Submitted:
09 October 2023
Posted:
10 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation and Characterization
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of gold nanostars
2.2.2. Preparation of gold nanostar-galactose dehydrogenase bioconjugate
2.2.3. Gold nanostar-galactose dehydrogenase biosensor colorimetric assay
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chirico, G.; Borzenkov, M.; Pallavicini, P. Gold Nanostars: Synthesis, Properties and Biomedical Application. Gold Nanostars 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; Ou, L.; Cutshaw, G.; Uthaman, S.; Ou, Y.C.; Zhu, T.; Szakas, S.; Carney, B.; Houghton, J.; Gundlach-Graham, A.; et al. Physicochemical Properties and Route of Systemic Delivery Control the In Vivo Dynamics and Breakdown of Radiolabeled Gold Nanostars. Small 2023, 19, e2204293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.-L.; Wang, J.-H.; Liang, S.; Yang, D.-J.; Nan, F.; Ding, S.-J.; Zhou, L.; Hao, Z.-H.; Wang, Q.-Q. Tuning Plasmon Resonance of Gold Nanostars for Enhancements of Nonlinear Optical Response and Raman Scattering. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2014, 118, 9659–9664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, J.; Ma, Z. Synthesis of gold nanostars with tunable morphology and their electrochemical application for hydrogen peroxide sensing. Electrochimica Acta 2013, 108, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, H.; Fales, A.M.; Register, J.K.; Vo-Dinh, T. Multifunctional gold nanostars for molecular imaging and cancer therapy. Front Chem 2015, 3, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, F.; Nehl, C.L.; Hafner, J.H.; Nordlander, P. Plasmon Resonances of a Gold Nanostar. Nano Letters 2007, 7, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrelescu, C.; Sau, T.K.; Rogach, A.L.; Jäckel, F.; Feldmann, J. Single gold nanostars enhance Raman scattering. Applied Physics Letters 2009, 94, 153113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, S.; Tsoulos, T.V.; Fabris, L. Shaping Gold Nanostar Electric Fields for Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy Enhancement via Silica Coating and Selective Etching. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2016, 120, 20749–20758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehl, C.L.; Liao, H.; Hafner, J.H. Optical properties of star-shaped gold nanoparticles. Nano Lett 2006, 6, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoulos, T.V.; Atta, S.; Lagos, M.J.; Beetz, M.; Batson, P.E.; Tsilomelekis, G.; Fabris, L. Colloidal plasmonic nanostar antennas with wide range resonance tunability. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 18662–18671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xianyu, Y.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Q.; Belessiotis-Richards, A.; Stevens, M.M.; Thomas, M.R. Iodide-Mediated Rapid and Sensitive Surface Etching of Gold Nanostars for Biosensing. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2021, 60, 9891–9896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eustis, S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Why gold nanoparticles are more precious than pretty gold: Noble metal surface plasmon resonance and its enhancement of the radiative and nonradiative properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chemical Society Reviews 2006, 35, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Gao, X.; Liu, D.; Chen, X. Gold nanoparticles for in vitro diagnostics. Chem Rev 2015, 115, 10575–10636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Covarrubias, A.J.; Perrone, R.; Grozio, A.; Verdin, E. NAD(+) metabolism and its roles in cellular processes during ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2021, 22, 119–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, N.; Zhang, L.; Gao, W.; Huang, C.; Huber, P.E.; Zhou, X.; Li, C.; Shen, G.; Zou, B. NAD+ metabolism: pathophysiologic mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2020, 5, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.F. Energetics of the one-electron steps in the NAD+/NADH redox couple. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 1980, 590, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Suh, H.N.; Yoon, S.H.; Lee, K.H.; Ahn, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.H. Non-Destructive Monitoring via Electrochemical NADH Detection in Murine Cells. Biosensors (Basel) 2022, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongeon, R.; Venkatachalam, V.; Yellen, G. Cytosolic NADH-NAD(+) Redox Visualized in Brain Slices by Two-Photon Fluorescence Lifetime Biosensor Imaging. Antioxid Redox Signal 2016, 25, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yu, J.; Men, X.; Zhang, J.; Ding, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, C.; Chiu, D.T. Reversible Ratiometric NADH Sensing Using Semiconducting Polymer Dots. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2021, 60, 12007–12012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brekasis, D.; Paget, M.S. A novel sensor of NADH/NAD+ redox poise in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Embo j 2003, 22, 4856–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, V.; Simmonds, H.A.; Bari, M.; Pompucci, G. HPLC determination of oxidized and reduced pyridine coenzymes in human erythrocytes. Clin Chim Acta 1993, 220, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, P.; Yu, H.; Guntupalli, B.; Xiao, Y. Paper-Based Device for Rapid Visualization of NADH Based on Dissolution of Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2015, 7, 15023–15030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, G.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, J. Nanoplasmonic sensing of NADH by inhibiting the oxidative etching of gold nanorods. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical 2019, 299, 126982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maenaka, Y.; Suenobu, T.; Fukuzumi, S. Efficient catalytic interconversion between NADH and NAD+ accompanied by generation and consumption of hydrogen with a water-soluble iridium complex at ambient pressure and temperature. J Am Chem Soc 2012, 134, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Lu, H.; Deng, L. A sensitive NADH and ethanol biosensor based on graphene–Au nanorods nanocomposites. Talanta 2013, 113, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Rica, R.; Stevens, M.M. Plasmonic ELISA for the ultrasensitive detection of disease biomarkers with the naked eye. Nature Nanotechnology 2012, 7, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atta, S.; Beetz, M.; Fabris, L. Understanding the role of AgNO3 concentration and seed morphology in the achievement of tunable shape control in gold nanostars. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 2946–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyayi, T.A.; Vorster, B.C.; Mulder, D.W. The Effect of Capping Agents on Gold Nanostar Stability, Functionalization, and Colorimetric Biosensing Capability. Nanomaterials (Basel) 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, D.W.P., M. M; Jordaan, A; Vorster, B. C. Modified HEPES one-pot synthetic strategy for gold nanostars. R Soc Open Sci 2019, 6, 190160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Carballares, D.; Morellon-Sterling, R.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Stabilization of enzymes via immobilization: Multipoint covalent attachment and other stabilization strategies. Biotechnology Advances 2021, 52, 107821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, J.A.; Leonardo, D.A.; D’Muniz Pereira, H.; Lopes, A.R.; Rodriguez, H.N.; Cobos, M.; Marapara, J.L.; Castro, J.C.; Garratt, R.C. Structural Characterization of L-Galactose Dehydrogenase: An Essential Enzyme for Vitamin C Biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol 2022, 63, 1140–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondrat, S.; Krauss, U.; von Lieres, E. Enzyme co-localisation: Mechanisms and benefits. Current Research in Chemical Biology 2022, 2, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, M.M.; Mulder, D.W.; Vorster, B.C. Plasmonic Detection of Glucose in Serum Based on Biocatalytic Shape-Altering of Gold Nanostars. Biosensors (Basel) 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdani, S.; Daneshkhah, A.; Diwate, A.; Patel, H.; Smith, J.; Reul, O.; Cheng, R.; Izadian, A.; Hajrasouliha, A.R. Model for Gold Nanoparticle Synthesis: Effect of pH and Reaction Time. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 16847–16853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, D.; Phiri, M.; Vorster, C. Tailor-made gold nanostar colorimetric detection determined by morphology change and used as an indirect approach by using hydrogen peroxide to determine glucose concentration. Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research 2019, 25, 100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Lorenzo, L.; de la Rica, R.; Álvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Stevens, M.M. Plasmonic nanosensors with inverse sensitivity by means of enzyme-guided crystal growth. Nature Materials 2012, 11, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Lee, J.; Wang, D. Seedless, Surfactantless, High-Yield Synthesis of Branched Gold Nanocrystals in HEPES Buffer Solution. Chemistry of Materials - CHEM MATER 2007, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Wang, D.I.C. Seedless, surfactantless, high-yield synthesis of branched gold nanocrystals in HEPES buffer solution. 2007.
- Xi, W.; Haes, A.J. Elucidation of HEPES Affinity to and Structure on Gold Nanostars. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2019, 141, 4034–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wu, J.; Li, H.; Cheng, G.; Lu, Z.; Che, C.-M. Fabrication of gold nanoparticles with different morphologies in HEPES buffer. Rare Metals 2010, 29, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebtsov, N. Anisotropic properties of plasmonic nanoparticles: depolarized light scattering, dichroism, and birefringence. Journal of Nanophotonics 2010, 4, 041587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, D.S.; Chatterjee, H.; Ghosh, S.K. Excess Surface Energy at the Tips of Gold Nanospikes: From Experiment to Modeling. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2015, 119, 14326–14337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazos-Perez, N.; Guerrini, L.; Alvarez-Puebla, R.A. Plasmon Tunability of Gold Nanostars at the Tip Apexes. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 17173–17179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BLACHNITZKY, E.