1. Introduction
Chagas disease (CD) is caused by the insect-transmitted protozoan parasite
Trypanosoma cruzi and has a major impact on public health throughout Latin America, where 6-7 million people are infected [
1]. Due to migration, CD is increasingly being diagnosed in non-endemic regions, particularly the US and Europe. Globally, infection with
T. cruzi is the most common cause of infectious cardiomyopathy [
2]. The initial acute stage of the disease is characterised by a widely disseminated infection and a readily detectable parasitemia. In most cases, symptoms are mild and non-specific, although on occasions there can be serious and life-threatening consequences including myocarditis or meningoencephalitis [
3,
4]. After 2-8 weeks, with the induction of an adaptive immune response, in which CD8
+ IFN-γ
+ T cells play a major role, the infection typically transitions to an asymptomatic chronic stage in which the parasite burden is extremely low [
5,
6]. Approximately 30% of infected individuals will develop Chronic Chagas Cardiomyopathy (CCC), although the condition can take many years or decades to become symptomatic. This can give rise to a wide-spectrum of manifestations, ranging from minor myocardial involvement to left ventricular systolic dysfunction, dilated cardiomyopathy (myofiber hypertrophy and interstitial fibrosis), arrhythmias, thromboembolic events and terminal cardiac failure, including sudden death [
3,
7,
8]. Electrocardiography (ECG) has played a key role in CD patient evaluation and management [
9,
10]. It represents a low-cost diagnostic method and can be predictive of CCC outcomes [
11,
12].
Overall, individuals with CD have a 40% prevalence of ECG abnormalities [
9], and conditions such as right bundle branch block (RBBB) can be up to 15 times higher than in seronegative individuals [
13]. In children and young adults, the incidence of ECG alterations has been found to be similar to that in older adults, suggesting a potential for early onset cardiac disease [
9,
13]. Identifying the triggers of ECG changes and their relative importance has been difficult in humans because of the long period over which CCC develops and the highly diverse nature of the symptoms. The mechanisms that drive these cardiac abnormalities in CD patients have been the subject of multiple studies, focused on the central question of whether parasite persistence is required to cause those changes. Experimental studies have shown that cardiac disease intensity can be linked to infection with specific parasite strains [
14,
15], and that such outcomes are also influenced by the genetic background of the animal model [
16,
17,
18]. However, the role of other factors such as environment, nutrition and health status, and how they contribute to the effectiveness of the host immune response and the development, or otherwise, of CCC are less well understood.
There is now a general view that the presence of the parasite is required to promote the development of CCC [
18,
19,
20]. However, in experimental murine models of CD, cardiac damage is often present in the absence of locally detectable infection at the time of tissue sampling [
16,
21]. This has led to the suggestion that transient episodes of low-level
T. cruzi infection of the heart trigger cycles of inflammation that result in local clearance of parasites, but give rise to cumulative damage to the myocardium [
22]. Elucidating the underlying mechanisms responsible for myocardial dysfunction in CD has major implications for diagnosis, risk stratification and clinical management. This highlights the need for improved predictive models to aid research on disease pathogenesis and therapies that might reverse or block the resulting pathology. It is a requirement of such models that they capture the heterogeneous nature of human Chagas heart disease in terms of both the temporal profile and disease severity.
Here, we evaluated C3H/HeN mice infected with
T. cruzi JR strain as an experimental model to monitor the development of heart disease. In terms of cardiac fibrosis, this infection model gives rise to a spectrum of pathology ranging from modest to severe [
16,
18]. Using highly sensitive
in vivo imaging technology, histological analysis and non-invasive, anaesthesia-free ECG, we undertook an longitudinal analysis of Chagas heart disease development during acute and chronic infections. This has allowed us to monitor the progressive impact of
T. cruzi infection on several parameters of cardiac function relevant to human CD.
2. Materials and Methods
Animal infections were performed under UK Home Office project licences PPL 70/8207 and PPL P9AEE04E4 and approved by the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine Animal Welfare and Ethical Review Board (AWERB). All protocols and procedures were conducted in accordance with the UK Animals (Scientific Procedures) Act 1986. Female BALB/c and C3H/HeN mice were purchased from Charles River (UK), and CB17 SCID mice were bred in-house. Animals were maintained under specific pathogen-free conditions in individually ventilated cages. They experienced a 12-hour light/dark cycle, with access to food and water ad libitum. SCID mice were infected with 1x10
4 culture trypomastigotes in 0.2 ml PBS via i.p. injection. Female C3H/HeN and BALB/c mice, aged 7-8 weeks, were infected by i.p injection with 1x10
3 trypomastigotes derived from SCID mouse blood [
23]. At experimental end-points, mice were sacrificed by exsanguination under terminal anaesthesia. To reflect the genetic diversity of
T. cruzi, we selected strains JR (Discrete Typing Unit (DTU) I) and CL Brener (DTU VI), both of which were modified to express a red-shifted luciferase [
16,
21,
24]. Initially, 3 infection combinations were investigated based on previous studies which had revealed a range of cardiac fibrosis outcomes [
16,
18]; strain JR in C3H/HeN mice, strain CL Brener in C3H/HeN mice, and strain CL Brener in BALB/c mice.
