Submitted:
15 October 2023
Posted:
18 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
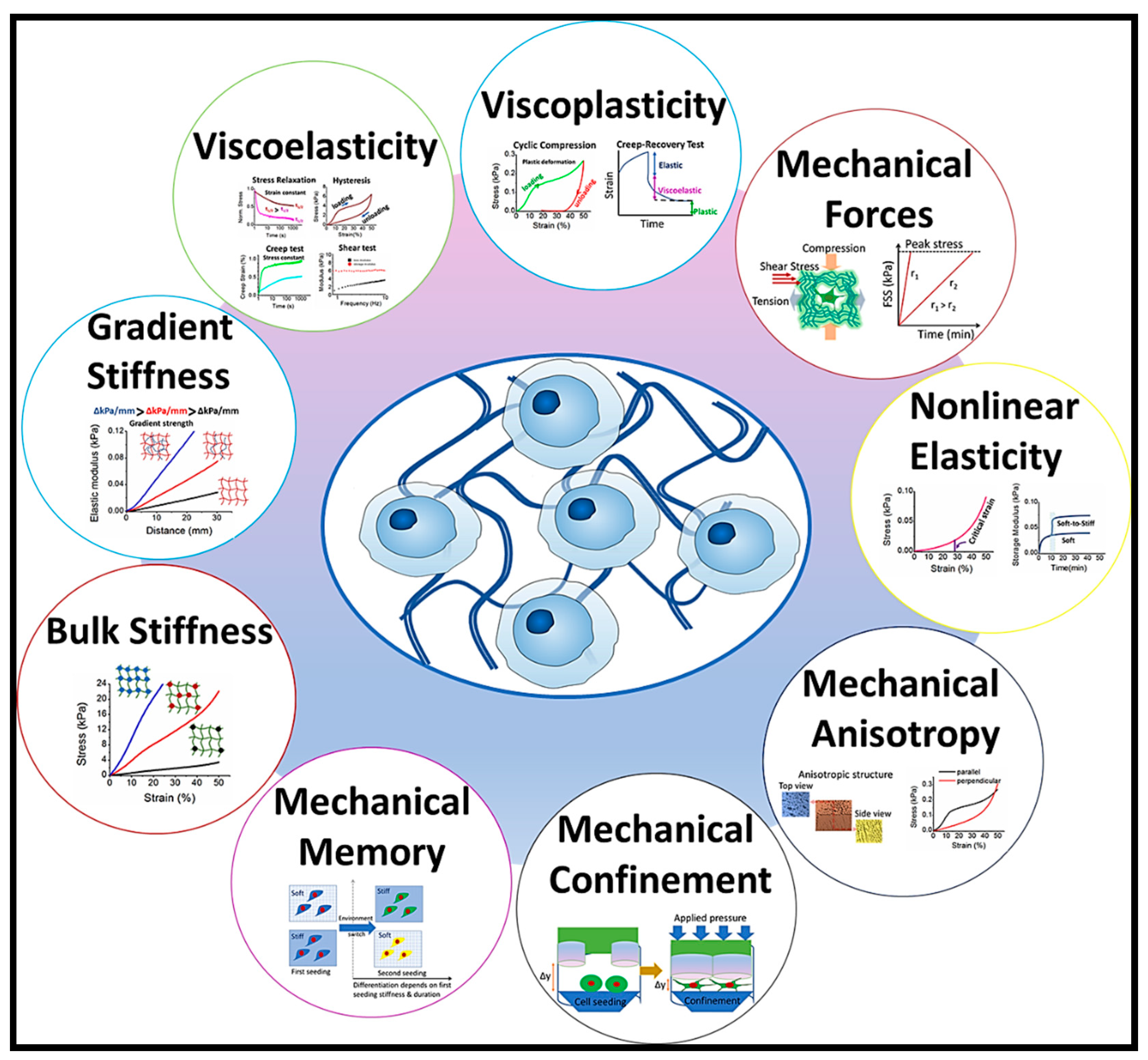
1. Introduction
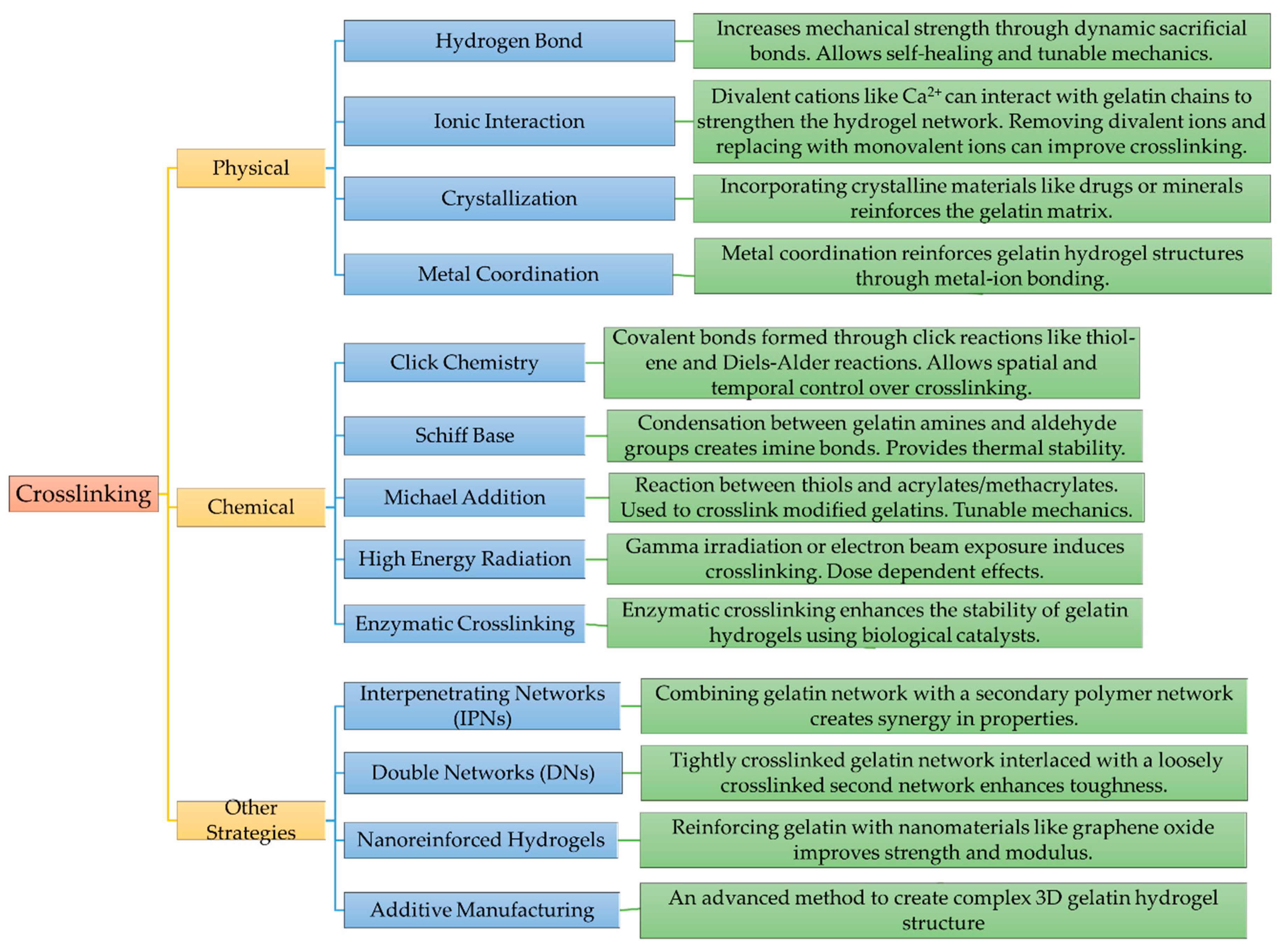
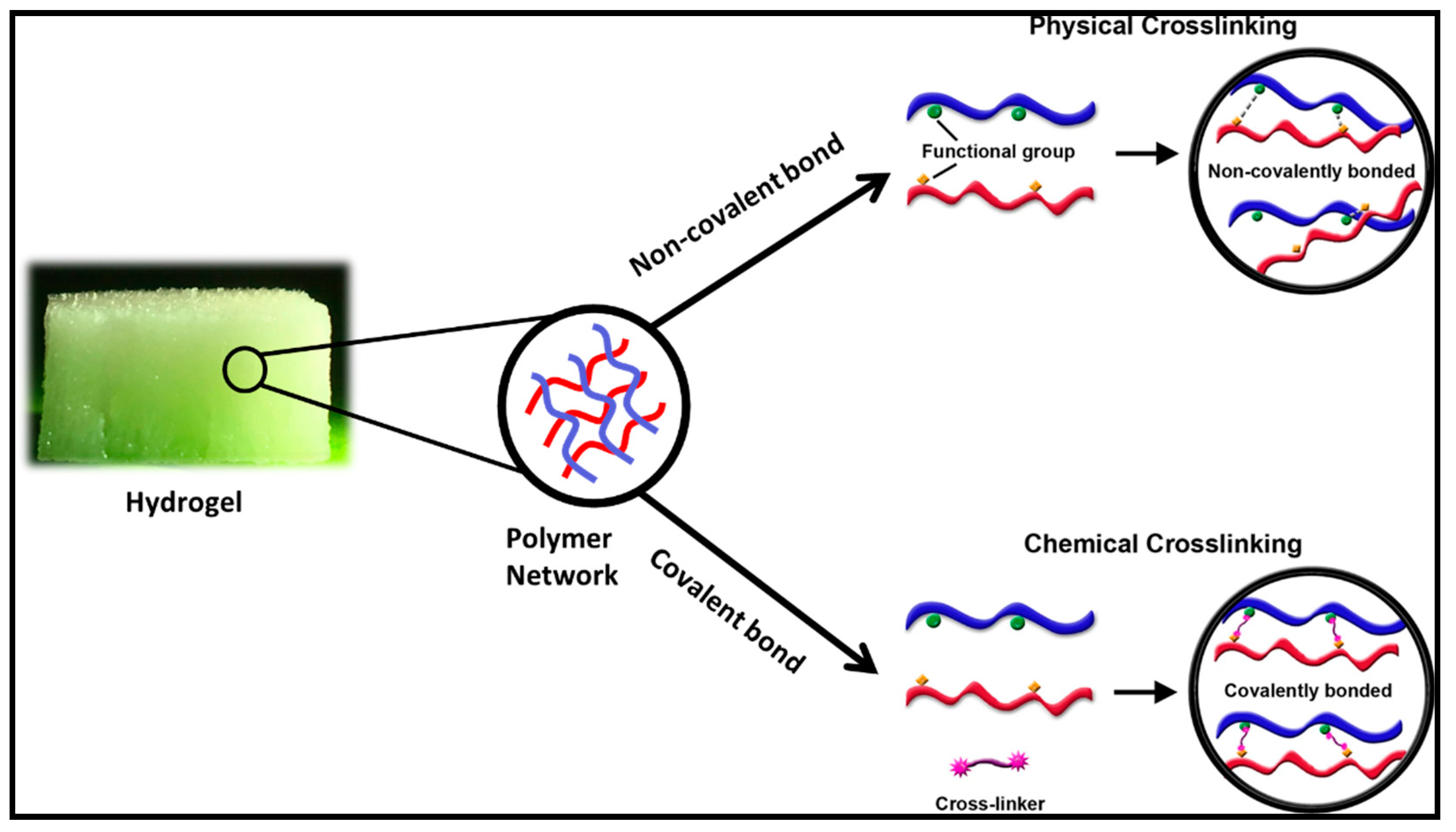
2. Strategies to improve mechanical properties of gelatin-based hydrogel
2.1. Physical crosslinking
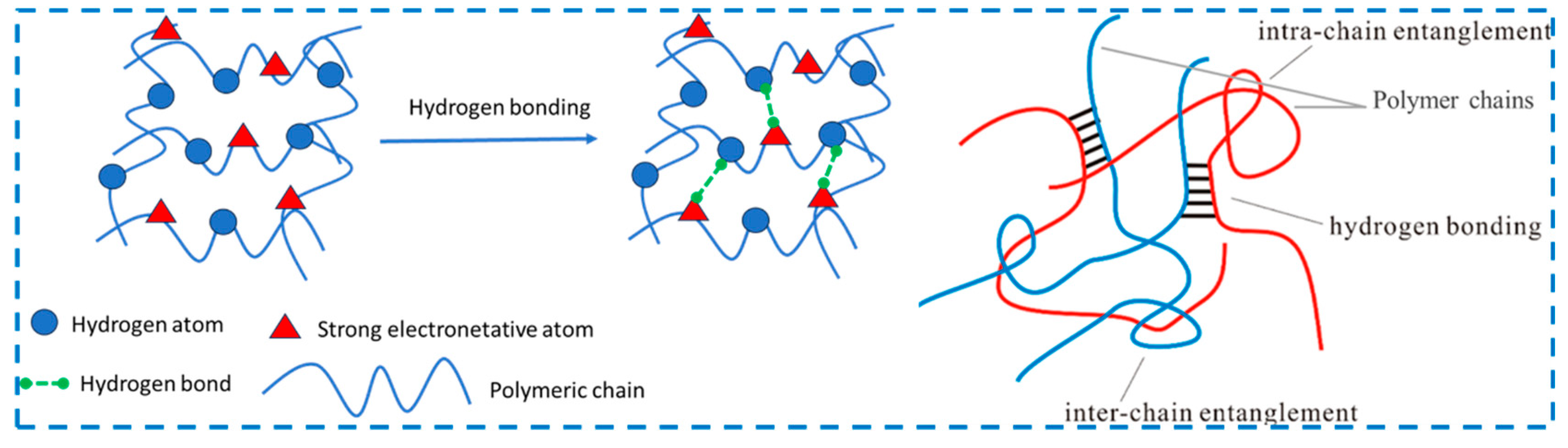
2.1.1. By Hydrogen Bond
2.1.2. By Ionic/Electrostatic Interactions
2.1.3. By Crystallization
2.1.4. By Metal Coordination
2.1.5. By Stereo Complex Formation
2.1.6. Supramolecular Hydrogel
2.2. Chemical Crosslinking
- Necessity of crosslinking in gelatin-based scaffolds
- Biocompatibility of crosslinkers
2.2.1. Crosslinking by Click Chemistry
2.2.2. Crosslinked by Schiff Base Reaction
2.2.3. Michael Addition Crosslinking
2.2.4. Crosslinking by Radiation (Photocrosslinking)
2.2.5. Enzymatic Crosslinking
2.3. Various Hybrid Crosslinked Hydrogels
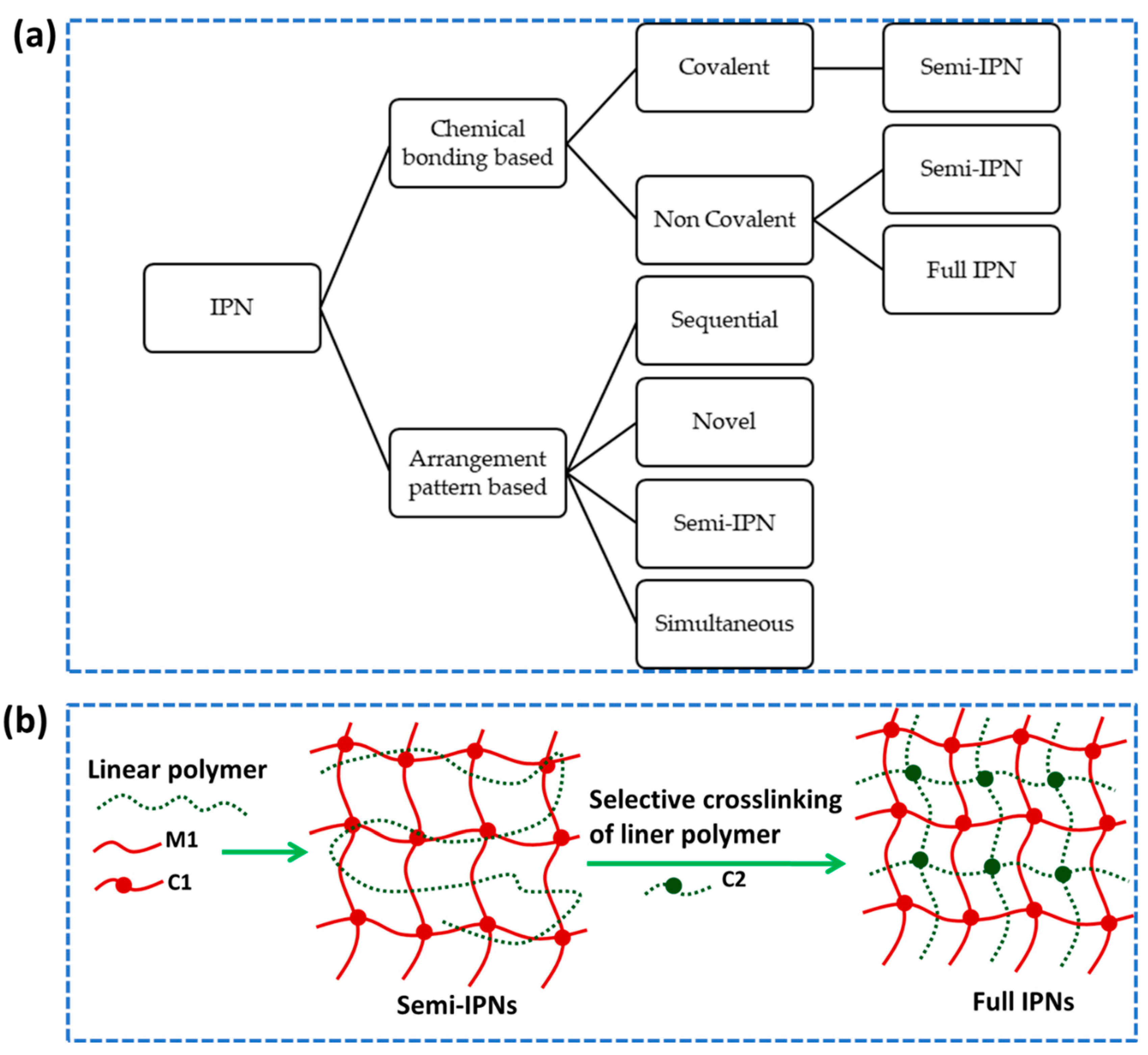
2.3.1. Interpenetrating polymer network (IPN)
- Mechanism of IPN
- Preparation of IPNs
2.3.2. Double Network Hydrogels
- Toughening Mechanism
- Preparation Methods of DN Hydrogels
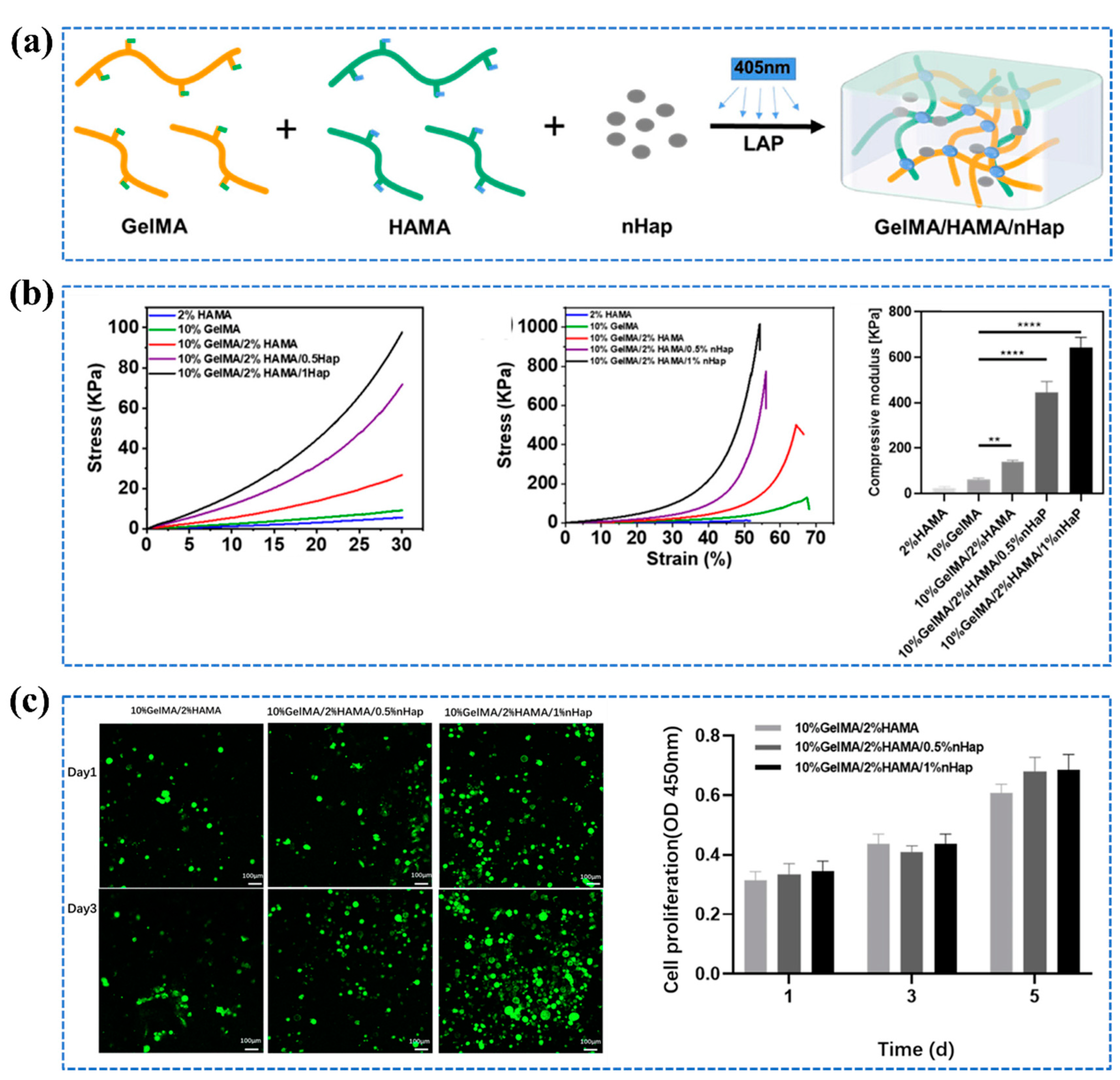
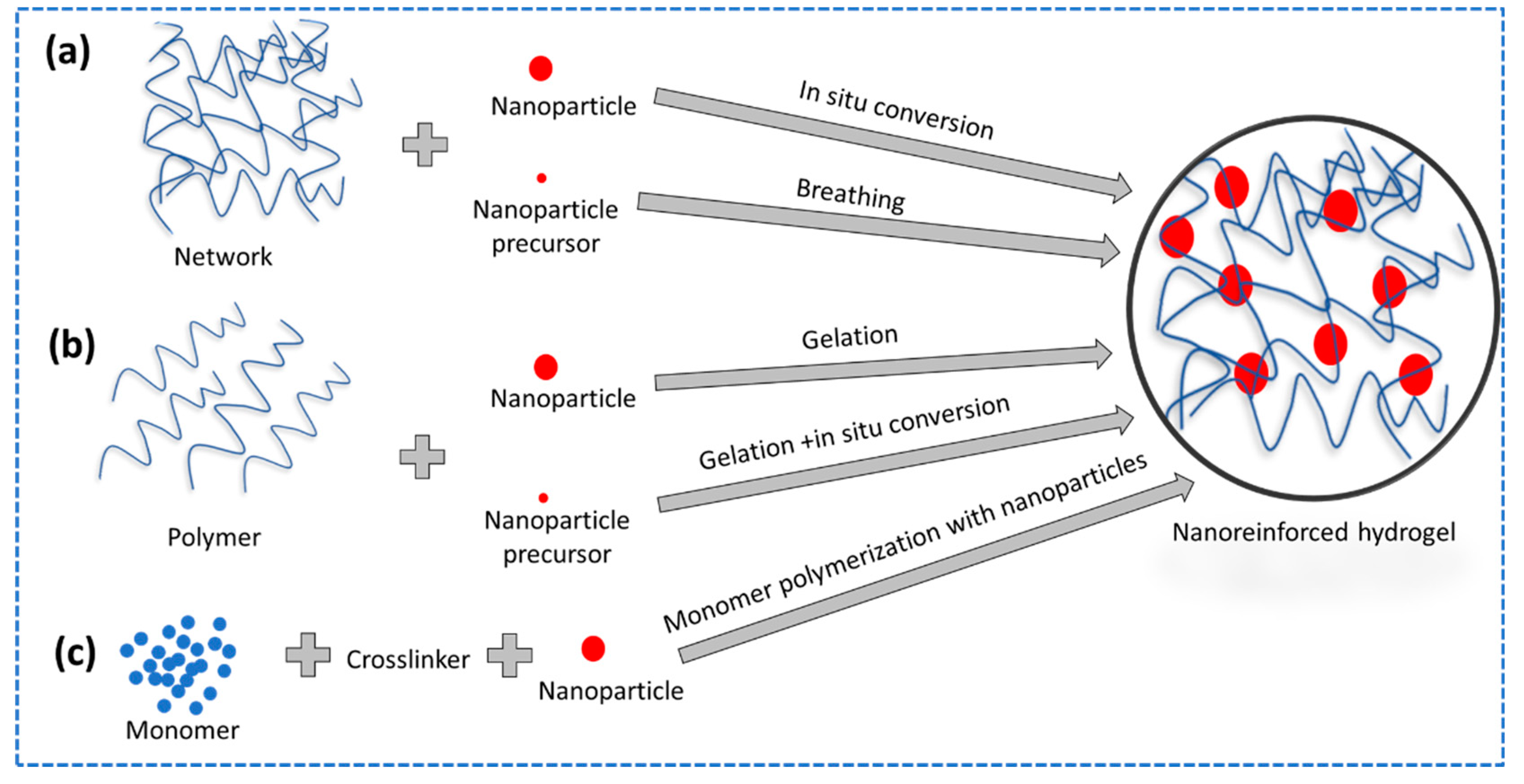
2.3.3. Nanoreinforced Hydrogels
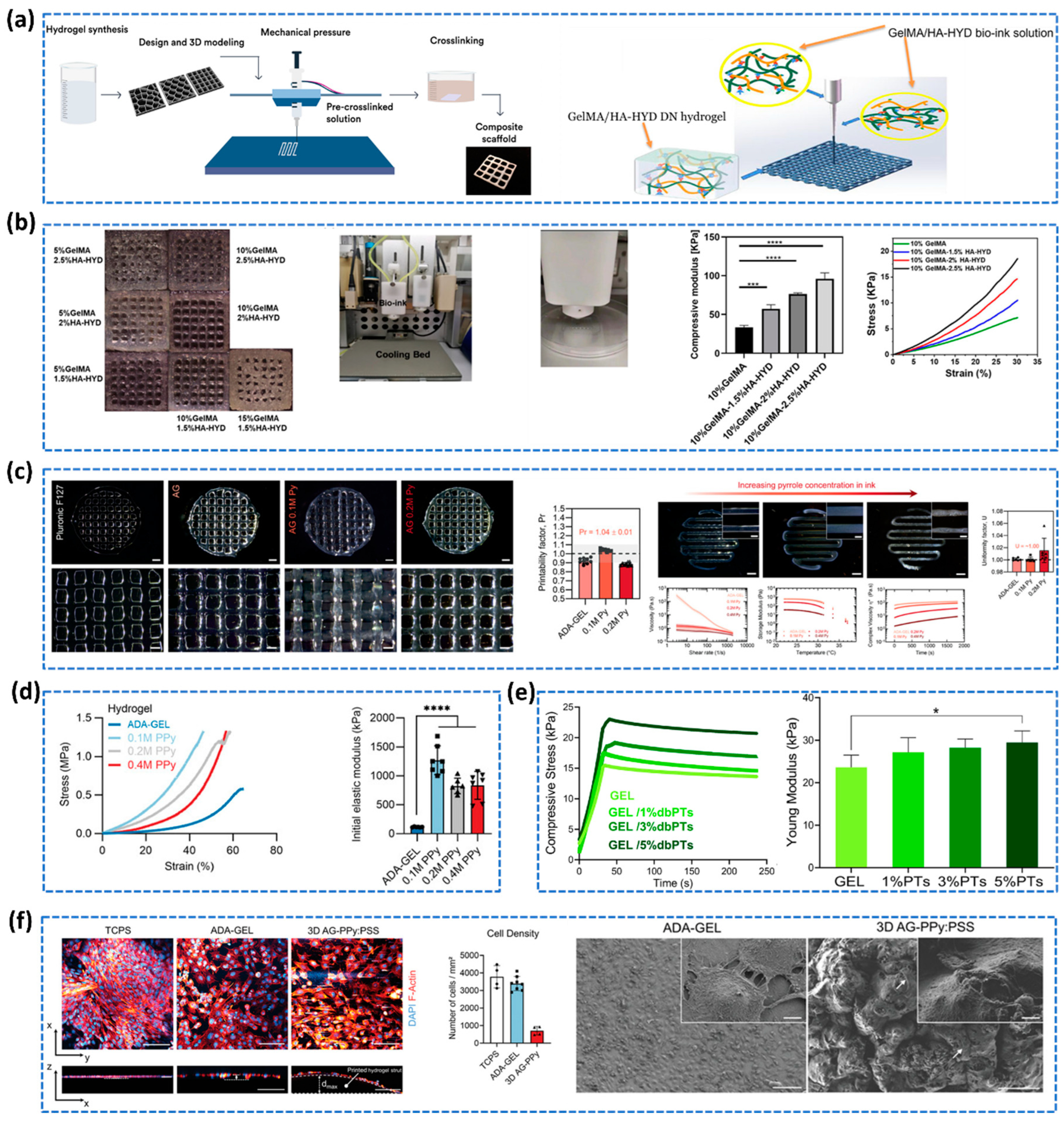
2.3.4. Additive Manufacturing of Hydrogels
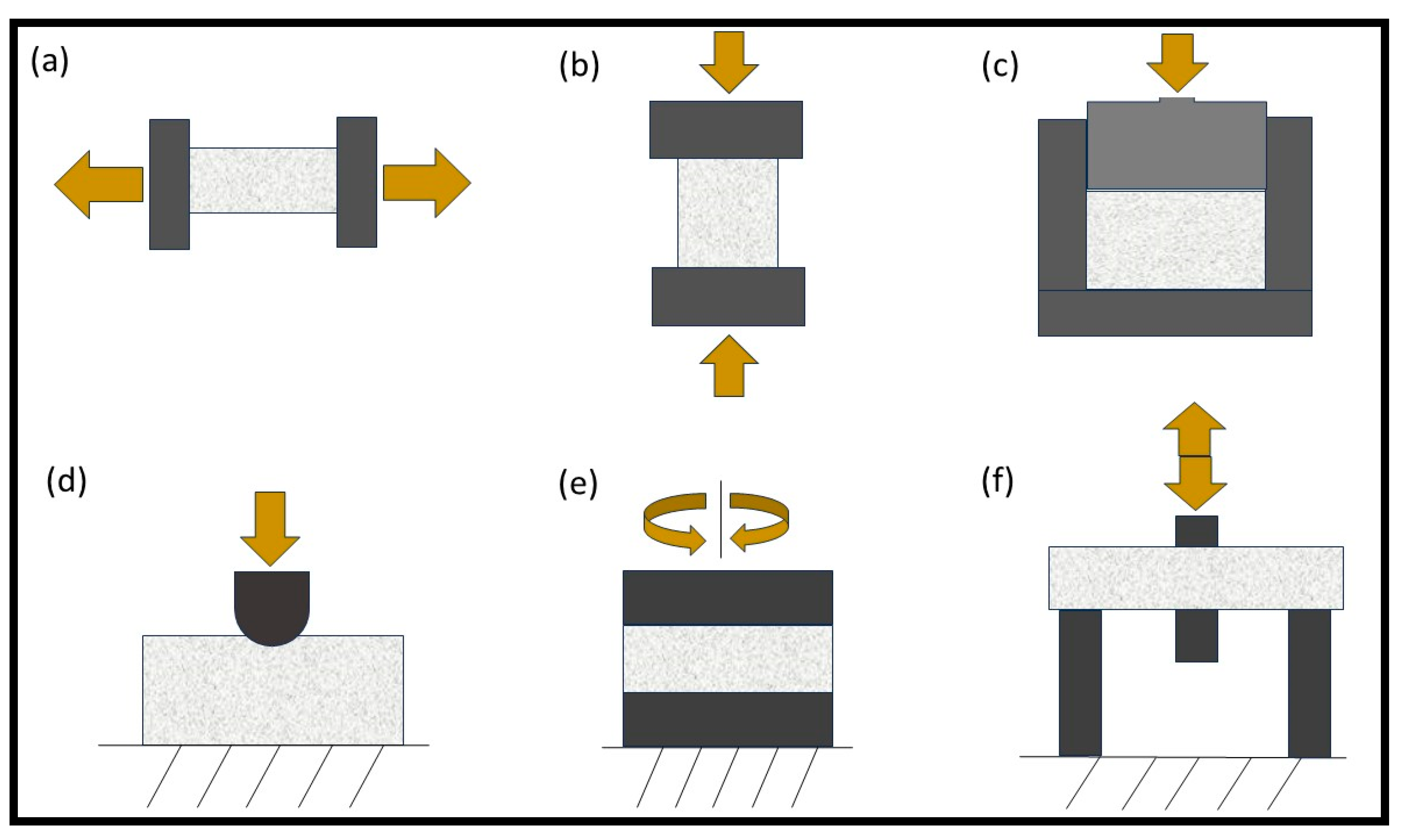
3. Mechanical Characterization Techniques of Hydrogel
- Tensile Testing
- Compression Testing
- Indentation
- Frequency-based Testing
4. Application of Mechanically Improved Gelatin-based Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering
4.1. In bone Tissue Regeneration
4.2. Cartilage Tissue Regeneration
4.3. Cardiac Tissue Regeneration
4.4. Nerve Tissue Regeenration
5. Conclusion and Future Prospective
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young, S.; Wong, M.; Tabata, Y.; Mikos, A.G. Gelatin as a Delivery Vehicle for the Controlled Release of Bioactive Molecules. Journal of Controlled Release 2005, 109, 256–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Bulcke, A.I.; Bogdanov, B.; De Rooze, N.; Schacht, E.H.; Cornelissen, M.; Berghmans, H. Structural and Rheological Properties of Methacrylamide Modified Gelatin Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, B.F.; Pittermann, E.; Ma, N.; Gebauer, T.; Neffe, A.T.; Hölscher, M.; Jung, F.; Lendlein, A. Viability of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Seeded on Crosslinked Entropy-Elastic Gelatin-Based Hydrogels. Macromol Biosci 2012, 12, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croome, R.J. Acid and Alkaline Hydrolysis of Gelatin. Journal of Applied Chemistry 1953, 3, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.R.; Shahid, M.A.; Alimuzzaman, S.; Khan, A.N. Sources, Extractions and Applications of Bio-Maker Collagen–A Review. Biomedical Engineering Advances 2022, 4, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogue, R.H. Conditions Affecting the Hydrolysis of Collagen to Gelatin. Ind Eng Chem 1923, 15, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, T.R. Gelatin. Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kharkar, P.M.; Kiick, K.L.; Kloxin, A.M. Designing Degradable Hydrogels for Orthogonal Control of Cell Microenvironments. Chem Soc Rev 2013, 42, 7335–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur Hanani, Z.A.; Roos, Y.H.; Kerry, J.P. Use and Application of Gelatin as Potential Biodegradable Packaging Materials for Food Products. Int J Biol Macromol 2014, 71, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slade, L.; Levine, H. Polymer-chemical properties of gelatin in foods. Advances in meat research (USA), 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Santoro, M.; Tatara, A.M.; Mikos, A.G. Gelatin carriers for drug and cell delivery in tissue engineering. Journal of controlled release 2014, 190, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandooren, J.; Van den Steen, P.E.; Opdenakker, G. Biochemistry and molecular biology of gelatinase B or matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9): the next decade. Critical reviews in biochemistry and molecular biology 2013, 48, 8222–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, M.; Abbasi, F.; Khoshfetrat, A.B.; Ghaleh, H. Microstructure and Characteristic Properties of Gelatin/Chitosan Scaffold Prepared by a Combined Freeze-Drying/Leaching Method. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2013, 33, 3958–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamplona, R.; González-Lana, S.; Romero, P.; Ochoa, I.; Martín-Rapún, R.; Sánchez-Somolinos, C. Tuning of Mechanical Properties in Photopolymerizable Gelatin-Based Hydrogels for In Vitro Cell Culture Systems. ACS Appl Polym Mater 2023, 5, 1487–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderhooft, J.L.; Alcoutlabi, M.; Magda, J.J.; Prestwich, G.D. Rheological Properties of Cross-Linked Hyaluronan–Gelatin Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering. Macromol Biosci 2009, 9, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidenko, N.; Schuster, C.F.; Bax, D.V.; Farndale, R.W.; Hamaia, S.; Best, S.M.; Cameron, R.E. Evaluation of Cell Binding to Collagen and Gelatin: A Study of the Effect of 2D and 3D Architecture and Surface Chemistry. J Mater Sci Mater Med 2016, 27, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramorino, G.; Gobetti, A.; Cornacchia, G.; Roca, E. Effect of Static Offsets on the Nonlinear Dynamic Mechanical Properties of Human Brain Tissue. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 2022, 130, 105204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Gao, Q.; Xie, C.; Fu, J.; Xiang, M.; He, Y. Synchronous 3D Bioprinting of Large-Scale Cell-Laden Constructs with Nutrient Networks. Adv Healthc Mater 2020, 9, 1901142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosellini, E.; Cristallini, C.; Barbani, N.; Vozzi, G.; Giusti, P. Preparation and Characterization of Alginate/Gelatin Blend Films for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A 2009, 91A, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, H.; Dickinson, E. "Influence of transglutaminase treatment on the thermoreversible gelation of gelatin. Food hydrocolloids 2001, 15, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Bhat, R. Fish Gelatin: Properties, Challenges, and Prospects as an Alternative to Mammalian Gelatins. Food Hydrocoll 2009, 23, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Panzavolta, S.; Rubini, K. Relationship between Triple-Helix Content and Mechanical Properties of Gelatin Films. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5675–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, B.J.; Gawlitta, D.; Rosenberg, A.J.W.P.; Malda, J.; Melchels, F.P.W. Gelatin-Methacryloyl Hydrogels: Towards Biofabrication-Based Tissue Repair. Trends Biotechnol 2016, 34, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, K.; Roca, E.; Ramorino, G.; Sartore, L. Progress in the Mechanical Modulation of Cell Functions in Tissue Engineering. Biomater Sci 2020, 8, 7033–7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeForest, C.A.; Anseth, K.S. Advances in bioactive hydrogels to probe and direct cell fate. Annual review of chemical and biomolecular engineering 2012, 3, 421–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisotzki, E.I.; Hennes, M.; Schuldt, C.; Engert, F.; Knolle, W.; Decker, U.; Käs, J.A.; Zink, M.; Mayr, S.G. Tailoring the Material Properties of Gelatin Hydrogels by High Energy Electron Irradiation. J Mater Chem B 2014, 2, 4297–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cataldo, F.; Ursini, O.; Lilla, E.; Angelini, G. Radiation-Induced Crosslinking of Collagen Gelatin into a Stable Hydrogel. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 2007, 275, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Lu, H.; Li, F.; Zhang, S.; Sun, Q.; Xiong, L. Enhanced Mechanical Properties and Gelling Ability of Gelatin Hydrogels Reinforced with Chitin Whiskers. Food Hydrocoll 2018, 75, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manish, V.; Arockiarajan, A.; Tamadapu, G. Influence of Water Content on the Mechanical Behavior of Gelatin Based Hydrogels: Synthesis, Characterization, and Modeling. Int J Solids Struct 2021, 233, 111219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlierberghe, S. van; Schacht, E.; Dubruel, P. Reversible Gelatin-Based Hydrogels: Finetuning of Material Properties. Eur Polym J 2011, 47, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaipan, P.; Nguyen, A.; Narayan, R.J. Gelatin-Based Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. MRS Commun 2017, 7, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Li, H.; Tang, K; Li, Q. Preparation of gelatin-based hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties and modulation on cell–matrix interactions. Journal of Biomaterials Applications 2021, 36, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Xiaohong, et al. Gelatin-based hydrogels for organ 3D bioprinting. Polymers 2017, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukin, I.; Erezuma, I.; Maeso, L.; Zarate, J.; Desimone, M.F.; Al-Tel, T.H.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Orive, G. Progress in Gelatin as Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salahuddin, B.; Wang, S.; Sangian, D.; Aziz, S.; Gu, Q. Hybrid Gelatin Hydrogels in Nanomedicine Applications. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2021, 4, 2886–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J. Il; Park, K.M. Advances in Gelatin-Based Hydrogels for Wound Management. J Mater Chem B 2021, 9, 1503–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echave, Mari Carmen, et al. Recent advances in gelatin-based therapeutics. Expert opinion on biological therapy 2019, 19, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzoghby, A.O. Gelatin-Based Nanoparticles as Drug and Gene Delivery Systems: Reviewing Three Decades of Research. Journal of Controlled Release 2013, 172, 1075–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, J.B.; Pacelli, S.; El Haj, A.J.; Dua, H.S.; Hopkinson, A.; White, L.J.; Rose, F.R.A.J. Gelatin-Based Materials in Ocular Tissue Engineering. Materials 2014, 7, 3106–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, D.M.R.; Black, C.R.M.; Dawson, J.I.; Oreffo, R.O.C. A Review of Hydrogel Use in Fracture Healing and Bone Regeneration. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 2016, 10, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asim, S.; Tabish, T.A.; Liaqat, U.; Ozbolat, I.T.; Rizwan, M. Advances in Gelatin Bioinks to Optimize Bioprinted Cell Functions. Adv Healthc Mater 2023, 12, 2203148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezhadi, Somayeh Hallaj, et al. "Gelatin-based delivery systems for cancer gene therapy." Journal of Drug Targeting 2009, 17, 731–738.
