Submitted:
21 September 2023
Posted:
25 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
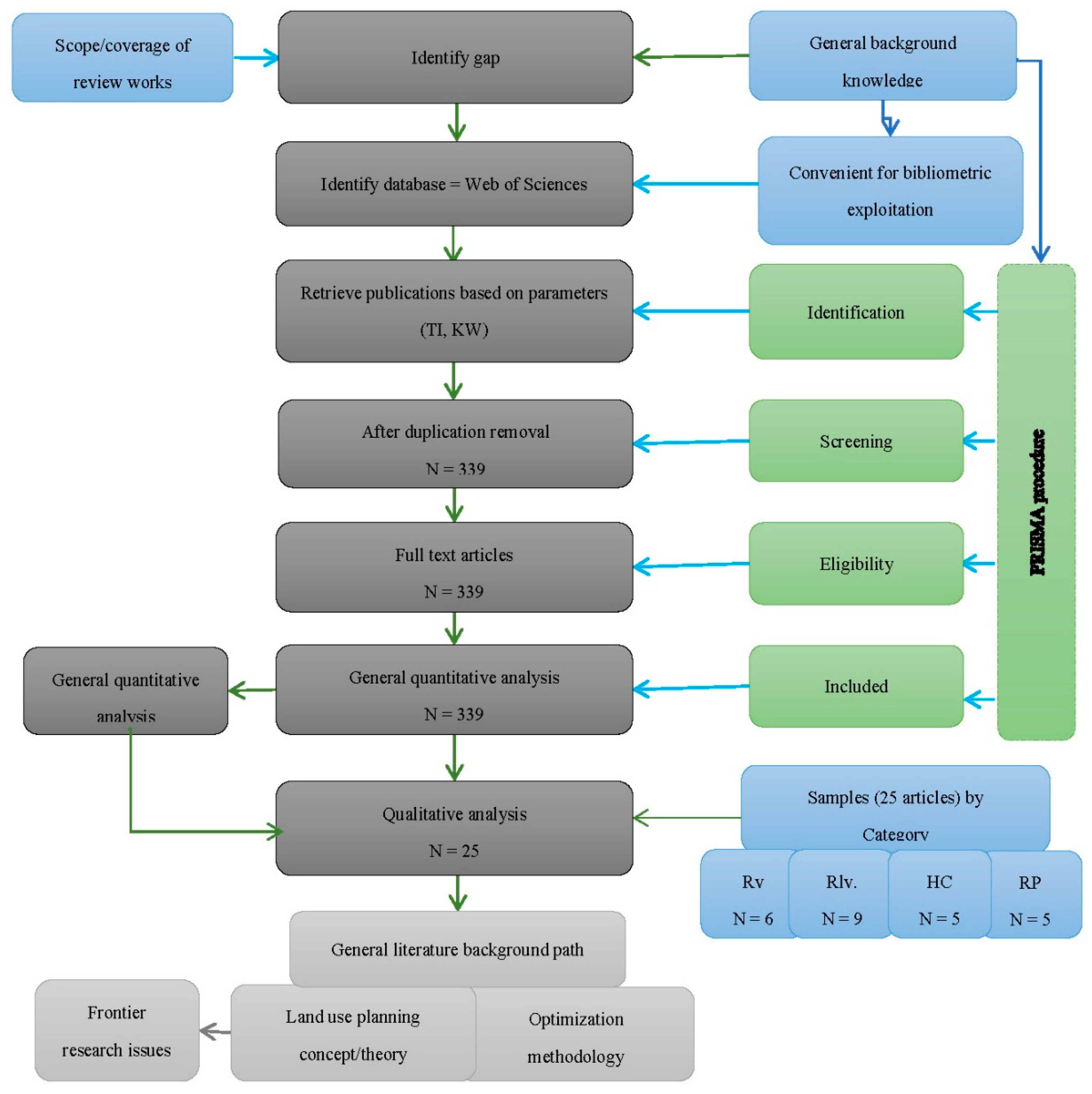
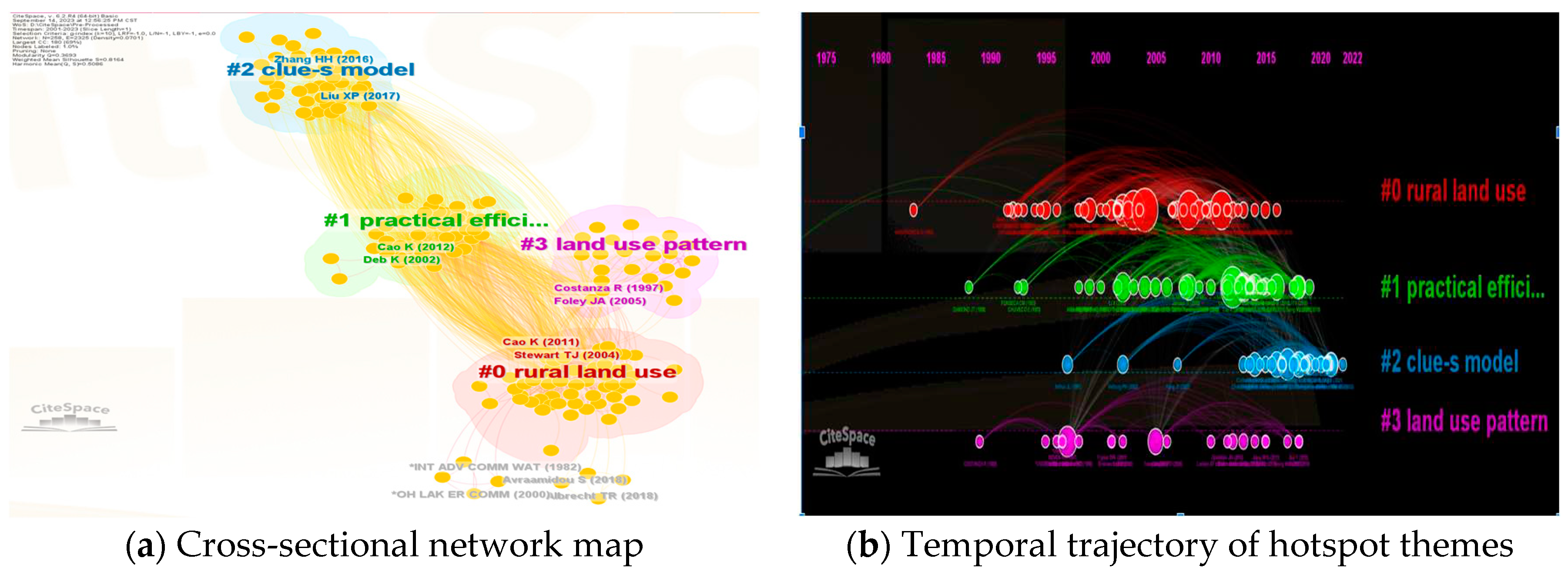
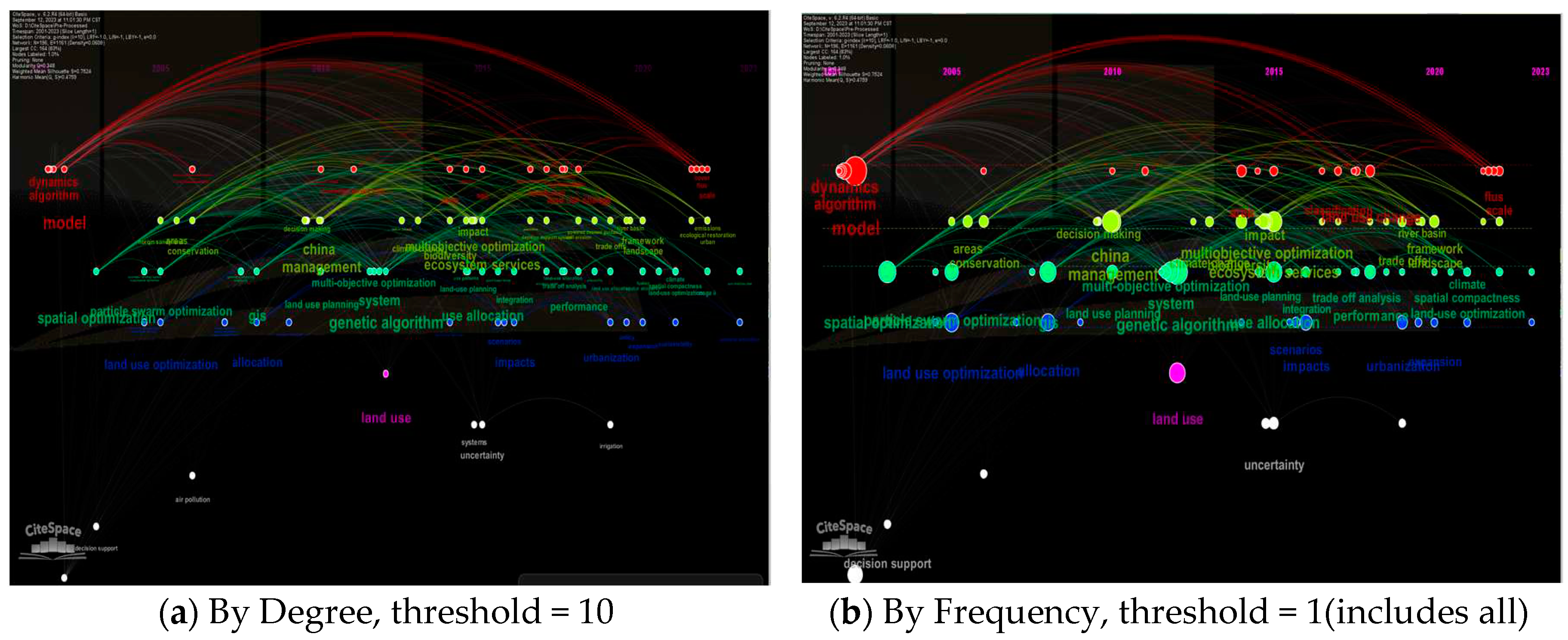
3. Bibliometric indications
4. Previous review works
4.1. Brief summary of content coverage
4.2. Value and frontiers
5. Review of the regular articles
5.1. Literature path building
- (i)
- The current state of the art of optimization method is hybridization, especially a combination of global and local optimizers. The spatial optimization part advanced to the level to consider both vertical completion and horizontal competition processes. It is further indicates that the demand for coupling is not just because of scalability problems but also because of the view that disaggregates planning from the assignment of activities over available space.
- (ii)
- The development of optimization knowledge is getting more in-depth both in method rigor and in conceptualizing land use planning as a discipline. Yet, breadth scope is more visible than depth advancement.
5.2. Land use planning context and method development
5.2.1. Land use planning context
5.2.2. Optimization method
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
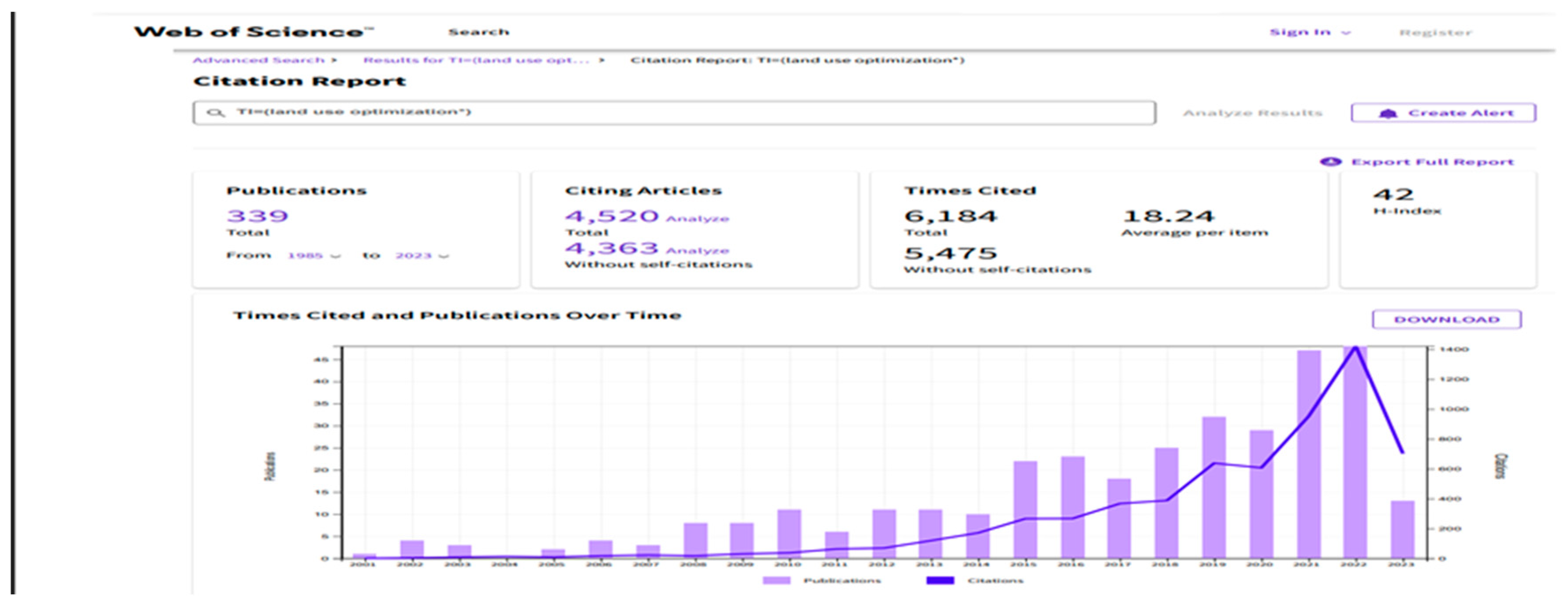
Appendix A. Database retrieval report indicating number of publications, citing articles, and times cited as of 1st August 2023
Appendex B. Citation counts by major clusters
| Cluster ID | Citation Counts | References | DOI |
| 0 | 49 | Stewart TJ, 2004, COMPUT OPER RES, V31, P2293 | 10.1016/S0305-0548(03)00188-6 |
| 1 | 42 | Cao K, 2012, COMPUT ENVIRON URBAN, V36, P257 | 10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2011.08.001 |
| 0 | 37 | Cao K, 2011, INT J GEOGR INF SCI, V25, P1949 | 10.1080/13658816.2011.570269 |
| 0 | 34 | Aerts JCJH, 2003, GEOGR ANAL, V35, P148 | 10.1353/geo.2003.0001 |
| 0 | 34 | Ligmann-Zielinska A, 2008, INT J GEOGR INF SCI, V22, P601 | 10.1080/13658810701587495 |
| 0 | 22 | Aerts JCJH, 2002, INT J GEOGR INF SCI, V16, P571 | 10.1080/13658810210138751 |
| 3 | 21 | Costanza R, 1997, NATURE, V387, P253 | 10.1038/387253a0 |
| 2 | 21 | Liu XP, 2017, LANDSCAPE URBAN PLAN, V168, P94 | 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2017.09.019 |
| 1 | 18 | Deb K, 2002, IEEE T EVOLUT COMPUT, V6, P182 | 10.1109/4235.996017 |
| 1 | 17 | Liu XP, 2013, ECOL MODEL, V257, P11 | 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2013.02.027 |
Appendex C. Summary of the largest 6 clusters
| Cluster ID | Size | Silhouette | Label (LSI) | Label (LLR) | Label (MI) | Avg. Year |
| 0 | 58 | 0.74 | land use | rural land use (43.41, 1.0E-4) | land-use pattern (1.65) | 2004 |
| 1 | 47 | 0.777 | case study | practical efficient regional land-use planning (25.91, 1.0E-4) | using accessibility map (1.85) | 2009 |
| 2 | 44 | 0.849 | case study | clue-s model (56.76, 1.0E-4) | potential area identification (1.39) | 2017 |
| 3 | 23 | 0.963 | land use pattern | land use pattern (75.62, 1.0E-4) | land use pattern evolution (0.41) | 2005 |
| 10 | 4 | 1 | a hierarchical optimization approach to watershed land use planning | watershed land use planning (16.92, 1.0E-4) | case study (0.08) | 1993 |
| 11 | 4 | 0.995 | two-stage land use optimization for a food-energy-water nexus system: a case study in Texas Edwards region | energy-water nexus system (12.42, 0.001) | case study (0.07) | 2018 |
Appendex D
| Cited paper | Citing paper | |||
| Author(s) and DOI | Research issue | Author(s) and DOI | Core research content | Cited content |
| Aerts and Heuvenlink (2002) https://doi.org/10.1080/13658810210138751 | Application of SA to high dimensional non-linear multi-objective multisite land allocation | Song and Chen (2018) https://doi.org/10.1080/10095020.2018.1489576 | Improved knowledge informed GA for Multiobjective land use allocation | BLI - Heuristic algorithms |
