643. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, I.; & Dilkes, B. J. The plant mining strategy theory and its implications for plant evolution and nutrient cycling. Journal of Ecology 2018, 106, 1696–1704. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, H. A. , Farooq, M., Ashraf, M., & Khan, M. I. R. Physiological and molecular mechanisms of drought tolerance in legumes: A review. Agronomy 2020, 10, 695. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, A.E.; Barea, J.M.; McNeill, A.M.; Prigent-Combaret, C. Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant Soil 2009, 321, 305–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, F. S. The Mineral Nutrition of Wild Plants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1980, 11, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