-O.; WENGENMAYER, F.; KURZ, G. d-Galactose Dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas fluorescens. European Journal of Biochemistry 1974, 47, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, S.; Sumi, Y.; Fukui, S. Kinetic studies on coenzyme binding and coenzyme dissociation in tryptophanase immobilized on sepharose. Biochemistry 1975, 14, 1464–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Flora, A.; Morelli, A.; Giuliano, F. Human erythrocyte glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Content of bound coenzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1974, 59, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagi, K.; Ozawa, T.; Ooi, T. COMPLEX FORMATION OF APOENZYME, COENZYME AND SUBSTRATE OF D-AMINO ACID OXIDASE. V. CHANGE IN CONFORMATION OF THE PROTEIN BY FORMING A MODEL OF ENZYME-SUBSTRATE COMPLEX. Biochim Biophys Acta 1963, 77, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UEBERSCHÄR, K.-H.; BLACHNITZKY, E.-O.; KURZ, G. Reaction Mechanism of d-Galactose Dehydrogenases from Pseudomonas saccharophila and Pseudomonas fluorescens. European Journal of Biochemistry 1974, 48, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, P.K. Enzymes: principles and biotechnological applications. Essays Biochem 2015, 59, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Yi, X.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold nanoparticles: Catalyst for the oxidation of NADH to NAD+. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology 2005, 81, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Shao, M.; Liu, C.-C. Electrochemical oxidation of dihydronicotinadmide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) on single crystal gold electrodes. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 1996, 406, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plapp, B.V. Conformational changes and catalysis by alcohol dehydrogenase. Arch Biochem Biophys 2010, 493, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Yu, B.; Lin, T.; Hou, L. Iodide-Mediated Etching of Gold Nanostar for the Multicolor Visual Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide. Biosensors (Basel) 2023, 13, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Wu, C.; Miao, A.