| Coa, et al., (2011) https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2011.570269 | Modified NSGA-II | BLI - Sustainable development | ||
| Luo and Huang (2023) https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2023.2178001 | Probabilistic based gradient multobjective land-use optimization | BLI - Gradient methods in optimization | ||
| Jahanishakib, et al (2022) https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2022.2037734 | validity and accuracy comparison b/n various algorithms in land-use allocation (including SA) | CRC - What SA it is and its application | ||
| Masoumi, et al. (2012) https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2012.698016 | Application of Particle Swarm Optimization for miultiobjective urban land use optimization | BLI - Heuristic algorithm | ||
| Huang et al (2012) https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2012.730147 | Application of improved artificial immune system for multi-objective land-use allocation | BLI - Heuristic algorithms | ||
| Damghani, et al (2014) https://doi.org/10.1080/13658816.2014.927471 | Application of hybrid heuristic algorithms to multiobjective land-use suitability assessment Quadratic Assignment Problem | BLI - Heuristic algorithms | ||
| Taromi, et al (2015) https://doi.org/10.1080/03081060.2014.997450 | multiobjective optimization model to consider transportation formulated as mixed integer programing | BLI - Iinteger programing | ||
| Yang, et al (2015) | Improved artificial bee colony algorithm optimize spatial problem | BLI - Heuristic algorithms | ||
| Paritosh, et al (2018) https://doi.org/10.1080/17509653.2018.1505566 | Application of GA and game theory to solve land allocation problem | BLI - Heuristic algorithms | ||
| Zhang et al (2016) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2015.10.017 |
Simulating optimal multiobjective land-use Applying multi-agent system and particle swarm |
Ma, et al (2022a) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.131191 | Urban growth boundary determination based on multiobjective land use optimization applying Pareto front degradation searching strategy where lands were defined as agents | CRC - application of agent in land use optimization |
| Ma, et al (2022b) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2022.103645 | Collaborative optimal allocation of urban land to determine growth boundary of urban agglomeration | BLI - The difficulty of transforming optimal land-use structures into spatial layout | ||
| Nauri, et al (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2022.100826 | An agent based optimization of water allocation (market) where farmers were represented as an agricultural agent | CRC - Application of agent in land use optimization | ||
| Ding and Achiten (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.134914 | Linking agent-based modeling with the territorial Life Cycle Assessment to land-use planning | BLI - Complexity of spatial and temporal dynamics of territorial transformation | ||
| Zhang et al (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2023.105046 | Optimizing Deep Underground Infrastructure layouts based on a multi-agent system where each DUI is represented by an agent | CRC - The se of multi-agent system | ||
| Fan et al (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/land12040917 | Land-use simulation (optimization) using CLUMondo mode | BLI - Complexity of quantifying conflicting interests; Use of fractal dimension; Sensitivity of complex landscape patch boundary to human disturbance | ||
| Meng, et al (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/su15053977 | Use of gray multiobjective optimization and Patch generating land-use simulation in land-use optimization (hybrid methods) | BLI - The relation of land-use structure optimization and sustainable development | ||
