Submitted:
17 October 2023
Posted:
18 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Fish
2.2. SAV3 Inoculum
2.3. Experimental Challenge
2.4. Experimental Tanks Management
2.5. Sampling
2.6. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
2.7. RT-qPCR
2.7.1. SAV Q_nsp1 Assay
2.7.2. Salmon Genes Expression
| Gene name | Primers sequences (5’- 3’) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Interferon alpha (IFN-α) | F: TGCAGTATGCAGAGCGTGTG R:TCTCCTCCCATCTGGTCCAG |
[26] |
| Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) | F: AAGGGCTGTGATGTGTTTCTG R: TGTACTGAGCGGCATTACTCC |
[27] |
| Virus inhibitory protein, endoplasmic reticulum-associated, interferon-inducible (viperin) | F: AGCAATGGCAGCATGATCAG R: TGGTTGGTGTCCTCGTCAAAG |
[28] |
| Myxovirus resistance (Mx ) | F:TGCAACCACAGAGGCTTTGAA A:GGCTTGGTCAGGATGCCTAAT |
[29] |
| Major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) | F:GAAGAGCACTCTGATGAGGACAG R:CACCATGACTCCACTGGGGTAG |
[28] |
| Cluster of differentiation 8 alpha (CD8a) | F:CGTCTACAGCTGTGCATCAATCAA R:GGCTGTGGTCATTGGTGTAGTC |
