Submitted:
27 September 2023
Posted:
28 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Demineralized bone matrixes
2.2. Quantification of Calcium and DNA Content
2.3. Remineralization of DBM
2.4. X-ray Diffraction Analysis and FTIR Spectroscopy
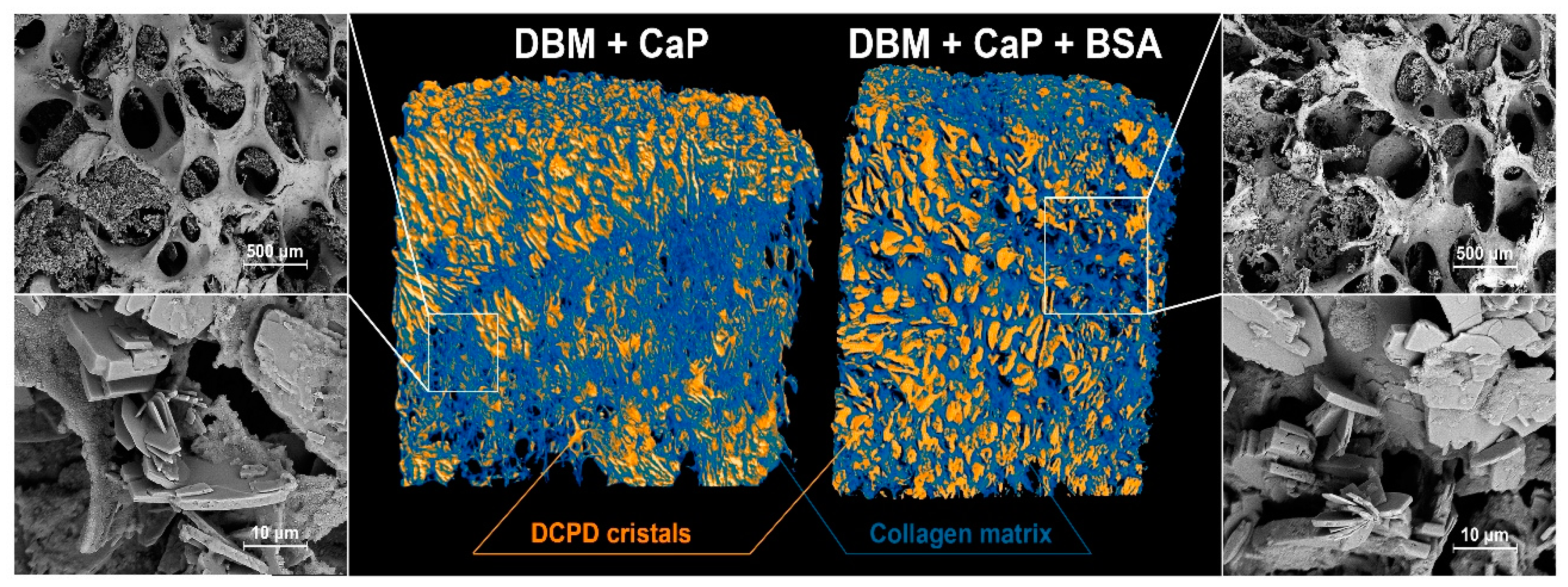
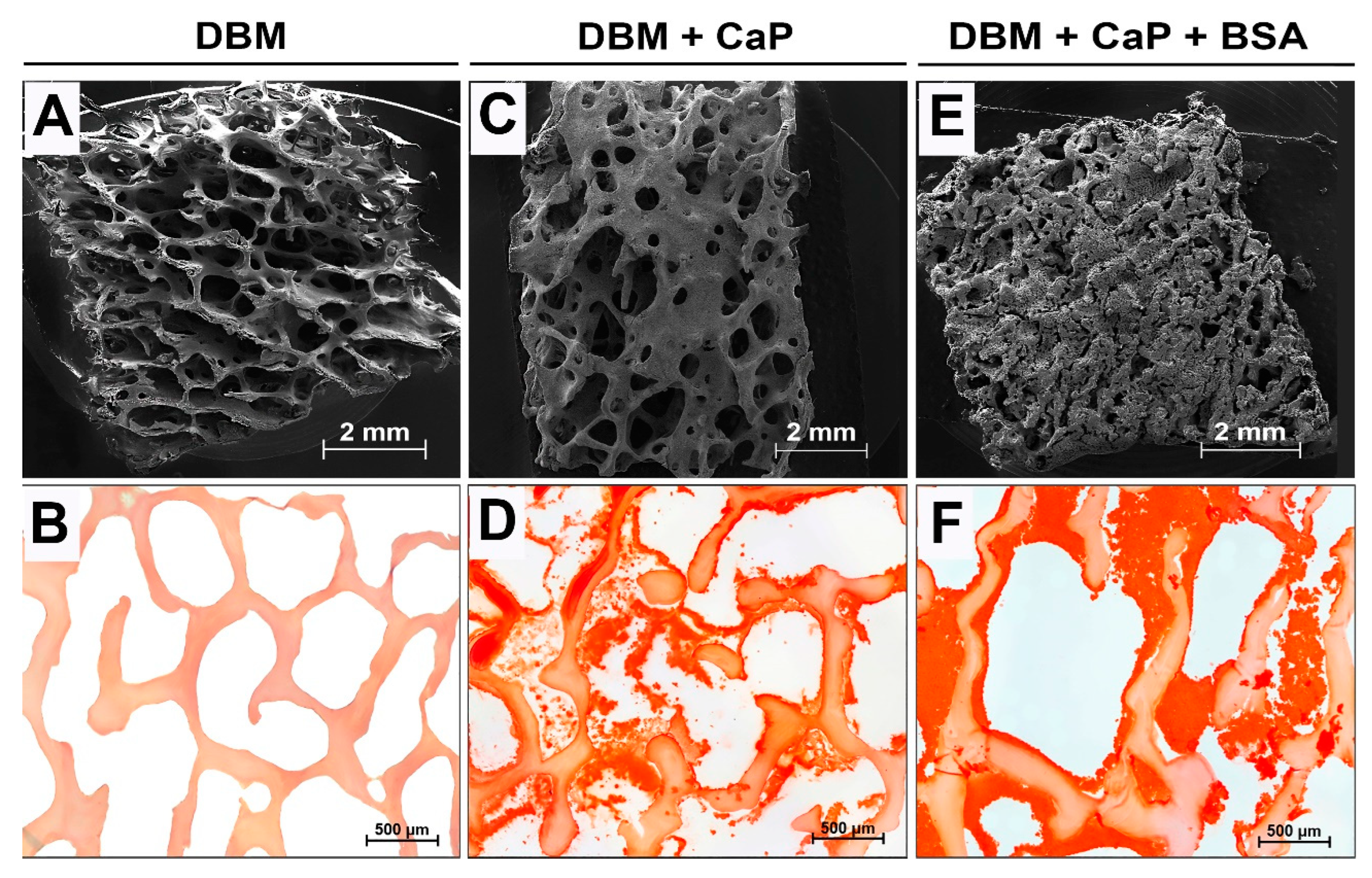
2.5. MicroCT and Microstructure Analysis
2.6. Cell Culture
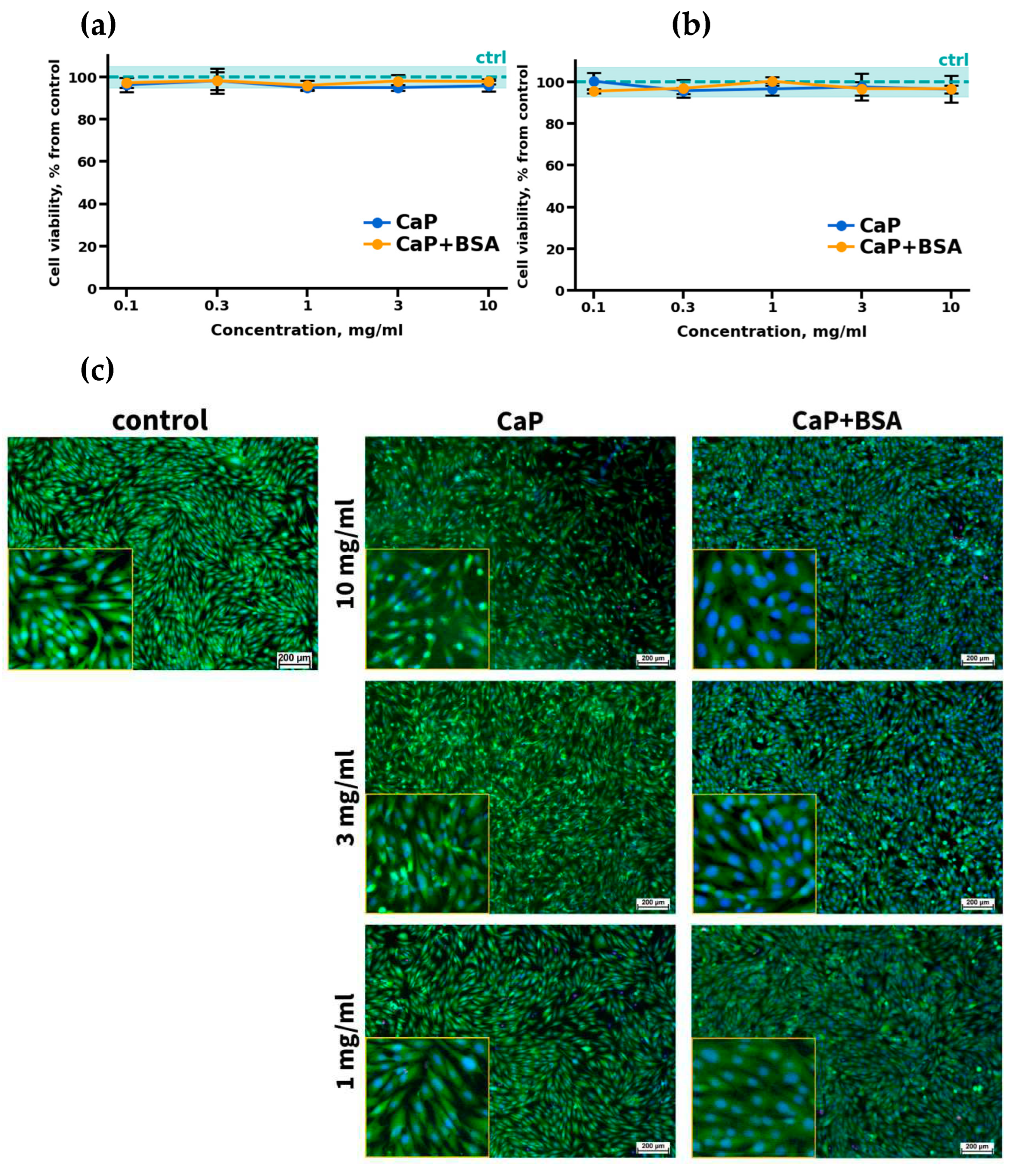
2.7. Cell Viability Assay
2.8. Fluorescence microscopy
2.9. Animals and Surgical Procedures
2.10. Histological Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Results of efficiency evaluation of Bone matrix demineralization
3.2. Results of physico-chemical analysis and morphology
3.3. In vitro cytocompatibility evaluation results
3.4. Results of the assessment of biocompatibility, osteoconductive, and osteoinductive potential of sammples in vivo
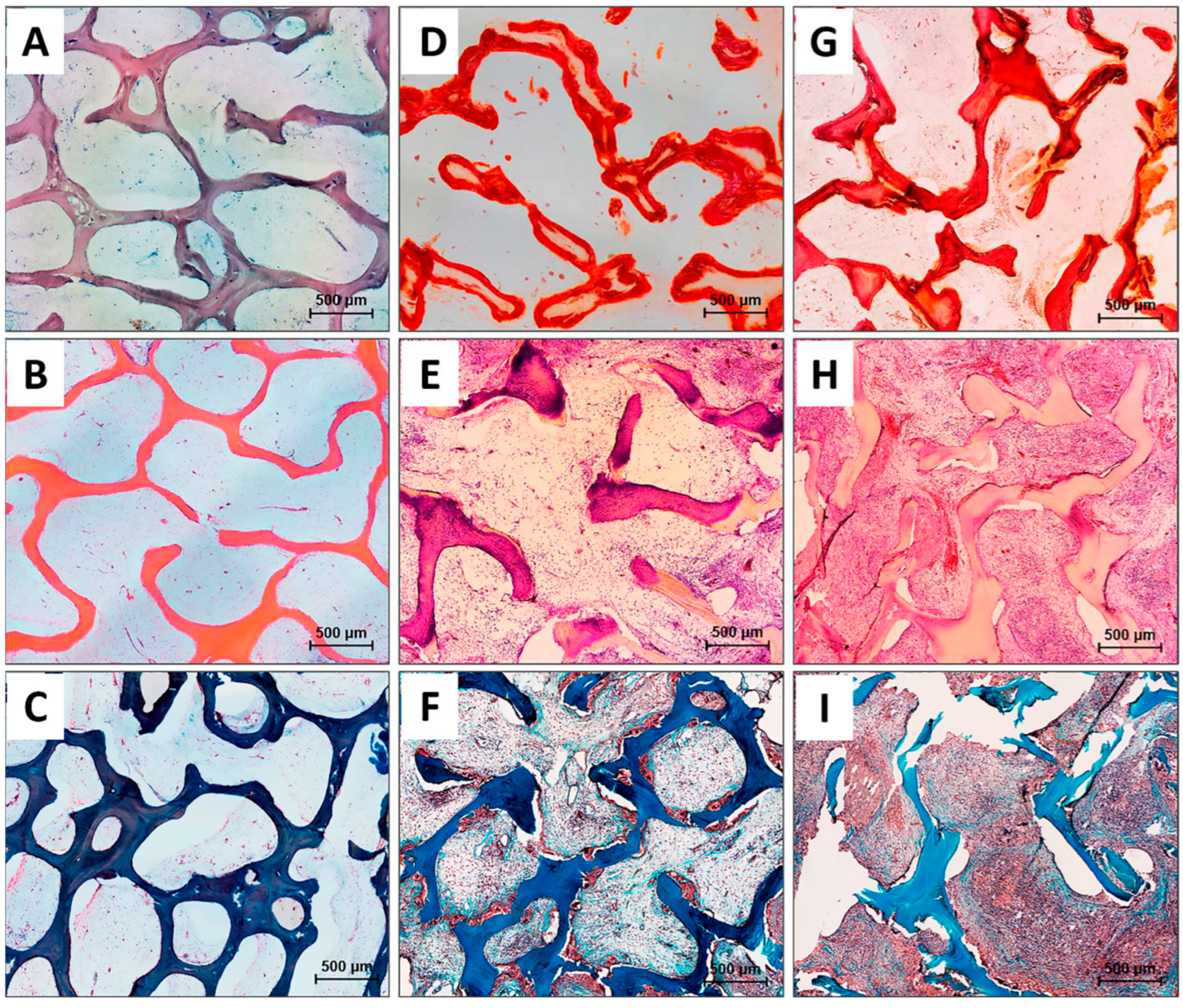
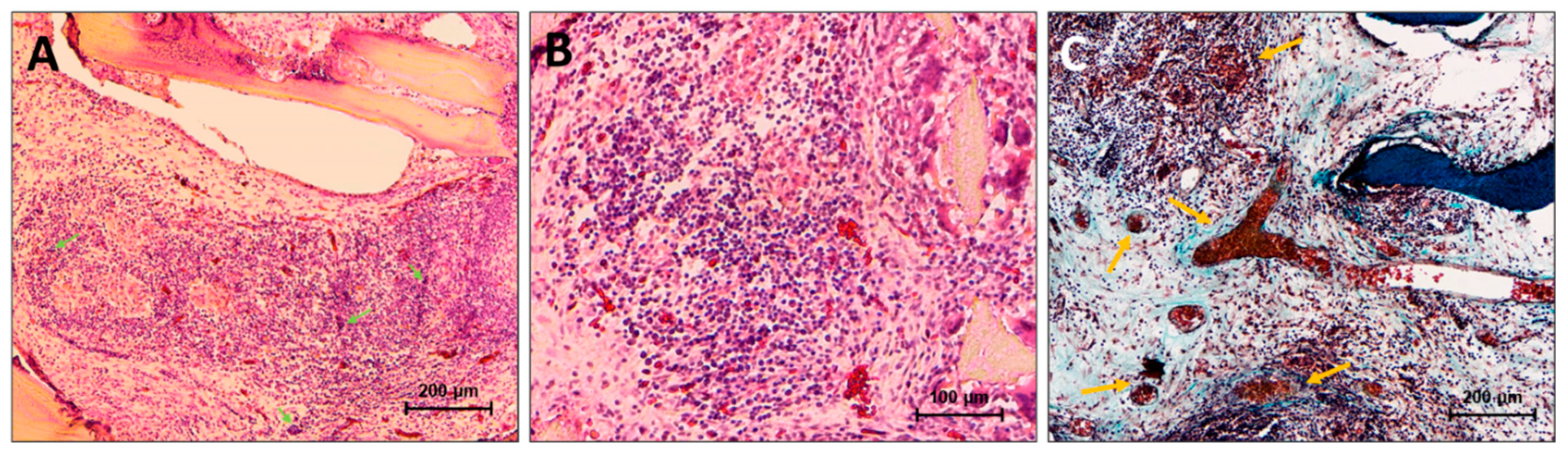
3.4.1. DBM implantation results
3.4.2. DBM+CaP implantation results
3.4.3. DBM+CaP+BSA implantation results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Busch, A.; Jäger, M.; Mayer, C.; Sowislok, A. Functionalization of Synthetic Bone Substitutes. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chu, C.; Xiao, W.; Liu, L.; Man, Y.; Lin, J.; Qu, Y. Strategies for advanced particulate bone substitutes regulating the osteo-immune microenvironment. Biomed Mater. 2022, 17, 022006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Merchán, E.C. Bone Healing Materials in the Treatment of Recalcitrant Nonunions and Bone Defects. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickramasinghe, M.L.; Dias, G.J.; Premadasa, K.M.G.P. A novel classification of bone graft materials. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022, 110, 1724–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SenGupta, S.; Parent, C.A.; Bear, J.E. The principles of directed cell migration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riederman, B.D.; Butler, B.A.; Lawton, C.D.; Rosenthal, B.D.; Balderama, E.S.; Bernstein, A.J. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 versus iliac crest bone graft in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: Dysphagia and dysphonia rates in the early postoperative period with review of the literature. J Clin Neurosci. 2017, 44, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, C.H. 3rd; Carreon, L.Y.; McGinnis, M.D.; Campbell, M.J.; Glassman, S.D. 3rd; Carreon, L.Y.; McGinnis, M.D.; Campbell, M.J.; Glassman, S.D. Perioperative complications of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 on an absorbable collagen sponge versus iliac crest bone graft for posterior cervical arthrodesis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2009, 34, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.C.; Tumialán, L.M.; Chou, D. Multilevel anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with and without rhBMP-2: a comparison of dysphagia rates and outcomes in 150 patients. J Neurosurg Spine 2013, 18, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Selph, S.; McDonagh, M.; Peterson, K.; Tiwari, A.; Chou, R.; Helfand, M. Effectiveness and harms of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 in spine fusion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 2013, 158, 890–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riederman, B.D.; Butler, B.A.; Lawton, C.D.; Rosenthal, B.D.; Balderama, E.S.; Bernstein, A.J. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 versus iliac crest bone graft in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: Dysphagia and dysphonia rates in the early postoperative period with review of the literature. J Clin Neurosci. 