| Qin et al (2023) https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-023-1327-3 | Ecosystem service value optimization for different scenarios | BLI - Previous studies on carbon sinks focus the relationship between carbon sinks and land use | ||
| Liu and Xia (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/su15021401 | Optimization of land-use using Multi-Agent System and Multiobjective Particle Swarm Optimization | BLI - Chinese land-use planning hierarchies | ||
| Song and Chen (2018) https://doi.org/10.1080/10095020.2018.1489576 | Improved knowledge-informed NSGA-II for multiobjective land-use optimization | Masoumi and Genderen (2023) https://doi.org/10.1080/10095020.2023.2184729 | Compare performances of multiobjective optimization algorithm, NSGA-II, multiobjective particle swarm optimization, and multiobjective evolutionary algorithm in solving urban land-use allocation problems | BLI - Many studies applied multiobjective optimization algorithms at regional level; Type of data model in LU optimization; Scalarization of objectives; CRC - Comparison of GA, PPSO, SA |
| Niyomubyeyi, et al (2022) https://doi.org/10.1080/10095020.2022.2127380 | Improved or multi-objective land-use allocation | CRC - Improvement mechanisms to NSGA-II | ||
| Liu et al (2013) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2013.02.027 | Integration of system dynamics and hybrid PS optimization for solving land use allocation problems | Ma, et al (2022b) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cities.2022.103645 | Collaborative optimal allocation of urban land to determine growth boundary of urban agglomeration | BLI - Planning process involves quantity predication and spatial arrangements |
| Sajith, et al (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2022.107638 | Comparison of Multiobjective GA, Cuckoo Search, and PPSO in agricultural land use optimization | BLI - Extensive application of artificial and swarm intelligence in land-use allocation optimization | ||
| Wei, et al (2022) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrh.2022.101180 | Investigating whether converting types of agricultural land can mitigate soil erosion | CRC - Advantage of PSO over others for land-use optimization | ||
| Qu, et al (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159319 | Coupling Markov and CA to solve the structural-spatial couple optimization problem | BLI - Wide application of hybrid models to solve land-use optimization | ||
| Yu, et al (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15143629 | Use of CA-Markov, Land Change Modeler, Patch-generating Land Use Simulation to simulate the LUCC | BLI - Description of quantitative prediction models in land-use optimization | ||
| Xu, et al (2023) https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-022-1077-y | Study on past and future land use changes in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau to reflect effects of different policies/scenarios | BLI - Dynamic system is among the main simulation modeling | ||
| Chen, et al (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/land12030710 | Multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm to find the best land use adjustment strategies for village classification | BLI - Land-use optimization accounts current situation and multiple objectives | ||
| Wnag et al (2022) | Integrating transport into urban land-use optimization | BLI - How different studies consider accessibility | ||
| Cao, et al (2022) https://doi.org/10.3390/su142214941 | Modeling land use spatial conflict measurement based on a quantitative analysis of land use changes using GIS, Yaahp, and SPSSAU software | BLI - Advantage of entropy method in weighting objectives | ||
