Submitted:
01 February 2024
Posted:
02 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
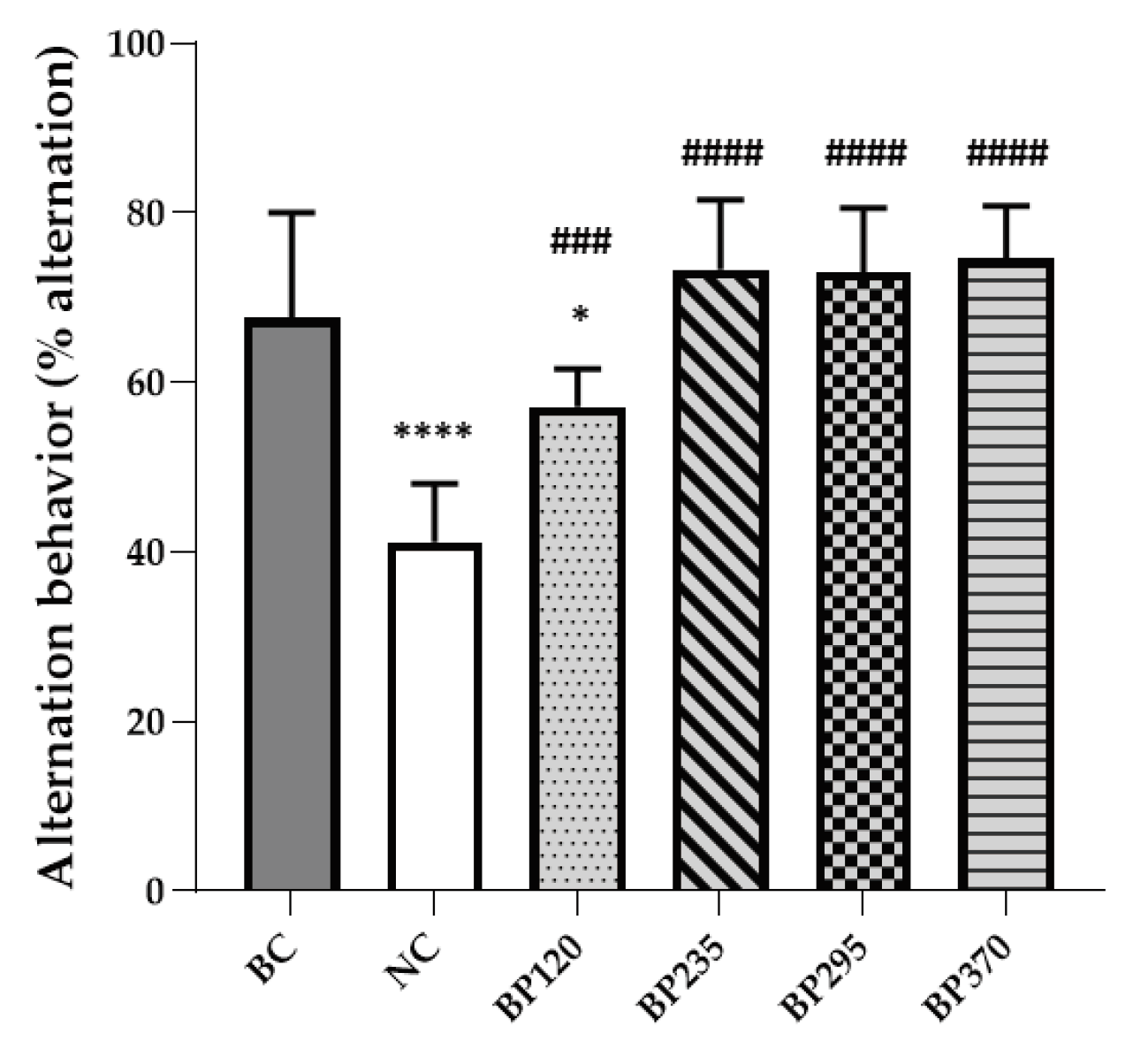
2.1. Effect on Y-Maze spontaneous alternation per
2.1.1. Y-Maze spontaneous alternation performance