- Liu, Mei, et al. Injectable hydrogels for cartilage and bone tissue engineering. Bone research 2017, 5, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Shao Qiong, et al. Synthetic hydrogels for controlled stem cell differentiation. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennink, W.E.; van Nostrum, C.F. Novel crosslinking methods to design hydrogels. Advanced drug delivery reviews 2012, 64, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voorhaar, L; Hoogenboom, R. Supramolecular polymer networks: hydrogels and bulk materials. Chemical Society Reviews 2016, 45, 4013–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.; Reist, M.; Mayer, J.M.; Felt, O; Gurny, R. Structure and interactions in chitosan hydrogels formed by complexation or aggregation for biomedical applications. European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics 2004, 57, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Liow, S.S.; Karim, A.A.; Li, Z.; Loh, X.J. A Recent Perspective on Noncovalently Formed Polymeric Hydrogels. The Chemical Record 2018, 18, 1517–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichol, J.W.; Koshy, S.T.; Bae, H.; Hwang, C.M.; Yamanlar, S.; Khademhosseini, A. Cell-Laden Microengineered Gelatin Methacrylate Hydrogels. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5536–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naahidi, S.; Jafari, M.; Logan, M.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Bae, H.; Dixon, B.; Chen, P. Biocompatibility of Hydrogel-Based Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. Biotechnol Adv 2017, 35, 530–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Jung, D.; Spokoyny, A.M. Cross-Linking Dots on Metal Oxides. NPG Asia Materials 2019, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Reist, M.; Mayer, J.M.; Felt, O.; Peppas, N.A.; Gurny, R. Structure and Interactions in Covalently and Ionically Crosslinked Chitosan Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2004, 57, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Peng, Q.Y.; Han, L.B.; Zeng, H.B. Self-Healing Hydrogels and Underlying Reversible Intermolecular Interactions. Chinese Journal of Polymer Science 2021, 39, 1246–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, T.; Zhao, B.; Yan, J. Investigation of the Impact of Hydrogen Bonding Degree in Long Single-Stranded DNA (SsDNA) Generated with Dual Rolling Circle Amplification (RCA) on the Preparation and Performance of DNA Hydrogels. Biosensors 2023, 13, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, A; Bansal, M. ; Collagen structure: the Madras triple helix and the current scenario. IUBMB life 2005, 57, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Choi, D.; Fu, B.; Reichmanis, E. Solvent Based Hydrogen Bonding: Impact on Poly(3-Hexylthiophene) Nanoscale Morphology and Charge Transport Characteristics. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5402–5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namchuk, M.N.; Withers, S.G. Mechanism of Agrobacterium β-Glucosidase: Kinetic Analysis of the Role of Noncovalent Enzyme/Substrate Interactions. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 16194–16202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleos, C.M.; Tsiourvas, D.; Sideratou, Z. Hydrogen Bonding Interactions of Liposomes Simulating Cell-Cell Recognition. A Review. Origins of Life and Evolution of the Biosphere 2004, 34, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, X.N.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Su, F.; Li, L.; Wu, Z.L.; Zheng, Q. Ultrastiff and Tough Supramolecular Hydrogels with a Dense and Robust Hydrogen Bond Network. Chemistry of Materials 2019, 31, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigata, M.; Meinert, C.; Bock, N.; Dargaville, B.L.; Hutmacher, D.W. Deciphering the Molecular Mechanism of Water Interaction with Gelatin Methacryloyl Hydrogels: Role of Ionic Strength, Ph, Drug Loading and Hydrogel Network Characteristics. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Han, Q.; You, X. Developing Super Tough Gelatin-Based Hydrogels by Incorporating Linear Poly(Methacrylic Acid) to Facilitate Sacrificial Hydrogen Bonding. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 4723–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.J.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Sun, T.L.; Dang, X.; King, D.R.; You, X. Dynamic bonds enable high toughness and multifunctionality in gelatin/tannic acid-based hydrogels with tunable mechanical properties. Soft Matter, 2021, 17, 9399–9409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tang, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, L. Self-Healing and Highly Stretchable Gelatin Hydrogel for Self-Powered Strain Sensor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2020, 12, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Lv, L.; Deng, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G.Z.; Wang, C.Y.; Lv, L.; Deng, Y.H. Self-Healing Gelatin Hydrogels Cross-Linked by Combining Multiple Hydrogen Bonding and Ionic Coordination. Macromol Rapid Commun 2017, 38, 1700018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Z.; Singh, G.; Zhang, X.; Xu, K.; Li, B.; Hu, Z.; et al. Hydrogen Bonds Autonomously Powered Gelatin Methacrylate Hydrogels with Super-Elasticity, Self-Heal and Underwater Self-Adhesion for Sutureless Skin and Stomach Surgery and E-Skin. Biomaterials 2018, 171, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Dai, C.; Fan, L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Z.; Guan, P.; Tian, Y.; Xing, J.; Li, X.; et al. Injectable Self-Healing Natural Biopolymer-Based Hydrogel Adhesive with Thermoresponsive Reversible Adhesion for Minimally Invasive Surgery. Adv Funct Mater 2021, 31, 2007457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, B.; Bhatia, N.; Kumar, A.; Gnanamani, A.; Thilagam, R.; Shanuja, S.K.; Vadakkadath Meethal, K.; Shiji, T.M. Bioinspired Gelatin Based Sticky Hydrogel for Diverse Surfaces in Burn Wound Care. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, W.; Chen, Y.L.; Horng, J.C. Promoting Self-Assembly of Collagen-Related Peptides into Various Higher-Order Structures by Metal-Histidine Coordination. Langmuir 2012, 28, 3194–3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, M.M.; Lee, J.; Ernenwein, D.; Chmielewski, J. Controlling the Morphology of Metal-Promoted Higher Ordered Assemblies of Collagen Peptides with Varied Core Lengths. Langmuir 2012, 28, 1993–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, C.; Xing, Q.; He, W.; Li, B.; Frost, M.C.; Zhao, F. Fabrication and Characterization of a Nitric Oxide-Releasing Nanofibrous Gelatin Matrix. Biomacromolecules 2013, 14, 2521–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
