Submitted:
07 October 2023
Posted:
10 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Solid electrolytes for Mg battery
2.1. Inorganic electrolyte
2.1.1. Oxides
2.1.2. Chalcogenides
2.1.3. Hydrides
| Electrolyte | σtotal (S cm-1) |
Temperature (oC) | Activation energy (eV) | Electrochemical window (V) | Ref |
| Mg(BH4)2 | 1 × 10-9 | 150 | - | - | [62] |
| Mg(BH4)(NH2) | 1 × 10-6 | 150 | - | 3 | |
| Mg(en)1(BH4)2 | 5 × 10-8 | 30 | 1.6 | 1.2 | [64] |
| 6 × 10-5 | 70 | ||||
| Mg(BH4)(NH2) glass ceramics | 3 × 10-6 | 100 | 1.3 | - | [71] |
| Mg(BH4)2 1.6NH3-75 wt.% MgO | 1.2 × 10-5 | RT | 1.12 | 1.2 | [69] |
| Oxidized Mg(BH4)2 | 7.89 × 10-6 | RT | - | - | [66] |
| Mg(BH4)2 1.5THF-75 wt.% MgO | 9.8 × 10-7 | 30 | 1.4 | 1.2 | [70] |
| 1.7 × 10-4 | 70 | ||||
| Mg(BH4)2(NH3BH3)2 | 1.3 × 10-5 | 30 | 1.47 | 1.2 | [65] |
| Mg3(BH4)4(NH2)2 | 4.1 × 10-5 | 100 | 0.84 | 1.48 | [72] |
| Amorphous Mg(BH4)2 2NH3 | 5 × 10-4 | 75 | 1.99 | 1.4 | [73] |
| Mg(BH4)2 1.5NH3-60wt.% YSZ | 3 × 10-4 | 50 | - | 1.3 | [67] |
| Mg(BH4)2 1.5NH3-60wt.% TiO2 | 1.12 × 10-3 | 50 | 0.87 | - | |
| Mg(BH4)2 1.6NH3-67 wt.% Al2O3 | 2.5 × 10-5 | 22 | 0.56 | 1.2 | [68] |
2.1.4. MOF (Metal-organic framework)
| MOF | Liquid electrolyte | σtotal (S cm-1) |
Temperature (oC) | Activation energy (eV) | Ref |
| Mg2(dobpdc) | Mg(TFSI)2/triglyme | 1.3 × 10-4 | RT | 0.11 ~ 0.19 | [80] |
| Mg(OPhCF3)2+Mg(TFSI)2/triglyme | 2.5 × 10-4 | RT | |||
| MIT-20 | MgBr2/PC | 8.8 × 10-7 | RT | 0.37 | [81] |
| Cu4(ttpm)2∙0.6CuCl2 | MgCl2/THF | 1.2 × 10-5 | RT | 0.32 | [82] |
| MgBr2/THF | 1.3 × 10-4 | RT | 0.24 | ||
| MOF-74 | Mg(TFSI)2/MgCl2/DME | 3.17 × 10-6 | RT | 0.53 | [79] |
| Mgbp3dc | α-Mg3(HCOO)6/DMF | 3.8 × 10-5 | RT | 0.669 | [76] |
| UiO-66 | Mg(TFSI)2/[EMIM][TFSI] | 5.8 × 10-5 | RT | 0.67 | [77] |
| MOF-177 | Mg(TFSI)2/diglyme | 1.6 × 10-5 | RT | 0.33 | [78] |
| MIL-101 | Mg(TFSI)2 + MeCN vapor | 1.9 × 10-3 | 25 | 0.18 | [83] |
2.2. Organic electrolyte
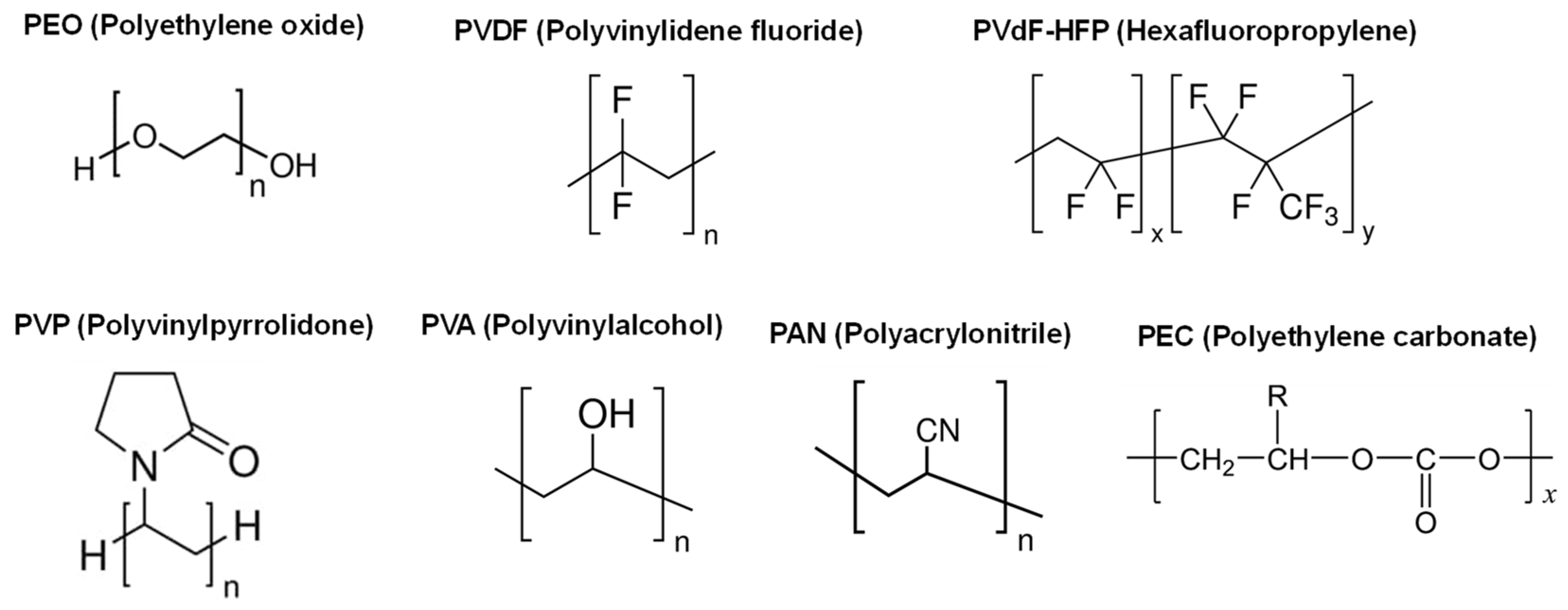
2.2.1. Solid polymer electrolytes
| Polymer | Mg salt | σtotal (S cm-1) |
Temp.(oC) | Ea (eV) | Window (V vs. Mg/Mg2+) |
Transference number |
Ref |
| PEO | Mg(TFSI)2 | 1.8 × 10-6 | 0 | 0.68 | - | - | [84] |
| 1.6 × 10-4 | 50 | ||||||
| PEO | Mg(ClO4)2 | 1.42 × 10-6 | RT | - | - | - | [85] |
| PVP | MgCl2 | 1.42 × 10-5 | RT | - | - | - | [86] |
| PVP | MgSO4 | 1.05 × 10-5 | RT | - | - | - | [87] |
| PVA | MgSO4 | 1 × 10-9 | 27 | 0.37 | - | - | [88] |
| PVA | MgCl2 | 5 × 10-7 | 35 | - | - | - | [89] |
| Polysaccharide | Mg(ClO4)2 | 5.66 × 10-4 | RT | 0.09 | 3.93 | 0.43 | [90] |
| PEC | Mg(ClO4)2 | 5.2 × 10-5 | 90 | - | - | - | [91] |
| PEC | Mg(TFSI)2 | 2.3 × 10-6 | 80 | - | 2.0 | - | [92] |
| PAGE | Mg(TFSI)2 | 4.1 × 10-4 | 90 | - | - | - | [93] |
| Potato starch | MgCl2 | 3.2 × 10-2 | RT | 0.002 | 4.6 | - | [94] |
| Sodium alginate | Mg(NO3)2 | 4.58 × 10-3 | RT | - | 3.5 | 0.31 | [95] |
| MC | Mg(NO3)2 | 1.02 × 10-4 | RT | - | 3.23 | - | [96] |
| Gellan gum | Mg(ClO4)2 | 1.06 × 10-2 | RT | - | 2.86 | 0.33 | [97] |
| Natural rubber | Mg(Tf)2 | 4.9 × 10-3 | 30 | - | 2.5 | - | [98] |
| I-Carrangeenan | Mg(NO3)2 | 6.1 × 10-4 | 30 | 0.17 | - | - | [99] |
| Agarose | Mg(NO3)2 | 1.48 × 10-5 | RT | 0.044 | 3.57 | - | [100] |
| CA | Mg(NO3)2 | 9.19 × 10-4 | RT | - | 3.65 | 0.35 | [101] |
| K-Carrageenan | MgCl2 | 4.76 × 10-3 | 30 | - | 1.94 | 0.26 | [102] |
| Chitosan | Mg(Tf)2 | 9.58 × 10-5 | RT | 0.36 | - | - | [103] |
| K-Carrageenan | Mg(NO3)2 | 7.05 × 10-4 | RT | - | 4.42 | 0.32 | [104] |
| Methyl cellulose | Mg(CH3COO)2 | 2.6 × 10-5 | RT | - | 3.47 | - | [105] |
| I-carrageenan | Mg(ClO4)2 | 2.18 × 10-3 | RT | 0.05 | - | 0.313 | [106] |
| Chitosan | MgCl2 | 4.6 × 10-4 | - | - | - | - | [107] |
| Pectin | Mg(NO3)2 | 7.7 × 10-4 | RT | - | 3.8 | 0.29 | [108] |
| Pectin | MgCl2 | 1.14 × 10-3 | RT | - | 2.05 | 0.301 | [109] |
| PEO-PVDF | MgTFSI | 1.2 × 10-5 | 25 | - | - | - | [111] |
| PEO/PVDF-HFP | MgBr2 | 3.9 × 10-4 | RT | 0.26 | 1.86 | - | [112] |
| PVA-PAN | Mg(ClO4)2 | 2.94 × 10-4 | RT | 0.21 | 3.65 | 0.27 | [113] |
| PVDF-HFP+ PVAc |
Mg(ClO4)2 | 1.60 × 10-5 | 30 | 0.33 | 3.5 | - | [114] |
| PVP-PVA | Mg(NO3)2 | 3.8 × 10-5 | 30 | 0.475 | - | - | [115] |
| PVA-PAN | MgCl2 | 1.01 × 10-3 | RT | 0.07 | 3.66 | - | [116] |
| Poly(VdCl-co-AN-co-MMA) | Mg(NO3)2 | 1.6 × 10-4 | RT | 0.19 | 3.2 | 0.36 | [117] |
| PEO/PO | Mg(TFSI)2 | 1.5 × 10-5 | 30 | - | - | - | [118] |
| PCL-PTMC | Mg(TFSI)2 | 2.52 × 10-8 | 25 | - | - | - | [119] |
| PVA-PAN | Mg(NO3)2 | 1.71 × 10-3 | RT | 0.36 | 3.4 | 0.30 | [120] |
| PVDF-HFP+PVAc | Mg(ClO4)2 | 3.85 × 10-5 | 30 | 3.37 | 3.68 | - | [121] |
| CS+MC | MgCl2 | 2.75 × 10-3 | 30 | - | 3.86 | - | [122] |
| Corn silk+PVA | MgCl2 | 1.28 × 10-3 | RT | - | 2.11 | 0.32 | [123] |
| Methyl cellulose-PVA | Mg(NO3)2 | 3.25 × 10-4 | 27 | - | 2.62 | - | [124] |
| PEO-Starch | MgBr2 | 7.8 × 10-9 | RT | - | - | - | [125] |
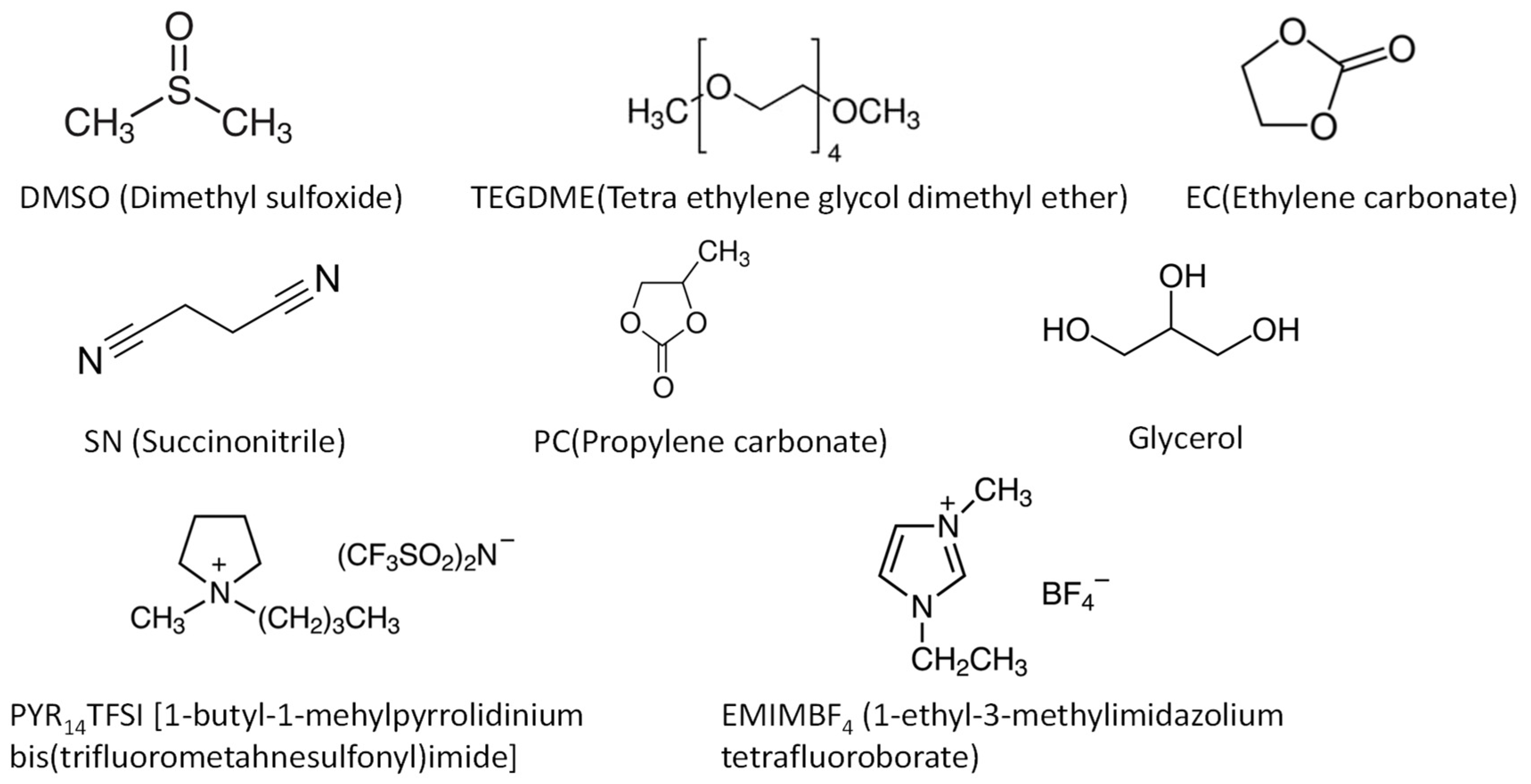
2.2.2. Polymer electrolytes with plasticizers (Gel-polymer electrolytes)
| Polymer | Mg salt | Plasticizer | σtotal (S cm-1) |
Temp. (oC) | Ea (eV) | Window (V vs. Mg/Mg2+) |
Transference number |
Ref |
| P(PEGDMA)-P(STFSI) | DMSO | 8.8 × 10-4 | 30 | - | 1.5 | (1.0) | [135] | |
| PVDF | Mg(SO3CF3)2 | TEGDME | 4.6 × 10-4 | 55 | 0.62 | 1.0 | 0.74 | [136] |
| PEO | Mg(Tf)2 | PYR14TFSI | 3.7 × 10-4 | RT | - | - | 0.40 | [127] |
| PEO | Mg(Tf)2 | EMIM-BF4 | 9.4 × 10-5 | RT | 0.26 | 4.0 | 0.22 | [137] |
| PVdC-co-AN | Mg(TFSI)2 | EC+SN | 1.9 × 10-6 | RT | 0.04 | 3.8 | 0.59 | [130] |
| PVdC-co-AN | Mg(TFSI)2 | SN | 1.6 × 10-6 | RT | 0.09 | 3.2 | - | [138] |
| PVDF-HFP | Mg(ClO4)2 | EDiMIMBF4 | 8.4 × 10-3 | RT | 0.33 | - | - | [139] |
| PVDF-HFP | Mg(ClO4)2 | EMIMBr,PC | 2.0 × 10-2 | RT | 0.02 | - | - | [129] |
| PEC | Mg(TFSI)2 | TEGDME | 5.2 × 10-6 | 80 | - | - | - | [140] |
| PECH-OH | MgCl2 | TEGDME | 6.2 × 10-5 | 30 | 0.25 | 3.2 | 0.79 | [128] |
| PVDF-HFP | Mg(Tf)2 | SN+EMITf | 4 × 10-3 | 26 | 0.104 | 4.1 | - | [141] Bull. Mater. Sci. 41 2018 147 |
| Poly(VdCl-co-An-co-MMA) | MgCl2 | SN | 1.4 × 10-3 | RT | 0.26 | 3.3 | 0.31 | [142] |
| c-PTHF | Mg(TFSI)2 | TEGDME | 4.5 × 10-5 | 30 | - | - | - | [143] |
| CS | Mg(CH3COO)2 | glycerol | 1.1 × 10-4 | RT | - | - | - | [144] |
| k-carrageenan | Mg(NO3)2 | EC | 7.3 × 10-3 | 30 | - | 4.59 | 0.39 | [145] |
| PVDF-HFP/PVAc | Mg(ClO4)2 | EMITF | 9.1 × 10-4 | 30 | 0.28 | 3.59 | - | [146] |
| Hydroxy propyl | Mg(TFSI)2 | TEGDME | 1.73 × 10-3 | 25 | - | - | - | [147] |
| PVDF-HFP | Mg(Tf)2 | EC-DEC | 2.4 × 10-4 | 70 | - | 5.0 | 0.42 | [131] |
| PVDF | Mg(ClO4)2 | PC | 1.5 × 10-3 | RT | - | 5.0 | 0.47 | [148] |
| PVDF-HFP | Mg(ClO4)2 | TEGDME | 9.8 × 10-4 | RT | - | 4.6 | - | [149] |
| PTHF | MgBOR | 2.0 × 10-3 | 25 | - | 2.57 | 0.3 | [150] | |
| PVA | Mg(Tf)2 | EMITf | 1.2 × 10-3 | RT | - | - | - | [151] |
| PVDF-HFP | Mg(ClO4)2 | PC | 1.6 × 10-3 | RT | - | 5.5 | - | [152] |
| PAN | Mg(ClO4)2 | PC | 3.3 × 10-3 | 30 | 0.1 | 4.6 | 0.6 | [153] |
| PVDF-HFP | MgCl2-AlCl3 | TEGDME | 4.7 × 10-4 | 25 | - | 3.1 | - | [134] |
| PEO | Mg(Tf)2 | PC-DEC | 3.0 × 10-5 | RT | 0.14 | 3.5 | 0.32 | [154] |
| CS:Dextran | Mg(CH3COO)2 | Glycerol | 1.2 × 10-6 | RT | - | 1.5 | - | [155] |
2.2.3. Organic crystal electrolytes
2.3. Organic-inorganic composite electrolytes
2.3.1. Solid polymer electrolytes with fillers
| Polymer | Mg salt | Filler | σtotal (S cm-1) |
Temp. (oC) | Ea (eV) | Window (V vs. Mg/Mg2+) |
Transference number | Ref |
| PVA/PVP | MgCl2 | CuS | 4.3 × 10-6 | RT | - | - | - | [160] |
| MC | MgCl2 | ZnO | 1.2 × 10-4 | RT | - | - | - | [161] |
| PVDF | Mg(NO3)2 | MgO | 1.0 × 10-4 | RT | 0.32 | - | - | [162] |
| PEG | Mg(CH3COO)2 | CeO2 | 3.4 × 10-6 | RT | - | - | - | [163] |
| PMMA | Mg(Tf)2 | TiO2 | 1.8 × 10-6 | RT | - | - | - | [164] |
| CS | Mg(NO3)2 | MnO2 | 1.2 × 10-3 | 30 | - | 1.7 | - | [165] |
| PVDF-HFP | Mg(Tf)2 | BaTiO3 | 4.1 × 10-4 | RT | - | - | - | [158] |
