1. Introduction
Anaerobic Digestion (AD) is an extensively used and accepted process, since it facilitates waste treatment along with energy recovery, in the form of methane contained in the biogas [
1]. Waste Activated Sludge (WAS) is a typical AD substrate, which is produced globally in large quantities, surpassing 45 million dry metric tons annually and has a high potential for energy recovery [
2,
3]. However, the AD process is susceptible to limitations, which result in limited conversion of organic compounds and low methane yield. This is attributed to the WAS characteristics and specifically, the non-availability of readily bio-degradable constituents of WAS, which render hydrolysis as the rate-limiting step of the process [
4,
5,
6,
7].
In order to overcome the challenges of the AD slow kinetics and the instabilities caused by an increase of the OLR of WAS, numerous pretreatment techniques have been proposed to enhance the biodegradability of WAS organic components. These include mechanical, chemical, thermal and enzymatic processes as well as combinations of them. Despite the fact that many pretreatment methods have yielded promising results, it has been reported that in many cases these methods can be energy intensive or require addition of chemicals, which result in ambiguous cost effectiveness [
8].
In this context, MEC-AD has emerged as a promising alternative to the conventional AD treatment of WAS [
9,
10,
11]. Specifically, it has been found that applying a small potential in AD can result in improved waste treatment along with higher methane yield. This is achieved by the increase of the oxidation rate of non-biodegradable organic compounds present in WAS and the enrichment of the microbial cultures, which boost methane productivity. As a result, the hydrolysis of non-biodegradable substrates is increased and the process is accelerated. Moreover, the MEC-AD energy recovery has been reported to far outperform that of conventional AD, while the energy input in the form of electricity is negligible, relative to the additional methane production, resulting in high cost effectiveness [
12].
Modeling has been increasingly used for understanding the intricate actions entailed in waste treatment processes, in order to ultimately design and control them. To this end, modeling of the AD process has been widely implemented, yielding important results regarding our understanding, foreseeing and optimization of the complex processes taking place [
13]. Anaerobic Digestion Model No. 1, developed by the International Water Association (IWA), is regarded as the most accepted and widely used model for AD [
12,
14]. The numerical simulation of AD can provide valuable insights as an effective means to optimize and regulate the AD processes. ADM1 entails all AD processes, from hydrolysis to methanogenesis, as well as physicochemical dependencies and phase transition processes, in order to enable the application of the model to obtain complete mass balances [
15]. Parker, 2005 [
16] and Batstone and Keller, 2003 [
17] summarized the application of ADM1 to advanced AD processes and while the ADM1 processes have been extensively elaborated over the past decades, studies have recently shifted towards model simplifications, modifications or integration with other analytical models [
18,
19,
20].
However, limited research has been conducted in the field of modeling of the MEC-AD process intricate processes, since this would require the integration of bio-electrochemical and abiotic redox reactions taking place on the electrodes, along with the established AD bio-chemical and physico-chemical processes. Zou et al, 2021 [
21] first developed an artificial neural network model for a MEC-AD fed with swine manure; however the model only predicted CH
4 production, while no substrate consumption was taken into account. Nguyen et al., 2022 [
22] recently developed an artificial neural network model for the optimization of alkaline-pretreated WAS-fed MEC-AD, which included both substrate consumption and CH
4 production. The results showed that at an applied potential of 0.63 V, the net energy output and monetary value of the MEC-AD were optimized, significantly increased relative to conventional AD. Nevertheless, no computational studies have been performed in order to describe the raw-WAS-fed MEC-AD, to extract the kinetic parameters of the MEC-AD along with delineation of the effect that the applied potential has on the kinetic processes, or the effect that the OLR has on raw-WAS treatment.
In this context, the purpose of the current study is to render the raw-WAS-fed MEC-AD process foreseeable and predictable, by using the ADM1 model. Experimental data obtained from the long-term operation of two identical reactors, one used as a conventional AD and the other as the MEC-AD reactor, were used for the present study. The aim was to derive a single kinetic and mathematical model for the study of AD in comparison with the MEC-AD reactor. This custom model can therefore serve as a guide of the quantitative difference that the effect of an applied potential has on the Monod-type and first-order kinetics of AD, involving substrate consumption, disintegration of particulates, hydrolysis and biomass concentrations. The ADM1 model extracts the kinetic parameters for the AD biochemical processes, while in the case of the MEC-AD process, the bio-electrochemical interactions and redox reactions on the electrodes are not taken into consideration. It can therefore serve as an imprint of the quantitative effect that MEC-AD process would have on the kinetics of its biochemical processes, in comparison with the conventional AD process.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental setup and operation
The experimental raw-WAS-fed AD and MEC-AD dataset was obtained from Kanellos et al., 2024 [
23] in order to extract the kinetic parameters of each process using the ADM1. As previously described, two identical 2 L reactors were constructed and operated as an AD and a MEC-AD reactor. The reactors were cylindrical glass vessels and were equipped with an inlet/outlet tube, in order to facilitate the draw-fill operation mode, as well as a biogas outlet at the top of each reactor, connected to a biogas sampling port and a U-shaped oil displacement technique which was recorded by an electro-optic level switch and a PLC for recording. The difference between the reactors laid in the two submerged carbon felt electrodes (each with an area of 25 cm
