Submitted:
13 October 2023
Posted:
16 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Materials
Synthesis of superparamagnetic Fe3-δO4 NPs
Synthesis of CMPETMS-Coated Fe3−δO4 MNPs (Fe3−δO4@ Silane).
Synthesis of Fe3−δO4@P(MEO2MAx−OEGMA100−x)
Drug Conjugation to MNCs
DOX Release Kinetics Analysis
3. Results
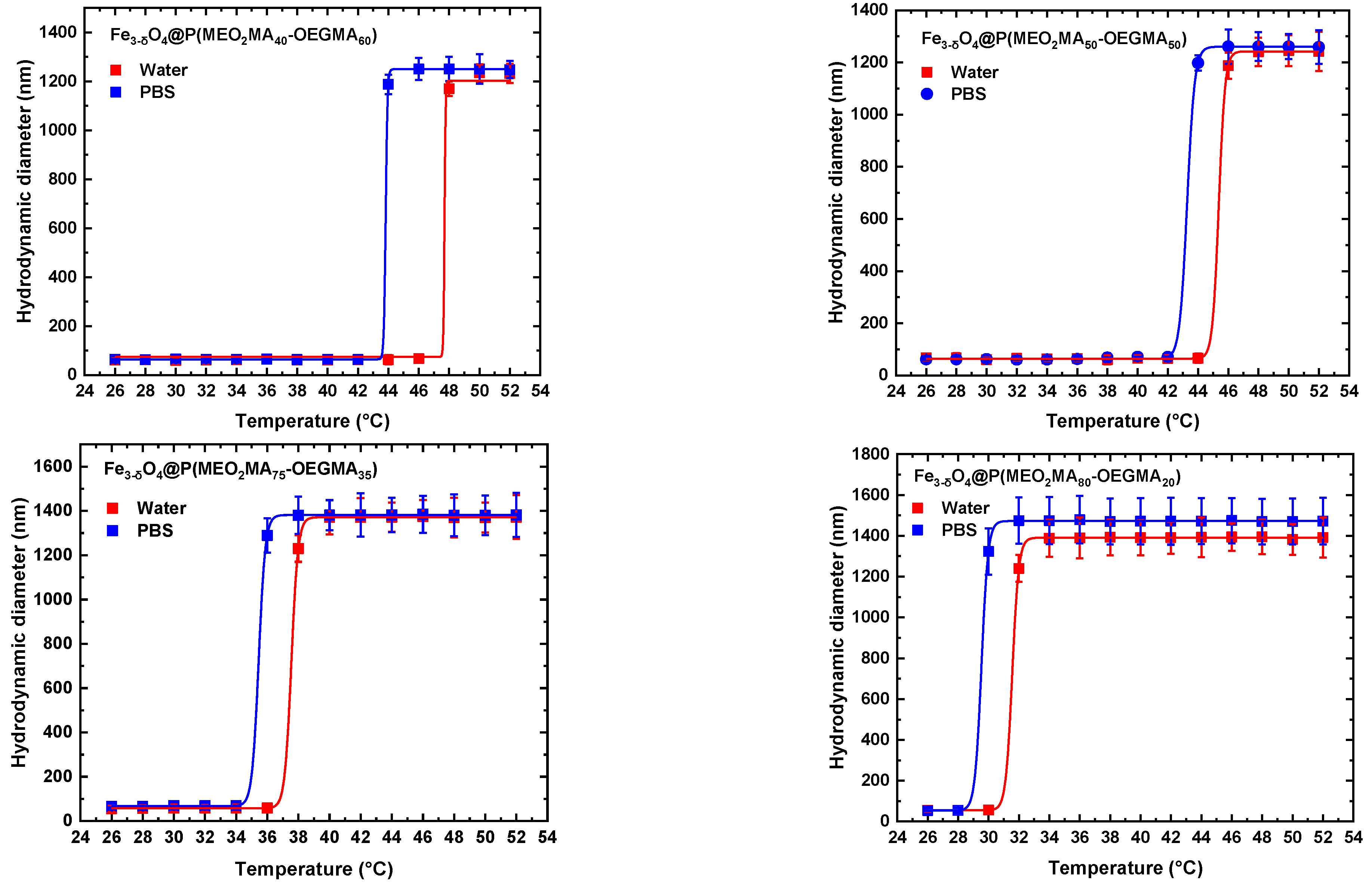
3.1. Colloidal behavior of nano-objects in physiological environments.
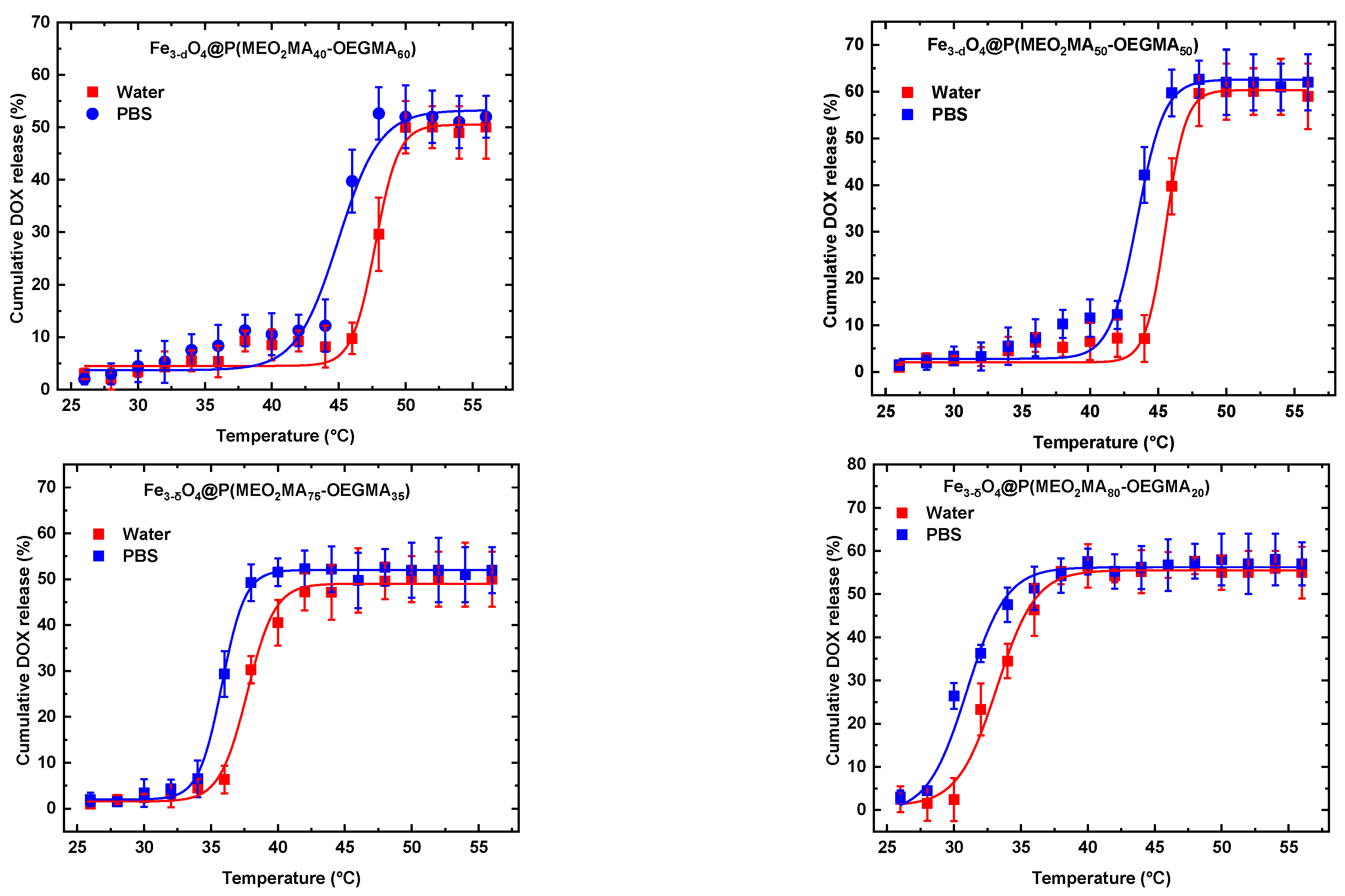
3.2. Release of DOX as a function of temperature.
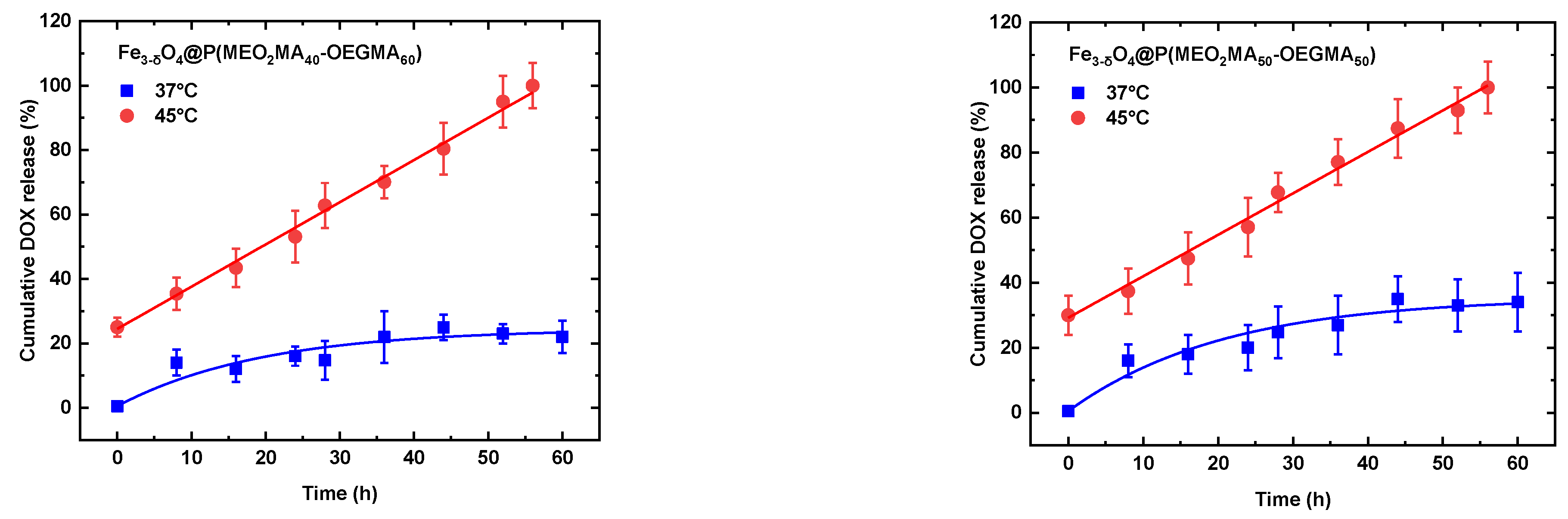
3.3. Release profile and mechanism of DOX over time.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
References
- D. T. Debela et al., « New approaches and procedures for cancer treatment: Current perspectives », SAGE Open Med., vol. 9, p. 205031212110343, janv. 2021. [CrossRef]
- X. Ma et H. Yu, « Global burden of cancer », Yale J. Biol. Med., vol. 79, no 3-4, p. 85-94, déc. 2006.
- K. S. Rallis, T. H. Lai Yau, et M. Sideris, « Chemoradiotherapy in Cancer Treatment: Rationale and Clinical Applications », Anticancer Res., vol. 41, no 1, p. 1-7, janv. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Szczęch et K. Szczepanowicz, « Polymeric Core-Shell Nanoparticles Prepared by Spontaneous Emulsification Solvent Evaporation and Functionalized by the Layer-by-Layer Method », Nanomaterials, vol. 10, no 3, p. 496, mars 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. U. Menon et al., « Dual-Drug Containing Core-Shell Nanoparticles for Lung Cancer Therapy », Sci. Rep., vol. 7, no 1, p. 13249, oct. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Deshpande, S. Sharma, V. Koul, et N. Singh, « Core–Shell Nanoparticles as an Efficient, Sustained, and Triggered Drug-Delivery System », ACS Omega, vol. 2, no 10, p. 6455-6463, oct. 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. Liu et al., « Thermo-responsive gold/poly(vinyl alcohol)-b-poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) core–corona nanoparticles as a drug delivery system », Polym Chem, vol. 5, no 18, p. 5289-5299, 2014. [CrossRef]