| PEO | Mg(Tf)2 | MgO | 1.6 × 10-4 | 25 | 0.14 | - | - | [166] |
| PVDF | Mg(NO3)2 | Al2O3 | 9.5 × 10-6 | RT | - | - | - | [167] |
| PVDF | Mg(NO3)2 | ZnO | 5.2 × 10-5 | RT | 0.29 | - | - | [168] |
| PEO | MgCl2 | B2O3 | 7.2 × 10-6 | 25 | - | - | - | [169] |
| PVDF-HFP/PVAc | Mg(ClO4)2 | MgTiO3 | 5.8 × 10-3 | 30 | 0.25 | 4.0 | 0.34 | [170] |
| CS | MgCl2 | V2O5 | 1.4 × 10-3 | RT | - | 1.7 | - | [171] |
| PVDF-HFP | MgClO4 | ZrO2 | 6.6 × 10-2 | 30 | - | - | - | [172] |
| PVDF-HFP | MgCl2 | ZnO | 1.3 × 10-5 | RT | - | - | - | [173] |
2.3.2. Solid polymer electrolytes including plasticizers and fillers
| Polymer | Mg salt | Plasticizer | Filler | σtotal (S cm-1) |
Temp. (oC) | Ea (eV) | Window (V vs. Mg/Mg2+) | Transference number | Ref |
| CS/MC | Mg(CH3COO)2 | Glycerol | Ni | 1.0 × 10-4 | RT | - | 2.48 | - | [174]] |
| PEO | Mg(ClO4)2 | EMIMFSI | SiO2 | 5.4 × 10-4 | RT | 0.36 | 4.0 | - | [175] |
| CS | Mg(CH3COO)2 | Glycerol | Ni | 1.1 × 10-5 | RT | - | 2.4 | - | [176] |
| PVDF-HFP | Mg(Tf)2 | EC-PC | MgAl2O4 | 4.0 × 10-3 | RT | - | - | 0.66 | [177] |
| PVDF-HFP | Mg(ClO4)2 | PTR14RFSI | TiO2 | 1.6 × 10-4 | 30 | 0.13 | - | 0.23 | [178] |
| PVDF-HFP | Mf(TFSI)2 | TEGDME | SiO2 | 8.3 × 10-4 | RT | - | - | - | [179] |
| PTHF | Mg(BH4)2-LiBH4 | diglyme | TiO2 | 4.2 × 10-4 | 40 | 0.003 | - | 0.5 | [180] |
3. All-solid-state Mg battery
3.1. Inorganic electrolyte
3.2. MOF
3.3. Organic electrolyte
3.3.1. Gel polymer electrolyte
3.4. Organic-inorganic composite electrolytes
| Electrolyte | Cathode | Initial capacity | Capacity retention | Temp. (oC) | Note | Ref |
| Borohydrides | ||||||
| Mg(BH4)(NH2) | Pt | - | - | - | Mg plating on Pt | [62] |
| Mg(BH4)(NH3BH3)2 | Mo | - | - | - | Mg plating on Mo | [65] |
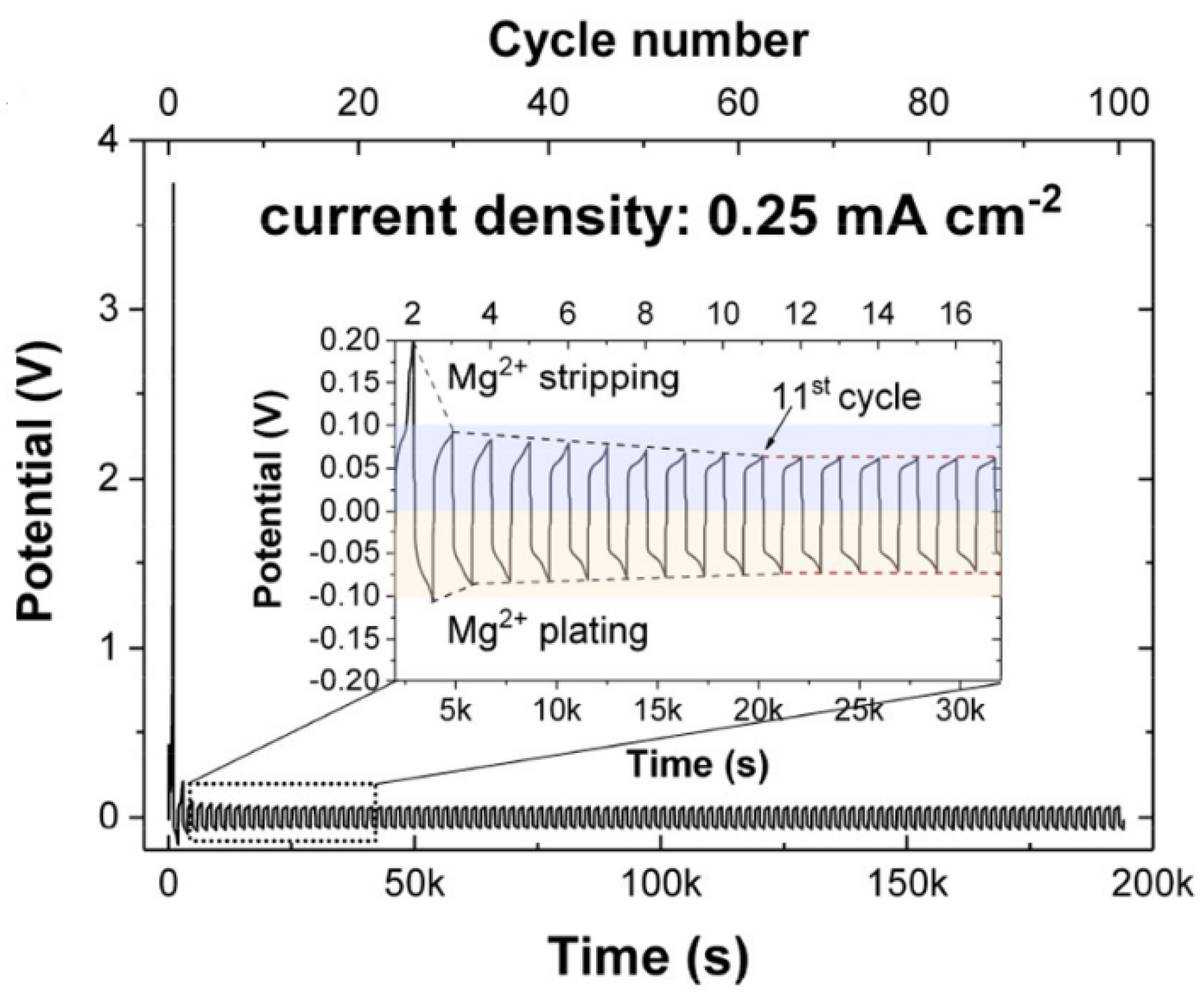
| 0.4Mg(BH4)2•NH3-0.6Mg(BH4)2•2NH3@MgO | Mg | - | - | 60 | Stable Mg stripping/plating more than 100 cycles at 0.25 mA cm-2 | [69] |
| Mg(en)1(BH4)2 | Pt | - | - | 60 | Stable Mg stripping/plating in 20 cycles at 10 mV s-1 | [64] |
| Mg(BH4)2 1.5NH3-YSZ | Mg | - | - | 60 | Stable Mg stripping/plating in 300 cycles at 0.1 mA cm-2 | [67] |
| Mg(BH4)∙2NH3 | TiS2 | 141 mAh/g at 0.05C | 31 % at 25th cycle | 75 | 111 mAh/g at 0.2C, 72 mAh/g at 0.5C |
[73] |
| Mg(BH4)2∙1.5THF-MgO | TiS2 | 94 mAh/g at C/50 | 32 % at 5th cycle | 55 | SS current collector was oxidized | [70] |
| MOF | ||||||
| Mg(TFSI)2/MgCl2/DME in MOF-74 |
Mg | - | - | RT | Stable Mg stripping/plating in 100 cycles at 0.05 mA cm-2 | [79] |
| Mgbp3dc in α-Mg3(HCOO)6/DMF | Mg | - | - | RT | Stable Mg stripping/plating in 8 cycles at 0.1 μA cm-2 | [76] |
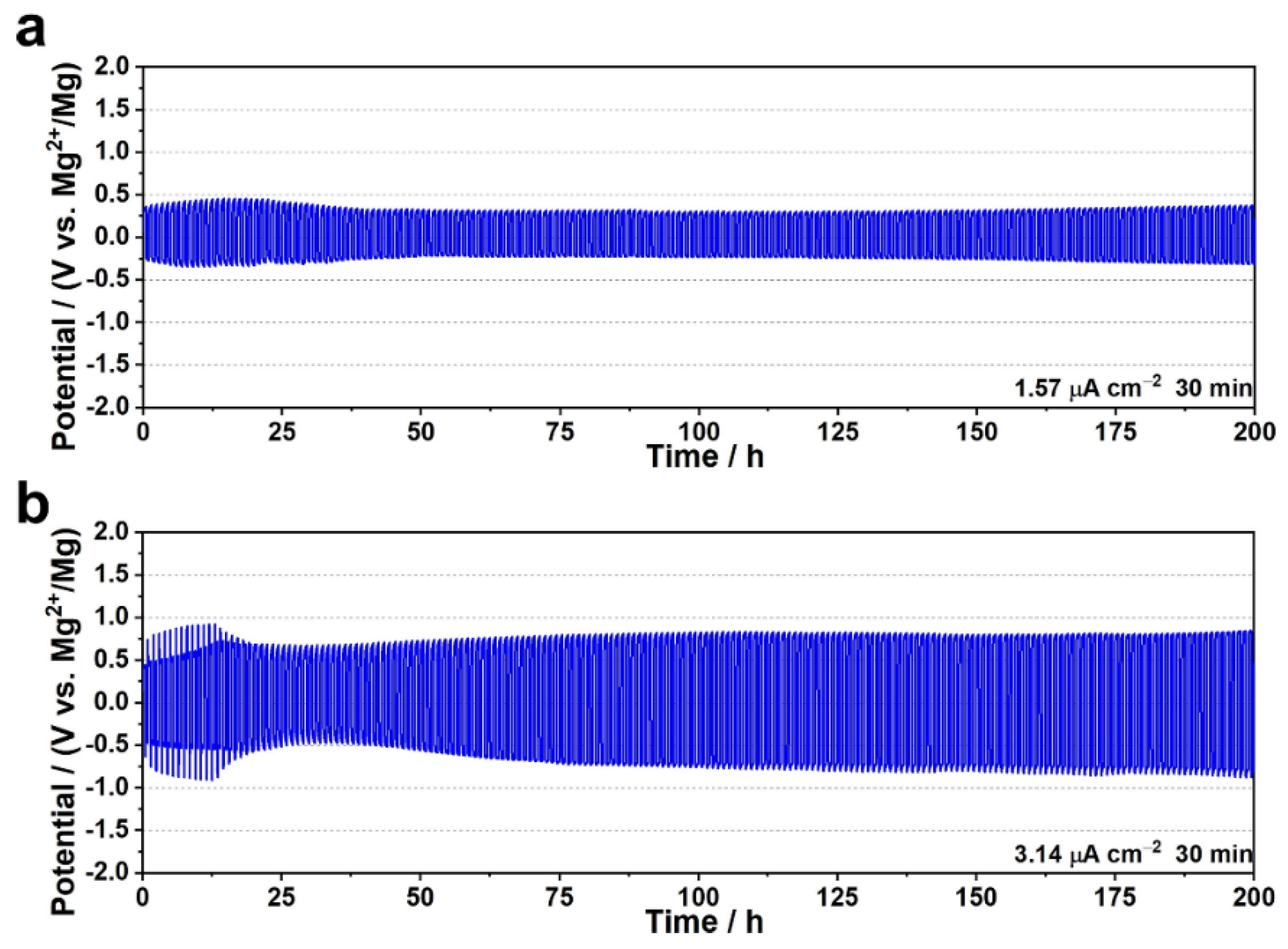
| Mg(TFSI)2/[EMIM][TFSI] in UiO-66 | PTCDA | 36 mAh/g at 1 mA/g | 61 % at 3rd cycle | 60 | Stable Mg stripping/plating more than 200 cycles at 3.14 μA cm-2 | [77] |
| GPE | ||||||
| PVDF-TEGDME-Mg(Tf)2 | BaTiO3 | 557 mAh/g at 20 mA/g | 12 % at 15th cycle | 55 |
|
[136] |
| PECH-OH-MgCl2-TEGDME | Mo6S8 | 73 mAh/g at 0.3 C | 84 % at 100th cycle | 30 | Pouch cell data | [128] |
| PVDF-HFP-Mg(Tf)2- SN+EMITf | MnO2 | 40 mAh/g at 38 μA cm-2 | 12.5 % at 8th cycle | RT | [141] | |
| PTHF-MgBOR | Mo6S8 | 68 mAh/g at 0.1 C | 74 % at 100th cycle | 25 | Stable Mg stripping/plating more than 1000 cycles at 0.1 mA cm-2 | [150] |
| PVDF/HFP-MgCl2/AlCl3-TEGDME | MoS2 | 121 mAh/g at 40 mA/g | 58 % at 1700th cycle | 25 | Stable Mg stripping/plating more than 400 cycles at 1.0 mA cm-2 | [134] |
| Filler | ||||||
| PVDF-HFP/PVAc-Mg(ClO4)2-MgTiO3 | Mo6S8 | 120 mAh/g at 0.5 C | 87 % at 30th cycle | RT | [170] | |
| SPE+filler+plasticizer | ||||||
| PVDF-HFP-Mg(TFSI)2-SiO2 | TiO2 | 129 mAh/g at 50 mA/g | 99 % at 100th cycle | RT | Stable Mg stripping/plating more than 100 cycles at 0.2 mA cm-2 | [179] |
| PTHF- Mg(BH4)2/LiBH4-Diglyme- TiO2 |
TiS2 | 225 mAh/g at 0.5 C | 98 % at 70th cycle | 22 | Stable Mg stripping/plating more than 100 cycles at 0.1 mA cm-2 | [180] |
4. Challenges
- (1)
- Inorganic electrolytes
- (2)
- Study on Mg salts
- (3)
- Mechanical properties of solid electrolytes
- (4)
- Construction of all-solid-state Mg battery
- (5)
- Cathode materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winter, M.; Barnett, N.; Xu, K. Before Li ion batteries. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 11433–11456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Lu, J.; Chen, Z.W.; Amine, K. 30 years of lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Chen, D.; Tan, H.; Zhang, X.; Rui, X.; Yu, Y. 3D porous V2O5 architectures for high-rate lithium storage. J. Energy Chem. 2020, 40, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Peng, C.; Wang, R.; Cao, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, J. Micro-sized FeS2@FeSO4 core-shell composite for advanced lithium storage. J. Alloy Compd. 2020, 814, 151922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, M.; Tarascon, J.M. Building better batteries. Nature 2008, 451, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittingham, M.S. Ultimate limits to intercalation reactions for lithium batteries. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11414–11443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wnag, J.L.; Ding, F.; Chen, X.L.; Nasybutin, E.; Zhang, Y.H.; Zhang, J.G. Lithium metal anodes for rechargeable batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liang, J.; Song, X.; Jin, Z. Recent progress in constructing halogenated interfaces for highly stable lithium metal anodes. Energy Storage Mater. 2023, 54, 732–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Thangadurai, V. Critical current densities for high-performance all-solid-state Li-metal batteries: fundamentals mechanisms, interfaces materials and applications. ACS Energy Lett. 2022, 7, 1492–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Kotobuki, M.; Song, S.; Lai, M.O.; Lu, L. Review on solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2018, 389, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebie, S.; Mgo, H.P.K.; Lepretre, J.-C.; Iojoiu, C.; Cointeaux, L.; Berthelot, R.; Alloin, F. Electrolyte based on easily synthesized, low cost triphenolate-borohydride salt for high performance Mg(TFSI)2-glyme rechargeable magnesium batteries. ACS Appl. Mater.&Interfaces 2017, 9, 28377–28385. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Tan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, B.; Xiong, S.; Feng, J.; Qian, Y. Highly reversible Mg metal anodes enabled by interfacial liquid metal engineering for high-energy Mg-S batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 48, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackle, M.; Helmbrecht, K.; Smits, M.; Stottmeister, D.; Gross, A. Self-diffusion barriers: possible descriptors for dendrite growth in batteries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 3400–3407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotobuki, M. Recent progress of ceramic electrolytes for post Li and Na batteries. Funct. Mater. Lett. 2021, 14(03), 2130003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, H.; Xu, J.; Huang, K. Progress in retrospect of electrolytes for secondary magnesium batteries. Coordination Chem. Rev. 2020, 422, 213478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wang, K.; He, H.; Hanc, E.; Kotobuki, M.; Lu, L. Processing and properties of garnet-type Li7La3Zr2O12 ceramic electrolytes. Small 2022, 2205550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Fu, K.; Kammampata, S.P.; McOwen, D.W.; Samson, A.J.; Zhang, L.; Hits, G.T.; Nolan, A.M.; Wachman, E.D.; Mo, Y.; Thangadurai, V.; Hu, L. Garnet-type solid-state electrolytes: materials, interfaces and batteries. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 4257–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, G.; CHongyang, Y.; Tengfei, Z.; Xuebin, Y. Solid state electrolytes for rechargeable magnesium-ion batteries: From structure to mechanism. Small 2022, 18(43), 2106981. [Google Scholar]