2), which were equipped in the MEC-AD reactor and connected with an external power supply through titanium wires, in order to control the applied potential. A constant voltage of 1 V was applied between the carbon felt electrodes, in a two-electrode configuration. The reactors were operated at a constant temperature of 30 ⁰C and were constantly stirred through magnetic stirring. The raw-WAS was obtained from the Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant of Lykovrisi, in Attica, Greece and its characteristics were: pH 6.8; total alkalinity 4 gCaCO
3 / L; conductivity 1.5 mS / cm; total solids 22 g / L; volatile solids 16 g / L; total suspended solids 21 g / L; volatile suspended solids 15 g / L; soluble COD 0.5-1 gO2 / L; total COD 25 gO2 / L; Acetic Acid 110 mg / L; Propionic Acid 75 mg / L; Iso-butyric Acid 21 mg / L; Butyric Acid 15 mg / L; Iso-valeric Acid 10 mg / L; Valeric Acid 2 mg / L; Ethanol 180 mg / L; Total Kjeldahl Nitrogen 1.25 gN / L; particulate organic carbon 8.5 gC/ L. The reactors operated for a total of 131 days with the raw-WAS, which were differentiated based on the Organic Loading Rates (OLRs) of 1.1, 1.7 and 2.9 g
COD / (L * d).
2.2. Model description
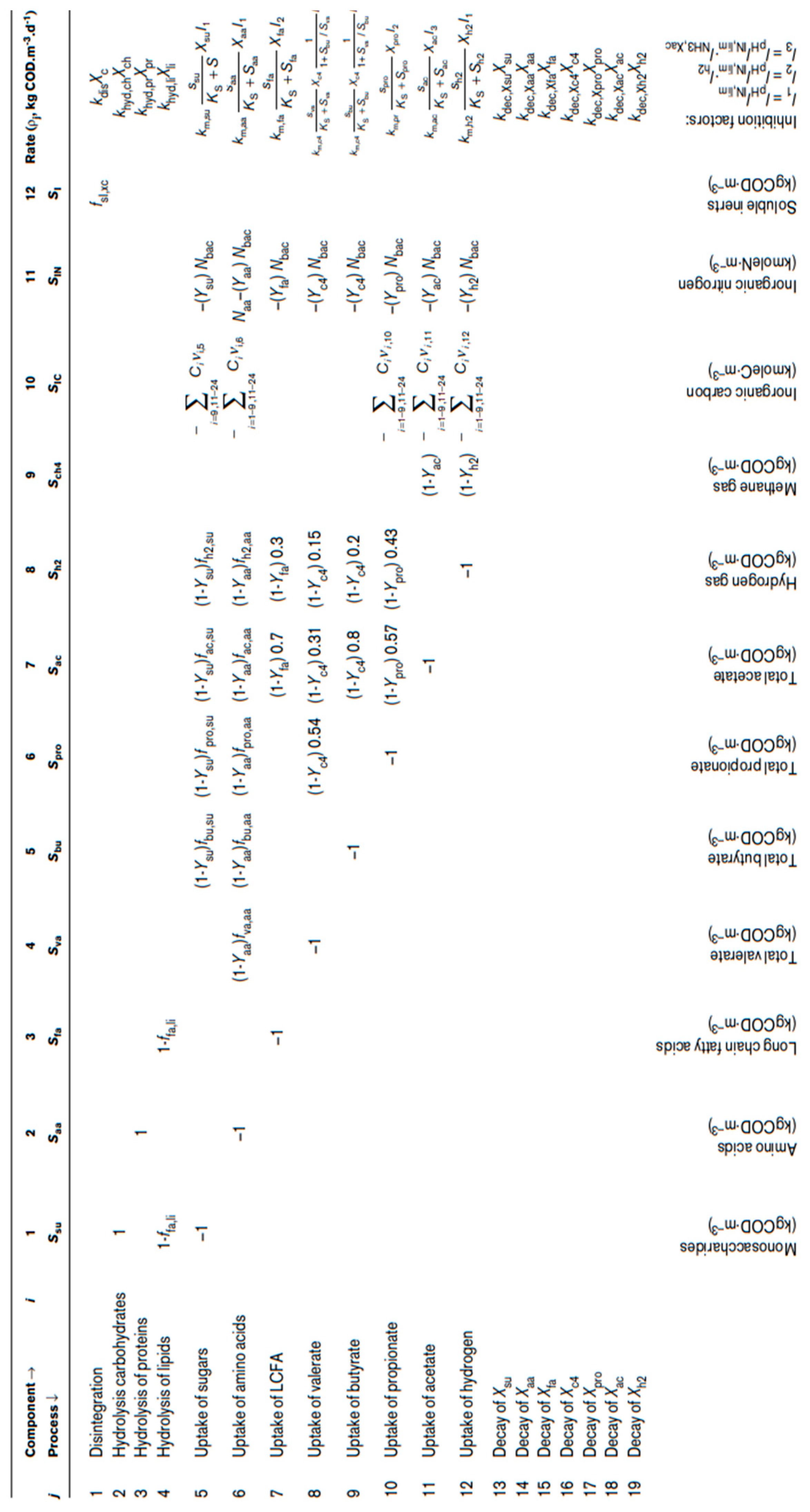
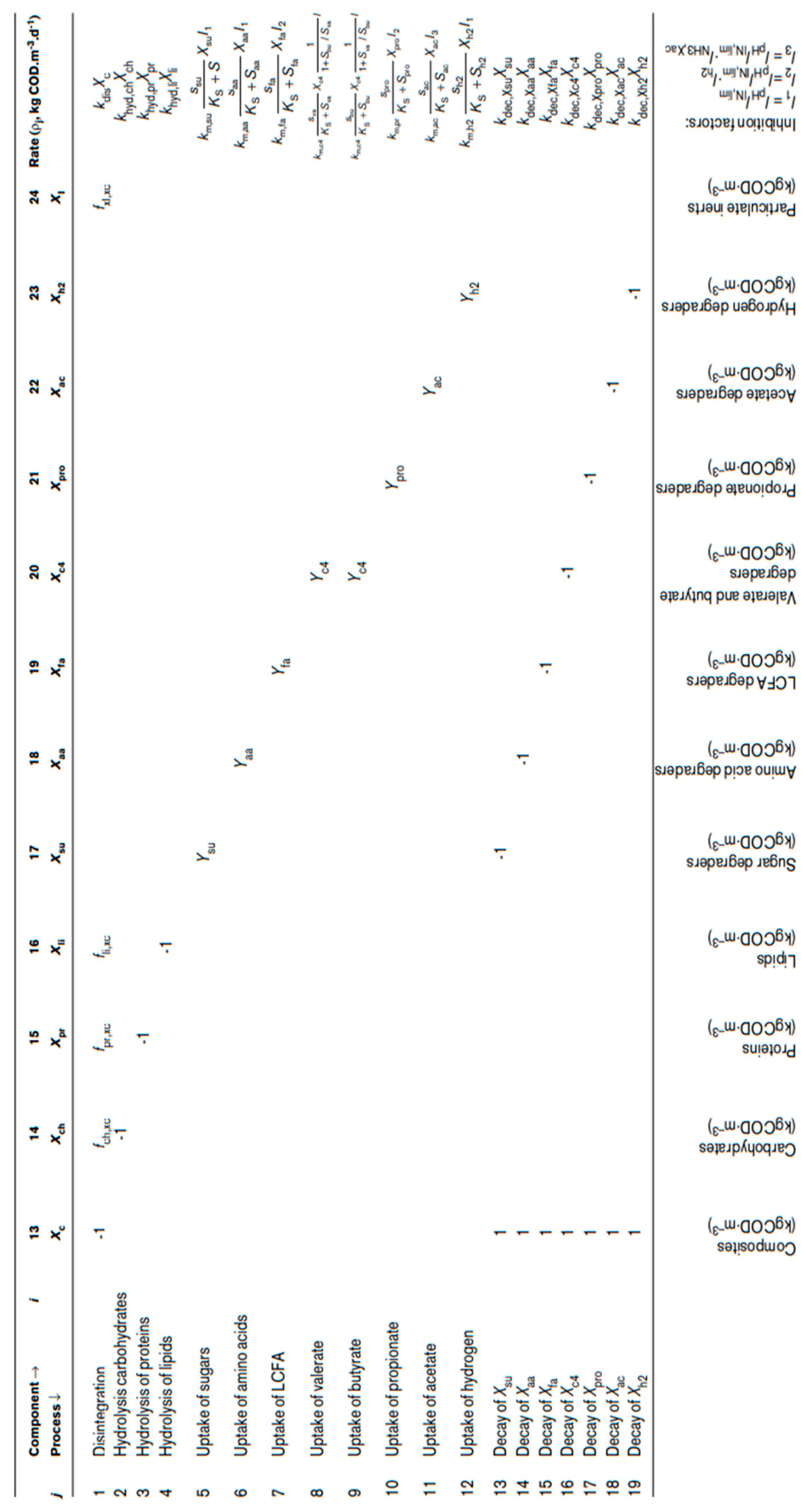
Modeling of the reactors’ operation was performed using the Aquasim 2.0 software and the mathematical model ADM1. The ADM1 includes the 5 stages of AD (degradation, hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis and methanogenesis) along with the action of biological enzymes at each stage. The processes simulated in the model are divided into biochemical and physicochemical. Biochemical processes are catalyzed by enzymes that act intracellularly or extracellularly and are considered irreversible. In contrast, physicochemical processes involve ion exchange (acid-base balance) and liquid-gas transfer phenomena (liquid-gas phase equilibrium) and are taken as reversible reactions [
17].
The model contains 26 variables, which are required to fully define the system at a given point. Of these, 12 refer to soluble components: monosaccharides, amino acids, long-chain fatty acids, total VFAs, hydrogen, methane, inorganic carbon (dissolved CO
2), inorganic nitrogen (dissolved ammonia) and soluble inerts. In addition, 5 variables refer to suspended particles in the reactor; complex particulates, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids and particulate inerts. An additional two variables serve to describe the acid-base balance of the described system: anion and cation concentrations. Finally, 7 important variables for the model are those of biomass. Specifically, for each soluble substrate (LCFAs, amino acids, sugars, valeric acid, butyric acid, propionic acid, acetic acid and hydrogen), the model also considers a type of biomass that metabolizes it (except for methane, which is the final product) [
24]. Intracellular biochemical reactions involving substrate consumption follow Monod-type kinetics. In contrast, disintegration of particulates, hydrolysis (extracellular reactions) and biomass death are represented by first-order kinetics. Dead biomass is retained in the system and is a composite particulate material, which acts as a substrate that is gradually degraded. These variables are presented in Tables 2 and 3. Inhibitory effects shown in the ADM1 model include pH (affects the action and growth of all microorganisms), hydrogen (affects acetic bacteria) and free ammonia (affects acetoclastic bacteria) [
17].
The ADM1 model was developed and adapted to the experimental data of both reactors during all operating phases in a continuous mode, to simulate the draw-fill operation. The modeling of the reactors was based on the carbon and nitrogen balance between solids decomposition and biogas production. During the simulation, the experimental data entered in the model for the feed as well as for both bioreactors were: the reactor volume, the inlet supply rate, the pH, the soluble and total COD, the soluble and particulate carbon, the soluble and particulate nitrogen and the total and volatile (suspended) solids (TS, VS, TSS, VSS).
2.3. Model setup and equations
As the ADM1 includes multiple kinetic parameters which have a certain impact on the process and the final products, certain assumptions were made in order to calibrate the model, before parameter estimation and sensitivity analysis. The simplified assumptions can be summarized as follows: the disintegration of dead biomass follows the same 1
st order kinetics as the rest of the complex particulates; all microorganisms decay following 1
st order kinetics with a decay coefficient of k
dec = 0.02 d
-1; the complex particulates disintegrate towards constant fractions of carbohydrates (f
ch = 0.2), lipids (f
li = 0.35), proteins (f
pr = 0.2) and particulate inerts (f
in = 0.25) as suggested by Batstone and Keller, 2003 [
17]; amino acids and sugars are hydrolyzed towards constant fractions of VFAs and H
2, as presented in
Table 1; yields of biomass on uptake of soluble substrates are considered constant and equal to Y_aa=0.08, Y_ac=0.05, Y_c4=0.06, Y_fa=0.06, Y_h2=0.06, Y_pro=0.04, Y_su=0.10, (where aa is amino acids; ac is acetate; c4 is butyrates; fa is fatty acids; h2 is hydrogen; pro is propionate; su is sugars) as suggested by Batstone and Keller, 2003 [
17]; the pH is set as constant and equal to 7, based on the experimental behavior of the reactors, therefore no inhibitory actions are considered due to pH variations in the substrate uptake processes; the uptake rates of butyrate and valerate are identical and metabolized by the same microorganisms; the Solids Retention Time (SRT) is initially considered equal to the Hydraulic Retention Time (HRT), as the experimental reactors described by the ADM1 are continuously stirred.
The complete ADM1 algorithm for the biological kinetic rate expressions and coefficients is presented in
Table 2 and
Table 3, as initially described by Henze et al., 1986 [
25,
26]. In order to extract the functions of the degree of influence of the kinetic constants on the soluble and particulate organic load, the ADM1 varies each constant, one at a time, by a small percentage (typically 1%) and the differences from the original calculation is used to establish a new balance on the system. Due to the constant pH applied in the ADM1, no empirical inhibition expressions were employed, which are a direct consequence of high or low pH in the reactors. Instead, non-competitive inhibition, caused by hydrogen and free ammonia inhibition, as well as substrate limitation inhibition, caused by total ammonia limitation, are considered [
17,
27].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model results and validation
3.1.1. ADM1 fit to the experimental data
The target variables which were selected to be fitted using the ADM1 included the reactors’ COD, carbon and nitrogen content, in both their particulate and soluble form, along with the produced biogas and its methane content.
