Submitted:
12 October 2023
Posted:
13 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Treatment protocol
2.2. Data collection
2.3. CAPA definition
2.4. Data analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Availability of data and material
Acknowledgments
Declaration of Competing Interests
References
- Brown, G.D.; Denning, D.W.; Gow, N.A.R.; Levitz, S.M.; Netea, M.G.; White, T.C. Hidden Killers: Human Fungal Infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 165rv13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauwvlieghe, A.F.A.D.; Rijnders, B.J.A.; Philips, N.; Verwijs, R.; Vanderbeke, L.; Van Tienen, C.; Lagrou, K.; Verweij, P.E.; Van De Veerdonk, F.L.; Gommers, D.; et al. Invasive aspergillosis in patients admitted to the intensive care unit with severe influenza: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, P.; Cornely, O.A.; Böttiger, B.W.; Dusse, F.; Eichenauer, D.A.; Fuchs, F.; Hallek, M.; Jung, N.; Klein, F.; Persigehl, T.; et al. COVID-19 associated pulmonary aspergillosis. Mycoses 2020, 63, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, G.; Almyroudi, M.-P.; Myrianthefs, P.; Rello, J. COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis (CAPA). J. Intensiv. Med. 2021, 1, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, J.P.; Chen, S.C.; Kauffman, C.A.; Steinbach, W.J.; Baddley, J.W.; Verweij, P.E.; Clancy, C.J.; Wingard, J.R.; Lockhart, S.R.; Groll, A.H.; et al. Revision and Update of the Consensus Definitions of Invasive Fungal Disease From the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer and the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulska, M.; Raiola, A.M.; Bruno, B.; Furfaro, E.; Van Lint, M.T.; Bregante, S.; Ibatici, A.; Del Bono, V.; Bacigalupo, A.; Viscoli, C. Risk factors for invasive aspergillosis and related mortality in recipients of allogeneic SCT from alternative donors: An analysis of 306 patients. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009, 44, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, P.E.; Rijnders, B.J.A.; Brüggemann, R.J.M.; Azoulay, E.; Bassetti, M.; Blot, S.; Calandra, T.; Clancy, C.J.; Cornely, O.A.; Chiller, T.; et al. Review of influenza-associated pulmonary aspergillosis in ICU patients and proposal for a case definition: An expert opinion. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 46, 1524–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Parra, J.; Moreno-Torres, V.; Mills-Sanchez, P.; Tejado-Bravo, S.; Romero-Sánchez, I.; Balandin-Moreno, B.; Calvo-Salvador, M.; Portero-Azorín, F.; García-Masedo, S.; Muñez-Rubio, E.; et al. Association of COVID-19-Associated Pulmonary Aspergillosis with Cytomegalovirus Replication: A Case–Control Study. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 Clinical Management: Living Guidance. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-clinical-2021-1 (accessed on 14 June 2021).