- Stefania, F.; Marisa, F.; Belen, B.G.A.; Matteo, B.; Segio, B.; Michele, P.; Claudio, G. Solid-state post Li metal ion batteries: A sustainable forthcoming reality? Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11(43), 2100785. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, B.; Wang, Z.; Ren, H.; Lu, X.; Qu, Y.; Liu, W.; Jiang, K.; Kotobuki, M. Interfacial modification of Na3Zr2Si2PO12 solid electrolyte by femtosecond laser etching. Ionics 2023, 29, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, F.; Sun, J.; Oh, J.A.S.; Wu, T.; Chen, G.; Huang, Q.; Kotobuki, M.; Zeng, K.; Lu, L. Ferroelectric engineered electrode-composite polymer electrolyte interfaces for all-solid-state sodium metal battery. Adv. Sci. 2022, 2105849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, M.; Nakano, K.; Harada, M.; Tanibata, N.; Takeda, H.; Noda, Y.; Kobatashi, R.; Karasuyama, M.; Takeuchi, I.; Kotobuki, M. Na superionic conductor-type LiZr2(PO 4)3 as a promising solid electrolyte for use in all-solid-state Li metal batteries. Chem. Comm. 2022, 58, 9328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotobuki, M.; Yanagiya, S. Li-ion conductivity of NASICON-type Li1+2xZr2-xCax(PO4)3 solid electrolyte prepared by spark plasma sintering. J. Alloy Compd. 2021, 862, 158641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotobuki, M.; Koishi, M. Preparation of Li1.3Al0.3Ti1.7(PO4)3 solid electrolyte via a sol-gel method using various Ti Sources. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2020, 8, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotobuki, M.; Koishi, M. Preparation of Li1.5Al0.5Ti1.5(PO4)3 solid electrolyte via a sol-gel route using various Al sources. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 4645–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayamizu, K.; Haishi, T. Ceramic-glass pellet thickness and Li diffusion in NASICON-type LAGP (Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3) studied by pulsed field gradient NMR spectroscopy. Solid State Ionics 2022, 380, 115924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; QU, Y.; Ren, H.; Lu, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Kotobuki, M.; Jiang, K. A solid-liquid composite electrolyte with a vertical microporous Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 skeleton that prepared by femtosecond laser structuring and filled with ionic liquid. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 287, 126265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Tamura, S.; Imanaka, N. Synthesis and characterization of divalent ion conductors with NASICON-type structures. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2019, 7, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.J.; Zhong, G.M.; Lu, Y.X.; Liu, L.L.; Zhao, C.L.; Zhang, Q.Q. A novel NASICON-based glass-ceramic composite electrolyte with enhanced Na-ion conductivity. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 23, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, S.; Takahashi, M.; Ishikawa, J.; Ito, K. Solid electrolytes with multivalent cation conduction. 1. Conducting species in MgZrPO4 system. Solid State Ionics 1987, 23, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, K.; Noda, Y.; Tanibata, N.; Nakayama, M.; Kajihara, K.; Kanamura, K. Computational investigation of the Mg-ion conductivity and phase stability of MgZr4(PO4)6. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 12590–12595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, J.; Morota, K.; Kuwata, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Maekawa, H.; Hattori, T.; Imanaka, N.; Okazaki, Y.; Adachi, G.-Y. High temperature 31P NMR study on Mg2+ ion conductors. Solid State Comm. 2001, 120, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, N.K.; Adnan, S.B.R.S.; Jaafar, M.H.; Mohamed, N.S. Studies on structural and electrical properties of Mg0.5+y(Zr2-yFey)2(PO4)3 ceramic electrolytes. Ionics 2016, 22, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, S.; Yamane, M.; Hoshino, Y.; Imanaka, N. Highly conducting divalent Mg2+ cation solid electrolytes with well-ordered three-dimensional network structure. J. Solid State Chem. 2016, 235, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, N.K.; Mohamed, N.S. Structural and electrical properties of novel Mg0.9+0.5yZn0.4AlyZr1.6-y(PO4)3 ceramic electrolytes synthesized via nitrate sol-gel method. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Tech. 2016, 80, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, Z.A.; Adnan, S.B.R.S.; Mohamed, N.S. Effect of sintering temperature on the structural, electrical and electrochemical properties of novel Mg0.5Si2(PO4)3 ceramic electrolytes. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 4452–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Tsuruoka, T.; Tsujita, T.; Nishitani, Y.; Nakura, K.; Terabe, K. Aromic layer deposition of a magnesium phosphate solid electrolyte. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 5566–5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, H.; Nakano, K.; Tanibata, N.; Nakayama, M. Novel Mg-ion conductive oxide of μ-cordierite Mg0.6Al1.2Si1.8O6. Sci. Tech. Adv. Mater. 2020, 21, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omote, A.; Yotsuhashi, S.; Zenitani, Y.; Yamada, Y. High ion conductivity in MgHf(WO4)3 solids with ordered structure: 1-D alignments of Mg2+ and Hf4+ ions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2011, 94(8), 2285–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Miura, A.; Rosero-Navarro, N.C.; Li, M.; Sun, J.; Kotobuki, M.; Tadanaga, K. Fe-P-S electrodes for all-solid-state lithium secondary batteries using sulfide-based solid electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2020, 449, 227576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, T.; Hayashi, A.; Yamauchi, A.; Tatsumisago, M. Preparation of magnesium ion conducting MgS-P2S5-MgI2 glasses by a mechanochemical technique. Solid State Ionics 2014, 262, 601–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
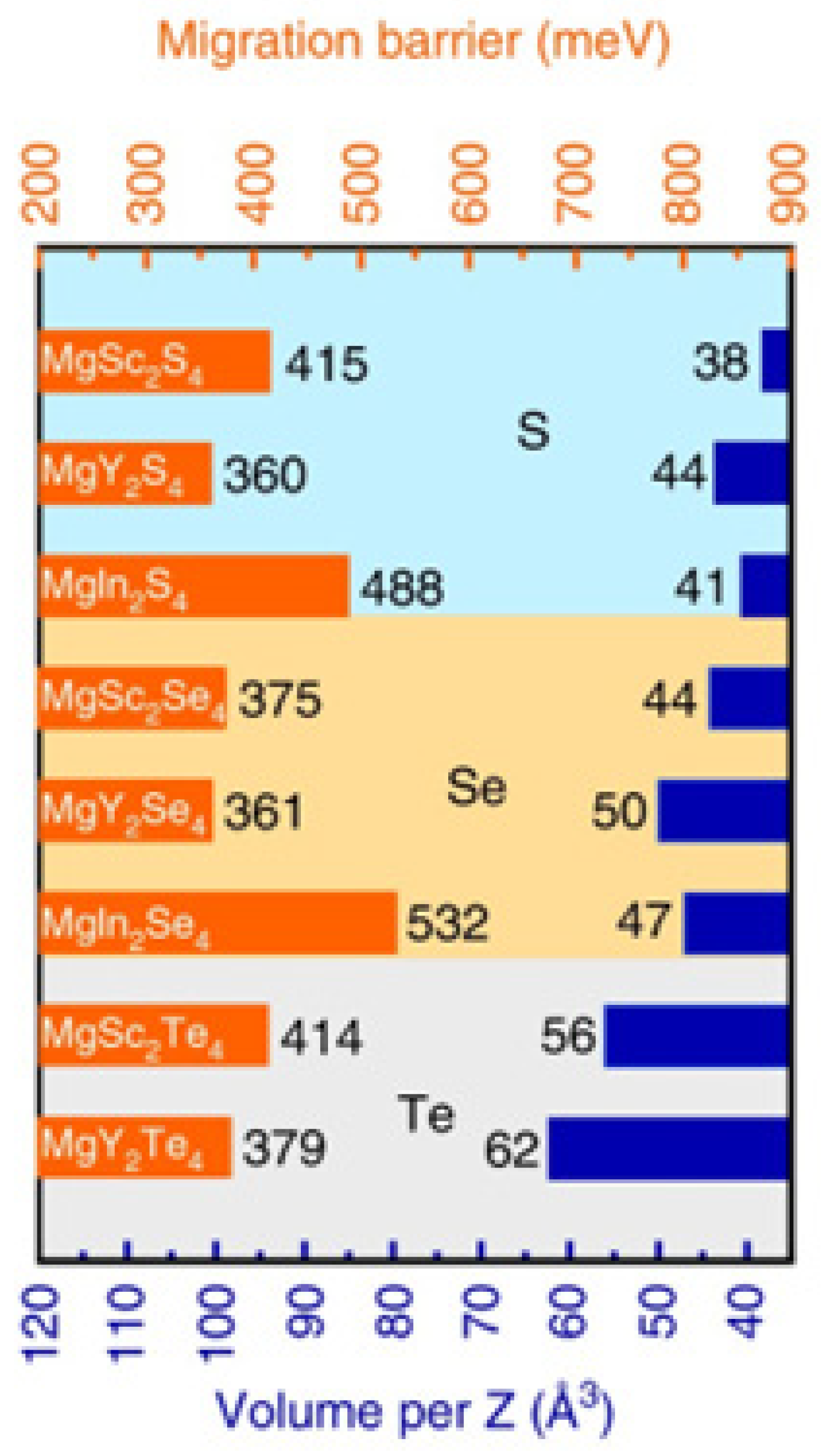
- Canepa, P.; Bo, S.-H. Gautam, G.S.; Key, B.; Richards, W.D.; Shi, T.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Ceder, G. High magnesium mobility in ternary spinel chalcogenides. Nat. Comm. 2017, 8, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koishi, M.; Kotobuki, M. Preparation of Y-doped Li7La3Zr2O12 by co-precipitation method. Ionics 2022, 28, 2065–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-P.; Zhao-Karger, Z.; Klein, F.; Chable, J.; Braun, T.; Schuer, A.R.; Wang, C.-R.; Guo, Y.-G.; Fichtner, M. MgSc2Se4-magnesium solid ionic conductor for all-solid-state Mg batteries? ChemSusChem 2019, 12(10), 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Solomatin, N.; Kauffmann, Y.; Kraytsberg, A.; Ein-Eli, Y. Revealing and excluding the root cause of the electronic conductivity in Mg-ion MgSc2Se4 solid electrolyte. Appl. Mater. Today 2021, 23, 100998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Solomatin, N.; Kraytsberg, A.; Ein-Eli, Y. MgSc2Se4 solid electrolyte for rechargeable Mg batteries: An electric field-assisted all-solid-state synthesis. Energy Tech. 2022, 10, 2200896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemenceau, T.; Andriamady, N.; Kumar, M.K.; Bardran, A.; Avila, V.; Dhal, K.; Hopkins, M.; Vendrell, X.; Marshall, D.; Raj, R. Flash sintering of Li-ion conducting ceramic in a few seconds at 850 oC. Scripta Materialia 2019, 172, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Kang, L.; Kotobuki, M.; He, L.; Liu, B.; Jiang, K. Boron group element doping of Li1.5Al0.5Ge1.5(PO4)3 based on microwave sintering. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2021, 25, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ping, W.; Bai, Q.; Cui, H.; Hensleigh, R.; Wang, R.; Brozena, A.H.; Xu, Z.; Dai, J.; Pei, Y.; Zheng, C.; Pastel, G.; Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, J.-C.; Yang, B.; Zheng, X.; Luo, J.; Mo, Y.; Dunn, B.; Hu, L. A general method to synthesize and sinter bulk ceramics in seconds. Science 2020, 368, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, N.K.; Adnan, S.B.R.S.; Mohamed, N.S. Characterization of Mg0.5Zr2(PO4)3 for potential use as electrolyte in solid state magnesium batteries. Ceram. Int. 2014, 40, 13719–13727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Kale, G.M. Novel sol-gel synthesis of MgZr4P6O24 composite solid electrolyte and newer insight into the Mg2+-ion conducting properties using impedance spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 17909–17915. [Google Scholar]