[28] |
| Granzyme A (gzma) | GGTGTTTCTAGGGGTCCACTC TGCCACAGGGACAGGTAACG |
[30] |
| Natural killer lysin (NK-lysin) | F:TGTTCTTATGCACCACGCAA R:CGGGTATGACGCAAAACGACTA |
[31] |
| Major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) | F:CCACCTGGAGTACACACCCAG R:TTCCTCTCAGCCTCAGGCAG |
[32] |
| Cluster of differentiation 4 (CD4) | F:GAGTACACCTGCGCTGTGGAAT R:GGTTGACCTCCTGACCTACAAAGG |
[33] |
| Secretory immunoglobulin M (sIgM) | F:CTACAAGAGGGAGACCGGAG R:AGGGTCACCGTATTATCACTAGTT |
[28] |
| Membrane immunoglobulin M (mIgM) | F:CCTACAAGAGGGAGACCGA R:GATGAAGGTGAAGGCTGTTTT |
[34] |
| Secretory immunoglobulin T (sIgT-B) | F:GAATGTTTGGGACACGGAAG R:TCACATATCTTGACATGAGTTACC |
[35] |
| Membrane immunoglobulin T (mIgT-B) | F:GAATGTTTGGGACACGGAAG R:GCTCAGTCAGTGGGATGTTCT |
[36] |
| Mucin 2 (Muc-2) | F: CGACTGCCACAAAGCCATTAGG R: GCGTGTTGCTGCGTGTCTT |
[37] |
| Mucin 5 (Muc-5) | F: CCGTGCTGGGAGACATTATGAAGT R: TGCTGGAGAGGGAAAGGGTAAC |
[37] |
| Elongation factor-1alpha (EF1α) | F:TGCCCCTCCAGGATGTCTAC R:CACGGCCCACAGGTACTG |
[38] |
