Submitted:
08 October 2023
Posted:
09 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The insects
2.2. Low temperature tolerance and discriminating temperature determination
2.3. Induction and detection of RCH
2.4. Measurement of trehalose content
2.5. Sequence determination and Bioinformatics Analysis of TPS gene
2.6. RNAi of TPS
2.7. Expression analysis using RT-qPCR
2.8. Rapid cold hardening assay
2.9. Data analysis
3. Results
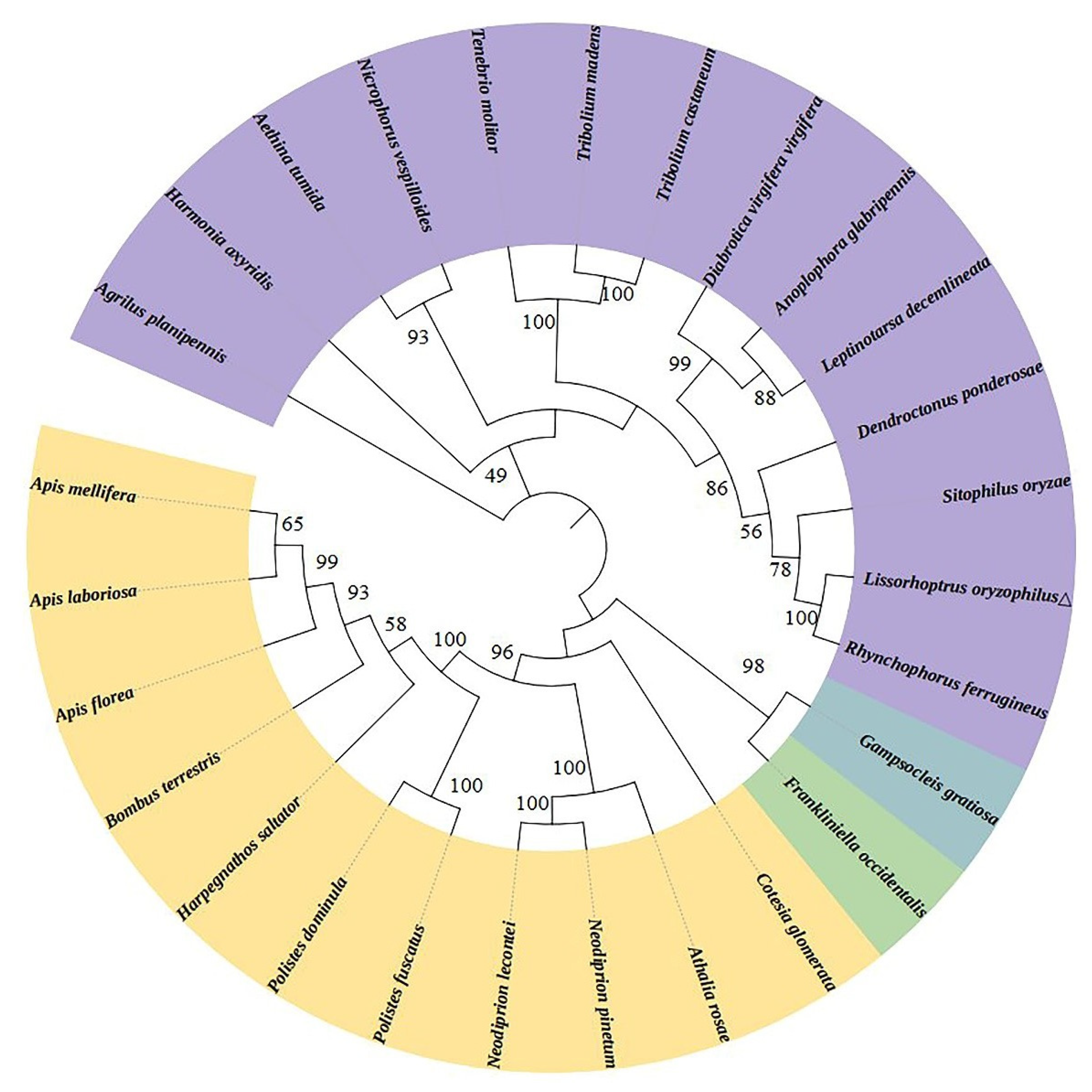
3.1. Identification and characterization of LoTPS
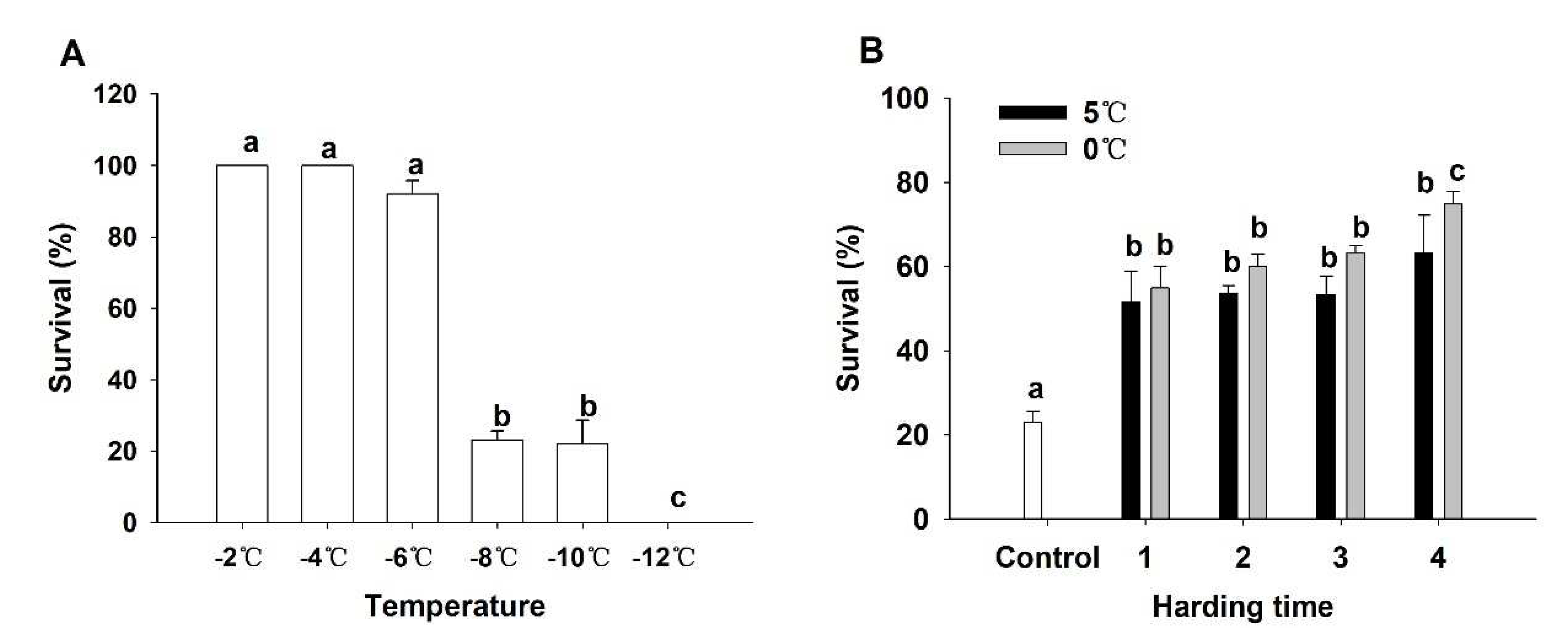
3.2. Induction of RCH in adult of L. oryzophilus
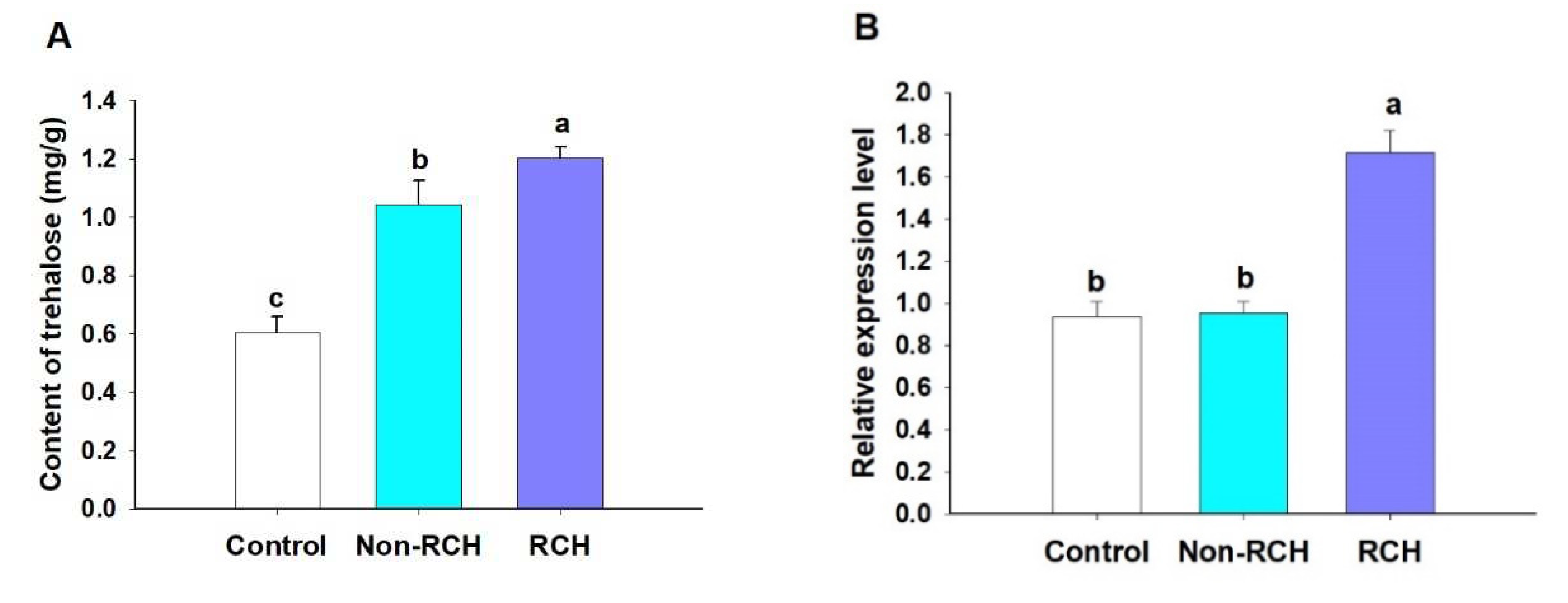
3.3. Trehalose content and LoTPS expression level increased during RCH
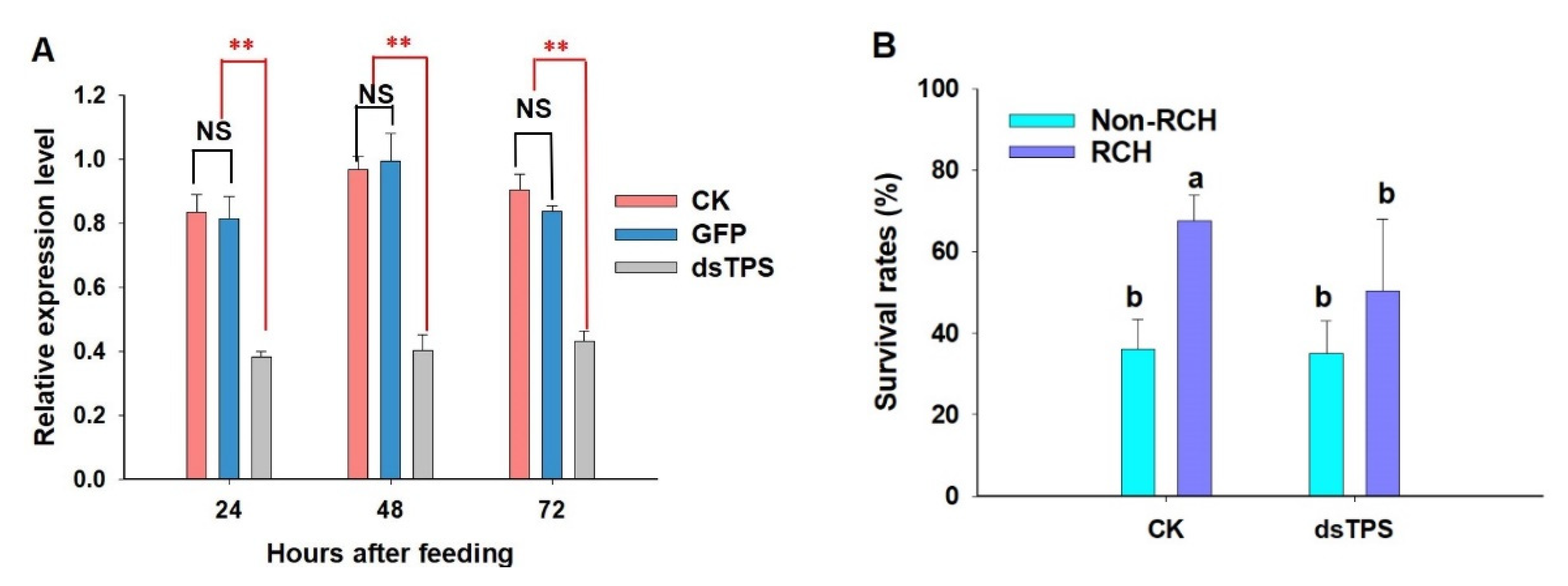
3.4. Knockdown of LoTPS expression reduces RCH efficiency.
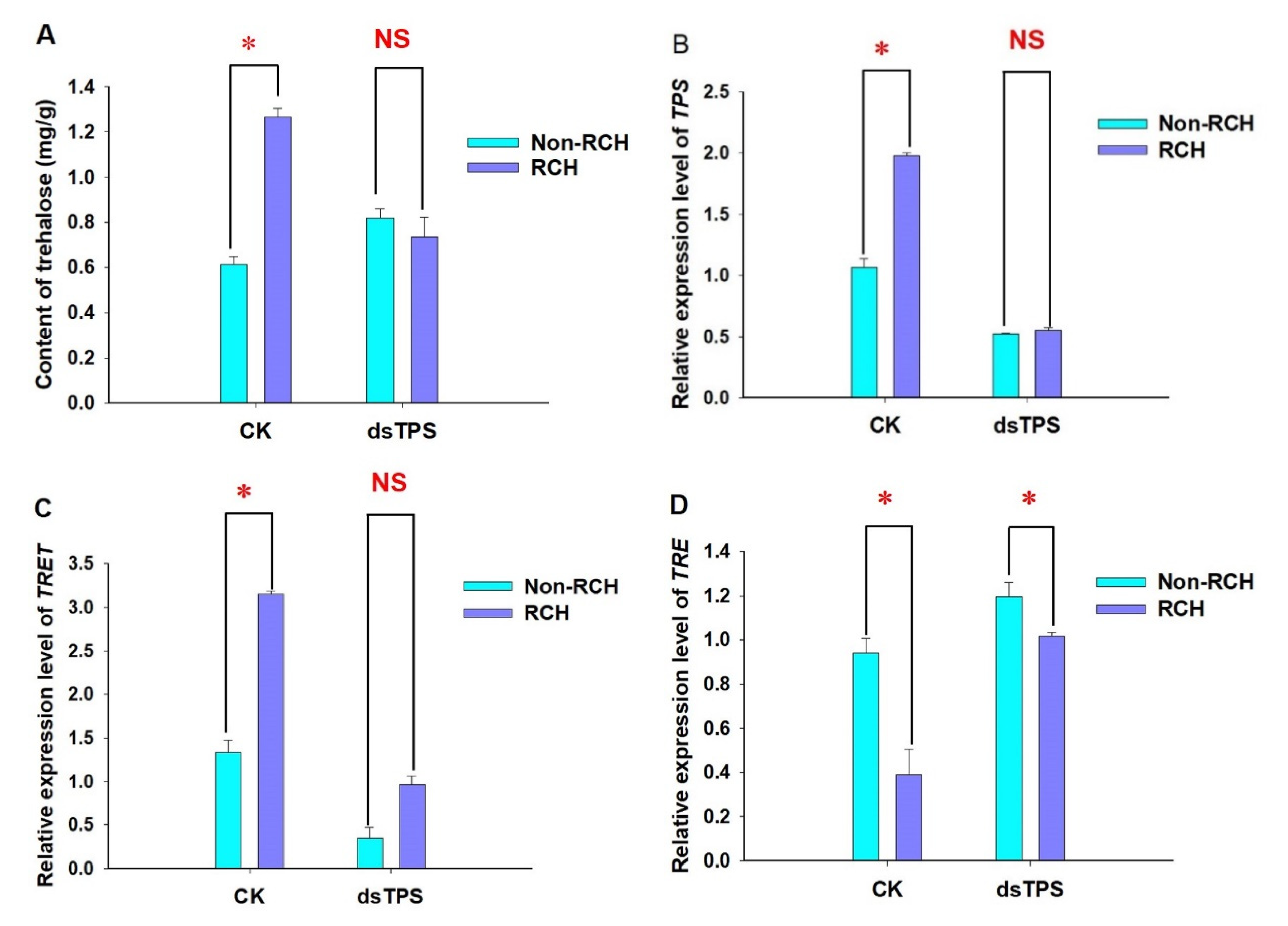
3.5. Roles of LoTPS on trehalose biosynthesis during RCH
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee:, R.E.; Chen, C.P.; Denlinger, D.L. A Rapid Cold-Hardening Process in Insects. Science 1987, 238, 1415–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teets, N.M.; Denlinger, D.L. Physiological Mechanisms of Seasonal and Rapid Cold-Hardening in Insects. Physiol. Entomol. 2013, 38, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wen, J.; Han, Y.; Hou, M. Rapid Cold Hardening Confers a Transient Increase in Low Temperature Survival in Diapausing Chilo suppressalis Larvae. Insects 2018, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatanparast, M.; Sajjadian, S.M.; Park, Y. Glycerol Biosynthesis Plays an Essential Role in Mediating Cold Tolerance the Red Imported Fire Ant, Solenopsis invicta. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 109, e21861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, W.H.; Lee, D. Identification of Rapid Cold Hardening-Related Genes in the Tobacco Budworm, Helicoverpa assulta. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2016, 19, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Jin, J.; Wu, Q.; Liang, X.; Lv, C.; Guo, J. Cold Acclimation and Supercooling Capacity of Agasicles aygrophila Adults. Insects 2023, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, M.R.; Denlinger, D.L. Shifts in the Carbohydrate, Polyol, and Amino Acid Pools during Rapid Cold-Hardening and Diapause-Associated Cold-Hardening in Flesh Flies (Sarcophaga crassipalpis): A Metabolomic Comparison. J. Comp. Physiol. B 2007, 177, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh, M.; Izadi, H. Cold Acclimation of Trogoderma granarium Everts Is Tightly Linked to Regulation of Enzyme Activity, Energy Content, and Ion Concentration. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, H.; Mohammadzadeh, M.; Mehrabian, M. Cold Tolerance of the Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), Under Different Thermal Regimes: Impact of Cold Acclimation. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Xu, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, N.; Qin, D.; Xiao, C.; Lu, Y.; Guo, Z. Rapid Cold Hardening and Cold Acclimation Promote Cold Tolerance of Oriental Fruit Fly, Bactrocera dorsalis (Hendel) by Physiological Substances Transformation and Cryoprotectants Accumulation. Bull Entomol. Res. 2023, 113, 574–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overgaard, J.; Malmendal, A.; Sørensen, J.G.; Bundy, J.G.; Loeschcke, V.; Nielsen, N. Chr.; Holmstrup, M. Metabolomic Profiling of Rapid Cold Hardening and Cold Shock in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Insect Physiol. 2007, 53, 1218–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.L.; Zhou, L.J.; Lu, W.; Xian, Z.H.; Yang, Z.D.; Lei, C.L.; Wang, X.P. Cold-Hardiness Mechanisms in Third Instar Larvae of Spodoptera exigua Hübner (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Afr. Entomol. 2014, 22, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, D.W.; Jung, J.K. Rapid Cold-Hardening of a Subtropical Species, Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), Accompanies Hypertrehalosemia by Upregulating Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase. Environ. Entomol. 