Submitted:
26 October 2023
Posted:
26 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Review and Analysis of Stiffness Theory
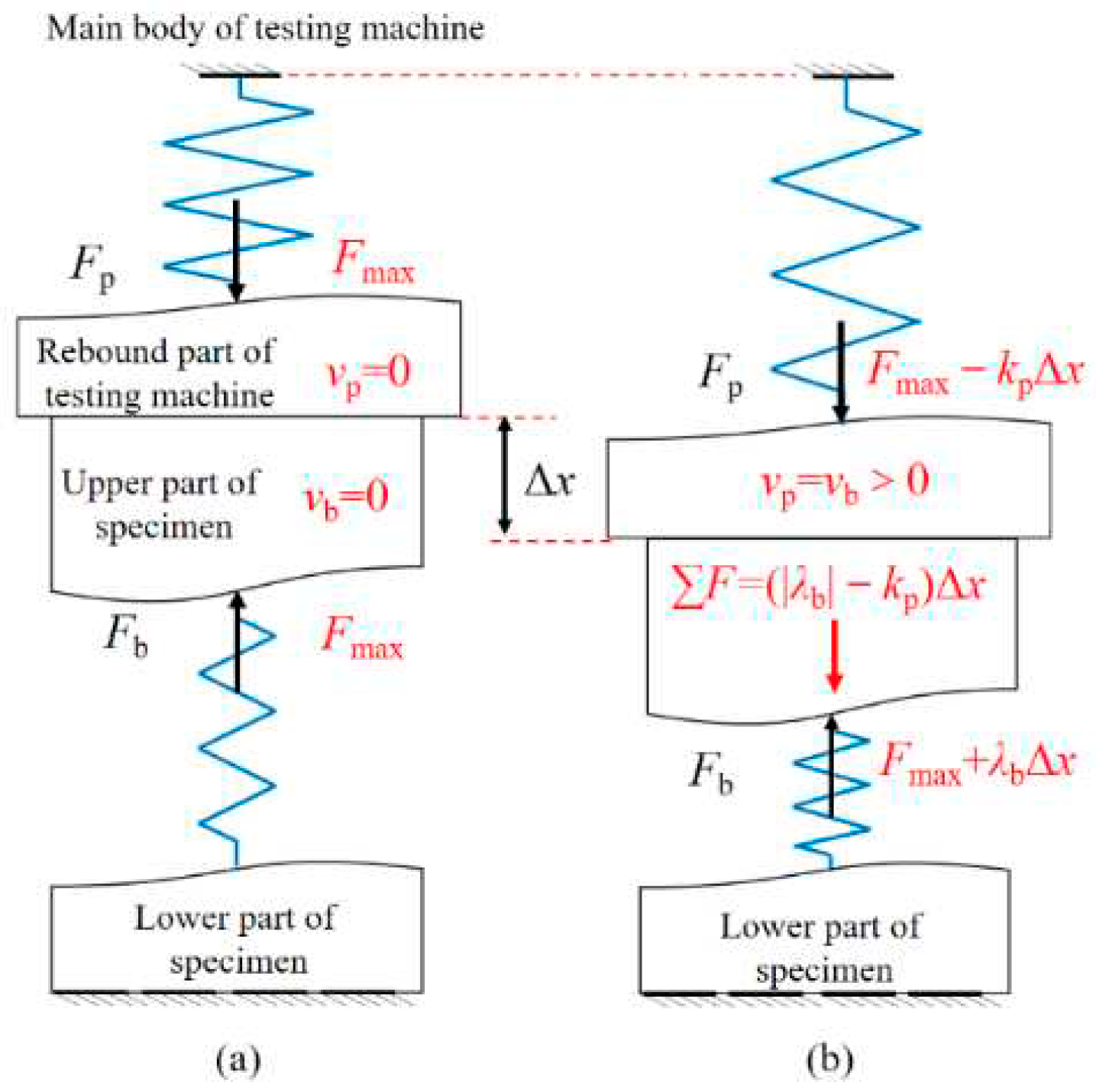
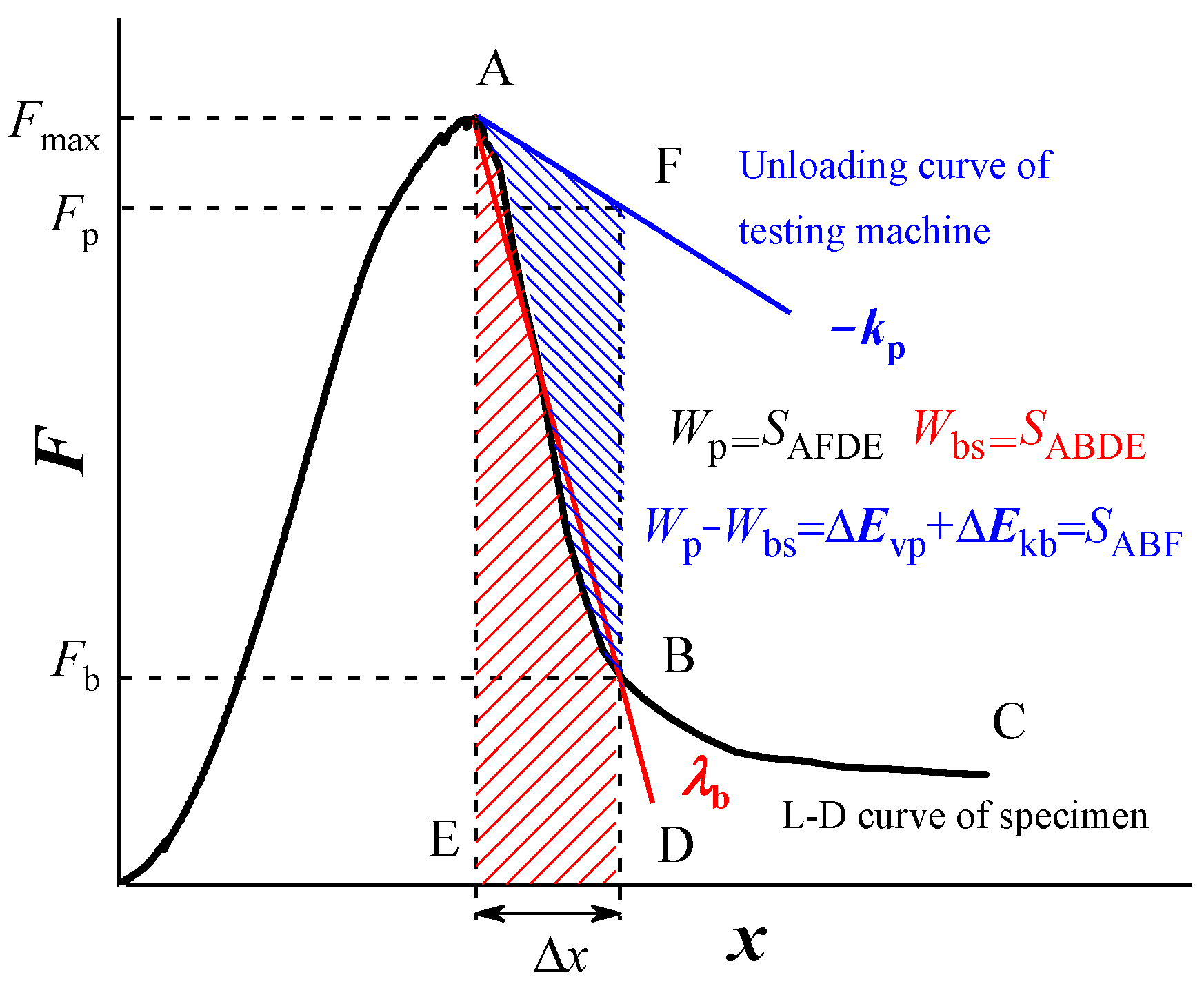
2.1. Stiffness Theory and Its Experimental and Theoretical Support
2.2. Important But Easily Overlooked Details in Stiffness Theory
3. Uneven Stiffness Coal Seam Structure (USCS)
