Submitted:
18 September 2023
Posted:
20 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Biochemical Analysis
2.4. Relative Telomere Length Measurement
2.5. Western Blotting Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Effects of PC and NR on Body Weight and Biochemical Parameters
3.2. The Effects of PC and NR on Liver Nicotinamide Metabolites and GSH
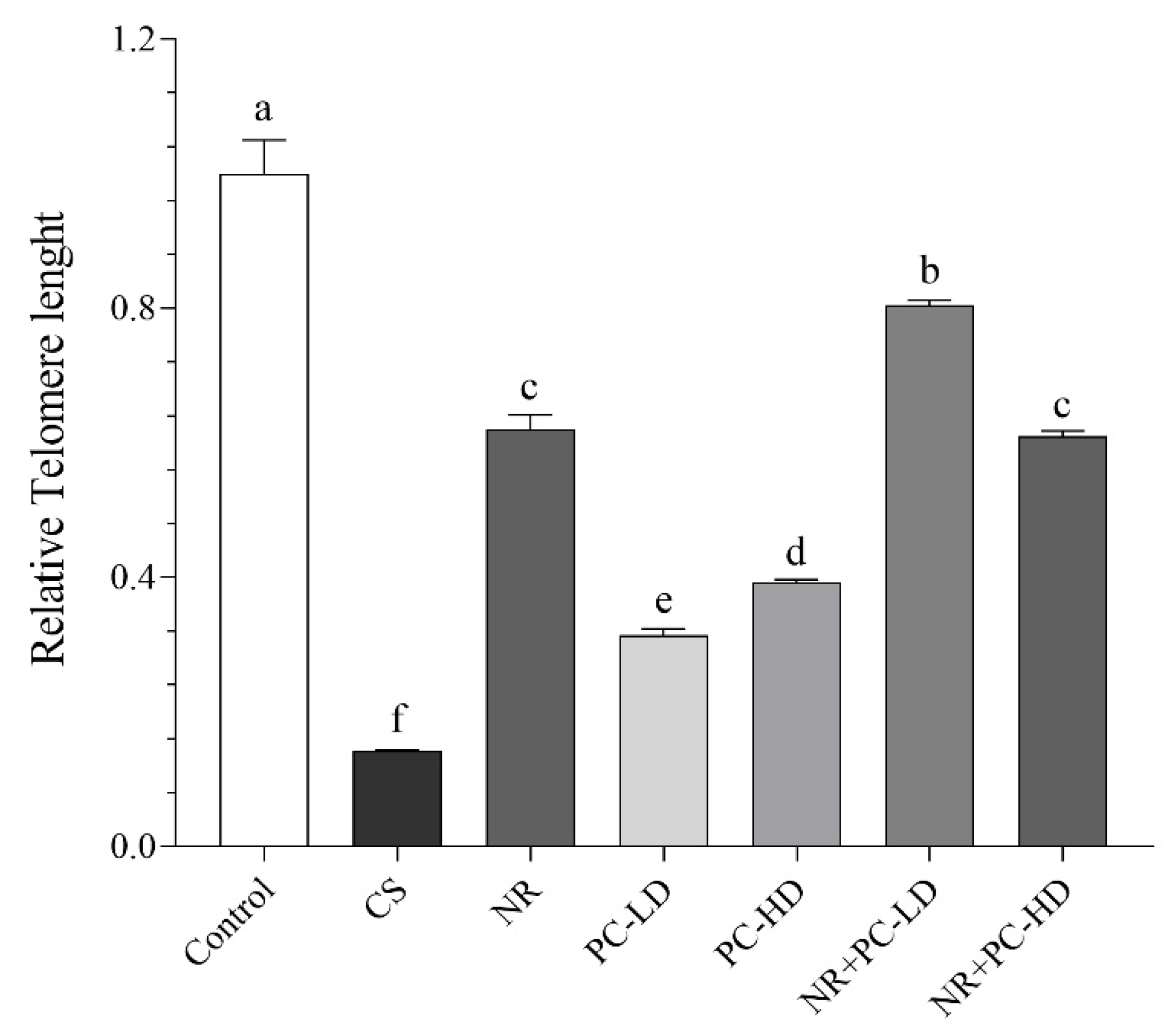
3.3. The Effects of PC and NR on Telomere Length
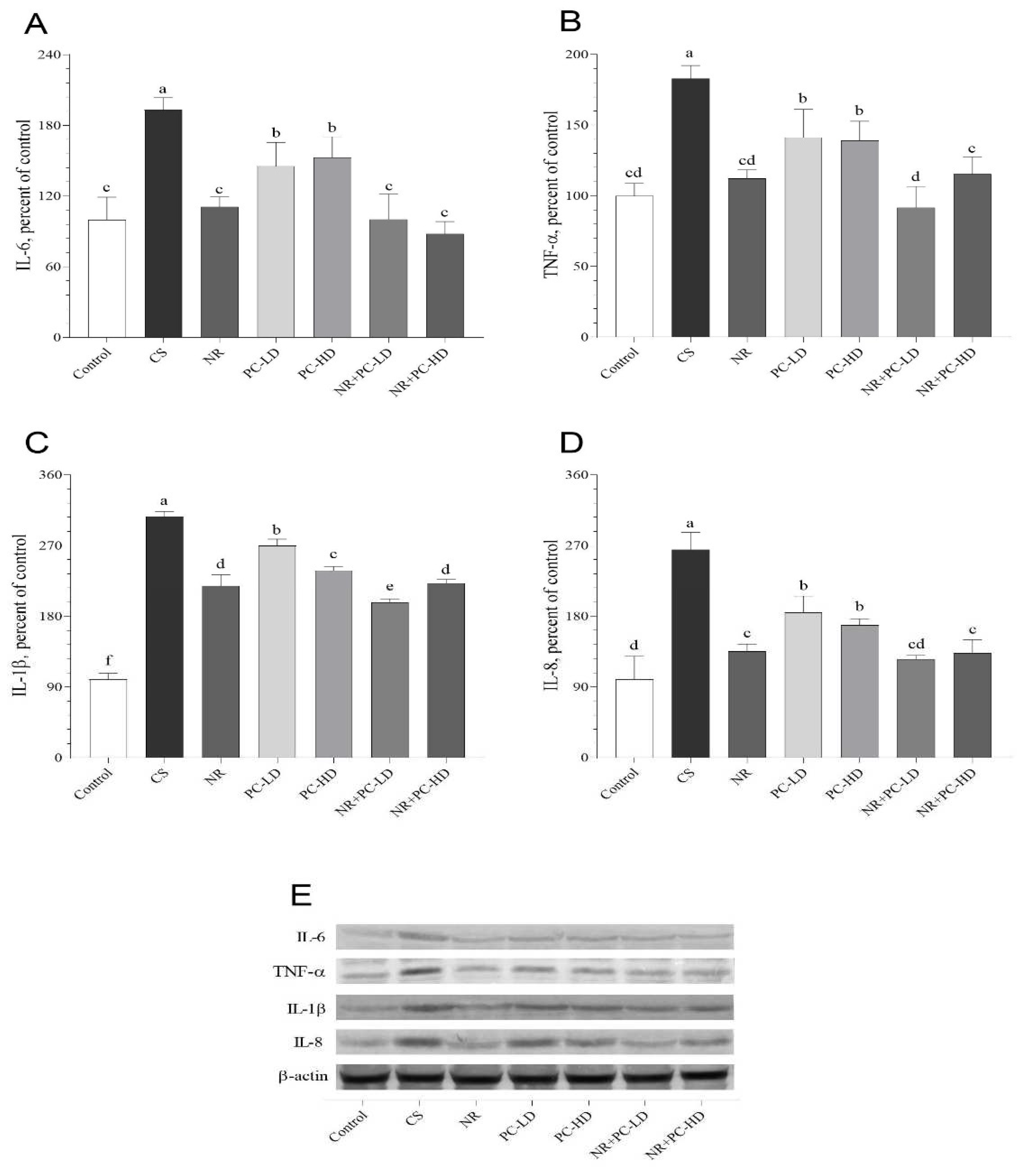
3.4. The Effects of PC and NR on İnflammatory Mediators
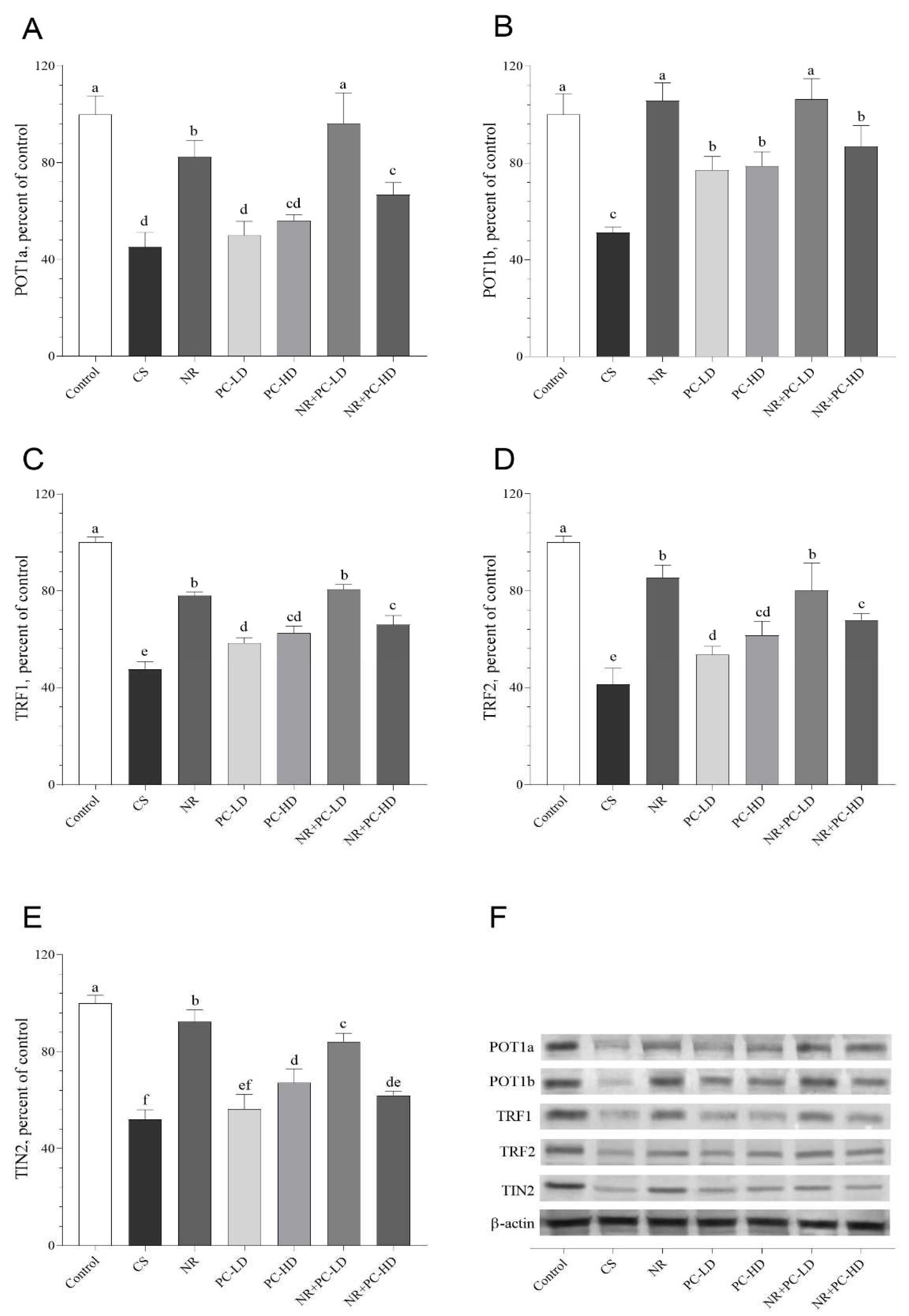
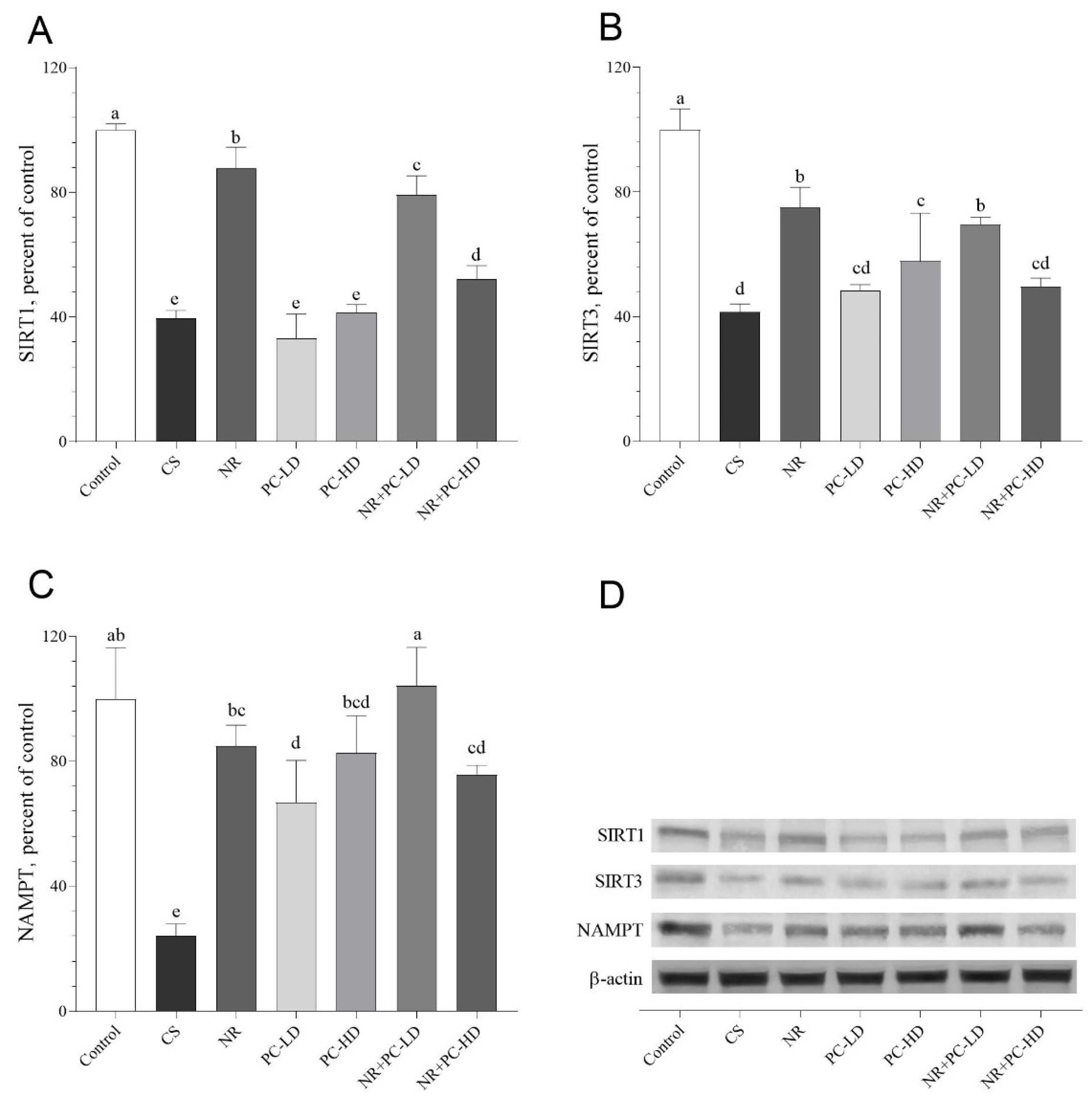
3.5. The Effects of PC and NR on Telomere Sheltering, SIRTs, and NAMPT
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhabhar, F.S. Effects of Stress on Immune Function: The Good, the Bad, and the Beautiful. Immunol Res 2014, 58, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, R.G.; Seligsohn, M.; Rubin, T.G.; Griffiths, B.B.; Ozdemir, Y.; Pfaff, D.W.; Datson, N.A.; McEwen, B.S. Stress and Corticosteroids Regulate Rat Hippocampal Mitochondrial DNA Gene Expression via the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2016, 113, 9099–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, S.J.; Batdorf, H.M.; Huang, T.