Submitted:
03 November 2023
Posted:
07 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Serum samples
2.2. Peptides Synthesis
2.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.4. Purification of RBM antibodies
2.5. Microscale thermophoresis (MST)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
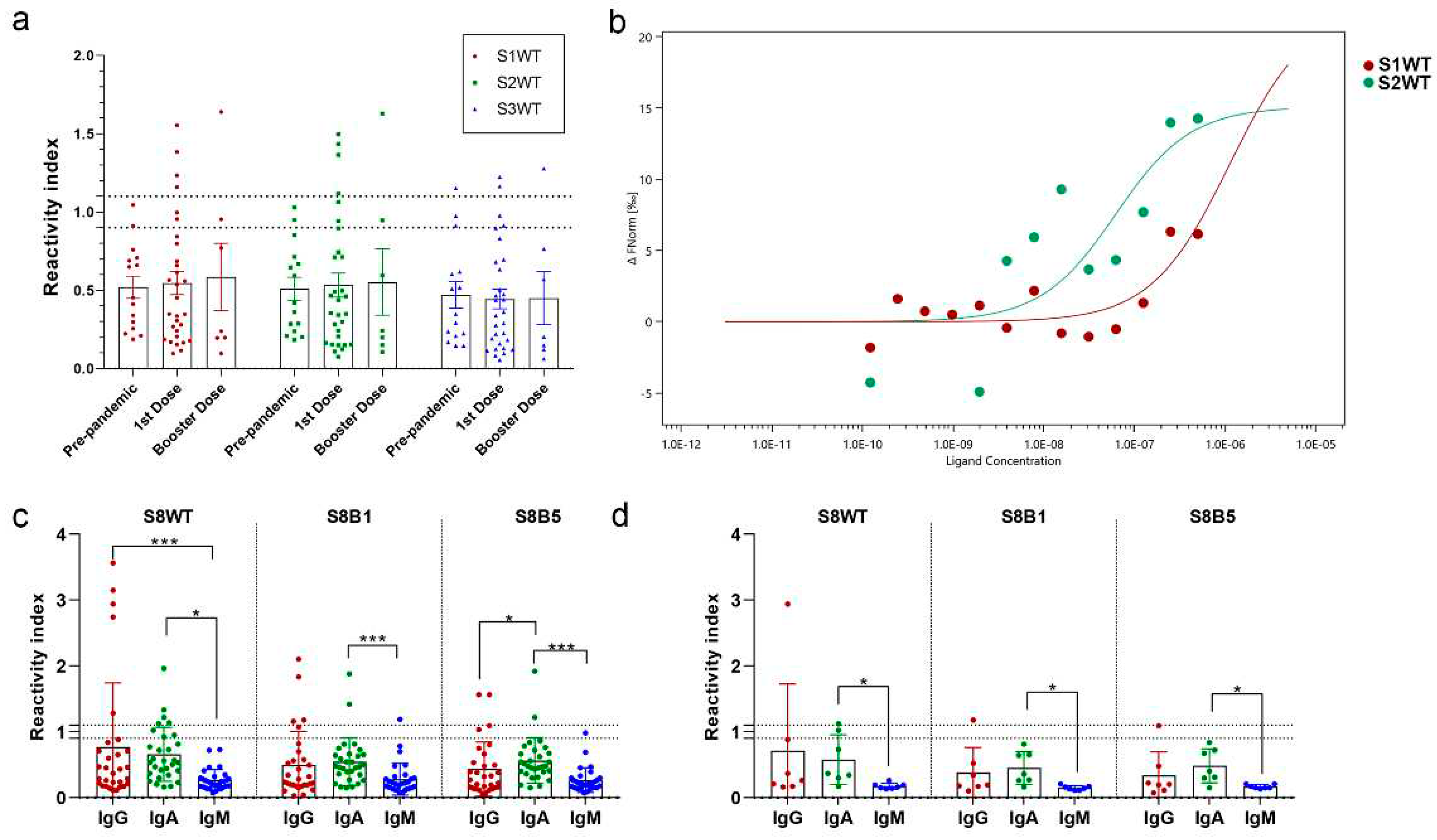
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
References
- Pal, M.; Berhanu, G.; Desalegn, C.; Kandi, V. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2): An Update. Cureus 2020, 12, e7423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenharo, M. WHO declares end to COVID-19’s emergency phase. Nature 2023, d41586-023-01559-z. [CrossRef]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A. COVID-19 genomics UK (COG-UK) Consortium; et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat Rev Microbiol 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Guo, Y.; Chan, J.F.-W.; Wang, M.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Chu, H.; Huang, Y.; Nair, M.S.; et al. Striking antibody evasion manifested by the omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2022, 602, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.; Yan, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, M.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, P.; Dong, Y.; Yang, Y.; et al. A Neutralizing human antibody binds to the n-terminal domain of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. Science 2020, 369, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Han, X.; Yan, J. Structure-based neutralizing mechanisms for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. Emerg Microbes Infect 2022, 11, 2412–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, L.; Park, Y.-J.; Tortorici, M.A.; Czudnochowski, N.; Walls, A.C.; Beltramello, M.; Silacci-Fregni, C.; Pinto, D.; Rosen, L.E.; Bowen, J.E.; et al. Mapping neutralizing and immunodominant sites on the SARS-CoV-2 Spike receptor-binding domain by structure-guided high-resolution serology. Cell 2020, 183, 1024–1042.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, A.; Harris, B.D.; Martinez-Sobrido, L.; Kobie, J.J.; Walter, M.R. Epitope classification and RBD binding properties of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. Front Immuno 2021, 12, 691715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, R.; Cloutier, M.; Prévost, J.; Fink, C.; Ducas, É.; Ding, S.; Dussault, N.; Landry, P.; Tremblay, T.; Laforce-Lavoie, A.; et al. Major Role of IgM in the Neutralizing Activity of Convalescent Plasma against SARS-CoV-2. Cell Rep 2021, 34, 108790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Q.-X.; Liu, B.-Z.; Deng, H.-J.; Wu, G.-C.; Deng, K.; Chen, Y.-K.; Liao, P.; Qiu, J.-F.; Lin, Y.; Cai, X.-F.; et al. Antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in patients with COVID-19. Nat Med 2020, 26, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, H.W.; Cavacini, L. Structure and function of immunoglobulins. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2010, 125, S41–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, A.; Beard, L.J.; Feldman, R.G. IgG subclass distribution of antibodies to bacterial and viral antigens. Ped Infect Dis J 1990, 9, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobova, Z.R.; Zueva, E.V.; Arsentieva, N.A.; Batsunov, O.K.; Liubimova, N.E.; Khamitova, I.V.; Kuznetsova, R.N.; Rubinstein, A.A.; Savin, T.V.; Stanevich, O.V.; et al. Changes in anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG subclasses over time and in association with disease severity. Viruses 2022, 14, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Casillas, A.; Redwan, E.M.; Uversky, V.N. Does SARS-CoV-2 induce IgG4 synthesis to evade the immune system? Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almanza, G.; Clark, A.E.; Kouznetsova, V.; Olmedillas, E.; Castro, A.; Tsigelny, I.F.; Wu, Y.; Gao, G.F.; Leibel, S.L.; Bray, W.; et al. Structure-selected RBM immunogens prime polyclonal memory responses that neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. PLoS Pathog 2022, 18, e1010686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratesi, F.; Errante, F.; Pacini, L.; Peña-Moreno, I.C.; Quiceno, S.; Carotenuto, A.; Balam, S.; Konaté, D.; Diakité, M.M.; Aréva-lo-Herrera, M.; et al. A SARS–CoV-2 spike receptor binding motif peptide induces anti-spike antibodies in mice and is recognized by COVID-19 patients. Front. Immunol 2022, 13, 879946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, S.; Wang, P. Broadly neutralizing antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses. Nat Rev Immunol 2023, 23, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Plante, K.S.; Plante, J.A.; Xie, X.; Zhang, X.; Ku, Z.; An, Z.; Scharton, D.; Schindewolf, C.; et al. The N501Y spike substitution enhances SARS-CoV-2 transmission. Nature 2022, 602, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, M.F.; Mohsen, M.O.; Zha, L.; Vogel, M.; Speiser, D.E. SARS-CoV-2 Structural features may explain limited neutralizing-antibody responses. npj Vaccines 2021, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Simone, S.G.; Gomes, L.R.; Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Lechuga, G.C.; de Pina, J.S.; da Silva, F.R. Epitope mapping of the diphtheria toxin and development of an ELISA-specific diagnostic assay. Vaccines (Basel) 2021, 9, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.R.; Durans, A.M.; Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Waterman, J.A.; Freitas, M.S.; De Sá, N.B.R.; Pereira, L.V.; Furtado, J.S.; Aquino, R.G.; Machado, M.C.R.; et al. Multiepitope proteins for the differential detection of IgG antibodies against RBD of the spike protein and non-RBD regions of SARS-CoV-2. Vaccines (Basel) 2021, 9, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechuga, G.C.; Napoleão-Pêgo, P.; Bottino, C.C.G.; Pinho, R.T.; Provance-Jr, D.W.; De-Simone, S.G. Trypanosoma cruzi prese-nilin-like transmembrane aspartyl protease: characterization and cellular localization. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Simone, S.G.; Nascimento, H.J.; Prado, I.C.; Aguiar, A.S.; Melgarejo, A.R.; Pina, J.L.S.; Ferreira, P.F.; Provance, D.W. Puri-fication of equine IgG3 by lectin affinity and an interaction analysis via microscale thermophoresis. Anal Biochem 2018, 561–562, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Med 2021, 27, 1205–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, M.F.; Mohsen, M.O.; Zha, L.; Vogel, M.; Speiser, D.E. SARS-CoV-2 Structural features may explain limited neutralizing-antibody responses. npj Vaccines 2021, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lai, D.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, H.; Tian, X.; Ma, M.; Qi, H.; Meng, Q.; Guo, S.; Wu, Y.; et al. Linear epitopes of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein elicit neutralizing antibodies in COVID-19 patients. Cell Mol Immunol 2020, 17, 1095–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Xie, C.; Bu, G.-L.; Zhong, L.-Y.; Zeng, M.-S. Molecular characteristics, immune evasion, and impact of SARS-CoV-2 variants. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupala, C.S.; Ye, Y.; Chen, H.; Su, X.-D.; Liu, H. Mutations on RBD of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant result in stronger binding to human ACE2 receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Communi 2022, 590, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Hotez, P.J.; Bottazzi, M.E. Potential for developing a SARS-CoV receptor-binding domain (RBD) recombinant protein as a heterologous human vaccine against coronavirus infectious disease (COVID)-19. Hum Vaccine Immunother 2020, 16, 1239–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chang, X.; Rothen, D.; Derveni, M.; Krenger, P.; Roongta, S.; Wright, E.; Vogel, M.; Tars, K.; Mohsen, M.O.; et al. AP205 VLPs based on dimerized capsid proteins accommodate RBM domain of SARS-CoV-2 and serve as an attractive vaccine candidate. Vaccines 2021, 9, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.; Ozturk, K.; Zanetti, M.; Carter, H. In silico analysis suggests less effective MHC-II Presentation of SARS-CoV-2 RBM Peptides: Implication for neutralizing antibody responses. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainio, O.; Toivanen, P.; Toivanen, A. Major histocompatibility complex and cell cooperation. Poul Sci 1987, 66, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lani, R.; Senin, N.A.; AbuBakar, S.; Hassandarvish, P. Knowledge of SARS-CoV-2 epitopes and population HLA types is important in the design of COVID-19 vaccines. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertinetto, F.E.; Magistroni, P.; Mazzola, G.A.; Costa, C.; Elena, G.; Alizzi, S.; Scozzari, G.; Migliore, E.; Galassi, C.; Ciccone, G.; et al. The humoral and cellular response to mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine is influenced by HLA polymorphisms. HLA 2023, 102, 301–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentzer, A.J.; Connor, D.; Bibi, S.; Chelysheva, I.; Clutterbuck, E.A.; Demissie, T.; Dinesh, T.; Edwards, N.J.; Felle, S.; Feng, S.; et al. Human leukocyte antigen alleles associate with COVID-19 vaccine immunogenicity and risk of breakthrough infection. Nat Med 2023, 29, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