| Stewart and Janssens (2014) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2014.04.002 | A special purpose GIS GA to solve both direct (additive) objectives and indirect (spatial) objective | Erosemiah and Viji (2023) https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-023-2421-y | Accuracy in the extraction of the drainage network and morphometric analysis for assessing geomorphological characteristics and hydrological processes | BLI - Mentioning works undertaken to study the areas that are vulnerable to flood |
| Li, et al (2023) https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20054286 | Analyzing change in green space in different scenarios and the index characteristics of landscape patterns using FLUUS | BLI - Mentioning the authors optimized the spatial distribution of land resources using handling multiple objectives | ||
| Li, et al (2023) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.109950 | Evaluating the Carbon and GDP reconciliation using a multi-objective particle swarm algorithm | BLI - The authors utilized multi-objective programming | ||
| Basirati, et al (2023) Annals of Mathematics and Artificial Intelligence https://doi.org/10.1007/s10472-023-09853-2 | Compare performance of Synchronous Hypervolume-based NSGA-II and a memetic algorithm (MA) in which SH-NSGA-II is enhanced with a local search in Multiobjective Marian Spatial Planning Problem | BLI - The iterative approach in land-use optimization | ||
| Teijeiro, et al (2022) https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11227-022-04627-9 | High performance GA in land-use optimization | BLI - The use of Ga in land use allocation | ||
| Sadeghi, et al (92009) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2008.02.007 Citations = 106 |
Land-use optimization based on ESV | Chen and Xu (2021) doi:10.1088/1755-1315/687/1/012042 | Adjusted dynamic two-stage optimization to explore comprehensive managerial insights of irrigative areas and forest expansion | BLI - The danger of water and soil erosion for sustainable development |
| Sheikh, et al (2021) https://doi.org/10.1111/nrm.12301 | NSGA-II for land use optimization that minimize runoff and sediment and maximize economic benefits, occupational opportunities, and land use suitability | BLI - Categorization of land optimization methods | ||
| Jiang et al (2021) https://doi.org/10.3390/su131810431 | Use multi-objective linear programming and CLUE-S to optimize under different scenarios | BLI - Land-use optimization need to address both economic and ecosystem elements | ||
| Zhang, et al (2021) https://doi.org/10.3390/land10111242 | Application of MOP and FLUS to optimize land-use allocation under strict ecological constraints | BLI - Optimization objectives are specific where the study area is small | ||
| Phinyoyang and Ongsomwang (2021) https://doi.org/10.3390/land10121317 | Allocate land use and land cover (LULC) to minimize the surface for flood mitigation using goal programing and CLUE-S | BLI - Land use optimization is one of the proper solutions for soil and water conservation at the watershed level | ||
References
- Alajmi, A. , and Wright, J. (2014). Selecting the most efficient genetic algorithm sets in solving unconstrained building optimization problem,” International Journal of Sustainable Built Environment, 3(1), 18-26. [CrossRef]
- Aerts, J.C.J.H. , van Herwijnen, M., Stewart, T.J. (2003). Using Simulated Annealing and Spatial Goal Programming for Solving a Multi Site Land Use Allocation Problem. In: Fonseca, C.M., Fleming, P.J., Zitzler, E., Thiele, L., Deb, K. (eds) Evolutionary Multi-Criterion Optimization. EMO 2003. Lecture Notes in Computer Science,. [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C. (1992). A City is Not a Tree. In The City Reader, 1st ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, pp. 118–131.