-Y.; Jackson, J.W.; Jones, K.A.; Martin, T.M.; Rohli, K.E.; Karlstad, M.D.; Sparer, T.E.; Burk, D.H.; et al. One Week of Continuous Corticosterone Exposure Impairs Hepatic Metabolic Flexibility, Promotes Islet β-Cell Proliferation, and Reduces Physical Activity in Male C57BL/6 J Mice. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2019, 195, 105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiers, J.G.; Chen, H.-J.C.; Cuffe, J.S.M.; Sernia, C.; Lavidis, N.A. Acute Restraint Stress Induces Rapid Changes in Central Redox Status and Protective Antioxidant Genes in Rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 67, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiber, A.; Kröller-Schön, S.; Oelze, M.; Hahad, O.; Li, H.; Schulz, R.; Steven, S.; Münzel, T. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Contribute to Traffic Noise-Induced Vascular and Cerebral Dysfunction via Uncoupling of Nitric Oxide Synthases. Redox Biology 2020, 34, 101506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Botchway, B.O.A.; Hu, Z.; Fang, M. Overexpression of SIRT1 Inhibits Corticosterone-Induced Autophagy. Neuroscience 2019, 411, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caixeta, D.C.; Teixeira, R.R.; Peixoto, L.G.; Machado, H.L.; Baptista, N.B.; De Souza, A.V.; Vilela, D.D.; Franci, C.R.; Salmen Espindola, F. Adaptogenic Potential of Royal Jelly in Liver of Rats Exposed to Chronic Stress. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes-Silva, A.P.; Vieira, E.L.M.; Xavier, G.; Barroso, L.S.S.; Bertola, L.; Martins, E.A.R.; Brietzke, E.M.; Belangero, S.I.N.; Diniz, B.S. Telomere Shortening in Late-life Depression: A Potential Marker of Depression Severity. Brain and Behavior 2021, 11, e2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, I.; Russo, G.; Curcio, F.; Bulli, G.; Aran, L.; Della-Morte, D.; Gargiulo, G.; Testa, G.; Cacciatore, F.; Bonaduce, D.; et al. Oxidative Stress, Aging, and Diseases. CIA 2018, Volume 13, 757–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pole, A.; Dimri, M.; P. Dimri, G.; Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine, School of Medicine and Health Sciences, The George Washington University, Washington DC, USA Oxidative Stress, Cellular Senescence and Ageing. AIMS Molecular Science 2016, 3, 300–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, H.B.S.; Williams, C.; King, S.J.; Allison, S.J. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD+): Essential Redox Metabolite, Co-Substrate and an Anti-Cancer and Anti-Ageing Therapeutic Target. Biochemical Society Transactions 2020, 48, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Wang, K.; Stock, A.J.; Gong, Y.; Demarest, T.G.; Yang, B.; Giri, N.; Harrington, L.; Alter, B.P.; Savage, S.A.; et al. Re-equilibration of Imbalanced NAD Metabolism Ameliorates the Impact of Telomere Dysfunction. The EMBO Journal 2020, 39, e103420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantó, C.; Menzies, K.J.; Auwerx, J. NAD+ Metabolism and the Control of Energy Homeostasis: A Balancing Act between Mitochondria and the Nucleus. Cell Metabolism 2015, 22, 31–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Epel, E. Stress and Telomere Shortening: Insights from Cellular Mechanisms. Ageing Research Reviews 2022, 73, 101507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vannini, N.; Campos, V.; Girotra, M.; Trachsel, V.; Rojas-Sutterlin, S.; Tratwal, J.; Ragusa, S.; Stefanidis, E.; Ryu, D.; Rainer, P.Y.; et al. The NAD-Booster Nicotinamide Riboside Potently Stimulates Hematopoiesis through Increased Mitochondrial Clearance. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-J.; Han, Z.; Ge, L.; Zhou, C.-J.; Zhao, Y.-F.; Wang, D.-H.; Ren, J.; Niu, X.-X.; Liang, C.-G. C-Phycocyanin Protects against Low Fertility by Inhibiting Reactive Oxygen Species in Aging Mice. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 17393–17409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Sonani, R.R.; Awasthi, A.; Prasad, B.; Patel, A.R.; Kumar, J.; Madamwar, D. Phycocyanin Moderates Aging and Proteotoxicity in Caenorhabditis Elegans. J Appl Phycol 2016, 28, 2407–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, W.; Qin, S. Therapeutic Effect of Phycocyanin on Acute Liver Oxidative Damage Caused by X-Ray. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2020, 130, 110553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komorowski, J.; Bernsley, D.; Sylla, S.; Ojalvo, S.P. Enhanced Antioxidant Activity of Phycocyanin Oligopeptides. Current Developments in Nutrition 2021, 5, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 20. Jang-Woo Shin; In-Chan Seol; Chang-Gue Son; Jang-Woo Shin; In-Chan Seol; Chang-Gue Son Interpretation of Animal Dose and Human Equivalent Dose for Drug Development. Journal of Korean Medicine 31.
