1. Introduction
Autoimmune diseases, particularly type 1 diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are associated with altered intestinal microbiota composition [
1]. Several recent studies provide evidence that abundance of some taxa increased in the microbiome of RA patients [
2,
3,
4].
Taxa-level alterations can be shared across the inflammatory arthritis phenotypes, e.g. including ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis [
5]. However, there are still contradictory results about the taxa involved. Nevertheless, targeting the microbiota seems promising since the diet, a major factor contributing to the microbial balance, has been shown to affect RA progression and the microbiota composition [
6,
7,
8]. Whereas fasting alleviates the symptoms, food intake is reported to exacerbate disease activity [
9]. Supplementation with probiotics can overcome the adverse effect of food intake [
10].
But screening for efficient probiotics in the context of inflammation is still at the beginning. Actually, the arthrogenic potential of intestinal probiotic bacteria explored in the 1980-1990s delayed research on the possible beneficial effect of their oral administration since both lactobacilli and bifidobacteria exhibited pro-arthrogenic properties [
11,
12,
13,
14]. New approaches using gnotobiotic animals and a finer analysis of arthrogenic peptidoglycans have led to a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms emphasizing the safety of the oral route [
15]. In the late 90s,
Lactobacilli casei strain Shirota was demonstrated to prevent arthritis onset [
16]. To date, a plethora of studies focusing onto lactobacilli showed efficacy in animal models [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25].
In contrast, the protective role of bifidobacteria is less extensively studied. Since RA patients harbor fewer bifidobacteria at the RA onset, their promotion could help preventing disease exacerbation [
26]. Administration of
Bifidobacterium pseudocatulatum prior the onset of the disease was shown to reduce arthritis index in an rident model of arthritis [
27].
B.breve and
B.longum intake also alleviate collagen-induced arthritis [
28,
29].
Still, the respective efficacy of the various strains remains to be ascertained in clinical trials. So far, only the
L.casei 01 strain has been tested in a clinical trial, showing an improvement in patients' condition [
30]. But, although promising, probiotic safety shall be taken into consideration. There have been reports of several pathological cases recently [
31,
32,
33,
34].
The alternative is to employ compounds from bacteria that can emulate the protective effects of the bacteria themselves. The free form of cell wall lipoproteins (Lpps) released by either
Bifidobacterium longum or
B. breve during milk fermentation reproduced the effects on the microbiota observed with the whole fermented milk. [
35]. The released Lpps are complex molecules sharing across the bifidobacterial species a 43-45 kDa protein exhibiting a lipobox and a CHAP domain on the N- and C- terminal sequences respectively. Di- or tri-acetylation on the lipobox cysteine led to a possible recognition of TLR2 receptors [
36].
Administration of
B.longum Lpps free form to gnotobiotic mice associated with the microbiota from a RA patient led to the increase of intestinal bifidobacteria and the restoration of a spleen CD11c+ DCs transcriptomic pattern resembling those observed in mice associated with the microbiota from a healthy individual [
37].
Furthermore, Lpps intake by rat following induction of osteoarthritis protected the animals against the disease’s progression [
38]. The results prompted us to further investigate the anti-arthritic potential of free form of cell wall Lpps using animal models.
In the present work, free lipoproteins from B.longum were administrated in collagen-induced (CIA) and anti-collagen antibody induced arthritis (CAIA) DBA/1OOaHsd mouse models. Selected bacteria already known to be targeted by Lpps were quantified along the intestine at the end of the surveys. Splenocytes were cultured and triggered by lipopolysaccharides to explore the elicitation of Il-10 secretion in Lpps treated CIA animals as well as in gnotobiotic mice associated with RA patient’s microbiota. The possible uptake of Lpps by DCs was as well studied by administrating labelled BC to CAIA and healthy mice.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
All experiments were conducted following the 2010 EU directory guidelines and were approved by the Ethical Committee for Animal Experimentation (Lille, France). DBA/1OOaHsd mice were purchased from Harlan France (Gannat, France). C3H/HeJ mice associated with RA donor microbiota (RA mice) were kept in sterile isolators (La Calhène,Vélizy, France) with free access to sterile RO3 pellets (UAR, Epinay-sur-Orge, France) and sterile water in the University animal facility [
37].
B.longum free lipoproteins were prepared as previously described [
38].
2.2. Arthritis induction
Arthritis was induced by collagen (CIA) as follows: 5-6 weeks old male DBA/1J mice were intravenously injected with collagen II (MDBioproducts, Zürich, Switzerland) at D0 (with complete Freund’s adjuvant) and D30 [
39]. Administration of Lpps started on day 0. Lpps were dissolved in sterile water at 0.25, 0.5 and 1 mg/L, distributed in sterile bottles and kept frozen at -20°C until use. Bottles were daily replaced on the cage by new ones (n=8 mice per group per assay). The volume left in the bottles removed on the morning was measured for an estimation of the dosing. Body weight was monitored all along the survey. Control group (n= 8 per assay) received sterile water instead of Lpps solution. The mice were daily monitored for the development and severity of joint inflammation (toes, tarsus, ankle, wrist and knee). Each paw was scored on a scale of 0-4 based on signs of swelling and inflammation by 2 observers who were blinded to the group assignments via a visual assessment scoring system (0: no evidence of erythema or swelling, 1: erythema and mild swelling confined to the midfoot or ankle joint, 2: erythema and mild swelling extending from the ankle to the midfoot, 3: erythema and moderate swelling extending from the ankle to the metatarsal joints, 4: erythema and severe swelling encompassing the ankle, foot and digits) [
40].
The combined limbs total score was recorded each day (max. score = 16). At the end of the assay (around D45), mice were euthanized and the following organs were collected: kidney, spleen, liver, lung, Peyer patches, ileum, caecum and colon.
The anti-collagen antibody cocktail was purchased from MD Bioproducts and used according to the manufacturer’s instructions to induce arthritis (anti-collagen antibodies induced arthritis-CAIA model). Male DBA/1OOaHsd mice aged 5-6 weeks were intravenously injected with the cocktail of anti-collagen antibodies. Three days later, mice were intraperitoneally injected with 50 μg of LPS (Sigma, Saint Quentin-Fallavier, France) to trigger the development of arthritis. Administration of Lpps at a concentration of 0.2 mg/L started ten days prior the cocktail injection for the prophylactic Lpps dosing regimen and after the LPS injection (day 0), for the curative Lpps dosing regimen. Control mice received sterile water. Lpps intake was estimated by daily measuring the remaining volume. Mice were monitored and scored daily as described above. At the end of the assay, mice were euthanized and the following organs were collected: kidney, spleen, liver, lung, Peyer patches, ileum, caecum colon.
2.3. Bacterial enumeration in organs
Organs (intestine fractions, spleen, Peyer’s patches) were weighted and suspended in 9 ml pre-reduced Ringer solution (Solabia, Pantin, France) supplemented with cysteine HCl (0.03%) (VWR, Fontenay-sous-Bois, France). Except for enterobacteria enumerated onto EMB medium, bacteria were counted using real time qPCR. The suspensions were kept frozen until total DNA extraction. After thawing, total DNA was extracted using the Nucleospin Tissue kit (Macherey Nagel, Hoerdt, France). DNA content was determined at 260-nm wavelength using Biophotometer Plus (Eppendorf, Montesson, France). qPCR was carried out as previously described [
38].
2.4. Enumeration of spleen CD11C+ DCs and CD4+ T cells and culture of splenocytes in CIA model.
Primary splenocytes were aseptically isolated from CIA mice (control group, n=10; 0.5 mg Lpps/L group, n=11; 1 mg Lpps/L, n=6) or from RA mice treated (n=7) or not (n=9) by Lpps. Briefly, spleen was dilacerated in sterile PBS and digested with 2 mg/ml of collagenase (Sigma, France). CD11c and CD4 (L3T4) cells were positively separated using MACS®MicroBead Technology (Miltenyi Biotec, Paris, France). CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T Cells were further positively separated from RA cell suspensions. Besides, splenocytes from four control and five CIA mice receiving 0.5 mg Lpps/L as well as four control and four Lpps treated RA male mice were kept in RPMI 1640 broth (Gibco®, Villebon-sur-Yvette, France) supplemented with foetal bovine serum (5%) (Gibco®) and 50U penicillin-streptomycin (Gibco®). Suitable cell numbers were evaluated using the trypan blue exclusion method and a hemocytometer. PBS washed cells were exposed to the fresh medium supplemented with or without lipopolysaccharides from E. coli O111:B4 (Sigma) (prepared in pH 7.2 PBS) ranging from 2 ng/ml up to 10 µg/ml. For the measurement of IL-10 level in the cell culture medium, approximately 2 × 105 cells/well of splenocytes were cultured in a 96-well plate. The cytokine was quantified by an ELISA kit (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) using the manufacturer's protocol.
2.5. In vivo and in vitro Lpps uptake
Lpps were labelled according to the manufacturer’s instructions with either tetramethylrhodamine-5(6)- isothiocyanate (TRITC) (Enzo Life Sciences) or Pacific Blue (Life Technologies). The conjugates were stored in the dark at -20°C until use.
CAIA DBA/1OOaHsd mice received by gavage TRITC labeled-Lpps at dose ranging 35-100μg/kg, or sterile water (control mice) supplemented with 10µl cell-permeable fluorescent dye 5’- carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE). Mice were euthanized 3h, 5h or 16h post-gavage. Peyer’s patches, spleen and bone marrow (BM) were suspended in RPMI medium and the suspensions were sieved in 70µm and 40µm devices. CD11c+ cells were isolated from splenocytes and BM cell suspensions using MACS®MicroBead Technology (Miltenyi, France). Cell numbers were evaluated using the trypan blue exclusion method and a hemocytometer. Bacteria and Lpps containing cells were then evaluated using fluorescence microscope (Nikon Eclipse E600). Besides, primary cells from bone marrow and thymus were aseptically isolated from CAIA mice. Suitable cell numbers were evaluated using the trypan blue exclusion method and a hemocytometer. PBS washed cells were exposed to fresh RPMI 1640 medium supplemented with or without Pacific blue labeled Lpps (0.15 and 0.3 mg/L).
A second in vivo analysis was performed in healthy and CAIA DBA/1OOaHsd mice fed R210 pellet (UAR) to avoid contaminating food fluorescence. They were gavaged at dose ranging 25-50 µg/kg with Pacific blue labeled-Lpps or broth extract and euthanized 15-17 h post-gavage. CD11c and mPDCA positive cells were isolated using MACS®MicroBead Technology.