2017, 46, 1432–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koštál, V.; Korbelová, J.; Rozsypal, J.; Zahradníčková, H.; Cimlová, J.; Tomčala, A.; Šimek, P. Long-Term Cold Acclimation Extends Survival Time at 0℃ and Modifies the Metabolomic Profiles of the Larvae of the Fruit Fly Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrese, E.L.; Soulages, J.L. Insect Fat Body: Energy, Metabolism, and Regulation. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanako, M.; Yasushi, K.; Mika Fujita, Ke.I.; Daisuke, T.; Shingo, K.; Masahiko, W.; Richard, C.; Takashi, O.; Takahiro, K. Enzymatic Control of Anhydrobiosis-Related Accumulation of Trehalose in the Sleeping Chironomid, Polypedilum vanderplanki. FEBS. J. 2010, 277, 4215–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ma, E.; Behar, K.L.; Xu, T.; Haddad, G.G. Role of Trehalose Phosphate Synthase in Anoxia Tolerance and Development in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 3274–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.T.; Gao, Y.L.; He, K.L.; Ge, F. Expression Profiles of the Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase Gene Associated with Thermal Stress in Ostrinia furnacalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). J. insect sci. 2018, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhao, L.; Shen, Q.; Xie, G.; Wang, S.; Tang, B. Knockdown of Two Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthases Severely Affects Chitin Metabolism Gene Expression in the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.F.; Xu, Q.Y.; Sun, Q.K.; Meng, Q.W.; Mu, L.L.; Guo, W.C.; Li, G.Q. Physiological Roles of Trehalose in Leptinotarsa Larvae Revealed by RNA Interference of Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase and Trehalase Genes. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 77, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Lyu, Z.