- Allen, P.M. , & Sanglier, M. (1981a). A dynamic model of central place system – II. Geographical Analysis, /: Wiley Online Library, https, 1111. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, P. M. , & Sanglier, M. (1981b). Urban evolution, self-organization, and decision making. Environment and Planning, /: https. [CrossRef]
- Al-Thani, S.K. , Amato, A., Kok, M., & Al-Ghamid, S. G. (2019). Urban sustainability and livability: An analysis of Doha’s urban-form and possible mitigation strategies. Sustainability. [CrossRef]
- Anas, A. , & Kim, I. (1996). General equilibrium models of polycentric endogenous congestion and job agglomeration. ( 40(2), 232–256. [CrossRef]
- Anas, A. , Arnott, R., & Small, K. A. (1997). Urban spatial structure. Transport Center, The University of California Working paper No. 357, 4981. [Google Scholar]
- Andersson, R. , & Samartin, A. (1985). A Model for Urban Commuting in a Multicenter City. University of Stockholm, Sweden. ( 20(2), 173–191. [CrossRef]
- Anthony, A.F. , Offia. I.E., Abidemi. B.R., Oladunjoye Kola, O., & Kamoru, G.G. (2018). Urban Sustainability Concepts and Their Implications on Urban Form. Urban and Regional Planning, /: https, 1164. [Google Scholar]
- Ashenafi, A. (2015). Optimization based approach for landuse/transportation policy making, /: thesis, Faculty of Sciences and Technology, University of Coimbra. https, 1031. [Google Scholar]
- Bertaud, A. (2004). The Spatial Organization of Cities : Deliberate Outcome or Unforeseen Consequence? Institute of Urban and Regional Development University of California at Berkeley, Working Paper No. 2004-01. 4513. [Google Scholar]
- Boussauw, K. & F. Witlox. (2009). Introducing a commute-energy performance index for Flanders. Transportation Research Part A. [CrossRef]
- Broitman, D. (2012). Dynamics of polycentric urban structure Dynamics of polycentric urban structure, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, E. (2000). The Potential of the Compact City for Promoting Social Equity. In Achieving Sustainable Urban Form. Taylor Francis: London, UK, pp. 19–29.
- Cao, K. , Batty, M., Huang, B., Liu, Y., Yu, L., & Chen, J. (2011). Spatial multi-objective land use optimization: Extensions to the non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-II. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K. , Huang, B., Wang, S., & Lin, H. (2012). Sustainable land use optimization using Boundary-based Fast Genetic Algorithm. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, 36(3), 257–269. [CrossRef]
- Chakir, R.; Le Gallo, J. (2013). Predicting land use allocation in France: A spatial panel data analysis. Ecological Economics. 92, 114–125. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. , Zhao, R. ( 12(6), 1164. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S. , Chan, C.W., & Huang, G.H (2003). An integrated multi-criteria decision analysis and inexact mixed integer linear programming approach for solid waste management. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 16(5–6): 543–554. /: https. [CrossRef]
- Chieng, H. , and Wahid, N. (2014). A performance comparison of genetic algorithm’s mutation operators in n-cities open loop travel salesman problem. Recent Advances on Soft Computing and Data Mining, /: https, 1007. [Google Scholar]
- Chuvieco, E. (1993). Integration of linear programming and GIS for land use modelling. International Journal of Geographical Information Science. [CrossRef]
- Clark, W.C. , van Kerkhoff, L., Lebel, L., & Gallopin, G.C. (2016). Crafting usable knowledge for sustainable development. C. ( 113, 4570–4578. [CrossRef]
- De Lara, M. , De Palma, A., Kilani, M., & Piperno, S. (2013). Congestion pricing and long term urban form: Application to Paris region. Reginal Science and Urban Economics, 43(2), 282–295. [CrossRef]
- Deb, K. , Pratap, A., Agrawal, S., & Meyarivan, T. (2002). A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation. [CrossRef]
- Ding, X. , Zheng, M., & Zheng, X. (2021). The application of genetic algorithm in land use optimization research: A review. Land. [CrossRef]
- Dong, C. , Huang, G. H., Tan, Q. Cai, Y. (2014). Coupled planning of water resources and agricultural landuse based on an inexact-stochastic programming model. Frontiers of Earth Science, /: 70–80. https. [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N. , Kumar, S., Mukherjee, D., Pandey, N., & Lim, W. M. (2021). How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research. [CrossRef]
- Ewing, R. (1997). Is Los Angeles Style Sprawl Desirable? Journal of the American Planning Association. [CrossRef]
- 30. Frost. A.D., Hróbjartsson, A., & Nejstgaard, C.A. (2022). Adherence to the PRISMA-P 2015 reporting guideline was inadequate in systematic review protocols. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology. [CrossRef]
- García, G.A. , Rosas, E.P., García-Ferrer, A., & Barrios, P.M. (2017). Multi-Objective Spatial Optimization: Sustainable Land Use Allocation at Sub-Regional Scale. Sustainability, 2071. [Google Scholar]
- Guth, D. , Holz-Rau, C., & Maciolek, M. (2009). Employment suburbanisation and commuter traffic in German city regions. 9th Swiss Transport Research Conference, 1: Switzerland, Sep. 9-11, 1-22. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID, 1301; -11. [Google Scholar]
- Handayanto, R.T. , Tripathi, N.K., Kim, S.M., & Guha, S. (2017). Achieving a sustainable urban form through land use optimisation: Insights from Bekasi City’s land use plan (2010-2030). Sustainability (Switzerland). [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, D. , Oyewola, D.O., Yahaya, Y. and Bolarin, G. (2016). Comparative analysis of genetic crossover operators in Knapsack problem. Journal of Applied Environmental Management, 1: 593-596. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID, 1259. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, T. , Fujimori, S., Ito, A., Takahashi, K., & Masui, T. (2017). Global land use allocation model linked to an integrated assessment model. ( 580, 787–796. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabareen, Y.R. (2006). Sustainable urban forms: Their typologies, models, and concepts. Journal of Planning Education and Research. [CrossRef]
- Jahanishakib, F. , Ardakani, T., Sabaee, M. S., & Salmanmahiny, A. (2022). Accuracy and validity assessment of application algorithms in land use allocation into comparison LP, SA, MOLA and MDCHOICE. Geocarto International, /: https, 1061. [Google Scholar]
- Jenks, M. , & Burgess, R. Eds. (2000). Compact cities: sustainable urban forms for developing countries. London and New York: Spon Press. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:152608747.