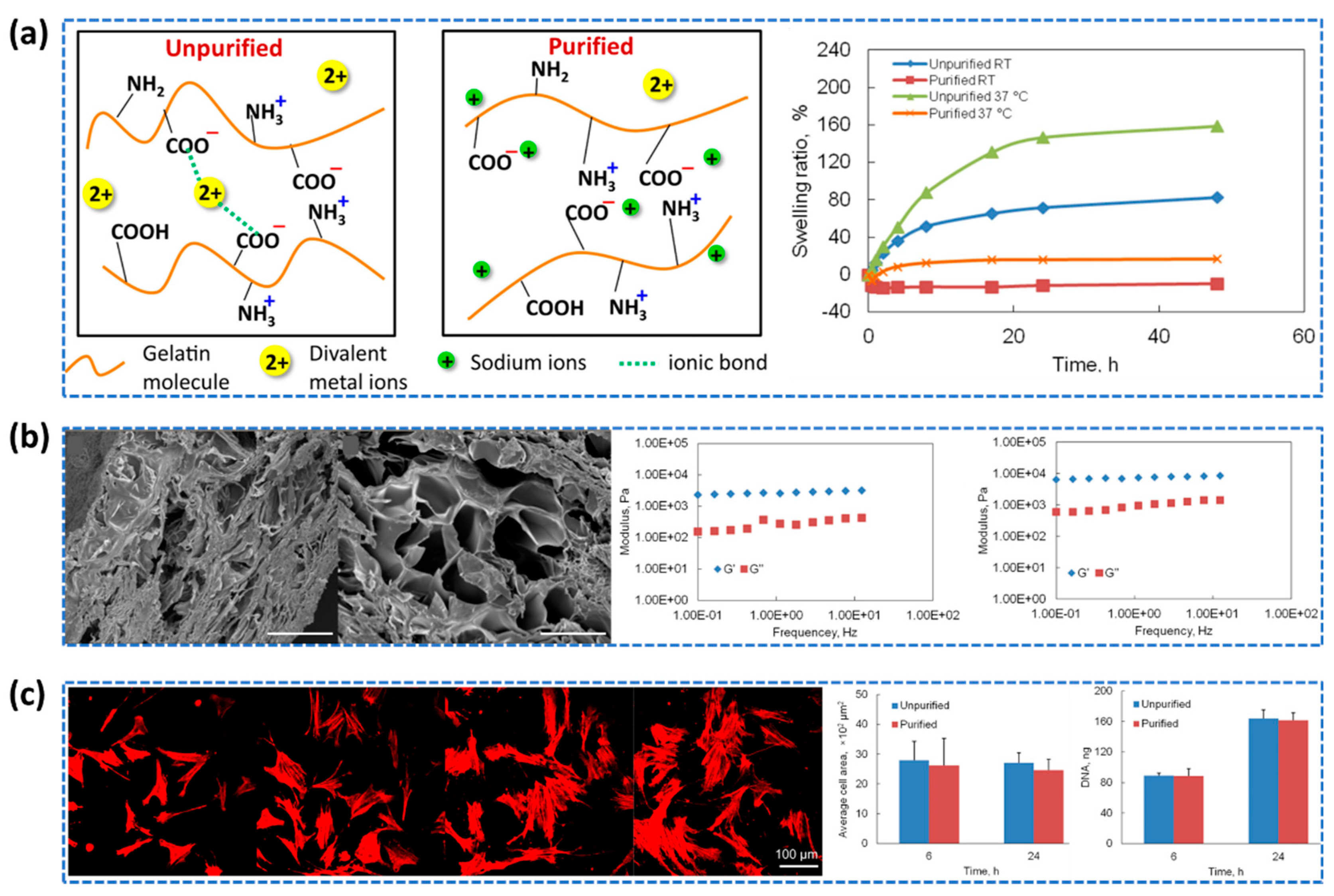
- Xing, Q.; Yates, K.; Vogt, C.; Qian, Z.; Frost, M.C.; Zhao, F. Increasing mechanical strength of gelatin hydrogels by divalent metal ion removal. Scientific reports, 2014, 4, 4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, S.L.M.; Rucker, R.B.; Niklason, L.E. Effects of Copper and Cross-Linking on the Extracellular Matrix of Tissue-Engineered Arteries. Cell Transplant 2005, 14, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Lv, L.; Deng, Y.; Wang, C. Self-Healing Gelatin Hydrogels Cross-Linked by Combining Multiple Hydrogen Bonding and Ionic Coordination. Macromol Rapid Commun 2017, 38, 1700018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steverink, J.G.; van Tol, F.R.; Oosterman, B.J.; Vermonden, T.; Verlaan, J.J.; Malda, J.; Piluso, S. Robust Gelatin Hydrogels for Local Sustained Release of Bupivacaine Following Spinal Surgery. Acta Biomater 2022, 146, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nindiyasari, F.; Fernández-Díaz, L.; Griesshaber, E.; Astilleros, J.M.; Sánchez-Pastor, N.; Schmahl, W.W. Influence of Gelatin Hydrogel Porosity on the Crystallization of CaCO 3. Cryst Growth Des 2014, 14, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; He, J.; Nichol, J.W.; Wang, L.; Hutson, C.B.; Wang, B.; Du, Y.; Fan, H.; Khademhosseini, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Photocrosslinkable Gelatin and Silk Fibroin Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogels. Acta Biomater 2011, 7, 2384–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Tian, Z.; Xiao, B.; Yi, S.; Duan, L. Coordination with Zirconium: A Facile Approach to Improve the Mechanical Properties and Thermostability of Gelatin Hydrogel. Int J Biol Macromol 2022, 205, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Ji, N.; Cui, S.; Xie, W.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; Xiong, L; Sun, Q. Coordination of covalent cross-linked gelatin hydrogels via oxidized tannic acid and ferric ions with strong mechanical properties. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 2019, 67, 11489–11497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; He, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, G.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, R.; Tian, W.; et al. Tunable Mechanical, Antibacterial, and Cytocompatible Hydrogels Based on a Functionalized Dual Network of Metal Coordination Bonds and Covalent Crosslinking. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2018, 10, 6190–6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Fan, X.; Liu, H.; Tang, K. Self-assembly and metal ions-assisted one step fabrication of recoverable gelatin hydrogel with high mechanical strength. Polymer-Plastics Technology and Materials 2020, 59, 1899–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.; Hong, P.; Li, Y. Synthesis of Poly(Acrylic Acid)–Fe3+/Gelatin/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol) Triple-Network Supramolecular Hydrogels with High Toughness, High Strength and Self-Healing Properties. Polym Int 2019, 68, 1710–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, E.; Huang, Y.; Li, X. Hybrid Hydrogel Based on Stereocomplex PDLA/PLLA and Gelatin for Bone Regeneration. J Appl Polym Sci 2020, 137, 49571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strandman, S.; Zhu, X.X. Self-Healing Supramolecular Hydrogels Based on Reversible Physical Interactions. Gels 2016, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Pitet, L.M.; Wyss, H.M.; Vos, M.; Dankers, P.Y.W.; Meijer, E.W. Tough Stimuli-Responsive Supramolecular Hydrogels with Hydrogen-Bonding Network Junctions. J Am Chem Soc 2014, 136, 6969–6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Zhou, J.; Shi, J.; Xu, B. Supramolecular Hydrogelators and Hydrogels: From Soft Matter to Molecular Biomaterials. Chem Rev 2015, 115, 13165–13307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, R.; Pang, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhu, X. Supramolecular Hydrogels: Synthesis, Properties and Their Biomedical Applications. Biomater Sci 2015, 3, 937–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, K.J.; Zhou, T.C.; Otim, K.J.; Shull, K.R. Ionically Cross-Linked Triblock Copolymer Hydrogels with High Strength. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 6193–6201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Kurokawa, T.; Kamita, G.; Gong, J.P. Lamellar Bilayers as Reversible Sacrificial Bonds to Toughen Hydrogel: Hysteresis, Self-Recovery, Fatigue Resistance, and Crack Blunting. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 8916–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.Y.; Zhao, X.; Illeperuma, W.R.; Chaudhuri, O.; Oh, K.H.; Mooney, D.J.; Vlassak, J.J; Suo, Z. Highly stretchable and tough hydrogels. Nature 2012, 489, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
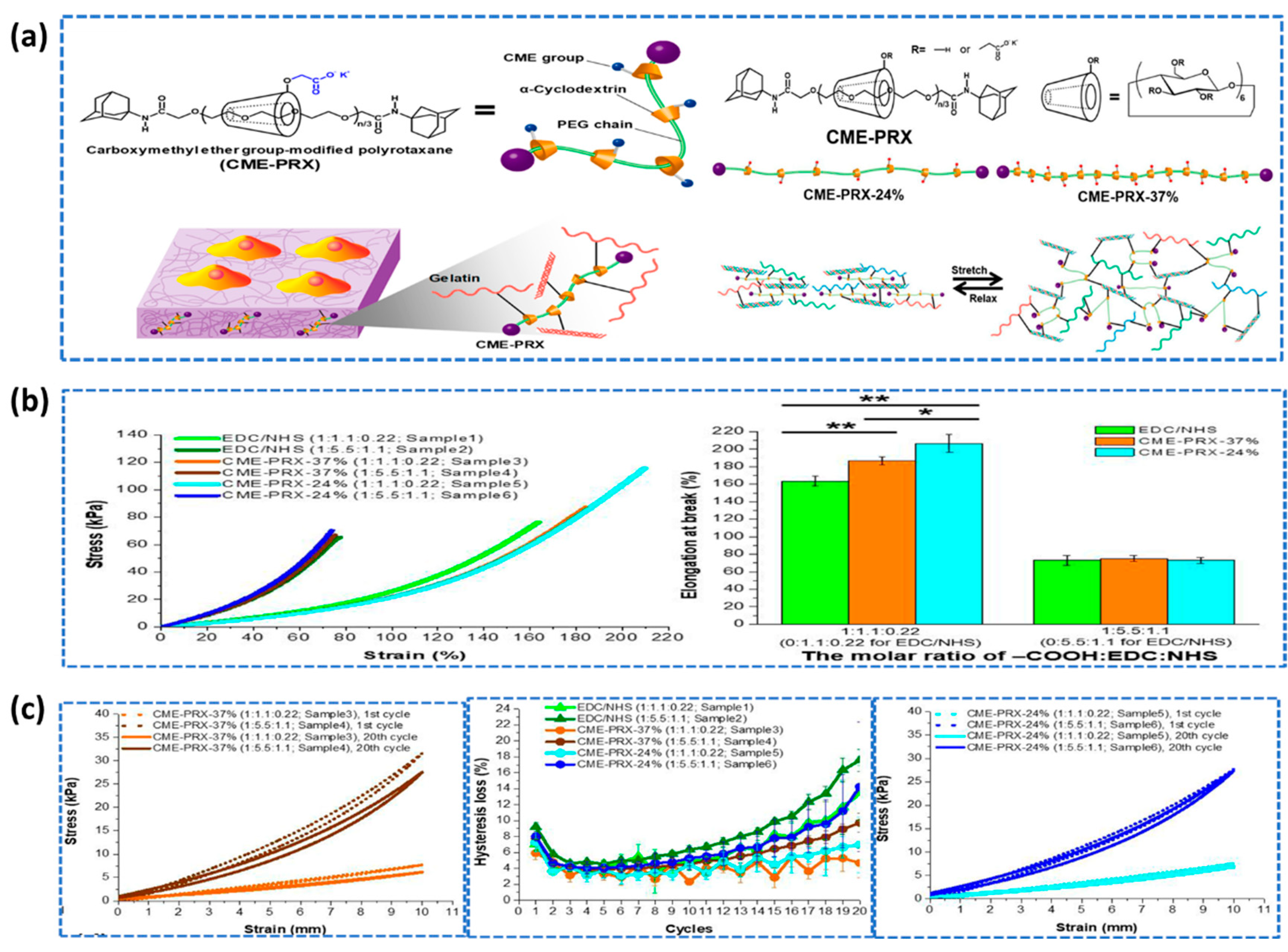
- Lee, D.H.; Tamura, A.; Arisaka, Y.; Seo, J.H.; Yui, N. Mechanically Reinforced Gelatin Hydrogels by Introducing Slidable Supramolecular Cross-Linkers. Polymers 2019, 11, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chen, Y.; Deng, Y.; Ngai, T.; Wang, C. Dynamic Supramolecular Hydrogels: Regulating Hydrogel Properties through Self-Complementary Quadruple Hydrogen Bonds and Thermo-Switch. ACS Macro Lett 2017, 6, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, E.; Chee, P.L.; Prasad, A.; Fang, X.; Owh, C.; Yeo, V.J.J.; Loh, X.J. Supramolecular soft biomaterials for biomedical applications, In-Situ Gelling Polym, Springer 2015, 17, 194–202. 17.
