Submitted:
21 October 2025
Posted:
22 October 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Buffers and Cell Media
- Wash buffer: 1X Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution without magnesium and calcium (HBSS -Mg/-Ca), 1 mM EDTA, 10 mM HEPES (pH 7.4) stored at 4°C.
- Collagenase buffer: 1X HBSS with magnesium and calcium (HBSS +Mg/+Ca), 10 mM HEPES, 150 U/mL collagenase (pH 7.5) stored at 4°C.
- Hepatocyte culture media: Leibovitz’s L-15 Medium, GlutaMAX™ Supplement (L-15) supplemented with 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS), 1X penicillin-streptomycin (Pen-Strep), 2.5 µg/mL Amphotericin B, 2 mM ascorbic acid-2P and 2 mM nicotinamide.
- ASG10 culture media: L-15 supplemented with 10% FBS and 1X Pen-Strep.
- Infection media: L-15 supplemented with 2% FBS and 1X Pen-Strep.
2.2. Viruses, Viral Propagation and Titration
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.4. Comparative Sequence and Structural Analysis of Viral Proteins
2.5. Investigating IPNV Isolates In Vivo and In Vitro
2.5.1. In Vivo Challenge Test in Atlantic Salmon Fry
2.5.2. In Vitro Challenge Test in Hepatocyte Cultures
2.6. DNA Extraction and Genotyping
2.7. Gene Expression