| SAV3-nsp1 | F: CCGGCCCTGAACCAGTT R: GTAGCCAAGTGGGAGAAAGCT Probe: FAM-5 -CTGGCCACCACTTCGA-3 -MGB |
[23] |
2.8. In Situ Hybridization (ISH)
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. In Situ Hybridization
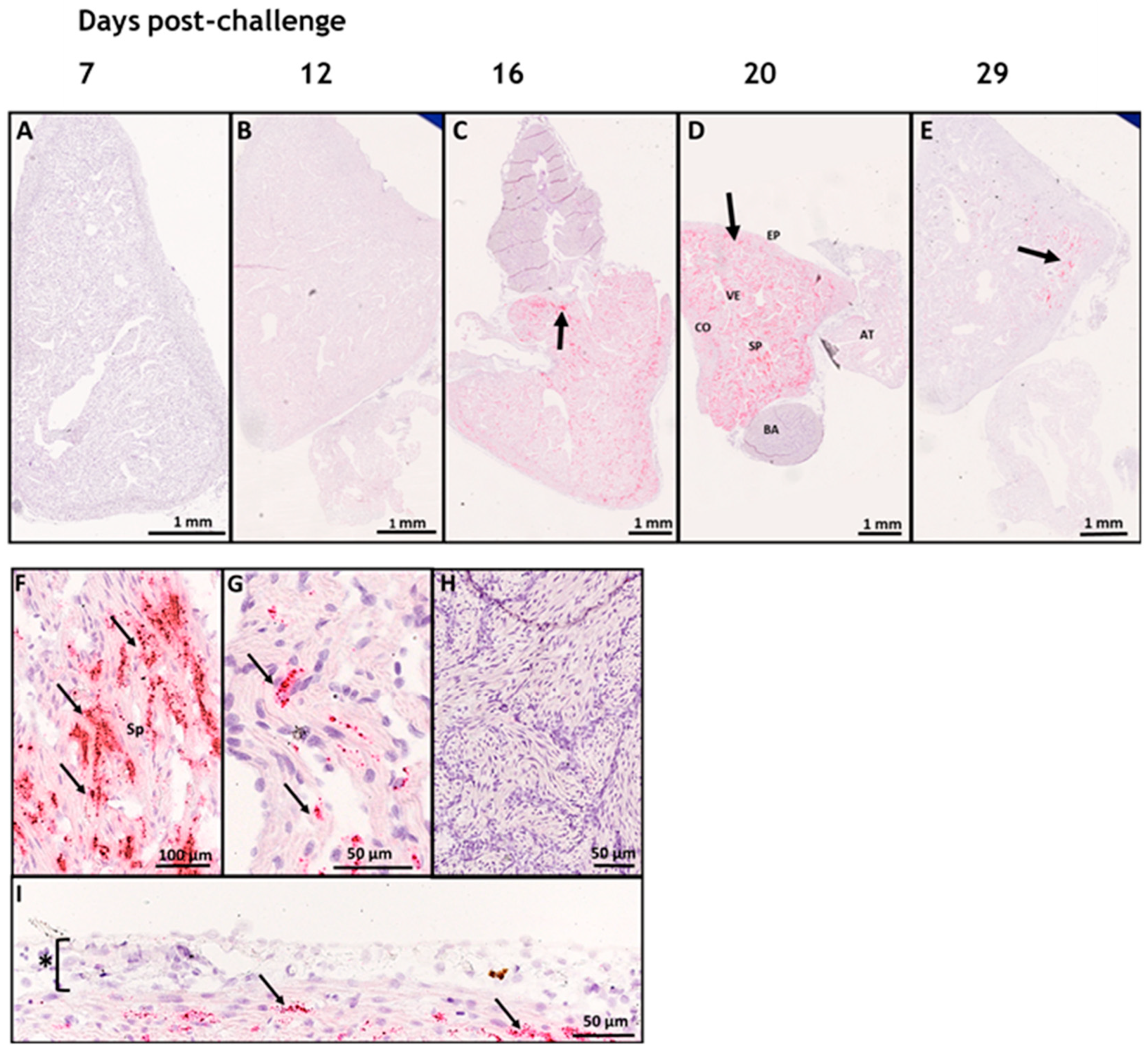
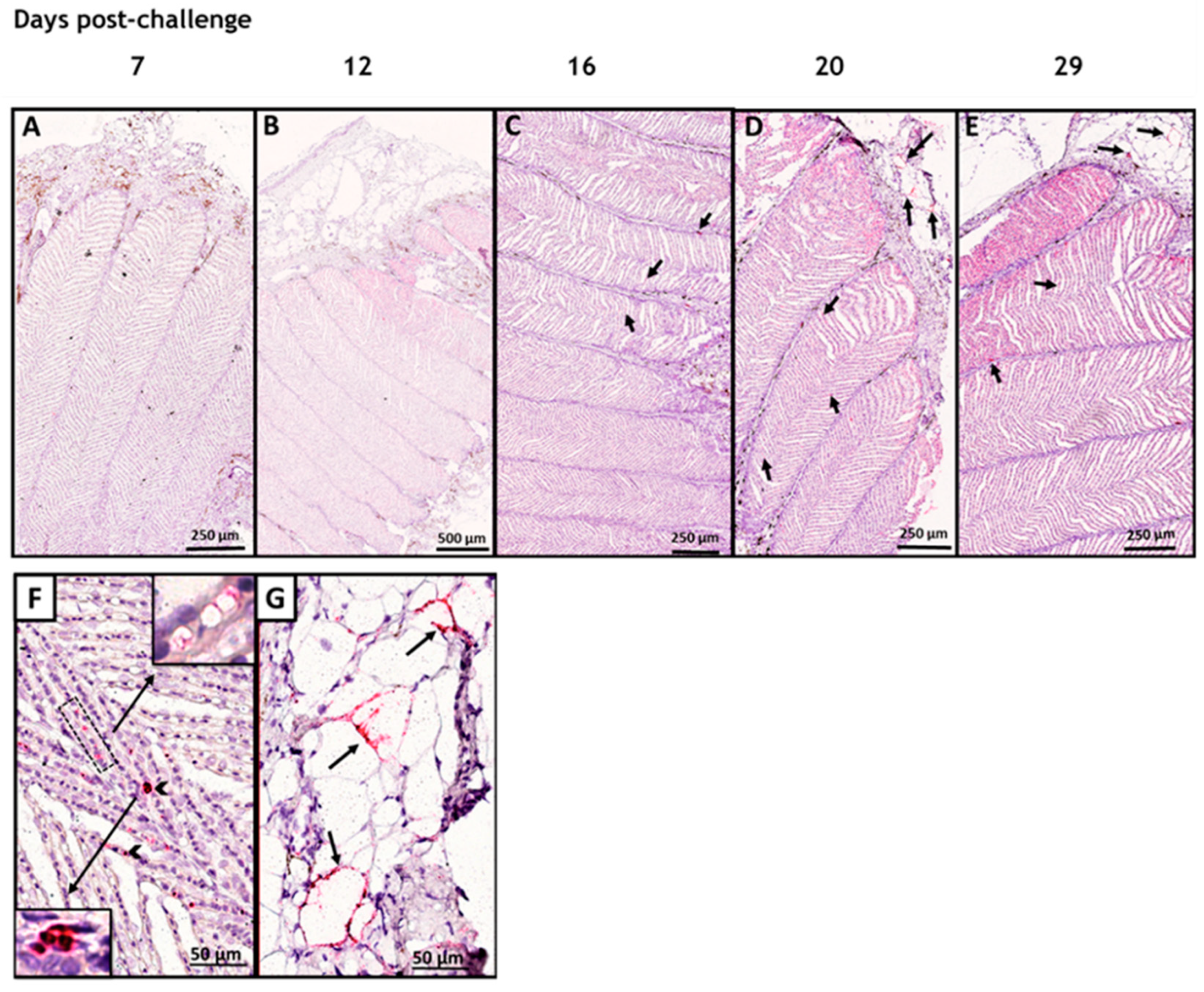
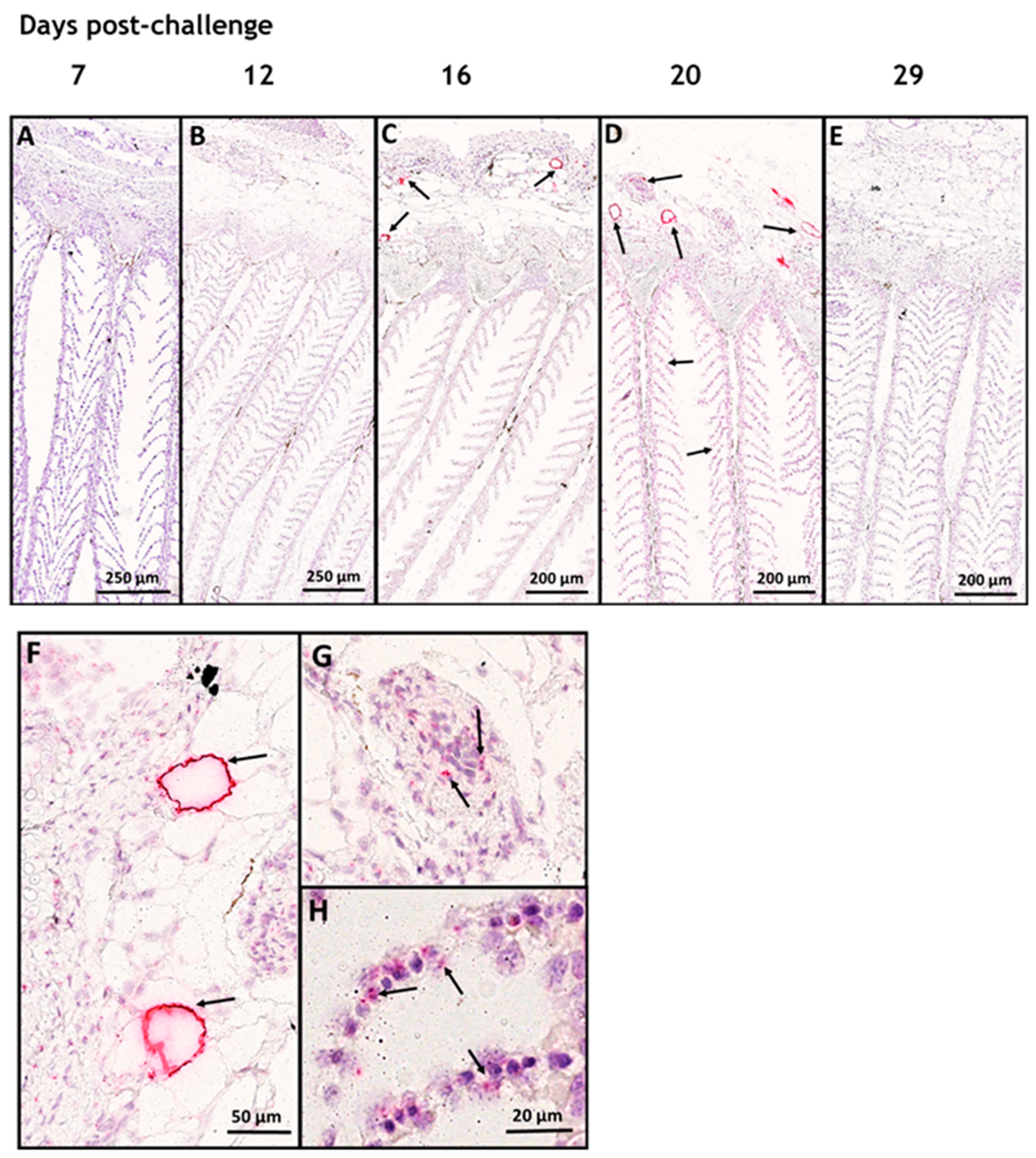
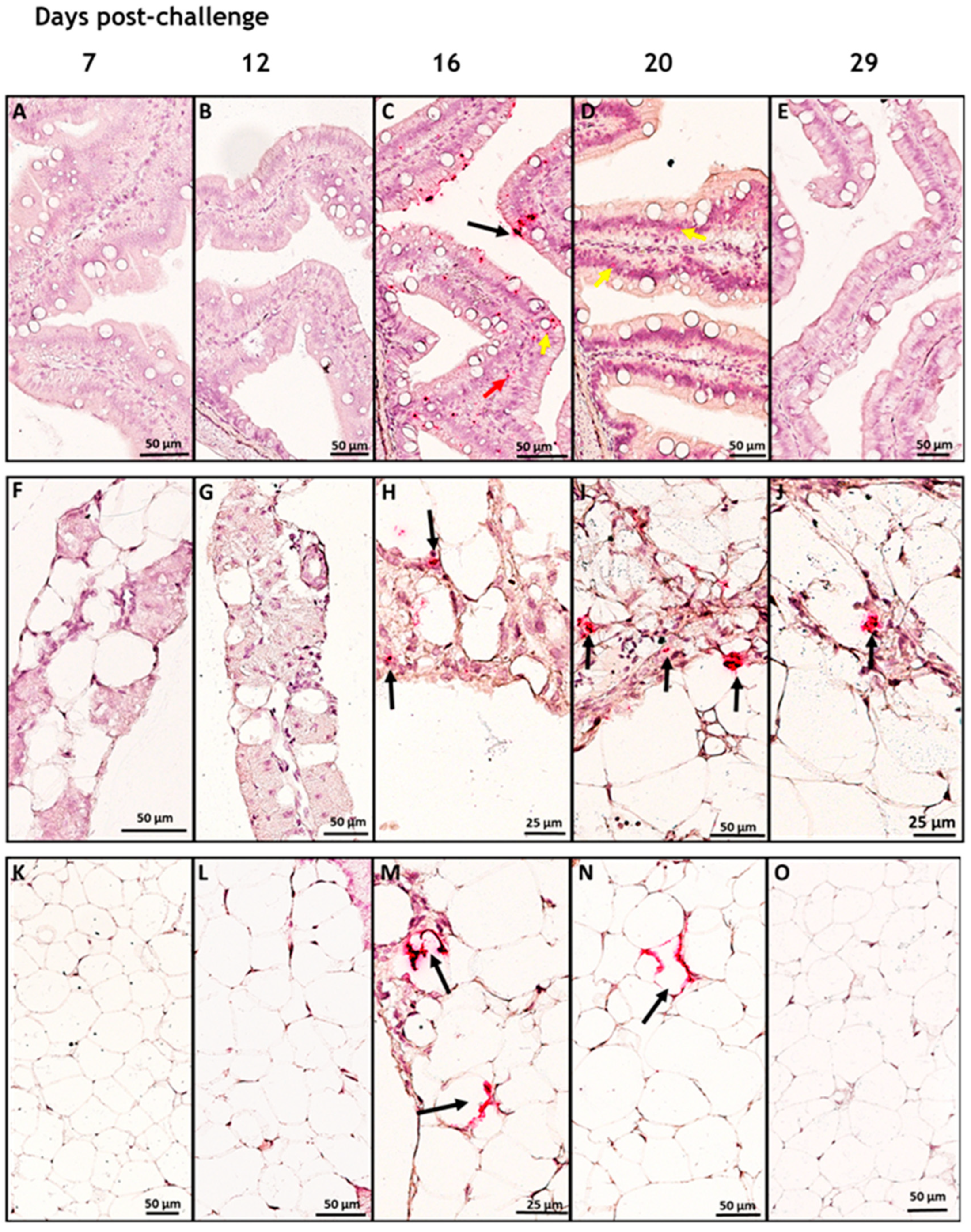
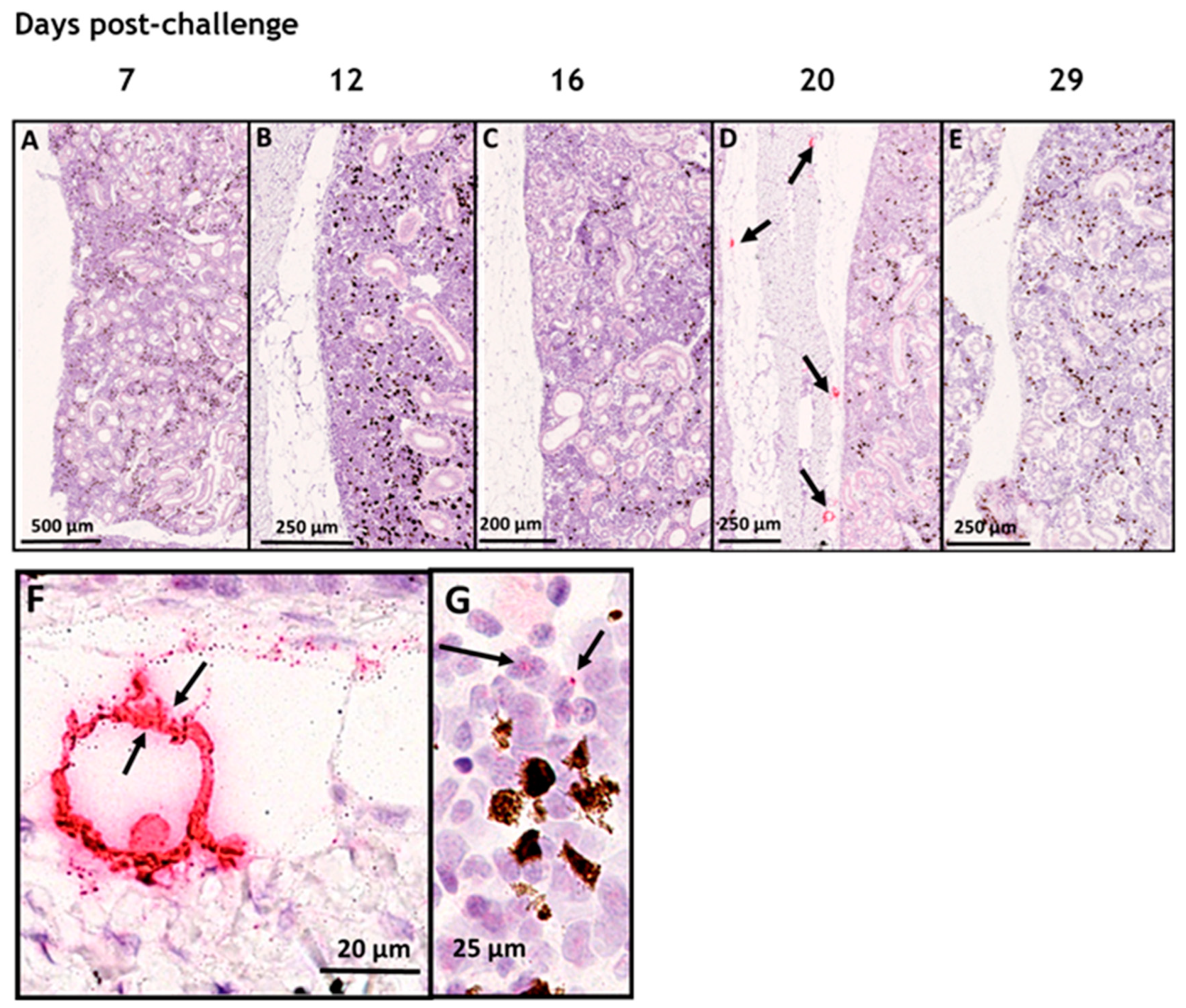
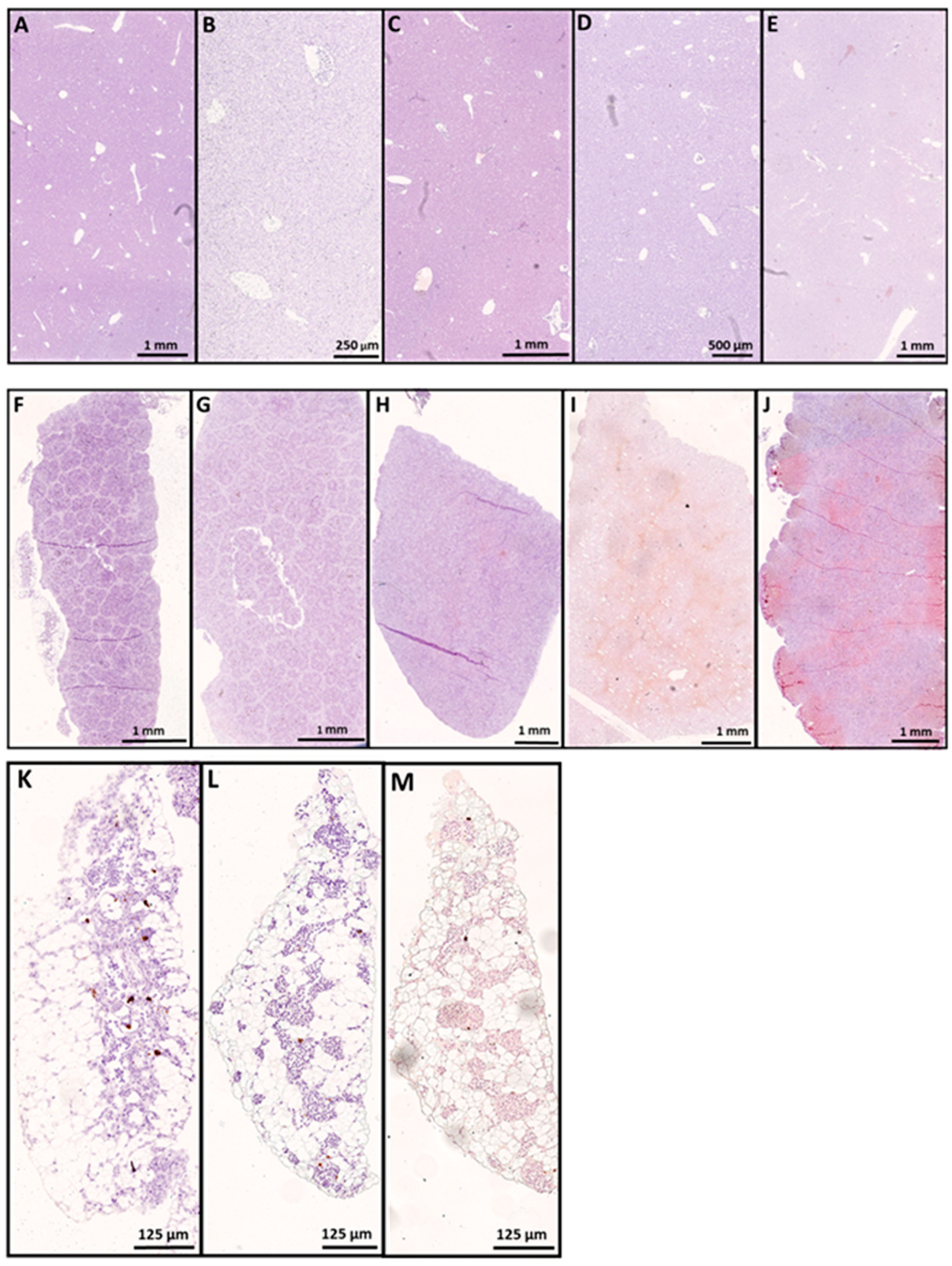
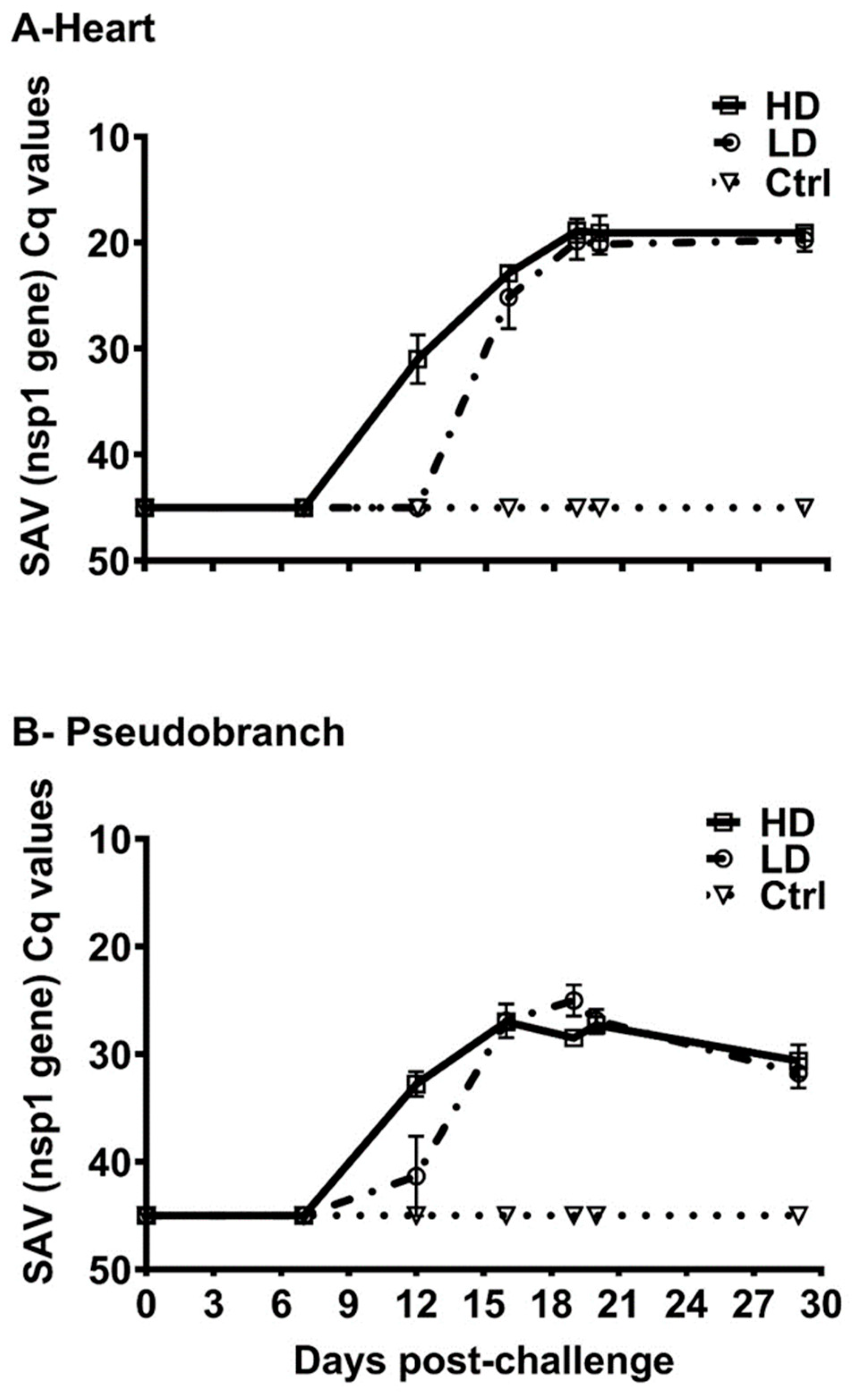
3.2. SAV-nsP1 Quantification
