Submitted:
24 September 2023
Posted:
26 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
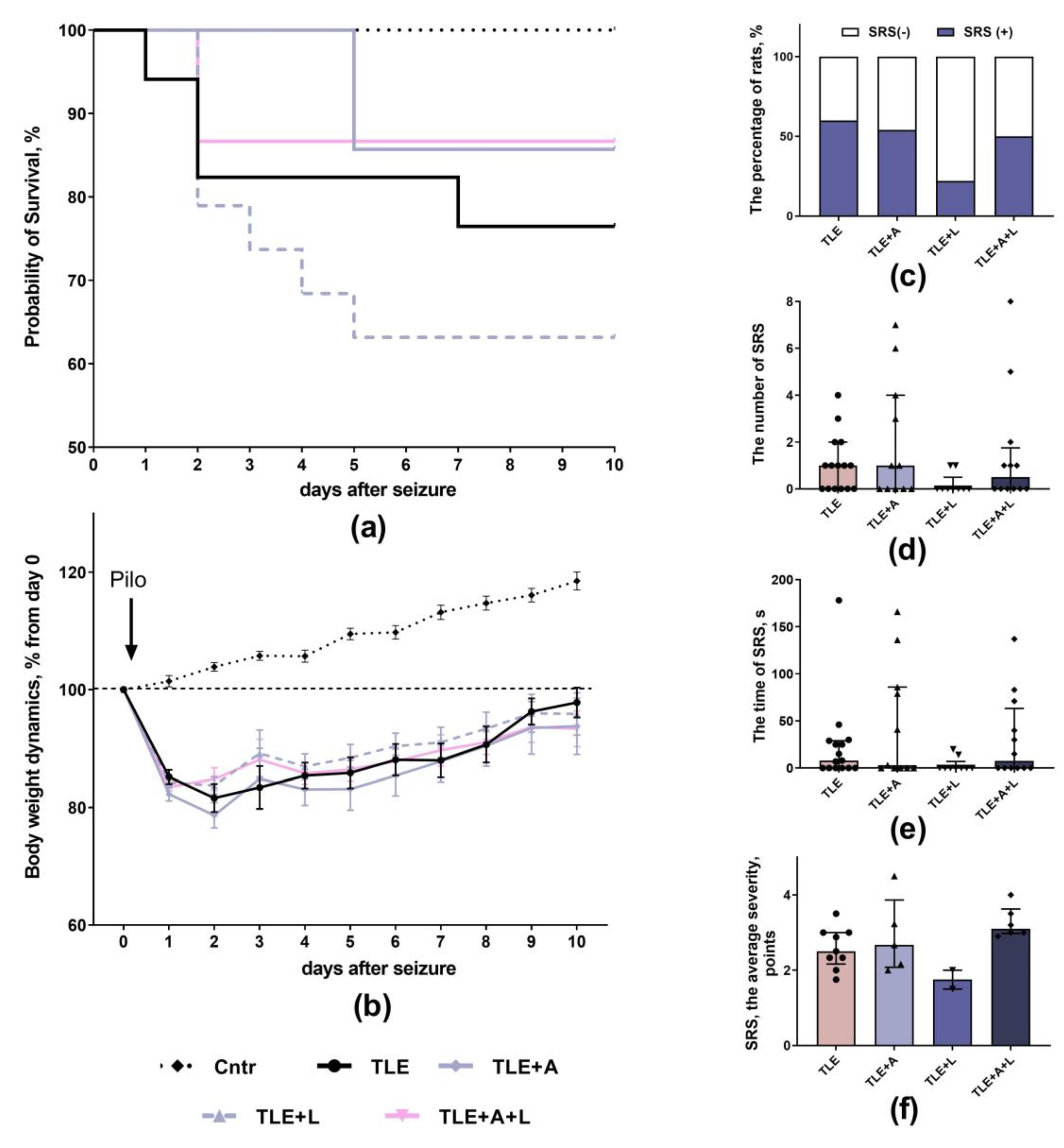
2.1. The effect of treatment with anakinra, lamotrigine and their combination effect on neurological parameters
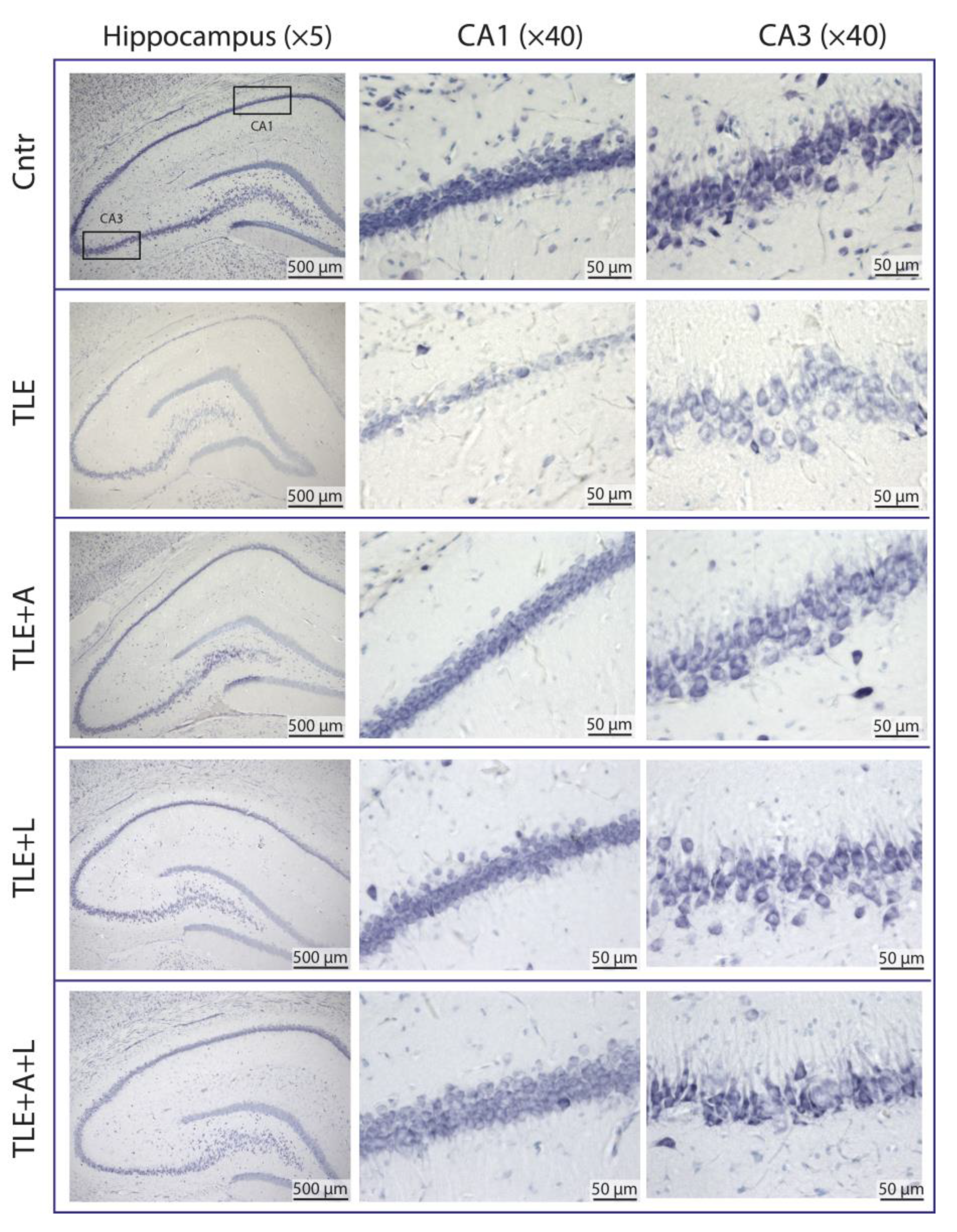
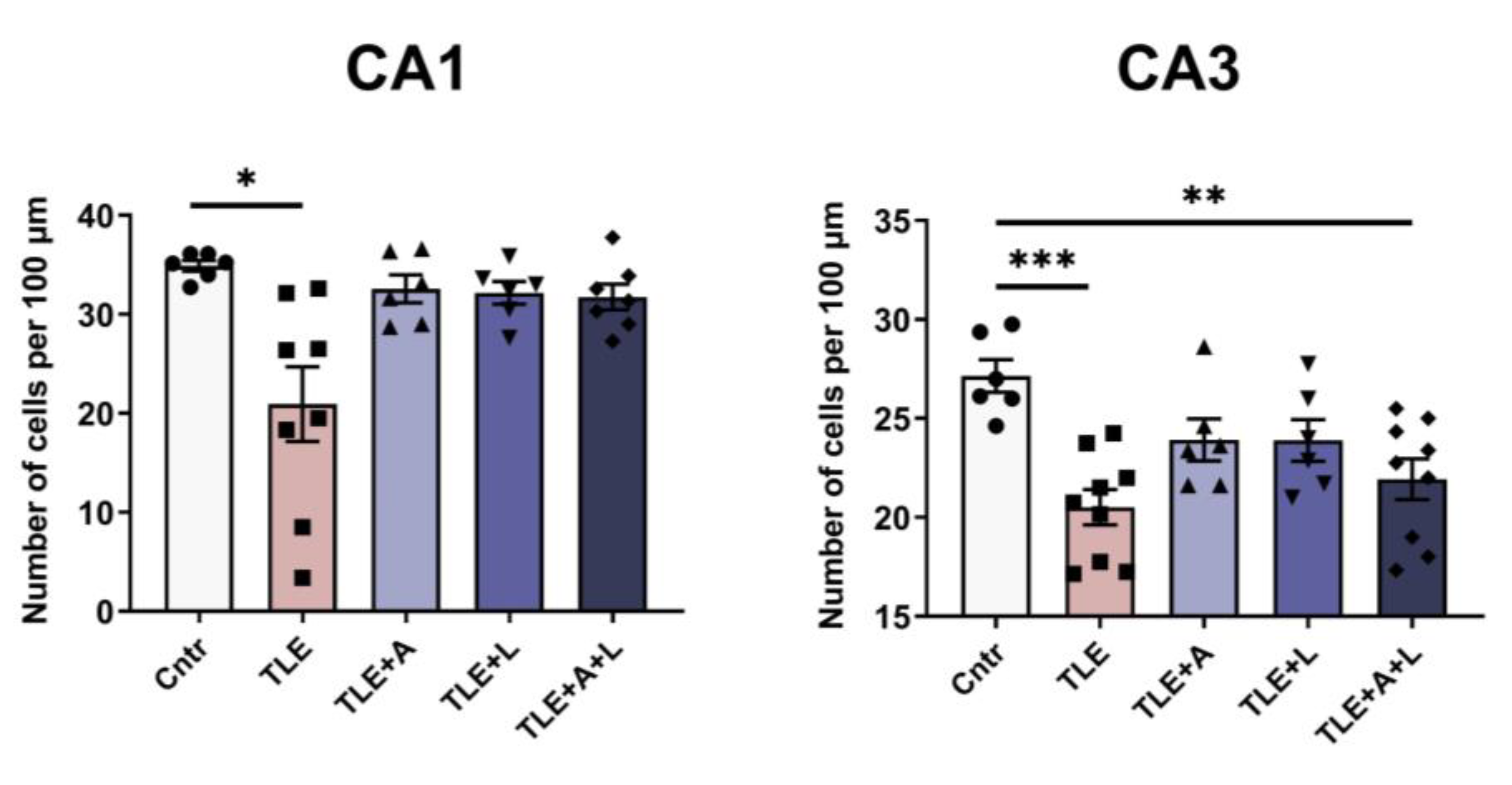