- Jeroen, C.J.H. Aerts, Gerard, B.M., & Heuvelink (2002). Using simulated annealing for resource allocation. International Journal of Geographical Information Science, /: https, 1080. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X. , Jiang, P., Ma, D., & Li, M. (2019). Land system evolution of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau under various development strategies. Applied Geography, 104, 1–9.
- Kaim, A. , Cord, A.F., & Volk, M. (2018). A review of multi-criteria optimization techniques for agricultural land use allocation. Environmental Modelling and Software. [CrossRef]
- Kenworthy, J. , Fansler, D., & Newman, P. (1989). Cities and automobile dependence: An international sourcebook.
- Krehl, A. , Siedentop, S., Taubenböck, H., & Wurm, M. (2016). A Comprehensive View on Urban Spatial Structure: Urban Density Patterns of German City Regions. International Journal of Geo-Information, 5(76), pp. 1-21. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:1366807.
- Kumar, S.G. , and Panneerselevam, R. (2017). A study of crossover operators for genetic algorithm to solve VRP and its variants and new Sinusoidal Motion crossover operator. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Research, 1: 1717-1735. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID, 1717. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C. , Wu, Y., Gao, B., Zheng, K., Wu, Y., & Li, C. (2021). Multi-scenario simulation of ecosystem service value for optimization of land use in the Sichuan-Yunnan ecological barrier, China. Ecological Indicators. [CrossRef]
- Li, G. , Zhao, Z. ( 149(1), 1–14. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.X. , Ma, W.Y., & Xu, L. (2013). Land use structure optimization research based on the Markov chain in the west of Jilin province. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 1: https://api. semanticscholar.org/CorpusID, 1317. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X. , & Ma, X. (2017). An uncertain programming model for land use structure optimization to promote effectiveness of land use planning. ( 27(6), 974–988. [CrossRef]
- Li, X. , & Ma, X. (2018). An improved simulated annealing algorithm for interactive multi-objective land resource spatial allocation. Ecological Complexity. [CrossRef]
- Li, X. , Xu, H., Ma, X., & Huang, Y. (2023). A two-step spatially explicit optimization approach of integrating ecosystem services (ES) into land use planning (LUP) to generate the optimally sustainable schemes. Land Degradation and Development, 2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.T. , He, P. , Gao, X.S., Lin, Z.Y., Huang, C.Y., Zhou, W., Deng, O.P., Xu, C.H., & Deng, L.J. (2022). Land use optimization of rural production-living-ecological space at different scales based on the BP-ANN and CLUE-S models. Ecological Indicators, 2022, 137, 108710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligmann-Zielinska, A. , Church, R., & Jankowski, P. (2008). Spatial optimization as a generative technique for sustainable multiobjective land use allocation. ( 22(6), 601–622. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. , Yu, Y., Guo, H.., Yang, P. (2009). Optimal land use management for surface source water protection under uncertainty: a case study of Songhuaba watershed (Southwestern China). Water Resources Management, /; 2069–2083. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C. , Deng, C., Li, Z., Liu, Y., & Wang, S. (2022). Optimization of Spatial Pattern of Land Use: Progress, Frontiers, and Prospects. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. [CrossRef]
- Liu, G. , Jin, Q., Li, J., Li, L., He, C., Huang, Y., & Yao, Y. (2017). Policy factors impact analysis based on remote sensing data and the CLUE-S model in the Lijiang River Basin, China. CATENA. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. , Yan, F., & Tian, H. (2022). Towards low-carbon cities: Patch-based multi-objective optimization of land use allocation using an improved non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-II. Ecological Indicators, 34, 108455. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. , Ou, J., Li, X., & Ai, B. (2013). Combining system dynamics and hybrid particle swarm optimization for land use allocation. ( 257, 11–24. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. , Tang, W., He, J., Liu, Y., Ai, T., & Liu, D. (2014). A land use spatial optimization model based on genetic optimization and game theory. ( 49, 1–14. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longato, D. , Cortinovis, C., Albert, C., & Geneletti, D. (2021). Practical applications of ecosystem services in spatial planning: Lessons learned from a systematic literature review. Environmental Science & Policy. [CrossRef]
- Lu, S. S. , Zhou, M., Guan, X. L., & Tao, L. (2015). An integrated GIS-based interval-probabilistic programming model for land use planning management under uncertainty: a case study at Suzhou, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 22(6): 4281–4296. https://doi.10.1007/ s11356-014-3659-0.
- Ma, S. , Zhang, Y., & Sun, C. (2019). Optimization and Application of Integrated Land Use and Transportation Model in Small-and Medium-Sized Cities in China. Sustainability, 11(9) 2555. [CrossRef]
- Magalhaes-Mendes, J. (2013). A comparative study of crossover operators for genetic algorithms to solve the job shape scheduling problem. WSEAS Transactions Computations, 9: https://api. semanticscholar.org/CorpusID, 9217. [Google Scholar]
- Masnavi, M.R. (2000). The New Millennium and the New Urban Paradigm: The Compact City in Practice. In Achieving Sustainable Urban Form. Taylor Francis: London, UK, pp. 64–73.