To confirm the possible uptake in steady conditions, healthy mice were gavaged with Pacific blue labeled-Lpps or broth extract and euthanized 15 or 72h post-gavage. The cell suspension was analyzed using FACSAria™ cell sorter (filter 450/40) (BD biosciences) with the following antibodies: anti-CD4 conjugated to Alexa fluor 647, anti-CD8a conjugated to APC/Cy7, anti-CD11c conjugated to Brillant Violet, anti-PDC-TREMconjugated to phycoerythrin (PE) (BioLegend, San Diego, CA, USA).
2.7. Statistical analysis
The data were analyzed using SAS Studio. Differences in arthritis index, body weight gain and splenocytes response to Lpps were analyzed using mixed model for repeated measures. Clustering of the data (microbiome, cells counts…) was analyzed using Principal component analysis. Correlations were assayed for their statistical significance using Pearson (spleen weight, CD11c+ DCs, CD4+ T, CD4+CD25+ cells), Spearman and Kendal’s tau test (bacterial data). Difference in microbial and cells counts was analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis test or nonparametric analysis of variance followed by the adapted post-hoc tests (Bonferroni or Wilcoxon and Kolmogorov-Smirnov with corrected p-values).
3. Results
3.1. Protection against arthritis progression depends on the Lpps dose and is primarily related to Ligilactobacillus murinus intestinal colonization.
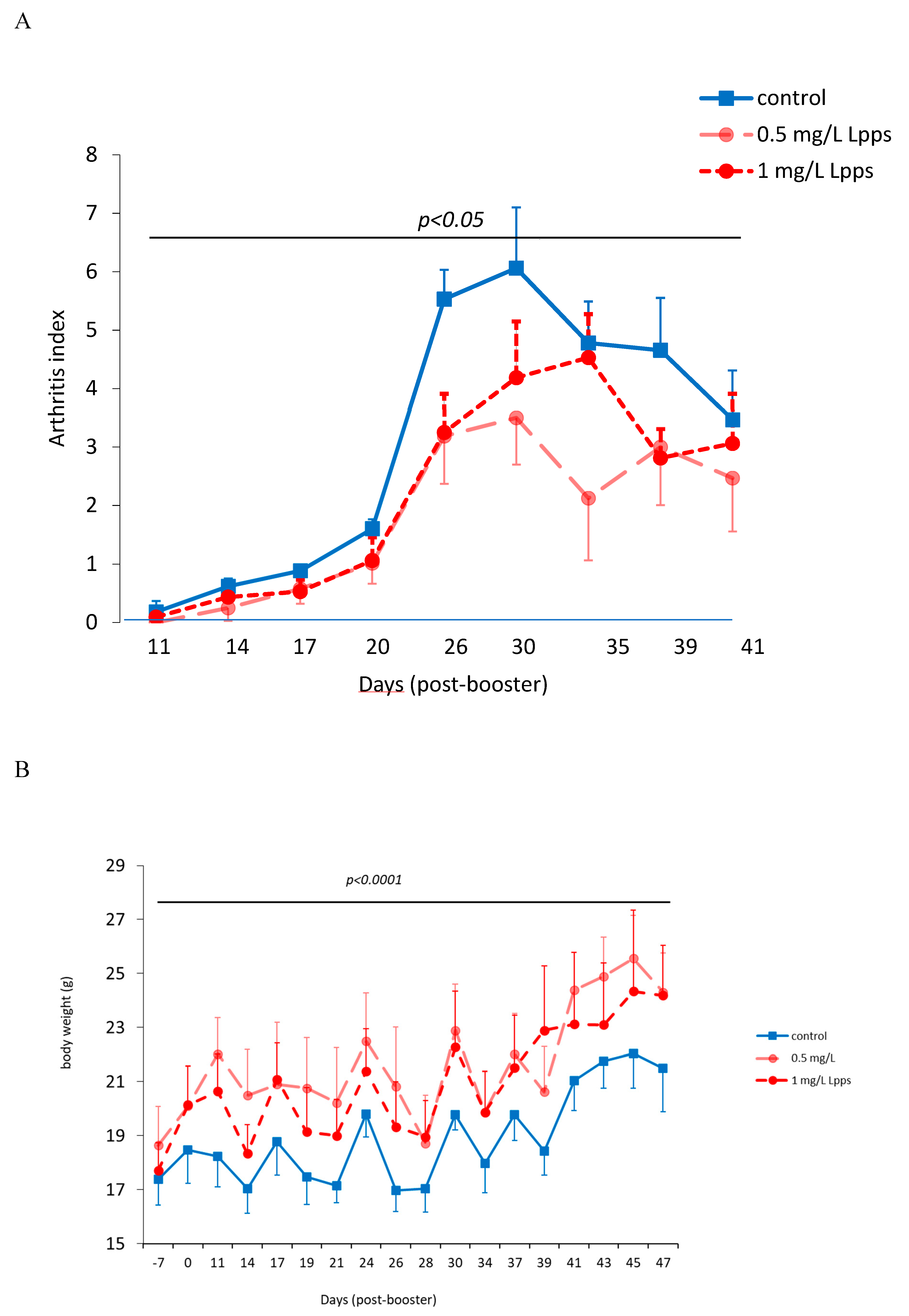
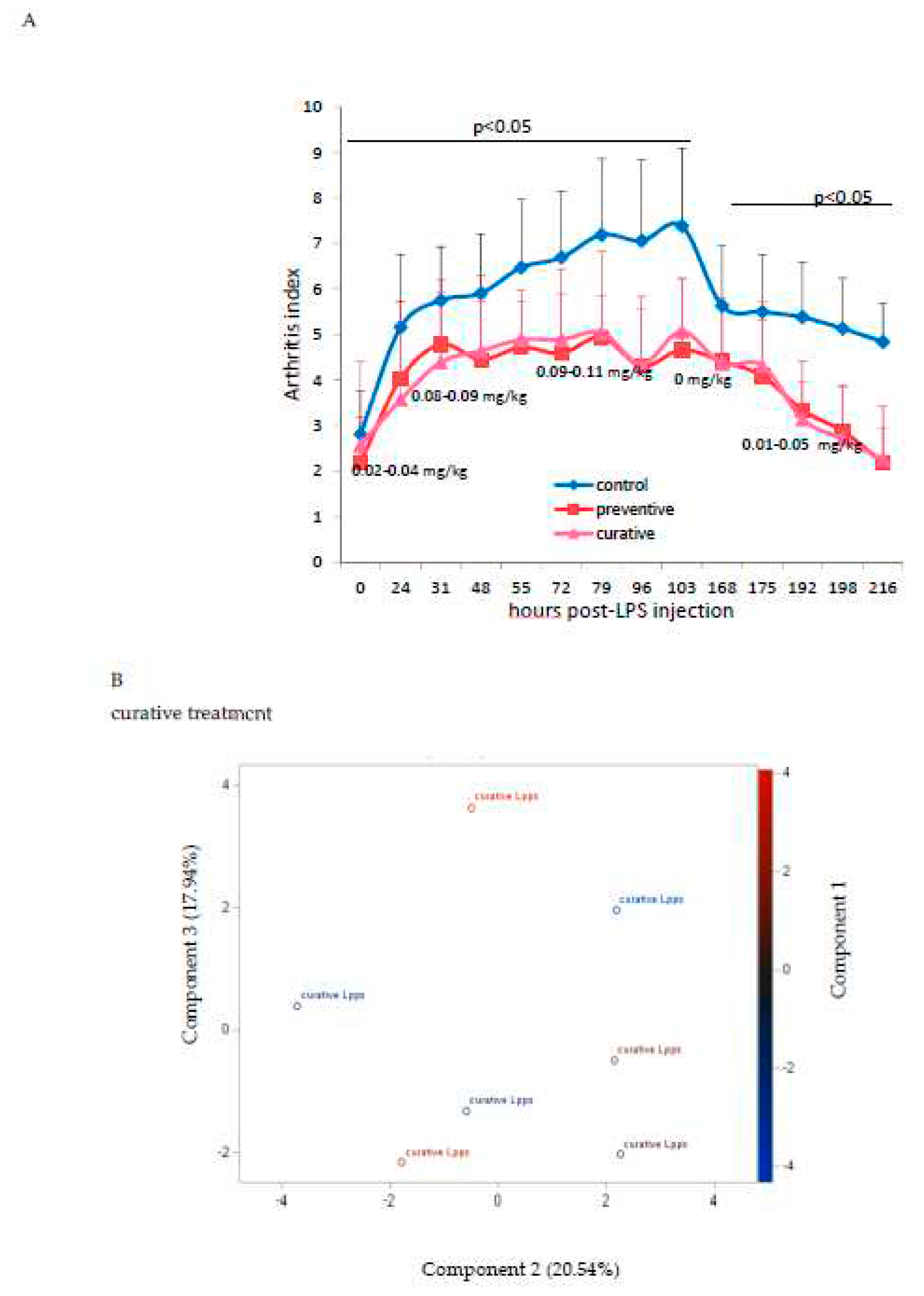
As showed on
Figure 1A, Lpps dosing at 0.5 but not 1 mg/L alleviated CIA progression (p<0.05). No protection was observed using 0.25 mg Lpps/L (data not shown). Increase in body weight was significant for the three treatments (p<0.0001,
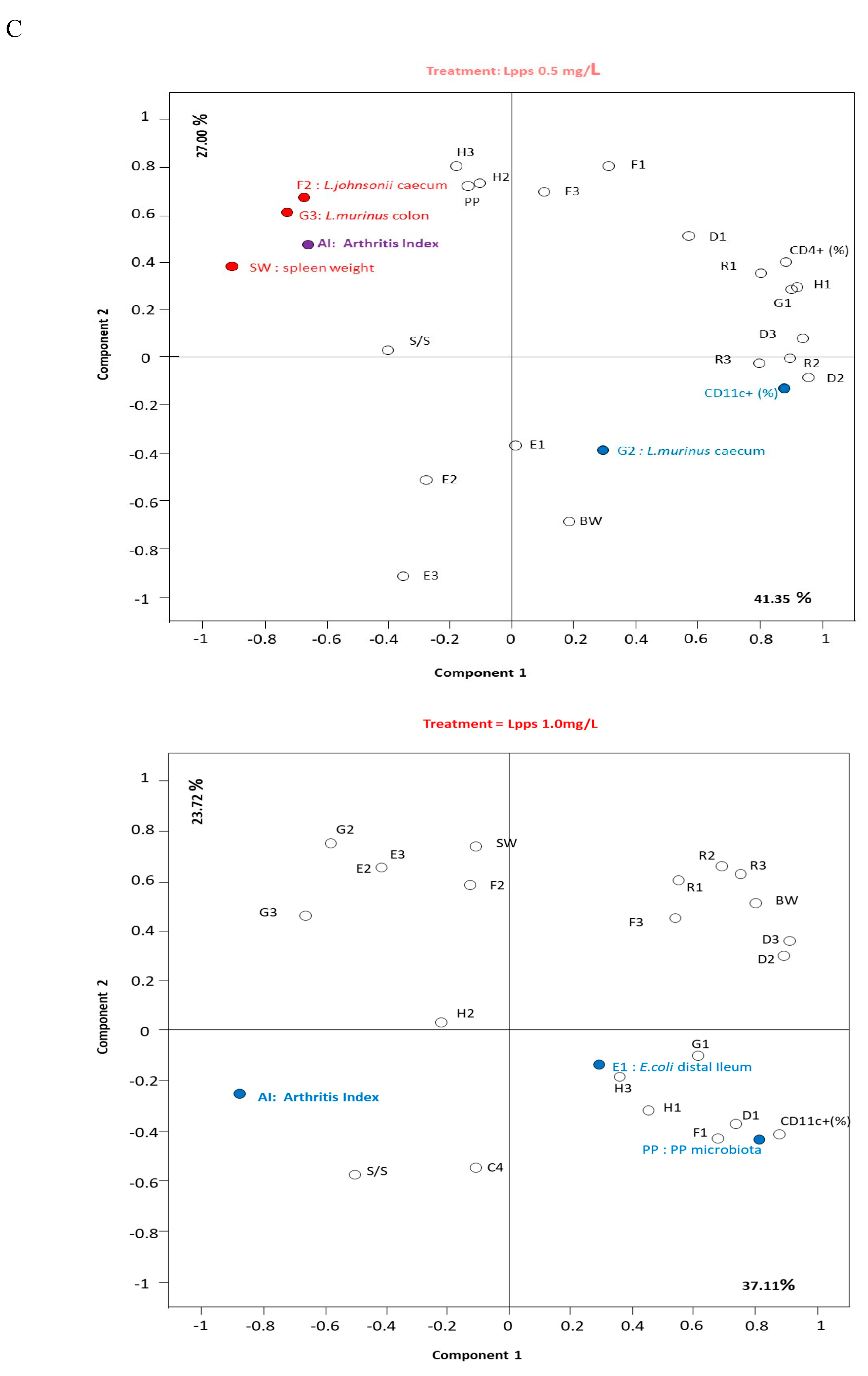
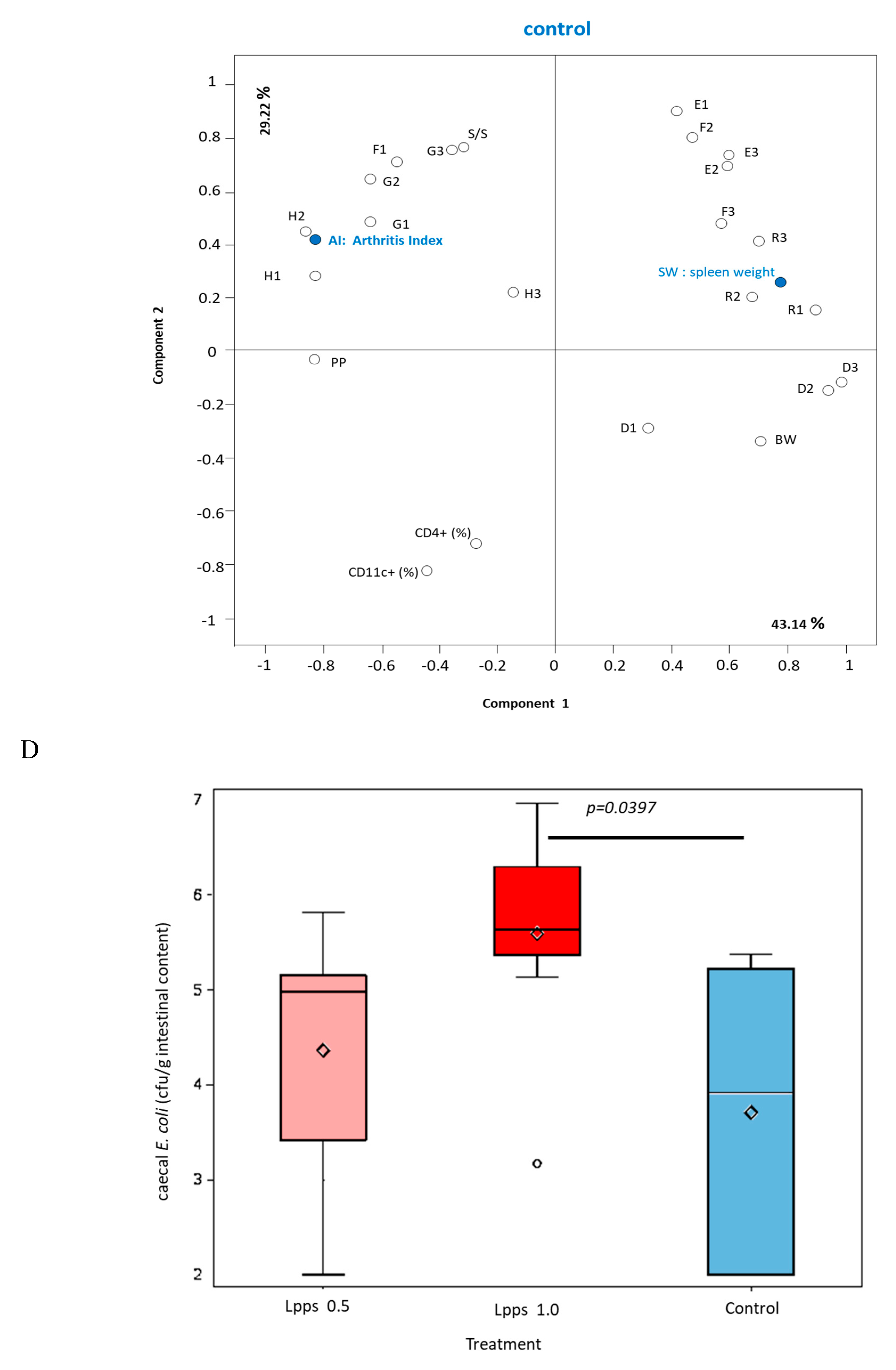
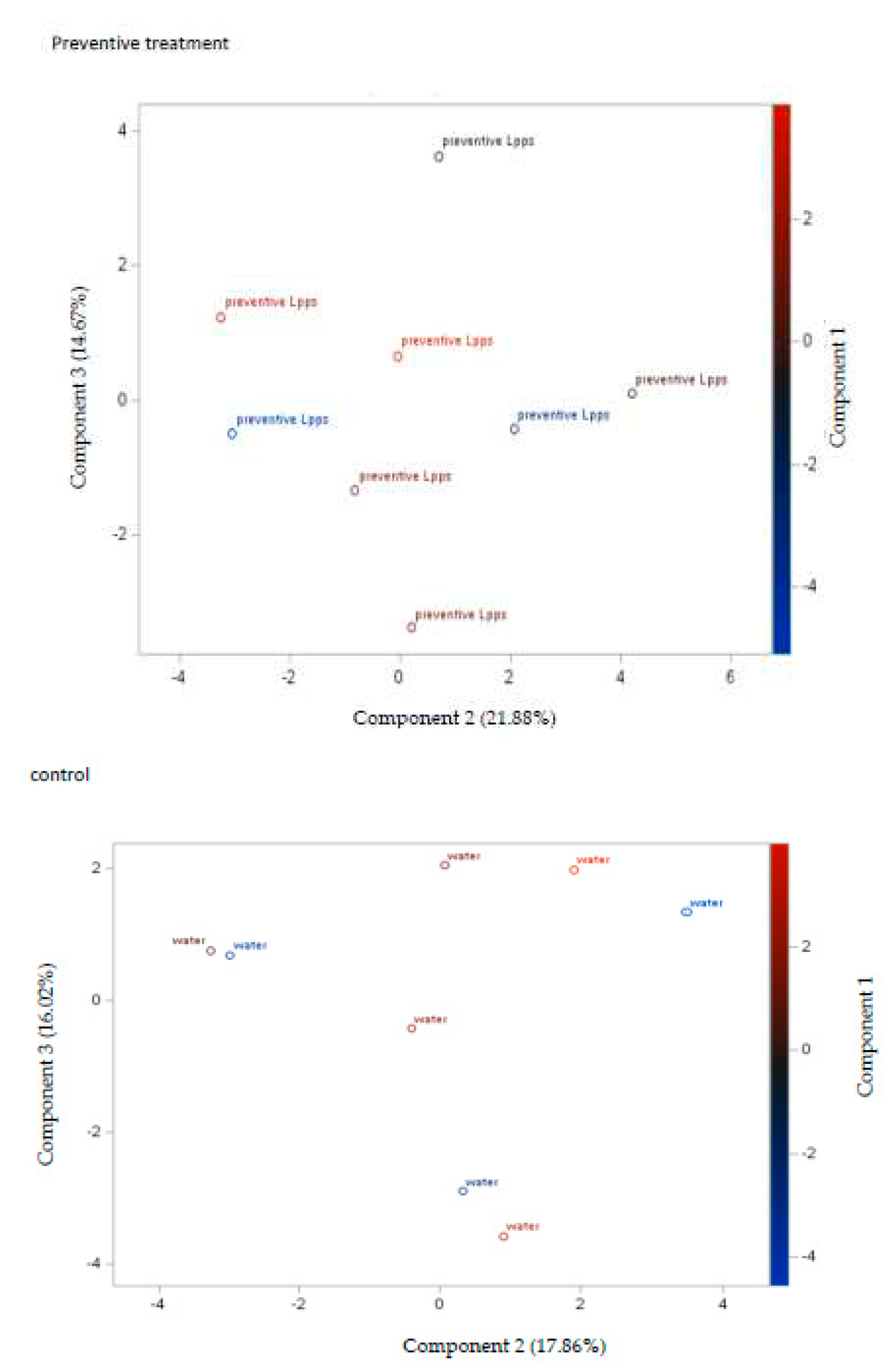
Figure 1B). Nonetheless, the body weight curves from both groups drinking Lpps showed significant higher increase as compared with the control one (p<0.0001). Principal component analysis (PCA) of data including bacterial counts, body weight and spleen characteristics (weight, splenocytes, CD11C+ dendritic cells (DCs) and CD4+ T cells) did not show clustering according to the treatment (
Figure 1C). But PCA depicted different bacterial or cell contribution to AI in the three groups. In CIA protected 0.5 mg/L Lpps group, colon
Ligilactobacillus murinus (p=0.0109), caecal
Lactobacillus johnsonii counts (p=0.0299) and spleen weight (p=0.0285) correlated with AI. On another hand, a negative correlation between spleen CD11c+ DCs and AI was noted (p=0.0347).