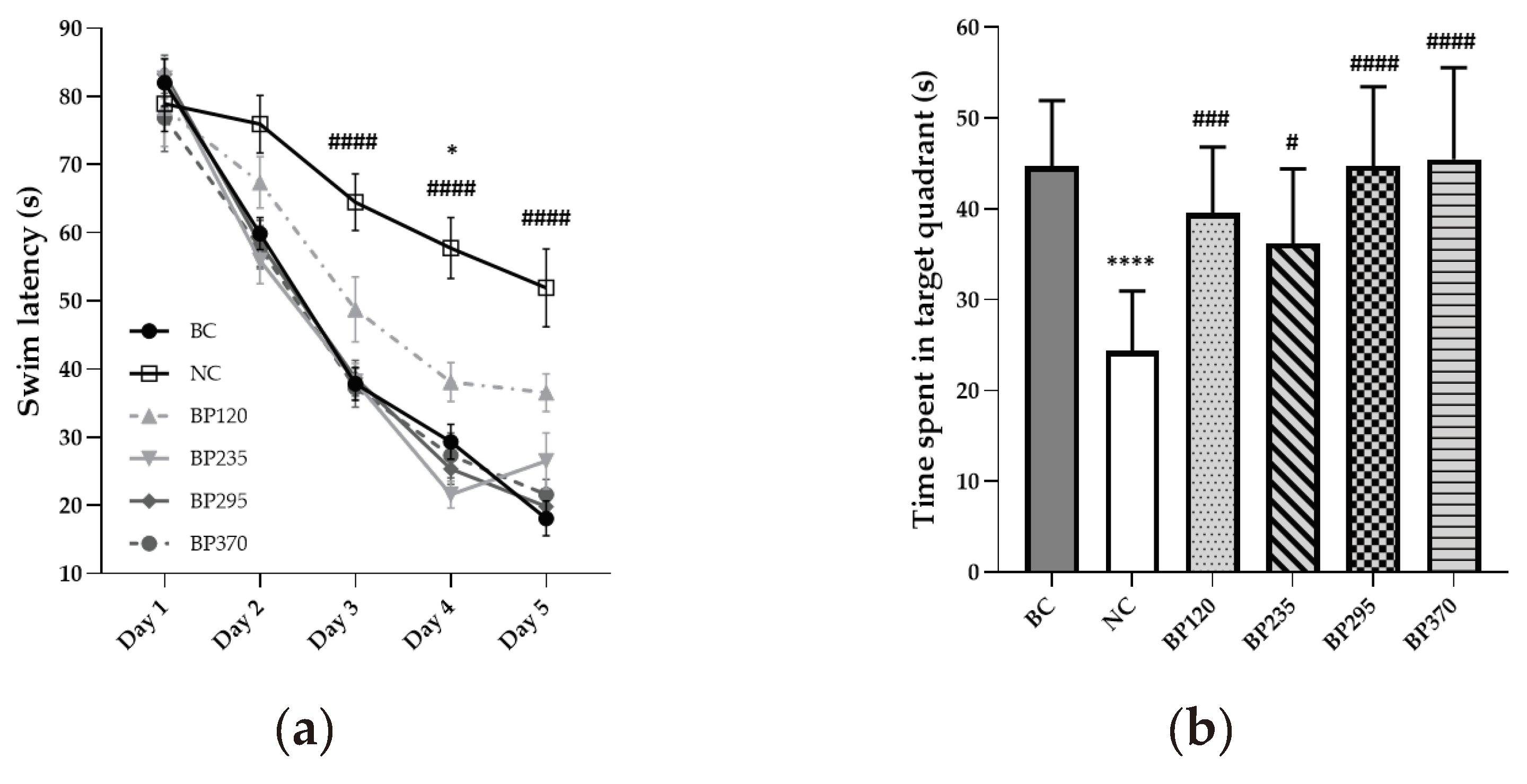
2.1.2. Place learning in the Morris Water-Maze
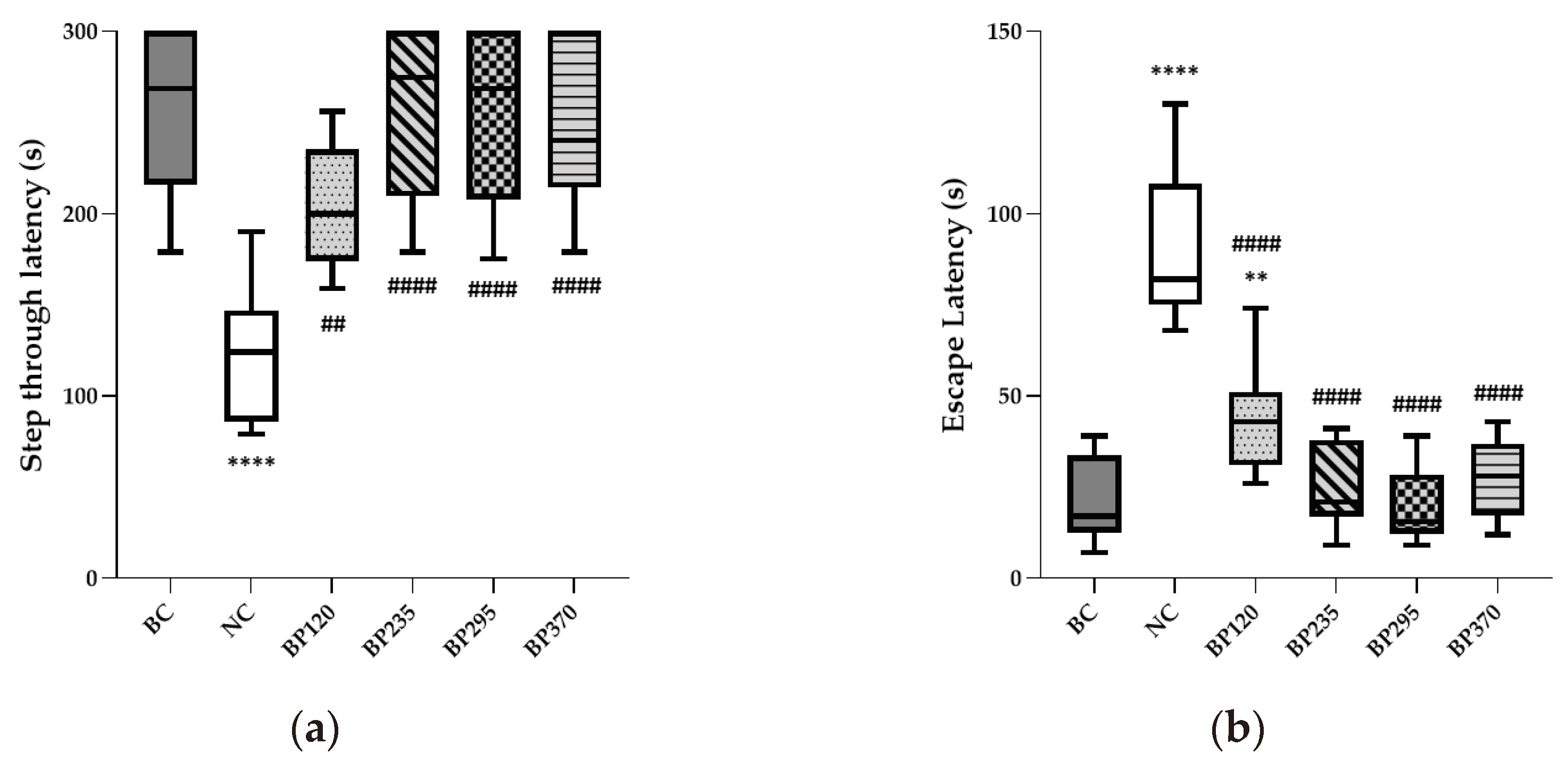
2.1.3. Passive avoidance test
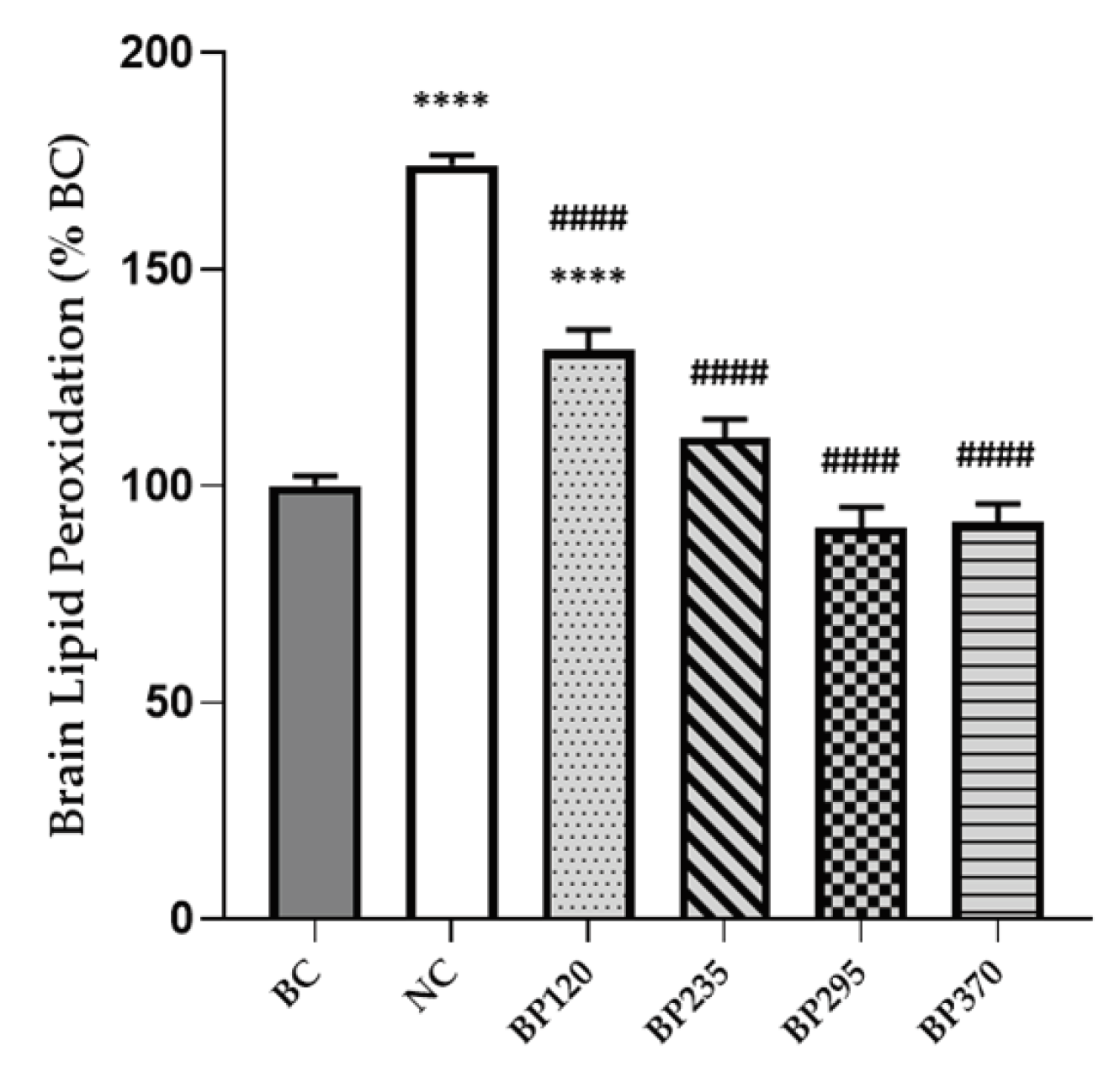
2.2. Effect on brain lipid peroxidation level
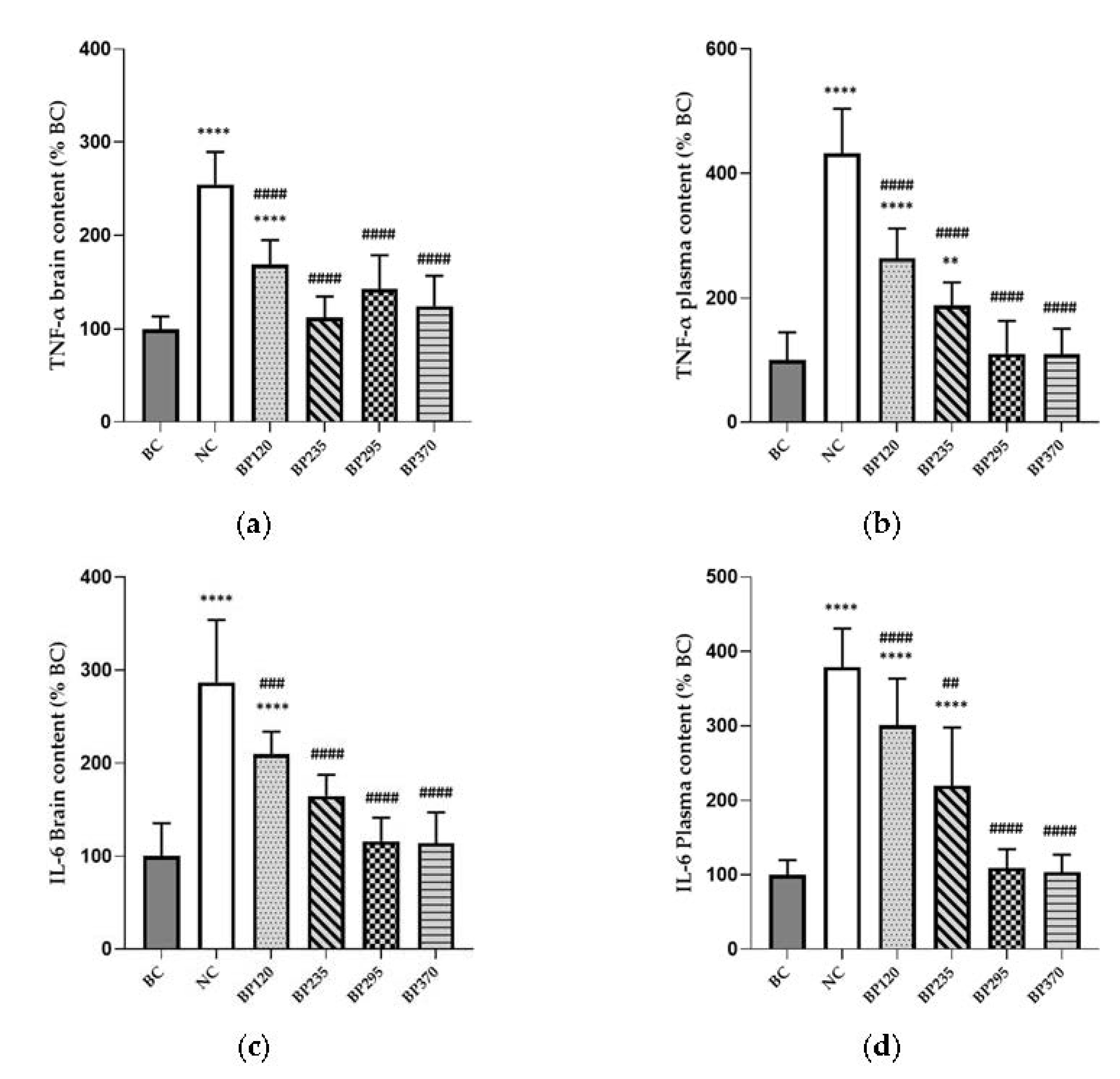