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A Flexible Statistical Power Analysis Program for the Social, Behavioral, and Biomedical Sciences. Behavior Research Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, M.; Wang, Y.; Li, B. Antidepressant Effect of Catalpol on Corticosterone-Induced Depressive-like Behavior Involves the Inhibition of HPA Axis Hyperactivity, Central Inflammation and Oxidative Damage Probably via Dual Regulation of NF-κB and Nrf2. Brain Research Bulletin 2021, 177, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Shen, Q.; Yang, S.; Xie, X.; Xiao, Q.; Yu, C.; Cao, L.; Fu, Z. Effect of Chronic Corticosterone-Induced Depression on Circadian Rhythms and Age-Related Phenotypes in Mice. ABBS 2018, 50, 1236–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Shen, Q.; Ma, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Fu, Z. Chronic Corticosterone-Induced Depression Mediates Premature Aging in Rats. Journal of Affective Disorders 2018, 229, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chini, C.C.S.; Tarragó, M.G.; Chini, E.N. NAD and the Aging Process: Role in Life, Death and Everything in Between. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 2017, 455, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Zhang, L.; Gao, W.; Huang, C.; Huber, P.E.; Zhou, X.; Li, C.; Shen, G.; Zou, B. NAD+ Metabolism: Pathophysiologic Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Sig Transduct Target Ther 2020, 5, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xue, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Emerging Roles of Sirtuins in Alleviating Alcoholic Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Review. International Immunopharmacology 2022, 108, 108712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garten, A.; Schuster, S.; Penke, M.; Gorski, T.; De Giorgis, T.; Kiess, W. Physiological and Pathophysiological Roles of NAMPT and NAD Metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2015, 11, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, A.J.; Liu, Y. NAD-Linked Metabolism and Intervention in Short Telomere Syndromes and Murine Models of Telomere Dysfunction. Front. Aging 2021, 2, 785171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhassan, Y.S.; Kluckova, K.; Fletcher, R.S.; Schmidt, M.S.; Garten, A.; Doig, C.L.; Cartwright, D.M.; Oakey, L.; Burley, C.V.; Jenkinson, N.; et al. Nicotinamide Riboside Augments the Aged Human Skeletal Muscle NAD+ Metabolome and Induces Transcriptomic and Anti-Inflammatory Signatures. Cell Reports 2019, 28, 1717–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, L.; Ni, R.; Wang, G.; Fan, G.-C.; Lu, Z.; Peng, T. Administration of Nicotinamide Riboside Prevents Oxidative Stress and Organ Injury in Sepsis. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2018, 123, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Feng, J.; Lin, X.; Liu, J.; Tang, Y.; Nie, S.; Gong, J.; Wang, L. Nicotinamide Riboside Alleviates Cardiac Dysfunction and Remodeling in Pressure Overload Cardiac Hypertrophy. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussein, M.M.A.; Ali, H.A.; Ahmed, M.M. Ameliorative Effects of Phycocyanin against Gibberellic Acid Induced Hepatotoxicity. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology 2015, 119, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Rojas, B.; Rodríguez-Rangel, D.S.; Granados-Castro, L.F.; Negrette-Guzmán, M.; León-Contreras, J.C.; Hernández-Pando, R.; Molina-Jijón, E.; Reyes, J.L.; Zazueta, C.