L. murinus counts in caecum also negatively correlated with AI (p=0.017). Of note, spleen CD11c+ DCs negatively correlated with colon
L. murinus (p=0.0188). In the unprotected 1mg Lpps/L treated group, ileal
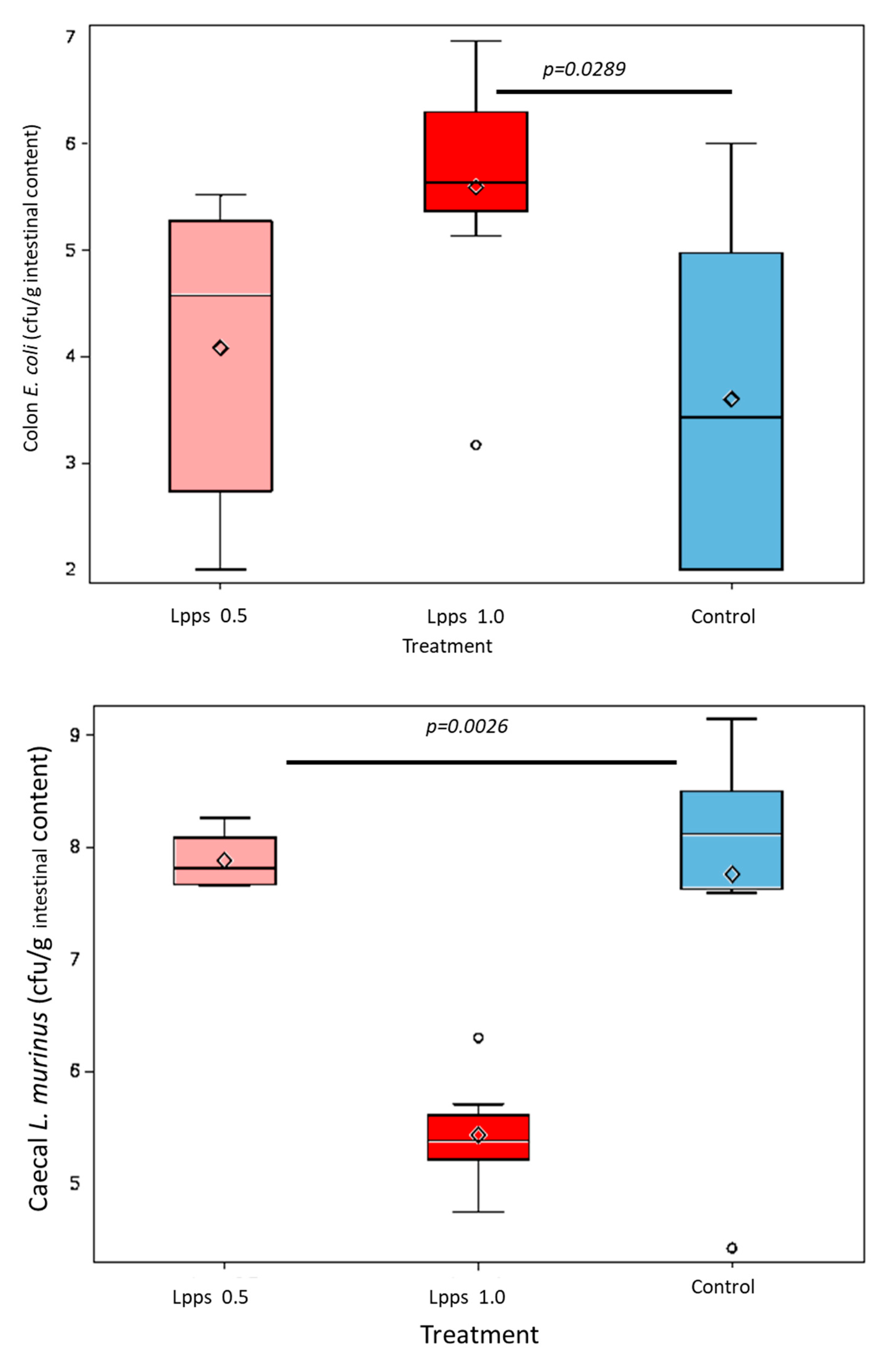
E.coli counts as well as the number of bacteria contaminating the Peyer’s patches negatively correlated with AI (p=0.0114 and p=0.0075, respectively). Interestingly, the control group did not exhibit significant correlation with bacterial counts. However, in contrast with the positive correlation observed in the responsive treated group, spleen weight was negatively correlated with AI (p=0.0448). Only a few differences in the bacterial counts colonizing the intestine were observed (
Figure 1D). Actually, variations were primarily detected in the 1 mg Lpps/L group with an increase in caecal and colon
E.coli (p=0.0195 and 0.0145, respectively) and a decrease in caecal
L.murinus (p=0.0026).
3.2. The degree of disease progression was significantly milder in both preventive and therapeutic Lpps CAIA groups.
Protection induced by 0.5 mg/L Lpps was similar in the preventive and curative groups (
Figure 2A). Clustering of the data according to the treatment was not observed (
Figure 2B). Besides, the contribution of the microbiome to the arthritis progression needs to be further explored, the set of selected bacteria showing no significant correlation with AI. The sole correlation noted in the preventive Lpps treated group was between AI and the body weight (p=0.0335). Significant difference in
E.plexicaudatum counts in colon was however observed (
Figure 2C). No
E.plexicaudatum was detected in the curative group (p=0.0325).
3.3. Higher IL-10 splenocytes response to LPS in CIA Lpps treated mice was likely related to CD11c+ DCs recruitment.
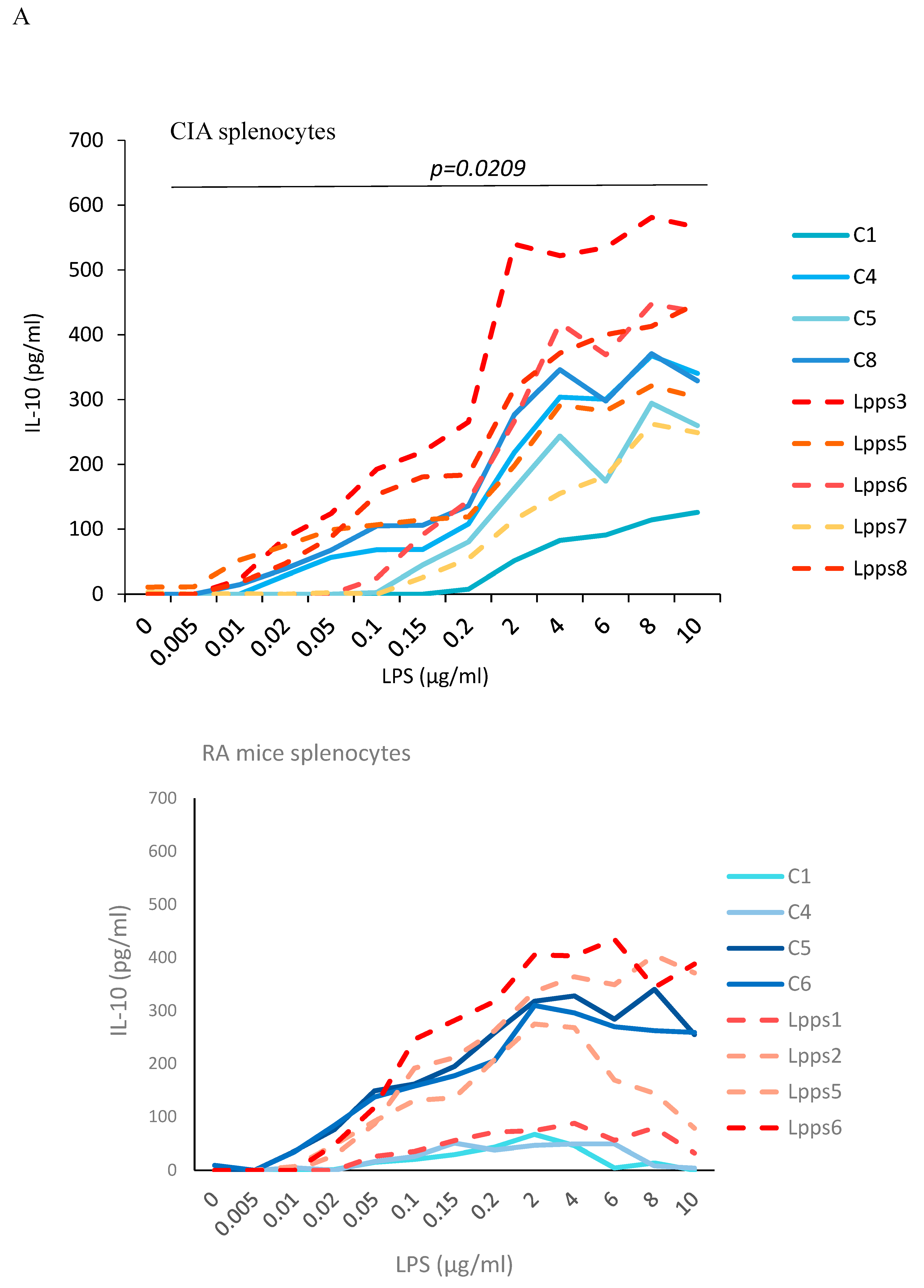
Negative correlation between CD11c+ DCs recruitment and AI prompted us to further analyze the splenic response to Lpps intake. Splenocytes were collected in CIA control and Lpps treated mice as well as in control and Lpps treated gnotobiotic mice associated with the microbiome of a patient with rheumatoid arthritis (RA mice) kept in isolators of the animal facilities. Splenocytes were triggered by increasing lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in the culture broth (
Figure 3A). All splenocytes groups showed a significant increased IL-10 response to the LPS augmentation (p<0.0001 each). Moreover, Lpps administration to mice was shown to elicit a higher IL-10 response in CIA splenocytes (p=0.0209), but not in RA splenocytes.