- Mussini, C.; Falcone, M.; Nozza, S.; Sagnelli, C.; Parrella, R.; Meschiari, M.; Petrosillo, N.; Mastroianni, C.; Cascio, A.; Iaria, C.; et al. Therapeutic strategies for severe COVID-19: A position paper from the Italian Society of Infectious and Tropical Diseases (SIMIT). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 27, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, K.P.; Hudson, L.D.; Goodman, R.B.; Lee Hough, C.; Lanken, P.N.; Hyzy, R.; Thompson, B.T.; Ancukiewicz, M. Efficacy and Safety of Corticosteroids for Persistent Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. New Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1671–1684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- White, P.L.; Dhillon, R.; Cordey, A.; Hughes, H.; Faggian, F.; Soni, S.; Pandey, M.; Whitaker, H.; May, A.; Morgan, M.; et al. A National Strategy to Diagnose Coronavirus Disease 2019–Associated Invasive Fungal Disease in the Intensive Care Unit. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 73, e1634–e1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Biesen, S.; Kwa, D.; Bosman, R.J.; Juffermans, N.P. Detection of Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in COVID-19 with Nondirected BAL. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 208, 1171–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, P.; Bassetti, M.; Chakrabarti, A.; Chen, S.C.A.; Colombo, A.L.; Hoenigl, M.; Klimko, N.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Oladele, R.O.; Vinh, D.C.; et al. Defining and managing COVID-19-associated pulmonary aspergillosis: The 2020 ECMM/ISHAM consensus criteria for research and clinical guidance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, e149–e162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoletti, M.; Pascale, R.; Cricca, M.; Rinaldi, M.; Maccaro, A.; Bussini, L.; Fornaro, G.; Tonetti, T.; Pizzilli, G.; Francalanci, E.; et al. Epidemiology of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis among COVID-19 intubated patients: A prospective study. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2021, 73, E3606–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.; Niederman, M.S.; Chastre, J.; Ewig, S.; Fernandez-Vandellos, P.; Hanberger, H.; Kollef, M.; Bassi, G.L.; Luna, C.M.; Martin-Loeches, I.; et al. International ERS/ESICM/ESCMID/ALAT guidelines for the management of hospital-acquired pneumonia and ventilator-associated pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manian, F.A. IDSA Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Intravascular Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 49, 1770–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuleerarux, N.; Thongkam, A.; Manothummetha, K.; Nematollahi, S.; Dioverti-Prono, V.; Torvorapanit, P.; Langsiri, N.; Worasilchai, N.; Plongla, R.; Chindamporn, A.; et al. Does Post-Transplant Cytomegalovirus Increase the Risk of Invasive Aspergillosis in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-W.; Wang, S.-Y.; Tsai, H.-P.; Su, P.-L.; Cia, C.-T.; Lai, C.-H.; Chen, C.-W.; Shieh, C.-C.; Lin, S.-H. Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis is associated with cytomegalovirus viremia in critically ill patients—A retrospective cohort study. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 55, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, I.; Biagioni, E.; Coloretti, I.; Farinelli, C.; Avoni, C.; Caciagli, V.; Busani, S.; Pecorari, M.; Gennari, W.; Guaraldi, G.; et al. Cytomegalovirus blood reactivation in COVID-19 critically ill patients: Risk factors and impact on mortality. Intensiv. Care Med. 2022, 48, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Stroever, S.; Rondain, P.; Scatena, R. Incidence of secondary bacterial infections following utilization of tocilizumab for the treatment of COVID-19—A matched retrospective cohort study. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2021, 13, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakike, E.; Dalekos, G.N.; Koutsodimitropoulos, I.; Saridaki, M.; Pourzitaki, C.; Papathanakos, G.; Kotsaki, A.; Chalvatzis, S.; Dimakopoulou, V.; Vechlidis, N.; et al. ESCAPE: An Open-Label Trial of Personalized Immunotherapy in Critically lll COVID-19 Patients. J. Innate Immun. 2021, 14, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| BASELINE | All population (n=579) |
No CAPA (n=483) |
CAPA (n=96) |
p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (Male; n, %) | 419 (72,4%) | 348 (72) | 71 (74) | 0,702 |
| Age (median, IQR) | 65 (56-72) | 63 (55-72) | 70 (63-75) | <0,001 |
| BMI (median, IQR) | 29 (26-33) | 29 (26-33) | 29 (26-33) | 0,761 |
| SAPSII score (median, IQR) |
34 (28-39) | 33 (28-38) | 36 (33-43) | <0,001 |
| D-dimer (mcg/l; median, IQR) |
1470 (820-3020) | 1510 (820-2850) | 1325 (780-3660) | 0,992 |
| LDH (U/l; median, IQR) |
823 (634-1104) | 815 (635-1096) | 916 (624-1239) | 0,341 |
| Leukocyte count (cells/mcl; median, IQR) | 8,3 (5,9-11,2) | 8,2 (5,9-10,9) | 8,5 (5,5-11,7) | 0,829 |