- C. Yang, R. Jie, L. Jianbo, et L. Yan, « Thermo-Responsive Mn–Zn Ferrite/Poly(N,N′-Isopropyl Acrylamide-co-N-Hydroxymethylacrylamide) Core/Shell Nanocomposites for Drug-Delivery Systems », J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed., vol. 22, no 11, p. 1473-1486, janv. 2011. [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, A. Paul, S. O. Sen, et K. K. Sen, « Studies on thermoresponsive polymers: Phase behaviour, drug delivery and biomedical applications », Asian J. Pharm. Sci., vol. 10, no 2, p. 99-107, avr. 2015. [CrossRef]
- J.-F. Lutz, K. Weichenhan, Ö. Akdemir, et A. Hoth, « About the Phase Transitions in Aqueous Solutions of Thermoresponsive Copolymers and Hydrogels Based on 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethyl Methacrylate and Oligo(ethylene glycol) Methacrylate », Macromolecules, vol. 40, no 7, p. 2503-2508, avr. 2007. [CrossRef]
- Lapresta-Fernández, A. Salinas-Castillo, et L. F. Capitán-Vallvey, « Synthesis of a thermoresponsive crosslinked MEO2MA polymer coating on microclusters of iron oxide nanoparticles », Sci. Rep., vol. 11, no 1, p. 3947, févr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Alem, A. Schejn, T. Roques-Carmes, J. Ghanbaja, et R. Schneider, « Thermo-responsive and aqueous dispersible ZnO/PNIPAM core/shell nanoparticles », Nanotechnology, vol. 26, no 33, p. 335605, août 2015. [CrossRef]
- Y. Liu, Y.-N. Luo, P. Zhang, W.-F. Yang, C.-Y. Zhang, et Y.-L. Yin, « The Preparation of Novel P(OEGMA-co-MEO2MA) Microgels-Based Thermosensitive Hydrogel and Its Application in Three-Dimensional Cell Scaffold », Gels, vol. 8, no 5, p. 313, mai 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. Alejo et al., « A facile method for the controlled polymerization of biocompatible and thermoresponsive oligo(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate copolymers », Polym. J., vol. 50, no 2, p. 203-211, févr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- E. Jamal Al Dine et al., « Thermo-responsive magnetic Fe 3 O 4 @P(MEO 2 MA X -OEGMA 100-X ) NPs and their