ECGenie (Mouse Specifics Inc., Boston, MA) is a rapid non-invasive device that facilitates ECG data acquisition from conscious mice without surgery, implants or anaesthesia [
25,
26,
27]. The instrument detects cardiac electrical activity through direct contact between the mouse paws and disposable footplate electrodes. For data recording, mice were gently removed from their cages and positioned on the ECG platform. An array of gel coated ECG electrodes embedded in the floor of the platform provided contact with paws. To avoid handling-induced alterations in heart rate, each mouse was permitted to acclimatise on the platform for at least 5 minutes prior to collection of baseline data. An average of ~229 signals per mouse per time point were acquired to evaluate changes in the heart physiology during long-term
T. cruzi infection.
Each signal was analysed using the software EzCG e-MOUSE, an internet-based physiological waveform analysis portal. The software incorporates Fourier analyses and linear time-invariant digital filtering of frequencies below 2 Hz and above 100 Hz to minimise environmental signal disturbances [
25,
26,
27]. The software uses peak detection algorithms to detect R waves, and a series of artificial intelligence algorithms to identify the PQRST morphology and interval durations. We cannot therefore comment on the amplitude of the ECG descriptors, though only signals in which clear PQRST morphology could be detected were included. After indeterminate signals were manually excluded, unbiased signal processing algorithms computed all ECG interval durations. Upon analysis, data were automatically compiled into a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. Arrhythmias were identified by analyses of ECG tracings as irregular RR intervals (the time between R-waves of the QRS signal), premature atrial or ventricular complexes, as well as the presence of broad complex tachycardia.
For
in vivo bioluminescence imaging, infected mice were injected with 150 mg kg
-1 d-luciferin i.p., anaesthetized using 2.5% (v/v) isoflurane in oxygen for 2-3 minutes, and then imaged using an IVIS Spectrum system (Caliper Life Sciences) [
23]. Exposure times varied from 10 seconds to 5 minutes, depending on signal intensity. The detection threshold was established from uninfected mice. After imaging, mice were revived and returned to cages. To avoid any influence of isoflurane on cardiac data, we allowed a gap of at least 48 hours between imaging and ECG analysis, and minimised the total number of imaging events.
For
ex vivo imaging, mice were injected with 150 mg kg
-1 d-luciferin i.p. 5-7 minutes before terminal euthanasia using dolethal (200 mg kg
-1). Trans-cardiac perfusion was performed with 10 ml of 0.3 mg ml
-1 d-luciferin in DPBS (Dulbecco′s Phosphate Buffered Saline). Tissues and organs of interest were collected and the heart was bisected along the coronal plane. Samples were soaked in DPBS containing 0.3 mg ml
-1 d-luciferin. Bioluminescence imaging was performed as above. To estimate parasite burden in the heart tissue, regions of interest (ROIs) were drawn using Living Image 4.7.3 to quantify bioluminescence expressed as total flux (photons/second; p/s). Data from infected mice were normalised using matching hearts from uninfected mice to establish the fold-change in radiance [
21].
For in-depth assessment of cardiac physiological changes during T. cruzi infection, mice were euthanised using dolethal (200 mg kg-1) and heart tissue samples collected. They were fixed in either 10% neutral buffered formalin (Sigma) or Glyo-Fixx (Epredia), then dehydrated in ethanol, cleared in Histo-clear, and embedded in paraffin. Three-micron heart sections were stained with Haematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) and analysed at 20X using a DFC295 camera attached to a DM3000 light-emitting diode microscope (Leica, Germany). Images were digitalised for histomorphometric analysis using the software Leica Application Suite V.4.12. For the inflammatory index, the total number of cells were counted in 10 microscope fields (area 2.66 x 105 μm²) from across the base of the heart (5 fields from different sides of the heart) at 200X magnification per tissue section. The inflammation index for each animal was calculated as the average of the 10 randomly selected images. Each individual mouse received a code so that tissue section analysis could be blinded.
For antigen retrieval, deparaffinised heart sections were submerged in 10 mM sodium citrate buffer (pH 6.0) containing 0.05% Tween-20 and heated to 96°C for 30 minutes. Sections were then blocked in 2.5% normal horse serum. Endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched by incubating with 3% hydrogen peroxide. Slides were then incubated with rabbit polyclonal anti-iNOS IgG antibody (ab15325, Abcam) at a 1:50 dilution at 4°C overnight. The secondary antibody ImmPRESS horse anti-rabbit IgG peroxidase polymer (VectorLabs) was used at its stock concentration without dilution. The reaction was visualised by incubating the section with 3,3’-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride ImmPACTTM DAB substrate kit (VectorLabs). Images were digitalised for histomorphometric analysis using the software Leica Application Suite V.4.12. For iNOS analysis, 15 images were taken across the whole heart, 5 of which were from the base (ventricular area). The top of the heart consists primarily of the atria and the proximal part of the coronary vessels; adipose rich areas were also found in some tissues. The number of DAB+ (brown) pixels was counted in 15 microscope fields (area 2.66 x 105 μm²) at 200X magnification per tissue section. The iNOS index was quantified as the total DAB+ area per image for each animal and calculated as the average of the 15 randomly selected images. As above, analysis of tissue sections was carried out under blinded conditions.
Heart tissue samples were snap frozen on dry ice and stored at −70°C. For RNA extraction, samples were thawed and homogenised in 1 ml Trizol (Invitrogen) per 30-50 mg of tissue using a Precellys 24 homogeniser (Bertin). To each sample, 200 µl of chloroform was added and mixed by vortex after which the phases were separated by centrifugation at 13,000 g at 4°C. RNA was extracted from the aqueous phase using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen) with on-column DNAse digestion, as per manufacturer’s protocol. The quantity and quality of RNA was assessed using Qubit Fluorimeter (Thermofisher). cDNA was synthesised from 1 µg of total RNA using Superscript IV VILO mastermix (Invitrogen), as per manufacturer’s protocol, in reaction volumes of 20 μl. qPCR reactions contained 4 µl of cDNA (1:50 dilution) and 100 nM of each primer (
Table 1) and QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR master mix (Qiagen). Reactions were run in duplicate using an Applied Biosystems 7500 fast RT-PCR machine (Thermofisher), using reaction conditions of 15 minutes at 95°C (holding) followed by 40 cycles of 15 seconds at 94°C, 30 seconds at 60°C and 30 seconds at 72°C. Each plate included a duplicate no template control. Data were analysed by the ΔΔCt method [
28] using murine Gapdh as the endogenous control gene. The significance level for the fold-difference in gene expression in the infected group was set at the average fold-difference ± 2 standard deviations (SDs) of the non-infected group.