| Lymphocyte count (cells/mcl; median, IQR) | 0,7 (0,5-1,0) | 0,7 (0,5-1,0) | 0,6 (0,4-0,9) | 0,008 |
| Platelet count (1000/mmᶾ; median, IQR) | 219 (170-288) | 222 (171-288) | 205 (155-269) | 0,182 |
| CRP (mg/l; median, IQR) |
6,3 (2,2-17,1) | 6,6 (2,6-17,4) | 5,6 (1,2-16,1) | 0,069 |
| PCT (ng/ml; median, IQR) |
0,2 (0,1-0,5) | 0,2 (0,1-0,5) | 0,2 (0,1-0,6) | 0,772 |
| PaO2/FiO2 (mmHg; median, IQR) |
102 (82-135) | 102 (81-136) | 103 (91-135) | 0,347 |
| IL-6 (pg/ml; median, IQR) |
276,6 (93,3-834) | 259,5 (80,0-770,3) | 295,3 (114,9-1177,6) | 0,170 |
| Steroid (n, %) | 533 (92,2) | 441 (91,3) | 92 (96,8) | 0,066 |
| Immunotherapy (n,%) | 477 (82,4) | 398 (82,4) | 79 (82,3) | 0,979 |
| SDD (n,%) | 83 (14,3) | 60 (12,4) | 23 (24,0) | 0,003 |
| Invasive mechanical ventilation (n,%) | 347 (59,9) | 263 (54,5) | 84 (87,5) | < 0,001 |
| Waves | ||||
|
1st wave February 25th, 2020- July 6th, 2020 |
102 | 88 (86,3) | 14 (13,7) | |
|
2nd wave September 20th, 2020-February 13th, 2021 |
166 | 142 (85,5) | 24 (14,5) | |
|
3rd wave February 14th, 2021-April 30th, 2021 |
172 | 136 (79,1) | 36 (20,9) | |
|
4th wave April 30th, 2021-May 8th, 2022 |
139 | 117 (84,2) | 22 (15,8) | |
| Variable |
Total (n=96) |
No CMV Reactivation (n=56) |
CMV Reactivation (n=40) |
P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (Male; n, %) | 71 (74) | 39 (69,9) | 32 (80,0) | 0,254 |
| Age (median-, QR) |
70 (63-75) | 70 (63-75) | 71 (63-76) | 0,663 |
| SOFA (median, IQR) |
4 (3-6) | 4 (3-6) | 5 (4-6) | 0,158 |
| SAPSII score (median, IQR) | 36 (33-43) | 36 (33-42) | 37 (32-44) | 0,519 |
| D-dimer (mcg/l; median, IQR) | 1325 (780-3660) | 1360 (760-3355) | 1305 (800-4866) | 0,994 |
| LDH (U/l; median, IQR) | 916 (624-1239) | 991 (697-1264) | 788 (532-1104) | 0,065 |
| Leukocyte count (cells/mcl; median, IQR) | 8,5 (5,5-11,7) | 8,7 (5,6-11,6) | 8,3 (5,4-15,8) | 0,749 |
| Lymphocyte count (cells/mcl; median, IQR) | 0,6 (0,4-0,9) | 0,6 (0,4-0,8) | 0,6 (0,4-0,9) | 0,624 |
| Platelet count (1000/mmᶾ; median, IQR) | 205 (155-269) | 219 (155-289) | 198 (153-255) | 0,205 |
| CRP (mg/l; median, IQR) | 5,6 (1,2-16,1) | 4,6 (1,4-16,9) | 6,0 (1,1-14,7) | 0,649 |
| PCT T0 (ng/ml; median, IQR) | 0,2 (0,1-0,6) | 0,2 (0,1-0,5) | 0,2 (0,1-0,6) | 0,777 |
| PaO2/FiO2 (mmHg; median, IQR) | 103 (91-135) | 107 (92-142) | 101 (91-129) | 0,483 |
| IL6 (pg/ml; median, IQR) | 295,3 (114,9-1177,6) | 385,6 (194,1-1491,0) | 165,2 (95,9-875,0) | 0,069 |