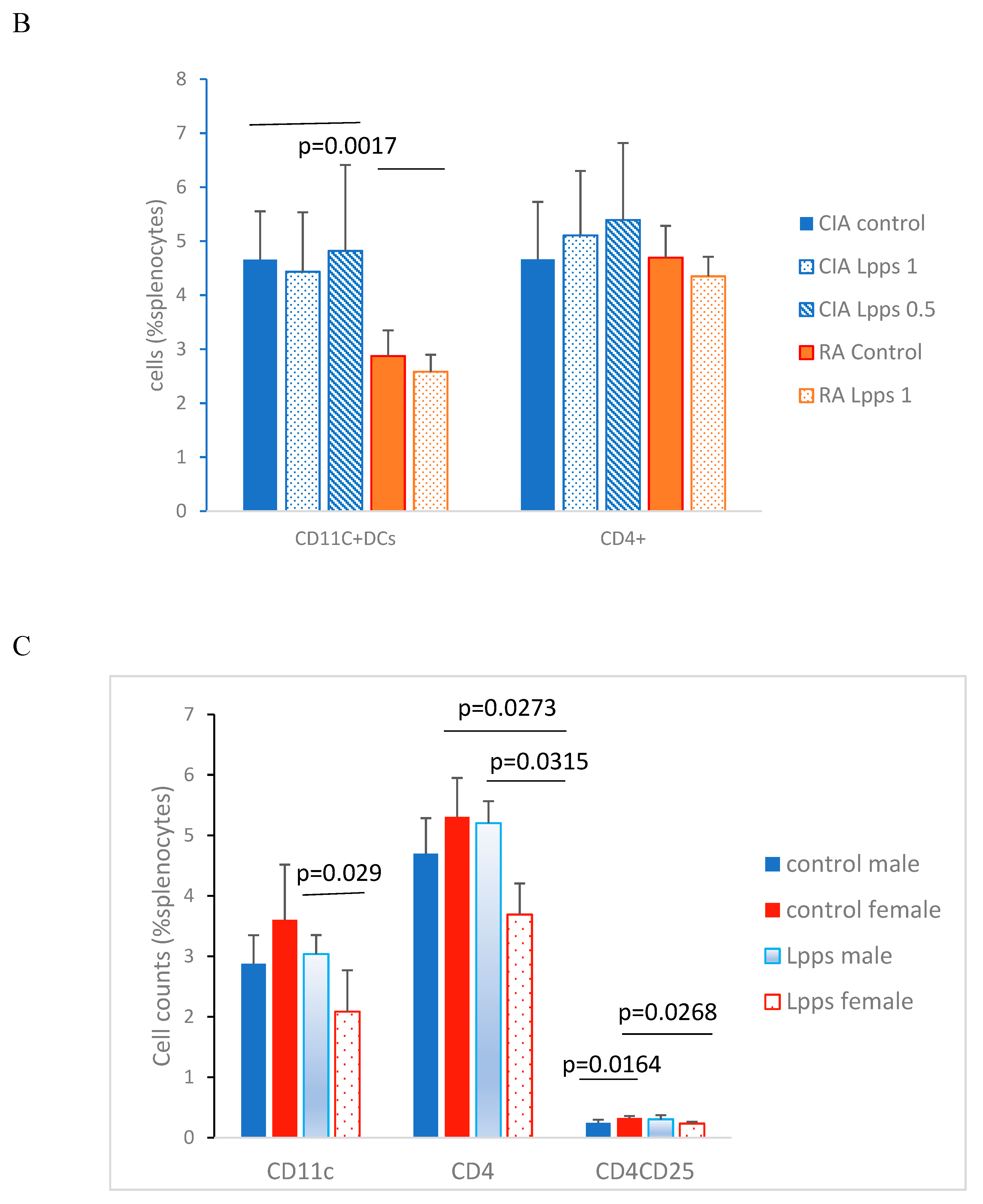
CD11c+ and CD4+ cells were enumerated in splenocytes from Lpps treated or control CIA and RA male mice. CD11c+ DCs were significantly lower in RA splenocytes compared with CIA splenocytes (
Figure 3B; p=0.0017). Interestingly, gnotobiotic mice associated with a human microbiome from a healthy volunteer was shown to harbor in their spleen CD11C+ DCs counts similar to DBA mice, i.e. 4.76% (SD 1.6). It indicated that recruitment of conventional DCs depends primarily onto the microbiome.
In contrast, CD4+ T cells compartments were similar in both murine lines whatever was the treatment. Nevertheless, Lpps administration did not affect the recruitment of CD11c+ DCs in the CIA and RA spleen. Conversely, CD11c+ DCs correlated with CD4+ T cells in CIA (r=0.9, p=0.0133) but not RA control group. In 0.5 mg Lpps/L CIA treated mice, CD11c+ DCs still correlated with CD4+ T cells (r=0.82, p=0.0449) but not in 1mg Lpps/L CIA treated mice.
Since RA mice received for a short time the Lpps solution, duration of intake could be too short for detecting an effect on cell recruitment in spleen. Female mice usually responded more rapidly to microbiome changes. Therefore, in addition to male RA mice, CD4+ T cells and CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells were analyzed in splenocytes from RA female mice control (n=4) and treated 1 mg Lpps/L (n=3) (
Figure 3C). In control RA mice, CD4+CD25+ Treg cells showed higher recruitment in female than male spleen (p=0.0164). When both groups received 1mg Lpps/L for 15 days, the female mice showed a lower recruitment of CD11c+DCs (p=0.029) and CD4+ T cells (p=0.0315) as compared to their male counterparts. Furthermore, female but not male mice responded to Lpps intake by reducing the recruitment of CD4+ T and CD4+CD25+ Treg cells. Nonetheless, CD11c+ DCs correlated with CD4+T cells (p=0.0269) and CD4+CD25 Treg (p=0.0263) in Lpps treated mice but not control ones. In contrast, CD4+T and CD4+CD25+ Treg correlated in the control (p=0.0429) but not in Lpps group.
To sum up, the difference in IL-10 response to LPS is likely related to the poorer recruitment of CD11C+ DCs in RA spleen as compared with CIA one. Moreover, female RA mice responded to Lpps by reducing significantly T cells, more specifically Treg cells recruitment, both cell compartments depending on CD11c+ Dcs recruitment as suggested by their positive correlations.
3.4. Lpps was primarily detected in bone marrow plasmacytoid DCs at a late post-gavage stage
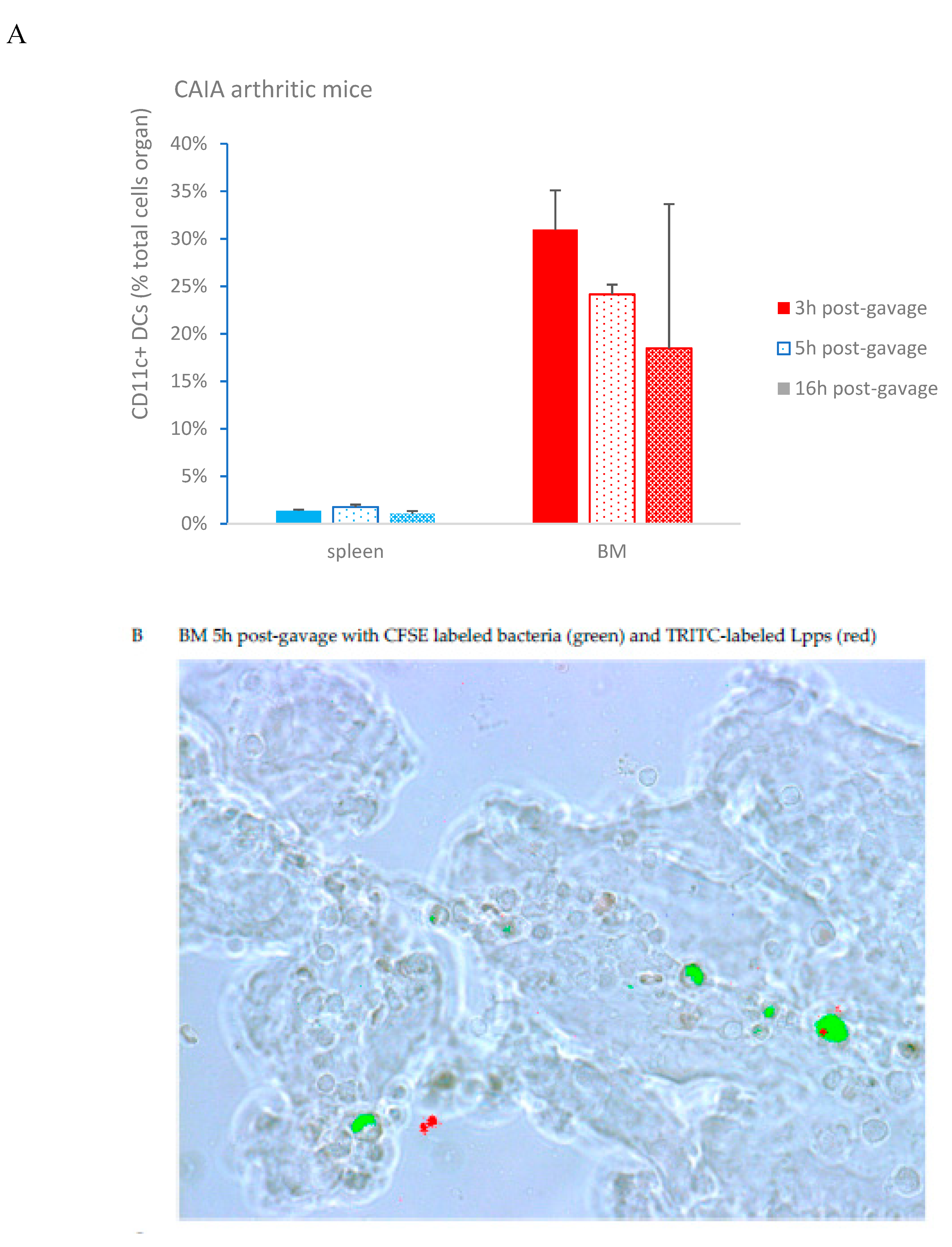
CAIA mice were force fed with a mixture of TRITC labeled Lpps and CFSE at the end of the week following LPS booster. Peyer’patches, spleen and bone marrow were collected 3,5 and 16h post-gavage. CD11c+ DCs were separated from splenocytes and bone marrow cells. In addition, two mice receiving only TRITC labeled Lpps and sacrificed 16h post-gavage, were used for monitoring the possible uptake of fluorescent food components. No significant difference was observed in the DCs counts whatever the organ (
Figure 4A). Though, DCs counts in bone marrow correlated with the arthritis index (p=0.0161). Red signal was detected only in bone marrow 5 and 16h post-gavage (
Figure 4B). More particularly, 16h post-gavage, the mouse with low AI did not exhibit detectable red signal. It is noticeable that TRITC fluorescence was always detected in CD11c+ DCs exhibiting a green fluorescence that indicated a parallel capture of bacteria and Lpps. Notably, mice forced fed with TRITC labeled Lpps deprived in CFSE showed lower DCs content. The labeled Lpps were not detected in DCs (data not shown).