- Mihajlovic, M.; Staropoli, M.; Appavou, M.S.; Wyss, H.M.; Pyckhout-Hintzen, W.; Sijbesma, R.P. Tough Supramolecular Hydrogel Based on Strong Hydrophobic Interactions in a Multiblock Segmented Copolymer. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 3333–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.C.; Xia, X.X.; Fan, R.X.; Qian, Z.G. Programmable Electrostatic Interactions Expand the Landscape of Dynamic Functional Hydrogels. Chemistry of Materials 2020, 32, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Yomota, C; Okada, S. Development and release characterization of hyaluronan–doxycycline gels based on metal coordination. Journal of controlled release 2001, 76, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, M.J.; Atgie, M.; Hoogland, D.; Scherman, O.A. Preparation and Supramolecular Recognition of Multivalent Peptide-Polysaccharide Conjugates by Cucurbit[8]Uril in Hydrogel Formation. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 2436–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appel, E.A.; del Barrio, J.; Loh, X.J.; Scherman, O.A. Supramolecular Polymeric Hydrogels. Chem Soc Rev 2012, 41, 6195–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.L.; Kurokawa, T.; Kuroda, S.; Ihsan, A. bin; Akasaki, T.; Sato, K.; Haque, M.A.; Nakajima, T.; Gong, J.P. Physical Hydrogels Composed of Polyampholytes Demonstrate High Toughness and Viscoelasticity. Nature Materials 2013, 12, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.; Galarraga, J.H.; Kwon, M.Y.; Lee, H.; Burdick, J.A. Gallol-Derived ECM-Mimetic Adhesive Bioinks Exhibiting Temporal Shear-Thinning and Stabilization Behavior. Acta Biomater 2019, 95, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Xiong, M.; Lin, F.; Tang, L.; Huang, B.; Chen, Y. One-Pot Construction of Cellulose-Gelatin Supramolecular Hydrogels with High Strength and PH-Responsive Properties. Carbohydr Polym 2018, 196, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cai, J.; Lois, K.; Taaca, M.; Prieto, E.I.; Vasquez, M.R. Current Trends in Biomedical Hydrogels: From Traditional Crosslinking to Plasma-Assisted Synthesis. Polymers 2022, 14, 2560. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, N.; Reddy, R.; Jiang, Q. Crosslinking Biopolymers for Biomedical Applications. Trends Biotechnol 2015, 33, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oryan, A.; Kamali, A.; Moshiri, A.; Baharvand, H.; Daemi, H. Chemical Crosslinking of Biopolymeric Scaffolds: Current Knowledge and Future Directions of Crosslinked Engineered Bone Scaffolds. Int J Biol Macromol 2018, 107, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, S; Wang, J. Advances in crosslinking strategies of biomedical hydrogels. Biomaterials science, 2019, 7, 843–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, C; McKinley, D. New approaches to pollution prevention in the healthcare industry. Journal of Cleaner Production 2008, 16, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, D.P.; Chvapil, M.; Eskelson, C.D.; Ulreich, J. Biological Effects of Residual Glutaraldehyde in Glutaraldehyde-Tanned Collagen Biomaterials. J Biomed Mater Res 1980, 14, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.Y. Biocompatibility of Chemically Cross-Linked Gelatin Hydrogels for Ophthalmic Use. J Mater Sci Mater Med 2010, 21, 1899–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, S.; Hanif, M.; Azeem, M.; Mahmood, K.; Gondal, S.A. Role of Crosslinkers for Synthesizing Biocompatible, Biodegradable and Mechanically Strong Hydrogels with Desired Release Profile. Polymer Bulletin 2022, 79, 9199–9219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Cid, P.; Jiménez-Rosado, M.; Romero, A.; Pérez-Puyana, V. Novel Trends in Hydrogel Development for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Ouyang, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Zhong, W; Xing, M. M. Cell-compatible hydrogels based on a multifunctional crosslinker with tunable stiffness for tissue engineering. Journal of Materials Chemistry 2012, 22, 23952–23962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, Q.; Dong, F.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J. In Vitro Blood Compatibility Evaluation of Silk Fibroin by Chemical Crosslinking. Materials Technology 2015, 30, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, H.C.; Finn, M.G; Sharpless, K.B. Click chemistry: diverse chemical function from a few good reactions. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2001, 40, 2004–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Z.; Xian, C.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, G.; Wu, J. Natural Polymer-Based Hydrogels with Enhanced Mechanical Performances: Preparation, Structure, and Property. Adv Healthc Mater 2019, 8, 1900670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdougall, L.J.; Truong, V.X.; Dove, A.P. Efficient in Situ Nucleophilic Thiol-Yne Click Chemistry for the Synthesis of Strong Hydrogel Materials with Tunable Properties. ACS Macro Lett 2017, 6, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Cao, X.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X. An Interpenetrating HA/G/CS Biomimic Hydrogel via Diels–Alder Click Chemistry for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Carbohydr Polym 2013, 97, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X.; Dong, H.; Li, Q.; Zeng, L.; Cao, X. Alginate Based Antimicrobial Hydrogels Formed by Integrating Diels–Alder “Click Chemistry” and the Thiol–Ene Reaction. RSC Adv 2018, 8, 11036–11042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contessi Negrini, N.; Angelova Volponi, A.; Sharpe, P.T.; Celiz, A.D. Tunable Cross-Linking and Adhesion of Gelatin Hydrogels via Bioorthogonal Click Chemistry. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2021, 7, 4330–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, V.X.; Hun, M.L.; Li, F.; Chidgey, A.P.; Forsythe, J.S. In Situ-Forming Click-Crosslinked Gelatin Based Hydrogels for 3D Culture of Thymic Epithelial Cells. Biomater Sci 2016, 4, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniele, M.A.; Adams, A.A.; Naciri, J.; North, S.H.; Ligler, F.S. Interpenetrating Networks Based on Gelatin Methacrylamide and PEG Formed Using Concurrent Thiol Click Chemistries for Hydrogel Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Bratlie, K.M. Click Chemistry and Material Selection for in Situ Fabrication of Hydrogels in Tissue Engineering Applications. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 2018, 4, 2276–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Hsu, S. hui Hydrogels Based on Schiff Base Linkages for Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jeong, D.; Lee, H.; Kim, D.; Jung, S. Succinoglycan Dialdehyde-Reinforced Gelatin Hydrogels with Toughness and Thermal Stability. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 149, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Qin, S.; Pei, Y.; Zheng, X.; Tang, K. High Mechanical Strength Gelatin Composite Hydrogels Reinforced by Cellulose Nanofibrils with Unique Beads-on-a-String Morphology. Int J Biol Macromol 2020, 164, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, Z.; Ehsani, M.; Zandi, M.; Daemi, H.; Ghanian, M.-H.; Foudazi, R. Modified Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles Reinforced Nanocomposite Hydrogels Based on Gelatin/Oxidized Alginate via Schiff Base Reaction. Carbohydrate Polymer Technologies and Applications 2021, 2, 100056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, B.D.; Viswanathan, K.; Miller, K.M.; Long, T.E. Michael Addition Reactions in Macromolecular Design for Emerging Technologies. Prog Polym Sci 2006, 31, 487–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; Ding, P.; Deng, Y.; Okoro, O.V.; Shavandi, A.; Nie, L. Mercaptolated Chitosan/Methacrylate Gelatin Composite Hydrogel for Potential Wound Healing Applications. Composites Communications 2022, 35, 101344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neffe, A.T.; Löwenberg, C.; Lendlein, A. Hydrogel Networks by Aliphatic Dithiol Michael Addition to Glycidylmethacrylated Gelatin. MRS Adv 2021, 6, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Okoro, O.V.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Wei, X.; Liu, S.; Deng, Y.; Fan, L.; Jiang, G.; Wang, L.; et al. Graphene Oxide-Reinforced Alginate/Gelatin Hydrogel via Schiff-Base Bond and Thiol-Michael Addition for Bone Regeneration. Mater Today Commun 2022, 33, 104904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
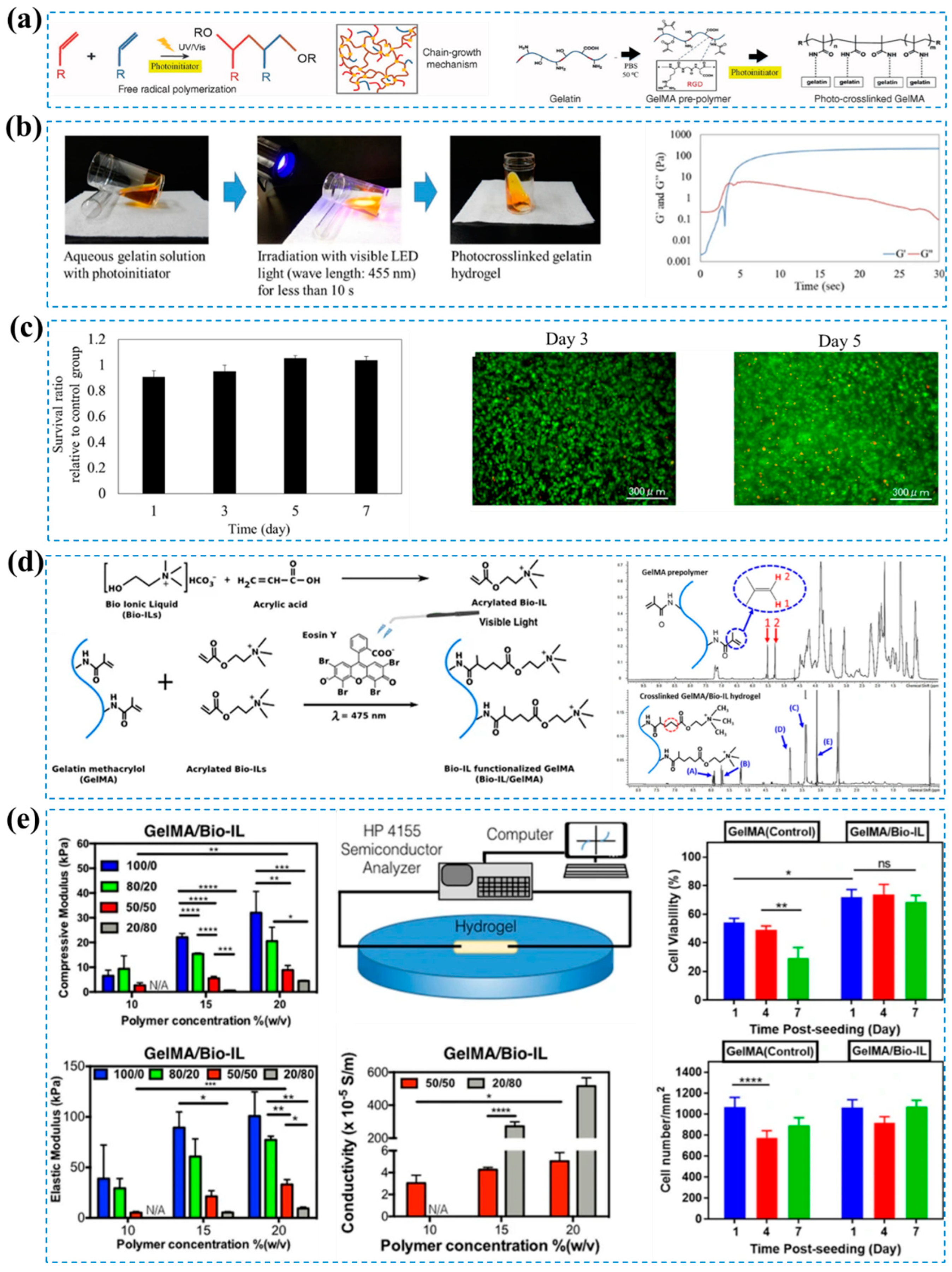
- Choi, J.R.; Yong, K.W.; Choi, J.Y.; Cowie, A.C. Recent Advances in Photo-Crosslinkable Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Biotechniques 2019, 66, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ifkovits, J.L.; Burdick, J.A. Review: Photopolymerizable and Degradable Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications. https://home.liebertpub.com/ten 2007, 13, 2369–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouillard, A.D.; Berglund, C.M.; Lee, J.Y.; Polacheck, W.J.; Tsui, Y.; Bonassar, L.J.; Kirby, B.J. Methods for photocrosslinking alginate hydrogel scaffolds with high cell viability. Tissue Engineering Part C: Methods 2011, 17, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.H.; Chun, H.J. Visible Light-Curable Hydrogel Systems for Tissue Engineering and Drug Delivery. Adv Exp Med Biol 2020, 1249, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kushibiki, T.; Mayumi, Y.; Nakayama, E.; Azuma, R.; Ojima, K.; Horiguchi, A.; Ishihara, M. Photocrosslinked Gelatin Hydrogel Improves Wound Healing and Skin Flap Survival by the Sustained Release of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benton, J.A.; Deforest, C.A.; Vivekanandan, V.; Anseth, K.S. Photocrosslinking of Gelatin Macromers to Synthesize Porous Hydrogels That Promote Valvular Interstitial Cell Function. Tissue Eng Part A 2009, 15, 3221–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lang, Q.; Yildirimer, L.; Lin, Z.Y.; Cui, W.; Annabi, N.; Ng, K.W.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Ghaemmaghami, A.M.; Khademhosseini, A. Photocrosslinkable Gelatin Hydrogel for Epidermal Tissue Engineering. Adv Healthc Mater 2016, 5, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucy, J.R.; Shirzaei Sani, E.; Portillo Lara, R.; DIaz, D.; DIas, F.; Weiss, A.S.; Koppes, A.N.; Koppes, R.A.; Annabi, N. Photocrosslinkable Gelatin/Tropoelastin Hydrogel Adhesives for Peripheral Nerve Repair. Tissue Eng Part A 2018, 24, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, T.; Lin, T.Y.; Andrisani, O.M.; Lin, C.C. Comparative Study of Visible Light Polymerized Gelatin Hydrogels for 3D Culture of Hepatic Progenitor Cells. J Appl Polym Sci 2017, 134, 44585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.S.; Klotz, B.J.; Lindberg, G.C.J.; Melchels, F.P.W.; Hooper, G.J.; Malda, J.; Gawlitta, D.; Woodfield, T.B.F. Visible Light Cross-Linking of Gelatin Hydrogels Offers an Enhanced Cell Microenvironment with Improved Light Penetration Depth. Macromol Biosci 2019, 19, 1900098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Hou, Y.; Park, H.; Choi, B.; Hou, S.; Chung, A.; Lee, M. Visible Light Crosslinkable Chitosan Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering. Acta Biomater 2012, 8, 1730–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamane, K.; Mazaki, T.; Shiozaki, Y.; Yoshida, A.; Shinohara, K.; Nakamura, M.; Yoshida, Y.; Zhou, D.; Kitajima, T.; Tanaka, M.; et al. Collagen-Binding Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) Alone or with a Gelatin- Furfurylamine Hydrogel Enhances Functional Recovery in Mice after Spinal Cord Injury. Scientific Reports 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairbanks, B.D.; Schwartz, M.P.; Bowman, C.N.; Anseth, K.S. Photoinitiated Polymerization of PEG-Diacrylate with Lithium Phenyl-2,4,6-Trimethylbenzoylphosphinate: Polymerization Rate and Cytocompatibility. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 6702–6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, D.; Alexander, P.G.; Yang, G.; Tan, J.; Cheng, A.W.M.; Tuan, R.S. Application of Visible Light-Based Projection Stereolithography for Live Cell-Scaffold Fabrication with Designed Architecture. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, H.; Lin, C.C. Visible-Light-Mediated Thiol-Ene Hydrogelation Using Eosin-Y as the Only Photoinitiator. Macromol Rapid Commun 2013, 34, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.M.; Pei, M.Y.; Pan, W.L.; Thissen, H.; Tsai, S.W. Gelatin Hydrogels Reinforced by Absorbable Nanoparticles and Fibrils Cured In Situ by Visible Light for Tissue Adhesive Applications. Polymers 2020, 12, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noshadi, I.; Walker, B.W.; Portillo-Lara, R.; Sani, E.S.; Gomes, N.; Aziziyan, M.R.; Annabi, N. Engineering Biodegradable and Biocompatible Bio-Ionic Liquid Conjugated Hydrogels with Tunable Conductivity and Mechanical Properties. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