Individual animals were used as the unit of analysis, unless otherwise stated. Groups were compared with the Kruskal-Wallis test for continuous variables and the Chi square test for categorical variables, and corrected for multiple testing with the post hoc Dunnett’s test or the Benjamini-Hochberg procedure to control the false discovery rate at 5%. The statistical analysis was conducted with GraphPad Prism 10.0.3 and SAS 9.4. For the histopathological investigation, unpaired two-sided Student’s t-tests were performed. A value of P < 0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
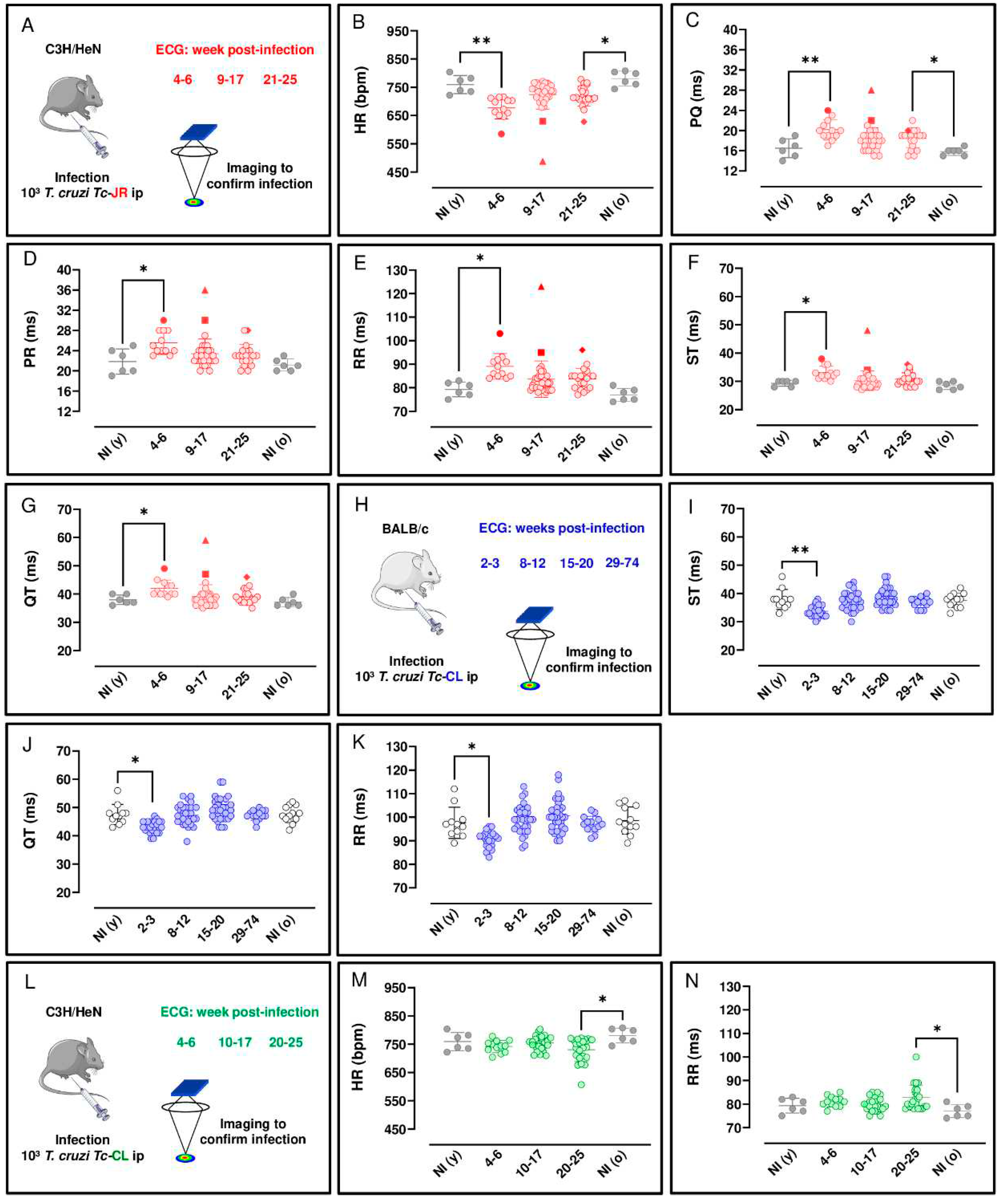
3.1. Longitudinal ECG monitoring of T. cruzi infected mice
Several reports have described the use of ECG to assess cardiac function during experimental T. cruzi infection [
29,
30,
31,
32]. However, these systems have required anaesthesia, surgery or implanted electrodes, interventions that can suppress cardiovascular activity and/or perturb heart rate (HR). As a more relevant approach, we used ECGenie, a cardiac monitoring device that allows rapid acquisition of data in a non-invasive, anaesthesia-free manner (Materials and Methods). First, we examined C3H/HeN mice infected with the T. cruzi JR strain, since severe cardiac fibrosis can develop in this infection model [
18]. Longitudinal ECG monitoring was carried out during the acute stage, weeks 4-6 in this model, and at various points following transition to the chronic infection (week 8 onwards). There were no significant age-matched differences between non-infected mice assessed at the beginning and end of the experimental period (i.e young vs old). Significant ECG changes were observed as a result of infection. These included a reduction in HR during both acute (P = 0.001) and chronic (P = 0.014) stages of infection, relative to non-infected age-matched controls (
Figure 1B). In line with the overall bradycardia, we observed prolonged PQ intervals (the period of atrial contraction) during both the acute (P = 0.009) and chronic (P = 0.025) stages (
Figure 1C) relative to non-infected age-matched controls. Similarly, there was an increase in the PR interval during the acute stage relative to non-infected age-matched controls (P = 0.039) (
Figure 1D). With the RR interval (the time between consecutive heart beats), and ST and QT intervals (two overlapping parameters that are indicators of ventricular repolarisation and depolarisation), there was an increase during the acute stage (P = 0.001, 0.019 and 0.044, respectively) relative to non-infected age-matched controls (
Figure 1E, F and G). Therefore, acute and chronic infections of C3H/HeN mice with the T. cruzi JR strain were both associated with a greater prevalence of ECG conduction abnormalities. Specifically, there was a clear bradycardia phenotype, which was more pronounced in the acute phase, linked with increased interval times across the cardiac cycle. During the chronic phase, bradycardia persisted, but the association became more specifically linked to an increased PQ interval. No other changes were detected during acute or chronic stage infections in comparison with age-matched controls.