2.7.1. RNA Extraction from Diverse Sources
2.7.2. Determination of Viral Load and Viral Production by RT-qPCR
2.7.3. RNA Sequencing
2.8. Gene Ontology and Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.9. Statistical Tests
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Analysis of IPNV Isolates
3.2. Sequence Analysis of Vir410/2018 and V1244 Shows Main Differences Reside in the VP2 Protein
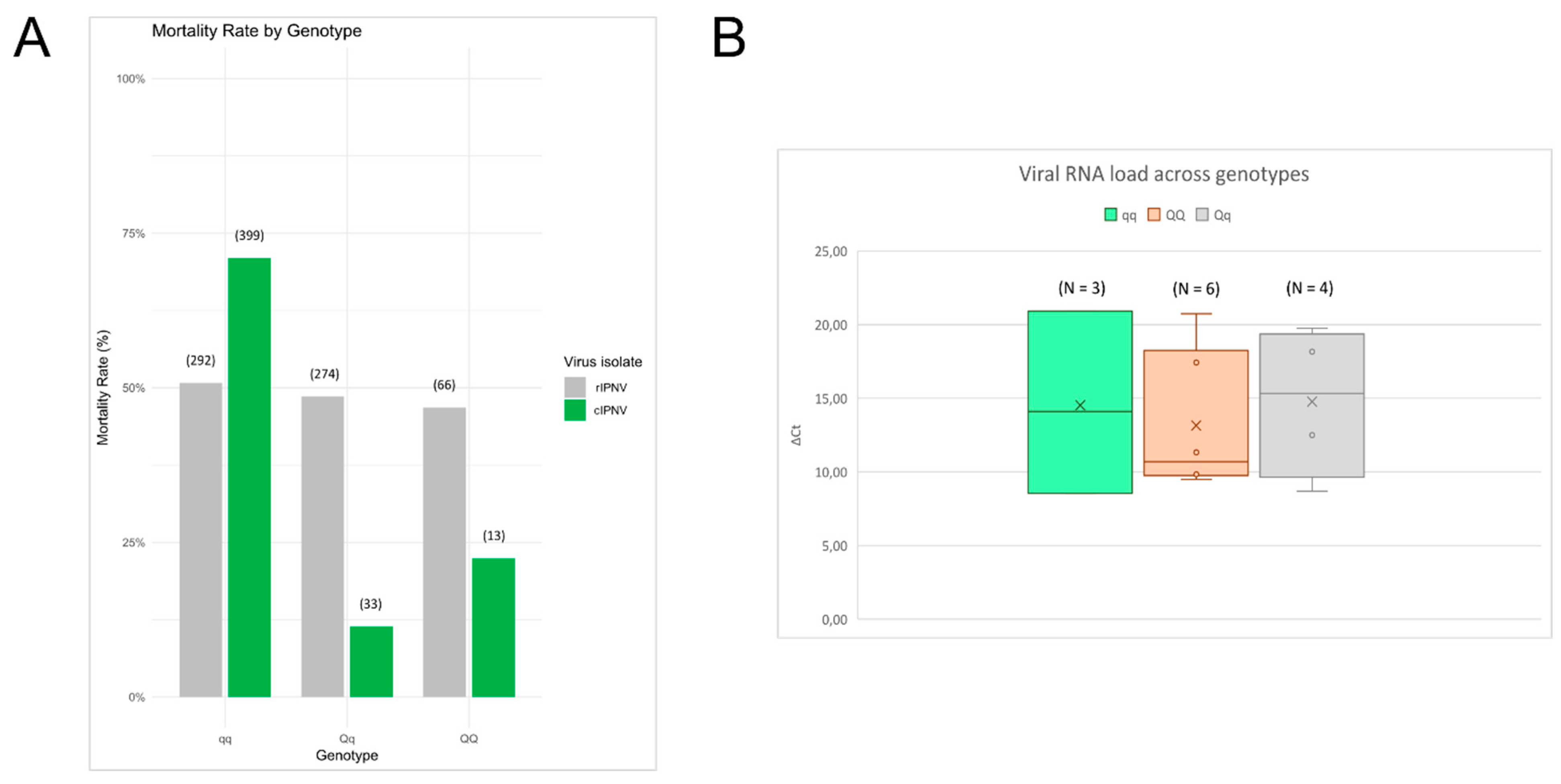
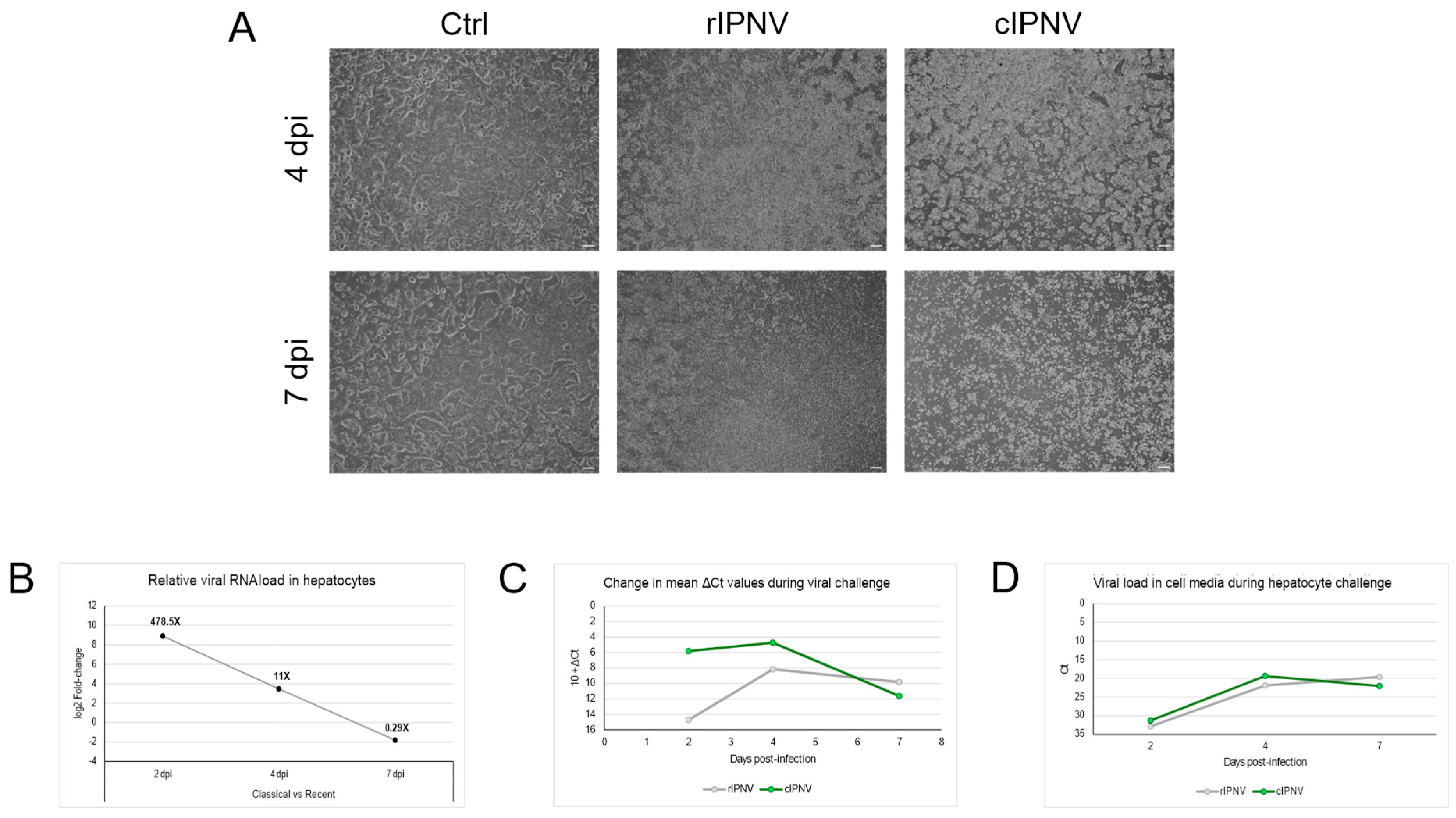
3.3. The isolates Display Differences in Viral Dynamics Based on In Vivo and In Vitro Challenge Tests
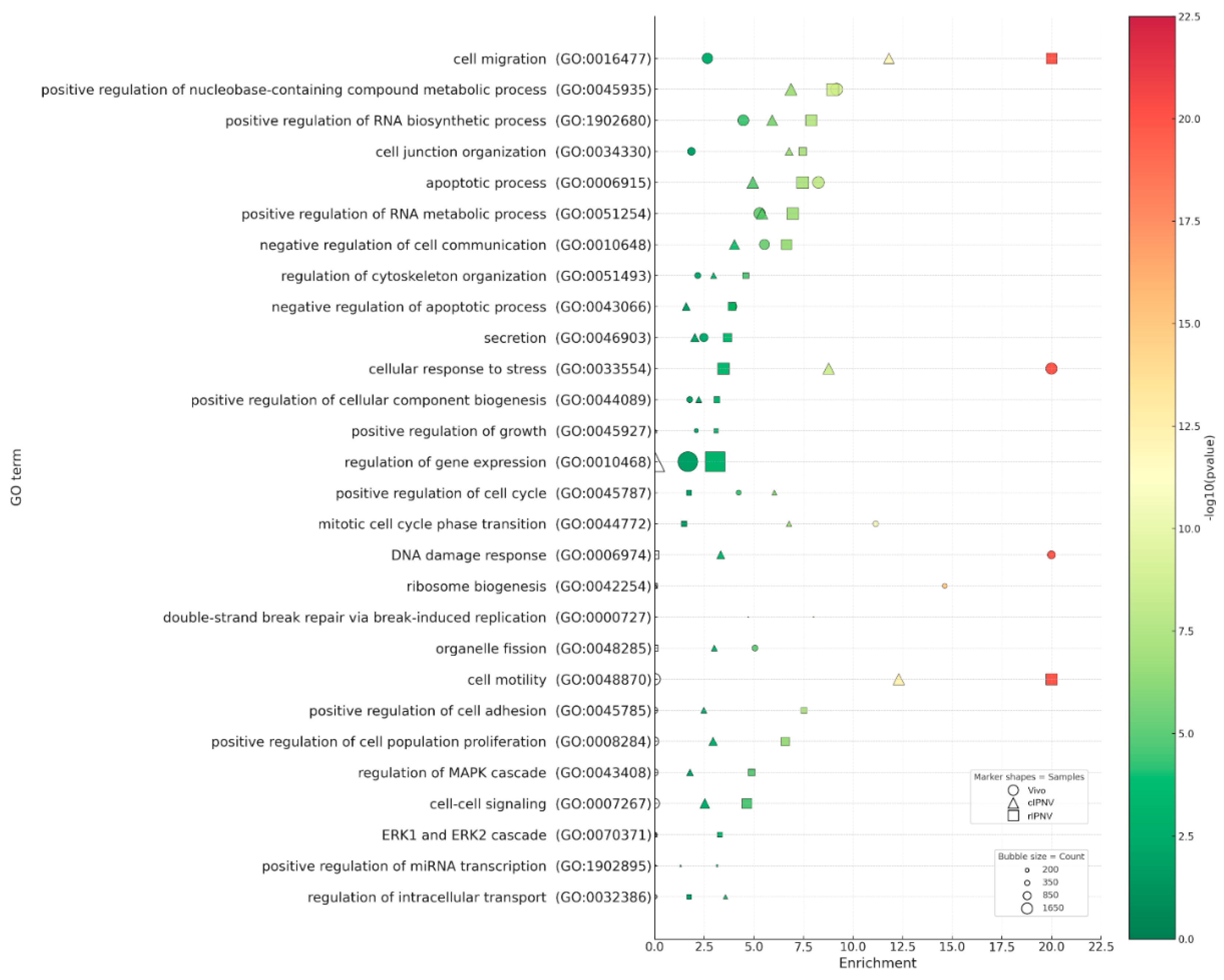
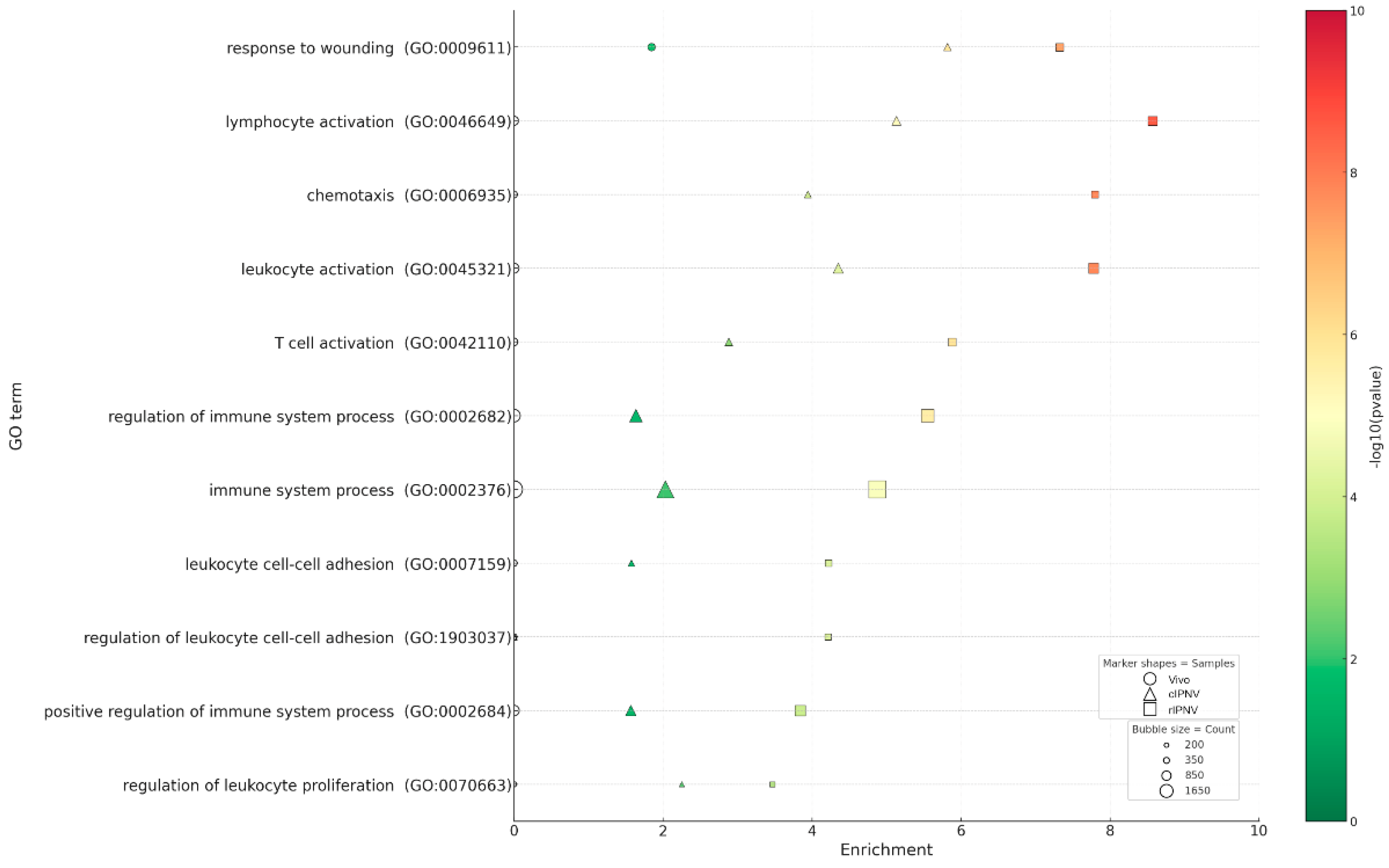
3.4. Enrichment Analysis of Host Responses to IPNV
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IPNV | Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus |
| IPN | Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis |
| QTL | Quantitative Trait Locus |
| cIPNV | Classical Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus |
| rIPNV | Recent Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| pVP2 | Premature VP2 |
| RNP | Ribonucleoprotein |
| IFN | Interferon |
| IRES | Internal Ribosomal Entry Site |
| UTR | Untranslated Region |
| VPg | Genomic-bound VP1 |
| IBDV | Infectious Bursal Disease Virus |
| IBD | Infectious Bursal Disease |
| vvIBDV | Very Virulent Infectious Bursal Disease Virus |
| nVarIBDV | Novel Variant Infectious Bursal Disease Virus |
| WOAH | World Organization for Animal Health |
| Sp | Spjarup |
| HBSS | Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution |
| L-15 | Leibovitz’s L-15 Medium, GlutaMAX™ Supplement |
| FBS | Foetal Bovine Serum |
| MOI | Multiplicity of Infection |
| CPE | Cytopathic Effect |
| TCID50 | Tissue Culture Infectious Dose 50 |
| dpi | Days post-infection |
| EGF | Epidermal Growth Factor |
| HGF | Hepatocyte Growth Factor |
| FC | Fold-change |
| PE | Paired-end |
| DEG | Differential Expressed Gene |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| CPM | Counts per Million |
References
- Roberts, R.J.; Pearson, M.D. Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis in Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salar L. Journal of Fish Diseases 2005, 28, 383–390. [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K. Fish Viruses and Fish Viral Diseases; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, 1988; ISBN 978-0-8014-2101-4.