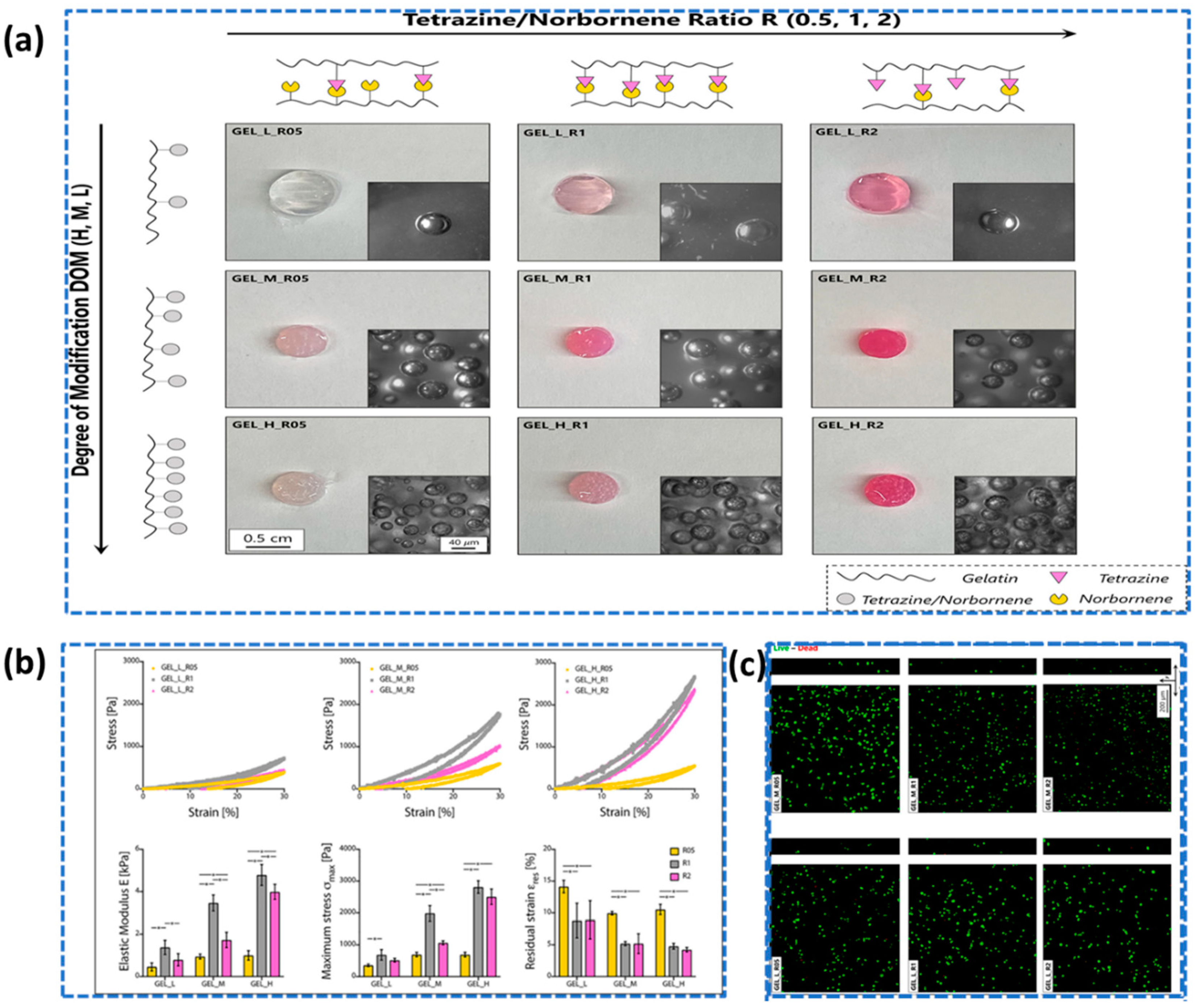
- Van Damme, L.; Van Hoorick, J.; Blondeel, P.; Van Vlierberghe, S. Toward Adipose Tissue Engineering Using Thiol-Norbornene Photo-Crosslinkable Gelatin Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 2408–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huang, W.; Yang, G.; An, Y.; Yin, Y.; Wang, N.; Jiang, B. Preparation of Gelatin/Poly (γ-Glutamic Acid) Hydrogels with Stimulated Response by Hot-Pressing Preassembly and Radiation Crosslinking. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2020, 116, 111259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisotzki, E.I.; Tempesti, P.; Fratini, E.; Mayr, S.G. Influence of High Energy Electron Irradiation on the Network Structure of Gelatin Hydrogels as Investigated by Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering (SAXS). Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2017, 19, 12064–12074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şener Raman, T.; Kuehnert, M.; Daikos, O.; Scherzer, T.; Krömmelbein, C.; Mayr, S.G.; Abel, B.; Schulze, A. A Study on the Material Properties of Novel PEGDA/Gelatin Hybrid Hydrogels Polymerized by Electron Beam Irradiation. Front Chem 2023, 10, 1094981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Uyama, H.; Ohmae, M. Enzymatic polymerization for precision polymer synthesis. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 2001, 74, 613–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elham Badali; Hosseini, M. ; Mohajer, M.; Hassanzadeh, S.; Saghati, S.; Hilborn, J.; Khanmohammadi, M. Enzymatic Crosslinked Hydrogels for Biomedical Application. Polymer Science, Series A 2022, 63, S1–S22. [Google Scholar]
- Besser, R.R.; Bowles, A.C.; Alassaf, A.; Carbonero, D.; Claure, I.; Jones, E.; Reda, J.; Wubker, L.; Batchelor, W.; Ziebarth, N.; et al. Enzymatically Crosslinked Gelatin–Laminin Hydrogels for Applications in Neuromuscular Tissue Engineering. Biomater Sci 2020, 8, 591–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Chen, R.; Lu, Y.; Zhan, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Jin, Z. Fabrication of Circular Microfluidic Network in Enzymatically-Crosslinked Gelatin Hydrogel. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2016, 59, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echave, M.C.; Pimenta-Lopes, C.; Pedraz, J.L.; Mehrali, M.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Ventura, F.; Orive, G. Enzymatic Crosslinked Gelatin 3D Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Int J Pharm 2019, 562, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, S.; Hirose, K.; Taguchi, K.; Ogushi, Y.; Kawakami, K. An Injectable, in Situ Enzymatically Gellable, Gelatin Derivative for Drug Delivery and Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 3371–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maji, K.; Dasgupta, S.; Pramanik, K.; Bissoyi, A. Preparation and evaluation of gelatin-chitosan-nanobioglass 3D porous scaffold for bone tissue engineering. International journal of biomaterials, 2016, 2016, 9825659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisson, K.; Zhang, C.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Evaluation of Cross-Linking Methods for Electrospun Gelatin on Cell Growth and Viability. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poursamar, S.A.; Lehner, A.N.; Azami, M.; Ebrahimi-Barough, S.; Samadikuchaksaraei, A.; Antunes, A.P.M. The effects of crosslinkers on physical, mechanical, and cytotoxic properties of gelatin sponge prepared via in-situ gas foaming method as a tissue engineering scaffold. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2016, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, Q.; Chi, B.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Chen, S; Xu, H. Enzyme-induced dual-network ε-poly-L-lysine-based hydrogels with robust self-healing and antibacterial performance. Chemical Communications 2017, 53, 4803–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, E.; Srivastava, A.; Kumar, A. Macroporous Interpenetrating Cryogel Network of Poly(Acrylonitrile) and Gelatin for Biomedical Applications. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine 2008, 20, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hago, E.E.; Li, X. Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogels Based on Gelatin and PVA by Biocompatible Approaches: Synthesis and Characterization. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering 2013, 2013, 328763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Choi, J.B.; Jang, Y.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Bae, T.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, J.M.; Lee, M.H. Mammalian and Fish Gelatin Methacryloyl-Alginate Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 17433–17441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, T.; Miller, E.J.; McKenzie, C.; Oldinski, R.A. Physically Crosslinked Polyvinyl Alcohol and Gelatin Interpenetrating Polymer Network Theta-Gels for Cartilage Regeneration. J Mater Chem B 2015, 3, 9242–9249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.; Olsen, B.D.; Khademhosseini, A. The Mechanical Properties and Cytotoxicity of Cell-Laden Double-Network Hydrogels Based on Photocrosslinkable Gelatin and Gellan Gum Biomacromolecules. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3143–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, L.; Chen, H.; Wei, D.; Chen, F.; Tang, Z.; Yang, J.; Zheng, J. High Strength and Self-Healable Gelatin/Polyacrylamide Double Network Hydrogels. J Mater Chem B 2017, 5, 7683–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, A.; Kakugo, A.; Gong, J.P.; Osada, Y.; Takai, M.; Erata, T.; Kawano, S. High Mechanical Strength Double-Network Hydrogel with Bacterial Cellulose. Adv Funct Mater 2004, 14, 1124–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Bu, X.; Da, Y.; Duan, P.; Wang, H.; Ren, J.; Lyu, B.; Gao, D.; Ma, J. Gelatin/PAM Double Network Hydrogels with Super-Compressibility. Polymer 2020, 210, 123021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, J.; Chen, F.; Zhu, L.; Tang, Z.; Qin, G.; Chen, Q.; Chen, G. Mechanical Properties of Gelatin/Polyacrylamide/Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite Double-Network Hydrogels. Compos Sci Technol 2018, 163, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, C.; Li, Z.; Luo, Y.; Gong, J.; Li, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Qiao, C. Bio-Based Poly (γ-Glutamic Acid)-Gelatin Double-Network Hydrogel with High Strength for Wound Healing. Int J Biol Macromol 2022, 202, 438–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Q. Three-Dimensional Printing Self-Healing Dynamic/Photocrosslinking Gelatin-Hyaluronic Acid Double-Network Hydrogel for Tissue Engineering. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 12076–12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.; Tripathi, A.; Kumar, A. Supermacroprous Chitosan–Agarose–Gelatin Cryogels: In Vitro Characterization and in Vivo Assessment for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. J R Soc Interface 2011, 8, 540–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Mu, C.; Lin, W.; Ngai, T. Gelatin Effects on the Physicochemical and Hemocompatible Properties of Gelatin/PAAm/Laponite Nanocomposite Hydrogels. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2015, 7, 18732–18741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, Y.; Chen, B. One-Pot Synthesis and Characterization of Reduced Graphene Oxide–Gelatin Nanocomposite Hydrogels. RSC Adv 2016, 6, 6171–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mu, C.; Lin, W. Novel Hemocompatible Nanocomposite Hydrogels Crosslinked with Methacrylated Gelatin. RSC Adv 2016, 6, 43663–43671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, Y.; Chen, B. Self-Assembled Graphene Oxide–Gelatin Nanocomposite Hydrogels: Characterization, Formation Mechanisms, and PH-Sensitive Drug Release Behavior. J Polym Sci B Polym Phys 2015, 53, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Li, M.; Ji, N.; Liu, J.; Mu, H.; Xiong, L.; Sun, Q. Preparation of a Strong Gelatin-Short Linear Glucan Nanocomposite Hydrogel by an in Situ Self-Assembly Process. J Agric Food Chem 2018, 66, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbari, M.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Mohandes, F.; Firouzi, Z. Modified Silicon Carbide NPs Reinforced Nanocomposite Hydrogels Based on Alginate-Gelatin by with High Mechanical Properties for Tissue Engineering. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2022, 15, 103520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
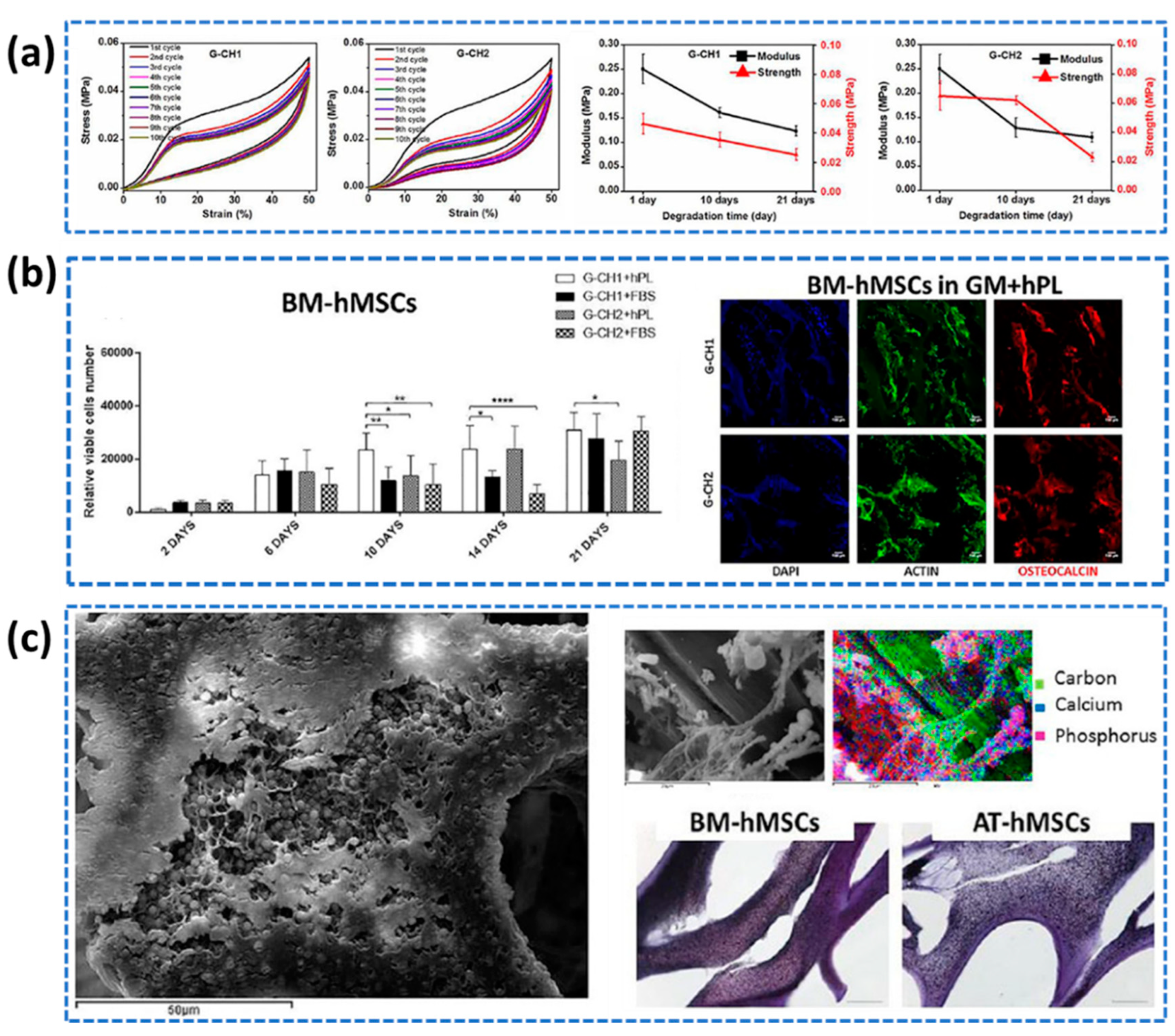
- Re, F.; Sartore, L.; Moulisova, V.; Cantini, M.; Almici, C.; Bianchetti, A.; Chinello, C.; Dey, K.; Agnelli, S.; Manferdini, C.; Bernardi, S. 3D gelatin-chitosan hybrid hydrogels combined with human platelet lysate highly support human mesenchymal stem cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation. Journal of tissue engineering 2019, 10, 2041731419845852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K. Polymer Letters, 1955, 4, 35. 4.
- Jenkins, A.D.; Stepto, R.F.T.; Kratochvíl, P.; Suter, U.W. Glossary of Basic Terms in Polymer Science (IUPAC Recommendations 1996). Pure and Applied Chemistry 1996, 68, 2287–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matricardi, P.; Di Meo, C.; Coviello, T.; Hennink, W.E; Alhaique, F. Interpenetrating polymer networks polysaccharide hydrogels for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Advanced drug delivery reviews 2013, 65, 1172–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, L.H.; Hu, R. Interpenetrating Polymer Networks. In Polymer Blends Handbook; Springer: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2014; pp. 677–724. [Google Scholar]
- Shivashankar, M; Mandal, B. K. A review on interpenetrating polymer network. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences 2012, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Chan-Park, M.B. Hydrogel Based on Interpenetrating Polymer Networks of Dextran and Gelatin for Vascular Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, C.; Lu, L.; Li, X. Mechanically Robust Gelatin–Alginate IPN Hydrogels by a Combination of Enzymatic and Ionic Crosslinking Approaches. Macromol Mater Eng 2014, 299, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, E.S. Design and applications of interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels. A review. Chemical Engineering Journal 2014, 243, 572–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourston, D.J; Schäfer, F.U. Poly (ether urethane)/poly (ethyl methacrylate) interpenetrating polymer networks: morphology, phase continuity and mechanical properties as a function of composition. Polymer 1996, 37, 3521–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Le, P.; Lai, K.; Fernandes-Cunha, G.M.; Myung, D. Simultaneous Interpenetrating Polymer Network of Collagen and Hyaluronic Acid as an in Situ-Forming Corneal Defect Filler. Chemistry of Materials 2020, 32, 5208–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverstein, M.S. Interpenetrating Polymer Networks: So Happy Together? Polymer 2020, 207, 122929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouf, C.; Derrough, S.; André, J.-J.; Widmaier, J.-M.; Meyer, G.C. Methacrylic—Allylic Interpenetrating Polymer Networks 1994, 239, 143–156.
