Submitted:
21 June 2024
Posted:
24 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. In epileptic rats, there is a notable loss of pyramidal neurons in the CA1 region of the hippocampus, yet the membrane properties of the neurons remain largely unaltered
2.2. In epileptic rats, there is a change in the ratio of inputs from the entorhinal cortex and the CA3 region of the hippocampus to CA1 pyramidal neurons
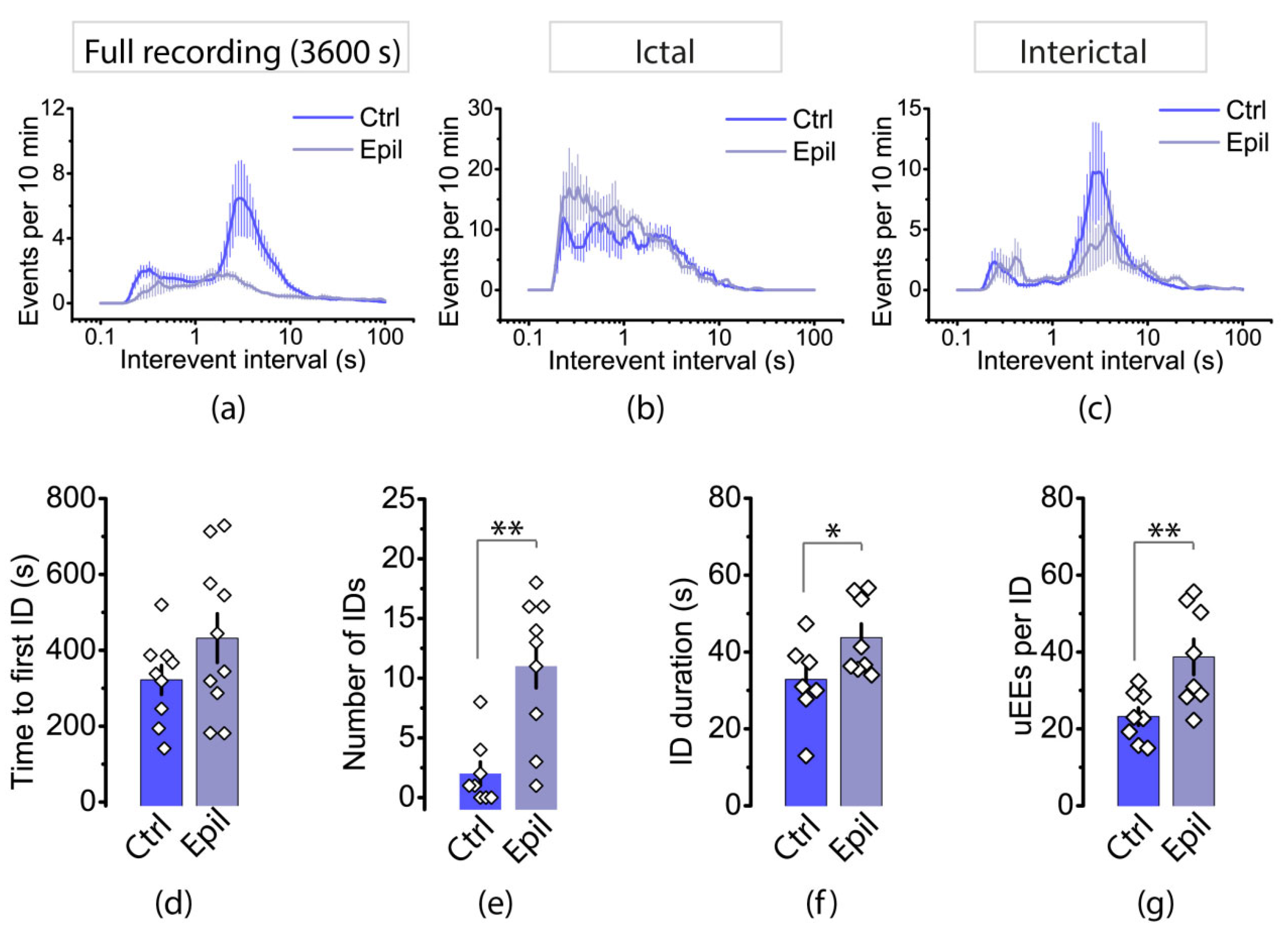
2.3. Epileptiform activity induced by 4-aminopyridine in hippocampus-entorhinal cortex slices differs between control and epileptic rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Lithium-pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy
4.3. Slice preparation and electrophysiological recordings
4.4. Induction of Epileptiform Activity Ex Vivo
4.5. Analysis of Epileptiform Activity
4.6. Histology
4.7. Statistical analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization Epilepsy Available online:. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy (accessed on 29 January 2024).
- Wong, R.K.; Traub, R.D.; Miles, R. Cellular Basis of Neuronal Synchrony in Epilepsy. Adv Neurol 1986, 44, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sills, G.J.; Rogawski, M.A. Mechanisms of Action of Currently Used Antiseizure Drugs. Neuropharmacology 2020, 168, 107966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloosterman, F.; van Haeften, T.; Lopes da Silva, F.H. Two Reentrant Pathways in the Hippocampal-entorhinal System. Hippocampus 2004, 14, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolls, E.T.; Kesner, R.P. A Computational Theory of Hippocampal Function, and Empirical Tests of the Theory. Prog Neurobiol 2006, 79, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thom, M. Review: Hippocampal Sclerosis in Epilepsy: A Neuropathology Review. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2014, 40, 520–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goubran, M.; Bernhardt, B.C.; Cantor-Rivera, D.; Lau, J.C.; Blinston, C.; Hammond, R.R.; de Ribaupierre, S.; Burneo, J.G.; Mirsattari, S.M.; Steven, D.A.; et al. In Vivo MRI Signatures of Hippocampal Subfield Pathology in Intractable Epilepsy. Hum Brain Mapp 2016, 37, 1103–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloviter, R.S. Hippocampal Epileptogenesis in Animal Models of Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy with Hippocampal Sclerosis: The Importance of the “Latent Period” and Other Concepts. Epilepsia 2008, 49, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, A.K. Entorhinal Axons Exhibit Sprouting in CA1 Subfield of the Adult Hippocampus in a Rat Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Hippocampus 2002, 12, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernhardt, B.C.; Fadaie, F.; Liu, M.; Caldairou, B.; Gu, S.; Jefferies, E.; Smallwood, J.; Bassett, D.S.; Bernasconi, A.; Bernasconi, N. Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: Hippocampal Pathology Modulates Connectome Topology and Controllability. Neurology 2019, 92, E2209–E2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, L.E.A.M.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Tan, A.M.; Kupfer, W.R.; Pretorius, J.K.; Babb, T.L.; Finch, D.M. Circuit Mechanisms of Seizures in the Pilocarpine Model of Chronic Epilepsy: Cell Loss and Mossy Fiber Sprouting. Epilepsia 1993, 34, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curia, G.; Lucchi, C.; Vinet, J.; Gualtieri, F.; Marinelli, C.; Torsello, A.; Costantino, L.; Biagini, G. Pathophysiogenesis of Mesial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy: Is Prevention of Damage Antiepileptogenic? Curr Med Chem 2014, 21, 663–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diespirov, G.P.; Postnikova, T.Y.; Griflyuk, A.V.; Kovalenko, A.A.; Zaitsev, A.V. Alterations in the Properties of the Rat Hippocampus Glutamatergic System in the Lithium-Pilocarpine Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2023, 88, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curia, G.; Longo, D.; Biagini, G.; Jones, R.S.G.; Avoli, M. The Pilocarpine Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. J Neurosci Methods 2008, 172, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bean, B.P. The Action Potential in Mammalian Central Neurons. Nat Rev Neurosci 2007, 8, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksoy-Aksel, A.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. The Temporoammonic Input to the Hippocampal CA1 Region Displays Distinctly Different Synaptic Plasticity Compared to the Schaffer Collateral Input in Vivo: Significance for Synaptic Information Processing. Front Synaptic Neurosci 2013, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, C.W.; Carlson, G.C.; Coulter, D.A. Massive and Specific Dysregulation of Direct Cortical Input to the Hippocampus in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Journal of Neuroscience 2006, 26, 11850–11856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafstrom, C.E.; Sutula, T.P. Models of Epilepsy in the Developing and Adult Brain: Implications for Neuroprotection. Epilepsy and Behavior 2005, 7, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukaino, T.; Uehara, T.; Yokohama, J.; Okadome, T.; Arakawa, T.; Yokoyama, S.; Sakata, A.; Takase, K.