applications as drug delivery systems », Int. J. Pharm., vol. 532, no 2, p. 738-747, nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. Xu et V. Abetz, « Nonionic UCST–LCST Diblock Copolymers with Tunable Thermoresponsiveness Synthesized via PhotoRAFT Polymerization », Macromol. Rapid Commun., vol. 42, no 7, p. 2000648, avr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- F. Gambinossi, M. Chanana, S. E. Mylon, et J. K. Ferri, « Programming nanoparticle aggregation kinetics with poly(MeO2MA-co-OEGMA) copolymers », Soft Matter, vol. 9, no 46, p. 11046, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Z. Ferjaoui, R. Schneider, A. Meftah, E. Gaffet, et H. Alem, « Functional responsive superparamagnetic core/shell nanoparticles and their drug release properties », RSC Adv., vol. 7, no 42, p. 26243-26249, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Z. Ferjaoui et al., « Layer-by-Layer Self-Assembly of Polyelectrolytes on Superparamagnetic Nanoparticle Surfaces », ACS Omega, vol. 5, no 10, p. 4770-4777, mars 2020. [CrossRef]
- Z. Ferjaoui et al., « Doxorubicin-Loaded Thermoresponsive Superparamagnetic Nanocarriers for Controlled Drug Delivery and Magnetic Hyperthermia Applications », ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 11, no 34, p. 30610-30620, août 2019. [CrossRef]
- Z. Ferjaoui et al., « Development of Folate-Superparamagnetic Nanoconjugates for Inhibition of Cancer Cell Proliferation », Adv. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 10, no 12, p. 2202364, avr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang, S. Gao, W.-H. Ye, H. S. Yoon, et Y.-Y. Yang, « Co-delivery of drugs and DNA from cationic core–shell nanoparticles self-assembled from a biodegradable copolymer », Nat. Mater., vol. 5, no 10, p. 791-796, oct. 2006. [CrossRef]