In vitro assay using cells from bone marrow and thymus from arthritic CAIA showed a rare uptake by cells from thymus and bone marrow (0.15µg/L after 24h) (
Figure 4C). Dying cells were identified by the production of green and red fluorescence. Pacific blue fluorescence was observed in living cells not emitting green or red autofluorescence.
A complementary
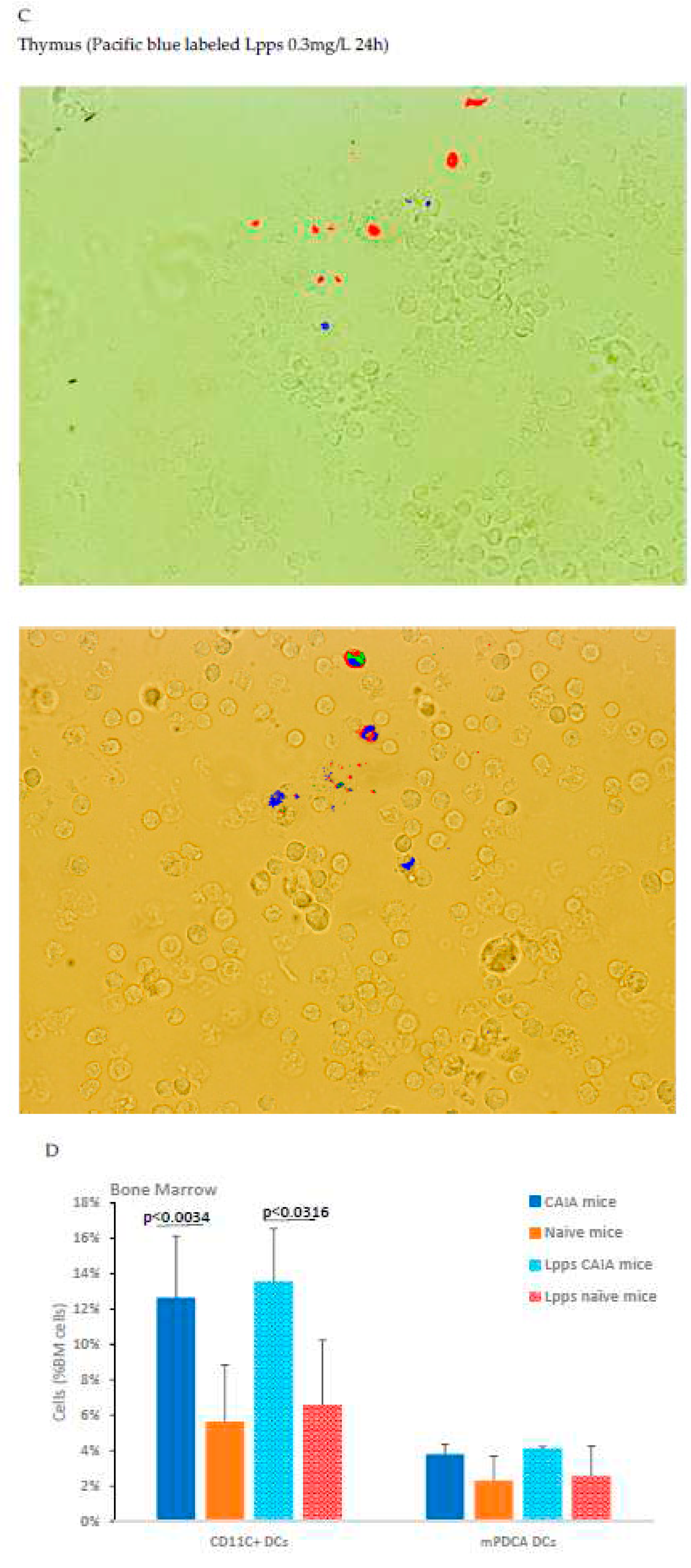
in vivo assay was performed in CAIA and naïve mice focusing in conventional CD11c+DCs and plasmacytoid mPDCA cells from bone marrow to work out which immune cell is able to capture Lpps. A first separation using MACS®MicroBead Technology showed that the distribution of DCs was not similar in the two groups. CD11c+ DCs expanded in bone marrow of CAIA mice as compared with naïve ones (
Figure 4D). Plasmacytoid cells were on the contrary at the same percentage in the two groups. A first tracking of cells harboring blue fluorescence showed that gavage with the labeled medium’s extract led to the detection of the signal in the sole CD11c+ DCs (data not shown). Gavage with Pacific blue labeled Lpps demonstrated an imbalance distribution in the two DCs subpopulations with 6.9% mPDCA in CAIA BM harboring the signal vs 1.4% CD11c+ DCs, and 2.1% vs 1.9% in naïve BM, respectively.
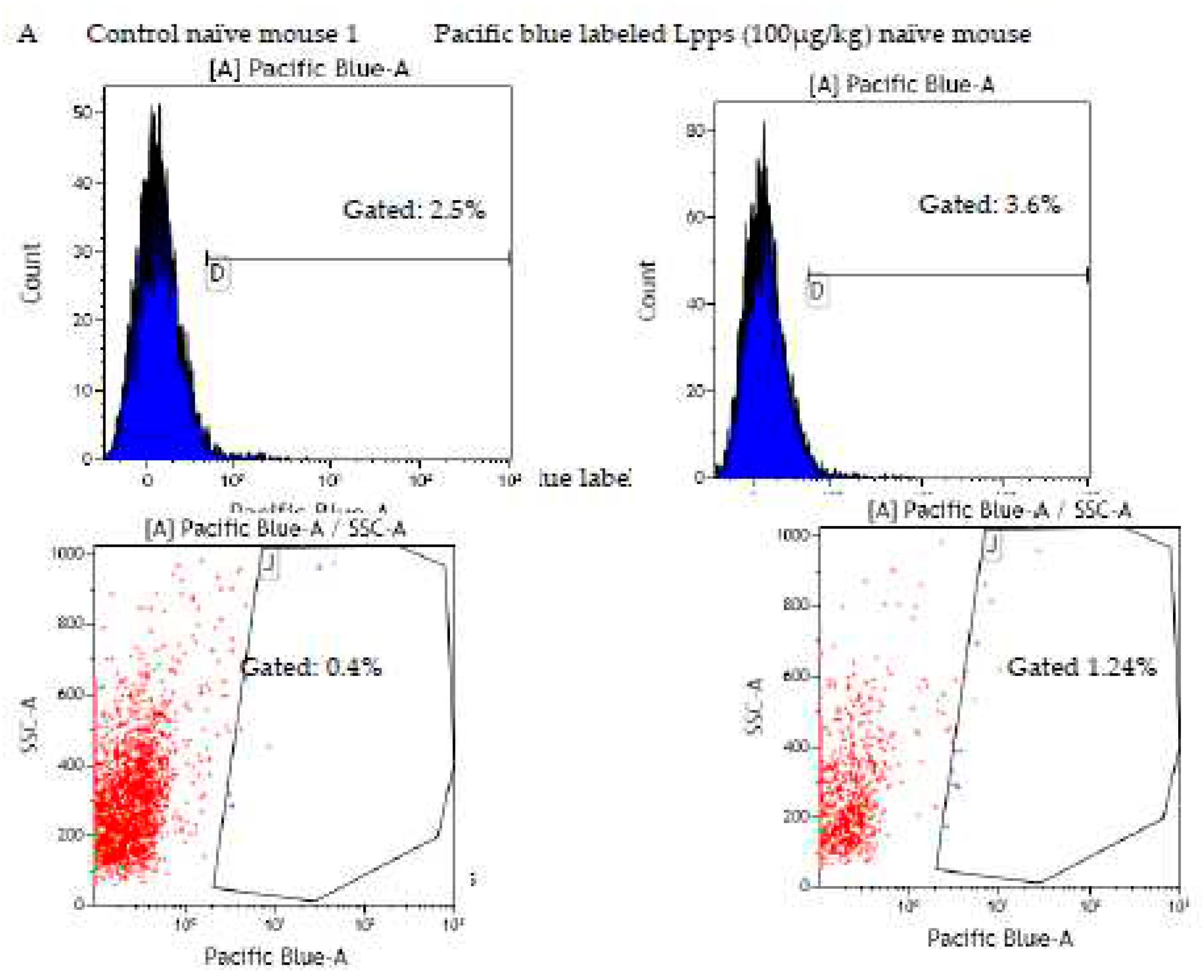
Since contamination from the culture medium cannot be avoided, cells with Pacific Blue signal from naïve mice BM were sorted by FACS. We confirmed that CD11c+ DCs did not exhibit blue fluorescent signal after gavage with dose of 25, 50 and 100 µg Lpps/kg at 15 and 72h post-gavage. The signal was however detected in the BM cell population as compared with the signal observed in BM cells from control mice forced fed with water (
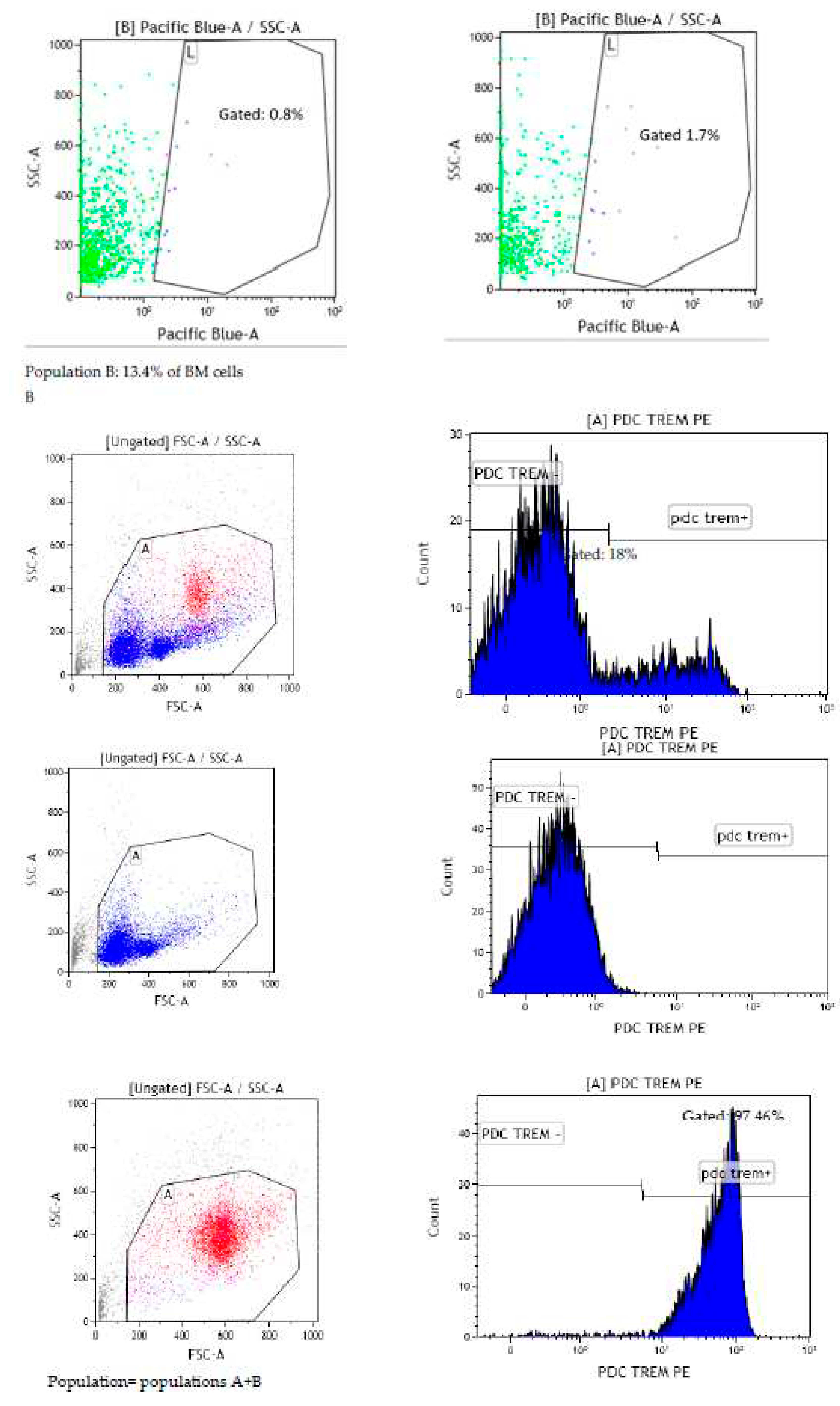
Figure 5A). Actually, sorting the cells according to their size allowed for a better Pacific Blue detection 15h post-gavage in the compartment comprising the largest cells (14.5% and 13.4% of the total BM cell suspension, e.g. less than 20% of the cell population). The latter were constituted of around 96-98% of PDC TREM (
Figure 5B). Thus, uptake of Lpps were not related to conventional DCs. Plasmacytoid cells were more likely involved in the capture.