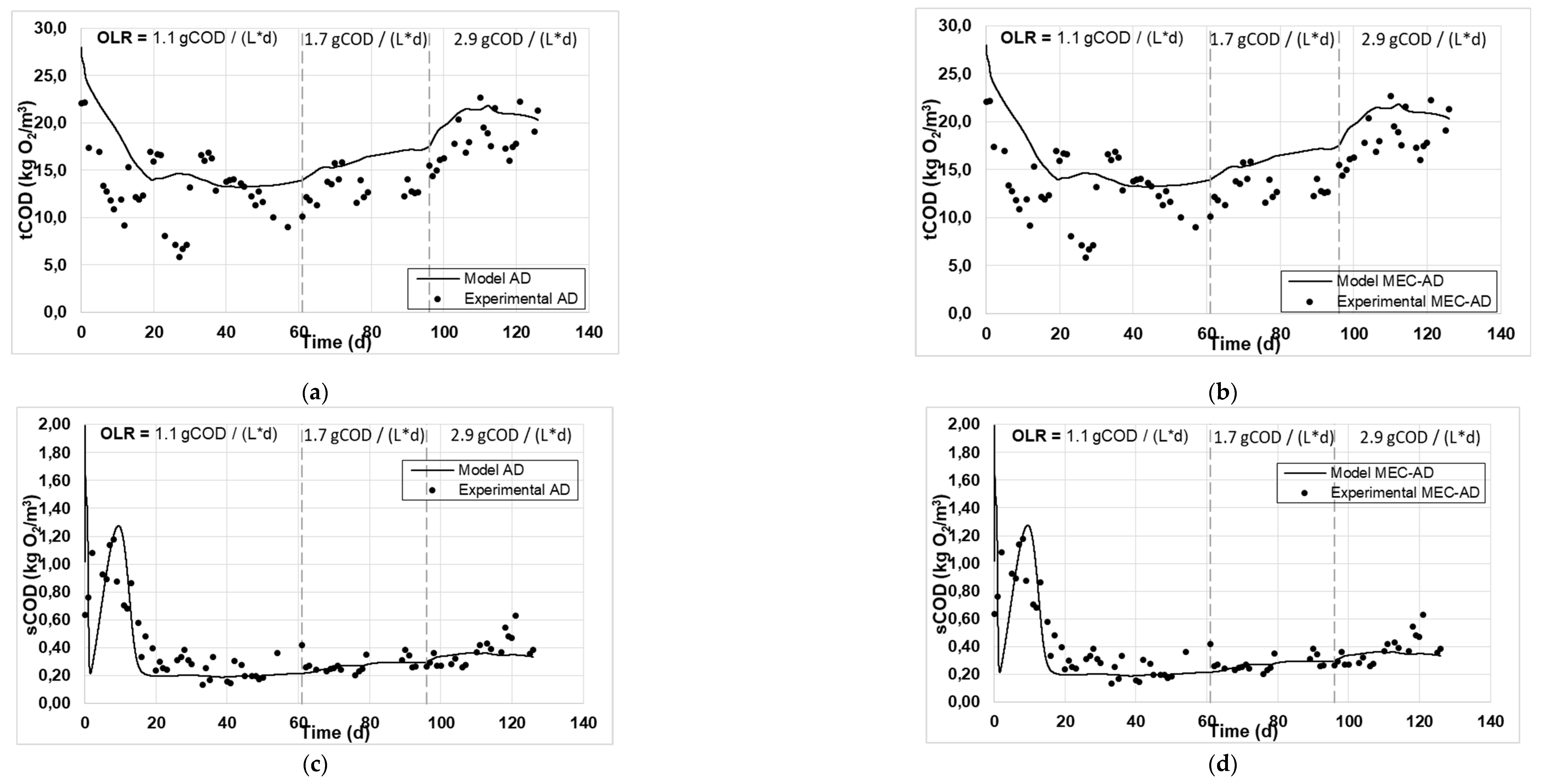
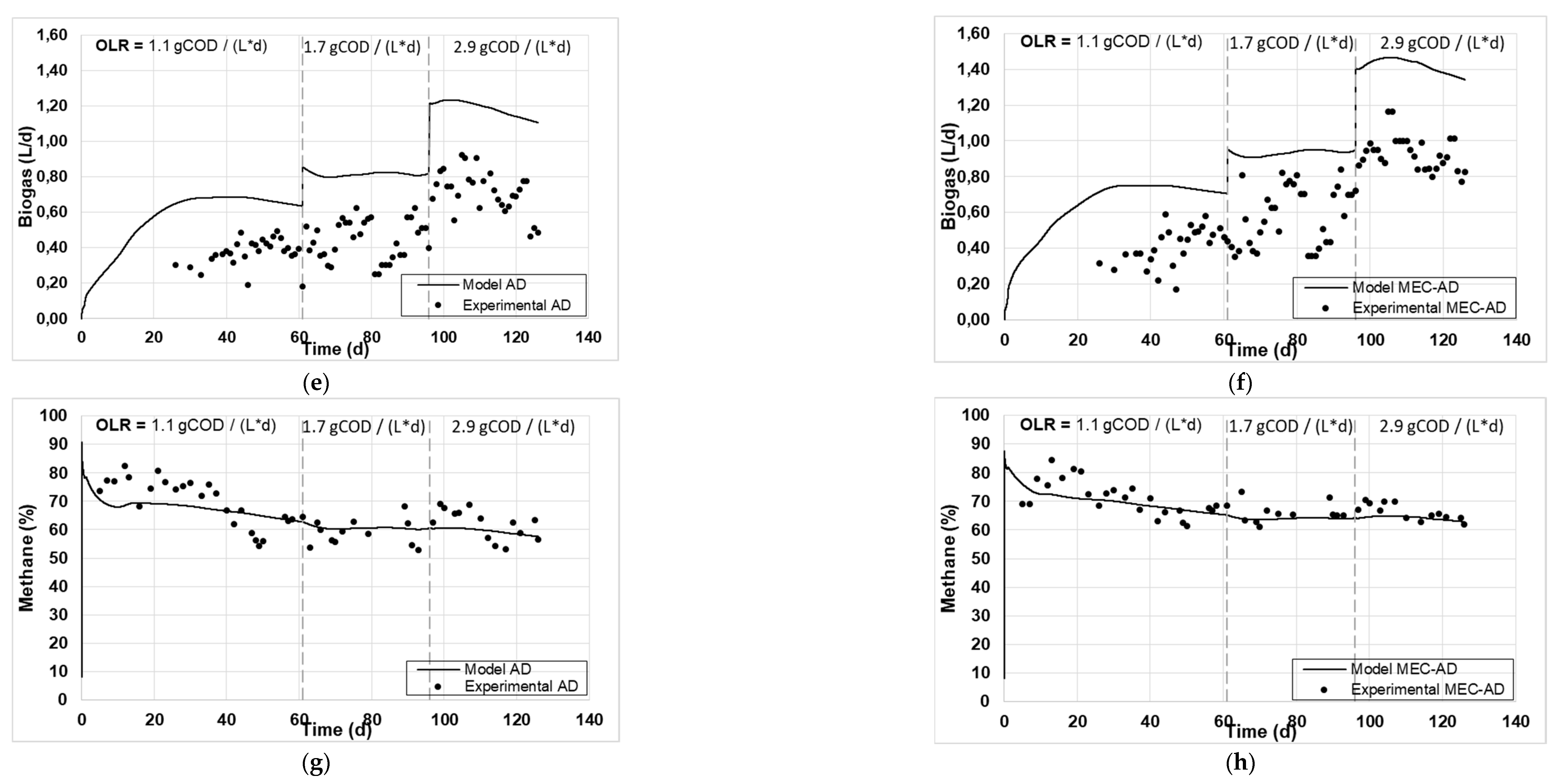
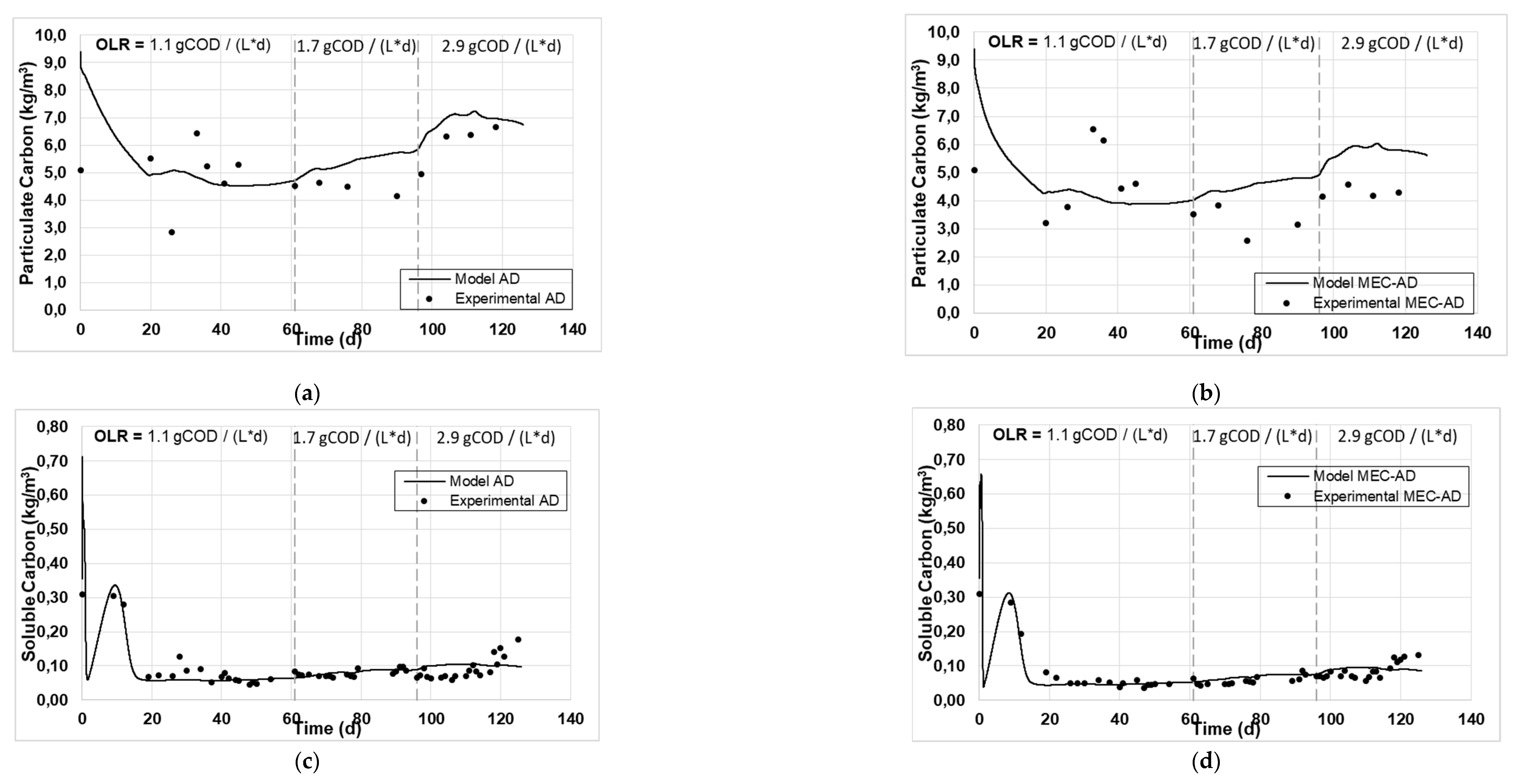
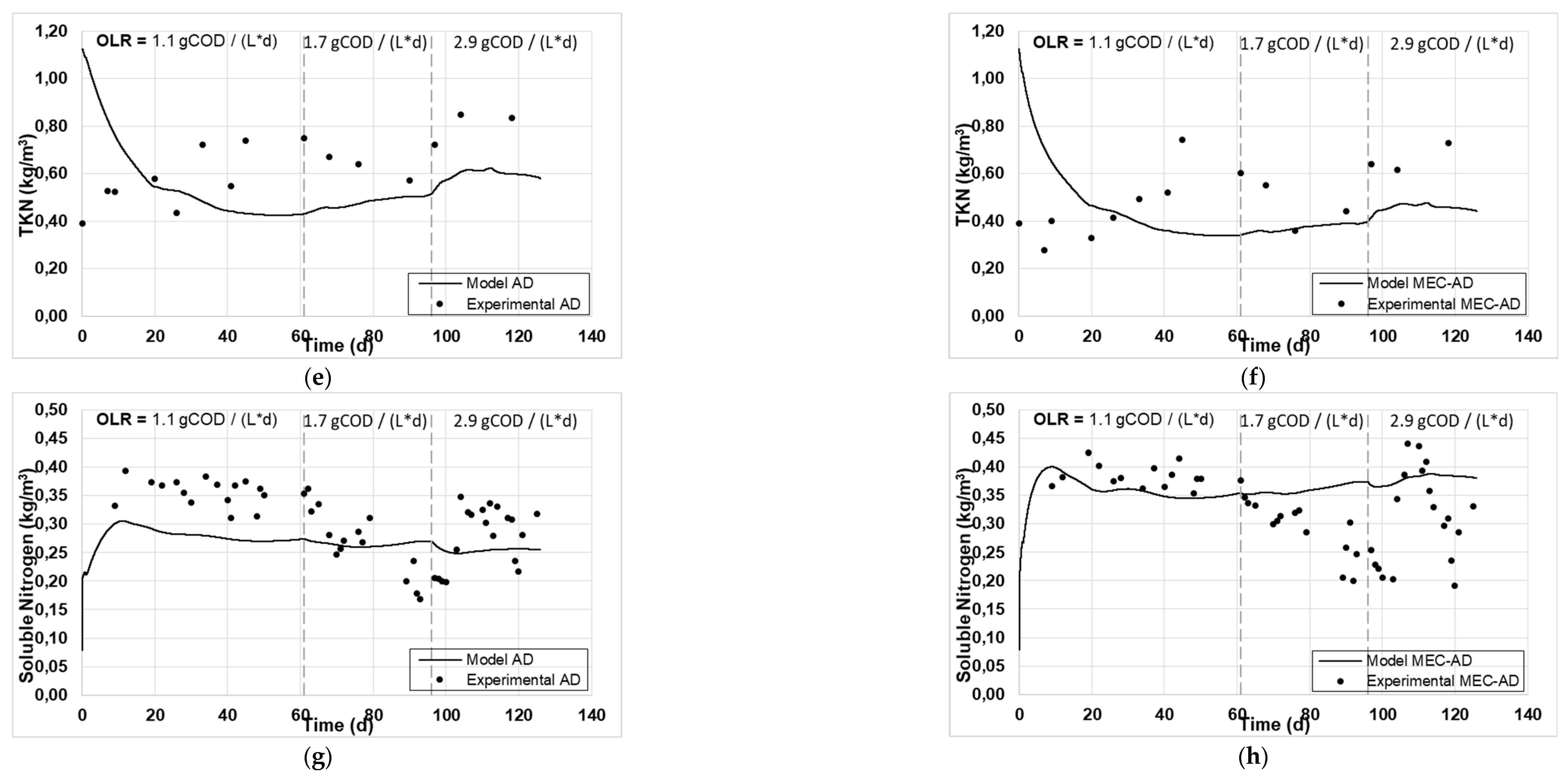
Figure 1 and
Figure 2 present the experimental and simulated values of the aforementioned parameters, following the carbon and nitrogen mass balances of the reactors.
The analysis showed an adequate fit of the variables studied for both reactors. Specifically, the values of particulate (
Figure 2a, b) and soluble carbon (
Figure 2c, d), as well as those of soluble COD (
Figure 1c, d), soluble nitrogen (
Figure 2g, h) and methane content (
Figure 1g, h) achieved the best fit, while some deviation was observed for the fitting of the Tcod (
Figure 1a, b) and the TKN (
Figure 2e, f), which are slightly overrated (by 2 g / L) and devalued (by 0.2 g / L), respectively. Accordingly, this deviation in the particulate parameters (Tcod and TKN) resulted in an equivalent deviation in the simulated produced biogas in both reactors (
Figure 1e, f), which was slightly overestimated by approximately 0.5 L / d. The deviation of the Tcod can be explained by the presence of oxidizable inorganic compounds in the raw-WAS which are not taken into account by the ADM1, while the deviation of TKN could be attributed to the fact that the amino acids content of the raw-WAS were not measured, but were instead considered based on an average WAS composition. These deviations appear marginally increasing as a function of the increase in OLR (from 1.1 to 2.9 g