3.3. Immune Response in Pseudobranch against SAV
3.3.1. Genes Linked to Antiviral Activity
3.3.2. Major Histocompatibility Molecules
3.3.3. Genes Linked to T Cell
3.3.4. Immunoglobulins
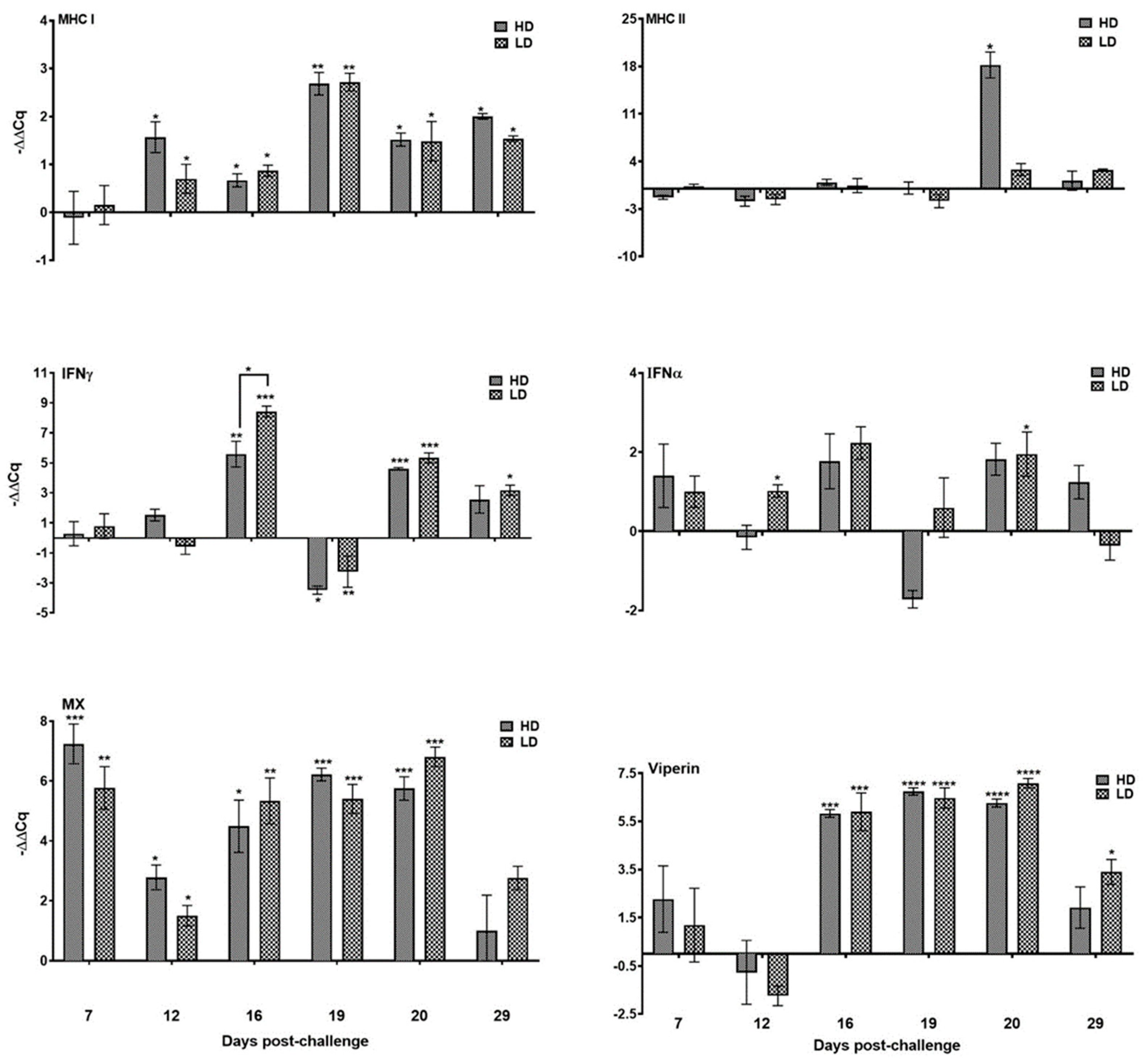
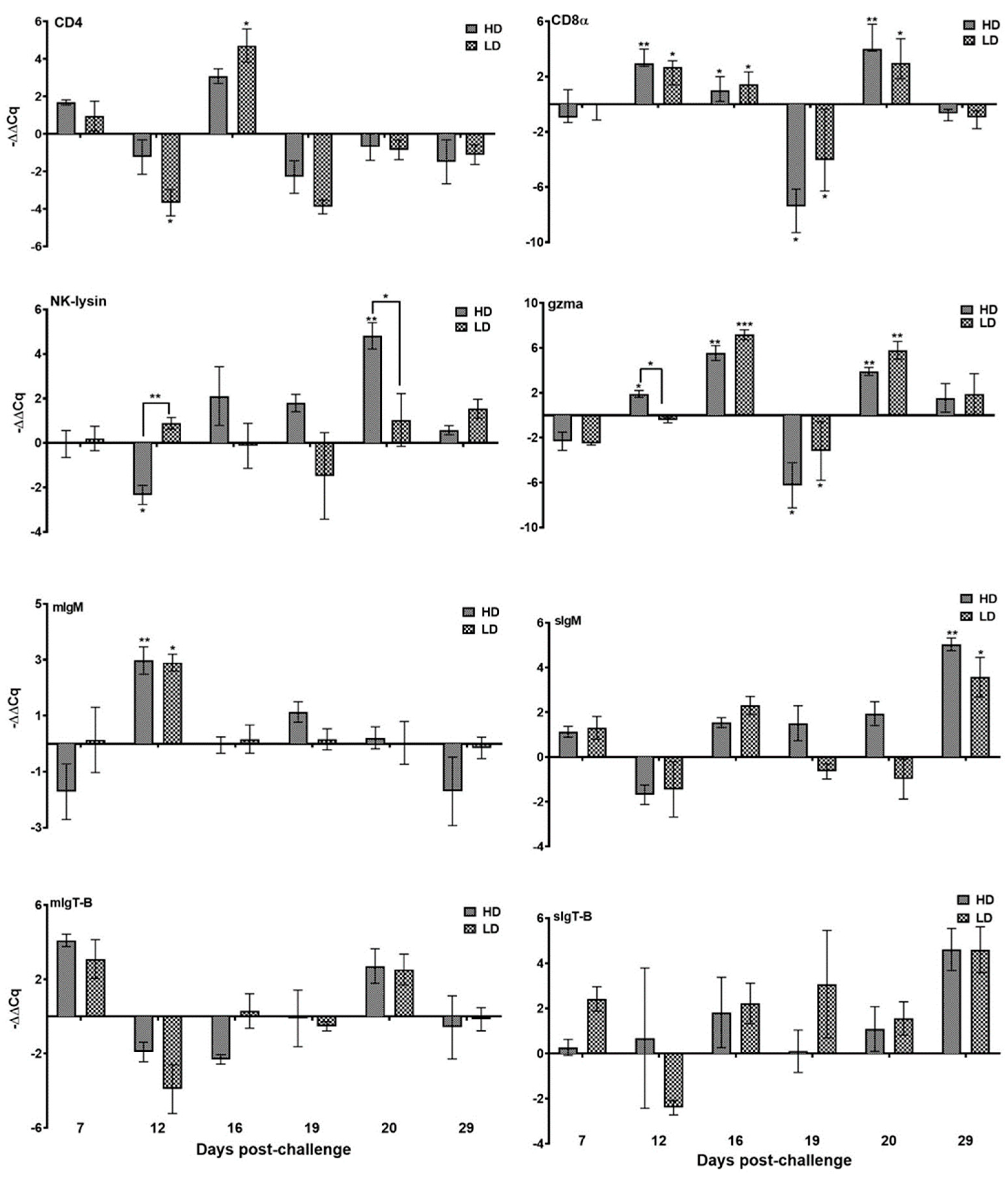
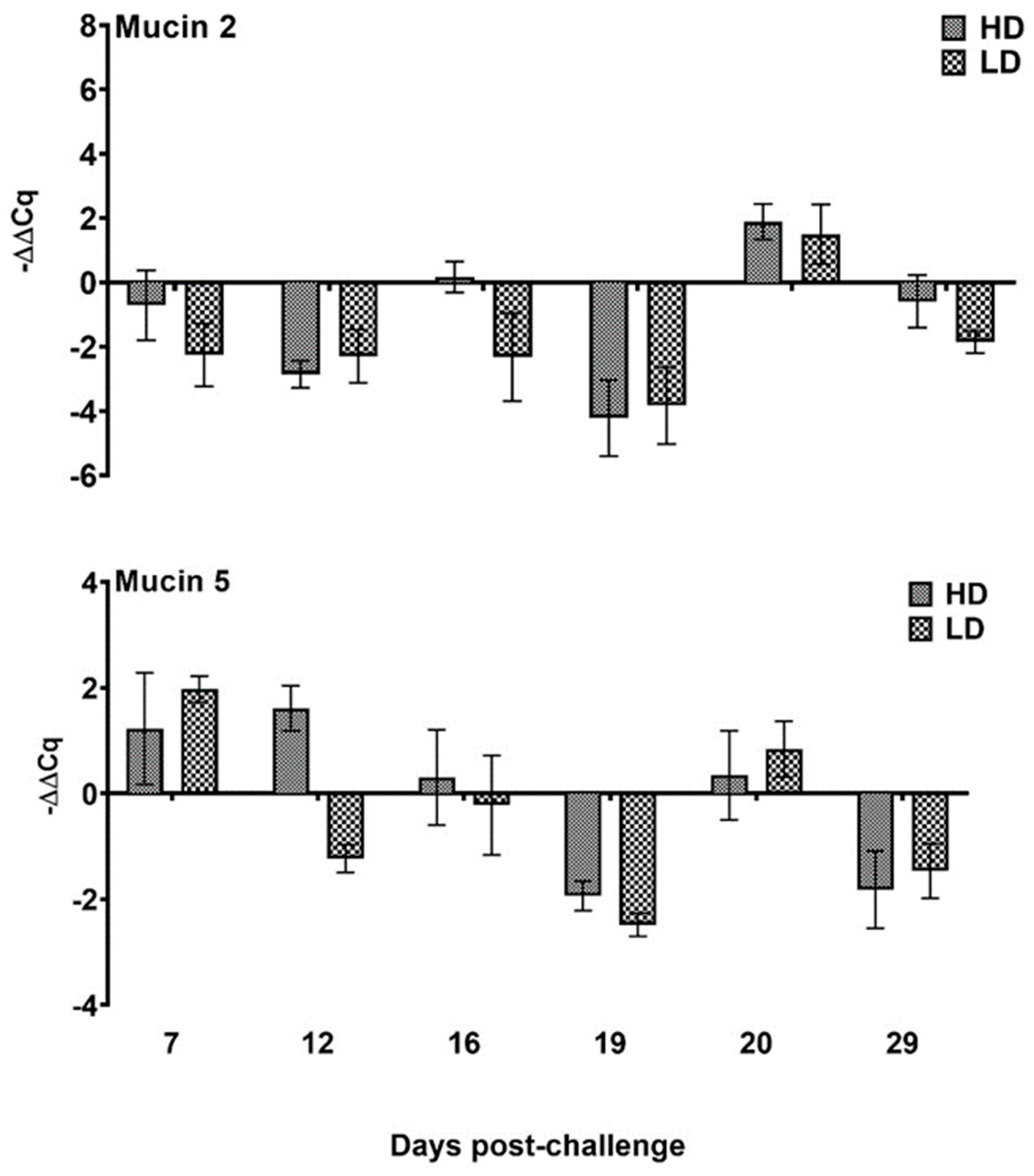
3.3.5. Mucin Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peters, C.J.; Dalrymple, J.M. Alphaviruses; ARMY MEDICAL RESEARCH INST OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES FORT DETRICK MD: 1990.
