Submitted:
26 October 2023
Posted:
27 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
INTRODUCTION
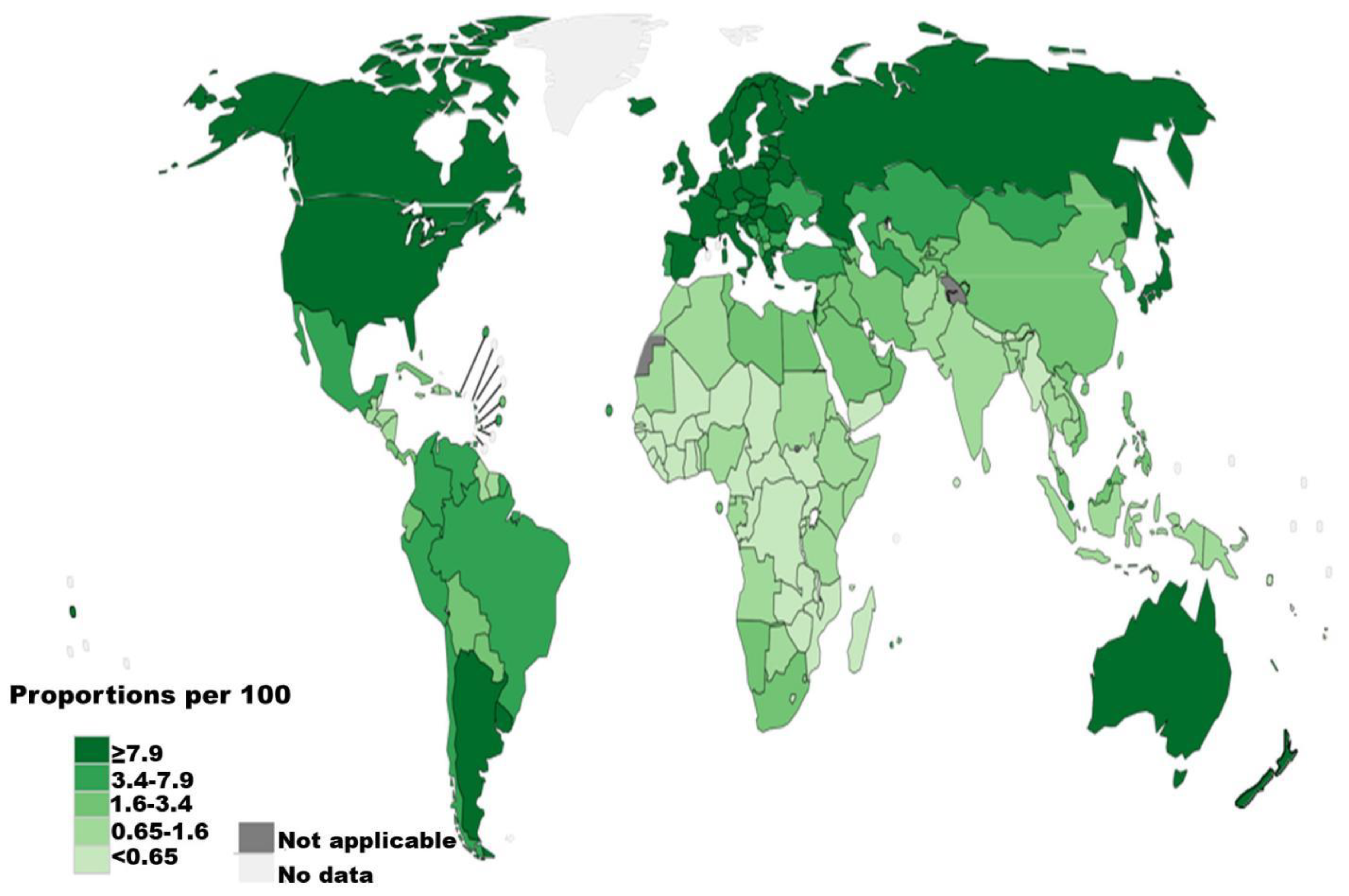
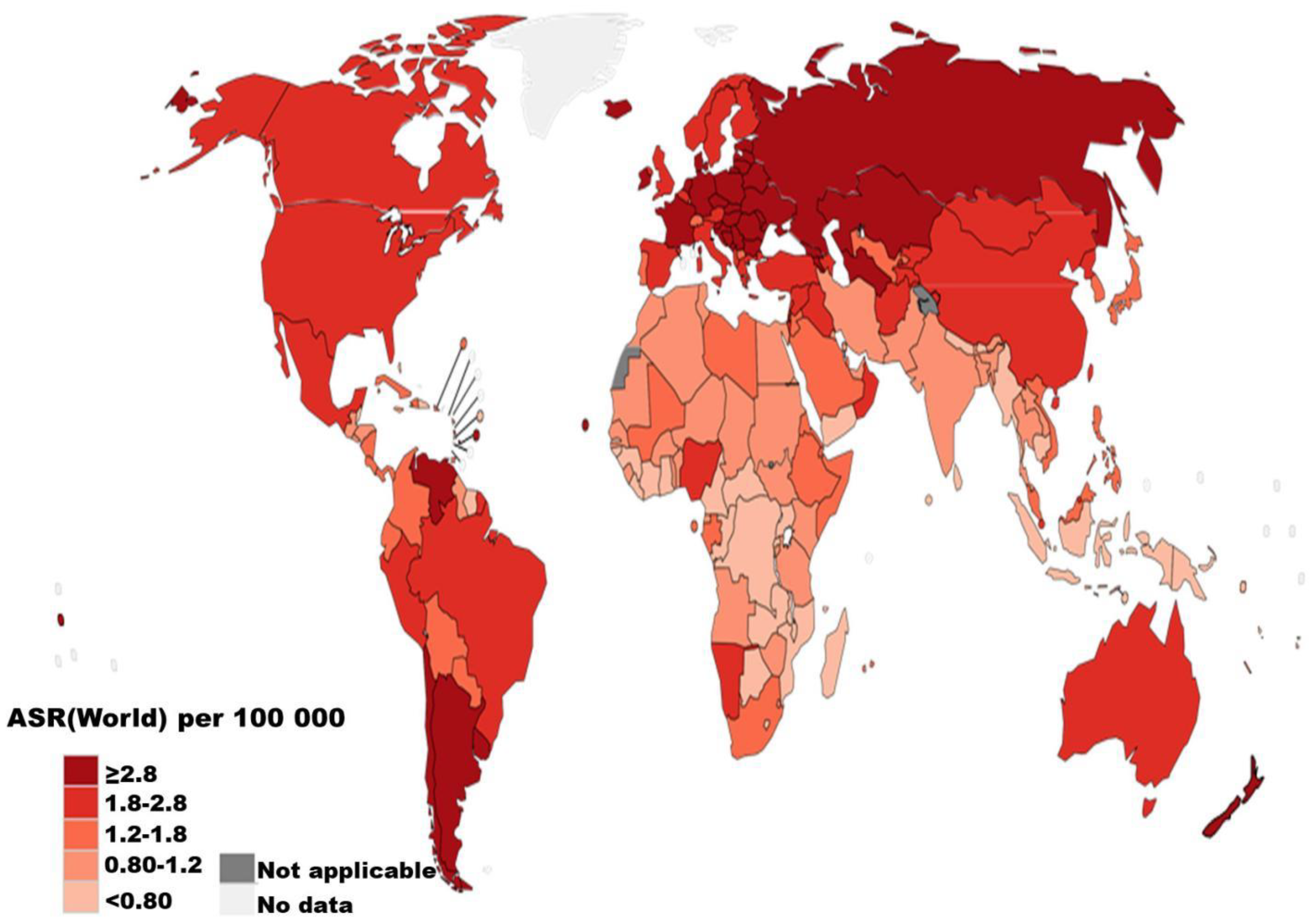
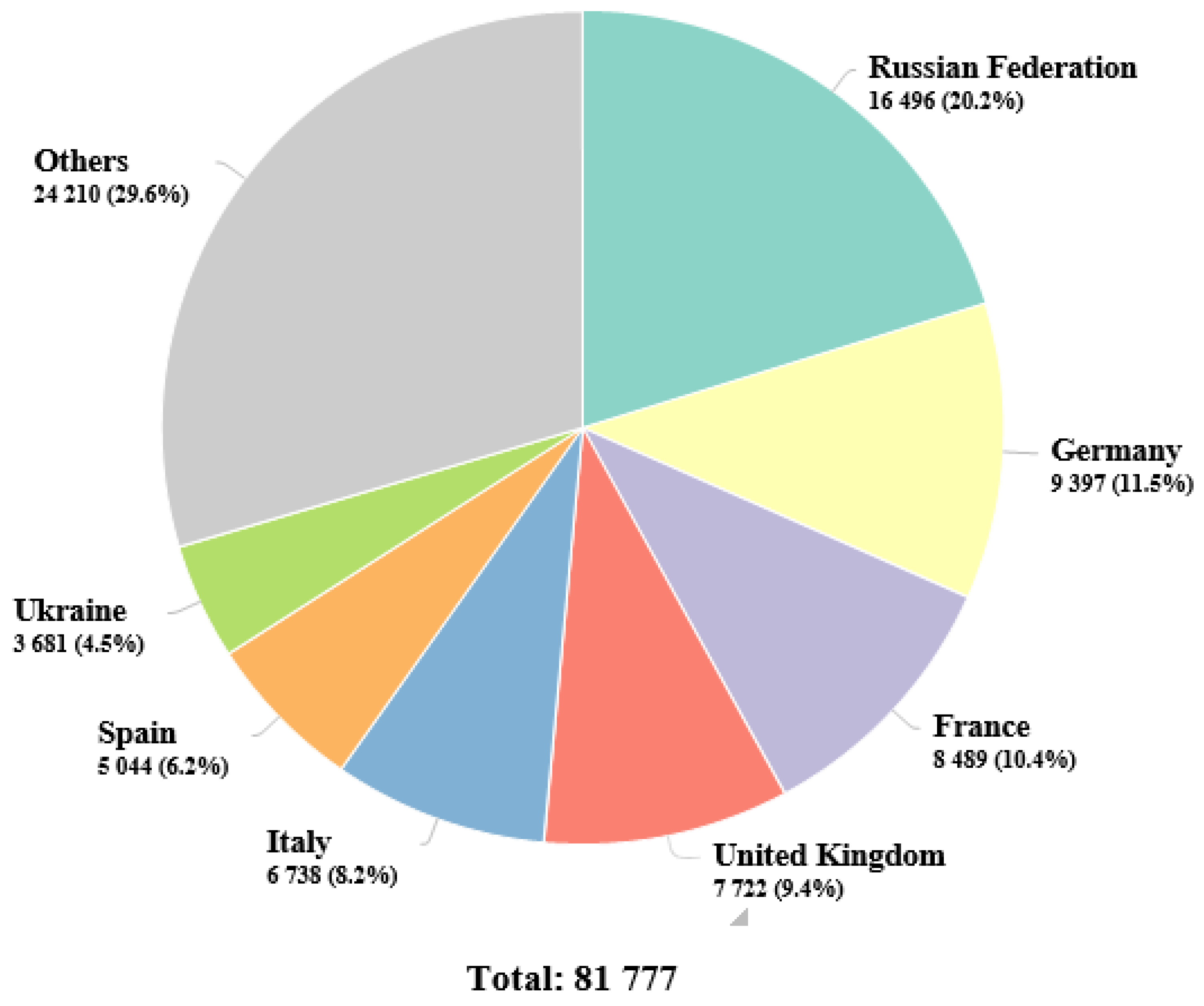
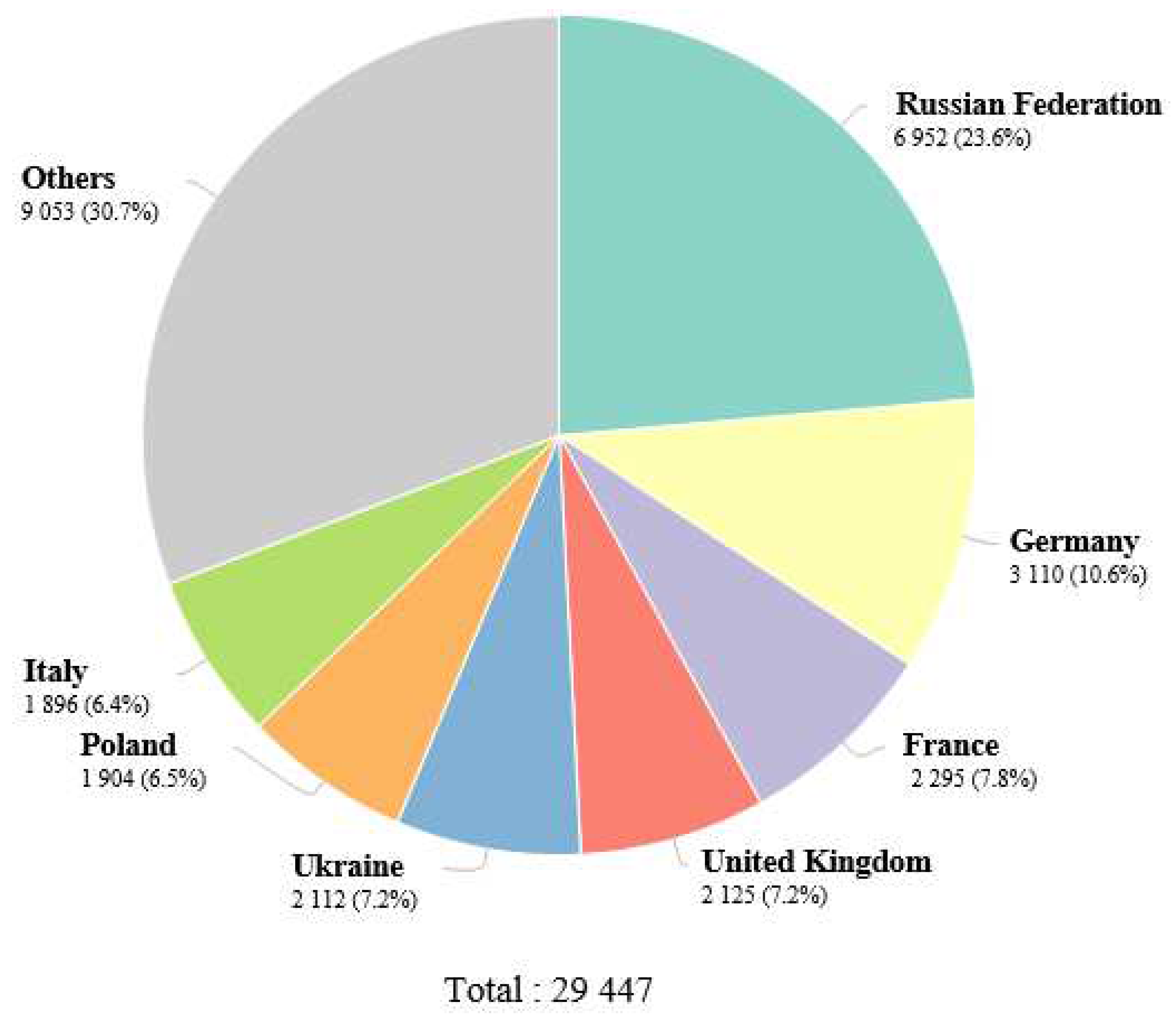
1. Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma
2. Causes and risk factors of kidney cancer
3. Current treatment of renal cell carcinoma
3.1. Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab
3.2. Belzutifan
3.3. Cabozantinib
3.4. Current standard of care
4. Area of prevention opportunities and future direction
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflict of interest
AVAILABILITY OF DATA AND MATERIALS
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication
Abbreviations
References
- Sharma R, Kadife E, Myers M, Kannourakis G, Prithviraj P, Ahmed N. Determinants of resistance to VEGF-TKI and immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Exp Clin Cancer Res 2021, 40(1), 1-27. [CrossRef]
- Shah A, Lal P, Toorens E, Palmer MB, Schwartz L, Vergara N, et al. Acquired cystic kidney disease–associated renal cell carcinoma (ACKD-RCC) harbor recurrent mutations in KMT2C and TSC2 genes. Am J Surg Pathol. 2020, 44(11), 1479-1486. [CrossRef]
- Gray RE, Harris GT. Renal cell carcinoma: diagnosis and management. Am. Fam. Physician. 2019, 99(3), 179-184. https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2019/0201/p179.html.