ECG correlations were observed in the C3H/HeN:JR mice during the acute stage (4-6 wpi) on infection. We found a significant, strong, negative association between HR x RR and QT, r(10) = -.99 and -.89, respectively, P <.001. A significant, strong, positive correlation was observed between PR x PQ, r(10) = .92, P <.001 and QT x ST and RR, r(10) = .92 and .90, respectively, P <.001.
Various ECG abnormalities were identified in this mouse model over the course of the infection with T. cruzi. During the acute stage, sinus bradycardia (SB) was detected in 33% of mice (4/12). This arrhythmia is defined by the presence of frequent sinus pauses in between bursts of normal activity, where a slower pulse rate originates from functional impairment of the heart sinus. In addition, during the chronic stage of infection, 9% of mice (3/38) displayed left anterior fascicular block (LAFB), an abnormality defined by axis left deviation, and which may be associated with myocardial fibrosis. Thus, heart conduction disorders have a heterogeneous pattern in this infection model, with a range of symptoms that parallel the diverse nature of the pathology in human disease. Right bundle branch block (RBBB), a heart conduction disorder defined as the presence of broad, notched, or split QRS complexes, was also prevalent, and was identified in 24% of mice (7/29) during the chronic stage. Also, ventricular extrasystole (VE), an arrhythmia that results in an extra beat due to premature ventricular contraction, was observed in one third of the acutely infected mice examined, although this fell to 15% (4/26) during the chronic stage of infection.
For comparison, we next examined BALB/c mice infected with the T. cruzi CL Brener strain on cardiac function. At the peak of the acute stage, (2-3 wpi in this experimental model), we found that there was an decrease for ST, QT and RR intervals at 2-3 wpi relative to non-infected age-matched controls (P = 0.006, 0.011 and 0.037, respectively), (Figures 1I, J and K, respectively). No other changes were detected in this model during acute or chronic stage infections in comparison with age-matched controls.
We also investigated the cardiac impact of C3H/HeN mice model infected with the
T. cruzi CL Brener strain. In the acute stage, 4-6 wpi, there was no observable impact on HR, although by the chronic stage of infection (20-25 wpi), compared to non-infected age-matched controls, there was a significant reduction (
P = 0.037) at a population level (
Figure 1M). We also observed prolonged RR intervals, the mean duration between depolarization repolarization cycles (
P = 0.0
32) during the chronic stage (