| BMI (median, IQR) | 29 (26-33) | 29 (26-33) | 29 (27-33) | 0,642 |
| Steroid (n, %) | 92 (96,8) | 52 (94,5) | 40 (100) | 0,133 |
| Immunotherapy (n,%) | 79 (82,3) | 47 (83,9) | 32 (80,0) | 0,619 |
| SDD (n,%) | 23 (24,0) | 14 (25,0) | 9 (22,5) | 0,777 |
| Invasive mechanical ventilation (n,%) | 84 (87,5) | 45 (80,4) | 39 (97,5) | 0,012 |
| Waves | ||||
|
1st wave February 25th, 2020- July 6th, 2020 |
14 (13,7) | 8 (14,3) | 6 (15,0) | 0,969 |
|
2nd wave September 20th, 2020-February 13th, 2021 |
24 (14,5) | 14 (25,0) | 10 (25,0) | |
|
3rd wave February 14th, 2021-April 30th, 2021 |
36 (20,9) | 22 (39,3) | 14 (35,0) | |
|
4th wave April 30th, 2021-May 8th,2022 |
22 (15,8) | 12 (21,4) | 10 (25,0) | |
| OUTCOME |
Total (n=96) |
No CMV Reactivation (n=56) |
CMV Reactivation (n=40) |
P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
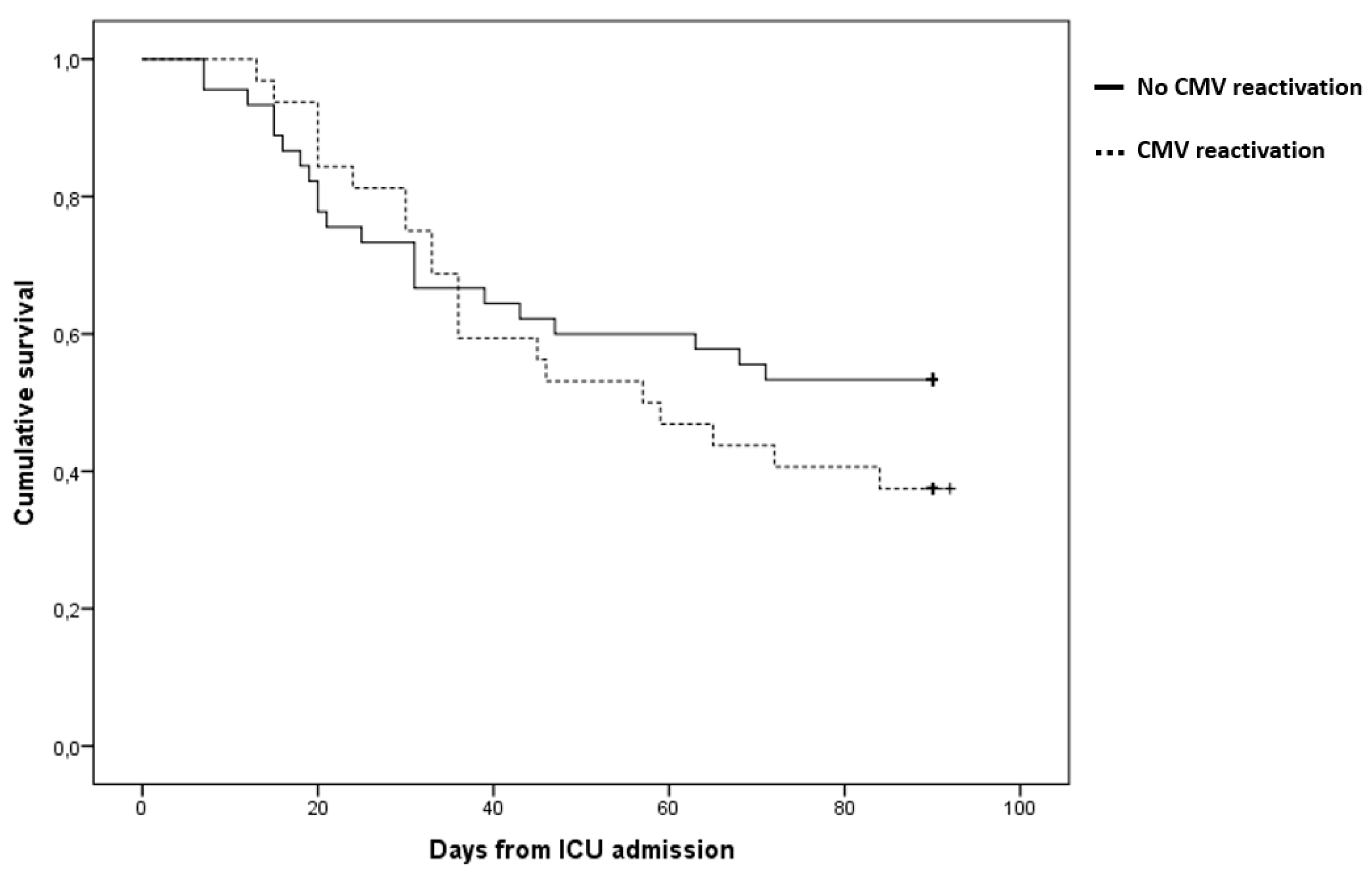
| 90-day mortality (n, %) | 52 (54,2%) | 27 (48,2) | 25 (62,5) | 0,166 |
| ICU mortality (n, %) | 48 (50%) | 24 (42,9) | 24 (60,0) | 0,098 |
| ICU length of stay (days; median, IQR) | 19 (8-39) | 12 (6-23) | 35 (20-59) | <0,001 |
| Invasive mechanical ventilation-free days at day 60 (days; median, IQR) | 9 (1-48) | 13 (1-56) | 7 (0-15) | 0,020 |
| Mechanical ventilation-free days at day 60 (days; median, IQR) | 0 (0-35) | 0 (0-53) | 0 (0-0) | 0,001 |
| Secondary bacterial infection (n, %) | 61 (63.5%) | 30 (53,6) | 31 (77,5) | 0,016 |
| Bacteremia (n, %) | 24 (25%) | 12 (21,4) | 12 (30) | 0,339 |
| Pneumonia (n, %) | 49 (51%) | 25 (44,6) | 24 (60) | 0,914 |
| Time to CAPA occurrence (days; median, IQR) | 5,5 (1,0-12,0) | 2 (1-7,5) | 9,5 (5-20,5) | <0,001 |
| Time to secondary bacterial infection (days; median, IQR) | 11 (6-17) | 10 (10-10) | 19 (6-29) | 0,667 |
| CMV blood reactivation at day 90 (n= 40) |
No CMV blood reactivation at at day 90 (n =56) |
Unadjusted HR (95% CI); |
p value | Adjusted HR (95% CI); |
p value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Invasive Mechanical Ventilation (n,%) | 39 (97,5) | 45 (80,4) | 7,02 (0,96-51,14) | 0,094 | 6,00 (0,74-48,75) | 0,094 |
| Secondary bacterial infection (n,%) | 31 (77,55) | 30 (53,6) | 2,20 (1,04-4,62) | 0,038 | 1,32 (0,60-2,93) | 0,491 |
| Immunotherapy (n,%) | 32 (80,0) | 47 (83,9) | 0,74 (0,34-1,60) | 0,438 | 0,98 (0,44-2,16) | 0,951 |
| Previous immune-suppression (n,%) | 16 (40,0) | 10 (17,9) | 2,33 (1,24-4,40) | 0,009 | 2,33 (1,21-4,48) | 0,011 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