- Y. Yao et al., « Nanoparticle-Based Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy and Its Role in Overcoming Drug Resistance », Front. Mol. Biosci., vol. 7, p. 193, août 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. Pasparakis et C. Tsitsilianis, « LCST polymers: Thermoresponsive nanostructured assemblies towards bioapplications », Polymer, vol. 211, p. 123146, déc. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. A. da Silva et al., « Thermoresponsive Triblock-Copolymers of Polyethylene Oxide and Polymethacrylates: Linking Chemistry, Nanoscale Morphology, and Rheological Properties », Adv. Funct. Mater., vol. 32, no 9, p. 2109010, févr. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Q. Li, L. Wang, F. Chen, A. P. Constantinou, et T. K. Georgiou, « Thermoresponsive oligo(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate based copolymers: composition and comonomer effect », Polym. Chem., vol. 13, no 17, p. 2506-2518, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Hu, V. Darcos, S. Monge, et S. Li, « Thermo-responsive drug release from self-assembled micelles of brush-like PLA/PEG analogues block copolymers », Int. J. Pharm., vol. 491, no 1-2, p. 152-161, août 2015. [CrossRef]
- Hervault et al., « Doxorubicin loaded dual pH- and thermo-responsive magnetic nanocarrier for combined magnetic hyperthermia and targeted controlled drug delivery applications », Nanoscale, vol. 8, no 24, p. 12152-12161, 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. Shen, Y. Wu, Y. Liu, et D. Wu, « High drug-loading nanomedicines: progress, current status, and prospects », Int. J. Nanomedicine, vol. Volume 12, p. 4085-4109, mai 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Mura, J. Nicolas, et P. Couvreur, « Stimuli-responsive nanocarriers for drug delivery », Nat. Mater., vol. 12, no 11, p. 991-1003, nov. 2013. [CrossRef]
- N. Andhariya, B. Chudasama, R. V. Mehta, et R. V. Upadhyay, « Biodegradable thermoresponsive polymeric magnetic nanoparticles: a new drug delivery platform for doxorubicin », J. Nanoparticle Res., vol. 13, no 4, p. 1677-1688, avr. 2011. [CrossRef]