Figure 1N) relative to non-infected age-matched controls. A predictable direct inverse relation between HR and RR interval duration was observed in the C3H/HeN mice infected with both parasite strains in this study (
Figure 1B, E, M and N). No other changes in the measured ECG parameters were detected in these infected mice.
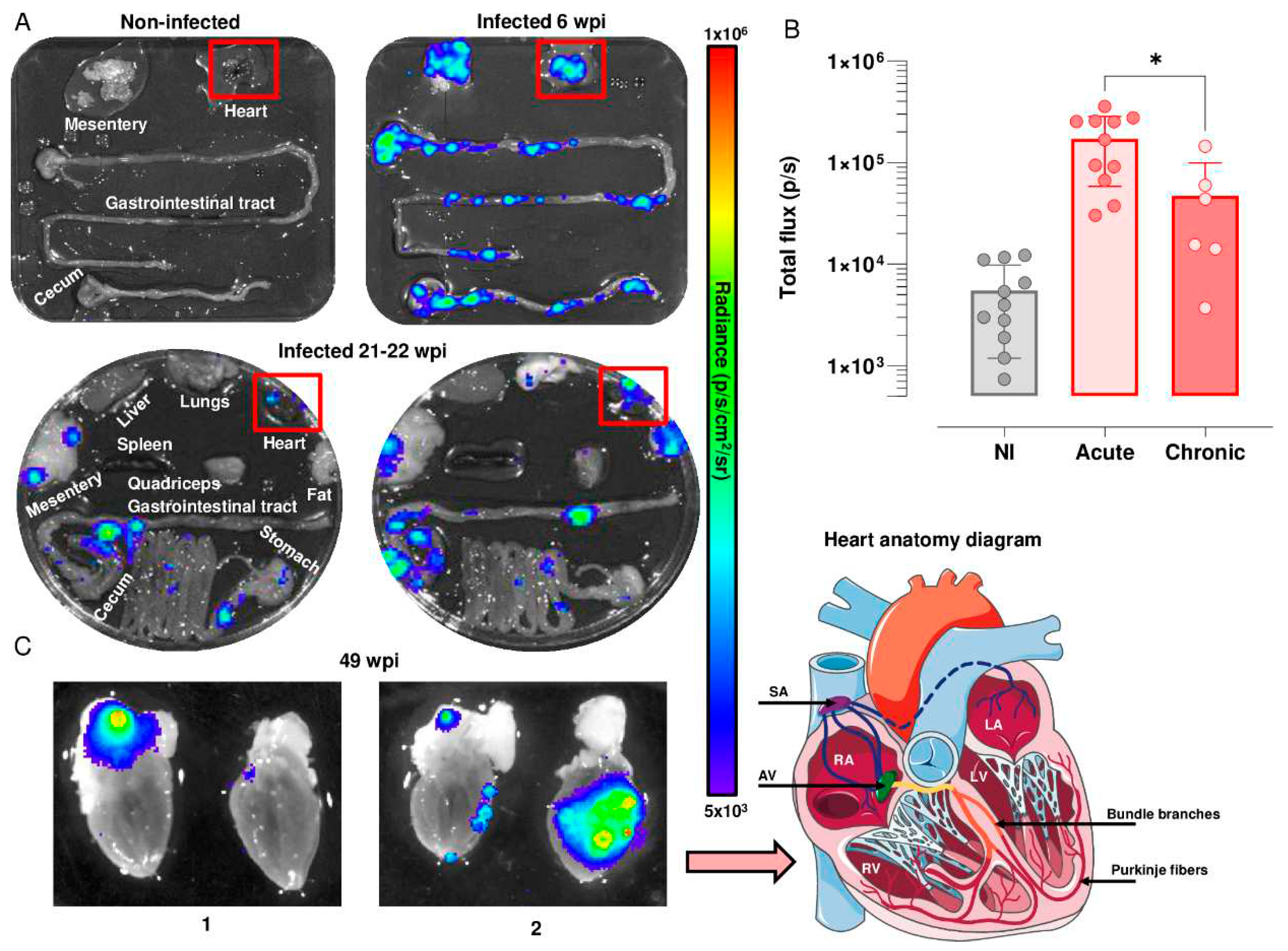
3.2. Analysis of heart-specific infection
We used highly sensitive bioluminescence imaging to further analyse temporal and spatial cardiac infection in the C3H/HeN:JR model. During the acute stage,
T. cruzi is pan-tropic and parasites can be routinely detected in heart tissue by
ex vivo imaging [
16,
21] (
Figure 2A). The highly dynamic nature of the infection was reflected in a wide variation in the cardiac parasite load, with a mean total flux of 150,000 p/s, which was derived from values in individual mice varying from 50,000 to 360,000 p/s. There is a linear relationship between bioluminescence and parasite load in this range [
21]. In the chronic stage, in line with previous reports [
16], ~80% of hearts displayed bioluminescence positivity in this infection model, although the parasite burden was significantly lower (p/s) (
P = 0.024) than in the acute stage, and again, there was considerable variability between individual mice (
Figure 2A and B). This compares to a ~10% level when snapshots of cardiac infection were assessed during the chronic stage in BALB/c mice, a strain that is better able to restrict the parasites to more immunotolerant sites, such as the GI tract [
16].
Mouse hearts were bisected into anterior and posterior halves to reveal all four chambers and cardiac valves. In the acute stage (6 wpi, n=11),
ex vivo image macroscopic analysis using Living Image 4.7.3 revealed intense bioluminescence over the entire cardiac muscle area and the aortic arch in both halves of the bisected heart in 55% of mice (n=6) (
Figure 2A). In the remaining animals (n=5), widespread parasite distribution was restricted to one half of the bisected heart and was observed intermittently in the aortic arches. During the chronic stage (21-22 wpi, n=6), parasites were more often localised in the epicardial adipose tissue, with only one mouse heart in this group being bioluminescence negative (
Figure 2A and B). In later stages of infection (49 wpi) (n=3), parasite distribution was comparable to that at 21-22 weeks (
Figure 2C), localized to the epicardial adipose, and close to the aorta and to both the left and right cranial vena cava. In other instances, additional bioluminescence was observed in the left and right ventricle (