- Imanaka, N.; Okazaki, Y.; Adachi, G.-Y. Divalent magnesium ion conducting characteristics in phosphate based solid electrolyte composites. J. Mater. Chem. C 2000, 10, 1431–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanaka, N.; Okazaki, Y.; Adachi, G. Optimization of divalent magnesium ion conduction in phosphate based polycrystalline solid electrolytes. Ionics 2001, 7, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Kreshishian, V.; Liu, S.; Yi, E.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y.; Kieffer, J.; Ye, B.; Kaine, R.M. Processing liquid-feed flame spray pyrolysis synthesized Mg0.5Ce0.2Zr1.8(PO4)3 nanopowders to free standing thin films and pellets as potential electrolytes in all-solid-state Mg batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 272, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajihara, K.; Nagano, H.; Tsujita, T.; Munakata, H.; Kanamura, K. High-temperature conductivity measurements of magnesium-ion-conducting solid oxide Mg0.5-x(Zr1-xNbx)2(PO4)3 (x = 0.15) using Mg metal electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164(9), A2183–A2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.; Rani, M.S.A.; Adnan, S.B.R.S.; Salleh, F.M.; Mohamed, N.S. Characteristics of new Mg0.5(Zr1-xSnx)2(PO4)3 NASICON structured compound as solid electrolytes. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 28145–28155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imanaka, N.; Okazaki, Y.; Adachi, G. Divalent magnesium ionic conduction in Mg1-2x(Zr1-xNbx)4P6O24 (x = 0-0.4) solid solutions. Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 2000, 3(7), 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, C.; Wang, Y.; Yi, E.; Wang, W.; Kieffer, J.; Laine, R.M. Processing combustion synthesized Mg0.5Zr2(PO4)3 nanopowders to thin films as potential solid electrolytes. Electrochem. Comm. 2020, 116, 106753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, Z.A.; Adnan, S.B.R.S.; Salleh, F.M.; Mohamed, N.S. Effects of Mg2+ interstitial ion on the properties of Mg0.5+x/2Si2-xAlx(PO4)3 ceramic electrolytes. J. Magnesium Alloy 2017, 5, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, M.; Su, N.C.; Mohamed, N.S. Sol-gel synthesis and characterization of β-MgSO4: Mg(NO3)2-MgO composite solid electrolyte. Ionics 2017, 23, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, M.; Oguchi, H.; Sato, T.; Takamura, H.; Tsuchida, E.; Ikeshoji, T.; Orimo, S.-I. Sodium and magnesium ionic conduction in complex hydrides. J. Alloy Compd. 2013, 580, S98–S101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, S.; Miwa, K.; Aoki, M.; Takechi, K. A novel inorganic solid state ion conductor for rechargeable Mg batteries. Chem. Comm. 2014, 50, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruyet, R.L.; Berthelot, R.; Salager, E.; Florian, P.; Fleutot, B.; Janot, R. Investigation of Mg(BH4)(NH2)-based composite materials with enhanced Mg2+ ionic conductivity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 10756–10763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roedern, E.; Kuhnel, R.-S.; Remhof, A.; Battaglia, C. Magnesium ethylenediamine borohydride as solid-state electrolyte for magnesium batteries. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisu, K.; Kim, S.; Inukai, M.; Oguchi, H.; Takagi, S.; Orimo, S.-I. Magnesium borohydride ammonia borane as a magnesium ionic conductor. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 3174–3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Rawal, A.; Cazorla, C.; Aguey-Zinsou, K.F. Facile self-forming superionic conductors based on complex borohydride surface oxidation. Adv. Sus. Syst. 2020, 1900113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Z.; Deng, H.; Cen, W.; Yan, Y.; Chen, Y. Oxygen vacancies boosted fast Mg2+ migration in solids at room temperature. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 51, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Grinderslev, J.B.; Burankova, T.; Wei, S.; Embs, J.P.; Skibsted, J.; Jensen, T.R. Fast room-temperature Mg2+ conductivity in Mg(BH4)2∙1.6NH3-Al2O3 nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 2211–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Grinderslev, J.B.; Jorgensen, M.; Skov, L.N.; Skibsted, J.; Jensen, T.R. Ammine magnesium borohydride nanocomposites for all-solid-state magnesium batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 9264–9270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, L.N.; Grinderslev, J.B.; Rosenkranz, A.; Lee, Y.-S.; Jensen, T.R. Towards solid-state magnesium batteries: Ligand-assisted superionic conductivity. Batteries&Supercaps 2022, 5, e202200163. [Google Scholar]
- Ruyet, R.L.; Berthelot, R.; Salager, E.; Florian, P.; Fleutot, B.; Janot, R. Investigation of Mg(BH4)(NH2)-based composite materials with enhanced Mg2+ ionic conductivity. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 10756–10736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruyet, R.L.; Fleutot, B.; Berthelot, R.; Benabed, Y.; Hatier, G.; Filinchuk, Y.; Janot, R. Mg3(BH4)4(NH2)2 as inorganic solid electrolyte with high Mg2+ ionic conductivity. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 6093–6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Xu, F.; Sun, L.; Yang, J.; Sun, D.; Fang, F.; Zheng, S. Borohydride ammoniate solid electrolyte design for all-solid-state Mg batteries. Energy Environ. Mater. 2022, 0, e12527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, F.; Rafizadeh-Masuleh, F.; Morsali, A. Highly electroconductive metal-organic framework: Tunable by metal ion sorption quantity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141(28), 11173–11182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, N.; Uemura, T.; Horike, S.; Shimomura, S.; Kiragawa, S. Inclusion and dynamics of a polymer-Li salt complex in coordination nanochannels. Chem. Comm. 2011, 47, 1722–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.K.; Farkas, A.; Varzi, A.; Jacob, T. Mixed metal-organic frameworks as efficient semi-solid electrolytes for magnesium-ion batteries. Batteries&supecaps 2022, 5, e202200260. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Maile, R.; Riegger, L.M.; Rohnke, M.; Muller-Buschbaum, K.; Janek, J. Ionic liquid-incorporated metal-organic framework with high magnesium ion conductivity for quasi-solid-state magnesium batteries. Batteries&supecaps 2022, 5, e202200318. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Guo, J.; Ning, D.; Hunag, Y.; Lei, W.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Schuck, G.; Shen, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, H.; Lan, H.; Shao, H. Design of metal-organic frameworks for improving pseudo-solid-state magnesium-ion electrolytes: Open metal sites, isoreticular expansion and framework topology. J. Mater. Sci. Tech. 2023, 144, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, A.; Lo, W.-S.; Dong, Q.; Wong, N.; Povinelli, C.; Shao, Y.; Chereddy, S.; Wunder, S.; Mohanty, U.; Tsung, C.