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Cheng, J.; Lin, T. RNA Interference of a Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase Gene Reveals Its Roles in the Biosynthesis of Chitin and Lipids in Heortia vitessoides (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.Z.; Wang, M.Q.; Xie, Y.Q.; Xiang, M.; Li, P.; Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.S. Gene Cloning and Expression Analysis of Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase, Glycogen Synthase and Glycogen Phosphorylase Reveal the Glycometabolism in the Diapause Process of Aphidius gifuensis. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2020, 23, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Feng, Q.; Wang, H.; Tang, T.; Huang, D.; Liu, F. Involvement of Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase in Innate Immunity of Musca domestica. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2019, 91, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.J.; Cui, M.Y.; Zhao, X.H.; Zhang, C.Y.; Hu, Y.S.; Fan, D. Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase Regulates Chitin Synthesis in Mythimna separate. Front. Physiol, 2023, 14, 1109661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushwaha, S.; Singh, P.K.; Shahab, M.; Pathak, M.; Bhattacharya, S.M. In Vitro Silencing of Brugia Malayi Trehalose-6-Phosphate Phosphatase Impairs Embryogenesis and In Vivo Development of Infective Larvae in Jirds. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, M.; Matsuda, H.; Kubo, H.; Nishimura, T. Molecular Characterization of Tps1 and Treh Genes in Drosophila and Their Role in Body Water Homeostasis. Sci. rep. 2016, 6, 30582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T.F.; Liu, Y.H. Trehalose-6-Phosphate Phosphatases Are Involved in Trehalose Synthesis and Metamorphosis in Bactrocera minax. Insect Sci. 2022, 29, 1643–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.G.; Wang, H.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Cui, S.Y. Invertebrate Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase Gene: Genetic Architecture, Biochemistry, Physiological Function, and Potential Applications. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Li, G.Y.; Liu, Y.K.; Luo, Y.J.; Xu, C.D.; Li, C.; Tang, B. Regulation of Carbohydrate Metabolism by Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase 3 in the Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 575485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Yang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Wang, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y. Silencing of the BtTPS Genes by Transgenic Plant-Mediated RNAi to Control Bemisia tabaci MED. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.W.; Jin, S.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Q.D.; Wei, P.; Wei, Z.M.; Wang, S.G.; Tang, B. Regulatory Functions of Trehalose-6-phosphate Synthase in the Chitin Biosynthesis Pathway in Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) Revealed by RNA Interference. B. Entomol. Res. 2018, 108, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.J; Li, G.Y.; Xu, C.D.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Z.S.; Wang, S.G.; Li, C. Regulatory Functions of Nilaparvata lugens GSK-3 in Energy and Chitin Metabolism. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 518876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Shen, Q.; Wang, SS.; Li, G.Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, C.D.; Tang, B.; Li, C. Regulatory Function of The Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase Gene TPS3 on Chitin Metabolism in Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Mo.l Biol. 2022, 31, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.Y.; Xia, Y.X. Isolation and Characterization of the Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase Gene from Locusta migratoria manilensis. Insect Sci. 2009, 16, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Nan, J.; Cheng, W.; Zhu-Salzman, K. Characterization of Trehalose Metabolic Genes and Corresponding Enzymatic Activities during Diapause of Sitodiplosis mosellana. J. Insect Physiol. 2021, 135, 104324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Hao, Y.-J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Ren, S.; Si, F.