- Ricketts CJ, De Cubas AA, Fan H, Smith CC, Lang M, Reznik E, et al. The cancer genome atlas comprehensive molecular characterization of renal cell carcinoma. Cell Rep. 2018, 23(1), 313-326. [CrossRef]
- Nabi S, Kessler ER, Bernard B, Flaig TW, Lam ET. Renal cell carcinoma: a review of biology and pathophysiology. F1000Research. 2018, 7, 307. [CrossRef]
- Znaor A, Lortet-Tieulent J, Laversanne M, Jemal A, Bray F. International variations and trends in renal cell carcinoma incidence and mortality. Eur. Urol. 2015, 67(3), 519-530. [CrossRef]
- Chow WH, Dong LM, Devesa SS. Epidemiology and risk factors for kidney cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 2010, 7(5), 245-257. [CrossRef]
- Singh D. Current updates and future perspectives on the management of renal cell carcinoma. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118632. [CrossRef]
- Tahbaz R, Schmid M, Merseburger AS. Prevention of kidney cancer incidence and recurrence: lifestyle, medication and nutrition. Curr Opin Urol. 2018, 28(1), 62-79. [CrossRef]
- Dizman N, Salgia NJ, Bergerot PG, Hsu J, Ruel N, Pal SK. Race/Ethnicity and Survival in Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Outcomes for Patients Receiving First Line Targeted Therapies. Kidney Cancer. 2020, 4(3), 159-166. [CrossRef]
- Elmore LW, Greer SF, Daniels EC, Saxe CC, Melner MH, Krawiec GM, et al. Blueprint for cancer research: Critical gaps and opportunities. CA: Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71(2), 107-139. [CrossRef]
- Graham J, Heng DY, Brugarolas J, Vaishampayan U. Personalized management of advanced kidney cancer. Am Soc Clin Oncol Edu Book. 2018, 38, 330-341. https://ascopubs.org/doi/pdf/10.1200/EDBK_201215?role=tab.
- Choueiri TK, Kaelin Jr. WG. Targeting the HIF2–VEGF axis in renal cell carcinoma. Nat Med. 2020, 26(10), 1519-1530. [CrossRef]
- Nocera L, Karakiewicz PI, Wenzel M, Tian Z, Shariat SF, Saad F, et al. Clinical outcomes and adverse events after first-line treatment in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Urol, 2022, 207(1), 16-24. [CrossRef]
- Ma X, Long L, Moon S, Adamson BH, Baxi SS. Comparison of population characteristics in real-world clinical oncology databases in the US: Flatiron Health, SEER, and NPCR. MedRxiv, 2020, 2020-03. [CrossRef]
- Fukushima H, Saito K, Yasuda Y, Tanaka H, Patil D, Cotta BH, et al. Female gender predicts favorable prognosis in patients with non-metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma undergoing curative surgery: results from the International Marker Consortium for Renal Cancer (INMARC). Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2020, 18(2), 111-116. [CrossRef]
- Usher-Smith J, Simmons RK, Rossi SH, Stewart GD. Current evidence on screening for renal cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 17(11), (2020), 637-642. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41585-020-0363-3.