-K.; Wang, D. A metal-organic framework thin film for selective Mg2+ transport. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 15313–15317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubrey, M.L.; Ameloot, R.; Wiers, B.M.; Long, J.R. Metal-organic frameworks as solid magnesium electrolytes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.S.; Tukchinsky, Y.; Dinca, M. Single-ion Li+, Na+ and Mg2+ solid electrolytes supported by a mesoporous anionic Cu-azolate metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13260–13263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miner, E.M.; Park, S.S.; Dinca, M. High Li+ and Mg2+ conductivity in a Cu-azolate metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4422–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Yamada, T.; Jing, Y.; Toyao, T.; Shimizu, K.-I.; Sadakiyo, M. Super Mg2+ conductivity around 10-3 S cm-1 observed in a porous metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 8669–8675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walke, P.; Venturini, J.; Spranger, R.j.; Wullen, L.; Nilges, T. Fast Magnesium Conductiong Electrospun Solid Polymer Electrolyte. Battery&Supercap. 2022, 5, e202200285. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, M.J.; Chu, P.P. Ion pair formation and its effect in PEO:Mg solid polymer electrolyte system. J. Power Sources 2002, 109(2), 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, S.K.S.; Rao, M.C. Spectroscopic and electrochemical properties of PVP based polymer electrolyte films. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 3641–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, S.K.S.; Sundari, G.S.; Kumar, K.V.; Rao, M.C. Preparation and dielectric properties of PVP-based polymer electrolyte films for solid-state battery application. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 925–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, M.; Dalvi, A. Electrical characterization of PVA-MgSO4 and PVA-Li2SO4 polymer salt composite electrolytes. Mater. Today: Proceedings 2019, 10(1), 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalagi, S.S. Activation energy dependence on doping concentration in PVA-MgCl2 composites. Mater. Today: Proceedings 2023, 72(5), 2691–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, P.; Abhilash, K.P.; Sivaraj, P.; Selvin, P.C. Study on Mg-ion conducting solid biopolymer electrlytes based on tamarind seed polysaccharide for magnesium ion batteries. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 118, 110490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.A.; Yominaga, Y. Magnesium ion-conductive polye(ethylene carbonate) electrolytes. Ionics 2018, 24, 3475–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.A.; Tominaga, Y. Effect of Li salt addition on electrochemical properties of poly(ethylene carbonate)-Mg salt electrolytes. Polymer J. 2019, 51, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viviani, M.; Meereboer, N.L.; Saeaswati, N.L.P.A.; Loos, K.; Portale, G. Lithium and magnesium polymeric electrolytes prepared using poly(glycidyl ether)-based polymers with short grafted chains. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 2070–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komal, B.; Yadav, M.; Kumar, M.; Tiwari, T.; Srivastava, N. Modifying potato starch by glutaraldehyde and MgCl2 for developing an economical and environment-friendly electrolyte system. e-Polymer 2019, 19, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamilosai, R.; Palanisamy, P.N.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Maheshwari, T. Solium alginate incorporated with magnesium nitrate as a novel solid biopolymer electrolyte for magnesium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Sci.:Mater. Electronics 2021, 32, 22270–22285. [Google Scholar]
- Ismayl, J.K.; Hegde, S.; Vasachar, R.; Sanjeev, G. Novel solid biopolymer electrolyte based on methyl cellulose with enhanced ion transport properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139(12), 51826. [Google Scholar]
- Buvaneshwari, P.; Mathavan, T.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Krishna, M.V.; Naachiyar, R.M. Preparation and characterization of biopolymer electrolyte based on gellan gum with magnesium perchlorate for magnesium battery. Ionics 2022, 28, 3843–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapaksha, H.G.N.; Perera, K.S.; Vidanapathirana, K.P. Characterization of a natural rubber based solid polymer electrolyte to be used for a magnesium rechargeable cell. Polym. Bull. 2022, 79, 4879–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, S.S.; Karthika, M.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Manjuladevi, R. Preparation and characterization of polymer electrolyte based on biopolymer I-Carrageenen with magnesium nitrate. Solid State Ionics 2018, 327, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.I.; Abidin, S.Z.Z.; Majid, S.R.; Jaafar, N.K. Role of Mg(NO3)2 as defective agent in ameliorating the electrical conductivity, structural and electrochemical properties of agarose-based polymer electrolytes. Polymers 2021, 13(19), 3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalakshmi, M.; Selvanayagam, S.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Chandra, M.V.L.; Sangeetha, P. Manjuladevi, R. Magnesium ion-conducting solid polymer electrolyte based on cellulose acetate with magnesium nitrate (Mg(NO3)2•6H2O) for electrochemical studies. Ionics 2020, 26, 4553–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, P.; Selvakumari, T.M.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Srikumar, S.R.; Manjukadevi, R.; Mahalakshmi, M. Preparation and characterization of biopolymer K-carrageenan with MgCl2 and its application to electrochemical devices. Ionics 2020, 26, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Al-Zangana, S.; Woo, H.J.; Kadir, M.F.Z.; Abdullah, O.G. The compatibility of chitosan with divalent salts over monovalent salts for the preparation of solid polymer. Results in Phys. 2018, 11, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, P.; Selvakumari, T.M.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Mahalakshmi, M. Characterization of solid biopolymer electrolytes based on kappa-carrageenan with magnesium nitrate hexahydrate and its application to electrochemical devices. Polymer-Plastics Tech. Mater. 2021, 60(12), 1317–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Ismayil, J.K.; Hegde, S.; Sanjeev, G.; Murari, M.S. An insight into the suitability of magnesium ion-conducting biodegradable methyl cellulose solid polymer electrolyte film in energy storage devices. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 5389–5412. [Google Scholar]
- Priya, S.S.; Karthika, M.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Manjuladevi, R.; Monisha, S. Study of biopolymer I-carrageenan with magnesium perchlorate. Ionics 2018, 24, 3861–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helen, P.A.; Perumal, P.; Sivaraj, P.; Diana, M.I.; Selvin, P.C. Mg-ion conducting electrolytes based on chitosan biopolymer host for the rechargeable Mg batteries. Mater. Today: Proceedings 2022, 50(7), 2668–2670. [Google Scholar]
- Kiruthika, S.; Malathi, M.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Tamilarasan, K.; Moniha, V.; Manjuladevi, R. Eco-friendly biopolymer electrolyte, pectin with magnesium nitrate salt, for application in electrochemical devices. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2019, 23, 2181–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiruthika, S.; Malathi, M.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Tamilarasan, K.; Maheshwari, T. Conducting biopolymer electrolyte based on pectin with magnesium chloride salt for magnesium battery application. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 6299–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayama, N.; Homma, K.; Yamakawa, Y.; Hirayama, M.; Kanno, R.; Yoneyama, M.; Kamiyama, T.; Kato, Y.; Hama, S.; Kawamoto, K.; Mitsui, A. A lithium superionic conductor, Nat. Mater. 2011, 10(9), 682–686. [Google Scholar]