COD / (L * d)), especially for the case of the AD reactor, which can be attributed to the fact that a less efficient AD process occurs at high OLRs, as has been previously observed [
23].
Moreover, comparing the curves predicted by the model for both cases, the AD reactor generates higher values for particulate carbon, Tcod and TKN content (
Figure 2a, 1a and 2e, respectively), in comparison with the MEC-AD reactor (
Figure 2b, 1b and 2f, respectively), for all OLRs examined, which is also the case with the experimental values. In addition, the generated values of soluble carbon, Scod and soluble nitrogen (
Figure 2d, 1d and 2h, respectively) appear slightly increased in the MEC-AD reactor simulation, which is a direct consequence of the increased decomposition of particulate matter and its hydrolysis towards their soluble forms. The results are in accordance with previous studies that have focused on the effect of the applied potential on the enhancement of the hydrolysis step in anaerobic digestion [
4,
5,
11,
23]. Furthermore,
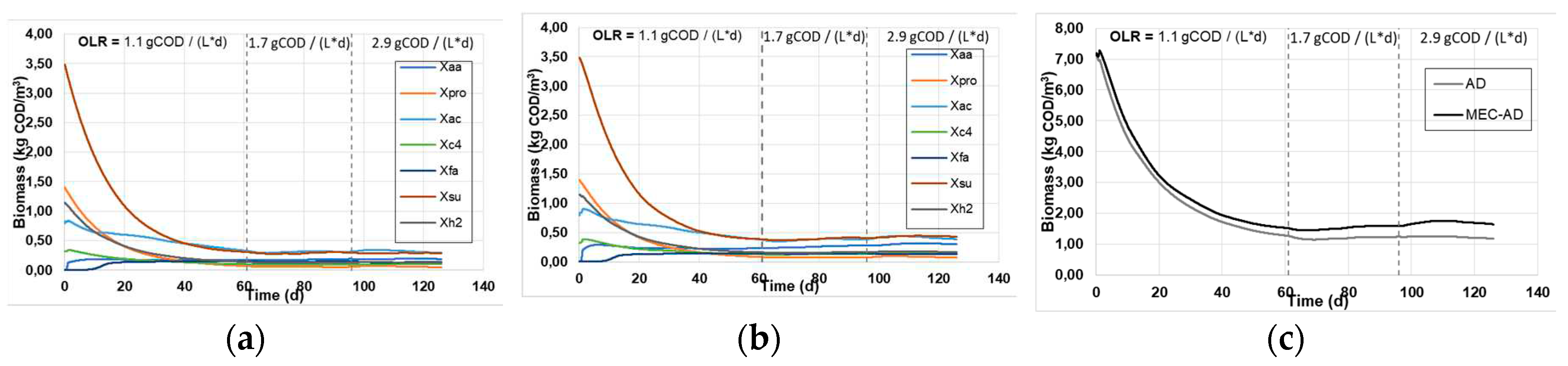
Figure 3 depicts the predicted biomass concentrations in both reactors, where the simulation predicts that the MEC-AD yields marginally increased cumulative biomass concentrations. This divergence became more apparent at high OLRs and reached a maximum divergence of ~0.2 g / L.