-L.; Chen, B. Gene Cloning, Characterization and Expression and Enzymatic Activities Related to Trehalose Metabolism during Diapause of the Onion Maggot Delia antiqua (Diptera: Anthomyiidae). Gene. 2015, 565, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitryjuk, M.; Łopieńska-Biernat, E.; Zaobidna, E.A. The In Vitro Effect of Ivermectin on the Activity of Trehalose Synthesis Pathway Enzymes and Their mRNA Expression in the Muscle of Adult Female Ascaris suum (Nematoda). Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 936560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, M.J.; Rice, W.C; Ring, D.R. The Influence of Plant Age on Tolerance of Rice to Injury by the Rice Water Weevil, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2002, 92, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reay-Jones, F.P.F.; Way, M.O.; Tarpley, L. Nitrogen Fertilization at the Rice Panicle Differentiation Stage to Compensate for Rice Water Weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) Injury. Crop Prot, 2008, 27, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaee, M.; Godfrey, L.D. A Century of Rice Water Weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): A History of Research and Management with an Emphasis on the United States. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2014, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Chang, Y.D.; Kim, Y.G. Trehalose, A Major Sugar Cryoprotectant of the Overwintering Rice Water Weevil, Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). J. Asia-Pacific Entomol. 2002, 5, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, X.X.; Wang, J.X; Wang, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Xi, J.H. Identification and Analysis of Up-Regulated Proteins in Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus Adults for Rapid Cold Hardening. Gene 2018, 642, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Fang, K.; Qi, L.; Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Xi, J.; Zhang, J. Purification and Functional Characterization of a Soluble Trehalase in Lissorhoptrus