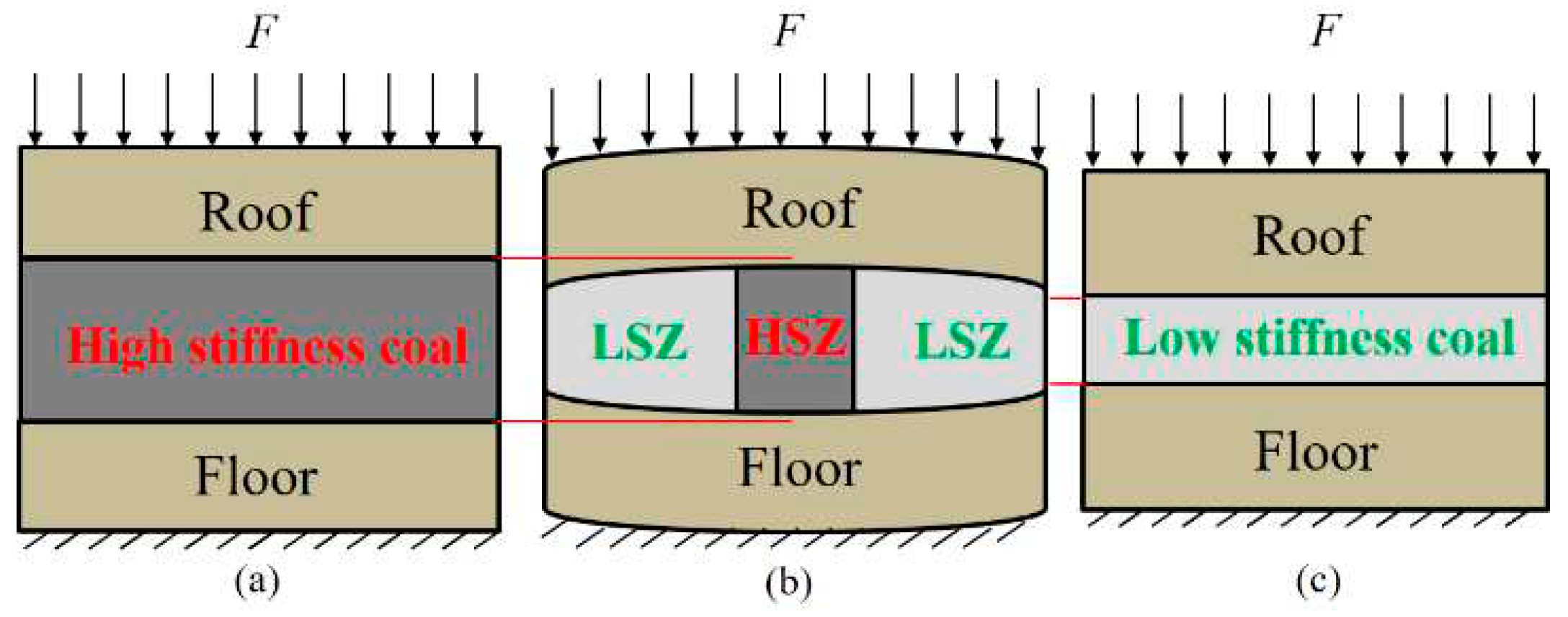
3.1. Structure Composition, Functions, and Typical Examples of USCS
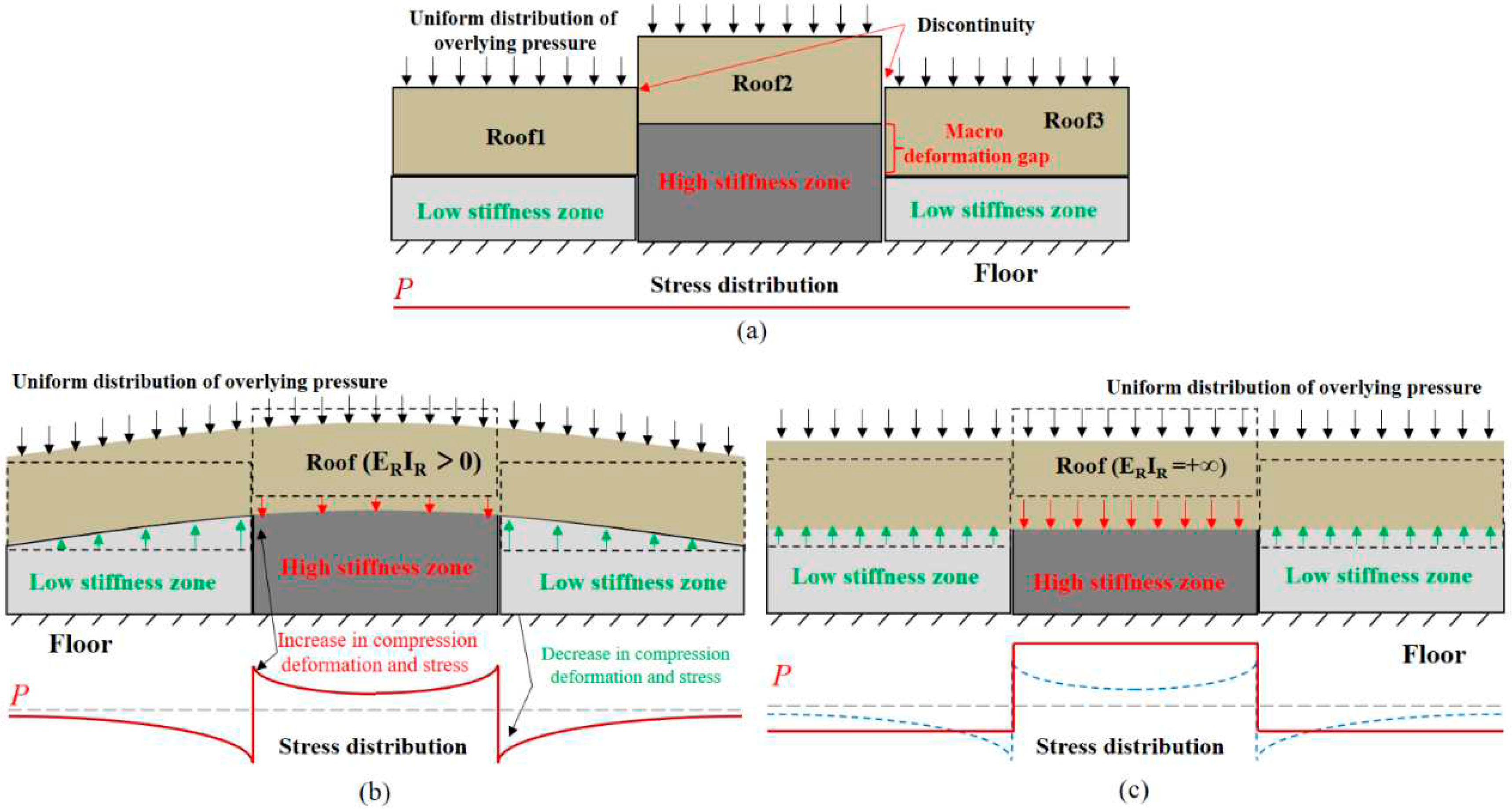
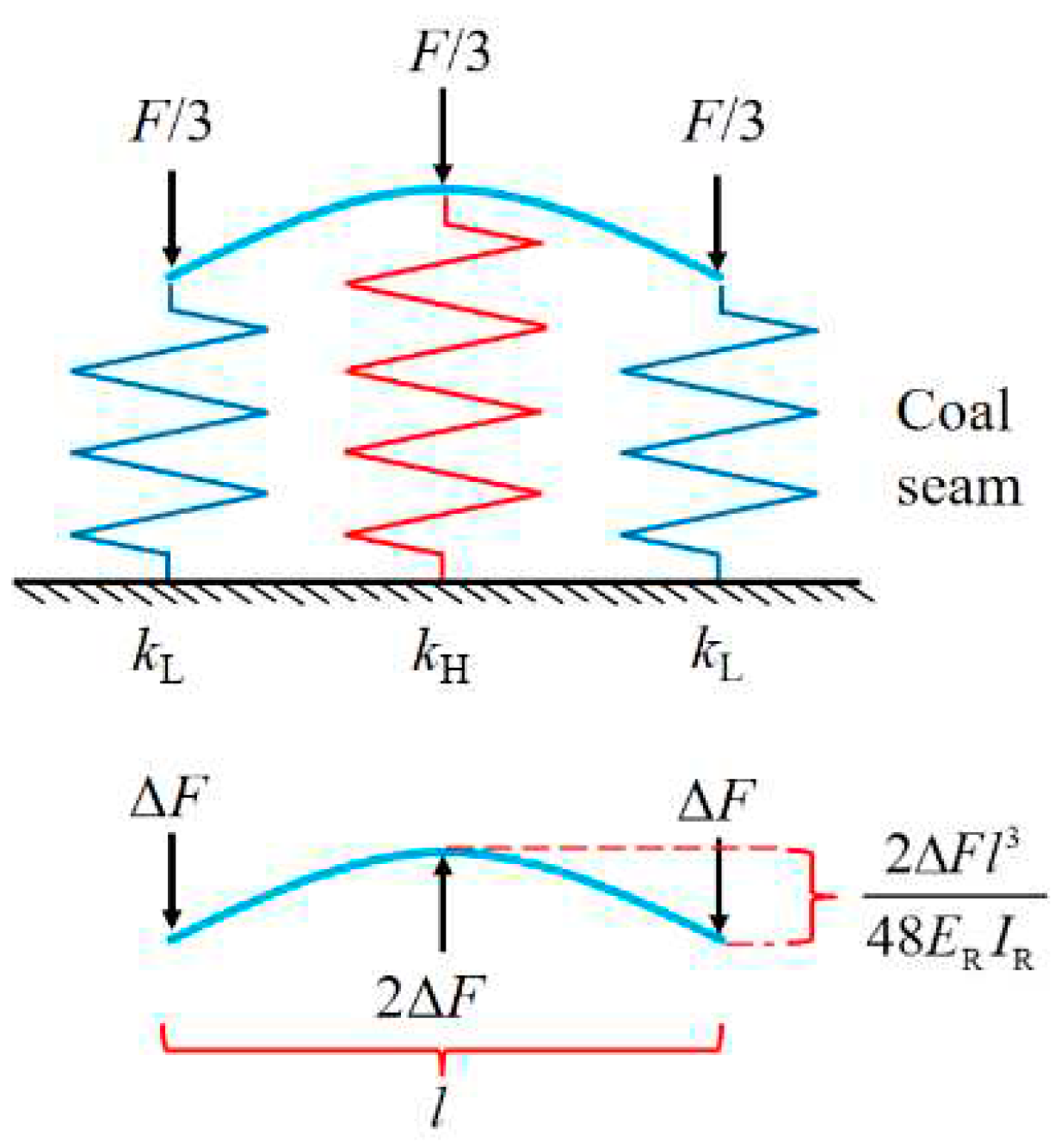
3.2. Analysis of Pressure Concentration Function of USCS
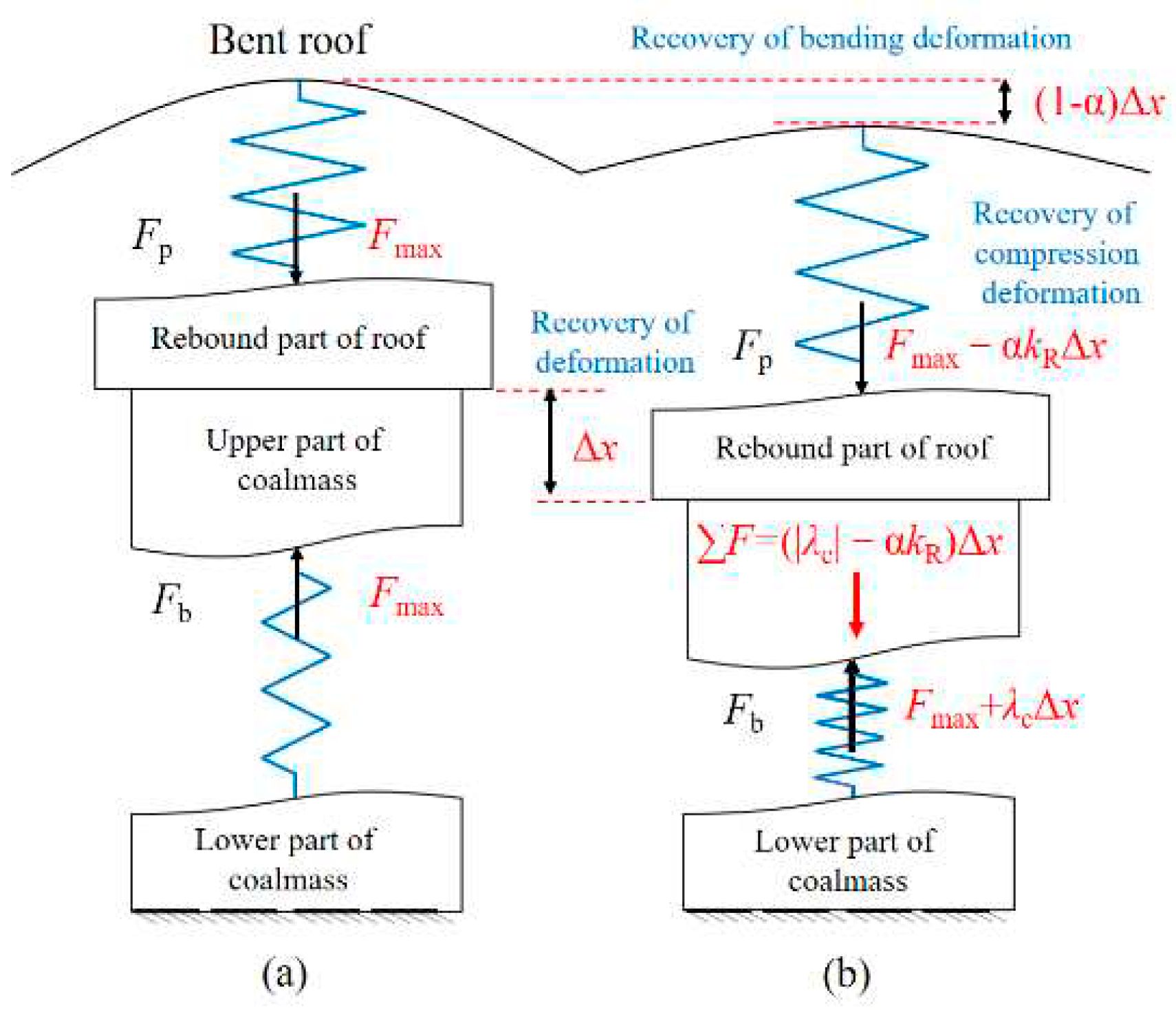
3.3. Analysis of Stiffness Reduction Function of USCS