-I.; Togao, O.; Akamatsu, N.; et al. Atrophy of the Hippocampal CA1 Subfield Relates to Long-Term Forgetting in Focal Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2022, 63, 2623–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maccotta, L.; Moseley, E.D.; Benzinger, T.L.; Hogan, R.E. Beyond the CA1 Subfield: Local Hippocampal Shape Changes in MRI-Negative Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2015, 56, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrand, J.J.; Pouliot, W.; Scheerlinck, P.; Dudek, F.E. Lithium Pilocarpine-Induced Status Epilepticus in Postnatal Day 20 Rats Results in Greater Neuronal Injury in Ventral versus Dorsal Hippocampus. Neuroscience 2011, 192, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffarzadeh, F.; Eslamizade, M.J.; Mousavi, S.M.M.; Abraki, S.B.; Hadjighassem, M.R.; Gorji, A. TRPV1 Receptors Augment Basal Synaptic Transmission in CA1 and CA3 Pyramidal Neurons in Epilepsy. Neuroscience 2016, 314, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Qin, J.; Ni, G.; Li, Y.; Xie, H.; Yu, J.; Li, H.; Sui, L.; Guo, Q.; Fang, Z.; et al. Downregulation of Hyperpolarization-Activated Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated Channels (HCN) in the Hippocampus of Patients with Medial Temporal Lobe Epilepsy and Hippocampal Sclerosis (MTLE-HS). Hippocampus 2020, 30, 1112–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, E.C.; McMurray, C.; Gray, R.; Johnston, D. Epilepsy-Induced Reduction in HCN Channel Expression Contributes to an Increased Excitability in Dorsal, but Not Ventral, Hippocampal CA1 Neurons. eNeuro 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.; Jones, T.D.; Lugo, J.N., Jr.; Sheerin, A.H.; Miller, J.W.; D’Ambrosio, R.; Anderson, A.E.; Poolos, N.P. Progressive Dendritic HCN Channelopathy during Epileptogenesis in the Rat Pilocarpine Model of Epilepsy. Journal of Neuroscience 2007, 27, 13012–13021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, R.; Kirschstein, T.; Brehme, H.; Porath, K.; Mikkat, U.; Köhling, R. Network Excitability in a Model of Chronic Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Critically Depends on SK Channel-Mediated AHP Currents. Neurobiol Dis 2012, 45, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, X.; Werkman, T.R.; Gorter, J.A.; Wadman, W.J.; Van Vliet, E.A. Expression of Sodium Channel α Subunits 1.1, 1.2 and 1.6 in Rat Hippocampus after Kainic Acid-Induced Epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 2013, 106, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Su, H.; Yue, C.; Remy, S.; Royeck, M.; Sochivko, D.; Opitz, T.; Beck, H.; Yaari, Y. An Increase in Persistent Sodium Current Contributes to Intrinsic Neuronal Bursting after Status Epilepticus. J Neurophysiol 2011, 105, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketelaars, S.O.M.; Gorter, J.A.; Van Vliet, E.A.; Lopes da Silva, F.H.; Wadman, W.J. Sodium Currents in Isolated Rat CA1 Pyramidal and Dentate Granule Neurones in the Post-Status Epilepticus Model of Epilepsy. Neuroscience 2001, 105, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, M.M.; Menegola, M.; Vacher, H.; Rhodes, K.J.; Trimmer, J.S. Altered Expression and Localization of Hippocampal A-Type Potassium Channel Subunits in the Pilocarpine-Induced Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neuroscience 2008, 156, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, D.B.; Brenner, R. A Computational Model for How the Fast Afterhyperpolarization Paradoxically Increases Gain in Regularly Firing Neurons. J Neurophysiol 2018, 119, 1506–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, C.; Melman, T.; Barth, A.L.; Ermentrout, G.B. Phase-Resetting Curve Determines How BK Currents Affect Neuronal Firing. J Comput Neurosci 2011, 30, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swann, J.W.; Al-Noori, S.; Jiang, M.; Lee, C.L. Spine Loss and Other Dendritic Abnormalities in Epilepsy. Hippocampus 2000, 10, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaram, S.B.; Rathipriya, A.G.; Bolla, S.R.; Bhat, A.; Ray, B.; Mahalakshmi, A.M.; Manivasagam, T.; Thenmozhi, A.J.; Essa, M.M.; Guillemin, G.J.; et al. Dendritic Spines: Revisiting the Physiological Role. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2019, 92, 161–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampuero, E.; Dagnino-Subiabre, A.; Sandoval, R.; Zepeda-Carreño, R.; Sandoval, S.; Viedma, A.; Aboitiz, F.; Orrego, F.; Wyneken, U. Status Epilepticus Induces Region-Specific Changes in Dendritic Spines, Dendritic Length and TrkB Protein Content of Rat Brain Cortex. Brain Res 2007, 1150, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Burgos, I.; López-Vázquez, M.A.; Beas-Zárate, C. Density, but Not Shape, of Hippocampal Dendritic Spines Varies after a Seizure-Inducing Acute Dose of Monosodium Glutamate in Rats. Neurosci Lett 2004, 363, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isokawa, M. Remodeling Dendritic Spines in the Rat Pilocarpine Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Neurosci Lett 1998, 258, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmore, L.J.; Ballinger, W.E., Jr.; Boggs, W.; Sypert, G.W.; Rubin, J.J. Dendritic Alterations in Rat Isocortex within an Iron-Induced Chronic Epileptic Focus. Neurosurgery 1980, 7, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Lee, C.L.; Smith, K.L.; Swann, J.W. Spine Loss and Other Persistent Alterations of Hippocampal Pyramidal Cell Dendrites in a Model of Early-Onset Epilepsy. Journal of Neuroscience 1998, 18, 8356–8368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossini, L.; de Santis, D.; Mauceri, R.R.; Tesoriero, C.; Bentivoglio, M.; Maderna, E.; Maiorana, A.; Deleo, F.; de Curtis, M.; Tringali, G.; et al. Dendritic Pathology, Spine Loss and Synaptic Reorganization in Human Cortex from Epilepsy Patients. Brain 2021, 144, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, L.; De Santis, D.; Cecchini, E.; Cagnoli, C.; Maderna, E.; Cartelli, D.; Morgan, B.P.; Torvell, M.; Spreafico, R.; di Giacomo, R.; et al. Dendritic Spine Loss in Epileptogenic Type II Focal Cortical Dysplasia: Role of Enhanced Classical Complement Pathway Activation. Brain Pathology 2023, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.N.; Dudek, F.E. Network Interactions Mediated by New Excitatory Connections between CA1 Pyramidal Cells in Rats with Kainate-Induced Epilepsy. J Neurophysiol 2002, 87, 1655–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isokawa, M. Remodeling Dendritic Spines of Dentate Granule Cells in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Patients and the Rat Pilocarpine Model. Epilepsia 2000, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, J.; Ledri, M.; Andersson, M.; Kokaia, M. Cell-Specific Switch for Epileptiform Activity: Critical Role of Interneurons in the Mouse Subicular Network. Cerebral Cortex 2023, 33, 6171–6183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, D.; Canal-Alonso, Á.; Panuccio, G. Mimicking CA3 Temporal Dynamics Controls Limbic Ictogenesis. Biology (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avoli, M.; Jefferys, J.G.R. Models of Drug-Induced Epileptiform Synchronization in Vitro. J Neurosci Methods 2016, 260, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhala, V.I.; Staley, K.J. Transition from Interictal to Ictal Activity in Limbic Networks in Vitro. Journal of Neuroscience 2003, 23, 7873–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avoli, M. Epileptiform Discharges and a Synchronous GABAergic Potential Induced by 4-Aminopyridine in the Rat Immature Hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 1990, 117, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ives, A.E.; Jefferys, J.G.R. Synchronization of Epileptiform Bursts Induced by 4-Aminopyridine in the in Vitro Hippocampal Slice Preparation. Neurosci Lett 1990, 112, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uva, L.; Librizzi, L.; Wendling, F.; De Curtis, M. Propagation Dynamics of Epileptiform Activity Acutely Induced by Bicuculline in the Hippocampal–Parahippocampal Region of the Isolated Guinea Pig Brain. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 1914–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhr, G.; Heinemann, U. Effects of NMDA Antagonists on Picrotoxin-, Low Mg2+- and Low Ca2+-Induced Epileptogenesis and on Evoked Changes in Extracellular Na+ and Ca2+ Concentrations in Rat Hippocampal Slices. Epilepsy Res 1989, 4, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landucci, E.; Mazzantini, C.; Lana, D.; Calvani, M.; Magni, G.; Giovannini, M.G.; Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.E. Cannabidiol Inhibits Microglia Activation and Mitigates Neuronal Damage Induced by Kainate in an In-Vitro Seizure Model. Neurobiol Dis 2022, 174, 105895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mody, I.; Lambert, J.D.; Heinemann, U. Low Extracellular Magnesium Induces Epileptiform Activity and Spreading Depression in Rat Hippocampal Slices. J Neurophysiol 1987, 57, 869–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirsa, V.K.; Stacey, W.C.; Quilichini, P.P.; Ivanov, A.I.; Bernard, C. On the Nature of Seizure Dynamics. Brain 2014, 137, 2210–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avoli, M.; D’Antuono, M.; Louvel, J.; Köhling, R.; Biagini, G.; Pumain, R.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Tancredi, V. Network and Pharmacological Mechanisms Leading to Epileptiform Synchronization in the Limbic System in Vitro. Prog Neurobiol 2002, 68, 167–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huberfeld, G.; Menendez De La Prida, L.; Pallud, J.; Cohen, I.; Le Van Quyen, M.; Adam, C.; Clemenceau, S.; Baulac, M.; Miles, R. Glutamatergic Pre-Ictal Discharges Emerge at the Transition to Seizure in Human Epilepsy. Nat Neurosci 2011, 14, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakhin, D.V.; Ergina, J.L.; Chizhov, A.V.; Zaitsev, A.V. Synaptic Conductances during Interictal Discharges in Pyramidal Neurons of Rat Entorhinal Cortex. Front Cell Neurosci 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avoli, M. Do Interictal Discharges Promote or Control Seizures? Experimental Evidence from an in Vitro Model of Epileptiform Discharge. In Proceedings of the Epilepsia; 2001; Vol. 42, pp. 2–4.