3.1.2. Estimation of kinetic parameters
Accordingly, the estimated parameters from the computational fitting were the Monod kinetic constants (k
m and K
s) for all soluble substrates, as well as the 1
st order kinetic constants for the disintegration of complex particulates and for the hydrolysis of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids to sugars, amino acids and LCFAs respectively.
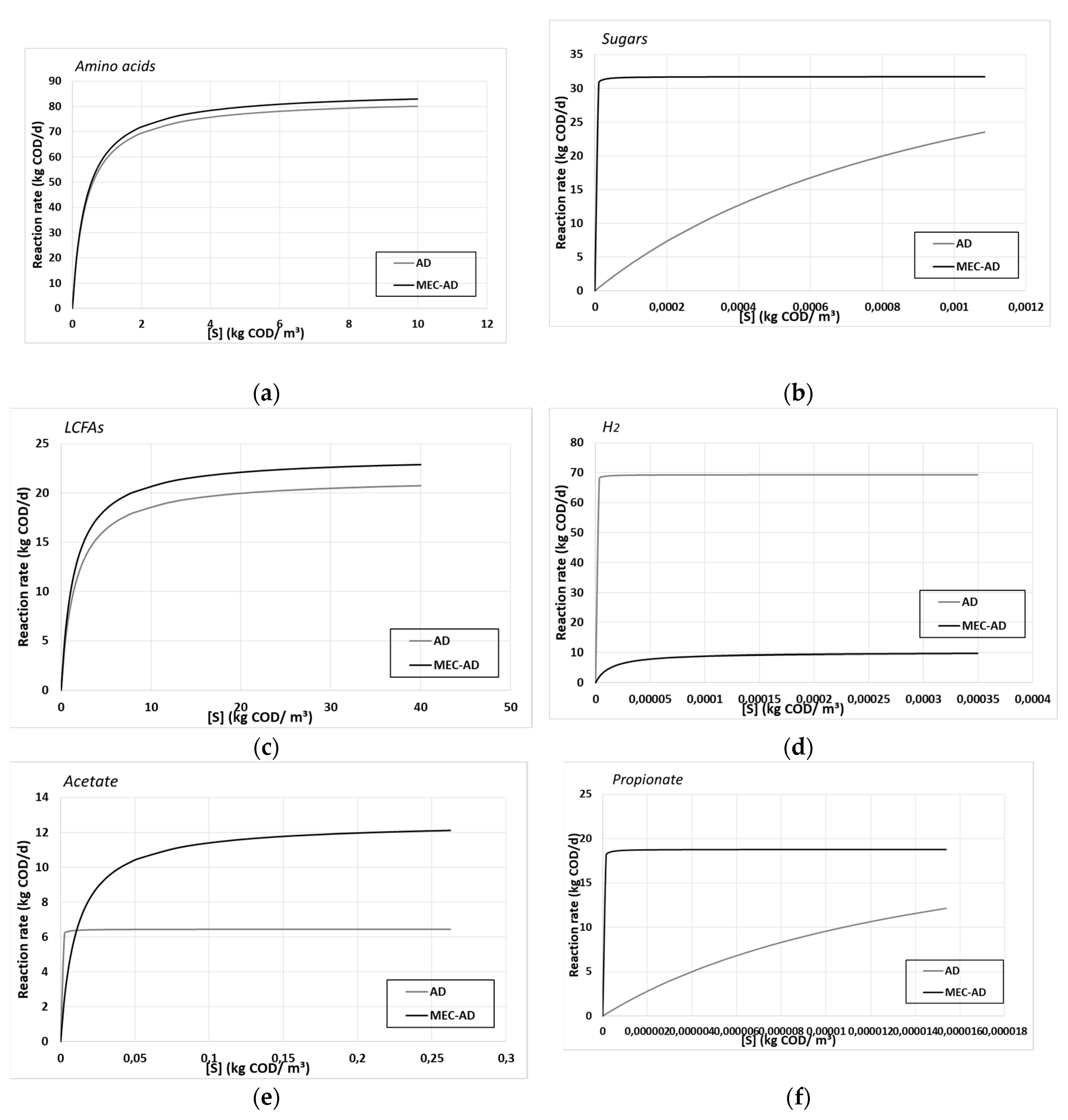
Table 4 shows the deduced kinetic values for both reactors, while the Monod reactions rates are described by
Figure 4.
The performed parameter estimation resulted in better kinetic processes for the MEC-AD reactor, which agrees with the faster hydrolysis of particulate matter presented in
Figure 1 and
Figure 2. The obtained values for the Monod and first order disintegration kinetic constants were estimated by utilizing upper and lower value limits, which were set independently for each parameter, as has been previously described [
17] (pp. 46-47, Table 6.1, 6.2). Specifically, the vast majority of the Monod kinetic constants (k
m and K
s) which describe the substrate uptake rate were noticeably improved and mostly resulted in both higher k
m and lower K
s values for each substrate. In addition, the deduced values could be interpreted as higher substrate to biomass and substrate to energy yields in the MEC-AD reactor, which may be translated to the fact that the same amount of metabolized substrate results in more biomass and energy production, respectively, and therefore more metabolic products and ultimately more methane. Despite the faster substrate uptake in the MEC-AD reactor, only the H
2 consumption appears higher in the AD reactor (
Figure 3d), which however does not compensate for the higher uptake rate of the amino acids, the sugars, the LCFAs and all the VFAs in the MEC-AD (
Figure 4a, 4b, 4c, 4e, 4f and 4g, respectively). These are the same parameters that are considered to be limiting factors for the AD process [
10], while the lower H
2 consumption of the MEC-AD reactor could be attributed to intermediate redox reaction that utilize H
2, such as the indirect electro-methanosynthesis or the abiotic H
2 production, which take place on the bio-cathode and are not considered in the present model [
28]. Furthermore, the MEC-AD reactor showed similar first order hydrolysis kinetic constants for the decomposition of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins as that of the AD (
Table 1), while a noticeable difference was obtained for the disintegration of complex particulates (0.4 g / L for the MEC-AD and 0.1 g / L for the AD).
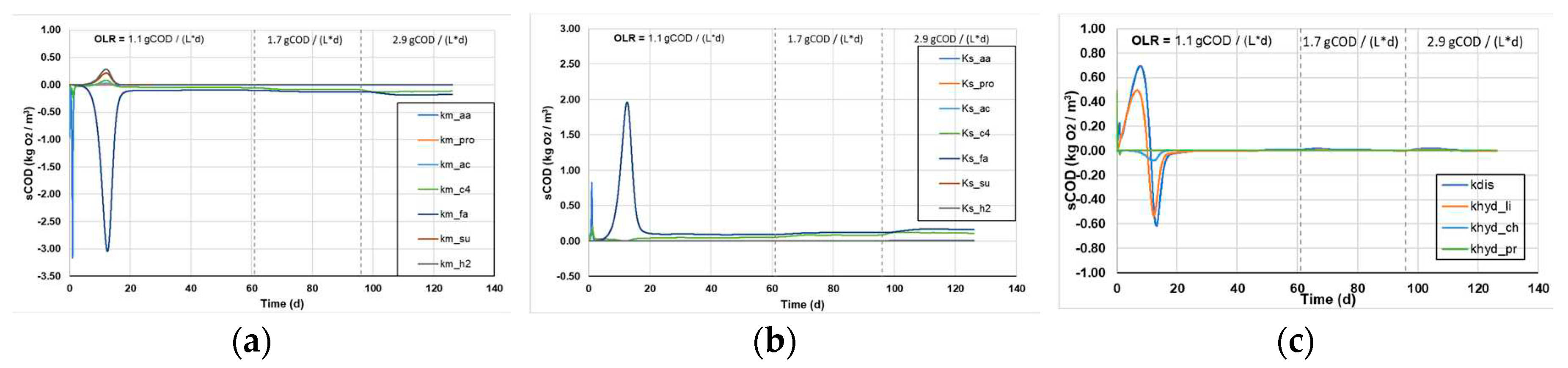
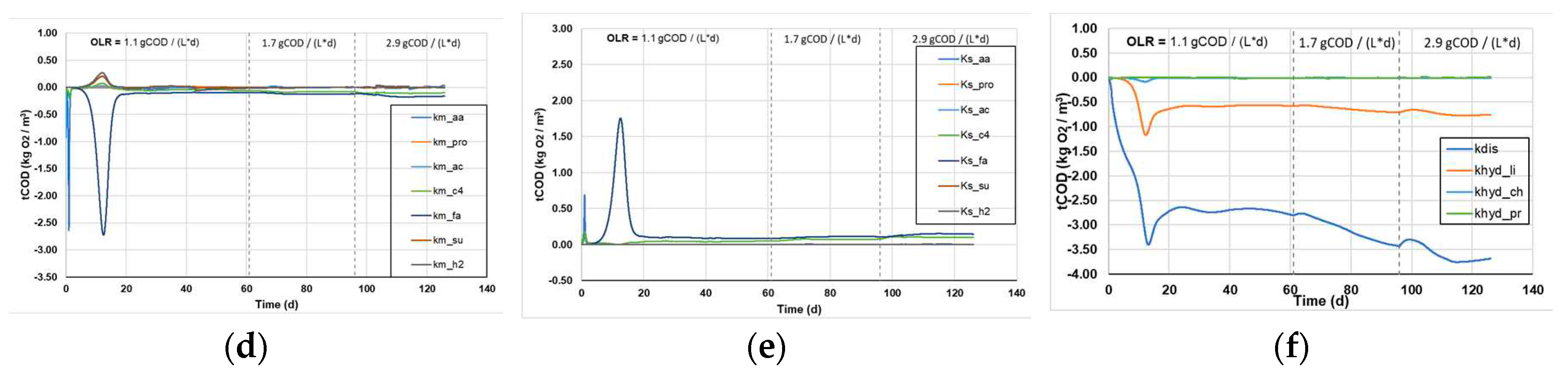
3.1.3. Sensitivity analysis of kinetic parameters
Figure 5 shows the sensitivity analysis for all kinetic parameters (Monod and 1
st order disintegration constants), and the effect their variation causes on the sCOD (
Figure 5a-c) and the tCOD content of the reactors (
Figure 5d-e).