- Masoumi, Z. & van Genderen, J. (2023). Artificial intelligence for sustainable development of smart cities and urban land use management. Geo-spatial Information Science. [CrossRef]
- Matthews, K.B. , Sibbald, A.R., & Craw, S. (1999). Implementation of a spatial decision support system for rural land use planning: Integrating geographic information system and environmental models with search and optimisation algorithms. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture. [CrossRef]
- Mehari, A. , and Genovese, Paolo. (2023). Modeling Global and Local Aspects of Spatial Structure Explicitly in land use Optimization: The Case of Mek’ele City, Ethiopia. Chinese Journal of Urban and Environmental Studies, /: 1-35. https, 1142. [Google Scholar]
- Memmah, M.M. , Lescourret, F. ( 35(3), 975–998. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M. , Cai, Guan, X., Tan, S., & Lu, S. (2015). A hybrid inexact optimization model for land use allocation of China. ( 25, 62–73. [CrossRef]
- Misevicius, A. , & Kilda, B. (2005). Comparison of crossover operators for the quadratic assignment problem. Information Technology and Control, 1: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID, 1409. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadyari, F. , Tavakoli, M., Zarandian, A., & Abdollahi, S. (2023). Optimization land use based on multi-scenario simulation of ecosystem service for sustainable landscape planning in a mixed urban - Forest watershed. Ecological Modelling. [CrossRef]
- Moher, D. , Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., & Altman, D. G. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Research Methods & Reporting, 1371. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, T. (2006). Monocentric versus polycentric models in urban economics. Kyoto Institute of Economic Research Kier discussion paper series No. 611. http://www.kier.kyoto-u.ac.jp/index.
- Nie, X.H. , Huang, G.H., Wang, D. && Li, H.L. (2008). Robust optimisation for inexact water quality management under uncertainty. Civil Engineering and Environmental Systems, 25(25): 167–184. https://doi.10.1080/10286600801908964.
- Ning, S. , Zhang, Z. N. ( 2019). Optimization of land use structure based on ecological service value in Manas River Basin. Acta Ecol. Sin. 39, 5208–5217.
- Otman, A. , and Jaafar, A. (2014). A comparative study of adaptive crossover for GA to resolve the travel salesman problem. International Journal of Computer Applications.
- Ou, D. , Zhang, Q., Tang a, H., Qin, J., Yu, D., Deng, O., Gao, X., & Liu, T. (2023). Ecological spatial intensive use optimization modeling with framework of cellular automata for coordinating ecological protection and economic development. Science of the Total Environment. [CrossRef]
- Pan, T. , Zhang, Y., Su, F., Lyne, V., Cheng, F., & Xiao, H. (2021). Practical Efficient Regional Land-Use Planning Using Constrained Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm Optimization. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(2), 100. [CrossRef]
- Paritosh, P. , Kalita, B. & Sharma, D. (2019). A game theory based land layout optimization of cities using genetic algorithm. International Journal of Management Science and Engineering Management, /: https, 1080. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, M.M. , & Szabó, G. (2021). Multi-objective urban land use optimization using spatial data: A systematic review. Sustainable Cities and Society, /: https, 1016. [Google Scholar]
- Randolph, J. (2004). Environmental Land Use Planning and Management.
- Reid, E. , Greenwald., M, Zhangm M., Walters, J., Feldman, M., Cervero, R., Frank, L., & Thomas, J. (2011). Traffic generated by mixed-use developments - Six-region study using consistent built environmental measures. Journal of Urban Planning and Development, /: https, 1061. [Google Scholar]
- Sajith, G. , Srinivas, R., Golberg, A., and Magner, J. (2022). Bio-inspired and artificial intelligence enabled hydro-economic model for diversified agricultural management. Agricultural Water Management. [CrossRef]
- Sdshu, W. , Wkh, H. ( 2008). Genetic algorithm for dynamic land use optimization. IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation, 3816–3821.
- Seppelt, R. , & Voinov, A. (2002). Optimization methodology for land use patterns using spatially explicit landscape models. In Ecological Modelling, 151. https://doi.10.1016/S0304-3800(01) 00455-0.
- Sharmin, T. (2011). A comparative study of sustainable urban forms: Compact city and short cycle strategy. AIUB Journal of Science and Engineering, /: 10(1), 1-9. https, 3135. [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds, D. & Coombe, D. (2000). The Transport Implication of Alternative Urban Form. In Achieving Sustainable Urban Form 2. Taylor Francis: London, UK, pp. 121–130.
- Snyder, H. (2019). Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of Business Research. [CrossRef]
- St. John, R., & Tóth, S.F. (2015). Spatially explicit forest harvest scheduling with difference equations. F. ( 232(1), 235–257. [CrossRef]
- Stead, D. , Williams, J., & Tifheridge, H. (2000). “Land Use, Transport and People: Identifying the Connections”. In Achieving Sustainable Urban Form, Taylor Francis: London, UK, pp. 174–186.
- Tayyebi, A. , & Pijanowski, B. C. (2014). Modeling multiple land use changes using ANN, CART and MARS: Comparing tradeoffs in goodness of fit and explanatory power of data mining tools. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation. [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H. , Tabeau, A., & Hatna, E. (2013).Assessing spatial uncertainties of land allocation using a scenario approach and sensitivity analysis: A study for land use in Europe. Journal of Environmental. Management, 127, S132–S144. [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H. , Soepboer, W., Veldkamp, A., Limpiada, R. & Espaldon, V. (2002). Modeling the spatial dynamics of regional land use: the CLUE-S model. Environmental Management. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. , Li, X., Zhang, Q., Li, J., & Zhou, X. (2018). Projections of future land use changes: Multiple scenarios-based impacts analysis on ecosystem services for Wuhan city, China. Ecological Indicators. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. , Han, Q., & De Vries, B. (2022). Land Use Spatial Optimization Using Accessibility Maps to Integrate Land Use and Transport in Urban Areas. ( 15(4), 1193–1217. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X. , Wang, S., Fu, B., Liu, Y., & Zhu, Y. (2018). Land use optimization based on ecosystem service assessment: A case study in the Yanhe watershed. Land Use Policy. [CrossRef]
- Yang, O. , & Hongyun, H. (2015). The study of the comparison of three crossover operators in genetic algorithm for solving single machine scheduling problem. In ICMSE, https://doi.10.2991/ icmse-15.2015.55.