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J. C-Phycocyanin Prevents Cisplatin-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress. Mol Cell Biochem 2015, 406, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Yan, Y.; Huang, W.; Gai, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, C. C-Phycocyanin Reduces Inflammation by Inhibiting NF-κB Activity through Downregulating PDCD5 in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Journal of Functional Foods 2018, 42, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, W.; Lu, L.; Liu, B.; Du, Z.; Qin, S. Phycocyanin Attenuates X-Ray-Induced Pulmonary Inflammation via the TLR2-MyD88-NF-κB Signaling Pathway. J. Ocean. Limnol. 2019, 37, 1678–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarty, M.F.; Barroso-Aranda, J.; Contreras, F. Oral Phycocyanobilin May Diminish the Pathogenicity of Activated Brain Microglia in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Medical Hypotheses 2010, 74, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Ma, Q.; Xu, M.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Bi, Y.; Tang, M. Ginsenoside Rb1 Attenuates High Glucose-Induced Oxidative Injury via the NAD-PARP-SIRT Axis in Rat Retinal Capillary Endothelial Cells. IJMS 2019, 20, 4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Yu, J.; Fan, R.; Zhang, C.; Xu, L.; Sun, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ruan, H.-B.; Qian, X. NAMPT Overexpression Alleviates Alcohol-Induced Hepatic Steatosis in Mice. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Chellappa, K.; Moffitt, A.; Ndungu, J.; Dellinger, R.W.; Davis, J.G.; Agarwal, B.; Baur, J.A. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Biosynthesis Promotes Liver Regeneration. Hepatology 2017, 65, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Xie, Z.; Cao, D.; Gong, M.; Yang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Ou, Y. C-Phycocyanin Inhibits Hepatic Gluconeogenesis and Increases Glycogen Synthesis via Activating Akt and AMPK in Insulin Resistance Hepatocytes. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 2829–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanez, M.; Jhanji, M.; Murphy, K.; Gower, R.M.; Sajish, M.; Jabbarzadeh, E. Nicotinamide Augments the Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Resveratrol through PARP1 Activation. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 10219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Wu, J.; Ni, Y.; Xie, X.; Yu, C.; Xiao, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Fu, Z. Exposure to Jet Lag Aggravates Depression-like Behaviors and Age-Related Phenotypes in Rats Subject to Chronic Corticosterone. ABBS 2019, 51, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKerlie, M.; Zhu, X.-D. Cyclin B-Dependent Kinase 1 Regulates Human TRF1 to Modulate the Resolution of Sister Telomeres. Nat Commun 2011, 2, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badmus, K.A.; Idrus, Z.; Meng, G.Y.; Sazili, A.Q.; Mamat-Hamidi, K. Telomere Length and Regulatory Genes as Novel Stress Biomarkers and Their Diversities in Broiler Chickens (Gallus Gallus Domesticus) Subjected to Corticosterone Feeding. Animals 2021, 11, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lange, T. Shelterin: The Protein Complex That Shapes and Safeguards Human Telomeres. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2100–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coluzzi, E.; Leone, S.; Sgura, A. Oxidative Stress Induces Telomere Dysfunction and Senescence by Replication Fork Arrest. Cells 2019, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, N.; Rachakonda, S.; Kumar, R. Telomeres and Telomere Length: A General Overview. Cancers 2020, 12, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, A.M.; Strong, M.A.; Ouyang, J.P.T.; Greider, C.W. TIN2 Functions with TPP1/POT1 To Stimulate Telomerase Processivity. Molecular and Cellular Biology 2019, 39, e00593–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.