Figure 2C). Therefore, across the chronic stage of infection, the cardiac parasite burden is much reduced and more local than during the acute stage (
Figure 2C).
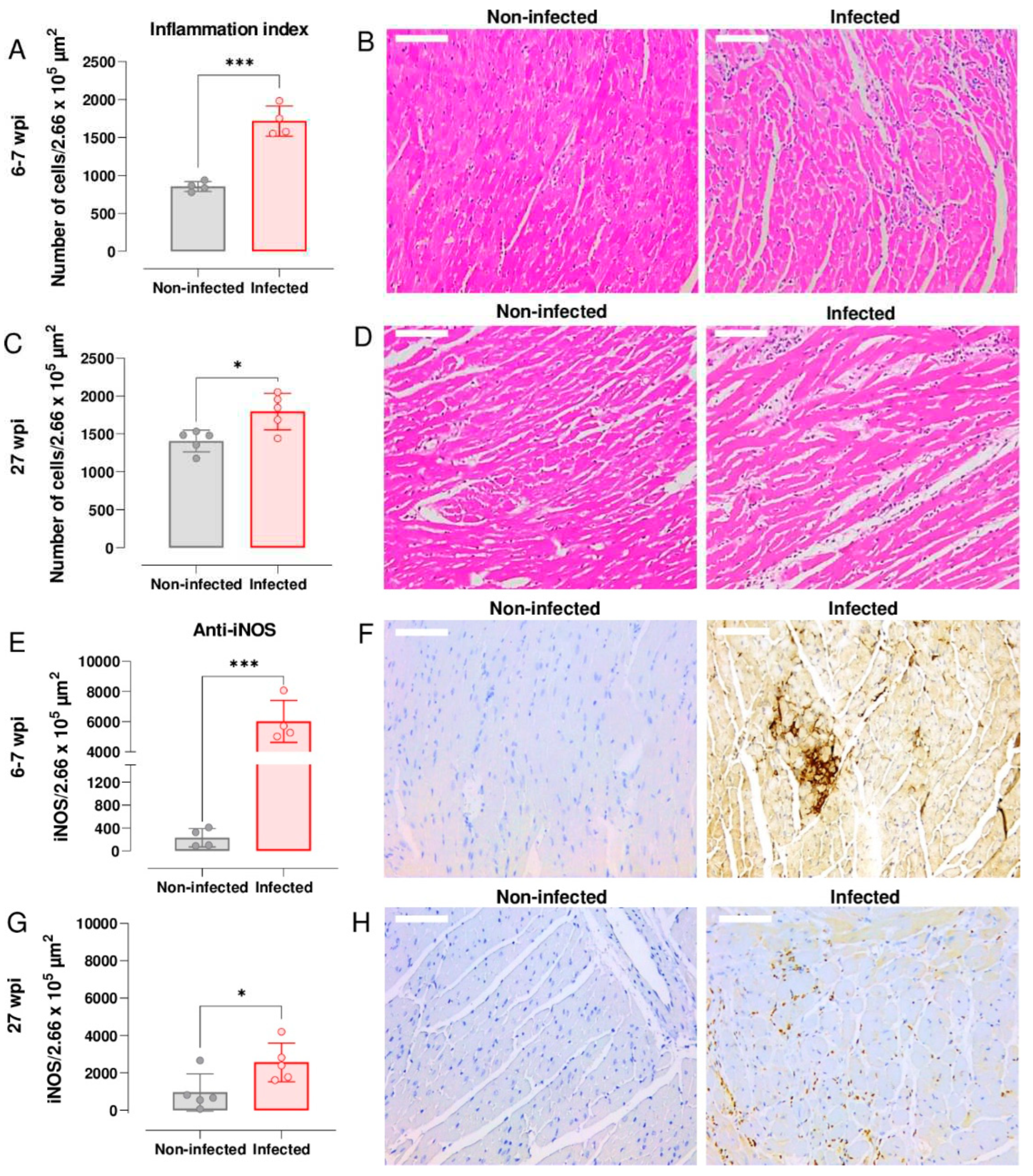
3.3. Upregulation of cardiac iNOS expression during acute and chronic T. cruzi infection
Nitric oxide (NO) has a central role in controlling murine
T. cruzi infections [
33]. However, high levels of this free radical have also been linked with chronic cardiac pathology [
34]. To investigate the temporal link between expression of iNOS and myocarditis in the C3H/HeN:JR infection model, we stained cardiac tissue sections with H&E and undertook histomorphometric analysis of digitalised images (Leica Application Suite V.4.12.; Materials and Methods). During the acute stage (6-7 wpi), the inflammation index was significantly greater in cardiac tissue from infected mice than from age-matched non-infected controls (
P = 0.0002) (
Figure 3A). Inflammatory infiltrates were widespread and were comprised predominantly of mononuclear cells with lymphocytic morphology. In some instances, the intensity of the cellular infiltrates forced the cardiac myofilaments to rearrange and adapt to a new tissue architecture (
Figure 3B). Although cardiac inflammation continued at a similar level during the chronic stage (27 wpi), the differential intensity compared to non-infected tissue was less pronounced (
P = 0.015;
Figure 3C and D), mostly due to a higher base-line inflammation level in the age-matched control mice.
Enhanced expression of iNOS in response to infection is a feature of many types of inflammatory cells. To determine if the inflammatory infiltrates accounted for the greatly increased abundance of the iNOS, we immuno-stained cardiac tissue sections with anti-iNOS antibody (Materials and Methods). Compared to non-infected controls, the amount of staining was significantly higher in tissue from both acutely (
P = 0.0002;
Figure 3E and F) and chronically infected (
P = 0.038;
Figure 3G and H) mice. Staining was more intense during the acute stage and was distributed across the whole heart, although in the infected mice there was no correlation between the extent of cardiac inflammation, iNOS levels, or parasite burden. However, in the chronic phase (27 wpi), we found a significant negative association between myocarditis and iNOS levels,
r(2) = -.98
, P = .001, perhaps reflecting differences in the ratio of inflammatory/anti-inflammatory immune cells within the cardiac infiltrate. Previously, we have shown that there is no significant association between end-point myocarditis intensity and cardiac parasite loads during chronic infections in the C3H/HeN model [
18].