- Roberts, R.J. Fish Pathology; 4th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-0-470-67119-5.
- Munro, E.S.; Midtlyng, P.J. Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis and Associated Aquatic Birnaviruses. Fish diseases and disorders. Volume 3: viral, bacterial and fungal infections 2011, 1–65. [CrossRef]
- Frasca, S.; Wolf, J.C.; Kinsel, M.J.; Camus, A.C.; Lombardini, E.D. Chapter 39 - Osteichthyes. In Pathology of Wildlife and Zoo Animals; Terio, K.A., McAloose, D., Leger, J.St., Eds.; Academic Press, 2018; pp. 953–1001 ISBN 978-0-12-805306-5.
- Bruno, D.W.; Poppe, T.T.; Noguera, Patricia A. A Colour Atlas of Salmonid Diseases; Academic Press: London, 1996; ISBN 978-0-12-137350-7.
- Munang’andu, H.M.; Fredriksen, B.N.; Mutoloki, S.; Dalmo, R.A.; Evensen, Ø. Antigen Dose and Humoral Immune Response Correspond with Protection for Inactivated Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus Vaccines in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar L). Vet Res 2013, 44, 7. [CrossRef]
- Munang’andu, H.M.; Fredriksen, B.N.; Mutoloki, S.; Brudeseth, B.; Kuo, T.-Y.; Marjara, I.S.; Dalmo, R.A.; Evensen, Ø. Comparison of Vaccine Efficacy for Different Antigen Delivery Systems for Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus Vaccines in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar L.) in a Cohabitation Challenge Model. Vaccine 2012, 30, 4007–4016. [CrossRef]
- Smail, D.A.; Munro, E.S. Isolation and Quantification of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus from Ovarian and Seminal Fluids of Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salar L. Journal of Fish Diseases 2008, 31, 49–58. [CrossRef]
- Dobos, P.; Hill, B.J.; Hallett, R.; Kells, D.T.; Becht, H.; Teninges, D. Biophysical and Biochemical Characterization of Five Animal Viruses with Bisegmented Double-Stranded RNA Genomes. Journal of Virology 1979, 32, 593–605. [CrossRef]
- Galloux, M.; Chevalier, C.; Henry, C.; Huet, J.-C.; Costa, B.D.; Delmas, B. Peptides Resulting from the pVP2 C-Terminal Processing Are Present in Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus Particles. Journal of General Virology 2004, 85, 2231–2236. [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, T.; Skjesol, A.; Jørgensen, J.B. VP3, a Structural Protein of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus, Interacts with RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase VP1 and with Double-Stranded RNA. Journal of Virology 2007, 81, 6652–6663. [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.-R.; Gong, H.-Y.; Wu, J.-L. IPNV VP5, a Novel Anti-Apoptosis Gene of the Bcl-2 Family, Regulates Mcl-1 and Viral Protein Expression. Virology 2002, 295, 217–229. [CrossRef]
- Santi, N.; Sandtrø, A.; Sindre, H.; Song, H.; Hong, J.-R.; Thu, B.; Wu, J.-L.; Vakharia, V.N.; Evensen, Ø. Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus Induces Apoptosis in Vitro and in Vivo Independent of VP5 Expression. Virology 2005, 342, 13–25. [CrossRef]
- Skjesol, A.; Aamo, T.; Hegseth, M.N.; Robertsen, B.; Jørgensen, J.B. The Interplay between Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV) and the IFN System: IFN Signaling Is Inhibited by IPNV Infection. Virus Res 2009, 143, 53–60. [CrossRef]
- Dobos, P. The Molecular Biology of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV). Annual Review of Fish Diseases 1995, 5, 25–54.
- Rivas-Aravena, A.; Muñoz, P.; Jorquera, P.; Diaz, A.; Reinoso, C.; González-Catrilelbún, S.; Sandino, A.M. Study of RNA-A Initiation Translation of The Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus. Virus Research 2017, 240, 121–129. [CrossRef]
- Delmas, B.; Attoui, H.; Ghosh, S.; Malik, Y.S.; Mundt, E.; Vakharia, V.N.; Ictv Report Consortium, null ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Birnaviridae. J Gen Virol 2019, 100, 5–6. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Niu, X.; Huang, M.; Gao, L.; Li, K.; Cui, H.; Liu, C.; et al. A Single Mutation of VP2 Is Responsible for the Lethality and Antigenicity Differences between Novel Variant and Very Virulent IBDV Strains. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases 2023, 2023, 6684304. [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Pathak, D.C.; Ramamurthy, N.; Maity, H.K.; Chellappa, M.M. Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in Chickens: Prevalence, Impact, and Management Strategies. Vet Med (Auckl) 2019, 10, 85–97. [CrossRef]
- Abdul, R.; Murgia, M.V.; Rodriguez-Palacios, A.; Lee, C.-W.; Saif, Y.M. Persistence and Tissue Distribution of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus in Experimentally Infected SPF and Commercial Broiler Chickens. avdi 2013, 57, 759–766. [CrossRef]
- Julin, K.; Johansen, L.-H.; Sommer, A.-I.; Jørgensen, J.B. Persistent Infections with Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV) of Different Virulence in Atlantic Salmon, Salmo Salar L. Journal of Fish Diseases 2015, 38, 1005–1019. [CrossRef]
- OIE Aquatic Animal Health Standards Commission Report of the Meeting of the OIE Aquatic Animal Health Standards Commission; World Organization for Animal Health: Paris, 2005; p. 289;.