- Avoli, M.; Panuccio, G.; Herrington, R.; D’Antuono, M.; de Guzman, P.; Lévesque, M. Two Different Interictal Spike Patterns Anticipate Ictal Activity in Vitro. Neurobiol Dis 2013, 52, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arcangelo, G.; Panuccio, G.; Tancredi, V.; Avoli, M. Repetitive Low-Frequency Stimulation Reduces Epileptiform Synchronization in Limbic Neuronal Networks. Neurobiol Dis 2005, 19, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarosie, M.; Avoli, M. CA3-Driven Hippocampal-Entorhinal Loop Controls Rather than Sustains In Vitro Limbic Seizures. The Journal of Neuroscience 1997, 17, 9308–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnatkovsky, V.; Librizzi, L.; Trombin, F.; De Curtis, M. Fast Activity at Seizure Onset Is Mediated by Inhibitory Circuits in the Entorhinal Cortex in Vitro. Ann Neurol 2008, 64, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uva, L.; Breschi, G.L.; Gnatkovsky, V.; Taverna, S.; de Curtis, M. Synchronous Inhibitory Potentials Precede Seizure-like Events in Acute Models of Focal Limbic Seizures. Journal of Neuroscience 2015, 35, 3048–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Antuono, M.; Benini, R.; Biagini, G.; D’Arcangelo, G.; Barbarosie, M.; Tancredi, V.; Massimo Avoli, A.N.D. Limbic Network Interactions Leading to Hyperexcitability in a Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. J Neurophysiol 2002, 87, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimova, A.M.; Amakhin, D.V.; Postnikova, T.Y.; Tiselko, V.S.; Alekseev, A.; Podoliak, E.; Gordeliy, V.I.; Chizhov, A.V.; Zaitsev, A.V. Light-Driven Sodium Pump as a Potential Tool for the Control of Seizures in Epilepsy. Mol Neurobiol 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiri, Z.; Lévesque, M.; Etter, G.; Manseau, F.; Williams, S.; Avoli, M. Optogenetic Low-Frequency Stimulation of Specific Neuronal Populations Abates Ictogenesis. The Journal of Neuroscience 2017, 37, 2999–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, E.Y.; Sinyak, D.S.; Chizhov, A.V.; Zaitsev, A.V. Age-Dependent Generation of Epileptiform Activity in the 4-Aminopyridine Model with Slices of the Rat Entorhinal Cortex. J Evol Biochem Physiol 