In general, higher values of each parameter function result in larger changes in the calculated variables following the small change in the kinetic constants, which means that the system is more susceptible to the respective change and has a greater sensitivity to each kinetic constant. The spikes in some kinetic parameters, presented in
Figure 5a-e, is attributed to the changes in the OLR and appear to stabilize within a few days, after the reactors have reached a new steady state. Regarding the sCOD consumption, it appears that the Monod and the 1
st order kinetic constants appear to have a marginally increasing sensitivity as a function of the increasing OLR. However, it shows the highest sensitivity to the LCFAs uptake, which is a major limiting factor in the AD process, while the uptake of other substrates influences the processes to a lesser extent (
Figure 5a and b).The results indicate that the disintegration of complex particulates poses the most sensitive parameter to changes, resulting in the highest variations of tCOD decomposition (
Figure 4f). Moreover, the 1
st order hydrolysis constant of lipids shows some sensitivity to changes, while the hydrolysis of proteins and carbohydrates do not significantly affect the processes (
Figure 4f).
3.2. Optimization of raw-WAS-fed MEC-AD by the ADM1
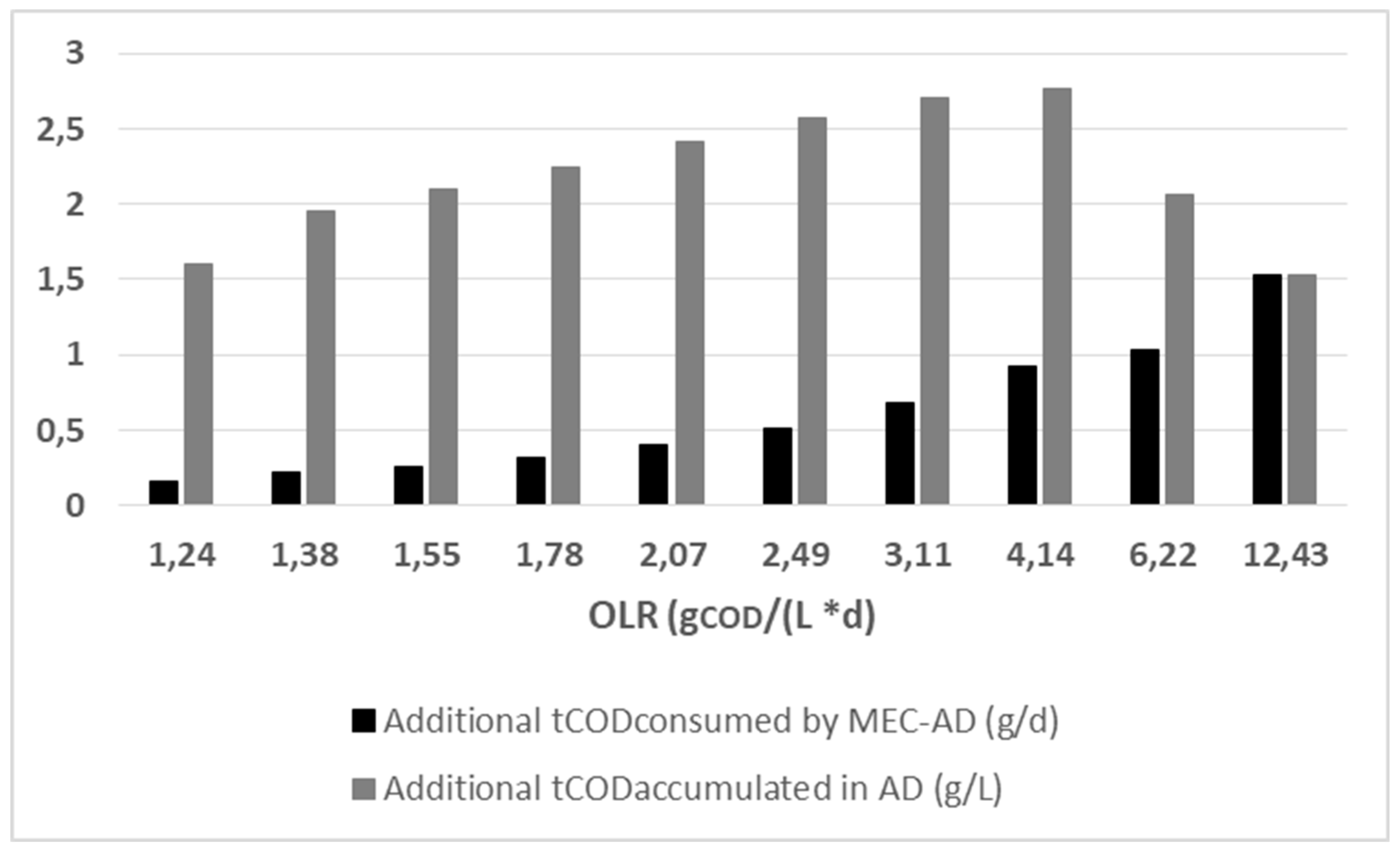
3.2.1. Organic loading rate
The obtained kinetic parameters from the ADM1 fit to the experimental data were utilized in order to extract the predicted tCOD consumption and accumulation in the reactors, in relation to varying OLR (from 1.2 to 12.4 g
COD / (L * d)).
Figure 6 depicts the results from the predicted differences between the two reactors.
As shown in
Figure 6, the ADM1 predicts a linearly increasing additional consumption in the MEC-AD process (from 0.2 to 1.5 g
COD / d), relative to the AD, as a function of the increasing OLR (from 1.2 to 12.4 g
COD / (L * d)). This result is a direct consequence of the higher disintegration rate of complex particulates (
Table 4). Furthermore, the comparative prediction shows that the MEC-AD process exhibits the highest divergence from the AD, at an OLR at 4.14 g
COD / (L * d), where the additional COD consumption rate of the MEC-AD, relative to AD, is 0.9 g
COD / d. At that OLR, the accumulated COD in the AD process presents a maximum concentration (accumulation rate of 2.7 g
COD / d in addition to that of the MEC-AD), while further increase in the OLR results in a simulated deterioration of both processes. The trends presented are consistent with previous studies, since a higher OLR means a higher substrate availability, which results in better utilization of the applied potential on the MEC-AD [
23,
29,
30]. At the same time, the deterioration of the processes at very high OLRs (>6.22 g
COD / (L * d)) is an a priori deduction. The results indicate that the optimization can significantly improve the treatment performance and economic efficiency of the raw-WAS-fed MEC-AD, since it achieves faster treatment times and better effluent quality, relative to AD.
3.2.2. Solids retention time
As has been previously described, the SRT of a reactor is a crucial parameter for its operation, since it directly affects the stability and activity of the microbial population involved in the digestion process [
31]. Moreover, taking into consideration that the SRT equals to the HRT during ideal reactor mixing, it stands to reason that the SRT deviates from the HRT, since some biomass can be withheld in the reactor. As a result, further optimization of the kinetic parameters took place, by simulating the MEC-AD operation at an increased SRT, which was set equal to the HRT plus 1.5 d.
The results for the predicted values of the kinetic parameters are presented in
Table 5. These show that the majority of the kinetic parameters appeared increased relative to the corresponding values at lower SRTs (
Table 4). Specifically, the majority of k
m values (for amino acids, sugars, LCFAs and all VFAs) increased, indicating a faster maximum uptake of each corresponding substrate, as a higher biomass concentration is present in the MEC-AD reactor. The exception to this is the k
m value for H
2 uptake, which appears slightly decreased relative to that at a lower SRT (
Table 4). Moreover, the SRT increase appears to have mixed effects on the saturation constants K
s for each substrate, as the K
s values for the sugars and propionate are improved, those for H
2, acetate and butyrate/valerate are deteriorated and the values for amino acids and LCFAs remain practically constant. Despite these changes, which were also shown to have a limited sensitivity to the reactor operation (
Figure 3 and
Figure 5d), the overall Monod substrate uptake kinetics are better as a function of increasing SRT. Furthermore, the 1
st order disintegration constants also show mixed results, with a slightly decreased carbohydrates disintegration, a constant disintegration of lipids and improved disintegration of proteins and complex particulates. Specifically, the disintegration of complex particulates, which was found to be the most sensitive parameter to changes (
Figure 5f) and the main cause of variation between the AD and the MEC-AD reactors, increases drastically (0.7 g / L relative to 0.4 g / L for high and low SRTs, respectively). Overall, the 1
st order disintegration constants, similarly to the Monod constants, contribute towards an improved process at higher SRTs.