- Sperling, L.H. Recent Advances in Interpenetrating Polymer Networks. Polym Eng Sci 1985, 25, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Mata, A; Fang, Y. Natural polymer-sourced interpenetrating network hydrogels: Fabrication, properties, mechanism and food applications. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 116, 342–356. [Google Scholar]
- Curtius, A.J.; Covitch, M.J.; Thomas, D.A; Sperling, L.H. Poly (Butadiene)/poly (styrene) interpenetrating polymer networks. Rubber Chemistry and Technology 1972, 45, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huelck, V.; Thomas, D.A.; Sperling, L.H. Interpenetrating Polymer Networks of Poly (Ethyl Acrylate) and Poly(Styrene-Comethyl Methacrylate). I. Morphology via Electron Microscopy. Macromolecules 1972, 5, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J; Wei, J. Interpenetrating network hydrogels with high strength and transparency for potential use as external dressings. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2017, 80, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Kurokawa, T; Gong, J. P. Super tough double network hydrogels and their application as biomaterials. Polymer 2012, 53, 1805–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ma, P.; Chen, M. Superior Mechanical Properties of Double-Network Hydrogels Reinforced by Carbon Nanotubes without Organic Modification. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2013, 14, 22380–22394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H; Brown, H. R. Jellyfish gel and its hybrid hydrogels with high mechanical strength. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.-O.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, Y.-A.; Yang, S.-J.; Jeong, S.-I.; Lee, J.-Y.; Lim, Y.-M. Gamma Ray-Induced Polymerization and Cross-Linking for Optimization of PPy/PVP Hydrogel as Biomaterial. Polymers 2020, 12, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duan, R; Liu, L. Gelatin/Hyaluronic Acid Photocrosslinked Double Network Hydrogel with Nano-Hydroxyapatite Composite for Potential Application in Bone Repair. Gels, 2023, 9, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.P.; Katsuyama, Y.; Kurokawa, T; Osada, Y. Double-network hydrogels with extremely high mechanical strength. Advanced materials 2003, 15, 1155–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.P. Why are double network hydrogels so tough? Soft Matter 2010, 6, 2583–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Furukawa, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Kurokawa, T.; Osada, Y.; Gong, J.P. True Chemical Structure of Double Network Hydrogels. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 2184–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhu, L; Zheng, J. Fundamentals of double network hydrogels. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2015, 3, 3654–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Sato, H.; Zhao, Y.; Kawahara, S.; Kurokawa, T.; Sugahara, K; Gong, J. P. A universal molecular stent method to toughen any hydrogels based on double network concept. Advanced functional materials 2012, 22, 4426–4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafim, A.; Tucureanu, C.; Petre, D.G.; Dragusin, D.M.; Salageanu, A.; van Vlierberghe, S.; Dubruel, P.; Stancu, I.C. One-Pot Synthesis of Superabsorbent Hybrid Hydrogels Based on Methacrylamide Gelatin and Polyacrylamide. Effortless Control of Hydrogel Properties through Composition Design. New Journal of Chemistry 2014, 38, 3112–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ao, Q.; Tian, X.; Fan, J.; Tong, H.; Hou, W; Bai, S. Gelatin-based hydrogels for organ 3D bioprinting. Polymers 2017, 9, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chen, W.; Chen, G.; Tian, J. Rapid Shape Memory TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Nanofibers/Polyacrylamide/Gelatin Hydrogels with Enhanced Mechanical Strength. Carbohydr Polym 2017, 171, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Kimura, S.; Nishiyama, Y.; Biomacromolecules, A.I.-. ; 2007, undefined Cellulose Nanofibers Prepared by TEMPO-Mediated Oxidation of Native Cellulose. ACS Publications 2007, 8, 2485–2491. [Google Scholar]
- Gaharwar, A.K.; Peppas, N.A.; Khademhosseini, A. Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Biotechnol Bioeng 2014, 111, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraguchi, K; Takehisa, T. Nanocomposite hydrogels: A unique organic–inorganic network structure with extraordinary mechanical, optical, and swelling/de-swelling properties. Advanced materials 2002, 14, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannert, C.; Stokke, B.T.; Dias, R.S. Nanoparticle-Hydrogel Composites: From Molecular Interactions to Macroscopic Behavior. Polymers 2019, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.F; Lee, S.C. Effect of hydrotalcite on the swelling and mechanical behaviors for the hybrid nanocomposite hydrogels based on gelatin and hydrotalcite. Journal of applied polymer science 2006, 100, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.V.; Hernandez, A. A Review of Additive Manufacturing. ISRN Mechanical Engineering 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Leu, M.C. Additive Manufacturing: Technology, Applications and Research Needs. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering 2013, 8, 215–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, I.; Rosen, D.; Stucker, B. Additive Manufacturing Technologies: 3D Printing, Rapid Prototyping, and Direct Digital Manufacturing, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Urruela-Barrios, R.; Ramírez-Cedillo, E.; de León, A.D.; Alvarez, A.J.; Ortega-Lara, W. Alginate/Gelatin Hydrogels Reinforced with TiO2 and β-TCP Fabricated by Microextrusion-Based Printing for Tissue Regeneration. Polymers 2019, 11, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distler, T.; Polley, C.; Shi, F.; Schneidereit, D.; Ashton, M.D.; Friedrich, O.; Kolb, J.F.; Hardy, J.G.; Detsch, R.; Seitz, H.; et al. Electrically Conductive and 3D-Printable Oxidized Alginate-Gelatin Polypyrrole:PSS Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering. Adv Healthc Mater 2021, 10, 2001876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kara, A.; Distler, T.; Polley, C.; Schneidereit, D.; Seitz, H.; Friedrich, O.; Tihminlioglu, F.; Boccaccini, A.R. 3D Printed Gelatin/Decellularized Bone Composite Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering: Fabrication, Characterization and Cytocompatibility Study. Mater Today Bio 2022, 15, 100309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tytgat, L.; van Damme, L.; van Hoorick, J.; Declercq, H.; Thienpont, H.; Ottevaere, H.; Blondeel, P.; Dubruel, P.; van Vlierberghe, S. Additive Manufacturing of Photo-Crosslinked Gelatin Scaffolds for Adipose Tissue Engineering. Acta Biomater 2019, 94, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoorick, J.; Gruber, P.; Markovic, M.; Rollot, M.; Graulus, G.J.; Vagenende, M.; Tromayer, M.; van Erps, J.; Thienpont, H.; Martins, J.C.; et al. Highly Reactive Thiol-Norbornene Photo-Click Hydrogels: Toward Improved Processability. Macromol Rapid Commun 2018, 39, 1800181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovsianikov, A.; Deiwick, A.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Dubruel, P.; Möller, L.; Dräger, G; Chichkov, B. Laser fabrication of three-dimensional CAD scaffolds from photosensitive gelatin for applications in tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoorick, J.; Ovsianikov, A.; Dubruel, P; Van Vlierberghe, S. Photo-crosslinkable gelatin hydrogels: versatile materials for high-resolution additive manufacturing. Mater Matters 2018, 13, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Oyen, M.L. Mechanical characterisation of hydrogel materials. International Materials Reviews 2014, 59, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.D. Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers, 3rd ed. Wiley, New York, 1980.
- Vedadghavami, A.; Minooei, F.; Mohammadi, M.H.; Khetani, S.; Rezaei Kolahchi, A.; Mashayekhan, S.; Sanati-Nezhad, A. Manufacturing of Hydrogel Biomaterials with Controlled Mechanical Properties for Tissue Engineering Applications. Acta Biomater 2017, 62, 42–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, E.; Corona, J.E.; Oliva, A.I.; Avilés, F.; González-Hernández, J. Universal Testing Machine for Mechanical Properties of Thin Materials. Revista mexicana de física 2010, 56, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Costa-Pinto, A.R.; Reis, R.L; Neves, N.M. Scaffolds based bone tissue engineering: the role of chitosan. Tissue Engineering Part B: Reviews 2011, 17, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A. Advent and Maturation of Regenerative Medicine. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine 2013, 10, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lickorish, D.; Guan, L.; Davies, J.E. A Three-Phase, Fully Resorbable, Polyester/Calcium Phosphate Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering: Evolution of Scaffold Design. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, C.; Dinda, A.K.; Potdar, P.D.; Chou, C.F.; Mishra, N.C. Fabrication and Characterization of Novel Nano-Biocomposite Scaffold of Chitosan–Gelatin–Alginate–Hydroxyapatite for Bone Tissue Engineering. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2016, 64, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Patil, S.; Gao, Y.G.; Qian, A. The Bone Extracellular Matrix in Bone Formation and Regeneration. Front Pharmacol 2020, 11, 521497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, C.; Dinda, A.K.; Mishra, N.C. Synthesis and Characterization of Glycine Modified Chitosan-Gelatin-Alginate Composite Scaffold for Tissue Engineering Applications. J Biomater Tissue Eng 2012, 2, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Chou, C.F.; Dinda, A.K.; Potdar, P.D.; Mishra, N.C. Surface Modification of Nanofibrous Polycaprolactone/Gelatin Composite Scaffold by Collagen Type I Grafting for Skin Tissue Engineering. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2014, 34, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Gautam, S.; Dinda, A.; Lett, N.M.-. Adv.Mater.; 2011, undefined Cartilage Tissue Engineering: Current Scenario and Challenges. aml.iaamonline.org 2011, 2, 90–99. [Google Scholar]