2021, 57, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liut, Z.; Nagao, T.; Desjardins’, G.C.; Gloor, P.; Avoli, M. Quantitative Evaluation of Neuronal Loss in the Dorsal Hippocampus in Rats with Long-Term Pilocarpine Seizures. Epilepsy Res 1994, 17, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postnikova, T.Y.; Diespirov, G.P.; Amakhin, D.V.; Vylekzhanina, E.N.; Soboleva, E.B.; Zaitsev, A.V. Impairments of Long-Term Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampus of Young Rats during the Latent Phase of the Lithium-Pilocarpine Model of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 13355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, R.J. Modification of Seizure Activity by Electrical Stimulation. II. Motor Seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1972, 32, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malkin, S.L.; Khachatryan, V.A.; Fedorov, E.V.; Zaitsev, A.V. The Electrophysiological Properties of Cortical Neurons in the Epileptic Foci of Children with Refractory Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. J Evol Biochem Physiol 2022, 58, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakhin, D.V.; Soboleva, E.B.; Ergina, J.L.; Malkin, S.L.; Chizhov, A.V.; Zaitsev, A.V. Seizure-Induced Potentiation of AMPA Receptor-Mediated Synaptic Transmission in the Entorhinal Cortex. Front Cell Neurosci 2018, 12, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postnikova, T.Y.; Griflyuk, A.V.; Amakhin, D.V.; Kovalenko, A.A.; Soboleva, E.B.; Zubareva, O.E.; Zaitsev, A.V. Early Life Febrile Seizures Impair Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity in Young Rats. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 8218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Plewczynski, D.; Saha, S.; Roszkowska, M.; Magnowska, M.; Baczynska, E.; Wlodarczyk, J. 2dSpAn: Semiautomated 2-d Segmentation, Classification and Analysis of Hippocampal Dendritic Spine Plasticity. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2490–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
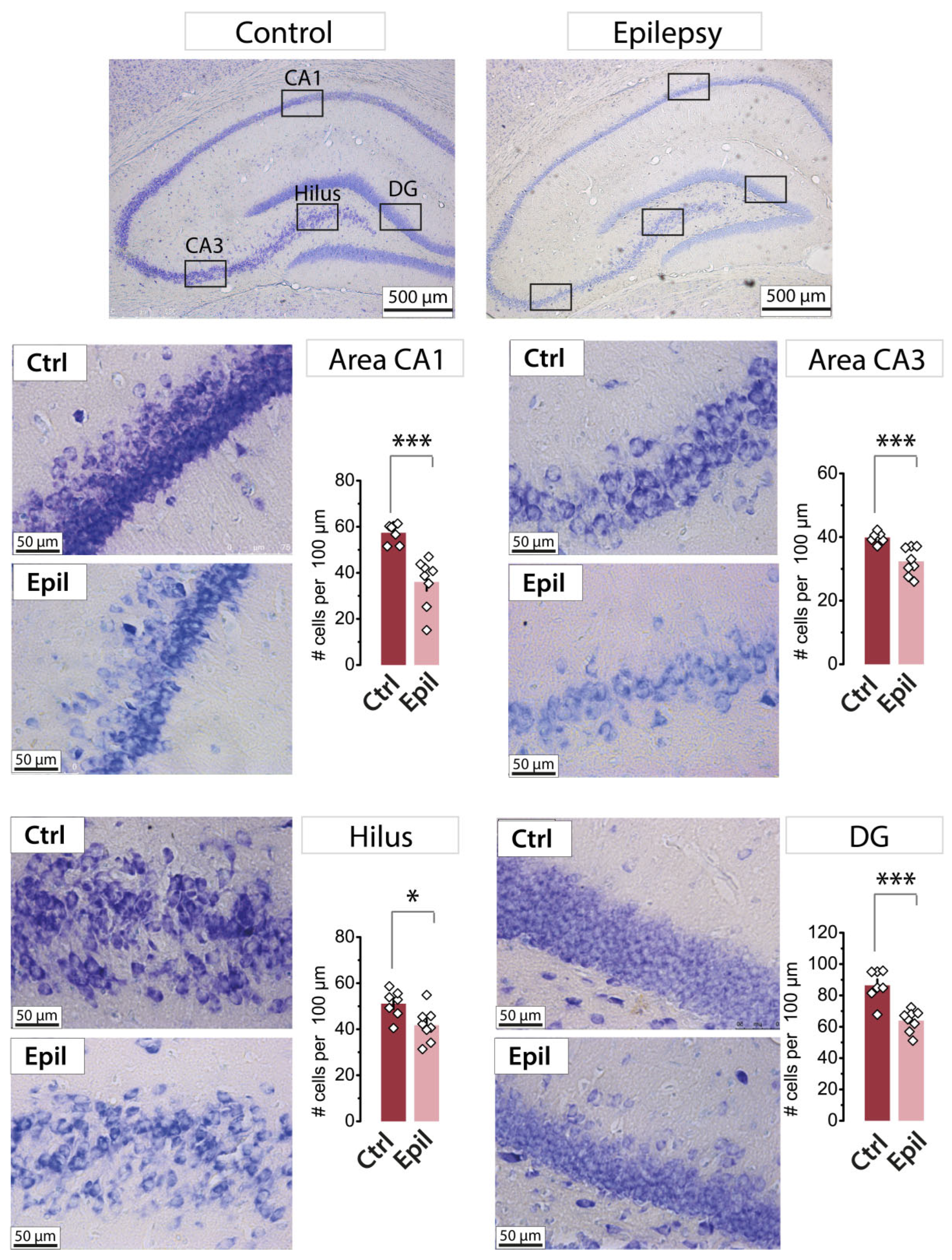
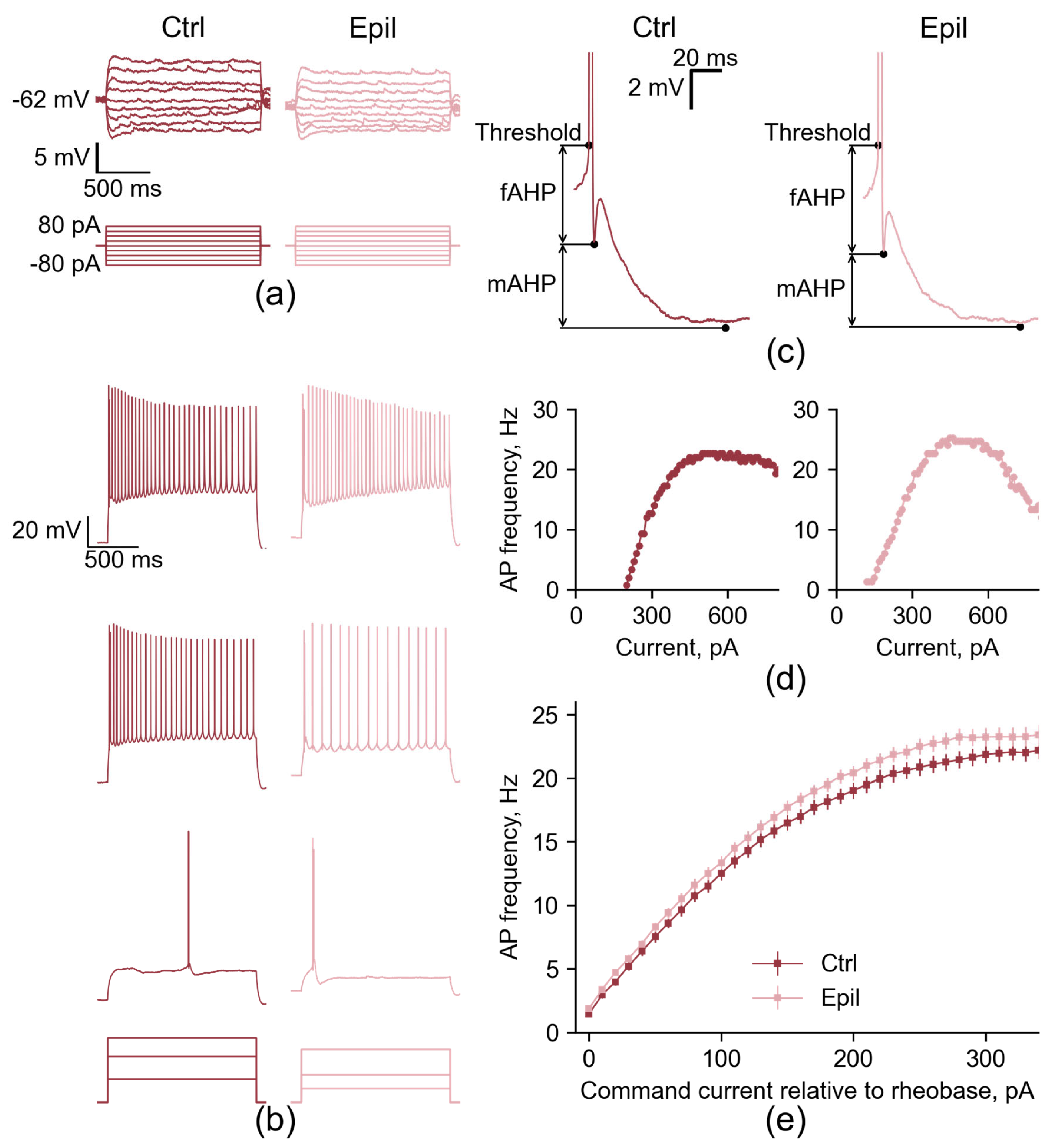
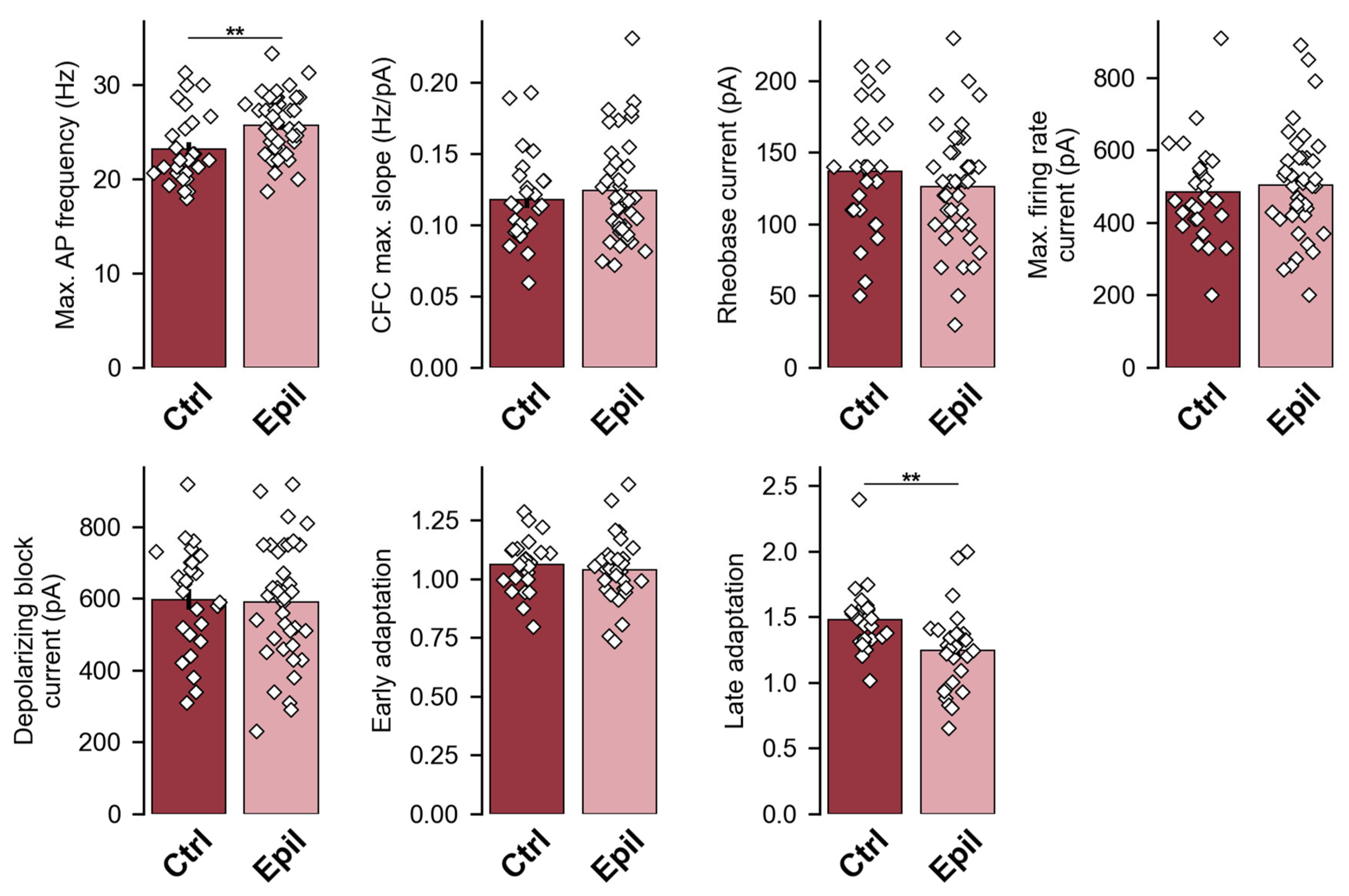