oryzophilus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Insects 2022, 13, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; He, J.; Chao, L.; Shi, Z.; Wang, S.; Yu, W.; Huang, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z. Regulatory Role of Trehalose Metabolism in Cold Stress of Harmonia axyridis Laboratory and Overwinter Populations. Agronomy 2023, 13, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, E.; Thorat, L.; Bendre, A.D.; Jadhav, S.; Pal, J.K.; Nath, B.B.; Gaikwad, S.M. Cloning and Characterization of Trehalase: A Conserved Glycosidase from Oriental Midge, Chironomus ramosus. 3 Biotech. 2018, 8, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.N.; Ji, S.X.; Wan, X.; Liu, W.X.; Guo, J.Y.; Lü, Z.C.; Wan, F.H. Molecular Charactristics of Three Cold Resistance Genes and Their Roles in Temperature Stress Response in Two Bemisia tabaci Cryptic Species. Entomol. Gen. 2021, 41, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellis, M.B.; Kotkar, H.M.; Joshi, R.S. Regulation of Trehalose Metabolism in Insects: From Genes to the Metabolite Window. Glycobiology 2023, 33, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, X.; Han, S.; Li, Z.; Li, L.; Li, J. Gene Characterization and Enzymatic Activities Related to Trehalose Metabolism of In Vitro Reared Trichogramma dendrolimi Matsumura (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) under Sustained Cold Stress. Insects 2020, 11, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teets, N.M.; Gantz, J.D.; Kawarasaki, Y. Rapid Cold Hardening: Ecological Relevance, Physiological Mechanisms and New Perspectives. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb203448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekera, M.J.; Acharya, R.; Hwang, H. S.; Lee, K. Y. Effect of Cold Acclimation and Rapid Cold-Hardening on the Survival of Spodoptera frugiperda (J.E. Smith) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) under Cold Stress. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2022, 25, 101862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Zhang, X.-X.; Chang, Y.-W.; Du, Y.