2017, 44, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagón-Escandón, A.; Hautefeuille, M.; Jimenez-Díaz, E.; Arenas-Alatorre, J.; Saniger, J.M.; Badillo-Ramírez, I.; Vazquez, N.; Piñón-Zarate, G.; Castell-Rodríguez, A. Three-Dimensional Porous Scaffolds Derived from Bovine Cancellous Bone Matrix Promote Osteoinduction, Osteoconduction, and Osteogenesis. Polymers (Basel) 2021, 13, 4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Qabbani, A.; Rani, K.G.A.; Syarif, J.; AlKawas, S.; Sheikh Abdul Hamid, S.; Samsudin, A.R.; Azlina, A. Evaluation of decellularization process for developing osteogenic bovine cancellous bone scaffolds in-vitro. PLoS One 2023, 18, e0283922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala-Ham, A.; Aguilar-Medina, M.; León-Félix, J.; Romero-Quintana, J.G.; Bermúdez, M.; López-Gutierrez, J.; Jiménez-Gastélum, G.; Avendaño-Félix, M.; Lizárraga-Verdugo, E.; Castillo-Ureta, H.; López-Camarillo, C.; Ramos-Payan, R. Extracellular matrix hydrogel derived from bovine bone is biocompatible in vitro and in vivo. Biomed Mater Eng. 2022, 33, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wei, M. Biomineralization of Collagen-Based Materials for Hard Tissue Repair. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collagen. Available online: URL https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/2457 (accessed on 14 June 2023).
- Oosterlaken, B.M.; Vena, M.P.; de With, G. In Vitro Mineralization of Collagen. Adv Mater. 2021, 33, e2004418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Sahai, N. Structure analysis of collagen fibril at atomic-level resolution and its implications for intra-fibrillar transport in bone biomineralization. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2018, 20, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynn, A.K.; Yannas, I.V.; Bonfield, W. Antigenicity and immunogenicity of collagen. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004, 71, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasravi, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Babajani, A.; Mazloomnejad, R.; Hatamnejad, M.R.; Shariatzadeh, S.; Bahrami, S. , Niknejad, H. Immunogenicity of decellularized extracellular matrix scaffolds: a bottleneck in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Biomater Res. 2023, 27, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Bai, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, C.; Che, Z.; Liu, He.; Wang, J.; Huang, L. Collagen-based biomaterials for bone tissue engineering. Materials & Design 2021, 210, 110049. [Google Scholar]
- Trindade, R.; Albrektsson, T.; Tengvall, P.; Wennerberg, A. Foreign Body Reaction to Biomaterials: On Mechanisms for Buildup and Breakdown of Osseointegration. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2016, 18, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.Á.; Monahan, D.S.; Brulin, B.; Gallinetti, S.; Humbert, P.; Tringides, C.; Canal, C.; Ginebra, M.P.; Layrolle, P. Biomimetic versus sintered macroporous calcium phosphate scaffolds enhanced bone regeneration and human mesenchymal stromal cell engraftment in calvarial defects. Acta Biomater. 2021, 135, 689–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, O.; Shiwaku, Y.; Hamai, R. Octacalcium phosphate bone substitute materials: Comparison between properties of biomaterials and other calcium phosphate materials. Dent. Mater. J. 2020, 39, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almulhim, K.S.; Syed, M.R.; Alqahtani, N.; Alamoudi, M.; Khan, M.; Ahmed, S.Z.; Khan, A.S. Bioactive Inorganic Materials for Dental Applications: A Narrative Review. Materials (Basel). 2022, 15, 6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadeeva, I.S.; Teterina, A.Y.; Minaychev, V.V.; Senotov, A.S.; Smirnov, I.V.; Fadeev, R.S.; Smirnova, P.V.; Menukhov, V.O.; Lomovskaya, Y.V.; Akatov, V.S.; Barinov, S.M.; Komlev, V.S. Biomimetic Remineralized Three-Dimensional Collagen Bone Matrices with an Enhanced Osteostimulating Effect. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, T.; Zou, X.; Lei, L.; Yan, W.; Yang, J.; Li, B. Strontium-substituted biphasic calcium phosphate microspheres promoted degradation performance and enhanced bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020, 108, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligasová, A.; Koberna, K. DNA Dyes-Highly Sensitive Reporters of Cell Quantification: Comparison with Other Cell Quantification Methods. Molecules. 2021, 26, 5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teterina, A.Y.; Minaychev, V.V.; Smirnova, P.V.; Kobiakova, M.I.; Smirnov, I.V.; Fadeev, R.S.; Egorov, A.A.; Ashmarin, A.A.; Pyatina, K.V.; Senotov, A.S.; et al. Injectable Hydrated Calcium Phosphate Bone-like Paste: Synthesis, In Vitro, and In Vivo Biocompatibility Assessment. Technologies 2023, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barradas, A.M.; Yuan, H.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Habibovic, P. Osteoinductive biomaterials: Current knowledge of properties, experimental models and biological mechanisms. Eur. Cell Mater 2011, 21, 407–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibovic, P.; de Groot, K. Osteoinductive biomaterials—Properties and relevance in bone repair. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2007, 1, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillie, R.D.; Fullmer, H.M. Histopathologic Technic and Practical Histochemistry; McGraw-Hill: New York, NA, USA, 1976; p. 942. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Barbieri, D.; Yuan, H.; Moroni, L.; Feng, G. The role of calcium phosphate surface structure in osteogenesis and the mechanisms involved. Acta Biomater. 2020, 106, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabadjieva, D.; Sezanova, K.; Gergulova, R.; Titorenkova, R.; Tepavitcharova, S. Precipitation and phase transformation of dicalcium phosphate dihydrate in electrolyte solutions of simulated body fluids: Thermodynamic modeling and kinetic studies. J Biomed Mater Res A 2020, 108, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenk, T.J.; Ratner, B.D.; Gendreau, R.M.; Chittur, K.K. IR spectral changes of bovine serum albumin upon surface adsorption. J Biomed Mater Res. 1989, 23, 549–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Yang, X.; Ji, Z.; Zhu, L.; Ma, N.; Chen, D.; Jia, X.; Tang, J.; Cao, Y. DFT-Calculated IR Spectrum Amide I, II, and III Band Contributions of N-Methylacetamide Fine Components. ACS Omega. 2020, 5, 8572–8578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhazmi, H.A. FT-IR spectroscopy for the identification of binding sites and measurements of the binding interactions of important metal ions with bovine serum albumin. Scientia Pharmaceutica 2019, 87, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, J.F.; Mattix, M.E.; Papenfuss, T.L. Hematopoietic System. In Atlas of Histology of the Juvenile Rat, 1nd ed.; Picut, C.A., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: San Diego, CA, U.S.A, 2016; pp. 349–371. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.-H.; He, H.; Chen, Y.-N.; Liu, Z.; Romani, M.D.; Xu, Z.-Y.; Xu, Y.; Lin, F.-Y. Exosomes derived from M2 Macrophages Improve Angiogenesis and Functional Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury through HIF-1α/VEGF Axis. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chang, T.; Wu, T.; Xu, W.; Dou, G.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C. M2 macrophages promote vasculogenesis during retinal neovascularization by regulating bone marrow-derived cells via SDF-1/VEGF. Cell Tissue Res 2020, 380, 469–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czekanska, E.; Stoddart, M.; Richards, R.; Hayes, J. In search of an osteoblast cell model for in vitro research. Eur. Cell. Mater. 