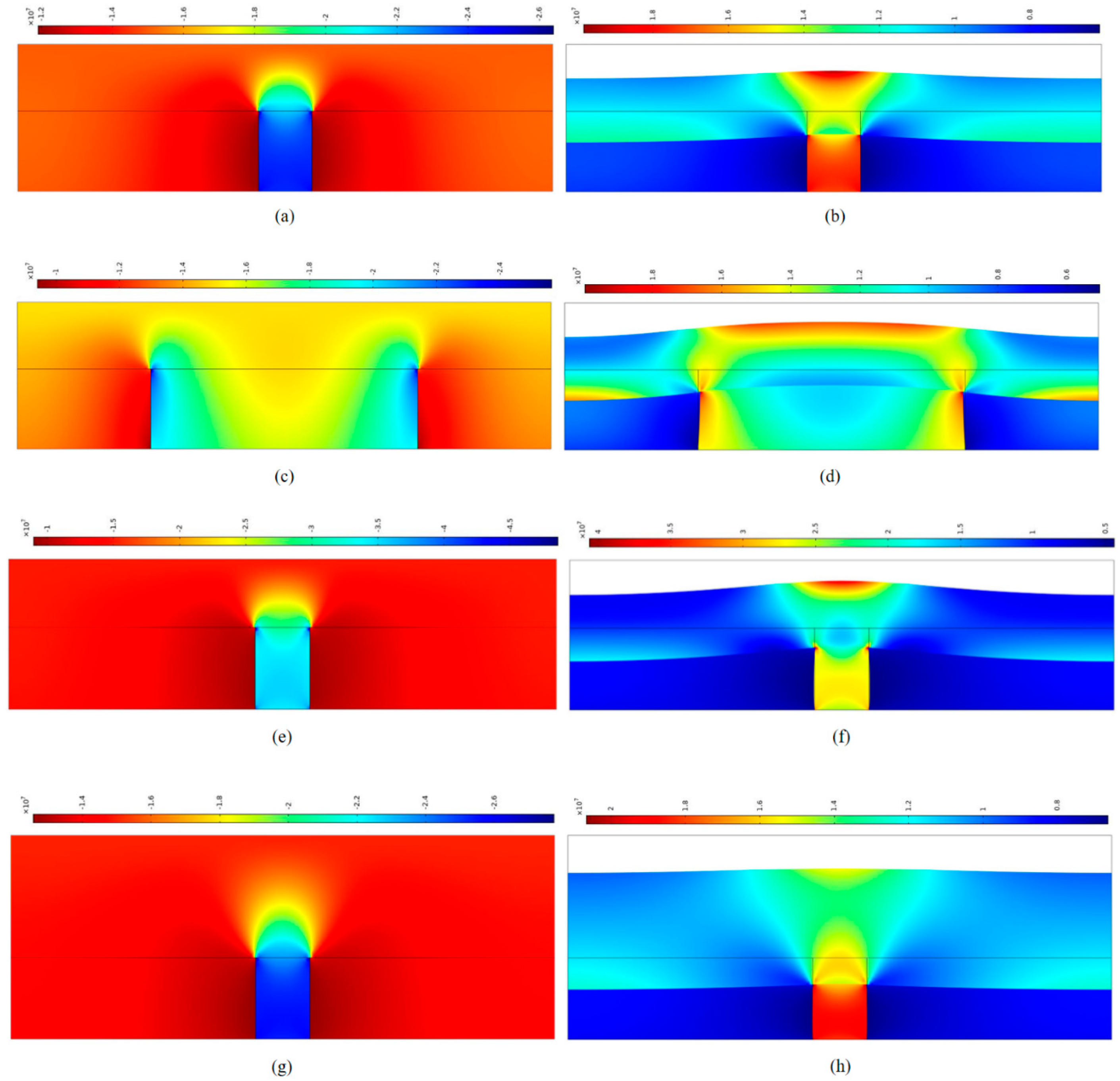
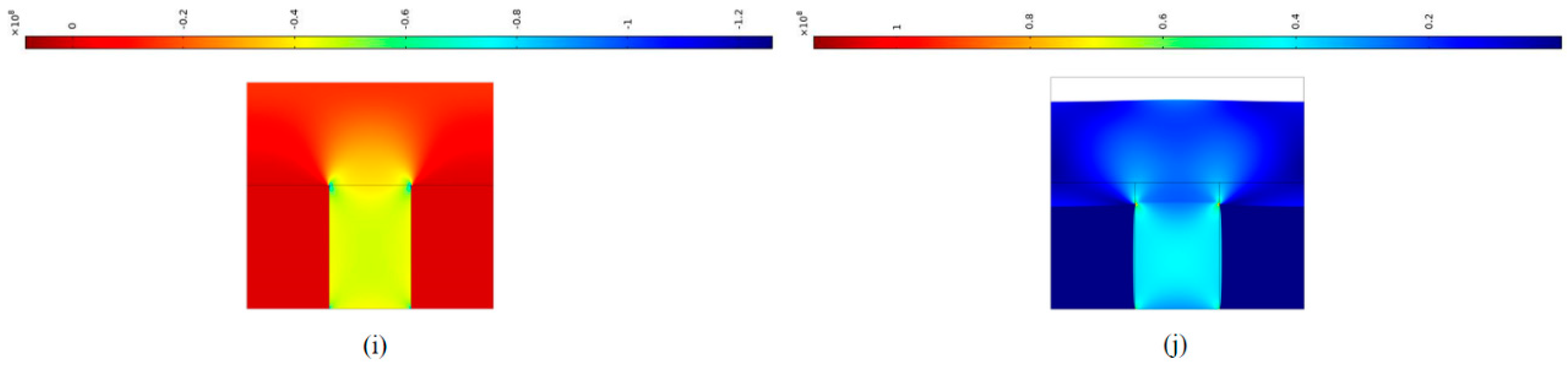
4. Simple Numerical Simulation of Uneven Stiffness Coal Seam Structure (USCS)
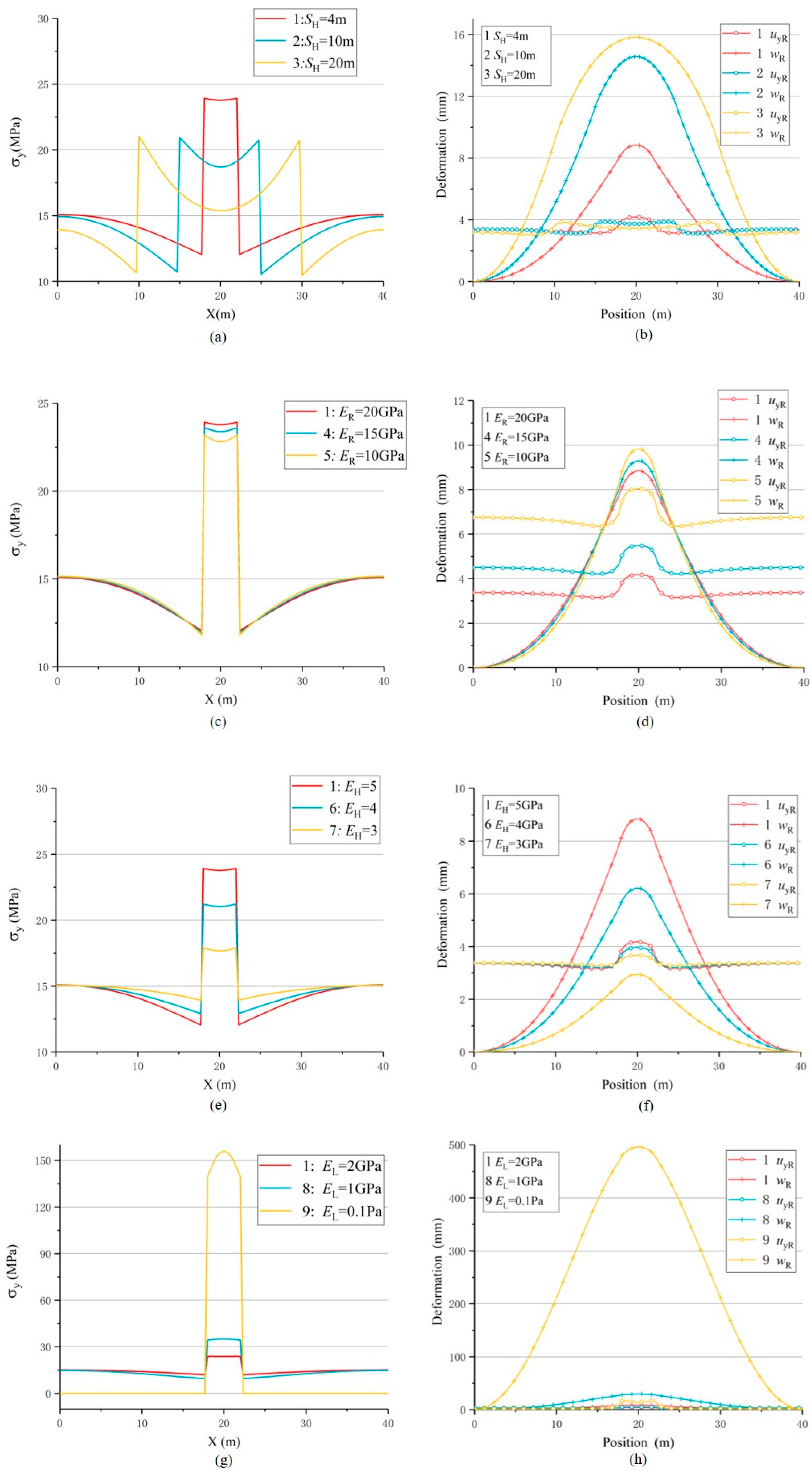
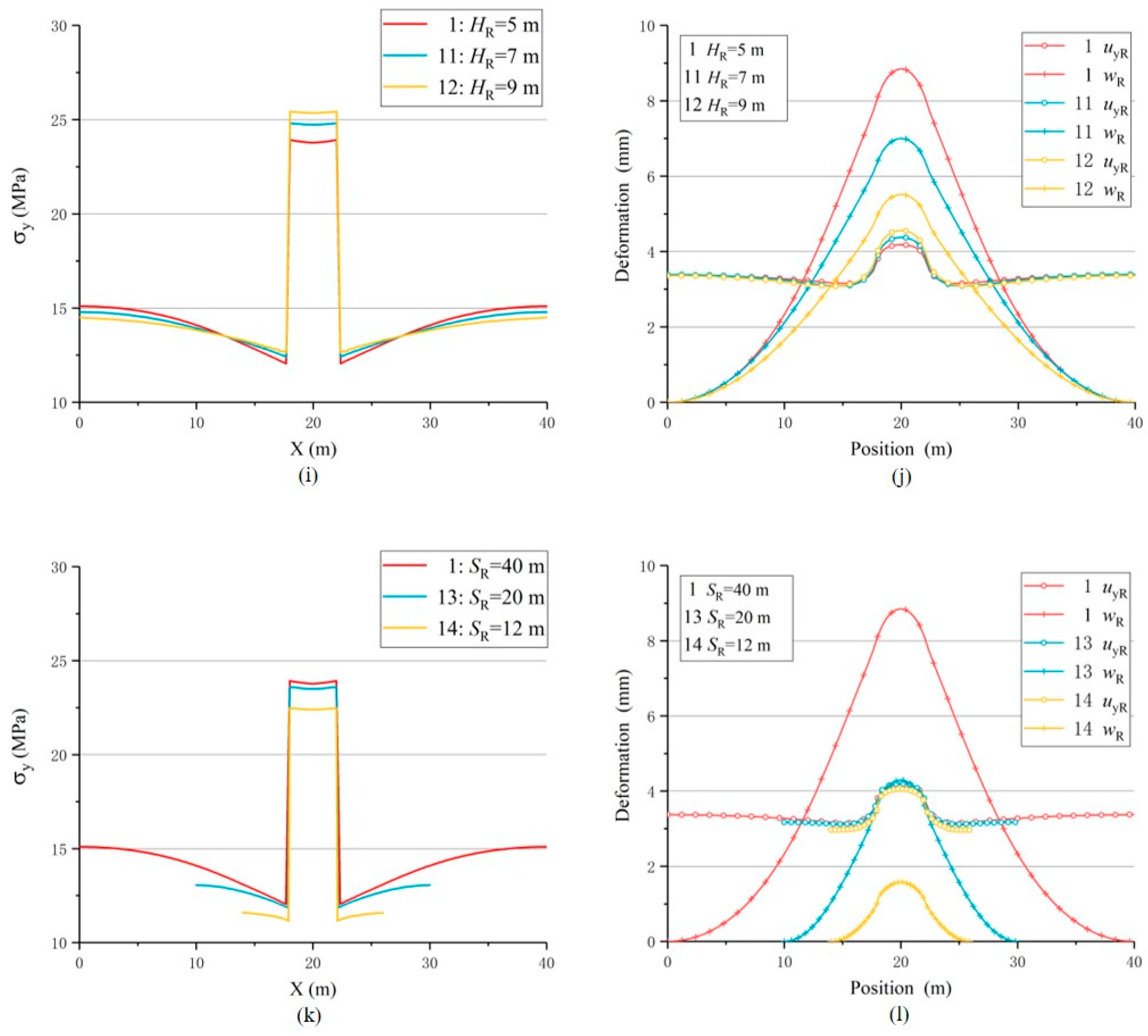
5. Further Discussion about USCS
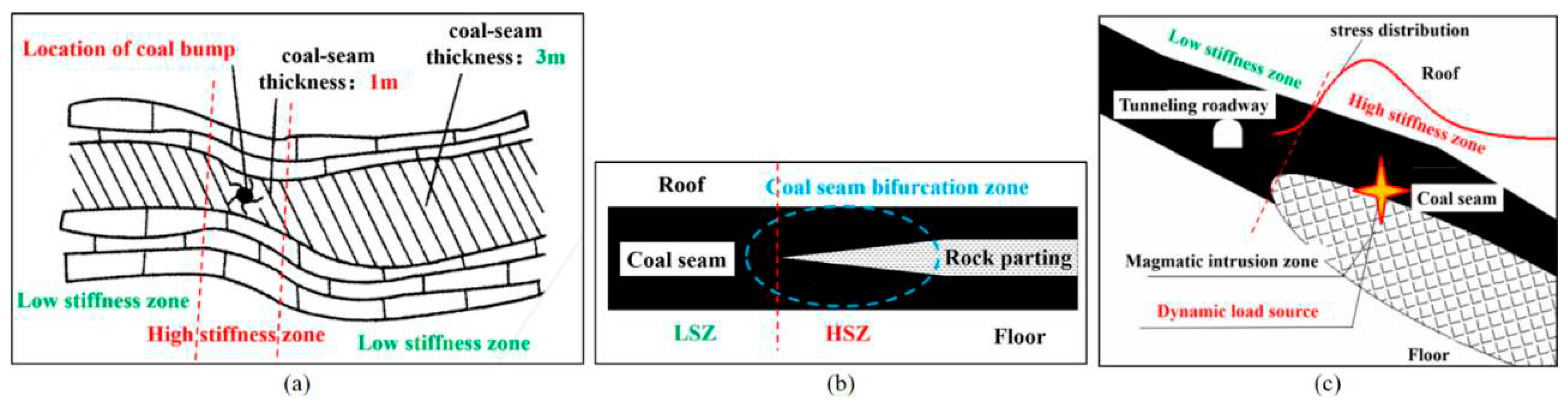
5.1. Connection between USCS and Existing Mechanism Research Results about Coal Bump