-Z. Differential Response of Leafminer Flies Liriomyza trifolii (Burgess) and Liriomyza sativae (Blanchard) to Rapid Cold Hardening. Insects 2021, 12, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamang, A.M.; Kalra, B.; Parkash, R. Cold and Desiccation Stress Induced Changes in the Accumulation and Utilization of Proline and Trehalose in Seasonal Populations of Drosophila immigrans. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A. Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2017, 203, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Zhao, R.; Zhou, W.; Pan, Y.; Tian, H.; Yin, Z.; Chen, W. Fruit Fly in a Challenging Environment: Impact of Short-Term Temperature Stress on the Survival, Development, Reproduction, and Trehalose Metabolism of Bactrocera dorsalis (Diptera: Tephritidae). Insects 2022, 13, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, W.H.; Lee, D.W. RNA Interference of Trehalose Phosphate Synthase Inhibits Metamorphosis and Decreases Cold Tolerance in the Diamondback Moth, Plutella xylostella (L.). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2018, 21, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Wang, S.; Wei, P.; Xu, C.D.; Tang, B.; Zhang, F. Molecular Cloning and Cold-Induced Expression of Trehalose-6-Phosphate Synthase Gene in Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2012, 55, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
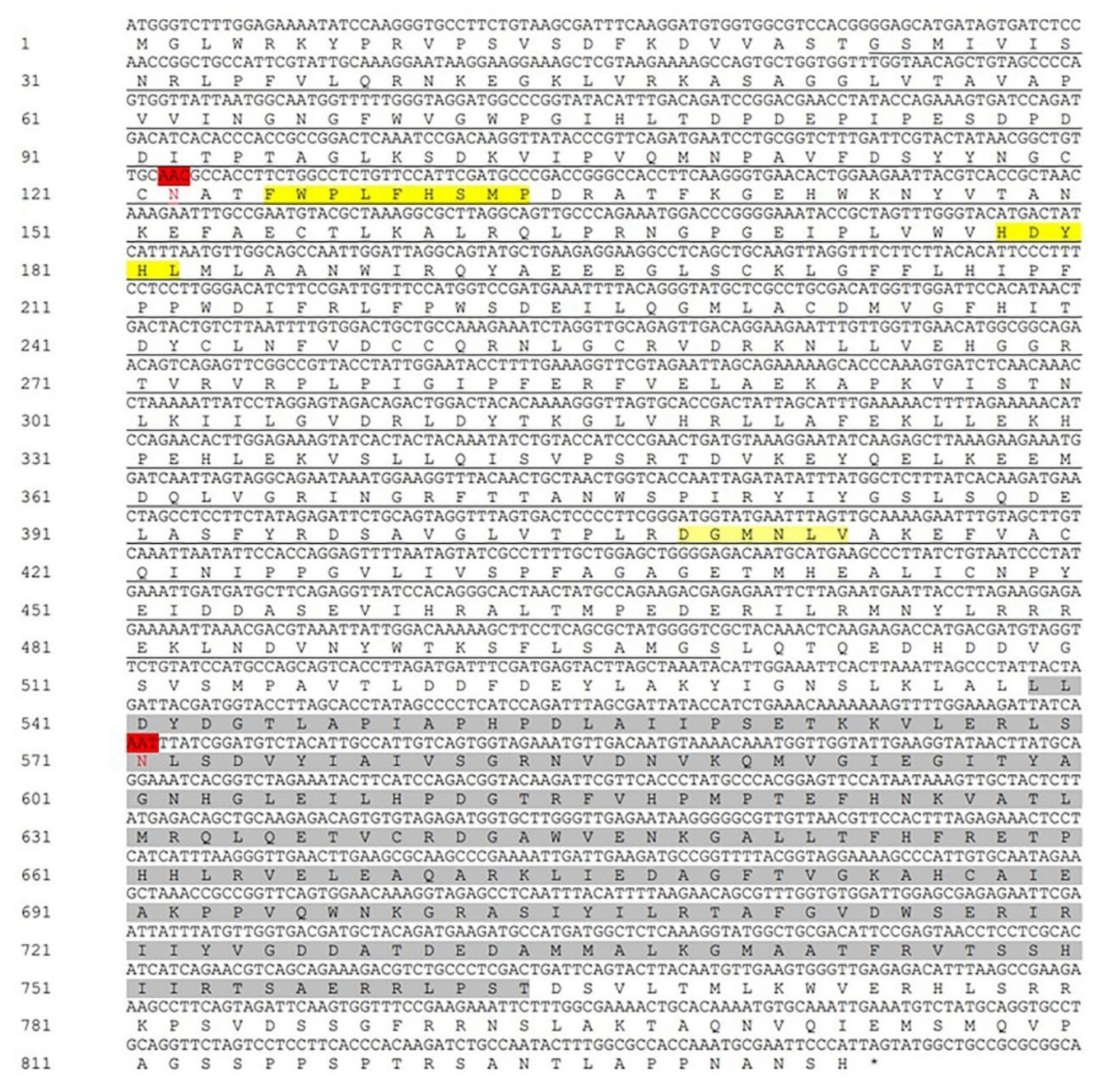

| Prime name | Primer sequence(5’-3’) | Purpose | |
| LoTPS | GCGTTTGGTGTGGATTGG /ATACGCTGACATCACCCC | ORF cloning | |
| LoTPS | GCGTTTGGTGTGGATTGG /GATGATGTGCGAGGAGGT | RT-qPCR | |
| TRET | ACCACGACTCAGGAAAAT/ACCAACGCATAAGATAGC | ||
| TRE | AACCTGTGATTGTCCCTG/TCCTTTGGCTGTTTCGTG | ||
| RpS18 | GTAATGTTTGCCTTGACTG/ TTTCTACTTCCTCTTCGG | ||
| dsTPS-F | taatacgactcactatagggGACAAAAAGCTTCCTCAGCG | RNAi | |
| dsTPS-RdsGFP-F | taatacgactcactatagggAGTGGAACGTTAACAACGCC | ||
| taatacgactcactatagggTGTTCTGCTGGTAGTGGTCG | |||
| dsGFP-R | taatacgactcactatagggTGTTCTGCTGGTAGTGGTCG | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