2.2. Anakinra, lamotrigine, or their combination can prevent neuronal death in the hippocampus following pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus.
2.3. Behavioral disturbances may be improved with anakinra, lamotrigine, or their combination.
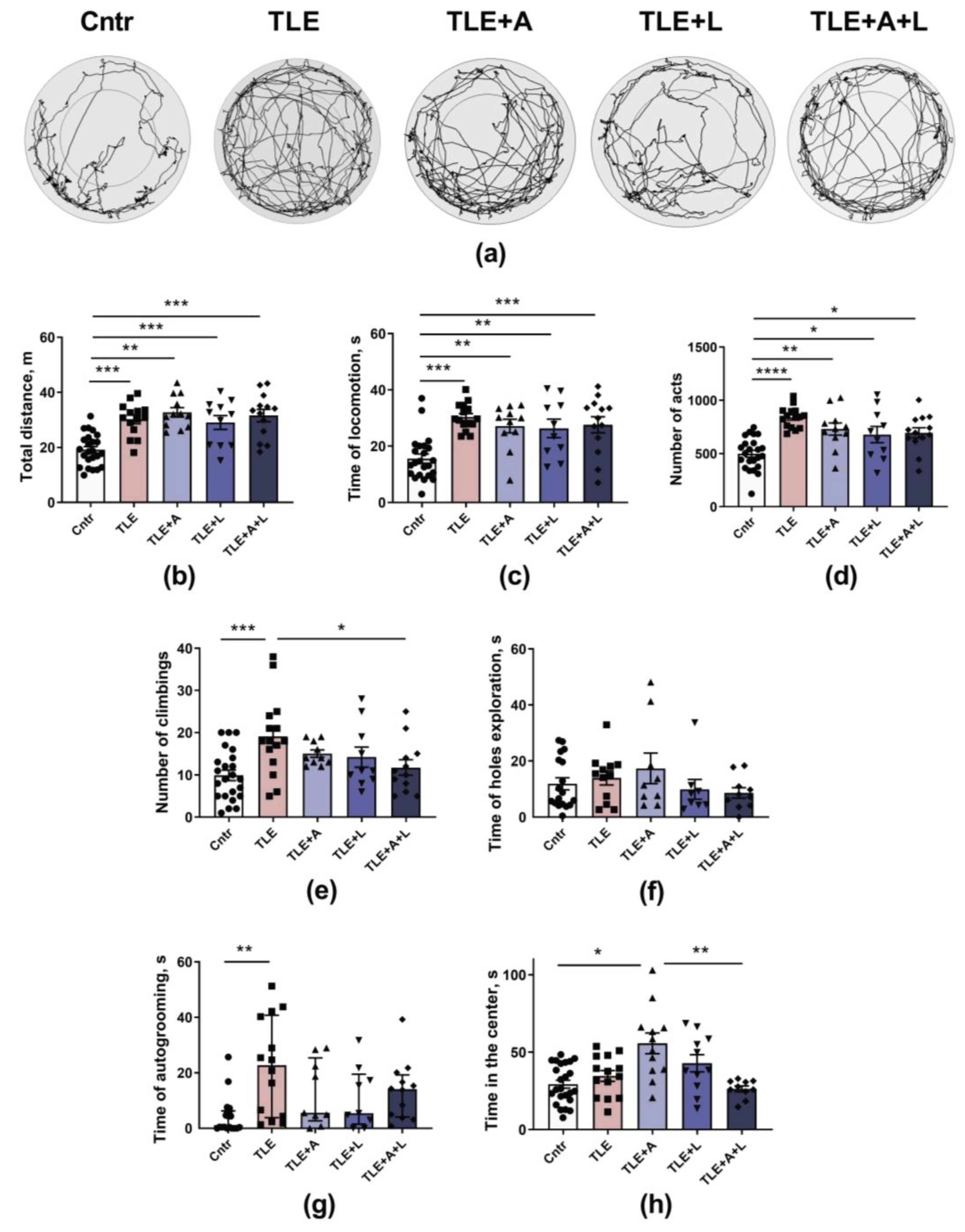
2.3.1. Treatment effects on activity levels, exploratory behavior, and anxiety in experimental and control animals in the Open field test.