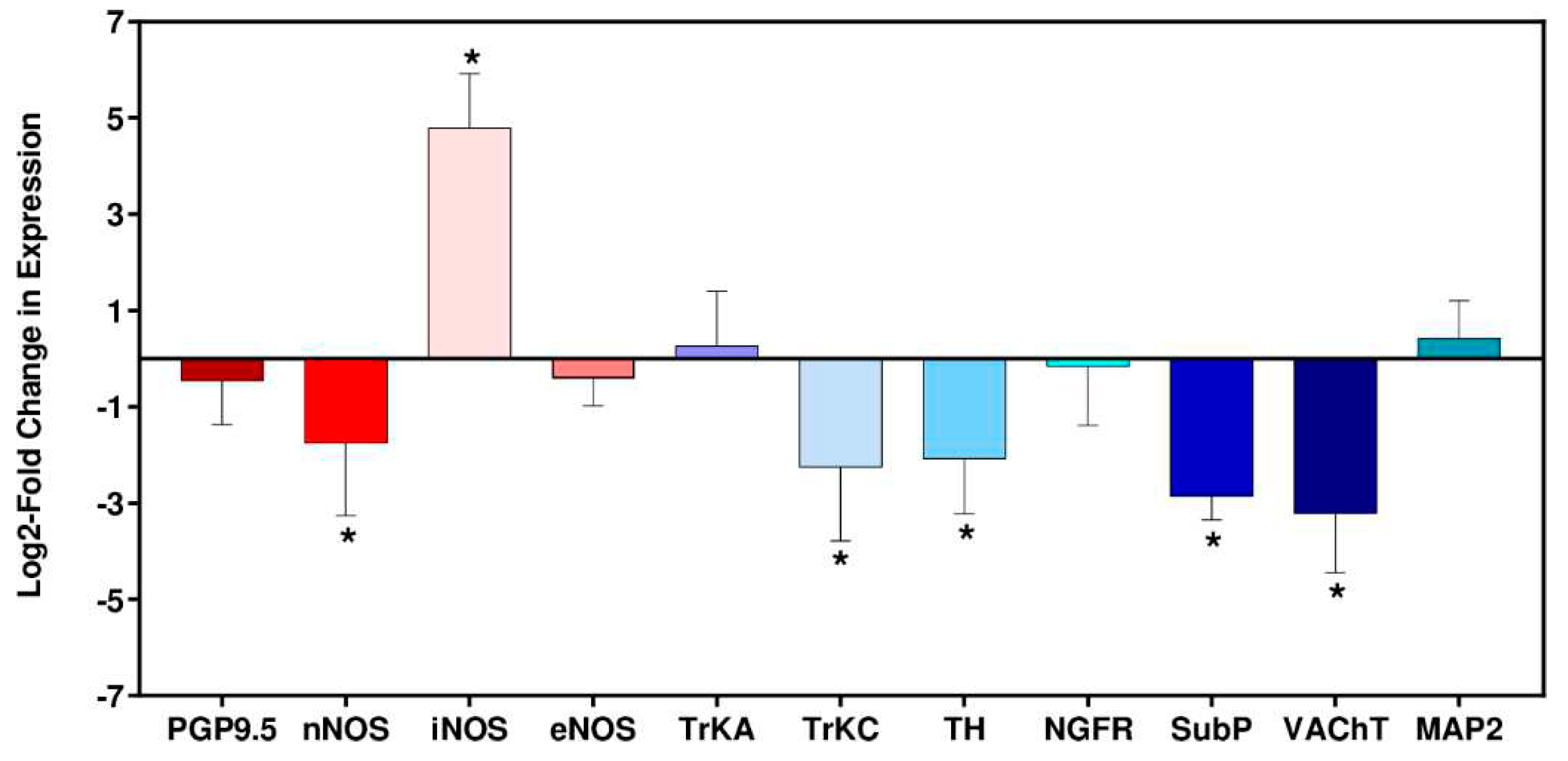
3.4. Expression of neuronal-specific genes in cardiac tissue during T. cruzi infection
Immune-mediated neuronal damage has been postulated as a possible mechanism of pathogenesis in Chagas heart disease [
2,
35]. To gain insight into potential disruption of cardiac autonomic function in the C3H/HeN:JR host:parasite infection model, we assessed expression of 9 nervous system related genes at 6 wpi (the late acute stage in this model), in addition to the inducible and endothelial nitric oxide synthases (Nos2/iNOS, Nos3/eNOS). When we examined the non-infected age-matched control group (6 biological replicates in each case), there was variability in the level of gene expression. The vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT) RNA showed the greatest variability (SD = 0.89), whilst the level of the neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) transcript, which has a role in protection against cardiac arrhythmia [
36,
37], was the most consistent between individual mice (SD = 0.10). Given this intrinsic variability, gene expression differences in infected mice were therefore only deemed significant if they were outside ±2 SDs of the non-infected controls.
Of the 11 marker genes investigated, 6 displayed significant differential expression in the heart tissue of
T. cruzi infected mice compared with the non-infected controls; nNOS, iNOS, tropomyosin receptor kinase C (TrkC), tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), substance P (SubP) and vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT) (
Figure 4). Amongst these, the only gene significantly upregulated was iNOS, which exhibited a 28-fold increase in response to infection, a finding that correlated with anti-iNOS staining of cardiac tissue (
Figure 4E). Of the downregulated genes, 4 of the corresponding proteins have a role in neurotransmission; VAChT (90% reduction), SubP (86% reduction), TH (76% reduction), nNOS (70% reduction). The absence of significant decreases in the pan-neuronal marker protein gene product 9.5 (PGP9.5) or the microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2), a structural marker associated with dendritic growth [
38], suggested that general infection-induced denervation was not linked with the cardiac abnormalities seen with this infection model, at least during the acute stage.
T. cruzi induced iNOS has been shown to contribute to denervation in vitro [
39] and enteric neuronal damage
in vivo [
40].
4. Discussion
T. cruzi parasites are restricted by immune pressure to a small number of sites in chronically infected mice, predominantly in the GI tract and skin [
16,
41]. Infection of other tissues and organs tends to be more sporadic and can be influenced by the host:parasite strain combination. For example,
ex vivo imaging, which provides an end-point snapshot of parasite location in tissues and organs, revealed that
T. cruzi CL Brener parasites can be detected in the hearts of only 10% of BALB/c and C3H/HeN mice during chronic stage infections. In contrast, with strain JR, cardiac infections reach 50% and >80%, respectively [
16,
18]. In the C3H/HeN model, other tissue sites such as lung and skeletal muscle also display similarly high rates of infection, indicating the absence of any intrinsic cardiac tropism. These observations reflect variable frequencies of transient infections in different host-parasite combinations [
22]. As a result, it can be inferred that stronger and/or more frequent cardiac immune responses will be induced in the C3H/HeN:JR infection model, resulting in greater collateral damage mediated, for example, by increased peroxynitrite generation [
38]. We propose that it is the higher frequency of intermittent cardiac infection in this model that leads to the increased development of disease pathology in a cumulative manner. The particular susceptibility of the heart to progressive chronic disease could result from its low regenerative capacity [
42] and the crucial role of neurological homeostasis.