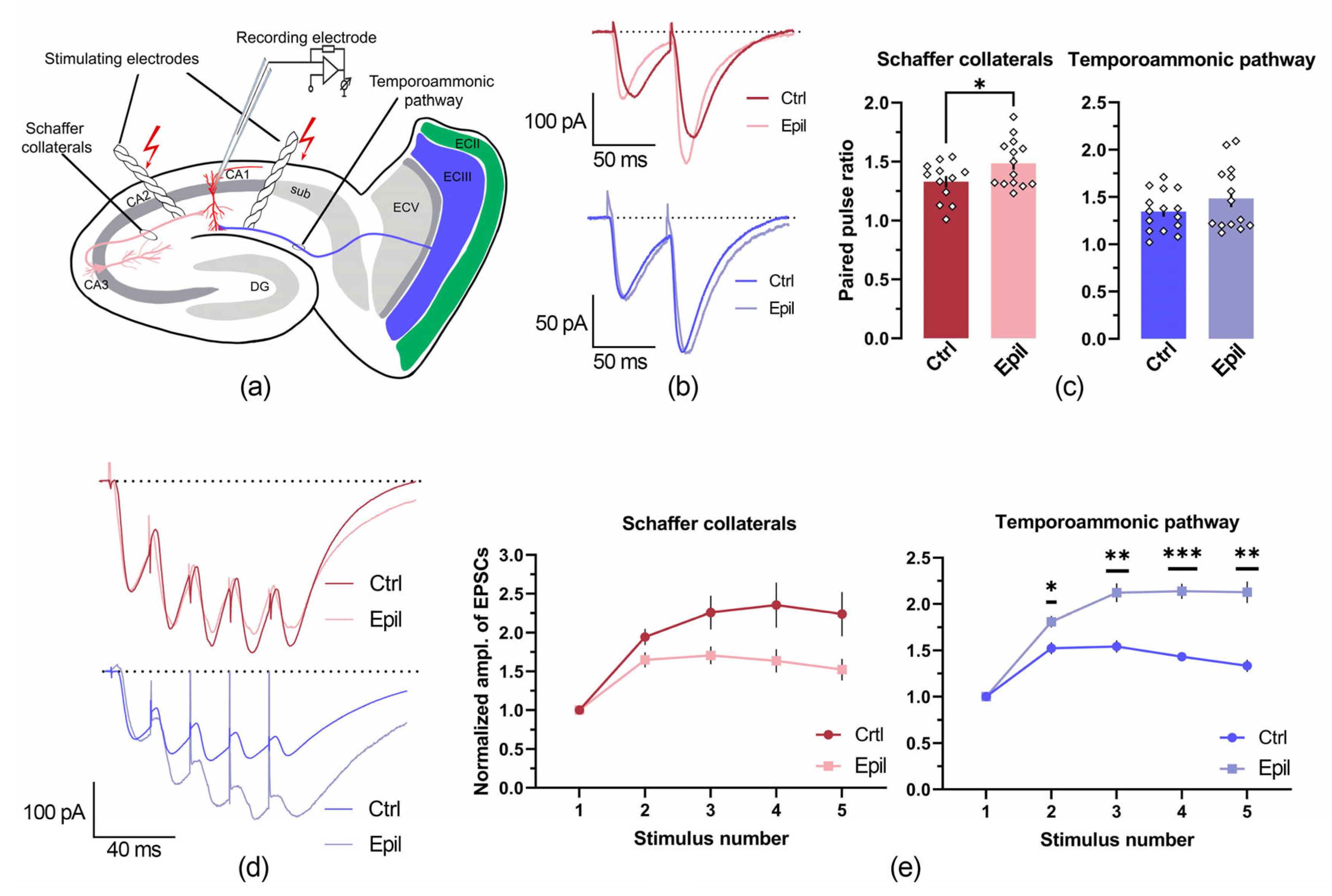
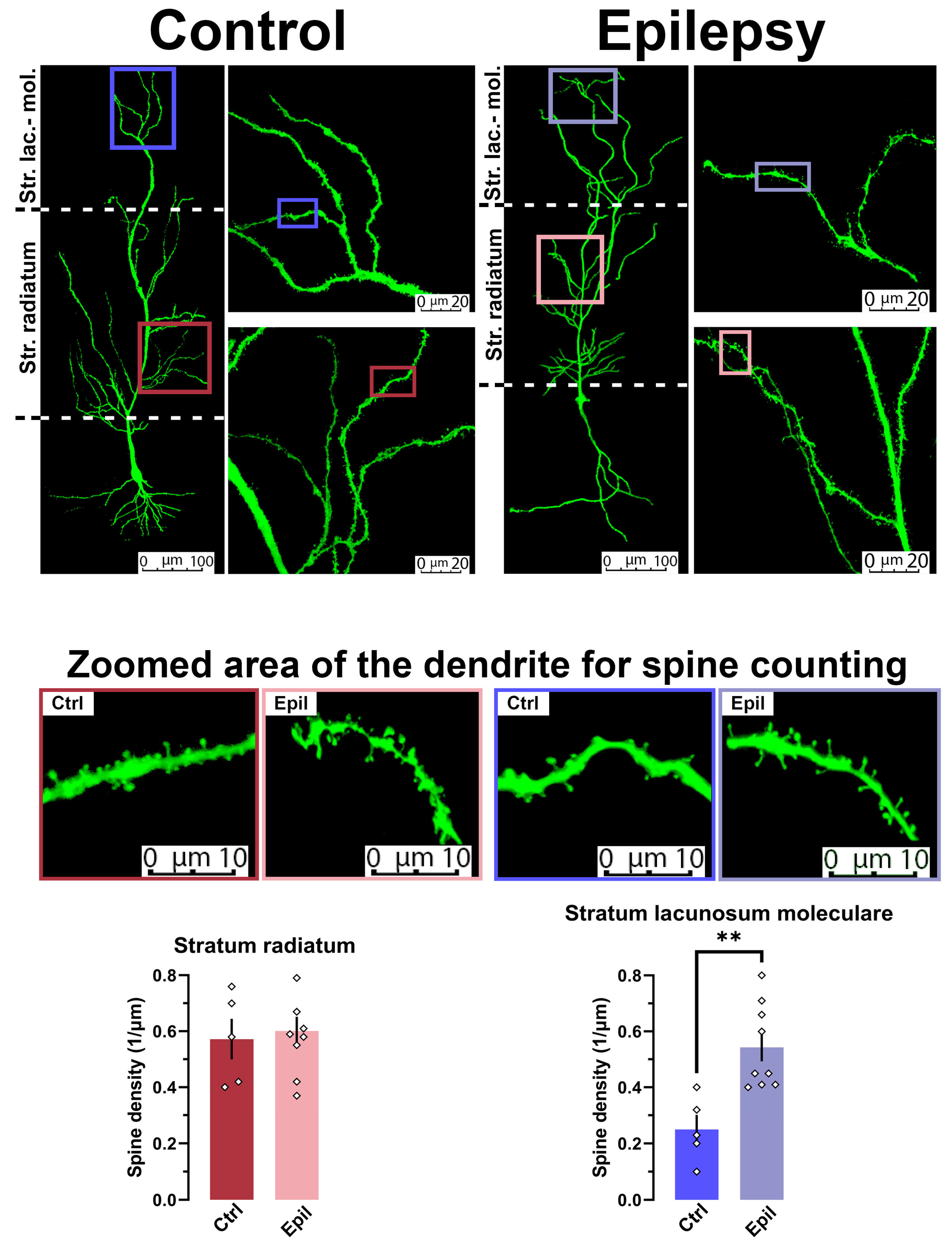
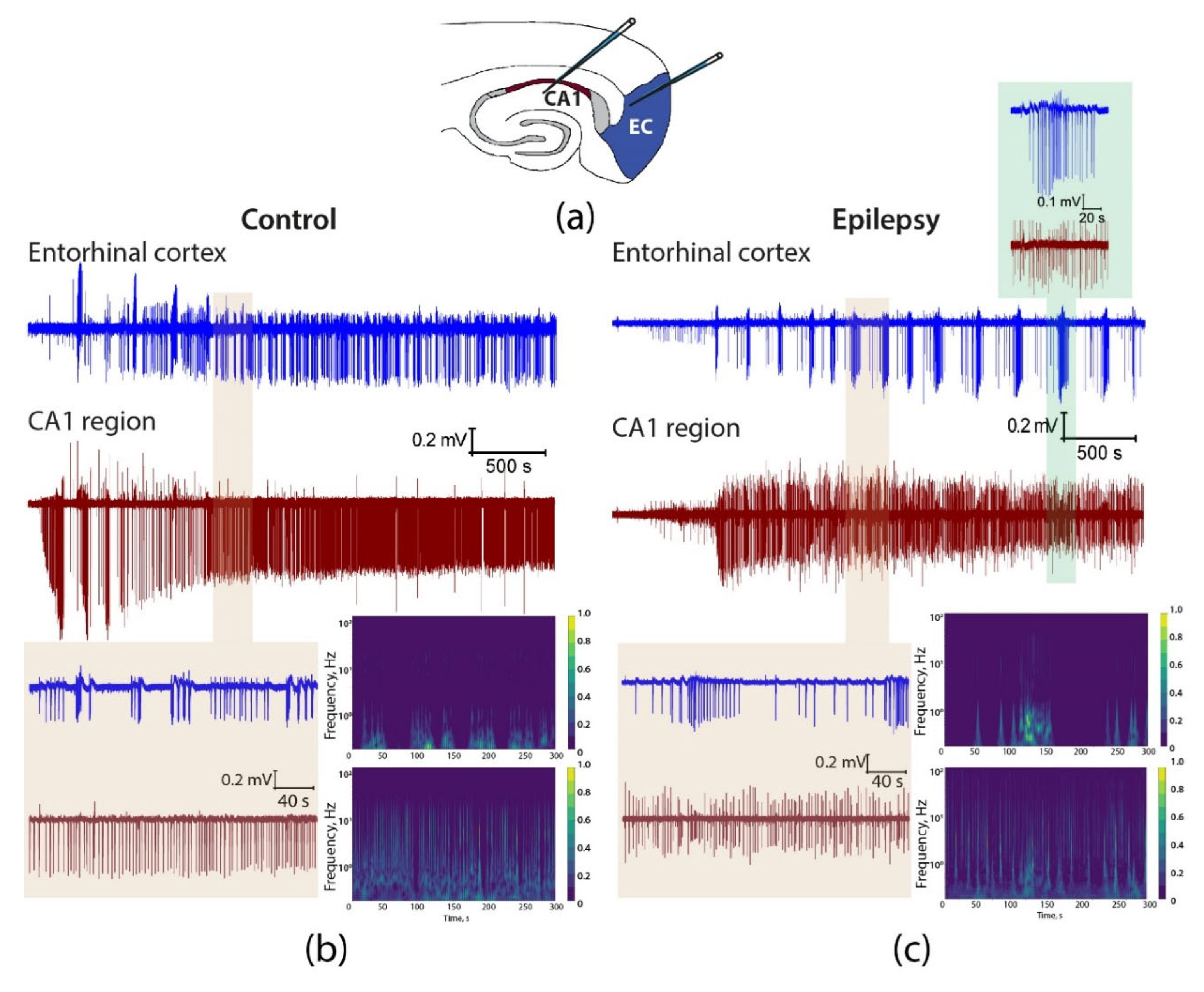
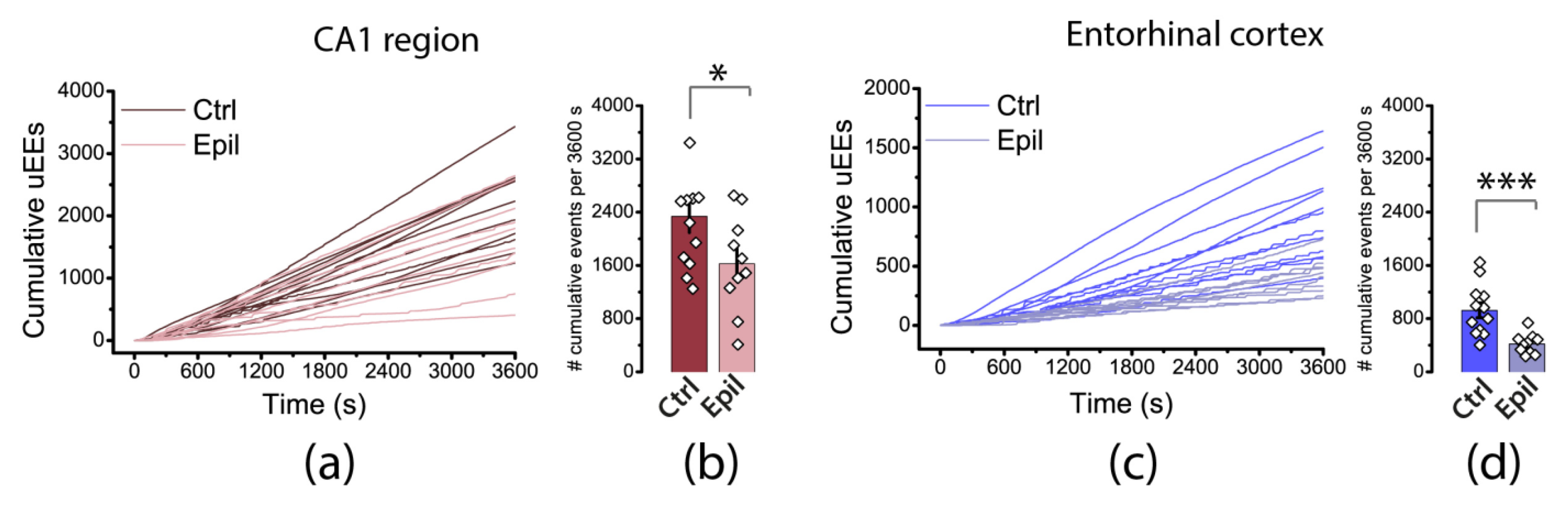
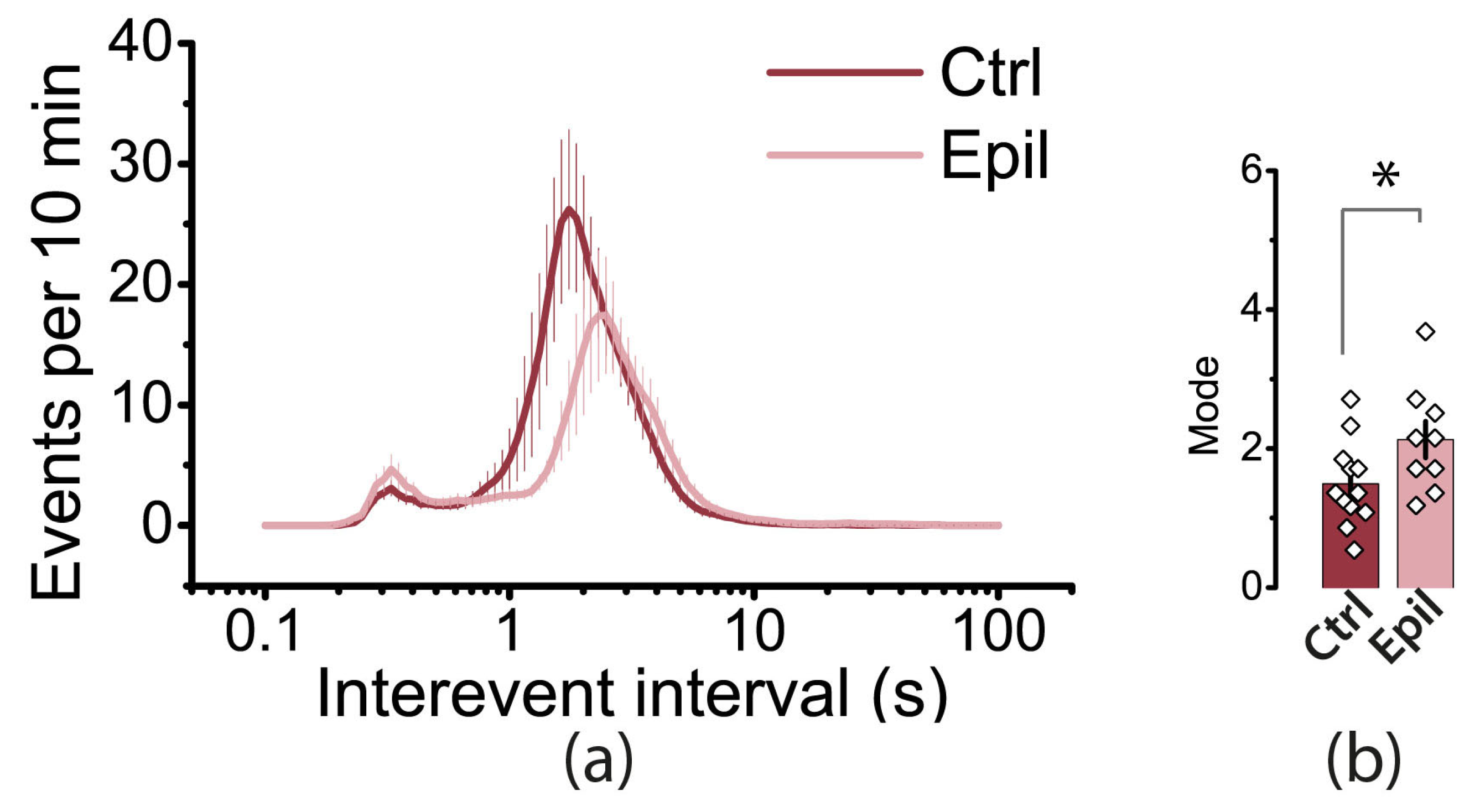
| Membrane property | Control (n = 27) | Epileptic (n = 40) | p |
| Resting membrane potential, mV | −62.6 ± 0.7 | −63.4 ± 0.4 | 0.32 |
| Input resistance, MΩ | 82.5 ± 3.8 | 91.0 ± 4.0 | 0.15 |
| Membrane τ, ms | 19.9 ± 1.2 | 22.7 ± 1.5 | 0.17 |
| Properties | Control (n = 27) | Epileptic (n = 40) | p |
| Hump amplitude, mV | 0.95 ± 0.21 | 0.35 ± 0.11 | 0.10 |
| Time of first spike, ms | 521 ± 66 | 536 ± 55 | 0.87 |
| Threshold, mV | −44.0 ± 0.6 | −43.6 ± 0.3 | 0.47 |
| Amplitude, mV | 99.8 ± 0.8 | 97.8 ± 0.8 | 0.14 |
| Rise time 10% to 90%, ms | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 0.84 |
| Half-width, ms | 1.28 ± 0.02 | 1.26 ± 0.02 | 0.35 |
| fAHP, mV | −6.0 ± 0.4 | −5.9 ± 0.5 | 0.95 |
| mAHP, mV | −9.9 ± 0.3 | −9.6 ± 0.3 | 0.48 |
| Time to mAHP, ms | 65 ± 3 | 74 ± 4 | 0.11 |
| ADP, mV | 1.9 ± 0.3 | 2.3 ± 0.3 | 0.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