4. Conclusions
The present study indicated that the ADM1 model can be effectively used for the extraction and optimization of the apparent Monod-type and first-order kinetic constants of the MEC-AD. The results showed that the obtained kinetics of the raw-WAS-fed MEC-AD improved significantly, comparatively with the conventional AD, while the applied voltage showed a predominant contribution to the biomass yields and the disintegration of complex particulates. In the case of the MEC-AD, the highest divergence from the AD in particulate and soluble COD content, was obtained at an OLR of 4.14 gCOD / (L * d), while its performance and kinetic constants further improved as a function of an increased SRT. The results can serve as a practical imprint of the potential that the MEC-AD operating parameters have, on improving and accelerating wastewater treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Gerasimos Kanellos and Georgios Arvanitakis; Data curation, Gerasimos Kanellos, Asimina Tremouli and Georgios Arvanitakis; Formal analysis, Gerasimos Kanellos, Asimina Tremouli and Georgios Arvanitakis; Funding acquisition, Gerasimos Kanellos; Investigation, Gerasimos Kanellos and Georgios Arvanitakis; Methodology, Gerasimos Kanellos and Georgios Arvanitakis; Project administration, Gerasimos Lyberatos; Resources, Gerasimos Lyberatos; Software, Georgios Arvanitakis; Supervision, Gerasimos Lyberatos; Validation, Gerasimos Kanellos, Asimina Tremouli and Georgios Arvanitakis; Visualization, Gerasimos Kanellos; Writing – original draft, Gerasimos Kanellos; Writing – review & editing, Asimina Tremouli and Gerasimos Lyberatos.
Funding
The research work was supported by the Hellenic Foundation for Research and Innovation (HFRI) under the 3rd Call for HFRI PhD Fellowships (Fellowship Number: 5675).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Stamatelatou, K.; Antonopoulou, G.; Lyberatos, G. Production of biogas via anaerobic digestion, vol. 1895. Woodhead Publishing Limited, 2011.
- Ferrentino, R.; Langone, M.; Fiori, L.; Andreottola, G. Full-Scale Sewage Sludge Reduction Technologies: A Review with a Focus on Energy Consumption. Water (Switzerland) 2023, 15, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domini, M.; Bertanza, G.; Vahidzadeh, R.; Pedrazzani, R. Sewage Sludge Quality and Management for Circular Economy Opportunities in Lombardy. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joicy, A.; Seo, H.; Lee, M. E.; Kim, D. H.; Cho, S. K.; Ahn, Y. Enhanced methane production using pretreated sludge in MEC-AD system: Performance, microbial activity, and implications at different applied voltages. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 40731–40741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. T.; Zhang, Y. F.; Wang, B.; Wang, S.; Xing, X.; Xu, X. J.; Liu, W. Z.; Ren, N. Q.; Lee, D. J.; Chen, C. Enhancement of methane production from waste activated sludge using hybrid microbial electrolysis cells-anaerobic digestion (MEC-AD) process – A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appels, L.; Baeyens, J.; Degrève, J.; Dewil, R. Principles and potential of the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 755–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, G.; Lu, X.; Kato, H.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y. Y. Overview of pretreatment strategies for enhancing sewage sludge disintegration and subsequent anaerobic digestion: Current advances, full-scale application and future perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 69, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Hendriks, A. T. W. M.; van Lier, J. B.; de Kreuk, M. Pre-treatments to enhance the biodegradability of waste activated sludge: Elucidating the rate limiting step. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 1434–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Song, H. Microbial electro-fermentation for synthesis of chemicals and biofuels driven by bi-directional extracellular electron transfer. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2020, 5, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dhar, B. R. A critical review of microbial electrolysis cells coupled with anaerobic digester for enhanced biomethane recovery from high-strength feedstocks. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 50–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhou, A.; Jia, J.; Liang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Xing, D.; Ren, N. Characterization of methane production and microbial community shifts during waste activated sludge degradation in microbial electrolysis cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, B.; Yin, C.; Zhang, C.; Dai, X.; Yuan, H.; Zhu, N. Biostimulation by direct voltage to enhance anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Tao, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, C.; Mu, L.; Ruan, H.; Yon, Y. R.; Su, H.; Yan, B.; Chen, G. Modification of anaerobic digestion model No.1 with Machine learning models towards applicable and accurate simulation of biomass anaerobic digestion. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 454, 140369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozgun, H. Anaerobic Digestion Model No. 1 (ADM1) for mathematical modeling of full-scale sludge digester performance in a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Biodegradation 2019, 30, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinrich, S.; Nelles, M. Systematic simplification of the Anaerobic Digestion Model No. 1 (ADM1) – Model development and stoichiometric analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 333, no. 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, W. J. Application of the ADM1 model to advanced anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1832–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batstone, D. J.; Keller, J. Industrial applications of the IWA anaerobic digestion model No. 1 (ADM1). Water Sci. Technol. 2003, 47, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emebu, S.; Pecha, J.; Janáčová, D. Review on anaerobic digestion models: Model classification & elaboration of process phenomena. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, R.; Guo, W.; Batstone, D.; Makinia, J.; Li, Y. Modifications to the anaerobic digestion model no. 1 (ADM1) for enhanced understanding and application of the anaerobic treatment processes – A comprehensive review. Water Res. 2023, 244, 120504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Li, L.; Zhao, X.; Peng, Y.; Yang, P.; Peng, X. Anaerobic digestion: A review on process monitoring. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 103, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, L.; Wang, C.; Zhao, X.; Wu, K.; Liang, C.; Yin, F.; Yang, B.; Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W. Enhanced anaerobic digestion of swine manure via a coupled microbial electrolysis cell. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 340, 125619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V. T.; Ta, Q. T. H.; Nguyen, P. K. T. Artificial intelligence-based modeling and optimization of microbial electrolysis cell-assisted anaerobic digestion fed with alkaline-pretreated waste-activated sludge. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 187, 108670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellos, G.; Tremouli, A.; Arvanitakis, G.; Lyberatos, G. Boosting methane production and raw waste activated sludge treatment in a microbial electrolysis cell-anaerobic digestion (MEC-AD) system: The effect of organic loading rate. Bioelectrochemistry 2024, 23, 108555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjusha, C.; Beevi, B. S. Mathematical Modeling and Simulation of Anaerobic Digestion of Solid Waste. Procedia Technol. 2016, 24, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henze, M.; Grady, C. P. L.; Gujer, W.; Marais, G. V. R.; Matsuo, T. A general model for single-sludge wastewater treatment systems. Water Res. 1987, 21, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batstone, D. J.; Keller, J.; Angelidaki, I.; Kalyuzhny, S. V.; Pavlostathis, S. G.; Rozzi, A.; Sanders, W. T. M.; Siegrist, H.; Vavilin, V. A. Anaerobic digestion model No. 1 (ADM1). IWA Publishing. Water Science and Technology 2002, 45, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutorial, A.; Reichert, P. Computer Program for the Identication and Simulation of Aquatic Systems, no. September. 1998.
- Gharbi, R.; Vidales, A. G.; Omanovic, S.; Tartakovsky, B. Mathematical model of a microbial electrosynthesis cell for the conversion of carbon dioxide into methane and acetate. J. CO2 Util. 2022, 59, 101956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dhar, B. R. Boosting resilience of microbial electrolysis cell-assisted anaerobic digestion of blackwater with granular activated carbon amendment. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 381, 129136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, D.; Sasaki, K.; Watanabe, A.; Morita, M.; Matsumoto, N.; Igarashi, Y.; Ohmura, N. Operation of a cylindrical bioelectrochemical reactor containing carbon fiber fabric for efficient methane fermentation from thickened sewage sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 129, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Rubia, M. A.; Perez, M.; Romero, L. I.; Sales, D. Effect of solids retention time (SRT) on pilot scale anaerobic thermophilic sludge digestion. Process Biochem. 2006, 41, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
The experimental values (symbol) and the computational fit (line) of (a, b) tCOD, (c, d) sCOD, (e, f) biogas and (g, h) methane content, for the AD and the MEC-AD respectively, as was obtained from the ADM1.
Figure 1.
The experimental values (symbol) and the computational fit (line) of (a, b) tCOD, (c, d) sCOD, (e, f) biogas and (g, h) methane content, for the AD and the MEC-AD respectively, as was obtained from the ADM1.
Figure 2.
The experimental values (symbol) and the computational fit (line) of (a, b) particulate carbon, (c, d) soluble carbon, (e, f) TKN and (g, h) soluble nitrogen, for the AD and the MEC-AD respectively, as was obtained from the ADM1.
Figure 2.
The experimental values (symbol) and the computational fit (line) of (a, b) particulate carbon, (c, d) soluble carbon, (e, f) TKN and (g, h) soluble nitrogen, for the AD and the MEC-AD respectively, as was obtained from the ADM1.