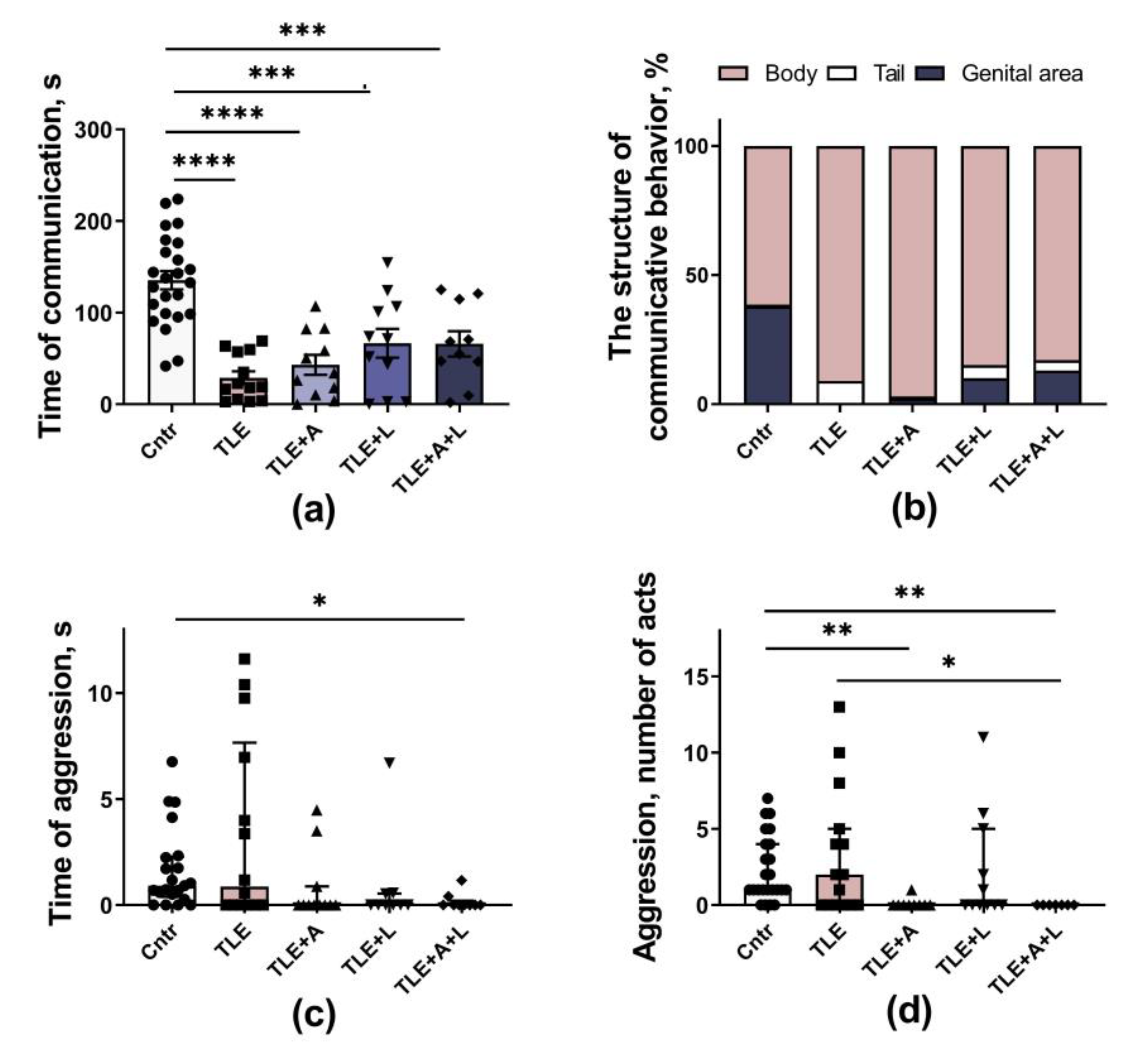
2.3.2. Social behavior
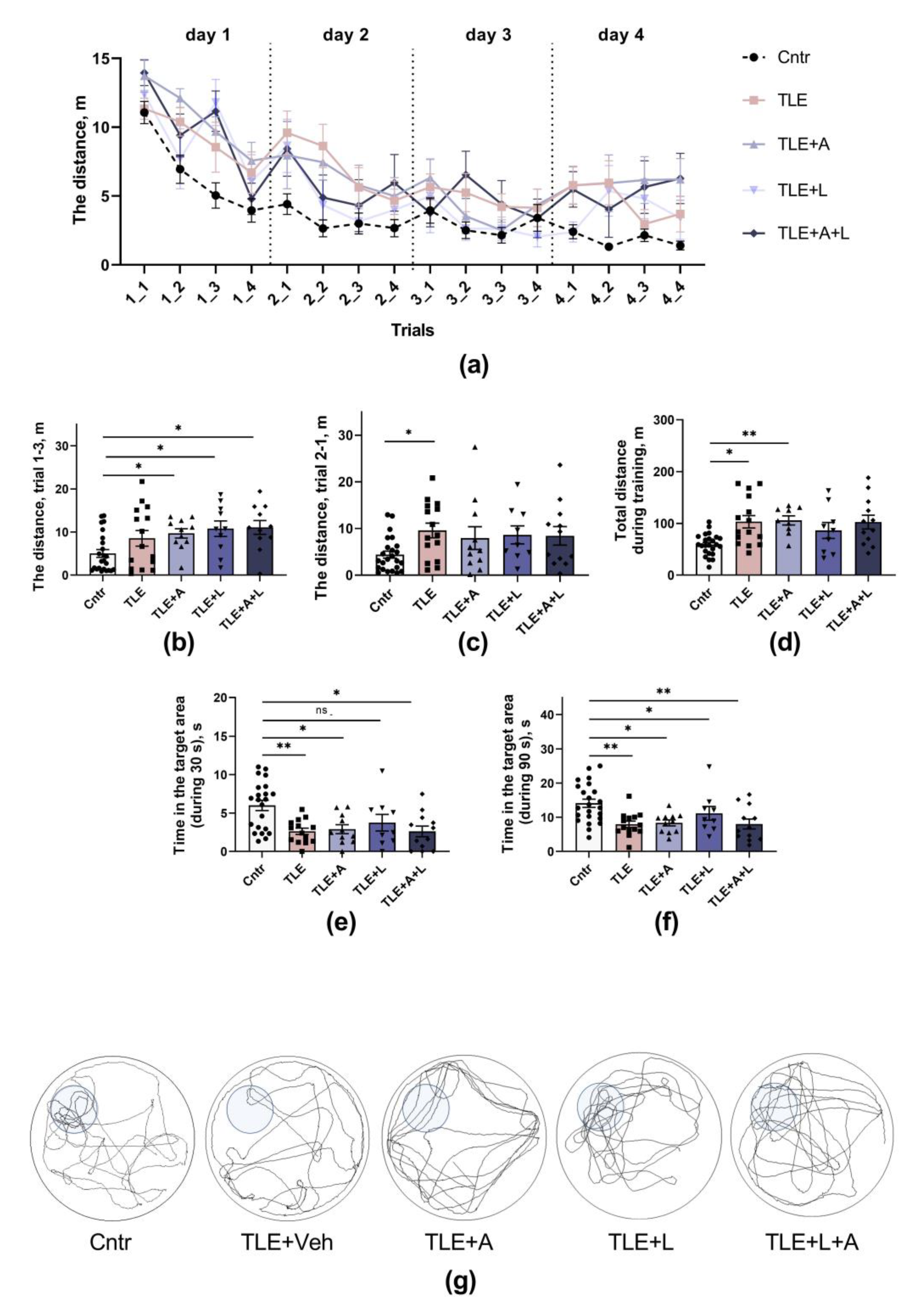
2.3.3. The memory impairments
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
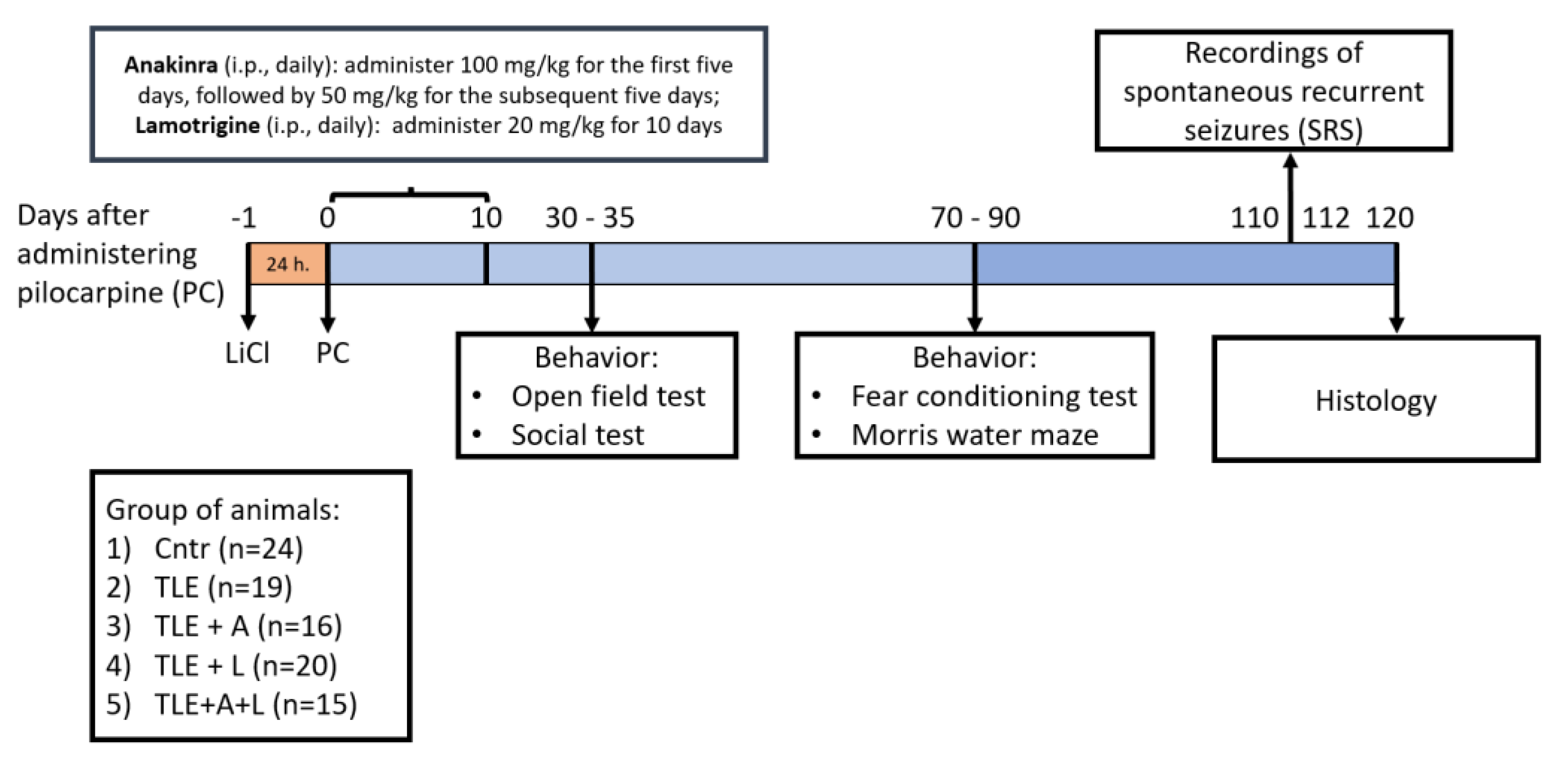
4.1. Animals
4.2. The lithium-pilocarpine model and treatment
4.3. Survival rate and Body Weight
4.4. Spontaneous Recurrent Seizures (SRS)
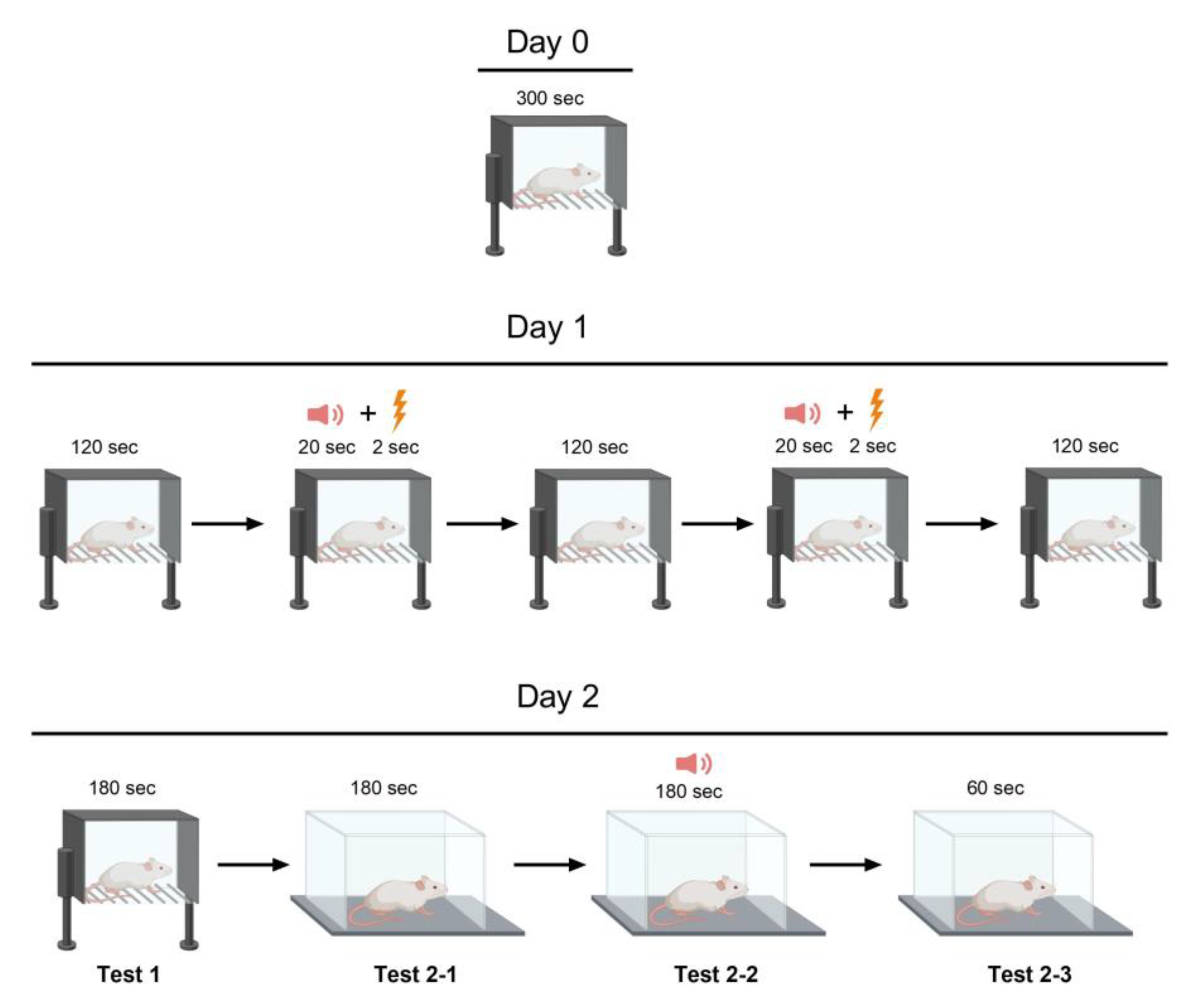
4.5. Behavioral Testing
4.5.1. Open field test
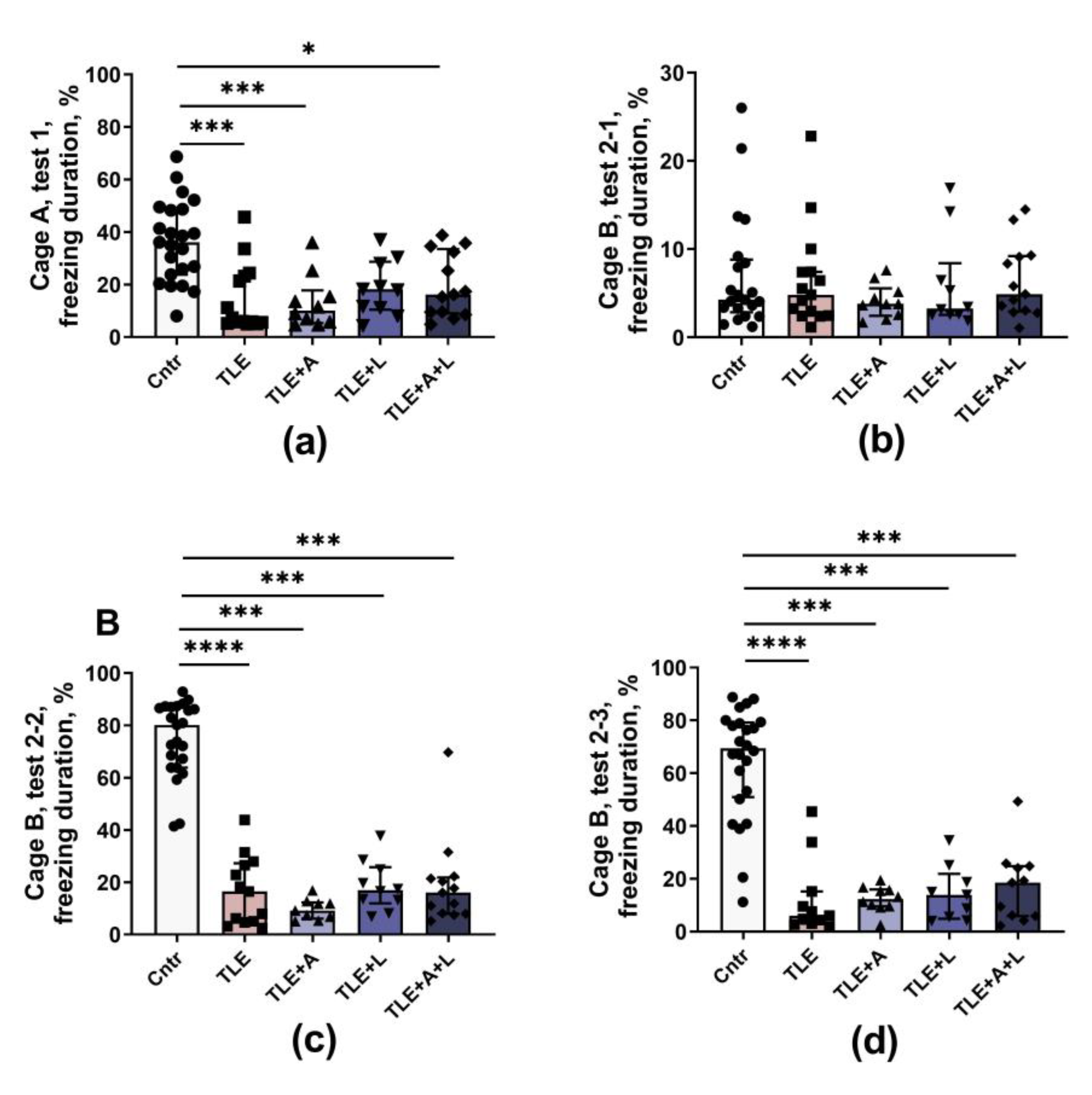
4.5.2. Fear conditioning test
4.5.3. Social interaction test
4.5.4. Morris water maze
4.6. Histology
4.7. Statistical analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A.
| The indicators | Untreated TLE rats (-3) vs treated with anakinra (TLE+A; +1); lamotrigine (TLE+L; +1) and combined treatment (TLE+A+L; +1) | Untreated TLE rats (-2) vs treated with anakinra (TLE+A; +1) and combined treatment (TLE+A+L; +1) | Untreated TLE rats (-2) vs treated with lamotrigine (TLE+L; +1) and combined treatment (TLE+A+L; +1) | Monotherapy with anakinra (-1) and lamotrigine (-1) vs combined therapy (TLE+A+L; +2) |
| Histological studies | ||||
| Neuronal death in CA1 hippocampal regions | t = 2.93; t = 0.02 | t = 2.89; p = 0.02 | t = 2.85; p = 0.022 | t = 0.4; p = 0.70 |
| Neuronal death in CA3 hippocampal regions | t = 2.50; p = 0.022 | t = 2.08; p>0.05 | t = 1.56; p >0.05 | t = 1.56; p = 0.14 |
| The Open Field test | ||||
| Time of locomotion | t = 1.30; p = 0.20 | t = 1.10; p = 0.28 | t = 1.24; p = 0.22 | t = 0.30; p = 0.76 |
| Number of climbing | t = 2.55; p = 0.013 | t = 2.50; p = 0.015 | t = 2.68; p = 0.009 | t = 1.15; p = 0.25 |
| Number of acts | t = 2.66; p = 0.01 | t = 2.31; p = 0.02 | t = 2.74; p = 0.98 | t = 1.15; p = 0.88 |
| Time in the center | t = 1.40; p = 0.17 | t = 1.20; p = 0.24 | t = 0.24; p = 0.01 | t = 3.86; p = 0.001 |
| Social test | ||||
| Time of communication | t = 0.67; p = 0.50 | t = 0.37; p = 0.71 | t = 1.09; p = 0.28 | t = 0.60; p = 0.55 |
| Morris water maze | ||||
| Total distance during training | t = 0.25; p = 0.80 | t = 0.22; p = 0.83 | t = 0,56; p = 0.58 | t = 0.26; p = 0.80 |
| Time in the target area (during 90 s) | t = 0.085; p = 0.93 | t = 0.17; p = 0.87 | t = 0,19; p = 0.87 | t = 0.19; p = 0.85 |
| Time in the target area (during 30 s) | t = 0.33; p = 0.74 | t = 0.18; p = 0.86 | t = 0,39; p = 0.70 | t = 0.78; p = 0.45 |
References
- Thijs, R.D.; Surges, R.; O’Brien, T.J.; Sander, J.W. Epilepsy in Adults. The Lancet 2019, 393, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, K.A.; Lopez Ramos, C.; Buch, V.P.; Mekary, R.A.; Amundson, J.R.; Shah, M.; Rattani, A.; Dewan, M.C.; Park, K.B. An Estimation of Global Volume of Surgically Treatable Epilepsy Based on a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Epilepsy. J Neurosurg 2019, 130, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Liu, Y.; Yu, X.; Wu, J.; Poon, A.N.; Demaio, A.; Wang, W.; Rudan, I.; Chan, K.Y. Prevalence of Epilepsy in China between 1990 and 2015: A Systematic Review and Meta–Analysis. J Glob Health 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querol Pascual, M.R. Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: Clinical Semiology and Neurophysiological Studies. Seminars in Ultrasound, CT and MRI 2007, 28, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, J.O. Cellular and Molecular Basis of Epilepsy. Journal of Neuroscience 1994, 14, 3413–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Téllez-Zenteno, J.F.; Hernández-Ronquillo, L. A Review of the Epidemiology of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Epilepsy Res Treat 2012, 2012, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, M.P.H.; Aldenkamp, A.P.; van der Vlugt, H.; Alpherts, W.C.J.; Vermeulen, J. Memory Complaints in Medically Refractory Epilepsy: Relationship to Epilepsy-Related