- Mancini M, Righetto M, Baggio G. Gender-related approach to kidney cancer management: Moving forward. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21(9), 3378. [CrossRef]
- Rossi SH, Klatte T, Usher-Smith J, Stewart GD. Epidemiology and screening for renal cancer. World J. Urol. 2018, 36, 1341-1353. [CrossRef]
- Lalani AKA, Heng DY, Basappa NS, Wood L, Iqbal N, McLeod D, et al. Evolving landscape of first-line combination therapy in advanced renal cancer: a systematic review. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2022, 14. [CrossRef]
- Scelo G, Larose TL. Epidemiology and risk factors for kidney cancer. J. Clin Oncol. 2018, 36(36), 3574. [CrossRef]
- Singh GK, Jemal A. Socioeconomic and racial/ethnic disparities in cancer mortality, incidence, and survival in the United States, 1950–2014: over six decades of changing patterns and widening inequalities. J. Environ Public Health. 2017, (2017), ID: 2819372. [CrossRef]
- Lipworth L, Tarone RE, McLaughlin JK. Renal cell cancer among African Americans: an epidemiologic review. BMC cancer. 2011, 11, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Al-Husseini MJ, Kunbaz A, Saad AM, Santos JV, Salahia S, Iqbal M, et al. Trends in the incidence and mortality of transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder for the last four decades in the USA: a SEER-based analysis. BMC cancer. 2019, 19(1), 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Padala SA, Barsouk A, Thandra KC, Saginala K, Mohammed A, Vakiti A, et al. Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. World J. Oncol. 2020, 11(3), 79-87. https://wjon.org/index.php/wjon/article/view/1279/989.
- Saly DL, Eswarappa MS, Street SE, Deshpande P. Renal Cell Cancer and Chronic Kidney Disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2021, 28(5), 460-468. [CrossRef]
- Escudier B, Porta C, Schmidinger M, Rioux-Leclercq N, Bex A, Khoo V, Grünwald V, et al. Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann.Oncol. 2019, 30(5), 706-720. [CrossRef]
- Capitanio U, Bensalah K, Bex A, Boorjian SA, Bray F, Coleman J, et al. Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol, 2019, 75(1), 74-84. [CrossRef]
- Haas NB, Nathanson KL. Hereditary kidney cancer syndromes. Adv chronic kidney Dis. 2014, 21(1), 81-90. [CrossRef]
- Albiñana V, Gallardo-Vara E, de Rojas-P I, Recio-Poveda L, Aguado T, Canto-Cano A, et al. Targeting β2-adrenergic receptors shows therapeutical benefits in clear cell renal cell carcinoma from Von Hippel–Lindau Disease. J. Clin Med. 2020, 9(9), 2740. [CrossRef]
- Nandagopal L, Sonpavde GP, Agarwal N. Investigational MET inhibitors to treat Renal cell carcinoma. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2019. 28(10), 851-860. [CrossRef]
- Boi SK, Orlandella RM, Gibson JT, Turbitt WJ, Wald G, Thomas L, et al. Obesity diminishes response to PD-1-based immunotherapies in renal cancer. J. immunother Cancer. 2020, 8(2), e000725. [CrossRef]
- Aurilio G, Piva F, Santoni M, Cimadamore A, Sorgentoni G, Lopez-Beltran A, et al. The role of obesity in renal cell carcinoma patients: clinical-pathological implications. Int J. Mol Sci. 2019, 20(22), 5683. [CrossRef]
- Cohen JB, Geara AS, Hogan JJ, Townsend RR. Hypertension in cancer patients and survivors: epidemiology, diagnosis, and management. Cardio Oncol. 2019, 1(2), 238-251. [CrossRef]
- Berkenblit R, Ricci Z, Kanmaniraja D, Sarungbam J. CT features of acquired cystic kidney disease-associated renal cell carcinoma. Clin Imaging. 2022, 83, 83-86. [CrossRef]
- Kondo T, Sassa N, Yamada H, Takagi T, Iizuka J, Kobayashi H, et al. Comparable survival outcome between acquired cystic disease associated renal cell carcinoma and clear cell carcinoma in patients with end-stage renal disease: a multi-institutional central pathology study. Pathol. 2021, 53(6), 720-727. [CrossRef]
- Wozniak MB, Brennan P, Brenner DR, Overvad K, Olsen A, Tjønneland A, et al. Alcohol consumption and the risk of renal cancers in the E uropean prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC). Int J. Cancer. 2015, 137(8), 1953-1966. [CrossRef]
- Singh S, Chaurasia A, Gopal N, Malayeri A, Ball MW. Treatment Strategies for Hereditary Kidney Cancer: Current Recommendations and Updates. Discovery Med. 2022, 34(173), 205-220. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36602871/.