5.2. Artificial USCS and stiffness perspective
6. New Explanation of Engineering Phenomena Based on USCS
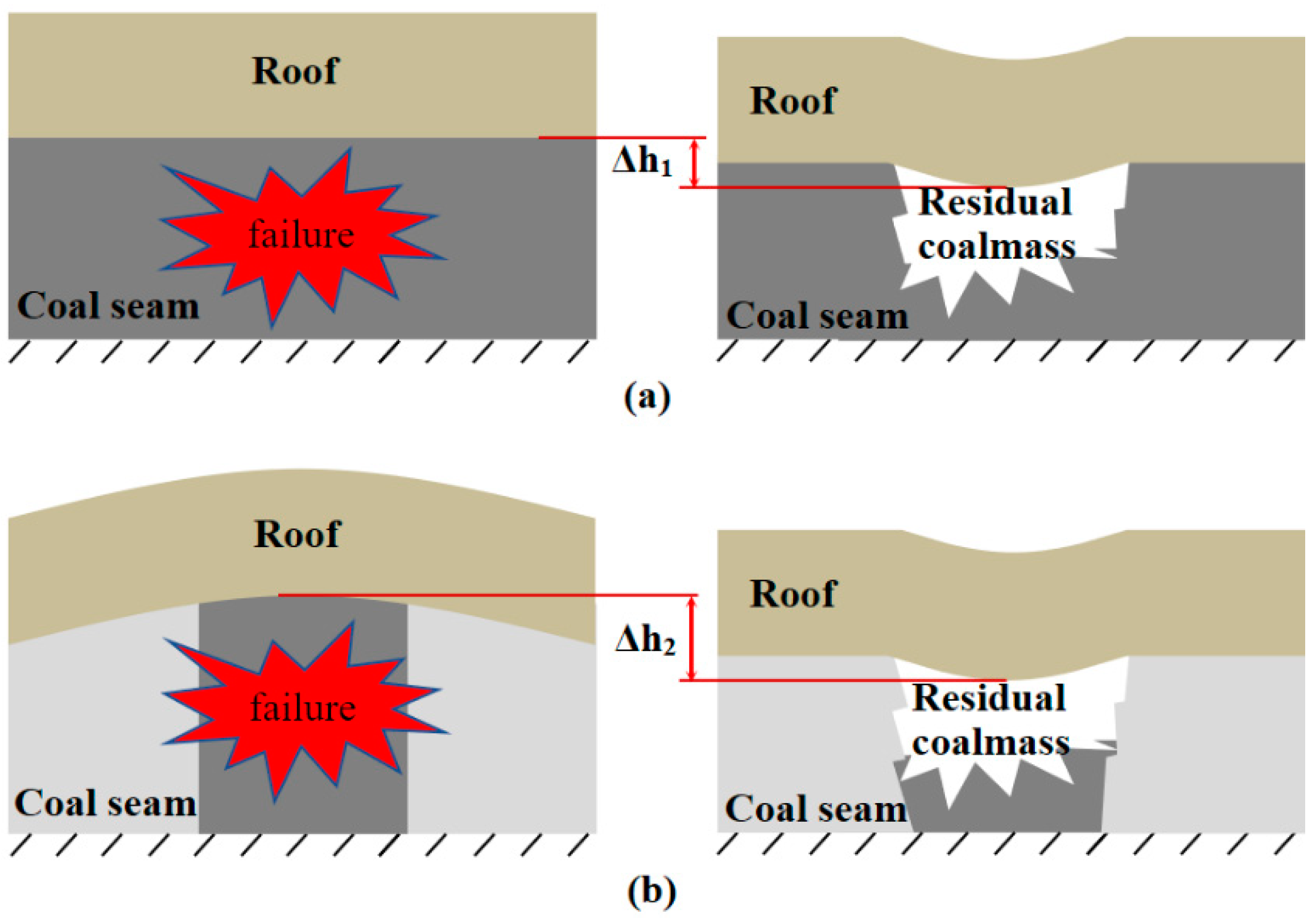
6.1. New Explanation of the Time-delayed of Partial Coal bumps
6.2. New explanation of the inefficient pressure relief in ultra thick coal seam
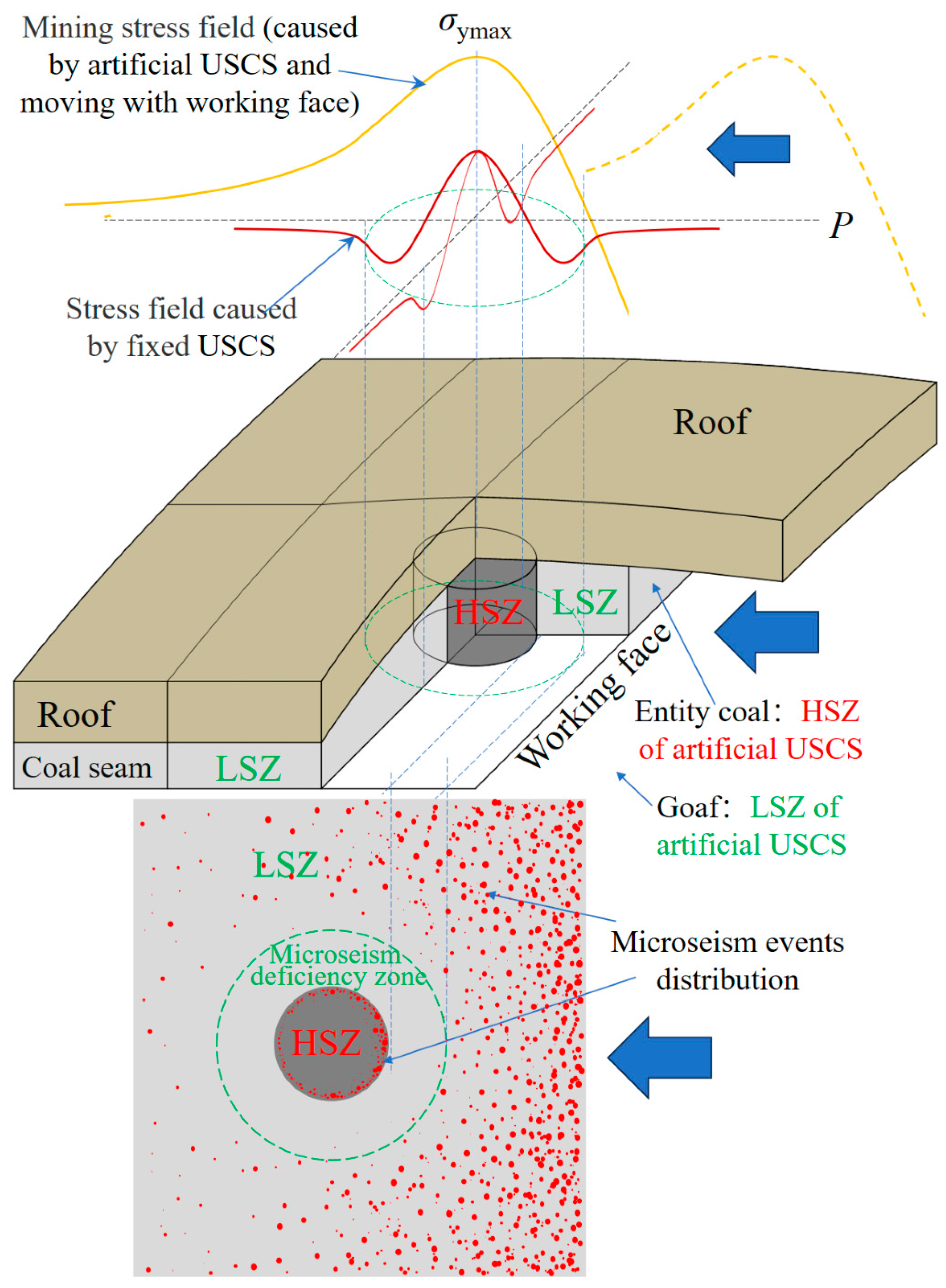
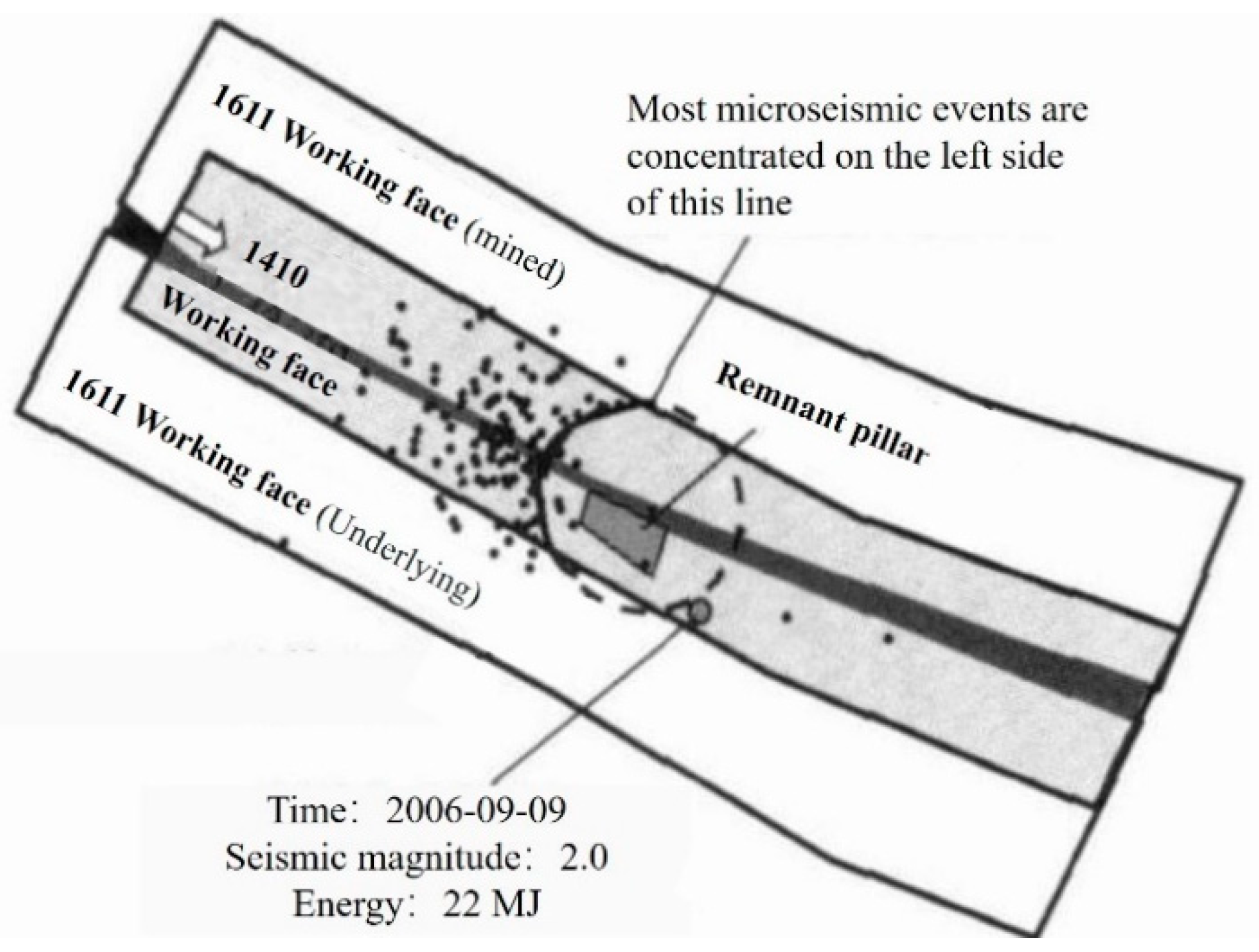
6.3. New Explanation of the “Microseism Deficiency” Phenomenon Before Coal bump
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- M. C., He; J.L., Miao; J.L., Feng. Rock burst process of limestone and its acoustic emission characteristics under true-triaxial unloading conditions. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences. 2010, 47:286–298.