- Sommerset, I.; Wiik-Nielsen, J.; Moldal, T.; Oliveira, V.H.S.; Svendsen, J.C.; Haukaas, A.; Brun, E. Norwegian Fish Health Report 2023; Norwegian Veterinary Institute Report; Norwegian Veterinary Institute, 2024;
- Houston, R.D.; Haley, C.S.; Hamilton, A.; Guy, D.R.; Tinch, A.E.; Taggart, J.B.; McAndrew, B.J.; Bishop, S.C. Major Quantitative Trait Loci Affect Resistance to Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar). Genetics 2008, 178, 1109–1115. [CrossRef]
- Moen, T.; Baranski, M.; Sonesson, A.K.; Kjøglum, S. Confirmation and Fine-Mapping of a Major QTL for Resistance to Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar): Population-Level Associations between Markers and Trait. BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 368. [CrossRef]
- Hillestad, B.; Johannessen, S.; Melingen, G.O.; Moghadam, H.K. Identification of a New Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV) Variant in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar L.) That Can Cause High Mortality Even in Genetically Resistant Fish. Frontiers in Genetics 2021, 12, 2172. [CrossRef]
- Benkaroun, J.; Muir, K.F.; Allshire, R.; Tamer, C.; Weidmann, M. Isolation of a New Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV) Variant from a Fish Farm in Scotland. Viruses 2021, 13, 385. [CrossRef]
- Godoy, M.; Kibenge, M.J.T.; Montes de Oca, M.; Pontigo, J.P.; Coca, Y.; Caro, D.; Kusch, K.; Suarez, R.; Burbulis, I.; Kibenge, F.S.B. Isolation of a New Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV) Variant from Genetically Resistant Farmed Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar) during 2021–2022. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1368. [CrossRef]
- Moldal, T.; Wiik-Nielsen, J.; Oliveira, V.H.S.; Svendsen, J.C.; Sommerset, I. Norwegian Fish Health Report 2024; Norwegian Veterinary Institute, 2025;
- 2013; 31. Fish Health Report 2013; Norwegian Veterinary Institute, 2014;
- Johansen, R.; Kongtorp, R.T.; Bornø, G.; Ringkjøb Skjelstad, H.; Olsen, A.B.; Flesjå, K.; Colquhoun, D.; Ørpetveit, I.; Hansen, H.; Garseth, Å.H.; et al. The Health Situation in Farmed Salmonids 2008; Norwegian Veterinary Institute, 2009;
- Gjessing, M.C.; Aamelfot, M.; Batts, W.N.; Benestad, S.L.; Dale, O.B.; Thoen, E.; Weli, S.C.; Winton, J.R. Development and Characterization of Two Cell Lines from Gills of Atlantic Salmon. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0191792. [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A Simple Method Of Estimating Fifty Per Cent Endpoints. American Journal of Epidemiology 1938, 27, 493–497. [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent Updates to the Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation Tool. Nucleic Acids Res 2024, 52, W78–W82. [CrossRef]