- Linehan LM, Pinto PA, Bratslavsky G, Pfaffenroth E, Merino M, Vocke CD, et al. Toro, J.R.; Bottaro, D.; Neckers, L.; Schmidt, L.S.; Srinivasan, R. Hereditary kidney cancer: unique opportunity for disease-based therapy. Cancer, 2009, 115(S10), 2252-2261. [CrossRef]
- Behrens G, Leitzmann MF. The association between physical activity and renal cancer: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J. Cancer. 2013, 108(4), 798-811. [CrossRef]
- Tseng CH. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and kidney cancer risk: a retrospective cohort analysis of the National Health Insurance. PloS one, 2015, 10(11), e0142480. [CrossRef]
- Buhagen M, Grønskag A, Ragde SF, Hilt B. Association between kidney cancer and occupational exposure to trichloroethylene. J. Occup Environ Med. 2016, 58(9), 957-959. [CrossRef]
- Zunarelli C, Godono A, Visci G. Violante FS, Boffetta P. Occupational exposure to asbestos and risk of kidney cancer: an updated meta-analysis. Eur J Epidemiol. 2021, 36(9), 927-936. [CrossRef]
- Nayan M, Juurlink DN, Austin PC. Macdonald, E.M.; Finelli, A.; Kulkarni, G.S.; Hamilton, R.J. Canadian Drug Safety and Effectiveness Research Network (CDSERN). Medication use and kidney cancer risk: A population-based study. Eur J Cancer, 2017, 83, 203-210. [CrossRef]
- Nayan M, Macdonald EM, Juurlink DN, Austin PC, Finelli A, Kulkarni GS, et al. Medication use and survival in diabetic patients with kidney cancer: A population-based cohort study. Pharmacological research, 2016, 113, 468-474. [CrossRef]
- Choueiri TK, Je Y, Cho E. Analgesic use and the risk of kidney cancer: A meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies. International journal of cancer. 2014, 134(2):384-96. [CrossRef]
- Rini BI, Plimack ER, Stus V, Gafanov R, Hawkins R, Nosov D, et al. Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019 Mar 21;380(12):1116–27. Available from: http://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa1816714.
- Ged Y, Lee CH. Lenvatinib plus pembrolizumab combination therapy for adult patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy. 2022 Oct 3;22(10):1049–59. Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14737140.2022.2128336.
- Motzer R, Alekseev B, Rha SY, Porta C, Eto M, Powles T, et al. Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab or Everolimus for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2021 Apr 8;384(14):1289–300. Available from: http://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2035716.
- Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Glen H, Michaelson MD, Molina A, Eisen T, et al., Lenvatinib, everolimus, and the combination in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, phase 2, open-label, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16(15), 1473-1482. [CrossRef]
- Bauer TM, Choueiri TK, Papadopoulos KP, Plimack ER, Merchan JR, McDermott DF, et al. The oral HIF-2 α inhibitor MK-6482 in patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (RCC): Updated follow-up of a phase I/II study. J. Clin Oncol. 2021, 39(6), 273-273. [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan R, Donskov F, Iliopoulos O, Rathmell WK, Narayan V, Maughan BL, et al. Phase 2 study of belzutifan (MK-6482), an oral hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) inhibitor, for Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease-associated clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). J. Clin Oncol. 2021, 39(15), 4555-4555. [CrossRef]
- Choueiri TK, Bauer TM, McDermott DF, Arrowsmith E, Roy A, Perini RF, et al. Tykodi, S.S.. Phase 2 study of the oral hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) inhibitor MK-6482 in combination with cabozantinib in patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). J. Clin Oncol. 2021, 39(6), 272-272. [CrossRef]
- Armstrong AJ, Halabi S, Eisen T, Broderick S, Stadler WM, Jones RJ, et al. Everolimus versus sunitinib for patients with metastatic non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ASPEN): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17(3), 378-388. [CrossRef]
- Song SH. Jeong IG, You D, Hong JH, Hong BS, Song C, et al. 609 VEGF/VEGFR2 or PDGF-β/PDGFR-β expression in non-metastatic, renal cell carcinoma: a prospective study with 1,091 consecutive cases. J. Urol. 2013, 189(4S), e249-e249. [CrossRef]
- Mayrhofer K, Niedersüß-Beke D. New targeted therapies in kidney cancer. Memo-Mag Eur Med Oncol. 2022, 15(2), 133-136. [CrossRef]
- Pal SK, Tangen C, Thompson IM, Balzer-Haas N, George DJ, Heng DY, et al.A comparison of sunitinib with cabozantinib, crizotinib, and savolitinib for treatment of advanced papillary renal cell carcinoma: a randomised, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet, 2021, 397(10275), 695-703. [CrossRef]
- Lee CH, Voss MH, Carlo MI Chen YB, Reznik E, Knezevic A, et al. Nivolumab plus cabozantinib in patients with non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma: results of a phase 2 trial. J. Clin Oncol. 2021, 39(15_suppl), 4509. [CrossRef]
- Choueiri TK, Powles T, Burotto M, Escudier B, Bourlon MT, Zurawski B, et al. Nivolumab plus cabozantinib versus sunitinib for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J. Med. 2021, 384(9), 829-841. [CrossRef]
- Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF, Arén Frontera O, Melichar B, Choueiri TK, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl J.. Med. 378(14), (2018), 1277-1290. [CrossRef]
| Risk factor | Inference | References |
|---|---|---|
| Established risk factor | ||
| Male gender | Positive correlation | [16,18] |
| Age | Positive correlation | [17] |
| Obesity | Positive correlation | [32,33] |
| Smoking | Positive correlation with a dosage response | [17] |
| Hypertension | Positive correlated to a dosage response. Uncertainty exists over how hypertensive drugs affect the risk of kidney cancer. | [34] |
| Renal disease | Renal cancer risk is increased in cases of ACKD, ESRD, and renal transplant. | [35,36] |
| Alcohol | Compared to abstinence, moderate alcohol use has a protective impact. Higher consumption has no added benefits | [37] |
| Family history | Renal cancer risk is increased by having an affected first-degree relative. Renal cancer is also predisposed by a number of rare inherited genetic diseases, such as von Hippel-Lindau, hereditary papillary renal carcinoma, Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome, hereditary leiomyomatosis RCC, succinate dehydrogenase RCC, and tuberous sclerosis. |
[38,39] |
| Unestablished risk factor | ||
| Physical activity | Greater exercise is beneficial. | [40] |
| Diabetes | Positive correlation | [41] |
| Occupational exposure | ♦ The IARC believes that there is enough evidence to classify trichloroethylene as a carcinogenic substance that can cause kidney cancer. | [42] |
| ♦ Arsenic and its inorganic compounds, cadmium and its compounds, perfluorooctanoic acid from printing operations, and welding fumes, according to the IARC, have little evidence. | [43] | |
| Analgesic use | Positive correlation with NSAIDs | [44,45,46] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