- Rathika, R.; Suthanthiraraj, S.A. Ionic interactions and dielectric relaxation of PEO/PVDF-Mg[(CF3SO2)2N2] blend electrolytes for magnesium ion rechargeable batteries. Macromolecular Res. 2016, 24, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenbagavalli, S.; Muthuvinayagam, M.; Revathy, M.S. Electrical properties of Mg2+ ion-conductive PEO:P(PVdF-HFP) based solid blend polymer electrolytes. Polymer 2022, 256, 125242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjuladevi, R.; Thamilselvan, M.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Mangalam, R.; Premalatha, M.; Monisha, S. Mg-ion conducting blend polymer electrolyte based on poly(vinyl alcohol)-poly(acrylonitrile) with magnesium perchlorate. Solid State Ionics 2017, 308, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponmani, S.; Prabhu, M.R. Development and study of solid polymer electrolytes based on PVdF-HFP/PVAc:Mg(ClO4)2 for Mg ion batteries. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electronics 2018, 29, 15086–15096. [Google Scholar]
- Polu, A.R.; Kumar, R.; Rhee, H.-W. Magnesium ion conducting solid polymer blend electrolyte based on biodegradable polymers and application in solid-state batteries. Ionics 2015, 21, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjuladevi, R.; Thamilselvan, M.; Selavasekarapandian, S.; Selvin, P.C.; Mangalam, R.; Monisha, S. Preparation and characterization of blend polymer electrolyte film based on poly(vinyl alcohol)-poly(aceylonitrile)/MgCl2 for energy storage devices. Ionics 2018, 24, 1083–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponraj, T.; Ramalingam, A.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Srikumar, S.R.; Manjuladevi, R. Mg-ion conducting triblock copolymer electrolyte based on poly(VdCl-co-AN-co-MMA) with magnesium nitrate. Ionics 2020, 26, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, K.; Inoue, M.; Takahashi, K.; Hayamizu, K.; Watanabe, M.; Seki, S. Analysis of ionic transport and electrode interfacial reaction, and NMR one-dimensional imaging of ther-based polymer electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168(6), 060501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.; Andersson, R.; Pate, S.G.; Liu, J.; O’brien, C.P.; Hernandez, G.; Mindemark, J.; Schaefer, J.L. Ion coordination and transport in magnesium polymer electrolytes based on polyester-co-polycarbonate. Energy Mater. Adv. 2021, 9895403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjuladevi, R.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Thamilselvan, M.; Mangalam, R.; Monisha, S.; Selvin, P.C. A study on blend polymwe electrolyte based on poly(vinyl alcohol)-poly(acrylonitrile) with magnesium nitrate for magnesium battery. Ionics 2018, 24, 3493–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponmani, S.; Kalaiselvimary, J.; Prabhu, M.R. Structural, electrical, and electrochemical properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexaflouropropylene)/poly(vinyl acetate)-based polymer blend electrolytes for rechargeable magnesium ion batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2018, 22, 2605–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.; Ismayil; Cyriac, V.; Hegde, S.; Sanjeev, G.; Murari, M.S.; Sudhakar, Y.N. Magnesium ion conducting free-standing biopolymer blend electrolyte films for electrochemical device application. J. Non-crystalline Solids 2022, 592, 121741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarnna, K.; Kirubavathy, S.J.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Krishna, M.V.; Ramaswamy, M. Corn silk extract-based solid-state biopolymer electrolyte and its application to electrochemical storage devices. Ionics 2022, 28, 1767–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakaraj, T.M.; Bhajantri, R.F.; Chavan, C.; Cyriac, V.; Bulla, S.S.; Ismayil. Investigation on the structural and ion transport properties of magnesium salt doped HPMC-PVA based polymer blend for energy storage applications. J. Non-crystalline Solids 2023, 603, 122276. [Google Scholar]
- Koduru, H.K.; Marinov, Y.G.; Kaleemulla, S.; Rafailov, P.M.; Hadjichristov, G.B.; Scaramuzza, N. Fabrication and characterization of magnesium-ion-conducting flexible polymer electrolyte membranes based on a nanocomposite of poly(ethylene oxide) and potate starch nanocrystals. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2021, 25, 2409–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotobuki, M.; Kanamura, K. Fabrication of all-solid-state battery using Li5La3Ta2O12 Ceramic electrolyte. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39(6), 6481–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarangika, H.N.M.; Dissanayake, M.A.K.L.; Senadeera, G.K.R.; Rathnayake, R.R.D.V.; Pitawala, H.M.J.C. Polyethylene oxide and ionic liquid-based solid polymer electrolyte for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Ionics, 2017, 23, 2829–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Song, F.; Du, A.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, B.; Huang, L.; Zhao, J.; Dong, S.; Zhou, X.; Cui, G. Robust self-standing single-ion polymer electrolytes enabling high-safety magnesium batteries at elevated temperature. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12(31), 2201464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Jain, A.; Tripathi, S.K. Structural and electrochemical studies of bromide derived ionic liquid-based gel polymer electrolyte for energy storage. J. Energy Storage, 2020, 32, 101723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambali, D.; Zainol, N.H.; Othman, L.; Isa, K.B.M.; Osman, Z. Magnesium ion-conducting gel polymer electrolytes based on poly(vinylidene chloride-co-acrylonitrile) (PVdC-co-AN): a comparative study between magnesium trifluoromethanesulfonate (MgTf2) and magnesium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonimide) (Mg(TFSI)2). Ionics, 2019, 25, 1187–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwaran, C.; Mishra, K.; Kanchan, D.K.; Kumar, D. Mg2+ conducting polymer gel electrolytes: physical and electrochemical investigations. Ionics, 2020, 26, 2969–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotobuki, M.; Yan, B.; Lu, L. Recent progress on cathode materials for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Energy storage Mater. 2023, 54, 227–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doe, R.E.; Han, R.; Hwang, J.; Gmitter, A.J.; Shterenberg, I.; Yoo, H.D.; Pour, N.; Aurbach, D. Novel electrolyte solutions comprisingly fully inorganic salts with high anodic stability for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Chem. Comm., 2014, 50, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, X.; Liu, F.; Fan, L.-Z. Porous polymer electrolytes for long-cycle stable quasi-solid-state magnesium batteries. J. Energy Chem., 2021, 59, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, L.C.; Ford, H.O.; Scaefer, J.L. Application of single-ion conducting gel polymer electrolytes in magnesium batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2019, 2, 6355–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
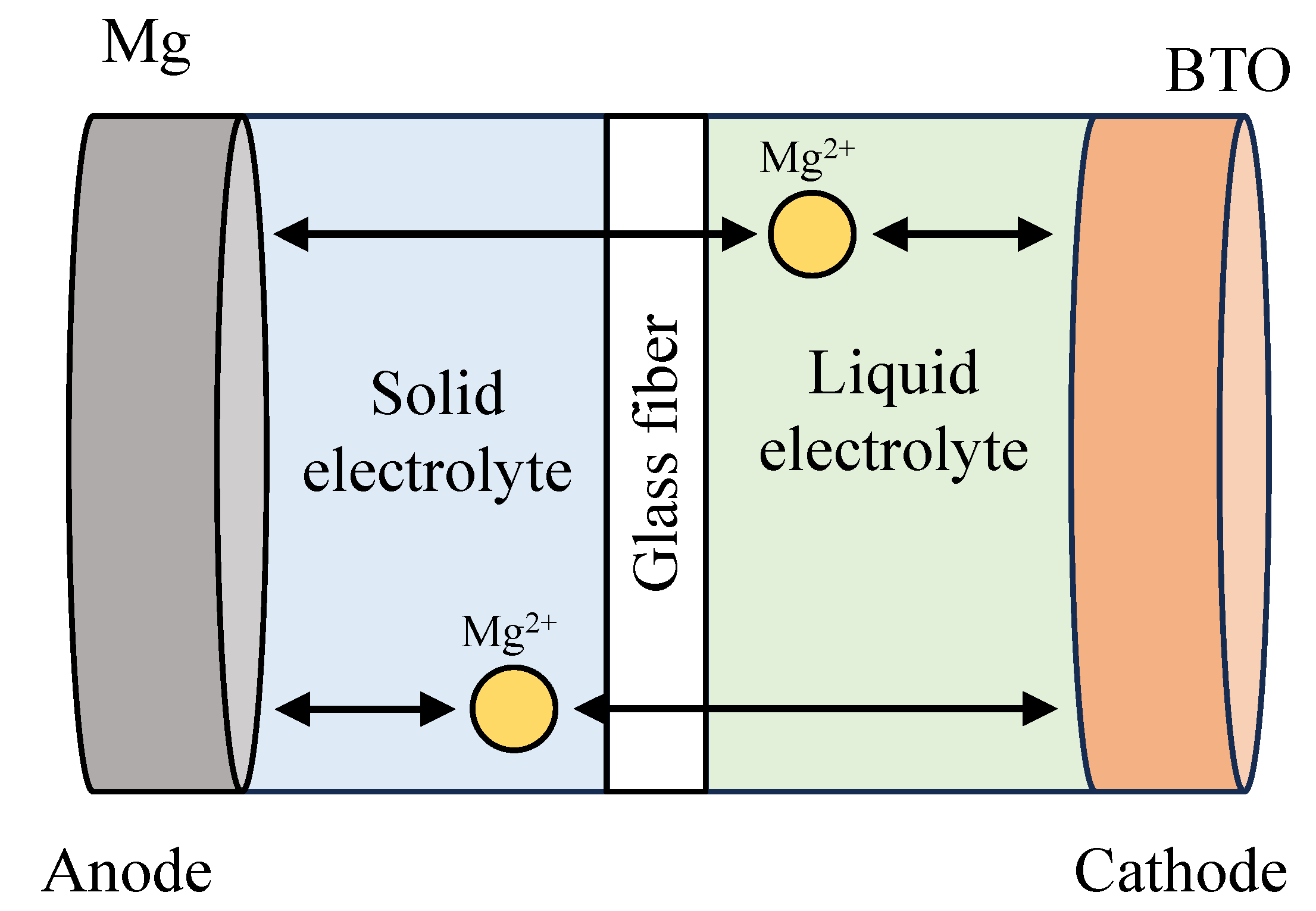