- Datsomor, A.K.; Wilberg, R.; Torgersen, J.S.; Sandve, S.R.; Harvey, T.N. Efficient Transfection of Atlantic Salmon Primary Hepatocyte Cells for Functional Assays and Gene Editing. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genetics 2023, jkad039. [CrossRef]
- Mölder, F.; Jablonski, K.P.; Letcher, B.; Hall, M.B.; Tomkins-Tinch, C.H.; Sochat, V.; Forster, J.; Lee, S.; Twardziok, S.O.; Kanitz, A.; et al. Sustainable Data Analysis with Snakemake 2021.
- Simon, A.; others FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Version 0.10 2010, 1.
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet.journal 2011, 17, 10–12. [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [CrossRef]
- Law, C.W.; Chen, Y.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. Voom: Precision Weights Unlock Linear Model Analysis Tools for RNA-Seq Read Counts. Genome Biology 2014, 15, R29. [CrossRef]
- Kolberg, L.; Raudvere, U.; Kuzmin, I.; Adler, P.; Vilo, J.; Peterson, H. G:Profiler—Interoperable Web Service for Functional Enrichment Analysis and Gene Identifier Mapping (2023 Update). Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, W207–W212. [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [CrossRef]
- Merico, D.; Isserlin, R.; Stueker, O.; Emili, A.; Bader, G.D. Enrichment Map: A Network-Based Method for Gene-Set Enrichment Visualization and Interpretation. PLOS ONE 2010, 5, e13984. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Rates of Conservative and Radical Nonsynonymous Nucleotide Substitutions in Mammalian Nuclear Genes. J Mol Evol 2000, 50, 56–68. [CrossRef]
- Santi, N.; Vakharia, V.N.; Evensen, Ø. Identification of Putative Motifs Involved in the Virulence of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus. Virology 2004, 322, 31–40. [CrossRef]
- Shivappa, R.B.; Song, H.; Yao, K.; Aas-Eng, A.; Evensen, Ø.; Vakharia, V.N. Molecular Characterization of Sp Serotype Strains of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus Exhibiting Differences in Virulence. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms 2004, 61, 23–32. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Saint-Jean, S.; de las Heras, A.I.; Pérez Prieto, S.I. The Persistence of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus and Its Influence on the Early Immune Response. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology 2010, 136, 81–91. [CrossRef]
- Mutoloki, S.; Jøssund, T.B.; Ritchie, G.; Munang’andu, H.M.; Evensen, Ø. Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus Causing Clinical and Subclinical Infections in Atlantic Salmon Have Different Genetic Fingerprints. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [CrossRef]
- Coulibaly, F.; Chevalier, C.; Delmas, B.; Rey, F.A. Crystal Structure of an Aquabirnavirus Particle: Insights into Antigenic Diversity and Virulence Determinism. Journal of Virology 2010, 84, 1792–1799. [CrossRef]