4. Discussion
As a whole, our results provided evidence that free lipoproteins released from the cell wall of
B.longum during fermentation alleviated the course of arthritis in acute (CAIA) or chronic (CIA) phases. The mean rate of Lpps release is around 10mg/11 log
10 cfu
B.longum in a fermented milk. Estimation in a dairy product is around 10µg per ml. Daily intake of the average content of a yogurt (100-200ml) could therefore deliver around 15-30µg/kg per day (adult body weight around 70 kg). The range of efficient dose in mice was comprised between 50-100µg/kg. Actually, increasing the Lpps supplementation above 1 mg/L aggravated the AI in CIA mice (data not shown). Therefore, to design appropriately clinical trials, especially the range of efficient dose, a key point is to delineate the sources of Lpps. Since no bifidobacteria were detected in the intestine of the two arthritis models, the drinking solution was the unique source of Lpps. In contrast, even if the bifidobacterial population is reduced in patients suffering of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), they are still detectable [
26]. Therefore
in vivo release of Lpps by indigenous bifidobacteria needs to be confirmed for adjusting Lpps dosage.
Exploiting the capacity of Lpps to neutralize virus infection by binding to the viral capside, we developed affinity column coupled with virus suitable to capture Lpps in various human secretions [
41]. So, we were able to detect free forms of Lpps in human feces (preliminary results). As a consequence, developing a functional food supplement for human RA patients will require to determine the intestinal free Lpps content otherwise activation of the illness is to be expected as a consequence of too high a Lpps dosage. A first approach relies on the quantification of intestinal bifidobacteria. Still, determination of the bifidobacterial carriage is not predictive of the free Lpps content. On one hand, all bifidobacteria do not display in their genome a homologous protein sequence with a lipobox [
42]. Accordingly, the even highly concentrated cell free whey from
B.bifidum - species deprived in the homologous sequence with lipobox- was unable to modulate
in vivo the microbiota [
43]. Hitherto, focusing on the secreting bifidobacterial species will not provide an accurate estimation, as the factors tuning
in vivo cell wall Lpps release remain to be identified.
A second aspect is the narrow range of efficient dose. Two main issues need to be envisaged: the possible too high uptake by BM immune cells reinforcing the inflammation and the susceptibility to oxidative conditions [
44]. The inflammation related to the arthritis induction is characterized by the release of oxidate compounds, with possible deleterious effects onto the ingested Lpps. Alike probiotics, Lpps could be protected through micro-encapsulation which creates a favorable local environment that enables the encapsulated products to remain functional until they reach their site of action [
45]. It can also prove to be useful for delaying Lpps uptake in the BM.
As a matter of fact, our results highlighted the subsidiary impact of the microbiome compared to the role of Lpps in alleviating the arthritis symptoms. First, the bacteria selected for their capacity to affect the progression of osteoarthritis did not contribute to the same extend to the alleviation of arthritis in both acute (CAIA) and chronic (CIA) models [
38]. In the acute model, reduced
E.plexicaudatum counts in colon of the sole mice receiving Lpps after the arthritis induction, although both groups were protected, indicated that transient change in the microbiome can occur without impacting the illness. In the chronic model, similar findings were made, drastic bacterial changes being observed primarily in the unresponsive treated group. However, as reported above, the microbiome constituted a key factor controlling conventional DCs recruitment in spleen and affecting the anti-inflammatory IL-10 response to lipopolysaccharides in the responsive CIA group. Furthermore, the highest spleen DCs counts contributed to the lowest arthritis score. Interestingly, PCA illustrated the influence of colon
L.murinus in reducing spleen DCs recruitment and at the same time favoring arthritis progression.
Intestinal bacteria were also transporter of Lpps as suggested by detection of two fluorescent signals in BM DCs following force feeding with CFSE and labeled Lpps. Surprisingly enough, spleen conventional DCs did not exhibit the two signals indicating that bacteria carrying Lpps were directed to BM location close to the damaged joint. Results from the gnotobiotic model associated with RA microbiome and CIA forced fed mice already suggested that spleen participated to a lesser degree than bone marrow in the regulation of the inflammation. Female response indicated a reduction to Treg cells in spleen following Lpps treatment likely related to the changes in genes expression of the splenic cDCS [
37].
However, the bacterial uptake within BM conventional DCs questioned the degree of cell maturity. Conventional DCs (cDCs), which include the cDC1 and cDC2 subsets derive from pre-committed BM precursors, the pre-cDC, that seed lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues where they further differentiate into mature cDC1 and cDC2. Processing and presenting antigens in the class II pathway is dedicated to thymus and spleen following toll-like receptor (TLR) stimulation [
46]. As a matter of fact, in RA patients, the synovial inflammatory tissue can reach the adjacent bone marrow by fully breaking the cortical barrier, which results in formation of B cell-rich aggregates. Plasma cells are present in the regions between aggregates and inflammatory tissue [
47]. The bacterial capture in BM from arthritic mice can therefore depend onto the inflammatory tissue.
Nonetheless, a bacterial carrier was not a pre-requisite for transporting Lpps, since BM and thymus cells were shown to capture Lpps added alone to the culture medium. FACS analysis also emphasized the absence of Lpps signal in BM CD11c+DCs indicating that the cells involved in Lpps uptake belonged to another compartment, almost certainly the plasmacytoid cells. It is already known that PDC-deficient mice showed exacerbation of inflammatory and arthritis symptoms [
48]. Conversely, enhancing PDC recruitment and activation to arthritic joints by topical application of the Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR-7) agonist imiquimod significantly ameliorated arthritis. The oral administration of Lpps, their detection in BM PDC TREM compartment and their absence in Peyer’s patches cells suggested that a route involving Lpps passage across the intestinal cell layers before reaching BM through the blood stream could prevail. Since pDCs complete their differentiation within the BM, it is most likely that they took up the Lpps as a soluble antigen, [
49,
50].
To sum up, our results highlighted the involvement of pDCs as a major contributor to Lpps-induced protection, with some gut bacteria modulating the response via their action on splenic conventional DCs.
5. Conclusions:
Although promising, this work requires confirmation in humans, particularly through clinical trials to determine the effective dose under conditions that are compatible with dietary practices. The key point that remains to be clarified is the presence of lipoproteins in the gut. This depends not only on bifidobacterial species colonizing the intestine of healthy individuals or patients with rheumatoid arthritis but also on yet unknown factors regulating the lipoprotein release at the bacterial level. Furthermore, a more thorough comprehension of the role of plasmacytoid cells in Lpps-induced protection is necessary for future applications in the field of functional foods.