2012, 24, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataiah, V.S.; Yahata, Y.; Kitagawa, A.; Inagaki, M.; Kakiuchi, Y.; Nakano, M.; Suzuki, S.; Handa, K.; Saito, M. Clinical Applications of Cell-Scaffold Constructs for Bone Regeneration Therapy. Cells 2021, 10, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torisawa, Y.S.; Spina, C.S.; Mammoto, T.; Mammoto, A.; Weaver, J.C.; Tat, T.; Collins, J.J.; Ingber, D.E. Bone marrow-on-a-chip replicates hematopoietic niche physiology in vitro. Nat Methods 2014, 11, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nudelman, F.; Lausch, A.J; Sommerdijk, N.A.; Sone, E.D. In vitro models of collagen biomineralization. J Struct Biol. 2013, 183, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, T. Jr. All about Albumin: Biochemistry, Genetics and Medical Applications. Academic Press: San Diego, USA, 1996; pp. 9–250.
- Evans, T.W. Review article: albumin as a drug – biological effects of albumin unrelated to oncotic pressure. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 16 (Suppl. 5), 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, C.M.; McClain, C.J.; Marsano, L.S. Albumin therapy in clinical practice. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2005, 20, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parving, H.H.; Gyntelberg, F. Transcapillary escape rate of albumin and plasma volume in essential hypertension. Circ. Res. 1973, 32, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez-Vick, J.; Vargas, F.F. Albumin modulation of paracellular permeability of pig vena caval endothelium shows specificity for pig albumin. Am J Physiol. 1993, 264, H1382–H1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, R.; Siflinger-Birnboim, A.; Lum, H.; Tiruppathi, C.; Malik, A.B. Albumin and Ricinus communis agglutinin decrease endothelial permeability via interactions with matrix. Am J Physiol. 1993, 265, C439–C446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, S.; Llera-Moya, M.; dela, Drazul-Schrader, D. ; Phillips, M.C.; Kellner-Weibel, G.; Rothblat, G.H. Serum albumin acts as a shuttle to enhance cholesterol efflux from cells. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petitpas, I.; Petersen, C.E.; Ha, C.E.; Bhattacharya, A.A.; Zunszain, P.A.; Ghuman, J.; Bhagavan, N.V.; Curry, S. Structural basis of albumin-thyroxine interactions and familial dysalbuminemic hyperthyroxinemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 2003, 100, 6440–6445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlfors, C.E.; Wennberg, R.P. Bilirubin-albumin binding and neonatal jaundice. Semin Perinatol. 2004, 28, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pico, G.A.; Houssier, C. Bile salts-bovine serum albumin binding: spectroscopic and thermodynamic studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989, 999, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, F. Superior Dialytic Removal of Bilirubin and Bile Acids by Free Fatty Acid Displacement and Its Synergy With Albumin-Based Dialysis. ASAIO J. 2023, 69, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamler, J.S.; Jaraki, O.; Osborne, J.; Simon, D.I.; Keaney, J.; Vita, J.; Singel, D.; Valeri, C.R.; Loscalzom, J. Nitric oxide circulates in mammalian plasma primarily as an S-nitroso adduct of serum albumin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 1992, 89, 7674–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Vusse, G.J. Albumin as fatty acid transporter. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2009, 24, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, M.; Curry, S.; Terreno, E.; Galliano, M.; Fanali, G.; Narciso, P.; Notari, S.; Ascenzi, P. The extraordinary ligand binding properties of human serum albumin. IUBMB Life 2005, 57, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundry, R.L.; Fu, Q.; Jelinek, C.A.; Van Eyk, J.E.; Cotter, R.J. Investigation of an albumin-enriched fraction of human serum and its albuminome. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2007, 1, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascenzi, P.; Bocedi, A.; Bolli, A.; Fasano, M.; Notari, S.; Polticelli, F. (). Allosteric modulation of monomeric proteins. Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education, 2005, 33, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, M.; Rondeau, P.; Singh, N.R.; Tarnus, E.; Bourdon, E. The antioxidant properties of serum albumin. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1783–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belinskaia, D.A.; Voronina, P.A.; Shmurak, V.I.; Jenkins, R.O.; Goncharov, N.V. Serum Albumin in Health and Disease: Esterase, Antioxidant, Transporting and Signaling Properties. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 10318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H. , Cha M.K., Kim I.H. Activation of thiol-dependent antioxidant activity of human serum albumin by alkaline pH is due to the B-like conformational change. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 380, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, R.; Bao, Y.; Ridley, S.; Williamson, G. Phospholipid hydroperoxide cysteine peroxidase activity of human serum albumin. Biochem. J. 1999, 338, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanali, G.; di Masi, A.; Trezza, V.; Marino, M.; Fasano, M.; Ascenzi, P. Human serum albumin: from bench to bedside. Mol Aspects Med. 2012, 33, 209–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudlow, G.; Birkett, D.J.; Wade, D.N. The characterization of two specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 1975, 11, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carter, D.C.; Ho, J.X. Structure of serum albumin. Adv. Protein Chem. 1994, 45, 153–203. [Google Scholar]
- Bertucci, C.; Domenici, E. Reversible and covalent binding of drugs to human serum albumin: methodological approaches and physiological relevance. Curr. Med. Chem. 2002, 9, 1463–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, S. Beyond expansion: structural studies on the transport roles of human serum albumin. Vox Sang 2002, 83 (Suppl. 1), 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curry, S. Lessons from the crystallographic analysis of small molecule binding to human serum albumin. Drug. Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2009, 24, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kragh-Hansen, U.; Chuang, V.T.; Otagiri, M. Practical aspects of the ligand-binding and enzymatic properties of human serum albumin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 25, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, Y.; Ma, S.F.; Watanabe, H.; Yamaotsu, N.; Hirono, S.; Kurono, Y.; Kragh-Hansen, U.; Otagiri, M. Esterase-like activity of serum albumin: characterization of its structural chemistry using p-nitrophenyl esters as substrates. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sułkowska, A.; Bojko, B.; Równicka, J.; Sułkowski, W.W. Competition of cytarabine and aspirin in binding to serum albumin in multidrug therapy. Biopolymers 2006, 81, 464–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuman, J.; Zunszain, P.A.; Petitpas, I.; Bhattacharya, A.A.; Otagiri, M.; Curry, S. Structural basis of the drug-binding specificity of human serum albumin. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 353, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragh-Hansen, U. , Vorum H. Quantitative analyses of the interaction between calcium ions and human serum albumin. Clin. Chem. 1993, 39, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowska, M.; Wszelaka-Rylik, M.; Poznański, J.; Bal, W. Spectroscopic and thermodynamic determination of three distinct binding sites for Co(II) ions in human serum albumin. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eatough, D.J.; Jensen, T.E.; Hansen, L.D.; Loken, H.F.; Rehfeld, S.J. The binding of Ca2+ and Mg2+ to human serum albumin: a calorimetric study. Thermochim. Acta 1978, 25, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.O. Binding of calcium to serum albumin. I. Stoichiometry and intrinsic association constant at physiological pH, ionic strength, and temperature. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1971, 28, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majorek, K.A.; Porebski, P.J.; Dayal, A.; Zimmerman, M.D.; Jablonska, K.; Stewart, A.J.; Chruszcz, M.; Minor, W. Structural and immunologic characterization of bovine, horse, and rabbit serum albumins. Mol Immunol, 2012; 52(3-4), 174–182. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, D.; Haag, S.L.; Patel, J.S.; Ytreberg, F.M.; Bernards, M.T. Paired Simulations and Experimental Investigations into the Calcium-Dependent Conformation of Albumin. J Chem Inf Model. 2022, 62, 1282–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Márton, K.; Tamás, S.B.; Orsolya, N.; Béla, C.; Ferenc, D.; Péter, N.; Csaba, D.N.; Lajos, C.; Zsombor, L.; Eitan, M.; György. S. Materials (Basel), 2018, 11, E202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Igarashi. A.; Misawa. H.; Tsurusaki. Y. Enhancement of albumin expression in bone tissues with healing rat fractures. J Cell Biochem. 2003, 89, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, K.; Yamaguchi, M. Albumin regulates Runx2 and alpha1 (I) collagen mRNA expression in osteoblastic cells: comparison with insulin-like growth factor-I. Int J Mol Med. 2005, 16, 689–694. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, K.; Yamaguchi, M. Role of albumin in osteoblastic cells: enhancement of cell proliferation and suppression of alkaline phosphatase activity. Int J Mol Med. 2004, 14, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Zhu, W.; Iqbal, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, D.A. Stabilized albumin coatings on engineered xenografts for attenuation of acute immune and inflammatory responses. J Mater Chem B. 2020, 8, 6080–6091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváthy, D.B.; Simon, M.; Schwarz, C.M.; Masteling, M.; Vácz, G.; Hornyák, I.; Lacza, Z. Serum albumin as a local therapeutic agent in cell therapy and tissue engineering. BioFactors 2016, 43, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanganeria, P.; Sachar, S.; Chandra, S.; Bahadur, D.; Ray, P.; Khanna, A. Cellular internalization and detailed toxicity analysis of protein-immobilized iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater, 2015; 103, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ostroverkhov, P.; Semkina, A.; Nikitin, A.; Smirnov, A.; Vedenyapina, D.; Vlasova, K.; Kireev, I.; Grin, M.; Chekhonin, V.; Majouga, A.; Abakumov, M. Human serum albumin as an effective coating for hydrophobic photosensitizes immobilization on magnetic nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 475, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiji, M.; Park, H.; Park, K. Study on the prevention of surface-induced platelet activation by albumin coating. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 1992, 3, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváthy, D.B.; Schandl, K.; Schwarz, C.M.; Renner, K.; Hornyák, I.; Szabó, B.T.; Niculescu-Morzsa, E.; Nehrer, S.; Dobó-Nagy, C.; Doros, A.; Lacza, Z. Serum albumin–coated bone allograft (BoneAlbumin) results in faster bone formation and mechanically stronger bone in aging rats. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2019, 13, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváthy, D.B.; Vácz, G.; Cselenyák, A.; Weszl, M.; Kiss, L.; Lacza, Z. Albumin-coated bioactive suture for cell transplantation. Surg Innov. 2013, 20, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváthy, D.B.; Vácz, G.; Szabó, T.; Szigyártó, I.C.; Toró, I.; Vámos, B.; Hornyák, I.; Renner, K.; Klára, T.; Szabó, B.T.; Dobó-Nagy, C.; Doros, A.; Lacza, Z. Serum albumin coating of demineralized bone matrix results in stronger new bone formation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2016, 104, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Cui, L.; Ren, Y.; Zou, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, C.