Factors. Epilepsy & Behavior 2002, 3, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramoni-Negre, E.; Lambert, I.; Bartolomei, F.; Felician, O. Long-Term Memory Deficits in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2017, 173, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinkels, W.A.M.; Kuyk, J.; Dyck, R. van; Spinhoven, Ph. Psychiatric Comorbidity in Epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior 2005, 7, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonora, A.; Benuzzi, F.; Monti, G.; Mirandola, L.; Pugnaghi, M.; Nichelli, P.; Meletti, S. Recognition of Emotions from Faces and Voices in Medial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior 2011, 20, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovagnoli, A.R.; Franceschetti, S.; Reati, F.; Parente, A.; Maccagnano, C.; Villani, F.; Spreafico, R. Theory of Mind in Frontal and Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: Cognitive and Neural Aspects. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 1995–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxer, K.D.; Trinka, E.; Hirsch, L.J.; Cendes, F.; Langfitt, J.; Delanty, N.; Resnick, T.; Benbadis, S.R. The Consequences of Refractory Epilepsy and Its Treatment. Epilepsy & Behavior 2014, 37, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.; Schachter, S.C. Drug Treatment of Epilepsy in Adults. BMJ (Online) 2014, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löscher, W.; Schmidt, D. Modern Antiepileptic Drug Development Has Failed to Deliver: Ways out of the Current Dilemma. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 657–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walia, K.S.; Khan, E.A.; Ko, D.H.; Raza, S.S.; Khan, Y.N. Side Effects of Antiepileptics- A Review. Pain Practice 2004, 4, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mula, M.; Kanner, A.M.; Schmitz, B.; Schachter, S. Antiepileptic Drugs and Suicidality: An Expert Consensus Statement from the Task Force on Therapeutic Strategies of the ILAE Commission on Neuropsychobiology. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, D. Is Antiepileptogenesis a Realistic Goal in Clinical Trials? Concerns and New Horizons. Epileptic Disorders 2012, 14, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galanopoulou, A.S.; Buckmaster, P.S.; Staley, K.J.; Moshé, S.L.; Perucca, E.; Engel Jr., J.; Löscher, W.; Noebels, J.L.; Pitkänen, A.; Stables, J.; et al. Identification of New Epilepsy Treatments: Issues in Preclinical Methodology. Epilepsia 2012, 53, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Musto, A.E. The Role of Inflammation in the Development of Epilepsy. J Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzani, A.; French, J.; Bartfai, T.; Baram, T.Z. The Role of Inflammation in Epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol 2011, 7, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Takemiya, T.; Sugiura, H.; Yamagata, K. Role of Inflammatory Mediators in the Pathogenesis of Epilepsy. Mediators Inflamm 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vezzani, A.; Ravizza, T.; Bedner, P.; Aronica, E.; Steinhäuser, C.; Boison, D. Astrocytes in the Initiation and Progression of Epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol 2022, 18, 707–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyomina, A.V.; Zubareva, O.E.; Smolensky, I.V.; Vasilev, D.S.; Zakharova, M.V.; Kovalenko, A.A.; Schwarz, A.P.; Ischenko, A.M.; Zaitsev, A.V. Anakinra Reduces Epileptogenesis, Provides Neuroprotection, and Attenuates Behavioral Impairments in Rats in the Lithium–Pilocarpine Model of Epilepsy. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilena, R.; Mauri, E.; Aronica, E.; Bernasconi, P.; Bana, C.; Cappelletti, C.; Carrabba, G.; Ferrero, S.; Giorda, R.; Guez, S.; et al. Therapeutic Effect of Anakinra in the Relapsing Chronic Phase of Febrile Infection–Related Epilepsy Syndrome. Epilepsia Open 2019, 4, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taraschenko, O.; Fox, H.S.; Zekeridou, A.; Pittock, S.J.; Eldridge, E.; Farukhuddin, F.; Al-Saleem, F.; Devi Kattala, C.; Dessain, S.K.; Casale, G.; et al. Seizures and Memory Impairment Induced by Patient-Derived Anti-N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Antibodies in Mice Are Attenuated by Anakinra, an Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.; Vale, N. Understanding Lamotrigine’s Role in the CNS and Possible Future Evolution. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; He, X.; Sun, Q.; Fang, Z.; Zhou, L. Effect of Lamotrigine on Seizure Development in a Rat Pentylenetetrazole Kindling Model. Brain Behav 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratton, S.C.; Large, C.H.; Cox, B.; Davies, G.; Hagan, R.M. Effects of Lamotrigine and Levetiracetam on Seizure Development in a Rat Amygdala Kindling Model. Epilepsy Res 2003, 53, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissinen, J.; Large, C.H.; Stratton, S.C.; Pitkänen, A. Effect of Lamotrigine Treatment on Epileptogenesis: An Experimental Study in Rat. Epilepsy Res 2004, 58, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; van Luijtelaar, G.; Sun, M. The Effects of Lamotrigine and Ethosuximide on Seizure Frequency, Neuronal Loss, and Astrogliosis in a Model of Temporal-Lobe Epilepsy. Brain Res 2019, 1712, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubareva, O.E.; Dyomina, A.V.; Kovalenko, A.A.; Roginskaya, A.I.; Melik-Kasumov, T.B.; Korneeva, M.A.; Chuprina, A.V.; Zhabinskaya, A.A.; Kolyhan, S.A.; Zakharova, M.V.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Probiotic Bifidobacterium Longum in a Lithium–Pilocarpine Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy in Rats. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabel, H.; Guinet, V.; Voltzenlogel, V.; Pradier, S.; Hennion, S. Social Cognition in Epilepsy: State of the Art and Perspectives. Rev Neurol (Paris) 2020, 176, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolensky, I.V.; Zubareva, O.E.; Kalemenev, S.V.; Lavrentyeva, V.V.; Dyomina, A.V.; Karepanov, A.A.; Zaitsev, A.V. Impairments in Cognitive Functions and Emotional and Social Behaviors in a Rat Lithium-Pilocarpine Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Behavioural Brain Research 2019, 372, 112044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalheiro, E.A. The Pilocarpine Model of Epilepsy. The Italian Journal of Neurological Sciences 1995, 16, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löscher, W.; Potschka, H. Role of Multidrug Transporters in Pharmacoresistance to Antiepileptic Drugs. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2002, 301, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löscher, W. Critical Review of Current Animal Models of Seizures and Epilepsy Used in the Discovery and Development of New Antiepileptic Drugs. Seizure 2011, 20, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, K.; Fahnestock, M.; Racine, R.J. Kindling and Status Epilepticus Models of Epilepsy: Rewiring the Brain. Prog Neurobiol 2004, 73, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, D.S.; Bhimani, A.; Kuruba, R.; Park, M.J.; Sohrabji, F. Prospects of Modeling Poststroke Epileptogenesis. J Neurosci Res 2017, 95, 1000–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitkänen, A.; Lukasiuk, K.; Dudek, F.E.; Staley, K.J. Epileptogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2015, 5, a022822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufthy, Y.; Bharadwaj, M.; Gupta, S.; Hussain, D.; Joseph, P.J.S.; Khan, A.; King, J.; Lahorgue, P.; Jayawardena, O.; Rostami-Hochaghan, D.; et al. Statins as Antiepileptogenic Drugs: Analyzing the Evidence and Identifying the Most Promising Statin. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sills, G.J.; Rogawski, M.A. Mechanisms of Action of Currently Used Antiseizure Drugs. Neuropharmacology 2020, 168, 107966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.-C.; Lu, L. Characterization of Lamotrigine Inhibition of Na + Channels in Rat Hippocampal Neurones. Br J Pharmacol 1997, 121, 1231–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-J.; Huang, C.-C.; Hsu, K.-S.; Tsai, J.-J.; Gean, P.-W. Inhibition of N-Type Calcium Currents by Lamotrigine in Rat Amygdalar Neurones. Neuroreport 1996, 7, 3037–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefani, A.; Spadoni, F.; Siniscalchi, A.; Bernardi, G. Lamotrigine Inhibits Ca2+ Currents in Cortical Neurons: Functional Implications. Eur J Pharmacol 1996, 307, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacher, A.; Zornow, M.H. Lamotrigine Inhibits Extracellular Glutamate Accumulation during Transient Global Cerebral Ischemia in Rabbits. Anesthesiology 1997, 86, 459–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, N.B.; Jiang, X.-P.; Heinkel, C.; Nemmers, B. Antiepileptic Drugs and Agents That Inhibit Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels Prevent NMDA Antagonist Neurotoxicity. Mol Psychiatry 2002, 7, 726–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakhin, D.V.; Malkin, S.L.; Ergina, J.L.; Kryukov, K.A.; Veniaminova, E.A.; Zubareva, O.E.; Zaitsev, A.V. Alterations in Properties of Glutamatergic Transmission in the Temporal Cortex and Hippocampus Following Pilocarpine-Induced Acute Seizures in Wistar Rats. Front Cell Neurosci 2017, 11, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diespirov, G.P.; Postnikova, T.Y.; Griflyuk, A.V.; Kovalenko, A.A.; Zaitsev, A.V. Alterations in the Properties of the Rat Hippocampus Glutamatergic System in the Lithium-Pilocarpine Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2023, 88, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, W.; Ma, C.; He, N. Comparison and Effects of Acute Lamotrigine Treatment on Extracellular Excitatory Amino Acids in the Hippocampus of PTZ-Kindled Epileptic and PTZ-Induced Status Epilepticus Rats. Neurochem Res 2013, 38, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, E. Lamotrigine: A Depression Mood Stabiliser. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 14, S89–S93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-rish, E.Y.; Dahabiyeh, L.A.; Bustanji, Y.; Mohamed, Y.S.; Browning, M.J. Effect of Lamotrigine on in Vivo and in Vitro Cytokine Secretion in Murine Model of Inflammation. J Neuroimmunol 2018, 322, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Muscal, E.; Wells, E.; Shukla, N.; Eschbach, K.; Hyeong Lee, K.; Kaliakatsos, M.; Desai, N.; Wickström, R.; Viri, M.; et al. Anakinra Usage in Febrile Infection Related Epilepsy Syndrome: An International Cohort. Ann Clin Transl Neurol 2020, 7, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Zheng, F.; Wang, X. Exploring Novel AEDs from Drugs Used for Treatment of Non-Epileptic Disorders. Expert Rev Neurother 2016, 16, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roginskaya, A.I.; Dyomina, A.V.; Kovalenko, A.A.; Zakharova, M.V.; Schwarz, A.P.; Melik-Kasumov, T.B.; Zubareva, O.E. Effect of Anakinra on the Gene Expression of Receptors Activated by the Peroxisome Proliferator in the Rat Brain in the Lithium Pilocarpine Model of Epilepsy. J Evol Biochem Physiol 2022, 58, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, B.; Chaves, J.; Carvalho, C.; Rangel, R.; Santos, A.; Bettencourt, A.; Lopes, J.; Ramalheira, J.; Silva, B.M.; da Silva, A.M.; et al. Brain Expression of Inflammatory Mediators in Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Patients. J Neuroimmunol 2017, 313, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litovchenko, A.V.; Zabrodskaya, Yu.M.; Sitovskaya, D.A.; Khuzhakhmetova, L.K.; Nezdorovina, V.G.; Bazhanova, E.D. Markers of Neuroinflammation and Apoptosis in the Temporal Lobe of Patients with Drug-Resistant Epilepsy. J Evol Biochem Physiol 2021, 57, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devinsky, O.; Vezzani, A.; Najjar, S.; De Lanerolle, N.C.; Rogawski, M.A. Glia and Epilepsy: Excitability and Inflammation. Trends Neurosci 2013, 36, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viviani, B.; Bartesaghi, S.; Gardoni, F.; Vezzani, A.; Behrens, M.M.; Bartfai, T.; Binaglia, M.; Corsini, E.; Di Luca, M.; Galli, C.L.; et al. Interleukin-1β Enhances NMDA Receptor-Mediated Intracellular Calcium Increase through Activation of the Src Family of Kinases. Journal of Neuroscience 2003, 23, 8692–8700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoltsev, I.G.; Frankevich, S.O.; Shirobokova, N.I.; Volkova, A.A.; Onufriev, M.V.; Moiseeva, J.V.; Novikova, M.R.; Gulyaeva, N.V. Neuroinflammation and Neuronal Loss in the Hippocampus Are Associated with Immediate Posttraumatic Seizures and Corticosterone Elevation in Rats. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Sheng, W.S.; Ehrlich, L.C.; Peterson, P.K.; Chao, C.C. Cytokine Effects on Glutamate Uptake by Human Astrocytes. Neuroimmunomodulation 2000, 7, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, A.V.; Smolensky, I.V.; Jorratt, P.; Ovsepian, S.V. Neurobiology, Functions, and Relevance of Excitatory Amino Acid Transporters (EAATs) to Treatment of Refractory Epilepsy. CNS Drugs 2020, 34, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazarati, A.M.; Pineda, E.; Shin, D.; Tio, D.; Taylor, A.N.; Sankar, R. Comorbidity between Epilepsy and Depression: Role of Hippocampal Interleukin-1β. Neurobiol Dis 2010, 37, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suleymanova, E.M. Behavioral Comorbidities of Epilepsy and Neuroinflammation: Evidence from Experimental and Clinical Studies. Epilepsy & Behavior 2021, 117, 107869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noe, F.M.; Polascheck, N.; Frigerio, F.; Bankstahl, M.; Ravizza, T.; Marchini, S.; Beltrame, L.; Banderó, C.R.; Löscher, W.; Vezzani, A. Pharmacological Blockade of IL-1β/IL-1 Receptor Type 1 Axis during Epileptogenesis Provides Neuroprotection in Two Rat Models of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 2013, 59, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingledine, R.; Varvel, N.H.; Dudek, F.E. When and How Do Seizures Kill Neurons, and Is Cell Death Relevant to Epileptogenesis? In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; 2014; Vol. 813, pp. 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyomina, A. V.; Kovalenko, A.A.; Zakharova, M. V.; Postnikova, T.Y.; Griflyuk, A. V.; Smolensky, I. V.; Antonova, I. V.; Zaitsev, A. V MTEP, a Selective MGluR5 Antagonist, Had a Neuroprotective Effect but Did Not Prevent the Development of Spontaneous Recurrent Seizures and Behavioral Comorbidities in the Rat Lithium–Pilocarpine Model of Epilepsy. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesley, S.; Sullenberger, T.; Crotty, K.; Ailani, R.; D’Orio, C.; Evans, K.; Ogunkunle, E.O.; Roper, M.G.; Kumar, S.S. D-Serine Mitigates Cell Loss Associated with Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citraro, R.; Iannone, M.; Leo, A.; De Caro, C.; Nesci, V.; Tallarico, M.; Abdalla, K.; Palma, E.; Arturi, F.; De Sarro, G.; et al. Evaluation of the Effects of Liraglutide on the Development of Epilepsy and Behavioural Alterations in Two Animal Models of Epileptogenesis. Brain Res Bull 2019, 153, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitiris, N.; Mohanraj, R.; Norrie, J.; Sills, G.J.; Brodie, M.J. Predictors of Pharmacoresistant Epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 