-J.; Zhou, W.; Guo, J.; Nie, Z.-W.; Shin, K.-T.; Kim, N.-H.; Lv, W.-F.; Cui, X.-S. C-Phycocyanin Protects against Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Parthenogenetic Porcine Embryos. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 16992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, F.; Branka, J.-E.; Darnis, E.; Lefeuvre, L. Telomere Protective Effects of a Cyanobacteria Phycocyanin against Blue Light and UV Irradiations: A Skin Anti-Aging and Photo-Protective Agent. JCDSA 2019, 09, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikalova, A.E.; Pandey, A.; Xiao, L.; Arslanbaeva, L.; Sidorova, T.; Lopez, M.G.; Billings, F.T.; Verdin, E.; Auwerx, J.; Harrison, D.G.; et al. Mitochondrial Deacetylase Sirt3 Reduces Vascular Dysfunction and Hypertension While Sirt3 Depletion in Essential Hypertension Is Linked to Vascular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Circ Res 2020, 126, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, V.; Cornelius, C.; Trovato-Salinaro, A.; Cambria, M.; Locascio, M.; Rienzo, L.; Condorelli, D.; Mancuso, C.; De Lorenzo, A.; Calabrese, E. The Hormetic Role of Dietary Antioxidants in Free Radical-Related Diseases. CPD 2010, 16, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Groups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | CS | NR | PC-LD | PC-HD | NR+PC-LD | NR+PC-HD | |
| Final BW, g | 276.57±9.85a | 210.43±8.28b | 222.86±23.11b | 221.29±11.25b | 221.86±9.92b | 225.14±13.23b | 217.86±19.42b |
| Glucose, mg/dL | 119.14±8.43ab | 127.86±5.05a | 119.86±7.10ab | 118.57±2.64abc | 114.14±5.24bc | 109.29±5.47c | 118.29±4.68bc |
| Creatine, mg/dL | 0.40±0.06 | 0.38±0.07 | 0.37±0.08 | 0.40±0.08 | 0.39±0.06 | 0.36±0.09 | 0.45±0.05 |
| BUN, mg/dL | 21.46±3.57 | 23.01±2.32 | 22.90±1.87 | 22.13±2.52 | 21.59±3.00 | 22.20±4.11 | 23.17±3.65 |
| ALT, U/L | 95.57±8.42 | 98.14±12.81 | 98.00±5.55 | 98.71±6.82 | 98.03±7.36 | 96.10±5.78 | 98.72±4.79 |
| AST, U/L | 110.69±11.79 | 117.46±7.53 | 114.71±10.92 | 112.60±13.13 | 117.43±15.25 | 114.06±12.59 | 116.20±19.06 |
| Groups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | CS | NR | PC-LD | PC-HD | NR+PC-LD | NR+PC-HD | |
| Corticosterone, ng/ml | 46.33±5.82b | 110.22±6.15a | 102.16±8.68a | 104.48±3.67a | 105.91±6.39a | 105.46±8.13a | 104.99±5.34a |
| MDA, nmol/ml | 0.55±0.07f | 1.97±0.13a | 1.74±0.07b | 1.53±0.07c | 1.41±0.07cd | 1.26±0.07e | 1.28±0.09de |
| SOD, U/ml | 128.00±5.48a | 54.54±6.39e | 61.36±4.5e | 72.70±3.05d | 86.41±6.34c | 96.84±6.77b | 98.27±4.65b |
| GSH-Px, U/ml | 64.87±3.08a | 19.62±1.37e | 26.28±1.98d | 31.76±4.96cd | 37.10±2.80c | 44.68±5.58b | 45.98±4.10b |
| CAT, U/ml | 164.98±6.13a | 102.03±4.80e | 114.69±4.82d | 124.55±5.48c | 131.43±3.76bc | 140.55±6.76b | 139.05±7.81b |
| Groups | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | CS | NR | PC-LD | PC-HD | NR+PC-LD | NR+PC-HD | |
| NAD+, µmol/g | 0.76±0.05a | 0.33±0.04f | 0.59±0.04c | 0.42±0.05e | 0.49±0.06de | 0.67±0.05b | 0.55±0.06cd |
| NAM, µmol/g | 2.36±0.15a | 1.01±0.08e | 1.60±0.06c | 1.31±0.09d | 1.43±0.13d | 1.78±0.10b | 1.66±0.10cb |
| NA, µmol/g | 1.79±0.09a | 1.22±0.12d | 1.63±0.09abc | 1.46±0.10c | 1.57±0.17bc | 1.71±0.13ab | 1.73±0.12ab |
| NMN, µmol/g | 0.45±0.05a | 0.15±0.02e | 0.30±0.02bc | 0.20±0.02de | 0.24±0.03cd | 0.36±0.05b | 0.32±0.07b |
| NADPH, nmol/g | 62.65±4.13a | 30.84±3.52e | 44.42±2.31c | 39.88±3.04cd | 41.38±3.57cd | 52.52±5.39b | 37.89±2.23d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