- B. T. Mai et al., « Thermoresponsive Iron Oxide Nanocubes for an Effective Clinical Translation of Magnetic Hyperthermia and Heat-Mediated Chemotherapy », ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 11, no 6, p. 5727-5739, févr. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Q. Guo et al., « Co-encapsulation of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles and doxorubicin into biodegradable PLGA nanocarriers for intratumoral drug delivery », Int. J. Nanomedicine, p. 1697, mars 2012. [CrossRef]
- B. Sahoo, K. S. P. Devi, R. Banerjee, T. K. Maiti, P. Pramanik, et D. Dhara, « Thermal and pH Responsive Polymer-Tethered Multifunctional Magnetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Delivery of Anticancer Drug », ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, vol. 5, no 9, p. 3884-3893, mai 2013. [CrossRef]
| Samples | MEO2MA | OEGMA |
|---|---|---|
| Fe3-δO4@P(MEO2MA80-OEGMA20) | 1.550 mL | 0.571 mL |
| Fe3-δO4@P(MEO2MA75-OEGMA25) Fe3-δO4@P(MEO2MA50-OEGMA50) Fe3-δO4@P(MEO2MA40-OEGMA60) |
1.450 mL 1mL 1.140 mL |
0.714 mL 1 mL 1.160 mL |
| Samples | LCST in water (°C) | LCST in PBS (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Fe3-δO4@P(MEO2MA80-OEGMA20) | 32 | 30 |
| Fe3-δO4@P(MEO2MA75-OEGMA25) Fe3-δO4@P(MEO2MA50-OEGMA50) Fe3-δO4@P(MEO2MA40-OEGMA60) |
38 45 48 |
36 43 44 |
| Zero Order | First Order | Higushi | Korsmeyer-Peppas | |||||||
| Samples | T(°C) | K0 | R2 | K1 | R2 | Kh | R2 | Kkp | R2 | n |
| Fe3-δO4@P(MEO2MA40-OEGMA60) | 37 | 1.215 | 0.935 | 0.686 | 0.979 | 1.101 | 0.820 | 0.491 | 0.831 | 0.375 |
| Fe3-δO4@P(MEO2MA50-OEGMA50) | 37 | 1.123 | 0.958 | 0.319 | 0.983 | 1.009 | 0.892 | 0.849 | 0.826 | 0.266 |
| Fe3-δO4@P(MEO2MA40-OEGMA60) | 45 | 1.310 | 0.998 | 0.309 | 0.870 | 1.122 | 0.783 | 0.792 | 0.809 | 0.230 |
| Fe3-δO4@P(MEO2MA50-OEGMA50) | 45 | 1.274 | 0.996 | 0.224 | 0.890 | 1.072 | 0.799 | 0.656 | 0.841 | 0.288 |
| Samples | DLC (%) | DLE (%) |
| Fe3-δO4@P(MEO2MA40-OEGMA60) | 6.5 | 60 |
| Fe3-δO4@P(MEO2MA50-OEGMA50) Fe3-δO4@P(DEGMA-co-PEGMA-b-[TMSPMA-co-VBA]) Fe3-δO4@P(DEGMEA-co-OEGMEMA) Fe3O4@PEO-PLGA-PEO DOX-MNPs DOX-AF-PNIPAM- Fe3O4 |
6.2 7.6 [26] 3.29 [29] 7.2 [28] 8.1 [31] 23 [32] |
55 82.3 [26] --- 23.1 [28] 90 [31] 74.4 [32] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