In humans, ECG abnormalities are prevalent in
T. cruzi infected individuals, the most common being ventricular (RBBB and LAFB), often progressing to bifascicular blocks. Later manifestations include left ventricular systolic dysfunction, apical aneurysms, high degree atrioventricular block, and sustained and non-sustained ventricular tachycardia [
43]. Such cardiac abnormalities can be detected at different stages of infection, but are not present in all infected individuals, a profile similar to that observed in the mouse model. A study of asymptomatic
T. cruzi-seropositive blood donors, found a moderate (1.85%) annual increase in the incidence of Chagas cardiomyopathy, although disease was generally mild at the point of diagnosis [
44]. Thus, the development of CCC is extremely heterogeneous in both timing and severity, presumably a consequence of diverse host and parasite genetics, complex behavioural and life-style issues, and environmental factors.
To further investigate the temporal development of cardiac abnormalities in the C3H/HeN:JR model, we undertook longitudinal heart monitoring. Importantly, this facilitates data acquisition without the requirement of anaesthesia, an intervention that might otherwise perturb cardiac function. Bradycardia, one of the most common clinical presentations in Chagas heart disease, was detected in 33% of strain JR infected C3H/HeN mice. We observed a significant decrease in HR during the acute phase, which was attributable to the elongation of overlapping PQ, PR, RR, ST and QT parameters, as depicted in
Figure 1. Notably, the prolonged PQ intervals observed in infected mice, in comparison to non-infected age-matched controls, suggest that the infection may be adversely affecting the function of the atrioventricular (AV) node or its associated pathways. This, in turn, could lead to progressive cardiac dysfunction, underscoring the importance of early diagnosis and management of Chagas disease. The occurrence of sinus bradycardia (an outcome of sinus node disfunction) and/or ventricular extrasystole (premature ventricular contraction) were also apparent in approximately one third of the ECG profiles obtained from acutely infected mice. As a general trend, these abnormalities became less pronounced when the infection transitioned to the chronic stage (21-25 wpi) and the parasite burden had been reduced by the immune response. ST and QT show abnormalities in ventricular repolarization, and HRV denotes changes in cardiac autonomic function [
45]. The main ECG change reported in
T. cruzi infected C57BL/6 mice was an increase in the duration of the PR interval, reflecting a delay in electrical conduction through atrioventricular (AV) nodal conduction in chronically infected mice [
46]. No abnormalities in QRS intervals were observed in any mice during the chronic phase of infection, analogous to the situation in humans, where a pooled analysis of 10 studies, comprising >5,000 individuals, found no statistically significant difference in prevalence of QRS abnormalities between CD and non-CD patients [
9].
Cardiac conductance defects that did develop in the model during the chronic stage were RBBB (24%) and LAFB (9%). In humans, RBBB has been observed in 15% of
T. cruzi seropositive individuals, compared with less than 1% of those that were seronegative [
47]. In contrast to the JR strain, chronic infection of C3H/HeN mice with the CL Brener strain had a minimal effect on cardiac function, with a slight reduction in HR being the only abnormality identified over the period assessed (
Figure 1H). Therefore, the observation that parasite genotype influences the extent of chronic stage fibrosis [
16] can be extended to include an impact on cardiac function. Both outcomes can be correlated with differences in the inferred cumulative heart-specific parasite loads during chronic infections with the JR and CL Brener strains. Interestingly, when digestive CD in these models was investigated, severity was greater in C3H/HeN mice than in the BALB/c strain, and JR infections were associated with more severe pathology than those with
T. cruzi CL Brener [
48].
In the C3H/HeN:JR experimental model [
18], the extent of cardiac fibrosis is highly variable, ranging from slight to severe, a profile that mirrors the heterogeneous nature of human CCC. Infection of C3H/HeN mice with
T. cruzi JR results in cardiac inflammation and increased iNOS expression at both the mRNA and protein levels, particularly during the acute phase. This extensive cellular infiltration into cardiac muscle coincides with the suppression of the parasite burden at this stage of the infection (6 wpi) (
Figure 3A and B). In this model, mice are also prone to sudden death during this period, with an approximate 10% fatality rate. However, general infection-induced denervation does not appear to be a cause of cardiac disfunction during this stage of the infection, at least based on the expression of transcripts encoding the pan-neuronal marker protein PGP9.5, or MAP2, a structural marker associated with dendritic growth (
Figure 4). During chronic stage
T. cruzi infection, when heart parasitism is considerably reduced (
Figure 2C), and not persistent in all mice, there is decreased levels of inflammation and iNOS expression (
Figure 3C and G). Interestingly, in this phase of the infection, there is negative association between inflammation and iNOS levels. This could result from disease stage-specific alterations in the inflammatory/anti-inflammatory make-up of the cellular infiltrate, a phenomenon that could influence pathological outcome and merits further study.
Because of the complexity and long-term nature of CD, much of the fundamental research that underpins advances in our understanding of disease pathogenesis and the development of new treatments must be undertaken in experimental models. The ability of these models to capture the spectrum of human disease pathology is critical for translation. As described here, the C3H/HeN:JR host:parasite combination displays many of the diverse features of
T. cruzi-induced pathology observed in humans, and therefore represents a valuable predictive model for experimental research on this debilitating disease. As recently reported [
49], ECG in mice can be obtained by telemetry, under anaesthesia, and in conscious animals, depending on the equipment available. It is important to note that in mice, ECG profiles do display some characteristics that are distinct from those of humans, mostly attributable to the heart rate, which is ~10 times that of humans.
In this exploratory study, we have focussed on a limited number of female mouse:parasite combinations. It will be important to extend this work to capture other variables such as parasite diversity, together with the gender and genetic background of the host. In addition, studies on cardiac neuronal gene expression in the chronic stage of infection, could provide further insights into the mechanisms of electrical disturbances caused by T. cruzi infection.
 ) identify individual mice where some of the
parameter values lie outside the typical range.
) identify individual mice where some of the
parameter values lie outside the typical range.
 ) identify individual mice where some of the
parameter values lie outside the typical range.
) identify individual mice where some of the
parameter values lie outside the typical range.