- Klaitong, P.; Smith, D.R. Roles of Non-Structural Protein 4A in Flavivirus Infection. Viruses 2021, 13, 2077. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wei, F.; Jiang, Z.; Song, J.; Li, C.; Liu, J. Influenza Virus NS1 Interacts with 14-3-3ε to Antagonize the Production of RIG-I-Mediated Type I Interferons. Virology 2022, 574, 47–56. [CrossRef]
- Smiley, J.R. Herpes Simplex Virus Virion Host Shutoff Protein: Immune Evasion Mediated by a Viral RNase? Journal of Virology 2004, 78, 1063–1068. [CrossRef]
- Jagger, B.W.; Wise, H.M.; Kash, J.C.; Walters, K.-A.; Wills, N.M.; Xiao, Y.-L.; Dunfee, R.L.; Schwartzman, L.M.; Ozinsky, A.; Bell, G.L.; et al. An Overlapping Protein-Coding Region in Influenza A Virus Segment 3 Modulates the Host Response. Science 2012, 337, 199–204. [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, E.; Maraver, A.; Espinosa, I.; Fernández-Arias, A.; Rodriguez, J.F. VP5, the Nonstructural Polypeptide of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus, Accumulates within the Host Plasma Membrane and Induces Cell Lysis. Virology 2000, 277, 345–357. [CrossRef]
- Friedel, C.C.; Whisnant, A.W.; Djakovic, L.; Rutkowski, A.J.; Friedl, M.-S.; Kluge, M.; Williamson, J.C.; Sai, S.; Vidal, R.O.; Sauer, S.; et al. Dissecting Herpes Simplex Virus 1-Induced Host Shutoff at the RNA Level. Journal of Virology 2021, 95, 10.1128/jvi.01399-20. [CrossRef]
- Bercovich-Kinori, A.; Tai, J.; Gelbart, I.A.; Shitrit, A.; Ben-Moshe, S.; Drori, Y.; Itzkovitz, S.; Mandelboim, M.; Stern-Ginossar, N. A Systematic View on Influenza Induced Host Shutoff. eLife 2016, 5, e18311. [CrossRef]
- Gervais, O.; Peñaloza, C.; Gratacap, R.; Papadopoulou, A.; Beltrán, M.; Henderson, N.C.; Houston, R.D.; Hassan, M.A.; Robledo, D. Understanding Host Response to Infectious Salmon Anaemia Virus in an Atlantic Salmon Cell Line Using Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. BMC Genomics 2023, 24, 161. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Luo, W.; Huang, Z.; Guo, M.; He, X.; Fan, Z.; Wang, Q.; Qin, Q.; Yang, M.; Lee, X. Genome-Wide Analysis of Differentially Expressed mRNAs and lncRNAs in Koi Carp Infected with Koi Herpesvirus. Viruses 2022, 14, 2555. [CrossRef]
- Woldemariam, N.T.; Agafonov, O.; Sindre, H.; Høyheim, B.; Houston, R.D.; Robledo, D.; Bron, J.E.; Andreassen, R. miRNAs Predicted to Regulate Host Anti-Viral Gene Pathways in IPNV-Challenged Atlantic Salmon Fry Are Affected by Viral Load, and Associated With the Major IPN Resistance QTL Genotypes in Late Infection. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11. [CrossRef]
- Aedo, JorgeE.; Aravena-Canales, D.; Dettleff, P.; Fuentes-Valenzuela, M.; Zuloaga, R.; Rivas-Aravena, A.; Molina, A.; Valdés, J.A. RNA-Seq Analysis Reveals the Dynamic Regulation of Proteasomal and Autophagic Degradation Systems of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss) Skeletal Muscle Challenged with Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus (IPNV). Aquaculture 2022, 552, 738000. [CrossRef]