2007, 75, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastens, A.M.; Brandt, C.; Bankstahl, J.P.; Löscher, W. Predictors of Pharmacoresistant Epilepsy: Pharmacoresistant Rats Differ from Pharmacoresponsive Rats in Behavioral and Cognitive Abnormalities Associated with Experimentally Induced Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2008, 49, 1759–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzezak, P.; Lima, E.M.; Gargaro, A.C.; Coimbra, E.; de Vincentiis, S.; Velasco, T.R.; Leite, J.P.; Busatto, G.F.; Valente, K.D. Everyday Memory Impairment in Patients with Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Caused by Hippocampal Sclerosis. Epilepsy & Behavior 2017, 69, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, E.; Catroppa, C.; Gonzalez, L.; Gill, D.; Webster, R.; Lawson, J.; Sabaz, M.; Mandalis, A.; Barton, B.; McLean, S.; et al. Theory of Mind and Social Competence in Children and Adolescents with Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neuropsychology 2019, 33, 986–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagrin, A.; Saiote, C.; Schiller, D. The Social Hippocampus. Hippocampus 2018, 28, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, J.C.M.; Moura, P.J.; Cysneiros, R.M.; Colugnati, D.B.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Scorza, F.A.; Xavier, G.F.; Zilbovicius, M.; Mercadante, M.T. Temporal Lobe Epilepsy and Social Behavior: An Animal Model for Autism? Epilepsy & Behavior 2008, 13, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Han, C.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Meng, F.; Zhang, J. Abnormal Hippocampal Functional Network and Related Memory Impairment in Pilocarpine-treated Rats. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 1785–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.; Jung, S.; Lee, S.-Y.; Yang, H.; Kim, B.S.; Choi, J.; Bang, M.; Shin, H.-S.; Jeon, D. Early Deficits in Social Behavior and Cortical Rhythms in Pilocarpine-Induced Mouse Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Exp Neurol 2013, 241, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Kustra, R.P.; Vuong, A.; Hammer, A.E.; Messenheimer, J.A. Depressive Symptoms in Epilepsy. Drugs 2008, 68, 1493–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Fukatsu, N.; Noguchi, T.; Oshima, T.; Tadokoro, Y.; Kanemoto, K. Lamotrigine Improves Aggression in Patients with Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Epilepsy & Behavior 2011, 21, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahfoz, A.M.; Abdel-Wahab, A.F.; Afify, M.A.; Shahzad, N.; Ibrahim, I.A.A.; ElSawy, N.A.; Bamagous, G.A.; Al Ghamdi, S.S. Neuroprotective Effects of Vitamin D Alone or in Combination with Lamotrigine against Lithium-Pilocarpine Model of Status Epilepticus in Rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2017, 390, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, R.J. Modification of Seizure Activity by Electrical Stimulation. II. Motor Seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1972, 32, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postnikova, T.Y.; Diespirov, G.P.; Amakhin, D.V.; Vylekzhanina, E.N.; Soboleva, E.B.; Zaitsev, A.V. Impairments of Long-Term Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampus of Young Rats during the Latent Phase of the Lithium-Pilocarpine Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 13355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furr, R.M. A Contrast Analysis Approach to Change. Educational Research and Evaluation 2008, 14, 335–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konietschke, F.; Bösiger, S.; Brunner, E.; Hothorn, L.A. Are Multiple Contrast Tests Superior to the ANOVA? International Journal of Biostatistics 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