- Sheha, E.; Liu, F.; Wang, T.; Farrag, M.; Liu, J.; Yacout, N.; Kebebe, M.A.; Sharma, N.; Fan, L.-Z. Dual polymer/liquid electrolyte with BaTiO3 electrode for magnesium batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3, 5882–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwaran, C.; Kanchan, D.K.; Gohel, K.; Mishra, K.; Kumar, D. Effect of Mg(CF3SO3)2 concentration on structural and electrochemical properties of ionic liquid incorporated polymer electrolyte membranes. J. Solid State Electrochem., 2020, 24, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambali, D.; Osman, Z.; Othman, L.; Isa, K.B.M.; Harudin, N. Magnesium (II) bis(trifluoromethanesulfonimide) doped PVdC-co-AN gel polymer electrolytes for rechargeable batteries. J. Polym. Res., 2020, 27, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Jain, A.; Tripathi, S.K. Structural, electrical and electrochemical studies of ionic liquid-based polymer gel electrolyte using magnesium salt for supercapacitor application. J. Polym. Res., 2021, 28, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.; Yoshimoto, N.; Yamabuki, K.; Tominaga, Y. Ion-conductive, thermal and electrochemical properties of poly(ethylene carbonate)-Mg electrolytes with glyme solution. Chem. Lett., 2018, 47, 1258–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Hashmi, S.A. Plastic crystal-incorporated magnesium ion conducting gel polymer electrolyte for battery application. Bull. Mater. Sci., 2018, 41, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponraj, T.; Tamalingam, A.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Srikumar, S.R.; Manjuladevi, R. Plasticized solid polymer electrolyte based on triblock copolymer polyvinylidene chloride-co-acrylonitrile-co-methyl methacrylate for magnesium ion batteries. Polym. Bull., 2021, 78, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, Y.; Kato, S.; Nishimura, N. Preparation and electrochemical characterization of magnesium gel electrolytes based on crosslinked poly(tetrahydrofuran). Polymer, 2021, 224, 123743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamsan, M.H.; Aziz, S.B.; Kadir, M.F.Z.; Brza, M.A.; Karim, W.O. The study of EDLC device fabricated from plasticized magnesium ion conducting chitosan based polymer electrolyte. Polym. Testing, 2020, 90, 106714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangeetha, P.; Selvakumari, T.M.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Mahalakshmi, M. Characterization of solid biopolymer electrolytes based on kappa-carrageenan with Magnesium nitrate hexahydrate and its application to electrochemical devices. Polym.-Plastic Tech. Mater. 2021, 60(12), 1317–1330. [Google Scholar]
- Ponmami, S.; Prabhu, M.R. Sulfonate based ionic liquid incorporated polymer electrolytes for Magnesium secondary battery. Polym.-Plastic Tech. Eng. 2019, 58(9), 978–991. [Google Scholar]
- Nishino, H.; Liu, C.; Kanehashi, S.; Mayumi, K.; Tominaga, Y.; Shimomura, T.; Ito, K. Ionics transport and mechanical properties of slide-ring gel swollen with Mg-ion electrolytes. Ionics, 2020, 26, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Janakiraman, S.; Khalifa, M.; Anandhan, S.; Ghosh, S.; Venimadhav, A.; Biswas, K. An electroactive β-phase polyvinylidene fluoride as gel polymer electrolyte for magnesium-ion battery application. J. Electroanal. Chem., 2019, 851, 113417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, P.J.; Pathak, N.; Mishra, K.; Kanchan, D.K.; Kumar, D. Effect of different cations on ion-transport behavior in polymer gel electrolytes intended for application in flexible electrochemical devices. J. Electronic Mater., 2022, 51, 1371–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Meng, Z.; Xiu, Y.; Dasari, B.; Zhao-Karger, Z.; Fichtner, M. Designing gel polymer electrolytes with synergetic properties for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Energy Storage Mater., 2022, 48, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Muchakayala, R.; Song, S. High-performance Mg-ion conducting poly(vinyl alcohol) membranes: Preparation, characterization and application in supercapacitors. J. Membrane Sci., 2018, 555, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Janakiraman, S.; Agrawal, A.; Ghosh, S.; Venimadhav, A.; Biswas, K. An amorphous poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) based gel polymer electrolyte for magnesium ion battery. J. Electroanal. Chem., 2020, 858, 113788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Janakiraman, S.; Khalifa, M.; Anandhan, S.; Ghosh, S.; Venimadhav, A.; Biswas, K. A high thermally stable polyacrylonitrile (PAN)-based gel polymer electrolyte for rechargeable Mg-ion battery. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron, 2020, 31, 22912–22925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwaran, C.; Kanchan, D.K.; Mishra, K.; Kumar, D.; Gohel, K. Flexible, magnesium-ion conducting polymer electrolyte membrane: mechanical, structural, thermal, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopic properties. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. In Electronics, 2020, 31, 15013–15027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulwahid, R.T.; Aziz, S.B.; Brza, M.A.; Kadir, M.F.Z.; Karim, W.O.; Hamsan, H.M.; Asnawi, A.S.F.M.; Abdullah, R.M.; Nofal, M.M.; Dannoun, E.M.A. Electrochemical performance of polymer blend electrolytes based on chitosan: dextran: impedance, dielectric properties, and energy storage study. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron, 2021, 32, 14846–14862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, T.; Uchiyama, S.; Tsukada, K.; Moriya, M. Room-temperature Mg-ion conduction through molecular crystal Mg{N(SO2CF3)2}2(CH3OC5H9)2. Front. Energy Res., 2021, 9, 640777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Obora, T.; Namaki, M.; Kondo, M.; Moriya, M. Organic crystalline solid electrolytes with high Mg-ion conductivity composed of nonflammable ionic liquid analogs and Mg(TFSA)2. Inorg. Chem., 2022, 61, 7358–7364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, S.; Kalapriya, K. Structural, transport, morphological, and thermal studies of nano barium titanate-incorporated magnesium ion conducting solid polymer electrolytes. Polym. Polym. Composites, 2021, 29, S1158–S1167. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, F.; Sun, J.; Oh, J.A.S.; WU, T.; Chen, G.; Huang, Q.; Kotobuki, M.; Lu, L. Ferroelectric engineered electrode-composite polymer electrolyte interfaces for all-solid-state sodium metal battery. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9(13), 2105849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyabanu, K.; Sundaramahalingam, K.; Devendran, P.; Manikandan, A.; Nallamuthu, N. Effect of electrical conductivity studied for CuS nanofillers mixed magnesium ion based PVA-PVP blend polymer solid electrolytes. Phys. B: Condenced Matter, 2019, 572, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayalakshmi, K.; Ismayil; Hedge, S.; Ravindrachary, V.; Sanjeev, G.; Mazumdar, N.; Sindhoora, K.M.; Masti, S.P.; Murari, M.S. Methyl cellulose-based solid polymer electrolytes with dispersed zinc oxide nanoparticles: A promising candidate for battery applications. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2023, 173, 111119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidhi, Patel, S.; Kumar, R. Synthesis and characterization of magnesium ion conductive in PVDF based nanocomposite polymer electrolytes disperse with MgO. J. Alloy Compd., 2019, 789, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polu, A.; Kumar, R. Preparation and characterization of PEG-Mg(CH3COO)2-CeO2 composite polymer electrolytes for battery application. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2014, 37(2), 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarojini, S.; Padmapriya, L. Effect of size of the filler on the electrical conductivity of magnesium ion conducting polymer electrolyte. Mater. Today: Proceedings, 2022, 68, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helen, P.A.; Selvin, P.C.; Lashmi, D.; Diana, M.I. Amelioration of ionic conductivity (303K) with the supplement of MnO2 filler in the chitosan biopolymer electrolyte for magnesium batteries. Polym. Bull., 2023, 80, 7715–7740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maheshwaran, C.; Kanchan, D.K.; Mishra, K.; Kumar, D.; Gohel, K. Effect of active MgO nano-particles dispersion in small amount within magnesium-ion conducting polymer electrolyte matrix. Nano-structures&nano-objects, 2020, 24, 100587. [Google Scholar]