- Yang, X. , Zheng, X. Q., & Lv, L. N. (2012). A spatiotemporal model of land use change based on ant colony optimization, Markov chain and cellular automata. N. ( 233, 11–19. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. , Zhu, X., & Moodie, D. R. (2015). Optimization of Land Use in a New Urban District. R. ( 141(2), 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Yao, J. , Zhang, X., & Murray, A. T. (2018). Spatial Optimization for land use Allocation: Accounting for Sustainability Concerns. International Regional Science Review. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M. , Liu, Y., He, J., & Liu, D. (2014). Regional land use allocation using a coupled MAS and GA model: From local simulation to global optimization, a case study in Caidian District, Wuhan, China. Cartography and Geographic Information Science. [CrossRef]
- 101. Zhang H H, Zeng Y N, & Bian L. (2010). Simulating multi-objective spatial optimization allocation of land use based on the integration of multi-agent system and genetic algorithm. International Journal of Environmental Research, 1766.
- Zhang, H. , Zeng, Y., Jin, X., Shu, B., Zhou, Y., & Yang, X. (2016). Simulating multi objective land use optimization allocation using Multi-agent system-A case study in Changsha, China. Ecological Modelling,. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.W. , Ke, X.L., Xiao, B.Y., & Zhou, T. (2019). Optimising land use allocation to balance ecosystem services and economic bene-fits - A case study in Wuhan, China. Journal of Environmental Management, 248, 109306. https://doi.0.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109306.
- Zheng, X.Q. , Zhao, L., Xiang, W.N., Li, N., Lv, L.N., &; Yang, X. (2012). A coupled model for simulating spatio-temporal dynamics of land use change: A case study in Changqing, Jinan, China. Landscape and Urban Planning. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W. , Gao, Y., Zhang, H., & Liu, L. (2020). Science of the Total Environment Optimization of the land use pattern in Horqin Sandy Land by using the CLUMondo model and Bayesian belief network. ( 739, 139929. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| [1] | |
| [2] | |
| [3] | |
| [4] |
| Ref. | Identified gap | Suggested direction/implication for |
| 2002 | Optimization methods are problem-dependent. No generalized behavior | Improve the efficiency of algorithms; Comparison of multiple scenarios |
| 2008 | Mismatch between optimization methods and planning perspective. I.e. assumption of determinate time | Intertemporal approach |
| Global optimization was implemented as general management. The problem still persists in urban land use problems | Detailing objectives to quantify resources | |
| 2015 | Coupling was not mature enough | Wide application and research |
| Limitations of local scale optimizers (game theory) applied independently | Hybridization with global optimizers | |
| 2017 | Determinate assumption of constraints | Modeling uncertainty |
| 2018 | Any trade-off is considered acceptable alternative | Minimizing magnitude of tradeoffs among objectives is a quality advantage |
| 2020 | Land use change driving factors are not considered. | Building probability of land use change factors into simulation |
| 2021 | Global optimizers lack layout capability while local optimizers lack structure capability | Coupling top-down and bottom-up becomes normative approach |
| 2023 | Spatial layout determined by local optimizers is affected by the historical trends of the land use change process | Spatial suitability analysis /horizontal process/ |
| Heterogeneity nature of spatial units providing ecosystem services is affected by the logical rule historical trend of the layout optimizers | Open |
| Author(s) | Geog. domain | Core content | Objectives | Method |
| Seppelt, et al (2002) | Watershed | ES based optimization under different land use management scenarios | Min. fertilizer use, Min. nutrient outflow and Max. economic yield | Monte Carlo; GA |
| Sadeghi et al. (2009) | Watershed | ES based optimization | Min. soil erosion and Max. Economic benefit | Simplex-LP |
| Jin, et al (2010) | Management farming | Temporal dimension of land use planning | Max. income | GA |
| Liu, et al (2015) | Urban-rural region | Coordination of land uses at local level | Max. Suitability of land for a certain use and Max. Compactness | GA; DyGT |
| Yang, et al (2015) | City | Residential choice model in land use planning | Max. Quality of life for workers and Max. Productivity of facilities | GA |
| Li and Ma (2017) | City | Uncertainty incorporation in land use planning | Max. GDP Ecological benefit (ESV) |
GA |
| Hadayanto, et al ((2017) | City | Zoning mechanism in land use planning | Max. Compactness; Max. Compactness; Max. Dependency; Max. suitability | PSO; GA; Local search |
| Zhu,et al (2020) | Large region | Land use change driving factors; Probability surface based land use optimization | Priority of land use type i | CLUMondo BBN |
| Wang, et al (2022) | City | Accessibility model in land use planning | Max. Accessibility; Max. Compactness; Max. Suitability | NSGA-II |
| Ligmann-Zielinska et al (2008) | City | Compact form of sustainable city concept in land use planning | Min. Open space development; Min. Redevelopment; Min. Distance of new development site; Max. compatibility | GIS-MOLA |
| Yang, et al (2012) | District of a city | Hybrid optimization method for modeling land use change | NA | Markov-CA; ACO-CA |
| Cao, et a (2012) | City | Efficiency of NSGA-II for implementation | Max. GDP; Max. Environmental benefit; Max. Ecological suitability; Max. Accessibility; Max. Compactness; Max. Compatibility; Min. Use conversion; Max. NIMBY |
NSGA-II |
| Wu, et al (2018) | Watershed | Effect of land use change over ES | Max. Agricultural production ; Max. Sediment retention ; Max. Carbon sequestration ; Max. Water quality; Max. sustainability of water production |
InVEST; Biophysical models |
| C Li, et al (2021) | Large region | Effect of land use change over ES | Economic benefits Max. ESV |
GMOP and PLUS |
| G Li, et al (2023a) | Large (rural + cities) | Application of hybrid methods for land use optimization | ESVs | DyMOO; CLUE-S; MCR |
| X Li, et al (2023b) | City region | Method of integrating ecological benefits into land use planning | ESVs Land use suitability |
MOOLP CLUE-S |
| Chen, et al (2023) | Urban agglomeration | Embedding land use optimization in ecological suitability | ESVs land use suitability |
MOLP; DyCLUE; MCR |
| Mohammedyari, et al (2023) | Urban region | Application of hybrid methods for land use optimization | Max. Farm production; Max. Water yield; Max. Habitat quality; Max. Sediment retention; Max. Recreational quality; Max. Aesthetic quality | SA-GA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