- Rottensteiner, U.; Sarker, B.; Heusinger, D.; Dafinova, D.; Rath, S.N.; Beier, J.P.; Kneser, U.; Horch, R.E.; Detsch, R.; Boccaccini, A.R.; et al. In Vitro and in Vivo Biocompatibility of Alginate Dialdehyde/Gelatin Hydrogels with and without Nanoscaled Bioactive Glass for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications. Materials 2014, 7, 1957–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Wu, Q.; Long, H.; Hu, K.; Li, P.; Wang, C.; Sun, M.; Dong, J.; Wei, X.; Suo, J.; Hua, D. Development of chitosan/gelatin hydrogels incorporation of biphasic calcium phosphate nanoparticles for bone tissue engineering. Journal of Biomaterials Science, Polymer Edition 2019, 30, 1636–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumaran, S.; Radhakrishnan, A.; Rauf, A.A.; Kurup, G.M. Nanohydroxyapatite Incorporated Photocrosslinked Gelatin Methacryloyl/Poly(Ethylene Glycol)Diacrylate Hydrogel for Bone Tissue Engineering. Prog Biomater 2021, 10, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, A.J.; Coutinho, O.P.; Reis, R.L. Bone Tissue Engineering: State of the Art and Future Trends. Macromol Biosci 2004, 4, 743–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Dubey, N.; Ribeiro, J.S.; Bordini, E.A.F.; Ferreira, J.A.; Xu, J.; Castilho, R.M.; Bottino, M.C. Metformin-Loaded Nanospheres-Laden Photocrosslinkable Gelatin Hydrogel for Bone Tissue Engineering. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 2021, 116, 104293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Banerjee, R. Biopolymer-Based Hydrogels for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Chem Rev 2011, 111, 4453–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asti, A; Gioglio, L. Natural and synthetic biodegradable polymers: different scaffolds for cell expansion and tissue formation. The International journal of artificial organs 2014, 37, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, M.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Mohandes, F.; Dolatyar, B.; Zeynali, B. In Vitro Study of Alginate–Gelatin Scaffolds Incorporated with Silica NPs as Injectable, Biodegradable Hydrogels. RSC Adv 2021, 11, 16688–16697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Jin, X.; Cong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fu, J. Degradable Natural Polymer Hydrogels for Articular Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology 2013, 88, 327–339. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.H.; Liu, H.C.; Lin, C.C.; Chou, C.H.; Lin, F.H. Gelatin–Chondroitin–Hyaluronan Tri-Copolymer Scaffold for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4853–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
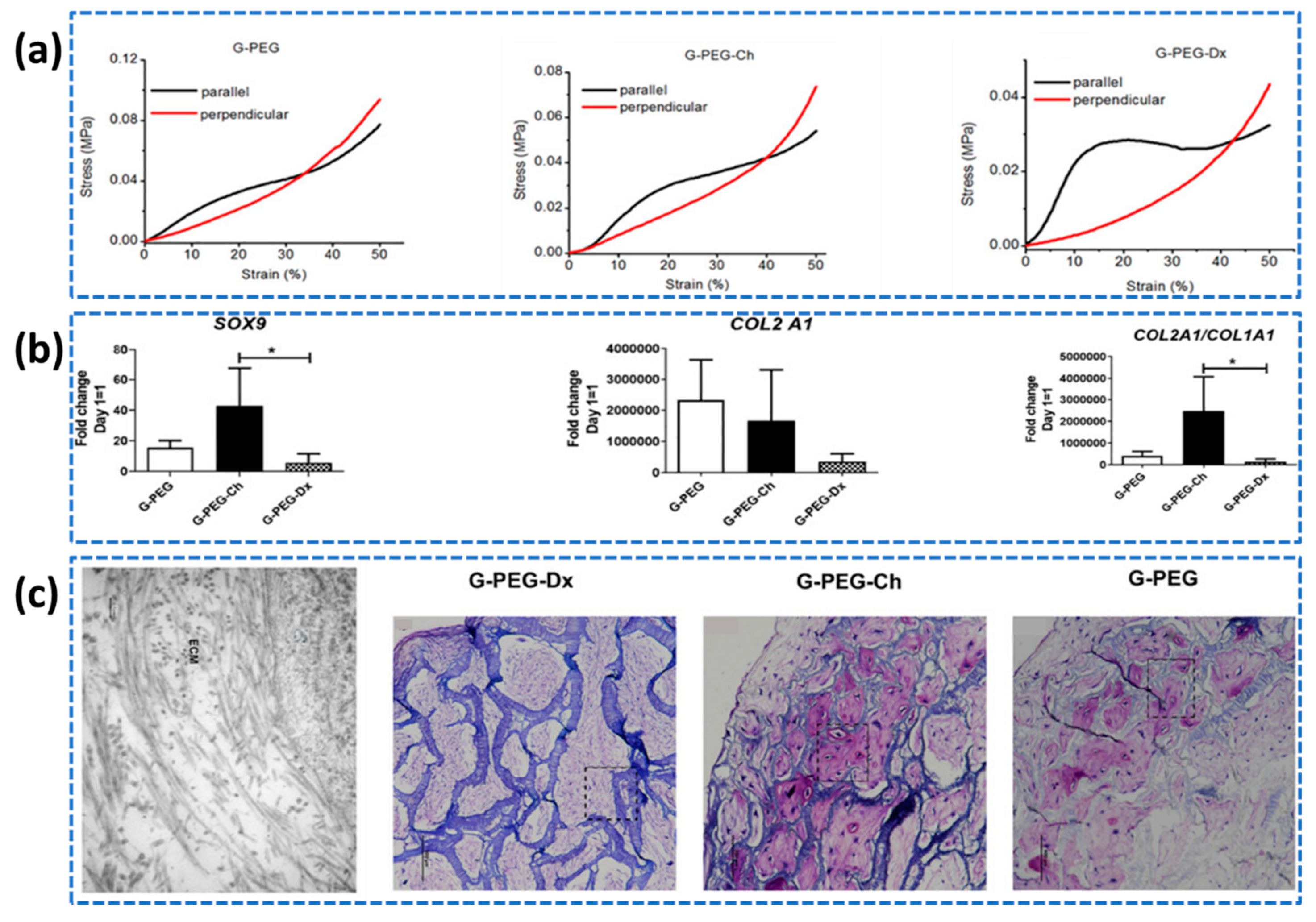
- Sartore, L.; Manferdini, C.; Saleh, Y.; Dey, K.; Gabusi, E.; Ramorino, G.; Zini, N.; Almici, C.; Re, F.; Russo, D.; Mariani, E. Polysaccharides on gelatin-based hydrogels differently affect chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2021; 126, 112175. [Google Scholar]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; de Ferranti, S.; Després, J.P.; Fullerton, H.J.; Howard, V.J.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2015 Update : A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 131, e29–e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlic, D.; Kajstura, J.; Chimenti, S.; Jakoniuk, I.; Anderson, S.M.; Li, B.; Pickel, J.; McKay, R.; Nadal-Ginard, B.; Bodine, D.M.; et al. Bone Marrow Cells Regenerate Infarcted Myocardium. Nature 2001, 410, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.R.; Hatzistergos, K.E.; Addicott, B.; McCall, F.; Carvalho, D.; Suncion, V.; Morales, A.R.; Da Silva, J.; Sussman, M.A.; Heldman, A.W.; et al. Enhanced Effect of Combining Human Cardiac Stem Cells and Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Reduce Infarct Size and to Restore Cardiac Function After Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2013, 127, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelmayr, G.C.; Cheng, M.; Bettinger, C.J.; Borenstein, J.T.; Langer, R.; Freed, L.E. Accordion-like Honeycombs for Tissue Engineering of Cardiac Anisotropy. Nature Materials 2008, 7, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, W.H.; Melnychenko, I.; Wasmeier, G.; Didié, M.; Naito, H.; Nixdorff, U.; Hess, A.; Budinsky, L.; Brune, K.; Michaelis, B.; et al. Engineered Heart Tissue Grafts Improve Systolic and Diastolic Function in Infarcted Rat Hearts. Nature Medicine 2006, 12, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leor, J.; Aboulafia-Etzion, S.; Dar, A.; Shapiro, L.; Barbash, I.M.; Battler, A. ; Granot, Y; Cohen, S. ; 2000. Bioengineered cardiac grafts: a new approach to repair the infarcted myocardium?. Circulation, 2000, 102, 56–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ungerleider, J.L.; Johnson, T.D.; Rao, N.; Christman, K.L. Fabrication and Characterization of Injectable Hydrogels Derived from Decellularized Skeletal and Cardiac Muscle. Methods 2015, 84, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C. Injectable Cardiac Tissue Engineering for the Treatment of Myocardial Infarction. J Cell Mol Med 2010, 14, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, A.; Khattab, A.; Islam, M.A.; Hweij, K.A.; Zeitouny, J.; Waters, R.; Sayegh, M.; Hossain, M.M.; Paul, A. Injectable Hydrogels for Cardiac Tissue Repair after Myocardial Infarction. Advanced Science 2015, 2, 1500122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaei, A.; Truong, D.; Heffernan, J.; Cutts, J.; Brafman, D.; Sirianni, R.W.; Vernon, B.; Nikkhah, M. PNIPAAm-Based Biohybrid Injectable Hydrogel for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Acta Biomater 2016, 32, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
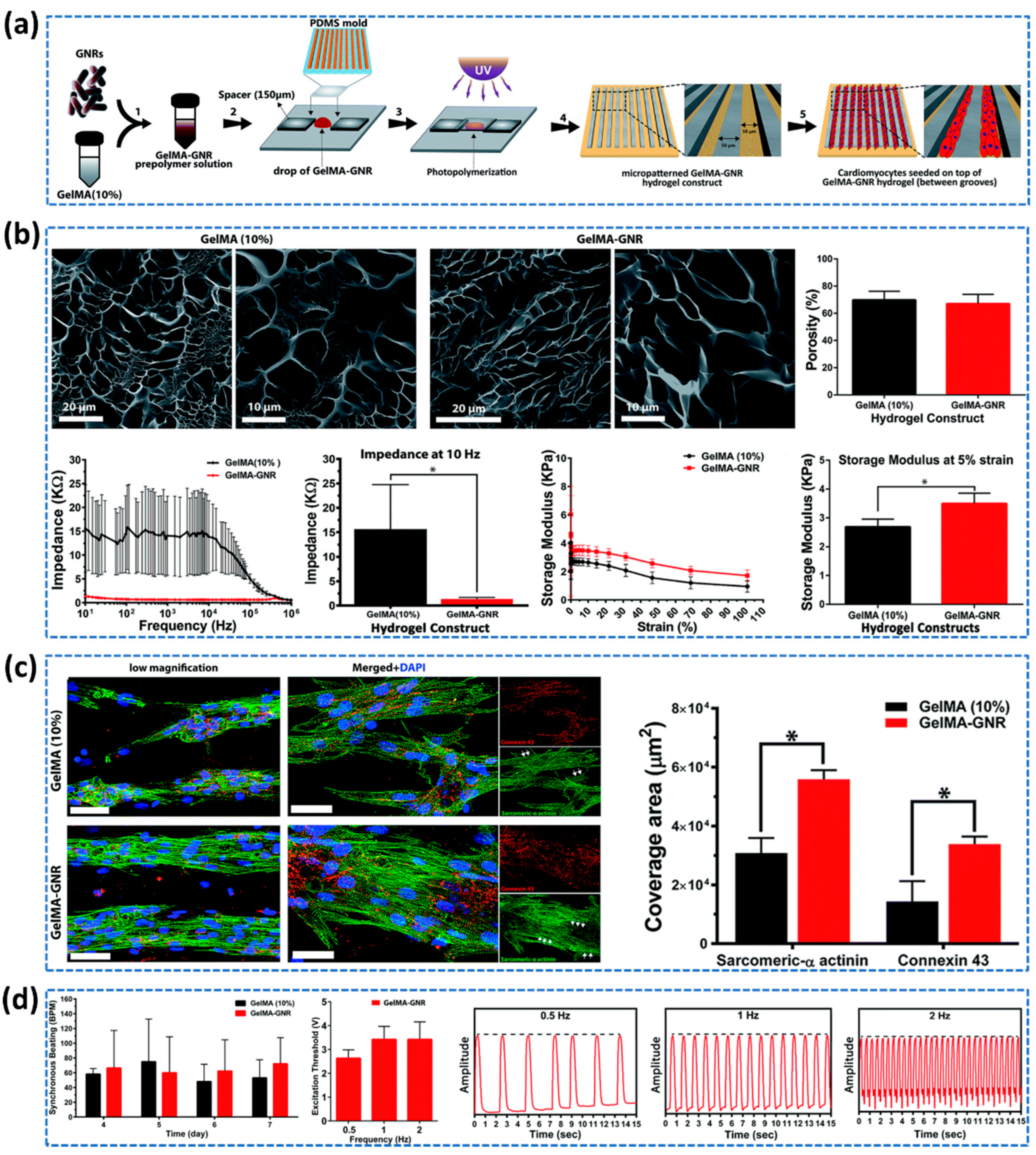
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, N.; Meng, H.X.; Liu, H.X.; Lu, Y.Q.; Liu, C.M.; Zhang, Z.M.; Qu, K.Y; Huang, N.P. Easy applied gelatin-based hydrogel system for long-term functional cardiomyocyte culture and myocardium formation. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering 2019, 5, 3022–3031. [Google Scholar]
- Navaei, A.; Saini, H.; Christenson, W.; Sullivan, R.T.; Ros, R.; Nikkhah, M. Gold Nanorod-Incorporated Gelatin-Based Conductive Hydrogels for Engineering Cardiac Tissue Constructs. Acta Biomater 2016, 41, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaei, A.; Moore, N.; Sullivan, R.T.; Truong, D.; Migrino, R.Q; Nikkhah, M. Electrically conductive hydrogel-based micro-topographies for the development of organized cardiac tissues. RSC advances 2017, 7, 3302–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
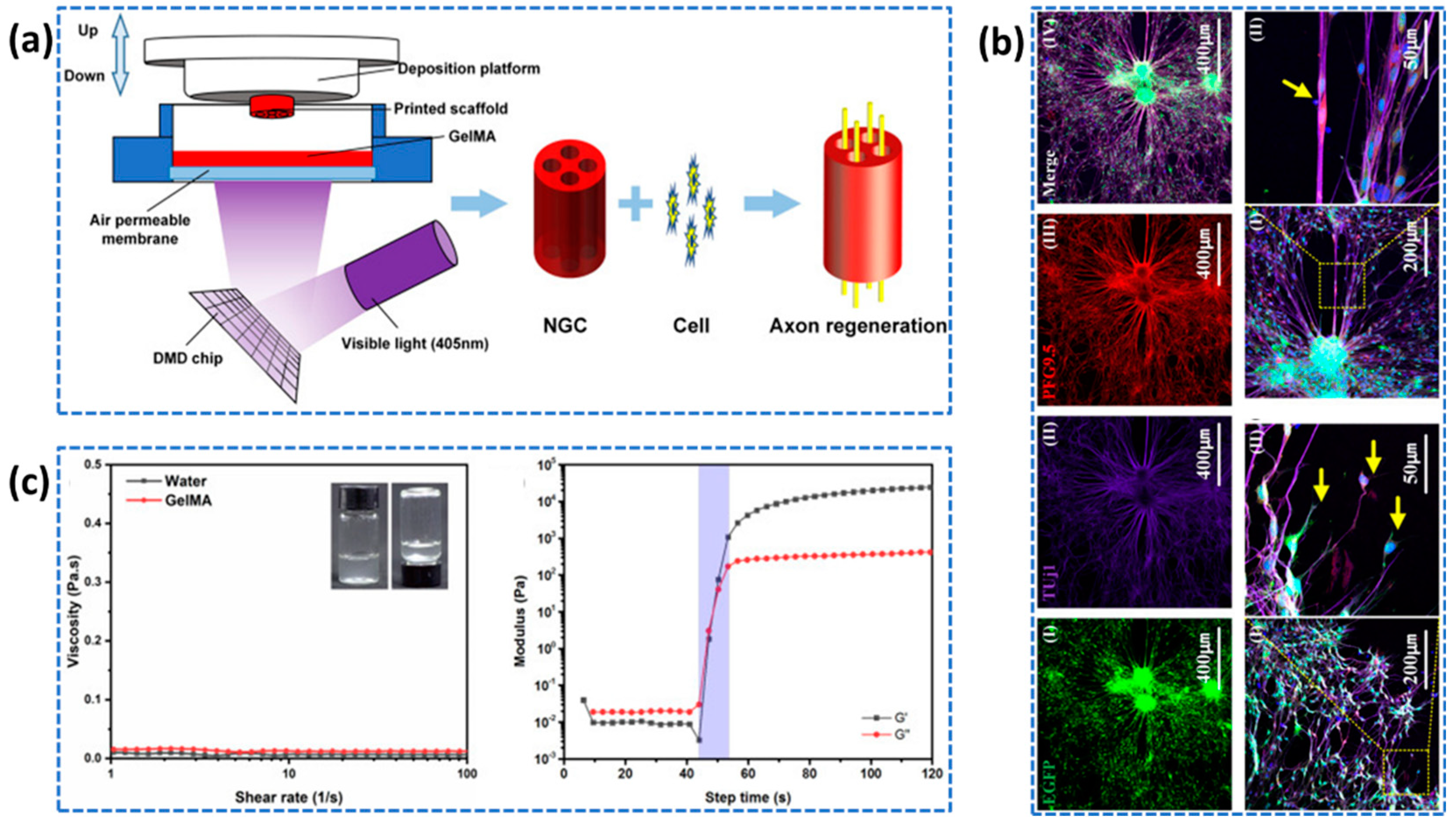
- Gnavi, S.; di Blasio, L.; Tonda-Turo, C.; Mancardi, A.; Primo, L.; Ciardelli, G.; Gambarotta, G.; Geuna, S.; Perroteau, I. Gelatin-Based Hydrogel for Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Release in Peripheral Nerve Tissue Engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 2017, 11, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Xiong, Z.; Lin, F.; Wu, R; Zhang, R. Three-dimensional gelatin and gelatin/hyaluronan hydrogel structures for traumatic brain injury. Journal of bioactive and compatible polymers 2007, 22, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Li, H.; Yu, K.; Xie, C.; Wang, P.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, P.; Xiu, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, F.; He, Y. 3D printing of gelatin methacrylate-based nerve guidance conduits with multiple channels. Materials & Design 2020, 192, 108757. [Google Scholar]
| Hydrogel system | Mode of testing/Testing instrument | Type of crosslinking | Crosslinker | Young’s modulus (kPa) | Tensile strength (kPa) |
Failure strength (kPa) | Compressive modulus (kPa) | Storage modulus (kPa) |
Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAN-gelatin cryogel | Dynamic mechanical analyzer (DMA) | Free radical polymerization | N,N’-methylene bis(acrylamide) and glutaraldehyde | 123-819 | [160] | ||||
| GelMA–SF | Instron 5542 mechanical tester | UV irradiation | ≈ 70 | [76] | |||||
| PVA/GE | Tensile | Enzymatic and physical | mTG | 980±2.45 | 750±0.18 | [161] | |||
| GelMA with alginate | Compression | UV irradiation | Ca2+ ion | 201.2±5.5 | [162] | ||||
| GelMA with alginate (fish gelatin) | Unconfined compression | UV irradiation | Ca2+ ion | 48.6±4.7 | [162] | ||||
| Gelatin/PVA/PEG | Unconfined compression | Physical crosslinking | PVA | 189-351 | [163] | ||||
| GGMA/GelMA DN | Unconfined, uniaxial compression test | Photo-crosslinking | 110 | 6900±100 | [164] | ||||
| Gelatin/PAAm | Uniaxial tensile test | Physical and covalent crosslinking | 84 | 268 | [165] | ||||
| Bacterial cellulose-gelatin | Tensile and compression | Chemical crosslinking | N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N’-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) | 6700 | 610 | [166] | |||
| Gelatin/PAM DN | Compression | Initiator-induced polymerization | 1.76 | 150 | 3.52 | [167] | |||
| Gelatin/PAAm/GO NC-DN gel | Free radical polymerization | N, N′-methyl-bis-acrylamide | 187.3 | 324 | [168] | ||||
| Gelatin/PAAm DN gel | Free radical polymerization | N, N′-methyl-bis-acrylamide | 76.4 | 306 | [168] | ||||
| γ-PGA-GEL DN hydrogel | Compression | Physical and covalent crosslinking | 270 | 38000 | [169] | ||||
| GelMA/HA-HYD DN hydrogel | Compression and tensile | Photo-crosslinking | 101±6.41 | [170] | |||||
| CAG cryogels | Unconfined compression | Chemical crosslinking | Glutaraldehyde | 120 | 44 | [171] | |||
| Gelatin/PAAm/Laponite Nanocomposite | Compression and Tensile | Radical polymerization | N,N′-Methylenebis- (acrylamide) |
20.5±0.2 | 337.9±4.9 | 208.4±5.9 | [172] | ||
| RGO-gelatin hydrogel | DMA | Chemical crosslinking | Graphene oxide | 172.3 | [173] | ||||
| MA-gelatin/PAAm hydrogel | Compressive and tensile | Free radical copolymerization |
22.4±0.3 | 15.5±0.1 | [174] | ||||
| Graphene Oxide–Gelatin Nanocomposite hydrogel | Oscillatory shear measurement |
Physical crosslinking | 114.5 | [175] | |||||
| Gelatin−short linear glucan (SLG) nanocomposite hydrogels | Texture profile analysis | 50 | 1.9 | [176] | |||||
| Oxidized Alginate/Grlatin/Silicon Carbide Nanoparticle hydrogel (OA/GEL/SiC NPs) | Compressive and tensile | Chemical or/and physical crosslinking | N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) and 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC) | 9.25±0.05 | [177] | ||||
| 3D gelatin-chitosan hybrid hydrogel | Compressive | Chemical and physical | PEG | 680 | 250 | [178] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