- Andersen, L.; Bratland, A.; Hodneland, K.; Nylund, A. Tissue tropism of salmonid alphaviruses (subtypes SAV1 and SAV3) in experimentally challenged Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Archives of virology 2007, 152, 1871–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, R.; McLoughlin, M.; Rowley, H.; Platten, M.; McCormick, J. Isolation of a toga-like virus from farmed Atlantic salmon Salmo salar with pancreas disease. Diseases of aquatic organisms 1995, 22, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castric, J.; Baudin Laurencin, F.; Bremont, M.; Jeffroy, J.; Ven, A.l.; Bearzotti, M. Isolation of the virus responsible for sleeping disease in experimentally infected rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Bulletin of the European Association of Fish Pathologists 1997, 17, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, D.; Rowley, H.; Walker, I.; Weston, J.; Branson, E.; Todd, D. First isolation of sleeping disease virus from rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), in the United Kingdom. Journal of fish diseases 2003, 26, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, K.; Fyrand, K.; Holtet, L.; Rowley, H. Isolation of pancreas disease virus from farmed Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., in Norway. Journal of Fish Diseases 1998, 21, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christie, K.; Graham, D.; McLoughlin, M.; Villoing, S.; Todd, D.; Knappskog, D. Experimental infection of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar pre-smolts by ip injection with new Irish and Norwegian salmonid alphavirus (SAV) isolates: a comparative study. Diseases of aquatic organisms 2007, 75, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenberie, S.; Peñaranda, M.M.D.; Thim, H.L.; Styrvold, M.B.; Strandskog, G.; Jørgensen, J.B.; Jensen, I. Salmonid alphavirus subtype 3 induces prolonged local B cell responses in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) after intraperitoneal infection. Frontiers in immunology 2020, 11, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakke, A.F.; Bjørgen, H.; Koppang, E.O.; Frost, P.; Afanasyev, S.; Boysen, P.; Krasnov, A.; Lund, H. IgM+ and IgT+ B cell traffic to the heart during SAV infection in Atlantic salmon. Vaccines 2020, 8, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.; Jarungsriapisit, J.; Nilsen, T.; Stefansson, S.; Taranger, G.; Secombes, C.; Morton, H.; Patel, S. Immune gene profiles in Atlantic salmon (salmo salar L.) post-smolts infected with SAV3 by bath-challenge show a delayed response and lower levels of gene transcription compared to injected fish. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2017, 62, 320–331. [Google Scholar]
- Hodneland, K.; Scientiarum, D. SALMONID ALPHAVIRUS (SAV).
- Parry, G.; Holliday, F. An experimental analysis of the function of the pseudobranch in teleosts. Journal of Experimental Biology 1960, 37, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waser, W. Transport and exchange of respiratory gases in the blood| root effect: root effect definition, functional role in oxygen delivery to the eye and swimbladder. 2011.
- Grassé, P.-P. Traité de zoologie: Agnathes et poissons; Masson: 1958.
- Barnett, C. The structure and function of the choroidal gland of teleostean fish. Journal of anatomy 1951, 85, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Karlsbakk, E.; Sæther, P.; Hostlund, C.; Fjellsoy, K.; Nylund, A. Parvicapsula pseudobranchicola n. sp.(Myxozoa), a myxosporidian infecting the pseudobranch of cultured Atlantic salmon (Salma salar) in Norway. BULLETIN-EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF FISH PATHOLOGISTS 2002, 22, 381–387. [Google Scholar]
- Valheim, M.; Håstein, T.; Myhr, E.; Speilberg, L.; Ferguson, H.W. Varracalbmi: a new bacterial panophthalmitis in farmed Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. Journal of Fish Diseases 2000, 23, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, A. A mortality and associated tissue reactions of chinook salmon, Oncorhynchus tshawytscha (Walbaum), caused by the microsporidan Loma sp. Journal of Fish Diseases 1984, 7, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.; Blindheim, S.H. Experimental challenge of flatfishes (Pleuronectidae) with salmonid alphavirus (SAV): Observations on tissue tropism and pathology in common dab Limanda limanda L. Aquaculture 2022, 551, 737944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhardt, L.-V.; Myrmel, M.; Lillehaug, A.; Qviller, L.; Weli, S.C. Concentration and detection of salmonid alphavirus in seawater during a post-smolt salmon (Salmo salar) cohabitant challenge. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 2021, 144, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, L.; Hodneland, K.; Nylund, A. No influence of oxygen levels on pathogenesis and virus shedding in Salmonid alphavirus (SAV)-challenged Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Virology journal 2010, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. American journal of epidemiology 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodneland, K.; Endresen, C. Sensitive and specific detection of Salmonid alphavirus using real-time PCR (TaqMan®). Journal of virological methods 2006, 131, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingerslev, H.-C.; Pettersen, E.F.; Jakobsen, R.A.; Petersen, C.B.; Wergeland, H.I. Expression profiling and validation of reference gene candidates in immune relevant tissues and cells from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Molecular immunology 2006, 43, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kileng, Ø.; Brundtland, M.I.; Robertsen, B. Infectious salmon anemia virus is a powerful inducer of key genes of the type I interferon system of Atlantic salmon, but is not inhibited by interferon. Fish & shellfish immunology 2007, 23, 378–389. [Google Scholar]
- Ingerslev, H.C.; Rønneseth, A.; Pettersen, E.; Wergeland, H. Differential expression of immune genes in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) challenged intraperitoneally or by cohabitation with IPNV. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology 2009, 69, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, S.; Austbø, L.; Hodneland, K.; Frost, P.; Løvoll, M.; McLoughlin, M.; Thim, H.L.; Braaen, S.; König, M.; Syed, M. Immune parameters correlating with reduced susceptibility to pancreas disease in experimentally challenged Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Fish & shellfish immunology 2013, 34, 789–798. [Google Scholar]
- Kileng, Ø.; Albuquerque, A.; Robertsen, B. Induction of interferon system genes in Atlantic salmon by the imidazoquinoline S-27609, a ligand for Toll-like receptor 7. Fish & shellfish immunology 2008, 24, 514–522. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, J.; Bøgwald, J.; Dalmo, R.A. Eomesodermin of Atlantic salmon: an important regulator of cytolytic gene and interferon gamma expression in spleen lymphocytes. PLoS One 2013, 8, e55893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braden, L.M.; Rasmussen, K.J.; Purcell, S.L.; Ellis, L.; Mahony, A.; Cho, S.; Whyte, S.K.; Jones, S.R.; Fast, M.D. Acquired protective immunity in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar against the myxozoan Kudoa thyrsites involves induction of MHIIβ+ CD83+ antigen-presenting cells. Infection and immunity 2018, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldal, T.; Løkka, G.; Wiik-Nielsen, J.; Austbø, L.; Torstensen, B.E.; Rosenlund, G.; Dale, O.B.; Kaldhusdal, M.; Koppang, E.O. Substitution of dietary fish oil with plant oils is associated with shortened mid intestinal folds in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). BMC veterinary research 2014, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, T. Phenotypic and Functional Similarity of Gut. J Immunol 2006, 176, 3942–3949. [Google Scholar]