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, X.-B.; Zeng, R.; Zheng, Y. In vitro and in vivo biodegradation and biocompatibility of an MMT/BSA composite coating upon magnesium alloy AZ31. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 47, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazoe, H.; Tanabe, T. Preparation of water-insoluble albumin film possessing nonadherent surface for cells and ligand binding ability. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A. 2008, 86, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazoe, H.; Uemura, T.; Tanabe, T. Facile Cell Patterning on an Albumin-Coated Surface. Langmuir. 2008, 24, 8402–8404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yoshinari, M.; Takemoto, S.; Hattori, M.; Kawada, E.; Liu, B.; Oda, Y. Adhesion of mouse fibroblasts on hexamethyldisiloxane surfaces with wide range of wettability. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2007, 81B, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, B.J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, W.H.; Woo, H.M.; Kweon, O.K. Collagen I gel promotes homogenous osteogenic differentiation of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in serum-derived albumin scaffold. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2013, 24, 1233–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijiritsky, E.; Gardin, C.; Ferroni, L.; Lacza, Z.; Zavan, B. Albumin-impregnated bone granules modulate the interactions between mesenchymal stem cells and monocytes under in vitro inflammatory conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2020, 110, 110678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaliczki, G.; Schandl, K.; Weszl, M.; Major, T.; Kovács, M.; Skaliczki, J.; Szendrői, M.; Dobó-Nagy, C.; Lacza, Z. Serum albumin enhances bone healing in a nonunion femoral defect model in rats: A computer tomography micromorphometry study. Int. Orthop. 2013, 37, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weszl, M.; Skaliczki, G.; Cselenyák, A.; Kiss, L.; Major, T.; Schandl, K.; Bognar, E.; Stadler, G.; Peterbauer, A.; Csonge, L.; Lacza, Z. Freeze-dried human serum albumin improves the adherence and proliferation of mesenchymal stem cells on mineralized human bone allografts. J. Orthop. Res. 2012, 30, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schandl, K.; Horváthy, D.B.; Doros, A.; Majzik, E.; Schwarz, C.M.; Csönge, L.; Abkarovits, G.; Bucsi, L.; Lacza, Z. Bone-Albumin filling decreases donor site morbidity and enhances bone formation after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with bone-patellar tendon-bone autografts. Int. Orthop. 2016, 40, 2097–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klára, T.; Csönge, L.; Janositz, G.; Pap, K.; Lacza, Z. The use of structural proximal tibial allografts coated with human albumin in treating extensive periprosthetic knee-joint bone deficiency and averting late complications. Case Rep. Orv. Hetil. 2015, 156, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonffy, L.; Minya, F.; Trimmel, B.; Lacza, Z.; Dobo-Nagy, C. Albumin-Impregnated Allograft Filling of Surgical Extraction Sockets Achieves Better Bone Remodeling Than Filling with Either Blood Clot or Bovine Xenograft. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2020, 35, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, M.D. The sites and topology of mitochondrial superoxide production. Exp Gerontol, 2010; 45(7-8), 466–472. [Google Scholar]