- Horst; Lippmann, H. Mechanics of “bumps” in coal mines: a discussion of violent deformations in the sides of road-ways in coal seams. Applied Mechanics Reviews. 1987, 40(8):1033–1043.
- Qi, Q.X.; Dou, L.M. Theory and Technology of Coal Bump; China University of Mining and Technology Press: Xuzhou, China, 2008. (In Chinese).
- Pan, Y.S.; Li, Z.H.; Zhang M.T. Distribution, type, mechanism and prevention of rockbrust in China. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2003,22(11):1844–1844. (In Chinese).
- Jiang, Y.D.; Pan Y.S.; Jiang, F.X.; et al. State of the art review on mechanism and prevention of coal bumps in China. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(2): 205–213. (In Chinese).
- Qi, Q.X.; Li, Y.Z.; Zhao, S.K., et al. Seventy years development of coal mine rockburst in China: establishment and consideration of theory and technology system. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(9): 1–40. (In Chinese).
- Brauner, G. Ground Pressure and Coal Bumps; Li, Y.S., Translator; Coal Industry Press: Beijing, China, 1985.
- Cook, N.G.W.; Hoek E.; Salamon, M.D.G. Rock Mechanics Applied to Study of Rockbursts [J]. Journal of South African Institute of Mining & Metallurgy,1966, 435-528.
- Cook, N.G.W. The failure of rock. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1965,2(4): 389-403.
- Cook, N.G.W. A note on rock bursts considered as a problem of stability. Journal of the South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, 1965, 65(1): 437-446.
- Salamon, M.D.G. Stability, instability and design of pillar workings. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 1970, 7(6):613-631.
- Blake, W. Rockburst mechanics. Quarterly of Colorado School of Mines, 1972, 67: 1-64.
- KIDYBINSKI A. Bursting liability indices of coal. International Journal of Roc Mechanics and Mining Sciences and Geomechanics Abstracts, 1981, 18(4): 295–304.
- Singh, S.P. Burst energy release index. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 1988, 21(2):149-155.
- Zhang M.T.Discussion on the mechanism of coal burst. Journal of Fuxin Mining Institute, 1985, 4(S1):65–72. (In Chinese).
- Li, G.P. The Mechanism of Compression-Shear Damage for Rock Mass with Its Application to Rockburst. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 1997, 19 (6): 49-55. (In Chinese).
- Tang, C.A.; Xu, X.H. A cusp catastrophic model of rock unstable failure. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 1990, 9(2): 100-107. (In Chinese).
- Pan, Y.S.; Zhang M.T.The study of coal burst by catastrophe theory. Journal of Fuxin Mining Institute, 1992, 11(1):12-18. (In Chinese).
- Wang, S.Y.; Lam, K.C.; Au, S.K.; et al. Analytical and Numerical Study on the Pillar Rockbursts Mechanism. Rock Mech. Rock Engng. 2006, 39 (5): 445–467. [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.P.; W.G.Pariseau. Fractal character and mechanism of rock bursts. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 1993, 12(1): 28-37. (In Chinese).
- Qi, Q.X.; Shi Y.W.; Liu T.Q.Experimental study on stick slip instability mechanism of rockburst. Journal of China Coal Society, 1997, 21(2): 34-38. (In Chinese).
- Pan, J.F.; Ning, Y.; Mao D.B.; et al.Theory of rockburst star-up during coal mining. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(3):586-596. (In Chinese).
- Dou, L.M.; He, J.; Cao, A.Y.; et al.Rock burst prevention methods based on theory of dynamic and static combined load induced in coal mine. Journal of China Coal Society, 2015, 40(7): 1469-1476. (In Chinese).
- Pan Y.S.Disturbance response instability theory of rockburst in coal mine. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(8): 2091-2098. (In Chinese).
- Dou, L.M.; Tian, X.Y.; Cao, A.Y.; et al. Present situation and problems of coal mine rock burst prevention and control in China. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(1): 152-171. (In Chinese).
- Dou, L.M.; Tian, X.Y.; Cao, A.Y.; et al. Present situation and problems of coal mine rock burst prevention and control in China. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 47(1): 152-171. (In Chinese).
- Liu, J.X.; Tang, C.A.; Zhu, W.C.; et al. Rock-coal model model for studying the rockburst. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2004, 26(2): 276-280. (In Chinese).
- Li, J.Q.; Qi, Q.X.; Mao, D.B.; et al.Discussion on evaluation method of bursting liability with composite model of coal and rock.Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(Supp.1): 4805—4810. (In Chinese).
- Dou, L.M.; Lu, C.P.; Mu, Z.L.; et al.Rock burst tendency of coal-rock combinations sample.Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering,2006,23(1): 43-46. (In Chinese).
- Gu, J.C.; Fan, J.Q.; Kong, F.L.; et al. Mechanism of ejective rockburst and model testing technology. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2014, 33(6): 1081-1089. (In Chinese).
- Yin, Y.C.; Zhao, T. B.; Li, H.T.; et al.Bursting liability test and evaluation index analysis of coal under different loading stiffness. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2023, https://doi.org/10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2023.0046. (In Chinese).
- Hudson, J.A.; Crouch, S.L.; Faihturst, C. Soft, stiff and servo-controlled testing machines: a review with reference to rock failure. Engineering Geology, 1972, 6:155-189. [CrossRef]
- Hojem, J.P.M.; Cook, N.G.W.; Heins, C. Stiff, two meganewton testing machine for measuring the work-softening behaviour of brittle materials. South Africa of Mechanical Engineering. 1975, 25: 250–270.
- Tan, Y.L.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Q.; et al.Study on occurrence mechanism and monitoring and early warning of rock burst caused by hard roof. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47 (1):166–172. (In Chinese).
- Qi, Q.X.; Zhao, S. K.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Ten typical accidents of coal mine rockburst and their analysis; Emergency Management Press: Beijing, China, 2021. (In Chinese).
- Liu, S.H.; Pan, J.F.; Wang, S.W.; et al. Rock burst mechanism of heading roadway in thick coal seam in magmatic intrusion areas. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering. 1975, 25: 250–270. (In Chinese).
- Pan, J.F.; Qi, Q.X.; Liu, S.H.; et al. Characteristics, types and prevention and control technology of rock burst in deep coal mining in China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(1):111-121. (In Chinese).
- Dong, F.T. Roadway Support Theory and Applied Technology Base on Broken Rock Zone; China University of Mining and Technology Press: Xuzhou, China, 2001. (In Chinese).
- Zhu; S.T.; Dong X.K.; Jiang; F.X.; et al. Failure mechanism of pressure relief with advance drilling in driving face of strong burst ultra thick coal seam in Liuhuanggou coal mine. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering. 2022, 39(1): 45-53.
- Zhang; D.X.; Wang; X.Y.; Guo; W.Y.; et al. The influence of coal seam thickness on the pressure relief and energy release mechanism of large-diameter drilling hole. Coal Science and Technology. 2022, https://doi.org/10.12438/cst.2023-0654. (In Chinese).
- Zhao; Y.X.; Jiang; Y.D.; Wang; T.; et al. Features of microseismic events and precursors of rock burst in underground coal mining with hard roof. Journal of China Coal Society, 2022, 37(12): 1960-1966. (In Chinese).