Author Contributions
MBR conceived the overall research idea and experimental framework, provided funds. MBR and FP wrote the manuscript. FS supervised the execution of the study, data collection and data analysis. FP, PG and YK gave feedback on the data analysis and interpretation of data. All authors agreed to the final manuscript
Funding
The work was supported by Feder (Astre Feder 11319) and Regional grants (Presage n°35372).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee N°120 (n° 4160-201602171657248).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We are deeply grateful to Sokhuntheany Ly and Frédéric Huguet for their technical support and Nathalie Jouy from PLBS-US41-UMS2014 for her support for FACS analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, X.; Chen, B.D.; Zhao, L.D.; Li, H. The Gut Microbiota: Emerging Evidence in Autoimmune Diseases. Trends Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Limón, P.; Mena-Vázquez, N.; Moreno-Indias, I.; Manrique-Arija, S.; Lisbona-Montañez, J.M.; Cano-García, L.; Tinahones, F.J.; Fernández-Nebro, A. Collinsella is associated with cumulative inflammatory burden in an established rheumatoid arthritis cohort. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishikawa, T.; Maeda, Y.; Nii, T.; Motooka, D.; Matsumoto, Y.; Matsushita, M.; Matsuoka, H.; Yoshimura, M.; Kawada, S.; Teshigawara, S.; et al. Metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiome revealed novel aetiology of rheumatoid arthritis in the Japanese population. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 79, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Jia, H.; Feng, Q.; Wang, D.; Liang, D.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; et al. The oral and gut microbiomes are perturbed in rheumatoid arthritis and partly normalized after treatment. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, K.N.; Bonham, K.S.; Ilott, N.E.; Britton, G.J.; Colmenero, P.; Bullers, S.J.; McIver, L.J.; Ma, S.; Nguyen, L.H.; Filer, A.; et al. IAMC Alterations in the gut microbiome implicate key taxa and metabolic pathways across inflammatory arthritis phenotypes. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabn4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sköldstam, L.; Hagfors, L.; Johansson, G. An experimental study of a Mediterranean diet intervention for patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häger, J.; Bang, H.; Hagen, M.; Frech, M.; Träger, P.; Sokolova, M.V.; Steffen, U.; Tascilar, K.; Sarter, K.; Schett, G.; et al. The Role of Dietary Fiber in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Feasibility Study. Nutrients. 2019, 11, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häupl, T.; Sörensen, T.; Smiljanovic, B.; Darcy, M.; Scheder-Bieschin, J.; Steckhan, N.; Hartmann, A.M.; Koppold, D.A.; Stuhlmüller, B.; Skriner, K.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota Reduction Followed by Fasting Discloses Microbial Triggering of Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badsha, H. Role of Diet in Influencing Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity. Open Rheumatol. J. 2018, 12, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peltonen, R.; Nenonen, M.; Helve, T.; Hänninen, O.; Toivanen, P.; Eerola, E. Faecal microbial flora and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis during a vegan diet. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 36, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohashi, O.; Kohashi, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Ozawa, A.; Shigematsu, N. Suppressive effect of Escherichia coli on adjuvant-induced arthritis in germ-free rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1986, 29, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, T.J.; Cremer, M.A.; Walker, S.M.; Dillon, A.M. The role of humoral immunity in Lactobacillus casei cell wall induced arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 1987, 14, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Severijnen, A.J.; van Kleef, R.; Hazenberg, M.P.; van de Merwe, J.P. Cell wall fragments from major residents of the human intestinal flora induce chronic arthritis in rats. J. Rheumatol. 1989, 16, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simelyte, E.; Rimpiläinen, M.; Lehtonen, L.; Zhang, X.; Toivanen, P. Bacterial cell wall-induced arthritis: chemical composition and tissue distribution of four Lactobacillus strains. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 3535–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simelyte, E.; Rimpiläinen, M.; Zhang, X.; Toivanen, P. Role of peptidoglycan subtypes in the pathogenesis of bacterial cell wall arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, I.; Endo-Tanaka, K.; Yokokura, T. Suppressive effects of the oral administration of Lactobacillus casei on type II collagen-induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice. Life Sci. 1998, 63, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, H.; Kaneko, T.; Kaminogawa, S. Oral intake of Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus OLL1073R-1 prevents collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J. Food Prot. 2002, 65, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharav, E.; Mor, F.; Halpern, M.; Weinberger, A. Lactobacillus GG bacteria ameliorate arthritis in Lewis rats. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1964–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- So, J.S.; Kwon, H.K.; Lee, C.G.; Yi, H.J.; Park, J.A.; Lim, S.Y.; Hwang, K.C.; Jeon, Y.H.; Im, S.H. Lactobacillus casei suppresses experimental arthritis by down-regulating T helper 1 effector functions. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2690–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Hou, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B.; Chen, W. Lactobacillus casei CCFM1074 Alleviates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats via Balancing Treg/Th17 and Modulating the Metabolites and Gut Microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 680073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Guo, R.; Ju, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, Z.; Lu, L.; et al. A single bacterium restores the microbiome dysbiosis to protect bones from destruction in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. Microbiome. 2019, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhun, J.; Min, H.K.; Ryu, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Ryu, J.G.; Choi, J.W.; Na, H.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Jung, Y.; Park, S.J.; et al. Lactobacillus sakei suppresses collagen-induced arthritis and modulates the differentiation of T helper 17 cells and regulatory B cells. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Endo, T.; Ukibe, K.; Hosoya, T.; Matsubara, Y.; Nakagawa, H.; Sakai, F.; Miyazaki, T. Preventive Effect of Lactobacillus helveticus SBT2171 on Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zou, Q.; Zhong, B.; Wang, H.; Mou, F.; Wu, L.; Fang, Y. Lactobacillus salivarius Isolated from Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Suppresses Collagen-Induced Arthritis and Increases Treg Frequency in Mice. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016, 36, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esvaran, M.; Conway, P.L. Lactobacillus fermentum PC1 has the Capacity to Attenuate Joint Inflammation in Collagen-Induced Arthritis in DBA/1 Mice. Nutrients. 2019, 11, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eerola, E.; Möttönen, T.; Hannonen, P.; Luukkainen, R.; Kantola, I.; Vuori, K.; Tuominen, J.; Toivanen, P. Intestinal flora in early rheumatoid arthritis. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1994, 33, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Ren, H.; Yang, N.; Xia, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, D.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Huang, W.; et al. Bifidobacterium pseudocatenulatum-Mediated Bile Acid Metabolism to Prevent Rheumatoid Arthritis via the Gut-Joint Axis. Nutrients. 2023, 15, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ding, M.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Yang, B.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1078 Alleviates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats via Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Repairing the Intestinal Barrier Damage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 14665–14678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Jhun, J.; Lee, S.Y.; Na, H.S.; Choi, J.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, A.R.; Park, S.J.; You, H.J.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of a Novel Bifidobacterium Identified Through Microbiome Profiling of RA Patients With Different RF Levels. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 736196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, B.; Homayouni-Rad, A.; Vaghef-Mehrabany, E.; Sharif, S.K.; Vaghef-Mehrabany, L.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Nakhjavani, M.R.; Mohtadi-Nia, J. Effects of Lactobacillus casei supplementation on disease activity and inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a randomized double-blind clinical trial. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 17, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagne, J.; Guichard, J.F.; Moulhade, M.C.; Kawski, H.; Maurier, F. Lactobacillus endocarditis: a case report in France and literature review. IDCases. 2020, 21, e00811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grazioli-Gauthier, L.; Rigamonti, E.; Leo, L.A.; Martinetti Lucchini, G.; Lo Priore, E.; Bernasconi, E. Lactobacillus jensenii mitral valve endocarditis: Case report, literature review and new perspectives. IDCases. 2022, 27, e01401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasala, S.; Singer, L.; Arshad, T.; Roach, K. Lactobacillus endocarditis in a healthy patient with probiotic use. IDCases. 2020, 22, e00915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikucka, A.; Deptuła, A.; Bogiel, T.; Chmielarczyk, A.; Nurczyńska, E.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Bacteraemia Caused by Probiotic Strains of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus-Case Studies Highlighting the Need for Careful Thought before Using Microbes for Health Benefits. Pathogens. 2022, 11, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romond, M.B.; Ais, A.; Guillemot, F.; Bounouader, R.; Cortot, A.; Romond, C. Cell-free whey from milk fermented with Bifidobacterium breve C50 used to modify the colonic microflora of healthy subjects. J. Dairy Sci. 1998, 81, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuotto, A.; Djorie, S.; Colavizza, M.; Romond, P.C.; Romond, M.B. Bifidobacterium breve C50 secretes lipoprotein with CHAP domain recognized in aggregated form by TLR2. Biochimie. 2014, 107 Pt B, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuotto, A.; Romond, P.C.; Djorie, S.; Alric, M.; Romond, M.B. In silico mining and characterization of bifidobacterial lipoprotein with CHAP domain secreted in an aggregated form. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 82, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sane, F.; Piva, F.; Romond, M.B. Free lipoproteins from Bifidobacterium longum alleviate osteoarthritis through modulation of the gut microbiome. Microbiome. Res. Rep. 2023, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, D.D.; Latham, K.A.; Rosloniec, E.F. Collagen-induced arthritis. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Cooney, L.A.; White, P.; Dunlop, D.B.; Endres, J.; Jorns, J.M.; Wasco, M.J.; Fox, D.A. Regulation of pathogenic IL-17 responses in collagen-induced arthritis: roles of endogenous interferon-gamma and IL-4. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kfoury, K.A.; Romond, M.B.; Scuotto, A.; Alidjinou, E.K.; Daboussi, F.; Hamze, M.; Engelmann, I.; Sane, F.; Hober, D. Bifidobacteria-derived lipoproteins inhibit the infection with coxsackievirus B4 in vitro. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2017, 50, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piva, F.; Romond, M.B. Bifidobactéries : de la bactérie commensale aux probiotiques et métabiotiques /postbiotiques. in : Génie des procédés enzymatiques, fermentaires et d’encapsulation appliqués aux industries agro-alimentaires, Ghoul, M.; ISTE Group, London, UK, 2023, Volume 3, pp. 154–196.
- Romond, M.B.; Ais, A.; Yazourh, A.; Romond, C. Cell-free wheys from bifidobacteria fermented milks exert a regulatory effect on the intestinal microflora of mice and humans. Anaerobe. 1997, 3, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullié, C. , Yazourh, A., Singer, E., Lecroix, F., Blareau, J.P., Romond, M.B., Romond, C. Partial Characterization of Bifidobacterium breve C50 Cell-Free Whey Compounds Inducing Modifications to the Intestinal Microflora. J Dairy Sci, 2002, 85, 1383–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolve, R.; Cela, N.; Condelli, N.; Di Cairano, M.; Caruso, M.C.; Galgano, F. Tolve, R.; Cela, N.; Condelli, N.; Di Cairano, M.; Caruso, M.C.; Galgano, F. Microencapsulation as a Tool for the Formulation of Functional Foods: The Phytosterols' Case Study. Foods. 2020 9:470. [CrossRef]
- Dresch, C.; Ackermann, M.; Vogt, B.; de Andrade Pereira, B.; Shortman, K.; Fraefel, C. Thymic but not splenic CD8(+) DCs can efficiently cross-prime T cells in the absence of licensing factors. Eur J Immunol. 2011, 41, 2544–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Boj, E. , Redlich, K., Türk, B., Hanslik-Schnabel, B., Wanivenhaus A, Chott A, Smolen JS, Schett, G. Interaction between Synovial Inflammatory Tissue and Bone Marrow in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J Immunol, 2005, 175, 2579–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehmar, R., Alsaleh, G., Voisin, B., Flacher, V., Mariotte, A., Saferding, V., Puchner, A., Niederreiter, B., Vandamme, T., Schabbauer, G., et al. Therapeutic modulation of plasmacytoid dendritic cells in experimental Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum, 2017, 69, 2124–2135. [CrossRef]
- Kool, M. , GeurtsVanKesse Cl, Muskens, F., Branco Madeira, F., van Nimwegen, M., Kuipers, H., Thielemans, K.., Hoogsteden HC., Hammad, H., Lambrech BN. Facilitated antigen uptake and timed exposure to TLR ligands dictate the antigen presenting potential of plasmacytoid DCs. J Leuk Biol, 2011, 90, 1170–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiecki, M.; Colonna, M. The multifaceted biology of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015, 15, 471–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).