- Hamanaka, R.B.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species regulate cellular signaling and dictate biological outcomes. Trends Biochem Sci. 2010, 35, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X. Fang, P. Mai, J. Choi, E.T. Wang, H. Yang, X.F. Targeting mitochondrial reactive oxygen species as novel therapy for inflammatory diseases and cancers. J Hematol Oncol. 2013, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuten Pella, O.; Hornyák, I.; Horváthy, D.; Fodor, E.; Nehrer, S.; Lacza, Z. Albumin as a Biomaterial and Therapeutic Agent in Regenerative Medicine. Int J Mol Sci. 2022, 23, 10557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klára, T.; Csönge, L.; Janositz, G.; Csernátony, Z.; Lacza, Z. Albumin-coated structural lyophilized bone allografts: A clinical report of 10 cases. Cell Tissue Bank. 2014, 15, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernards, M.T.; Qin, C.; Jiang, S. MC3T3-E1 cell adhesion to hydroxyapatite with adsorbed bone sialoprotein, bone osteopontin, and bovine serum albumin. Colloids Surf. B 2008, 64, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W.; Cheng, K.J.; Geesey, G.G.; Ladd, T.I.; Nickel, J.C.; Dasgupta, M.; Marrie, T.J. Bacterial biofilms in nature and disease. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1987, 41, 435–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnari, T.J.; I Peltonen, L.; Kuusela, P.; Kivilahti, J.; Könönen, M.; Jero, J. Bacterial Adherence to Titanium Surface Coated with Human Serum Albumin. Otol. Neurotol. 2005, 26, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zheng, W.; Zhu, G.; Lian, J.; Wang, J.; Hui, P.; He, S.; Chen, W.; Jiang, X. Albumin Broadens the Antibacterial Capabilities of Nonantibiotic Small Molecule-Capped Gold Nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2019, 11, 45381–45389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marelli, D.; Paul, A.; Samson, R.; Edgell, D.; Angood, P.; Chiu, R.C. Does the addition of albumin to the prime solution in the cardiopulmonary bypass circuit affect clinical outcome? A randomized study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1989, 98, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishima, Y. Albumin-Based Nitric Oxide Traffic System for the Treatment of Intractable Cancers. Biol Pharm Bull, 2017; 40, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Stamler, J.S.; Jaraki, O.; Osborne, J.; Simon, D.I.; Keaney, J.; Vita, J.; Singel, D.; Valeri, C.R.; Loscalzo, J. Nitric oxide circulates in mammalian plasma primarily as an S-nitroso adduct of serum albumin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992, 89, 7674–7677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvihill, J.N.; Faradji, A.; Oberling, F.; Cazenave, J.-P. Surface passivation by human albumin of plasmapheresis circuits reduces platelet accumulation and thrombus formation. Experimental and clinical studies. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1990, 24, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maul, T.M.; Massicotte, P.; Wearden, P.D. ECMO Biocompatibility: Surface Coatings, Anticoagulation, and Coagulation Monitoring In Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation-Advances in Therapy; Firstenberg, M.S., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016; Volume 3, pp. 27–61. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, P.; Wang, D.; Ruff, P.; Austin, B.; DeBraux, S.; Wolcott, K.; Burris, D.; Ling, G.; Sun, L. Human neutrophil activation and increased adhesion by various resuscitation fluids. Crit Care Med. 2000, 28, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, C.; Xie, Q.W.; Halbwachs-Mecarelli, L.; Jin, W.W. Albumin inhibits neutrophil spreading and hydrogen peroxide release by blocking the shedding of CD43 (Sialophorin, Leukosialin). J Cell Biol. 1993, 122, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
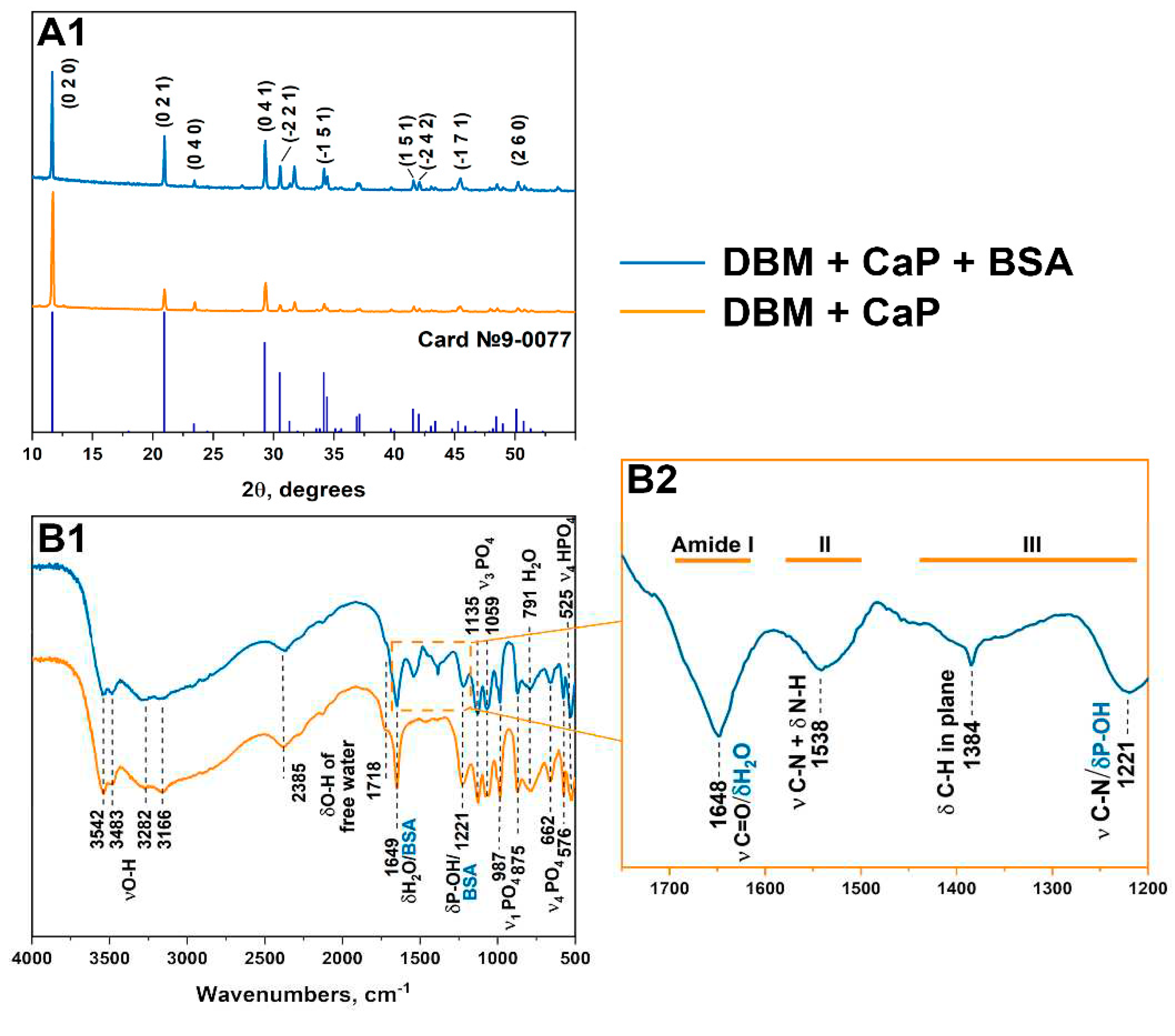
| a, Å | b, Å | c, Å | α, ° | β, ° | γ, ° | V, Å3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Card №9-0077 | 6.36 | 15.19 | 5.82 | 90.00 | 118.50 | 90.00 | 493.93 |
| CaP | 6.362(3) | 15.1609(24) | 5.8083(14) | 90.00 | 118.545(21) | 90.00 | 492.13(18) |
| CaP+BSA | 6.3610(20) | 15.168(3) | 5.8121(12) | 90.00 | 118.571(24) | 90.00 | 492.47(18) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