- Zhao; S.K.; Mechanism of force-structure cooperative prevention and control of deep hole roof pre-blasting for rock burst. Journal of China Coal Society, 2021, 46(11):3419- 3432. (In Chinese).
- Wang; C.W.; Jiang; F.X.; Wang; P.; et al. Microseismic events distribution characteristic and mechanism of rock bursting induced by a coal pillar. Journal of China Coal Society, 2009, 34(11): 1169-1173. (In Chinese).

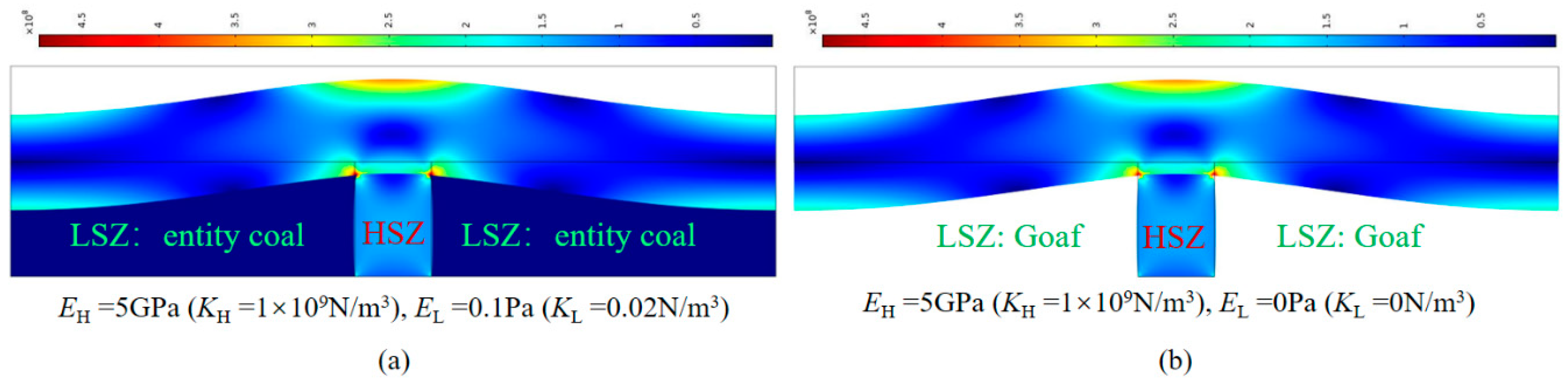
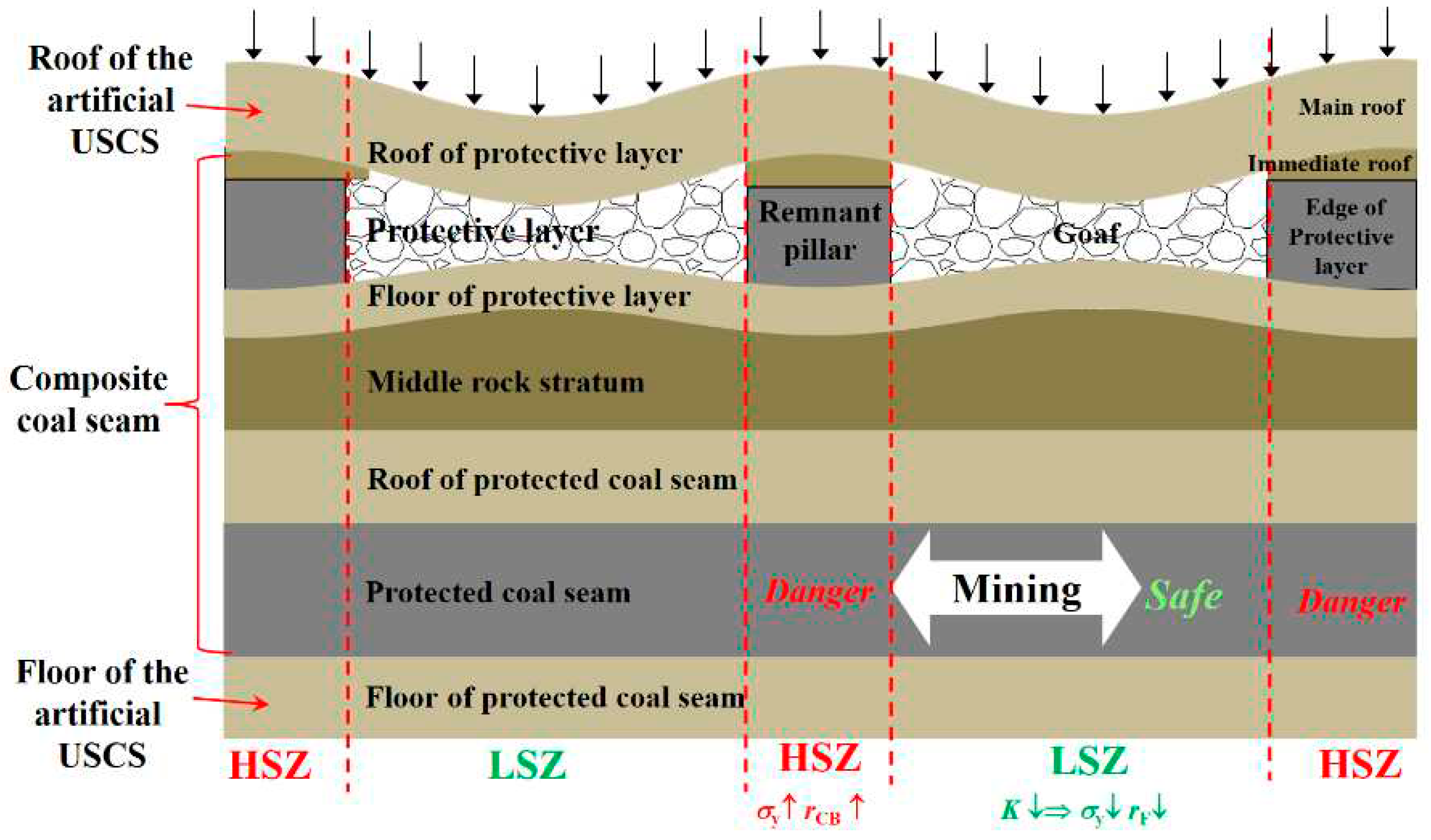
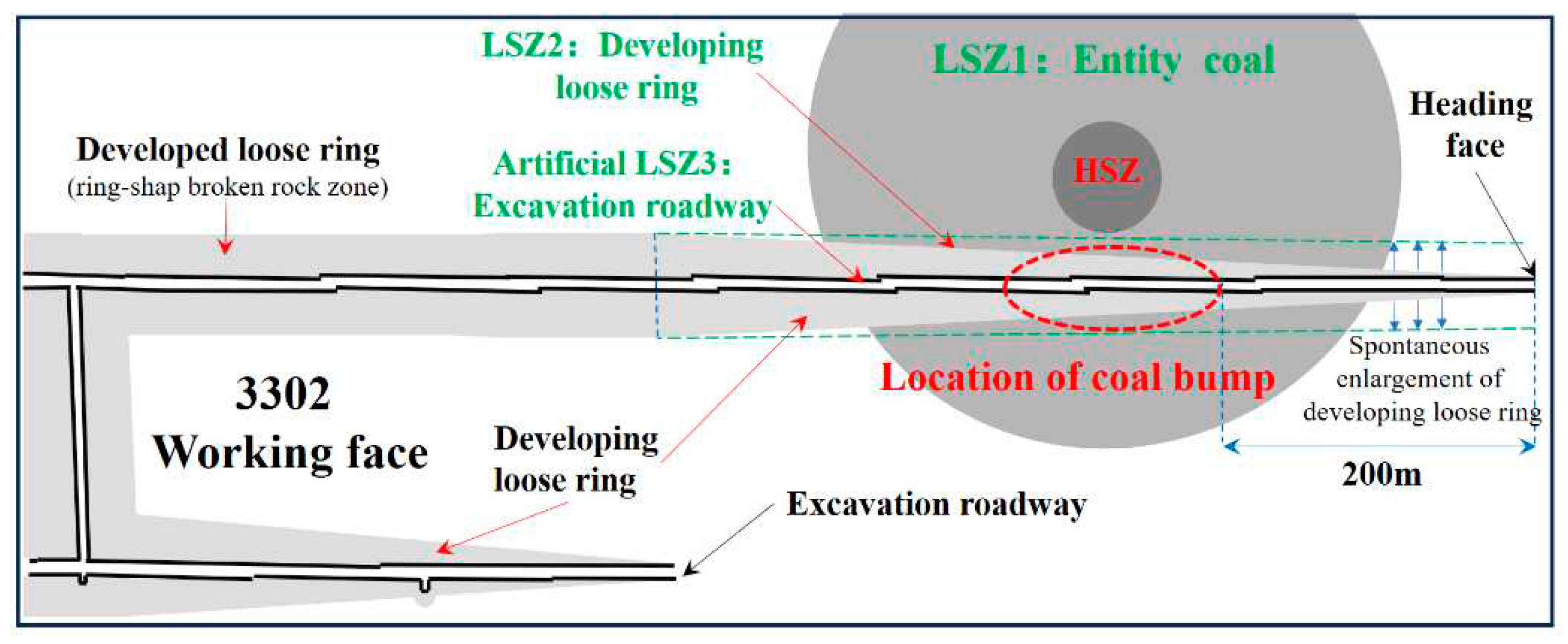
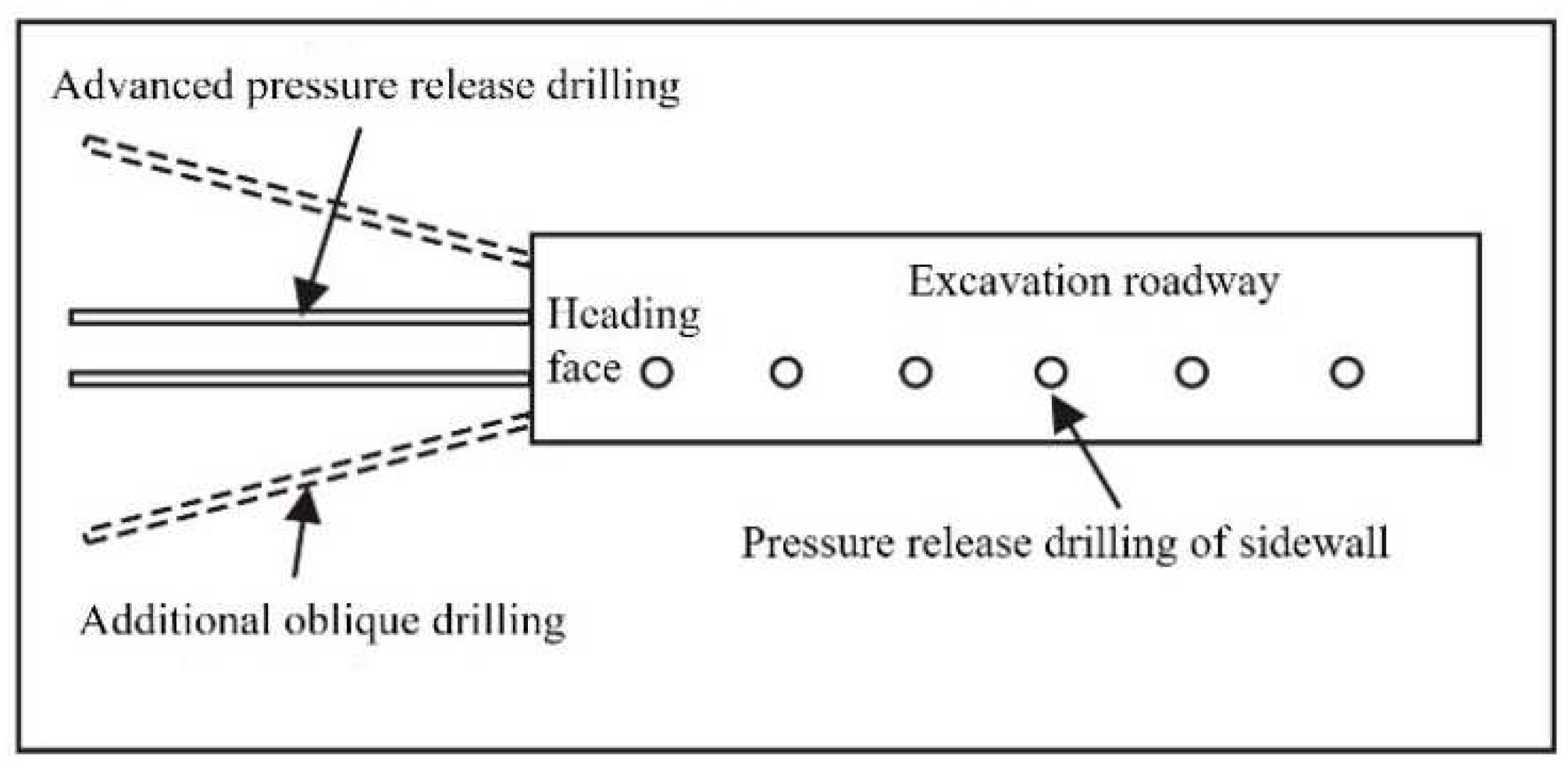
| Model | Aera (Width) of Roof SR/m |
Thickness of Roof HR /m |
Young’s modulus of Roof ER /GPa |
Young’s modulus of Hard Coal EH /GPa |
Young’s modulus of Soft Coal EL /GPa |
Aera (Width) of High Stiffness Zone SH /m | Aera (Width) of Low Stiffness Zone (one side) SL /m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 40 | 5 | 20 | 5 | 2 |
4 0 20.14 |
18 |
| 2 | 40 | 5 | 20 | 5 | 2 |
10 0 20.14 |
15 |
| 3 | 40 | 5 | 20 | 5 | 2 |
20 0 20.14 |
10 |
| 4 | 40 | 5 | 15 | 5 | 2 | 4 0 20.14 |
18 |
| 5 | 40 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 2 | 4 0 20.14 |
18 |
| 6 | 40 | 5 | 20 | 4 | 2 | 4 0 20.14 |
18 |
| 7 | 40 | 5 | 20 | 3 | 2 | 4 0 20.14 |
18 |
| 8 | 40 | 5 | 20 | 5 | 1 | 4 0 20.14 |
18 |
| 9 | 40 | 5 | 20 | 5 | 1×10-10 | 4 0 20.14 |
18 |
| 10 | 40 | 5 | 20 | 5 | 0 | 4 0 20.14 |
No Coal (goaf) |
| 11 | 40 | 7 | 20 | 5 | 2 | 4 0 20.14 |
18 |
| 12 | 40 | 9 | 20 | 5 | 2 | 4 0 20.14 |
18 |
| 13 | 20 | 5 | 20 | 5 | 2 | 4 0 20.14 |
8 |
| 14 | 12 | 5 | 20 | 5 | 2 | 4 0 20.14 |
4 |
| No. | Controlled Variable |
Controlled Variable Value |
Normal Stress /MPa |
Stress Concentration Factor |
Compression Deformation /mm |
Bending Deflection /mm |
Total Deformation /mm |
NSC of Roof KR/N•mm-3 |
NSC of Pressure provider /N•mm-3 |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SH/m | 4 | 23.837 | 1.589 | 4.065 | 8.569 | 12.635 | 4.000 | 0.322 | 1.287 |
| 2 | 10 | 19.576 | 1.305 | 3.798 | 13.471 | 17.269 | 4.000 | 0.220 | 0.880 | |
| 3 | 20 | 17.442 | 1.163 | 3.602 | 13.638 | 17.241 | 4.000 | 0.209 | 0.836 | |
| 1 |
ER/GPa | 20 | 23.847 | 1.589 | 4.065 | 8.569 | 12.635 | 4.000 | 0.322 | 1.287 |
| 4 | 15 | 23.469 | 1.564 | 5.346 | 8.978 | 14.324 | 3.000 | 0.373 | 1.120 | |
| 5 | 10 | 22.955 | 1.530 | 7.861 | 9.453 | 17.314 | 2.000 | 0.454 | 0.908 | |
| 1 |
EH /Gpa (KH) |