- Tapia, D.; Kuznar, J.; Farlora, R.; Yáñez, J.M. Differential Transcriptomic Response of Rainbow Trout to Infection with Two Strains of IPNV. Viruses 2022, 14, 21. [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, K.; McBeath, A.J.A.; Collet, B.; Snow, M.; Ellis, A.E. Expression of Mx mRNA Following Infection with IPNV Is Greater in IPN-Susceptible Atlantic Salmon Post-Smolts than in IPN-Resistant Atlantic Salmon Parr. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2007, 22, 151–156. [CrossRef]
- McBeath, A.J.A.; Snow, M.; Secombes, C.J.; Ellis, A.E.; Collet, B. Expression Kinetics of Interferon and Interferon-Induced Genes in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar) Following Infection with Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus and Infectious Salmon Anaemia Virus. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2007, 22, 230–241. [CrossRef]
- Robledo, D.; Taggart, J.B.; Ireland, J.H.; McAndrew, B.J.; Starkey, W.G.; Haley, C.S.; Hamilton, A.; Guy, D.R.; Mota-Velasco, J.C.; Gheyas, A.A.; et al. Gene Expression Comparison of Resistant and Susceptible Atlantic Salmon Fry Challenged with Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus Reveals a Marked Contrast in Immune Response. BMC Genomics 2016, 17, 1–16. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.S.; Ruiz Daniels, R.; Dobie, R.; Naseer, S.; Clark, T.C.; Henderson, N.C.; Boudinot, P.; Martin, S.A.M.; Macqueen, D.J. Single Cell Transcriptomics of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar L.) Liver Reveals Cellular Heterogeneity and Immunological Responses to Challenge by Aeromonas Salmonicida. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13. [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Cerpa, S.; Reyes-López, F.; Toro-Ascuy, D.; Montero, R.; Maisey, K.; Acuña-Castillo, C.; Sunyer, J.O.; Parra, D.; Sandino, A.M.; Imarai, M. Induction of Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Expression by IPNV in Persistent Infection. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 2014, 41, 172–182. [CrossRef]
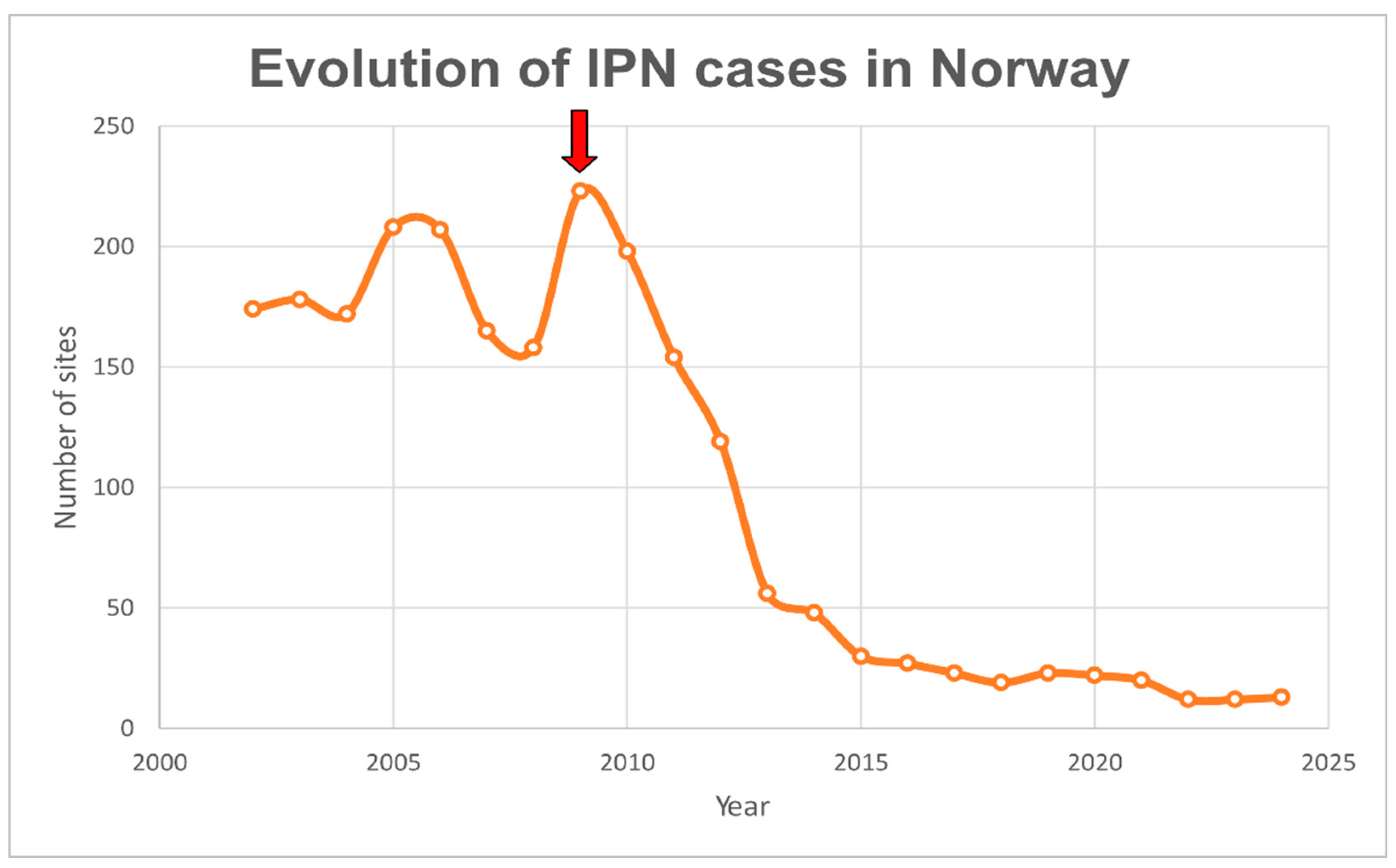
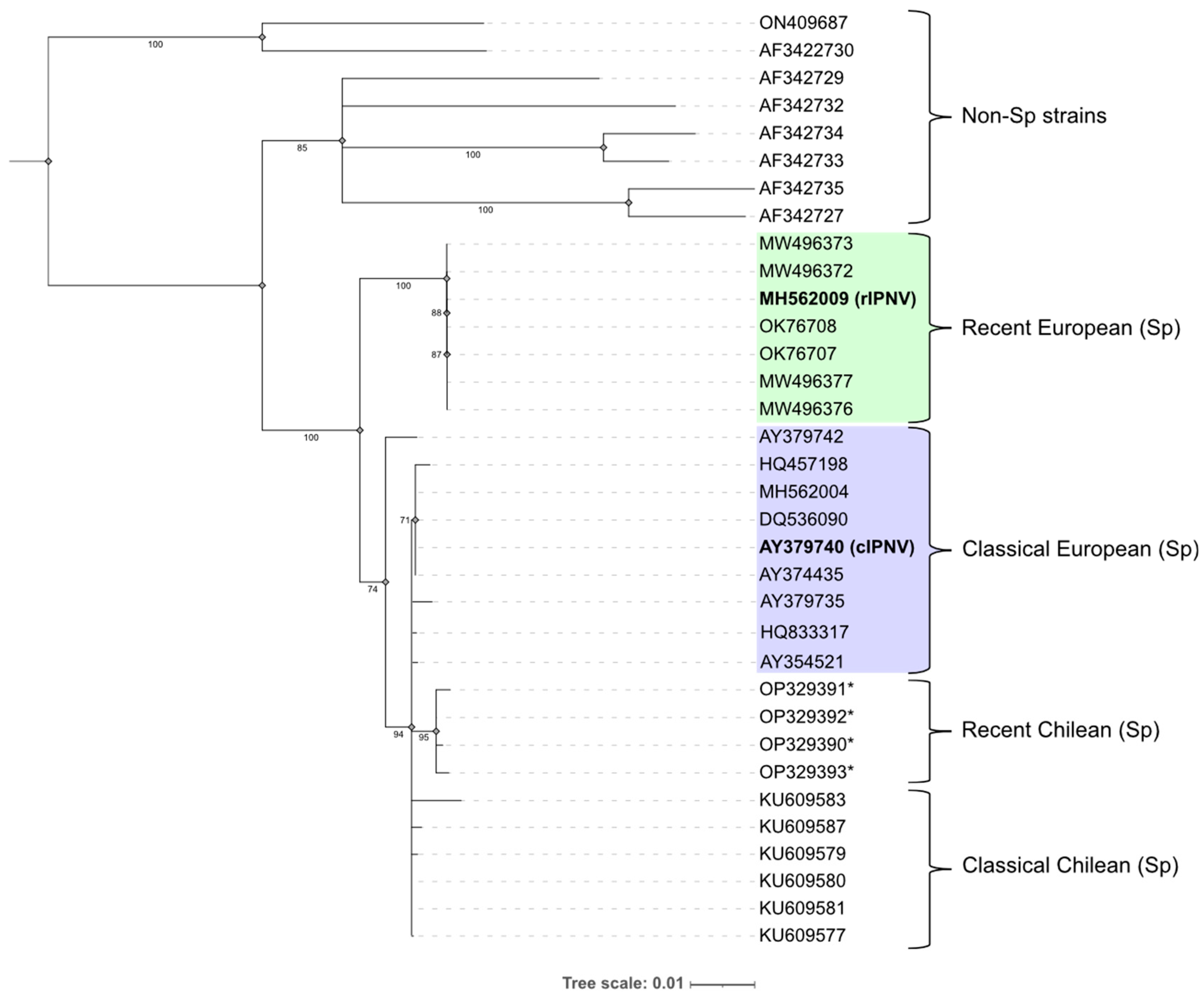
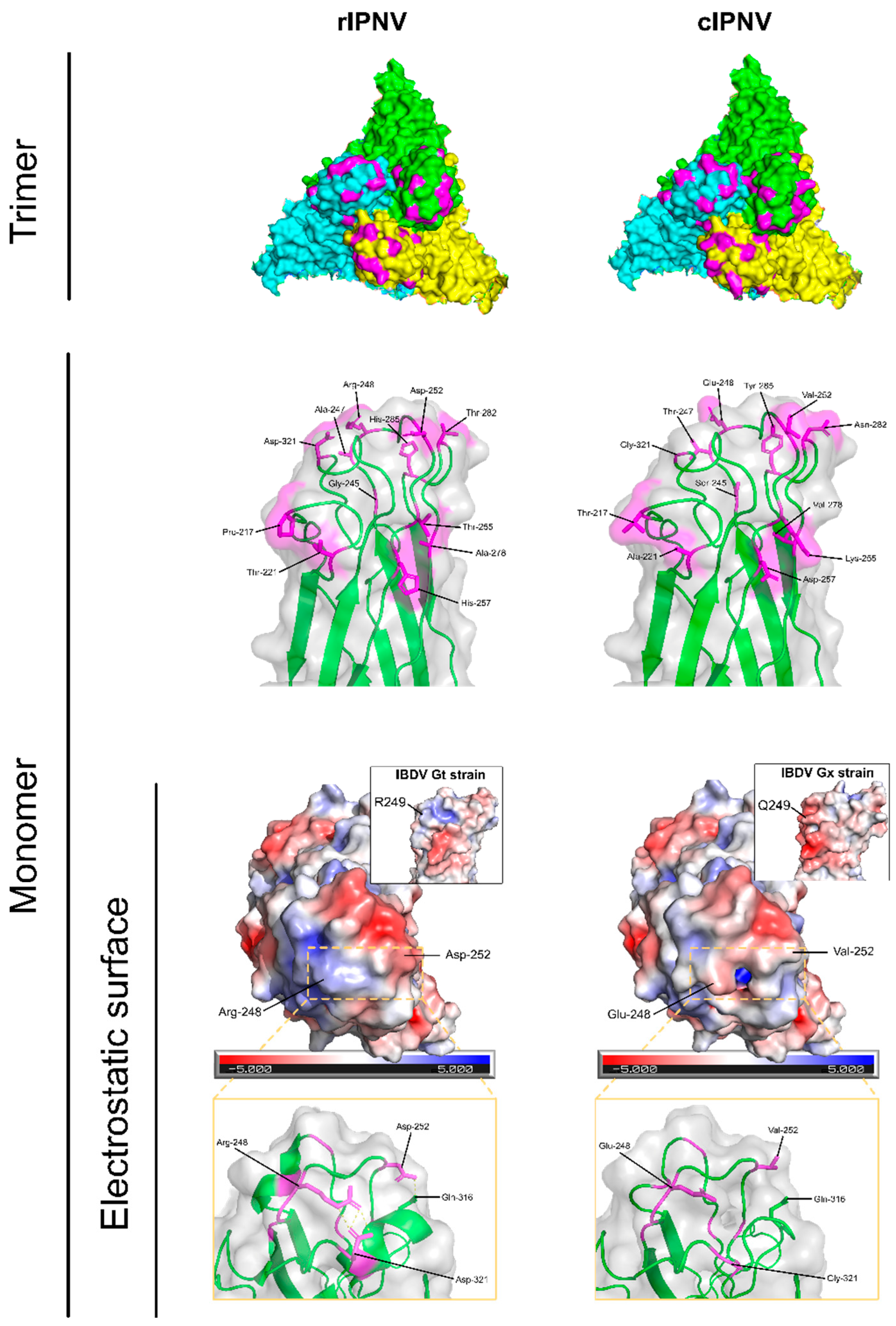
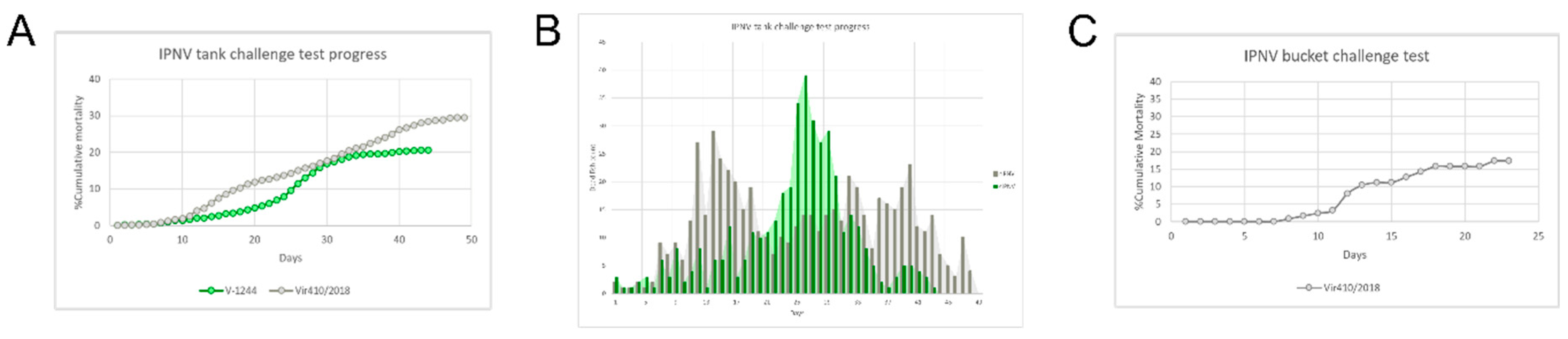
| Study | N samples | Sequencing provider |
| Bucket challenge (in vivo) | 41 | NovoGene |
| In vitro challenge 1 | 14 | NovoGene |
| In vitro challenge 2 | 34 | BMKGene |
| Position | cIPNV | rIPNV | |
| 217 | T | P |  |
| 221 | A | T | |
| 245 | S | G | |
| 247 | T | A | |
| 248 | E | R | |
| 252 | V | D | |
| 255 | K | T | |
| 257 | D | H | |
| 278 | V | A | |
| 282 | N | T | |
| 285 | Y | H | |
| 321 | G | D |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