Figure 3.
The simulated individual biomass concentrations in the (a) AD and (b) MEC-AD reactors, and (c) the cumulative biomass concentration in the reactors, as was obtained from the ADM1.
Figure 3.
The simulated individual biomass concentrations in the (a) AD and (b) MEC-AD reactors, and (c) the cumulative biomass concentration in the reactors, as was obtained from the ADM1.
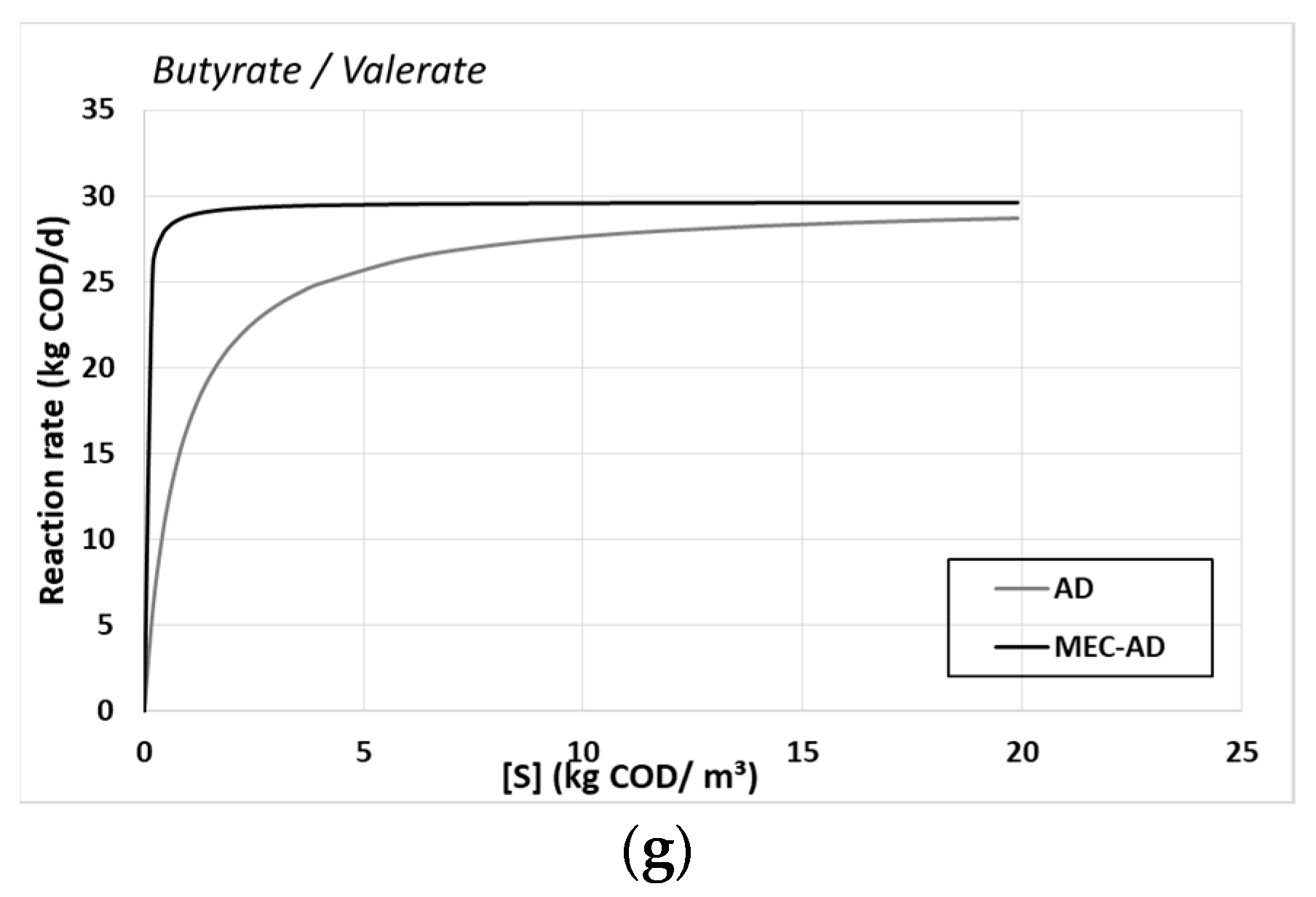
Figure 4.
The substrates’ uptake Monod kinetic constants of (a) amino acids, (b) sugars, (c) LCFAs, (d) H2, (e) acetate, (f) propionate and (g) butyrate/valerate, for the AD (grey) and the MEC-AD (black), as a function of each substrate concentration.
Figure 4.
The substrates’ uptake Monod kinetic constants of (a) amino acids, (b) sugars, (c) LCFAs, (d) H2, (e) acetate, (f) propionate and (g) butyrate/valerate, for the AD (grey) and the MEC-AD (black), as a function of each substrate concentration.
Figure 5.
The sensitivity analysis of sCOD as a function of the (a) km Monod, (b) Ks Monod, (c) 1st order disintegration kinetic constants and the sensitivity analysis of tCOD as a function of the (d) km Monod, (e) Ks Monod and (f) 1st order disintegration kinetic constants, as was obtained from the ADM1.
Figure 5.
The sensitivity analysis of sCOD as a function of the (a) km Monod, (b) Ks Monod, (c) 1st order disintegration kinetic constants and the sensitivity analysis of tCOD as a function of the (d) km Monod, (e) Ks Monod and (f) 1st order disintegration kinetic constants, as was obtained from the ADM1.
Figure 6.
The simulated divergence in the MEC-AD consumed tCOD (black) and the AD additional accumulated tCOD relative to the MEC-AD (grey), in relation to the reactors OLR, as was obtained from the ADM1.
Figure 6.
The simulated divergence in the MEC-AD consumed tCOD (black) and the AD additional accumulated tCOD relative to the MEC-AD (grey), in relation to the reactors OLR, as was obtained from the ADM1.
Table 1.
Fractions of amino acids and sugars disintegrated to different VFAs and hydrogen [
17].
Table 1.
Fractions of amino acids and sugars disintegrated to different VFAs and hydrogen [
17].
| Disintegration fraction |
Amino acids |
Sugars |
| Acetate |
0.40 |
0.41 |
| Propionate |
0.05 |
0.27 |
| Butyrates |
0.26 |
0.13 |
| Valerates |
0.23 |
- |
| H2 |
0.06 |
0.19 |
Table 2.
The biochemical rate coefficients (ν
i,j) and kinetic rate equations (ρ
j) for soluble components [
26].
Table 2.
The biochemical rate coefficients (ν
i,j) and kinetic rate equations (ρ
j) for soluble components [
26].
Table 3.
The biochemical rate coefficients (ν
i,j) and kinetic rate equations (ρ
j) for soluble components [
26].
Table 3.
The biochemical rate coefficients (ν
i,j) and kinetic rate equations (ρ
j) for soluble components [
26].
Table 4.
The substrates’ uptake Monod kinetic constants and the particulates disintegration and hydrolysis 1st order kinetic constants, as they occur from the fitting of ADM1 model to the experimental values.
Table 4.
The substrates’ uptake Monod kinetic constants and the particulates disintegration and hydrolysis 1st order kinetic constants, as they occur from the fitting of ADM1 model to the experimental values.
| Substrate uptake Monod kinetic constants |
Disintegration 1st order kinetic constants |
| |
AD |
MEC-AD |
|
AD |
MEC-AD |
| |
km |
Ks |
km |
Ks |
Carbohydrates |
19.9 |
19.9 |
| Amino acids |
83.3 |
0.4 |
86.3 |
0.4 |
Lipids |
0.1 |
0.1 |
| Sugars |
57.1 |
1.1E-03 |
31.7 |
3.3E-07 |
Proteins |
39.9 |
39.5 |
| LCFAs |
21.6 |
1.6 |
23.7 |
1.5 |
Particulates |
0.1 |
0.4 |
| H2 |
69.3 |
6.7E-08 |
10.1 |
1.4E-05 |
|
|
|
| Acetate |
6.4 |
1.1E-04 |
12.6 |
1.1E-02 |
|
|
|
| Propionate |
24.3 |
1.5E-05 |
12.8 |
5.5E-09 |
|
|
|
| Butyrate / Valerate |
29.9 |
7.9E-01 |
29.7 |
2.9E-02 |
|
|
|
Table 5.
The substrates’ uptake Monod kinetic constants and the particulates disintegration and hydrolysis 1st order kinetic constants, as they occur from the fitting of ADM1 model to the experimental values of the MEC-AD at an increased SRT.
Table 5.
The substrates’ uptake Monod kinetic constants and the particulates disintegration and hydrolysis 1st order kinetic constants, as they occur from the fitting of ADM1 model to the experimental values of the MEC-AD at an increased SRT.
| Substrate uptake Monod kinetic constants |
Disintegration 1st order kinetic constants |
| |
MEC-AD |
|
MEC-AD |
| |
km |
Ks |
Carbohydrates |
19.8 |
| Amino acids |
95.2 |
0.4 |
Lipids |
0.1 |
| Sugars |
51.2 |
4.7E-03 |
Proteins |
31.7 |
| LCFAs |
23.7 |
1.5 |
Particulates |
0.7 |
| H2 |
8.7 |
1.1E-05 |
|
|
| Acetate |
13.6 |
4.6E-04 |
|
|
| Propionate |
23.3 |
9.1E-04 |
|
|
| Butyrate / Valerate |
37.6 |
0.2 |
|
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).