- Strandskog, G.; Villoing, S.; Iliev, D.B.; Thim, H.L.; Christie, K.E.; Jørgensen, J.B. Formulations combining CpG containing oliogonucleotides and poly I: C enhance the magnitude of immune responses and protection against pancreas disease in Atlantic salmon. Developmental & Comparative Immunology 2011, 35, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Wiik-Nielsen, J.; Løvoll, M.; Fritsvold, C.; Kristoffersen, A.B.; Haugland, Ø.; Hordvik, I.; Aamelfot, M.; Jirillo, E.; Koppang, E.O.; Grove, S. Characterization of myocardial lesions associated with cardiomyopathy syndrome in A tlantic salmon, S almo salar L., using laser capture microdissection. Journal of Fish Diseases 2012, 35, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauscher, A.; Krossøy, B.; Frost, P.; Grove, S.; König, M.; Bohlin, J.; Falk, K.; Austbø, L.; Rimstad, E. Immune responses in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) following protective vaccination against infectious salmon anemia (ISA) and subsequent ISA virus infection. Vaccine 2011, 29, 6392–6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos-López, M.; Calduch-Giner, J.A.; Mirimin, L.; MacCarthy, E.; Rodger, H.D.; O’Connor, I.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A.; Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Piazzon, M.C. Gene expression analysis of Atlantic salmon gills reveals mucin 5 and interleukin 4/13 as key molecules during amoebic gill disease. Scientific reports 2018, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, L.; Somamoto, T.; Lie, K.; Dijkstra, J.; Hordvik, I. Characterisation of salmon and trout CD8α and CD8β. Molecular immunology 2005, 42, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raynard, R.; Houghton, G. Development towards an experimental protocol for the transmission of pancreas disease of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 1993, 15, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McVicar, A. Infection as a primary cause of pancreas disease in farmed Atlantic salmon. Bulletin of the European Association of Fish Pathologists 1990, 10, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Houghton, G. Kinetics of infection of plasma, blood leucocytes and lymphoid tissue from Atlantic salmon Salmo salar experimentally infected with pancreas disease. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 1995, 22, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M.; Wasmuth, M.; Olsen, A.; Gjerset, B.; Modahl, I.; Breck, O.; Haldorsen, R.; Hjelmeland, R.; Taksdal, T. Pancreas disease (PD) in sea-reared Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L., in Norway; a prospective, longitudinal study of disease development and agreement between diagnostic test results. Journal of fish diseases 2010, 33, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taksdal, T.; Bang Jensen, B.; Böckerman, I.; McLoughlin, M.; Hjortaas, M.; Ramstad, A.; Sindre, H. Mortality and weight loss of Atlantic salmon, Salmon salar L., experimentally infected with salmonid alphavirus subtype 2 and subtype 3 isolates from Norway. Journal of fish diseases 2015, 38, 1047–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarungsriapisit, J.; Moore, L.; Taranger, G.L.; Nilsen, T.; Morton, H.C.; Fiksdal, I.U.; Stefansson, S.; Fjelldal, P.G.; Evensen, Ø.; Patel, S. Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) post-smolts challenged two or nine weeks after seawater-transfer show differences in their susceptibility to salmonid alphavirus subtype 3 (SAV3). Virology journal 2016, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, D.; Brown, A.; Savage, P.; Frost, P. Detection of salmon pancreas disease virus in the faeces and mucus of A tlantic s almon, S almo salar L., by real-time RT-PCR and cell culture following experimental challenge. Journal of fish diseases 2012, 35, 949–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stene, A.; Hellebø, A.; Viljugrein, H.; Solevåg, S.; Devold, M.; Aspehaug, V. Liquid fat, a potential abiotic vector for horizontal transmission of salmonid alphavirus? Journal of fish diseases 2016, 39, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourronc, F.A.; Rebagliati, M.R.; Kramer-Riesberg, B.; Fleck, A.M.; Patten, J.J.; Geohegan-Barek, K.; Messingham, K.N.; Davey, R.A.; Maury, W.; Klingelhutz, A.J. Adipocytes are susceptible to Ebola Virus infection. Virology 2022, 573, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangavel, H.; Dhanyalayam, D.; Lizardo, K.; Oswal, N.; Dolgov, E.; Perlin, D.S.; Nagajyothi, J.F. Susceptibility of Fat Tissue to SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Female hACE2 Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuong, C.; Bates, T.A.; Akter, S.; Werre, S.R.; LeRoith, T.; Weger-Lucarelli, J. Nutritional status impacts dengue virus infection in mice. BMC biology 2020, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tontonoz, P.; Hu, E.; Spiegelman, B.M. Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPARγ2, a lipid-activated transcription factor. Cell 1994, 79, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couderc, T.; Chrétien, F.; Schilte, C.; Disson, O.; Brigitte, M.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Touret, Y.; Barau, G.; Cayet, N.; Schuffenecker, I. A mouse model for Chikungunya: young age and inefficient type-I interferon signaling are risk factors for severe disease. PLoS pathogens 2008, 4, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsson, K.A.; Benktander, J.; Quintana-Hayashi, M.P.; Sharba, S.; Lindén, S.K. Mucin O-glycosylation and pathogen binding ability differ between rainbow trout epithelial sites. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2022, 131, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Herath, T.K.; Ferguson, H.W.; Weidmann, M.W.; Bron, J.E.; Thompson, K.D.; Adams, A.; Muir, K.F.; Richards, R.H. Pathogenesis of experimental salmonid alphavirus infection in vivo: an ultrastructural insight. Veterinary research 2016, 47, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhelst, J.; Hulpiau, P.; Saelens, X. Mx proteins: antiviral gatekeepers that restrain the uninvited. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews 2013, 77, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochs, G.; Haller, O. Mx Proteins: High Molecular Weight GTPases with Antiviral Activity. In Handbook of Cell Signaling, Elsevier: 2010; pp. 1855–1864.
- Ashley, C.L.; Abendroth, A.; McSharry, B.P.; Slobedman, B. Interferon-independent innate responses to cytomegalovirus. Frontiers in immunology 2019, 10, 2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, K.; Hall, M.; Urquhart, K.; Gahlawat, S.; Collet, B. Development of an in vitro system to measure the sensitivity to the antiviral Mx protein of fish viruses. Journal of virological methods 2012, 182, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlawat, S.K.; Ellis, A.E.; Collet, B. Expression of interferon and interferon–Induced genes in Atlantic salmon Salmo salar cell lines SHK-1 and TO following infection with Salmon AlphaVirus SAV. Fish & shellfish immunology 2009, 26, 672–675. [Google Scholar]
- Verrier, E.R.; Langevin, C.; Benmansour, A.; Boudinot, P. Early antiviral response and virus-induced genes in fish. Developmental & Comparative Immunology 2011, 35, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Guo, T.-C.; Mutoloki, S.; Haugland, Ø.; Marjara, I.S.; Evensen, Ø. Alpha interferon and not gamma interferon inhibits salmonid alphavirus subtype 3 replication in vitro. Journal of virology 2010, 84, 8903–8912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Guo, T.-C.; Mutoloki, S.; Haugland, Ø.; Evensen, Ø. Gene expression studies of host response to Salmonid alphavirus subtype 3 experimental infections in Atlantic salmon. Veterinary research 2012, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gascoigne, N.R.; Zal, T.; Yachi, P.P.; Hoerter, J.A. Co-receptors and recognition of self at the immunological synapse. Immunological Synapse 2010, 171–189. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, A.B. MHC and adaptive immunity in teleost fishes. Immunogenetics 2017, 69, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Barreda, D.R.; Zhang, Y.-A.; Boshra, H.; Gelman, A.E.; LaPatra, S.; Tort, L.; Sunyer, J.O. B lymphocytes from early vertebrates have potent phagocytic and microbicidal abilities. Nature immunology 2006, 7, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, M.F.; Hengartner, H.; Zinkernagel, R.M. T helper cell-independent neutralizing B cell response against vesicular stomatitis virus: role of antigen patterns in B cell induction? European journal of immunology 1995, 25, 3445–3451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teige, L.H.; Aksnes, I.; Røsæg, M.V.; Jensen, I.; Jørgensen, J.; Sindre, H.; Collins, C.; Collet, B.; Rimstad, E.; Dahle, M.K. Detection of specific Atlantic salmon antibodies against salmonid alphavirus using a bead-based immunoassay. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2020, 106, 374–383. [Google Scholar]
- Salinas, I.; Fernández-Montero, Á.; Ding, Y.; Sunyer, J.O. Mucosal immunoglobulins of teleost fish: A decade of advances. Developmental & Comparative Immunology 2021, 121, 104079. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