- Nidhi, Patel, S.; Kumar, R. Effect of Al2O3 on electrical properties of polymer electrolyte for electrochemical device application. Mater. Today: Proceedings 2021, 46, 2175–2178. [Google Scholar]
- Nidhi, Patel, S.; Kumar, R. Effect of nanoparticles on electrical properties of PVDF-based Mg2+ ion conducting polymer electrolytes. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2021, 44, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, M.; Selladurai, S. Effect of fillers on magnesium-poly(ethylene oxide) solid polymer electrolyte. Ionics, 2006, 12, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponmani, S.; Selvakumar, K.; Prabhu, M.R. The effect of the geikeilite (MgTiO3) nanofiller concentration in PVdF-HFP/PVAc-based polymer blend electrolytes for magnesium ion battery. Ionics, 2020, 26, 2353–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helen, P.A.; Ajith, K.; Diana, M.I.; Lakshmi, D.; Selvin, P.C. Chitosan based biopolymer electrolyte reinforced with V2O5 filler for magnesium batteries: an inclusive investigation. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron, 2022, 33, 3925–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallikarjun, A.; Sangeetha, M.; Mettu, M.R.; Reddy, J.M.; Kumar, S.J.; Sreekanth, T.; Rao, V.S. Impedance spectroscopy and electrochemical cell studies of Mg2+ ion conducting with dispersed ZrO2 nano filler in PVDF-HFP based nano composite solid polymer electrolytes. Mater. Today: Proceedings, 2022, 62, 5204–5208. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, N.S.; Kumar, R. PVDF-HFP based nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for energy storage devices dispersed with various nano-fillers. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2020, 2220, 080044. [Google Scholar]
- Dannoun, E.M.A.; Aziz, S.B.; Brza, M.A.; Nofal, M.M.; Asnawi, A.S.F.M.; Yusof, Y.M.; Al-Zangana, S.; Hamsan, M.H.; Kadir, M.F.Z.; Woo, H.J. The study of plasticized solid polymer blend electrolytes based on natural polymers and their application for energy storage EDLC devices. Polymers 2020, 12(11), 2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Kotobuki, M.; Zheng, F.; Li, Q.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.D.Z.; Hu, N.; Lu, L. Communication-A composite polymer electrolyte for safer Mg batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164(4), A741–A743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, S.B.; Dannoun, E.M.A.; Hamsan, M.H.; Abdulwahid, R.T.; Mishra, K.; Nofal, M.M.; Kadir, M.F.Z. Improving EDLC device performance constructed from plasticized magnesium ion conducting chitosan based polymer electrolytes via metal complex dispersion. Membranes 2021, 11(4), 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Hashmi, S. Magnesium ion-conducting gel polymer electrolyte nanocomposites: Effect of active and passive nanofillers. Polym. Composites 2019, 40(4), 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deivanayagam, R.; Cheng, M.; Wang, M.; Vasudevan, V.; Foroozan, T.; Medhekar, N.V.; Shahbazian-Yassar, R. Composite polymer electrolyte for highly cyclable room-temperature solid-state magnesium batteries. ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2019, 2, 7980–7990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zou, Y.; Gao, S.; Shao, L.; Chen, C. Robust strategy of quasi-solid-state electrolytes to boost the stability and compatibility of Mg ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 54711–54719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Truck, J.; Hacker, J.; Schlosser, A.; Kuster, K.; Starke, U.; Reinders, L.; Buchmeiser, M.R. A design concept for halogen-free Mg2+/Li+-dual salt-containing gel-polymer-electrolytes for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Energy Storage Mater., 2022, 49, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Allen, M.; Raji, V.; Ji, X. An organic pigment as a high-performance cathode for sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4(15), 1400554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, W.; Cater, M.; Zhou, L.; Dai, J.; Fu, K.; Lacey, S.; Li, T.; Wan, J.; Han, J.; Bao, Y.; Hu, L. Organic electrode for non-aqueous potassium-ion batteries. Nano Energy, 2015, 18, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Parent, L.R.; Shao, Y.; Wang, C.; Sprenkle, V.L.; Li, G.; Liu, J. Facile synthesis of chevrel phase nanocubes and their applications for multivalent energy storage. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 4904–4907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Lin, Z.; Tong, Y.; Yue, J.; Zhao, C.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, L.; Suo, L.; Hu, Y.S.; Li, H.; Huang, X.; Chen, L. Iodine vapor transport-triggered preferential growth of chevrel Mo6S8 nanosheets for advanced multivalent batteries. ACS Nano, 2020, 14, 1102–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Li | Na | K | Mg | Ca | Zn | Al | |
| Standard redox potential (E vs. SHE) |
-3.04 | -2.71 | -2.93 | -2.37 | -2.87 | -0.76 | -1.66 |
| Volumetric capacity (mAh/cm3) | 2062 | 1128 | 591 | 3883 | 2073 | 5851 | 8046 |
| Specific capacity (mAh/g) | 3861 | 1166 | 685 | 2205 | 1337 | 820 | 2980 |
| Abundance (%) | 0.002 | 2.7 | 2.4 | 2.08 | 5 | 0.008 | 8.2 |
| Ionic radius (Å) | 0.76 | 1.02 | 1.38 | 0.72 | 1.00 | 0.74 | 0.535 |
| Relative atomic mass | 6.94 | 22.98 | 39.1 | 24.31 | 40.08 | 65.39 | 26.98 |
| Mass to charge | 6.94 | 22.98 | 39.1 | 12.16 | 20.04 | 32.7 | 8.99 |
| Electrolyte | σtotal (S cm-1) |
Temperature (oC) | Activation energy (eV) | Electrochemical window (V) | Ref |
| Oxides | |||||
| MgZr4(PO4)6 | 2.9 × 10-5 | 400 | 0.868 | - | [30] |
| 6.1 × 10-3 | 800 | ||||
| Mg0.5Zr2(PO4)3 | 1.1 × 10-6 | 30 | 0.0977 | ~ 2.5 | [50] |
| 7.1 × 10-5 | 500 | ||||
| MgZr4(PO4)6 | 7.23 × 10-3 | 725 | 0.84 | - | [51] |
| MgZr4(PO4)6+Zr2O(PO4)2 | 6.9 × 10-3 | 800 | 1.41 | - | [52] |
| Mg0.7(Zr0.85Nb0.15)4(PO4)6 | 5.71 × 10-3 | 800 | 0.95 | - | [32] |
| Mg1.4Zr4P6O24.4+0.4Zr2O(PO4)2 | 6.89 × 10-3 | 800 | 1.41 | - | |
| Mg1.1(Zr0.85Nb0.15)4P6O24+0.4Zr2O(PO4)2 | 9.53 × 10-3 | 800 | 1.28 | - | |
| Mg1.1Zr3.4Nb0.6P6O24.4 + Zr2O(PO4)2 | 9.53 × 10-3 | 800 | 1.26 | - | [53] |
| Mg0.9Zr1.2Fe0.8(PO4)3 | 1.25 × 10-5 | RT | 0.14 | - | [33] |
| 7.2 × 10-5 | 500 | ||||
| Mg0.5Ce0.2Zr1.8(PO4)3 | 3.8 × 10-7 | 200 | 0.307 | - | [54] |
| Mg1.05Zn0.4Al0.3Zr1.3(PO4)3 | 3.97 × 10-4 | RT | 0.039 | - | [35] |
| 5.82 × 10-4 | 500 | ||||
| Mg0.35(Zr0.85Nb0.15)2(PO4)3 | 1.1 × 10-6 | 350 | 1.18 | - | [55] |
| Mg0.5ZrSn(PO4)3 | 2.47 × 10-5 | 500 | 0.79 | - | [56] |
| Mg0.7Zr3.4Nb0.6(PO4)6 | 7.7 × 10-4 | 600 | 0.954 | - | [57] |
| 3.7 × 10-3 | 750 | ||||
| Mg0.6Zr1.8Fe0.2(PO4)3 thin film | 1.8 × 10-7 | 25 | 0.141 < 175oC 0.511 > 175oC |
- | [58] |
| 2.3 × 10-6 | 200 | ||||
| Mg0.625Si1.75Al0.25(PO4)3 | 1.54 × 10-4 | RT | - | 2.51 | [59] |
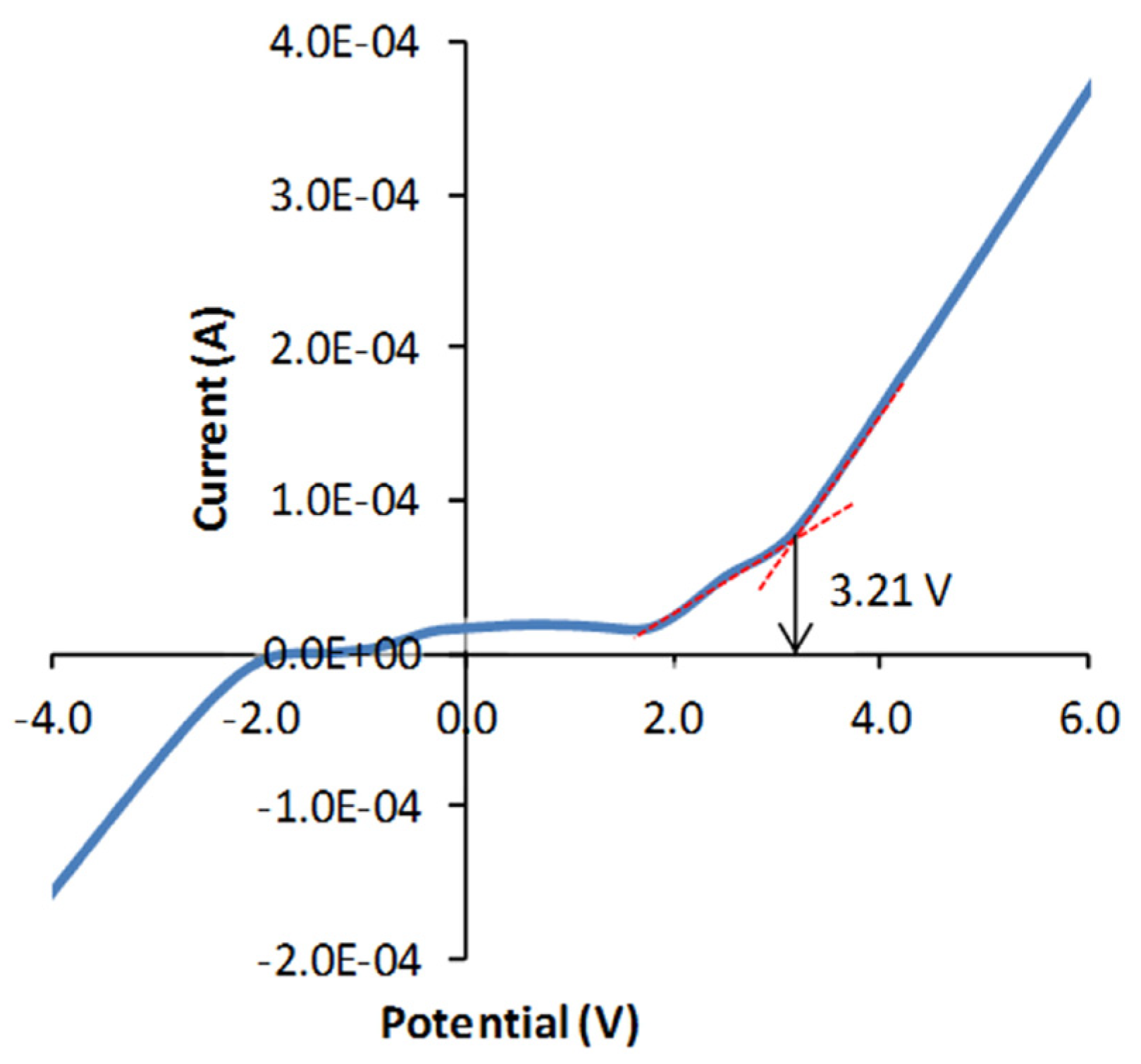
| Mg0.5Si2(PO4)3 | 1.83 × 10-5 | - | ~ 3.21 | [36] | |
| Mg0.105Hf0.95Nb(PO4)3 | 1.2 × 10-4 | 600 | 0.639 | - | [34] |
| Mg2.4P2O5.4 ALD | 1.6 × 10-7 | 500 | 1.37 | - | [37] |
| Mg0.6Al1.2Si1.8O 6 | 2.3 × 10-6 | 500 | 1.32 | - | [38] |
| MgSO4-Mg(NO3)2-MgO | 2.2 × 10-6 | RT | 0.17 | - | [60] |
| MgHf(WO4)3 | 2.5 × 10-4 | 600 | 0.835 | - | [39] |
| Chalcogenides | |||||
| 80(0.6MgS 0.4P2S5) 20MgI2 | 2.1 × 10-7 | 200 | - | - | [41] |
| MgSc2Se4 | 9.2 × 10-5 | RT | - | - | [44] |
| MgSc2Se4 | ~1 × 10-4 | 25 | 0.38 | [42] | |
| MgSc2Se4 | 8 × 10-5 | RT | - | - | [45] |
| MgSc2Se4 | 1.78 × 10-5 | RT | - | - | [46] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