-J.; Pan, K. Reduction of silver ions to form silver nanoparticles by redox-active organic molecules: coupled impact of the redox state and environmental factors. Environmental Science: Nano 2021, 8, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brumaghim, J.L.; Li, Y.; Henle, E.; Linn, S. Effects of hydrogen peroxide upon nicotinamide nucleotide metabolism in Escherichia coli: changes in enzyme levels and nicotinamide nucleotide pools and studies of the oxidation of NAD(P)H by Fe(III). J Biol Chem 2003, 278, 42495–42504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Lin, L.; Li, G. Wavelength selection method based on test analysis of variance: application to oximetry. Analytical Methods 2014, 6, 1082–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Liu, C.; Tsow, F.; Yang, Y.; Du, Z.; Iriya, R.; Yu, H.; Tao, N. Noncontact Monitoring of Blood Oxygen Saturation Using Camera and Dual-Wavelength Imaging System. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2016, 63, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, S.A.; Kumar, V.; Karimi, J.; Singh, A.P.; Kumar, S. Role of gold nanoparticles in advanced biomedical applications. Nanoscale Advances 2020, 2, 3764–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Puig, H.; Tam, J.O.; Yen, C.-W.; Gehrke, L.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Extinction Coefficient of Gold Nanostars. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2015, 119, 17408–17415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qiu, L.; Sun, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, T. Optimal hemoglobin extinction coefficient data set for near-infrared spectroscopy. Biomed Opt Express 2017, 8, 5151–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maugeri, L.; Messina, M.A.; Ruggieri, M.; Petralia, S. Photothermal-Contrast Method Based on In Situ Gold Nanostructure Formation for Phenylalanine Detection in Human Blood. ACS Applied Nano Materials 2023, 6, 12673–12678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, P.; Beigi, S.M.; Yousefi, F.; Aghabalazadeh, S.; Mousavizadegan, M.; Hosseini, M.; Hosseinkhani, S.; Ganjali, M.R. Colorimetric biosensor for phenylalanine detection based on a paper using gold nanoparticles for phenylketonuria diagnosis. Microchemical Journal 2021, 163, 105909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoulos, T.V.; Han, L.; Weir, J.; Xin, H.L.; Fabris, L. A closer look at the physical and optical properties of gold nanostars: an experimental and computational study. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 3766–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayats, M.; Baron, R.; Popov, I.; Willner, I. Biocatalytic Growth of Au Nanoparticles: From Mechanistic Aspects to Biosensors Design. Nano Letters 2005, 5, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezuneh, T.T.; Fereja, T.H.; Kitte, S.A.; Li, H.; Jin, Y. Gold nanoparticle-based signal amplified electrochemiluminescence for biosensing applications. Talanta 2022, 248, 123611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Ye, Y.; Liu, S. Gold nanoparticle-based signal amplification for biosensing. Analytical Biochemistry 2011, 417, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, G.A.; Dean, S.N.; Walper, S.A.; Medintz, I.L. Quantum Dots and Gold Nanoparticles as Scaffolds for Enzymatic Enhancement: Recent Advances and the Influence of Nanoparticle Size. Catalysts 2020, 10, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
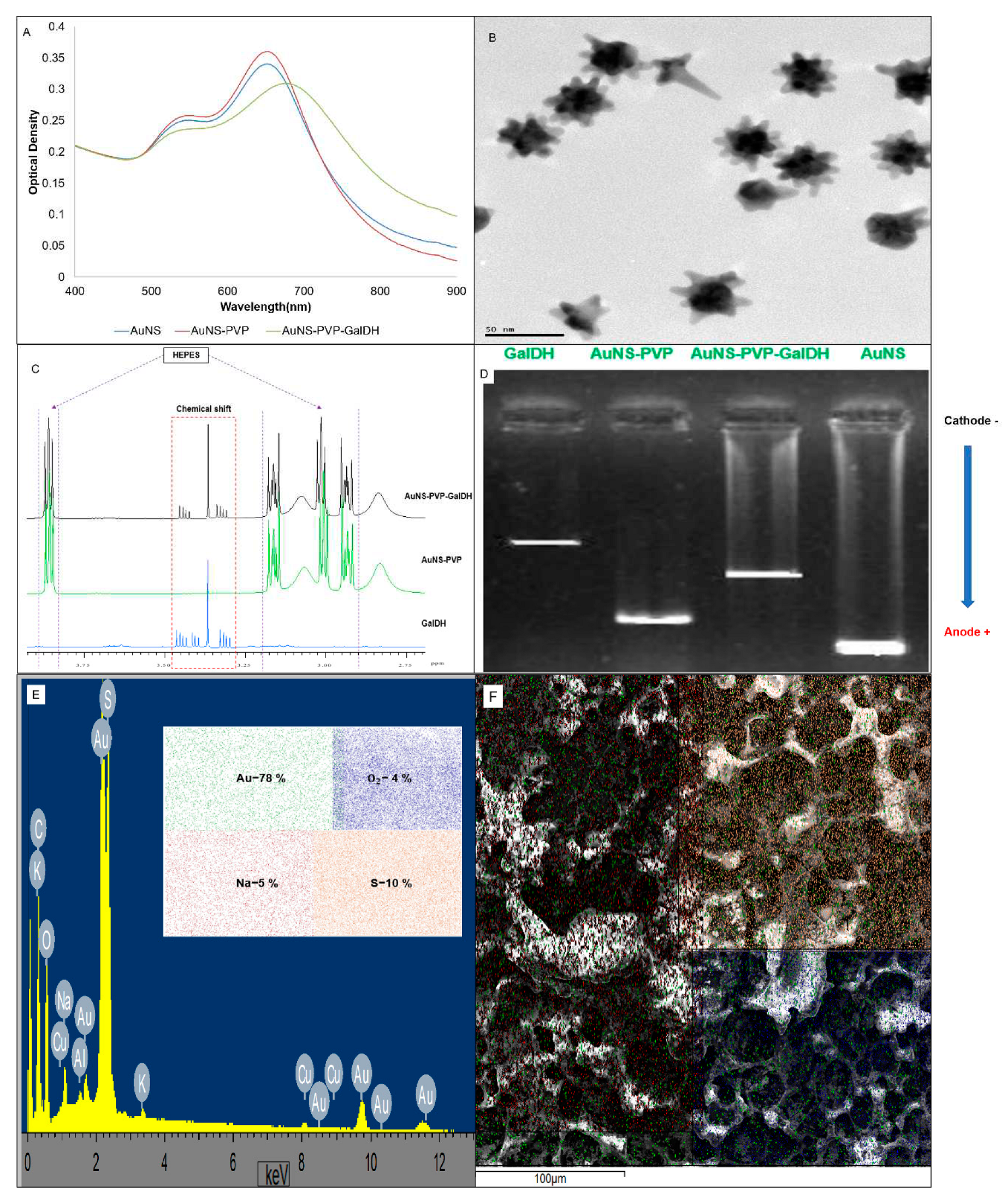
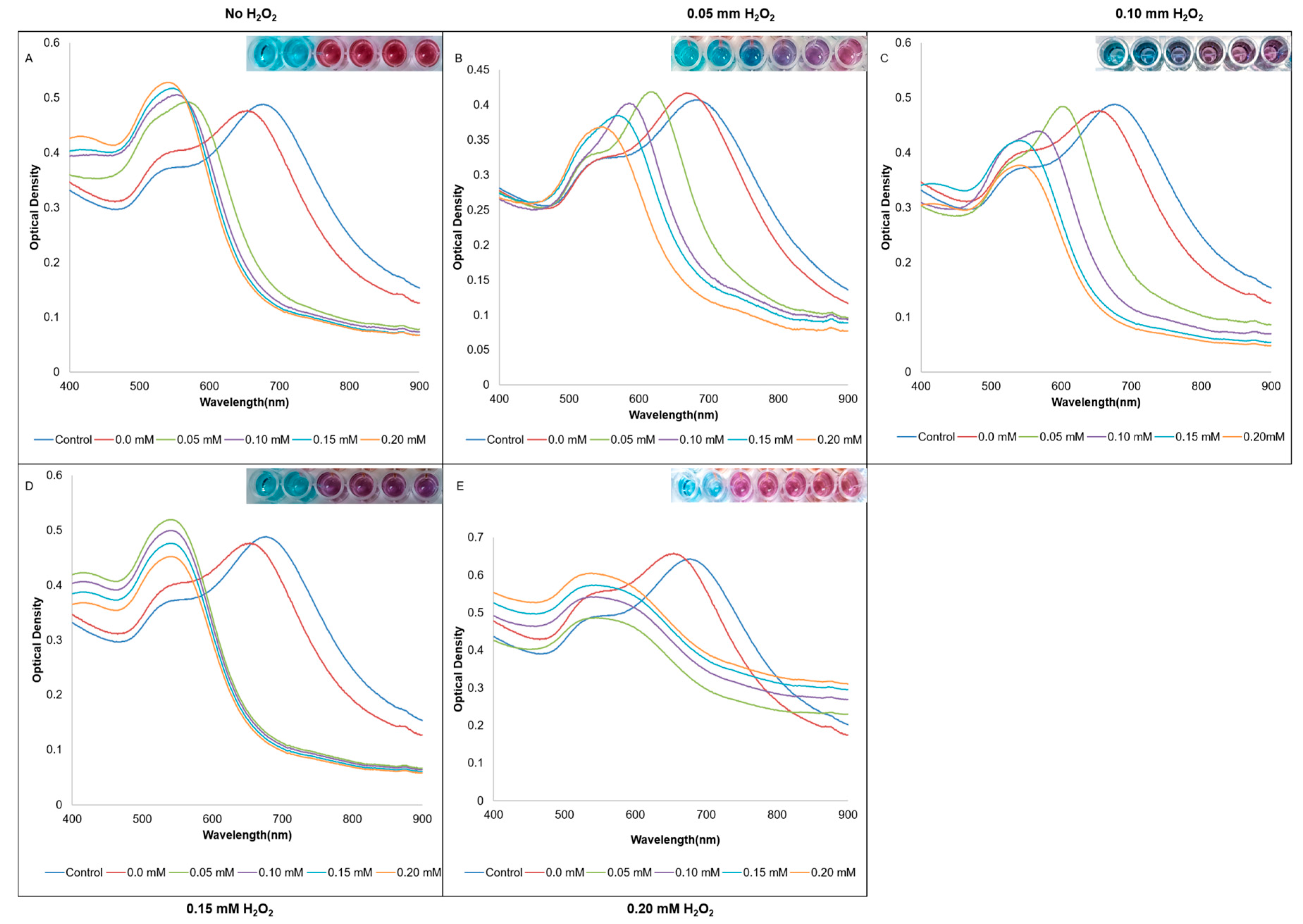
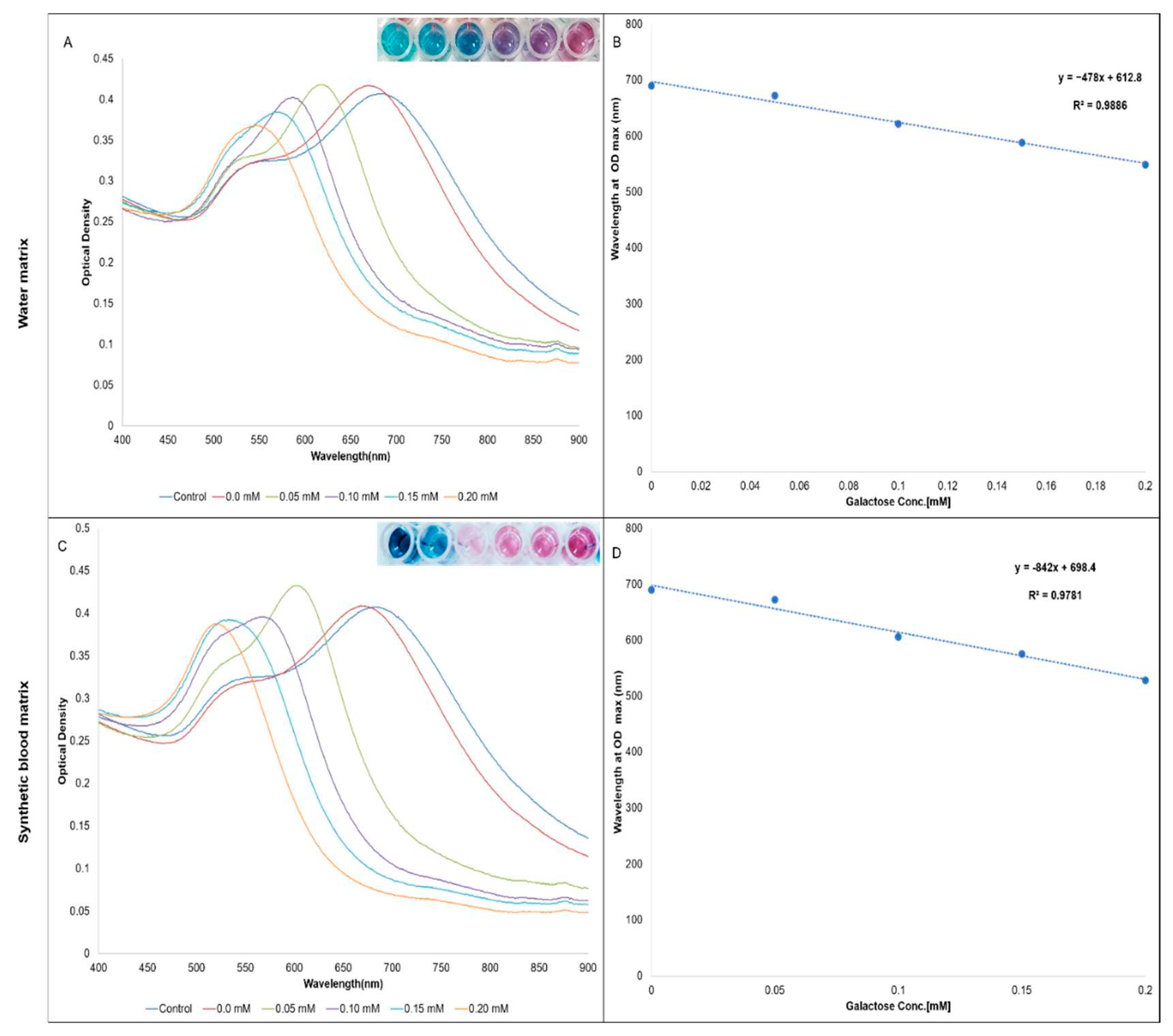
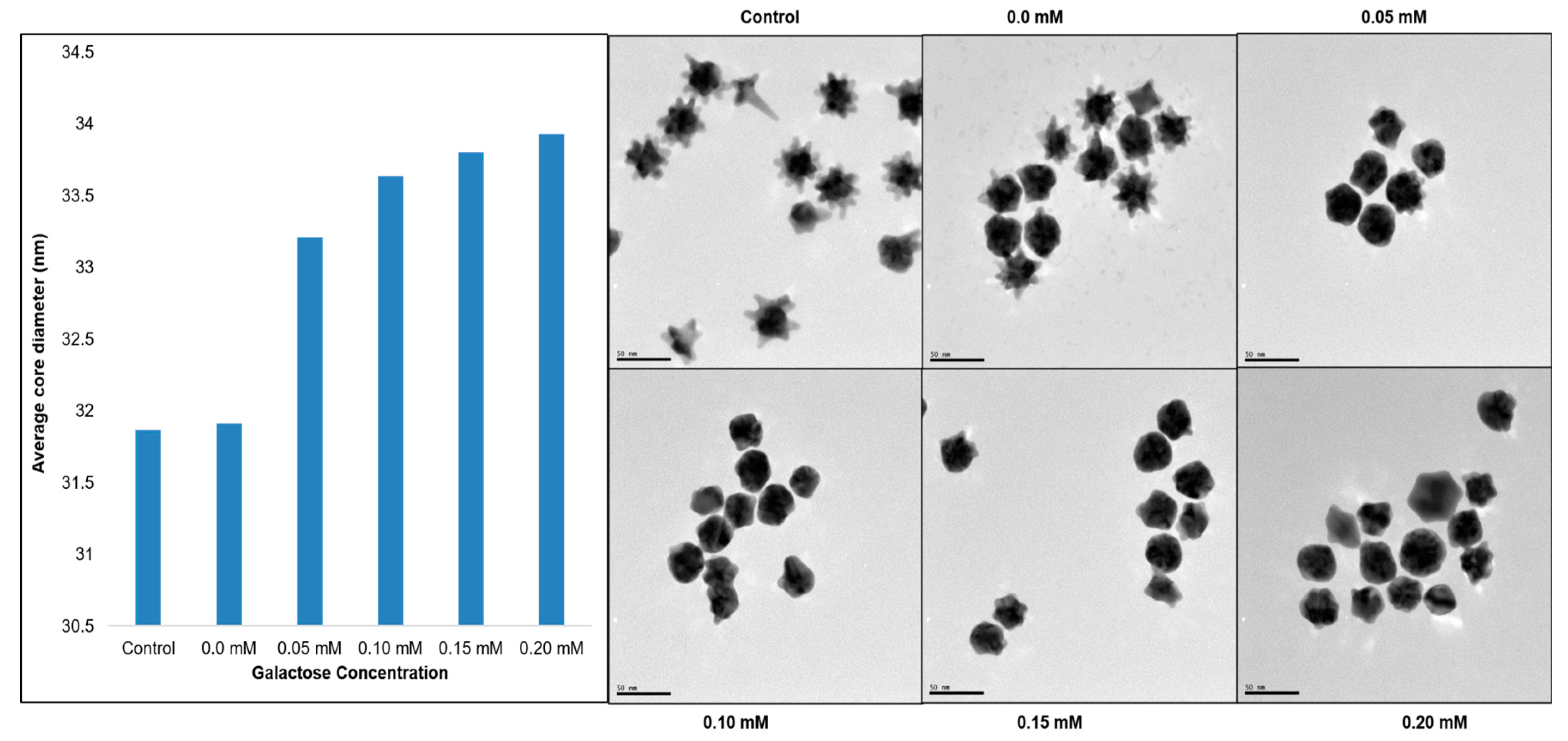
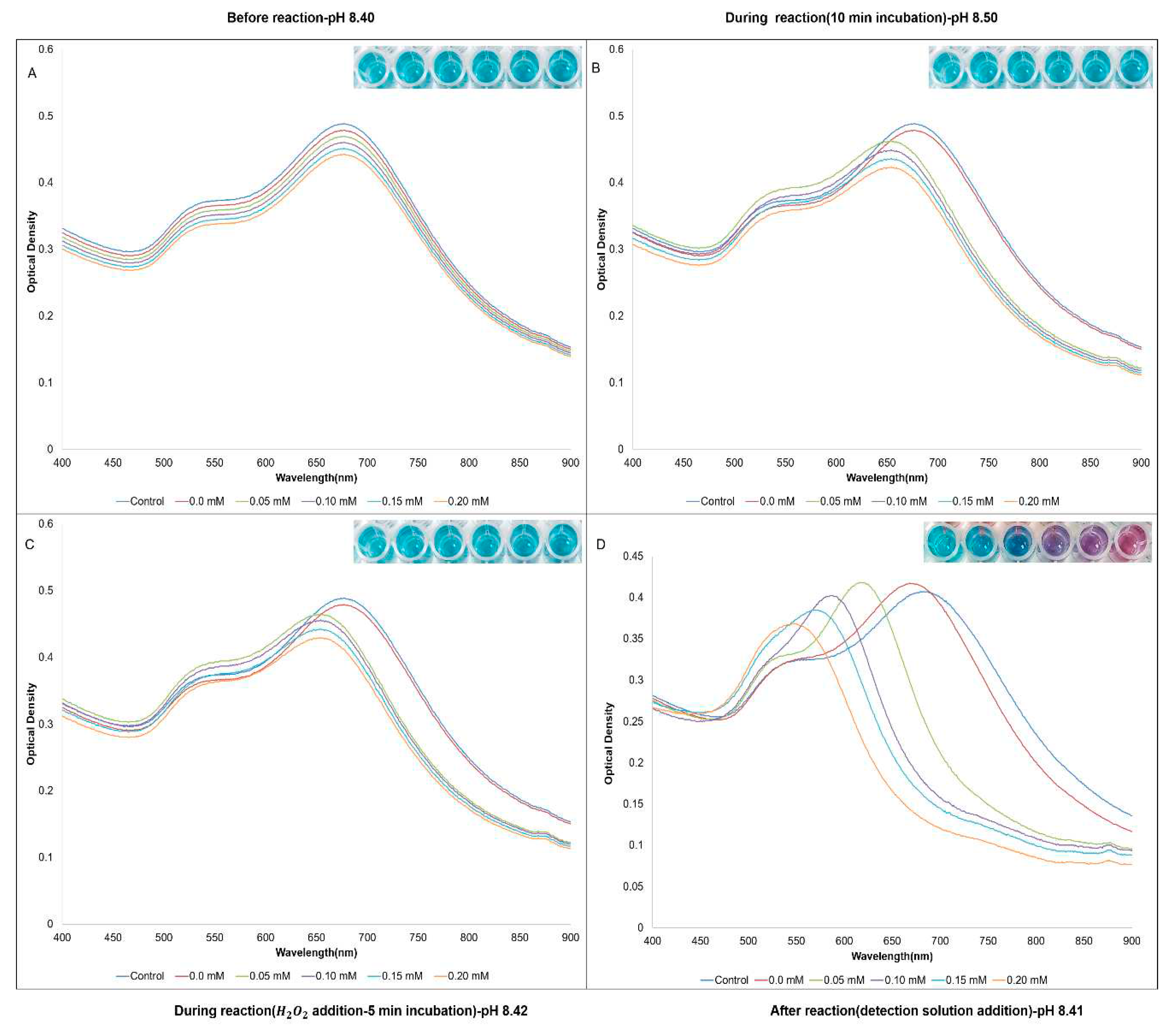
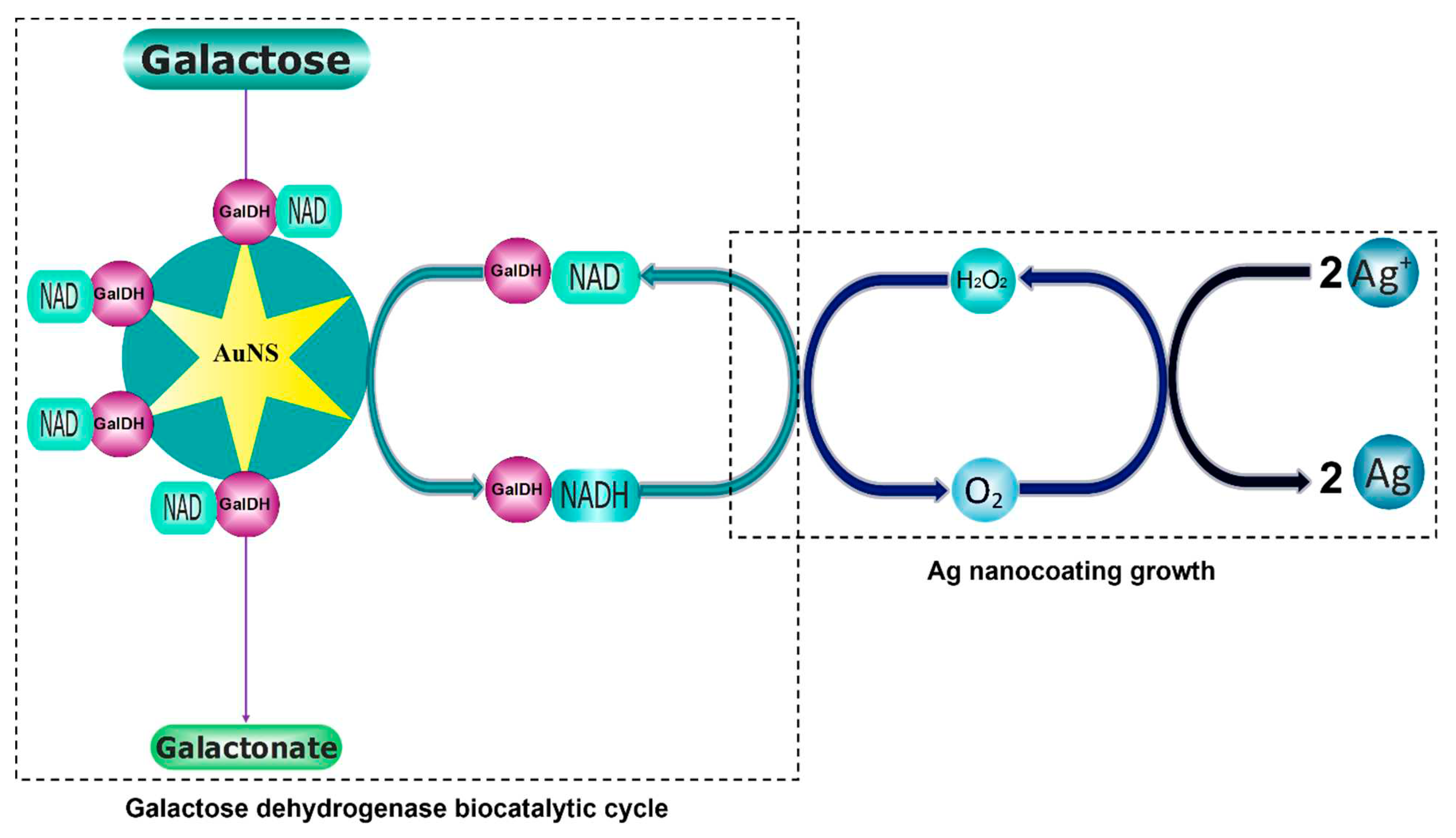
| Sample | Control | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Water | 165 µL | 148 | 138 µL | 128 µL | 118 µL | 108 µL |
| 10 mM Tris (pH 8.4) | 15 µL | 15 µL | 15 µL | 15 µL | 15 µL | 15 µL |
| AuNS-PVP-GalDH | 20 µL | 20 µL | 20 µL | 20 µL | 20 µL | 20 µL |
| 2 mM galactose | 0 µL | 0 µL | 5 µL | 10 µL | 15 µL | 20 µL |
| 10 min Incubation | ||||||
| H2O2 | 0 µL | 0 µL | 5 µL | 10 µL | 15 µL | 20 µL |
| 5 min Incubation | ||||||
| 10 mM AgNO3 | 0 µL | 2 µL | 2 µL | 2 µL | 2 µL | 2 µL |
| 150 mM NaOH | 0 µL | 15 µL | 15 µL | 15 µL | 15 µL | 15 µL |
| 2 min Incubation | ||||||
| Colorimetric signal generation | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