5 | 23.837 | 1.589 | 4.065 | 8.569 | 12.635 | 4.000 | 0.322 | 1.287 |
| 6 | 4 | 21.110 | 1.407 | 3.862 | 6.007 | 9.869 | 4.000 | 0.391 | 1.565 | |
| 7 | 3 | 17.759 | 1.184 | 3.608 |
2.830 | 6.438 | 4.000 | 0.564 | 2.242 | |
| 1 |
EL /GPa (KL) |
2 | 23.837 | 1.589 | 4.065 | 8.569 | 12.635 | 4.000 | 0.322 | 1.287 |
| 8 | 1 | 34.829 | 2.322 | 4.996 | 29.159 | 34.155 | 4.000 | 0.146 | 0.585 | |
| 9 | 1×10-10 | 149.758 | 9.984 | 15.640 | 490.043 | 505.683 | 4.000 | 0.031 | 0.124 | |
| 10 | 0 | 149.776 | 9.984 | 15.640 | 490.043 | 505.683 | 4.000 | 0.031 | 0.124 | |
| 1 | HR/m | 5 | 23.837 | 1.589 | 4.065 | 8.569 | 12.635 | 4.000 | 0.322 | 1.287 |
| 11 | 7 | 24.762 | 1.651 | 4.220 | 6.785 | 11.005 | 2.857 | 0.383 | 1.096 | |
| 12 | 9 | 25.385 | 1.692 | 4.379 | 6.003 | 10.382 | 2.222 | 0.422 | 0.937 | |
| 1 | SR(SL) /m | 40(36) | 23.837 | 1.589 | 4.065 | 8.569 | 12.635 | 4.000 | 0.322 | 1.287 |
| 13 | 20(16) | 23.541 | 1.569 | 4.093 | 4.059 | 8.152 | 4.000 | 0.502 | 2.008 | |
| 14 | 12(8) | 22.427 | 1.495 | 3.961 | 1.431 | 5.393 | 4.000 | 0.735 | 2.938 |
| Key Parameters |
Mechanical Analysis | Numerical Simulation | Engineering Experience | Corresponding Available Ways of Coal Bump Prevention |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fscH | rF | KpH | rI | rCB | fscH | rF | KpH | rI | rCB | fscH | rCB | ||
| SH | - | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | Avoiding a decrease inSH: Avoid mining isolated working faces and expanding existing roadways |
||||
| ER | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | Reduce ER of continuous composite roof: Carried out roof cutting measures in rock stratum with higher ER. |
||
| EH (KH) | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | Reduce KH: coal seam slotting or blasting, large diameter boreholes, water injection softening, high pressure water jet cutting |
| EL (KL) | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | Increase KL: hydraulic support, single prop, anchor bolts and cables, grouting, goaf filling |
| HR | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | Reduce HR of continuous composite roof: Carried out roof cutting measures in rock stratum with higher HR. |
|||
| SR(SL) | + | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | + | Cutting roof or floor to reduce the SR(SL): directional hydraulic fracturing, deep hole blasting | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