2.3. Effect on brain and plasma inflammatory markers level
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals, diet and treatment groups
4.2. Microalgae extract of PT production and characterization
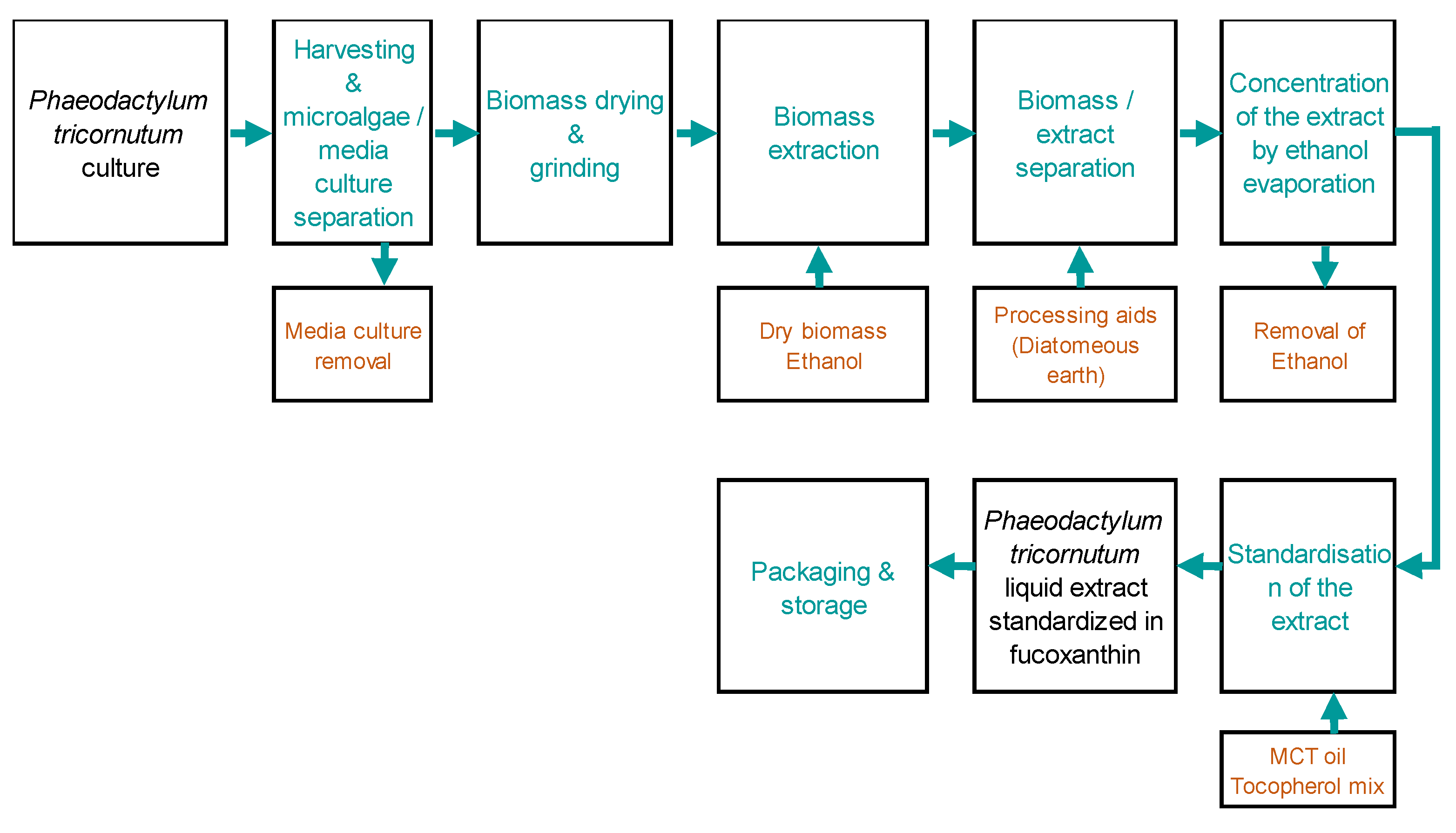
| Composition (%) | |
|---|---|
| Phaeodactylum tricornutum extract | 40 – 70 (w:w) |
| MCT oil based on coconut oil | 30 – 60 (w:w) |
| Mix on non-GMO tocopherols | 0.45 – 0.55 (w:w) |
| Total lipids | 60 – 90 (w:w) |
| Proteins | 5 – 15 (w:w) |
| Humidity | <2 (w:w) |
| Ashes | <10 (w:w) |
| Carbohydrates | 0.5 – 20 (w:w) |
| Total PUFAs-w3 | ≥4 (w:w) |
| All-trans-fucoxanthin | 2.0 ± 0.4% (w:w) |
4.3. Y-Maze spontaneous alternation performance
4.4. Place learning in the Morris Water-Maze
4.5. Passive avoidance test
4.6. Biochemical analysis
4.7. Statistical analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Population Prospects, the 2012 Revision; 2013.
- Salthouse, T. Consequences of Age-Related Cognitive Declines. Annu Rev Psychol 2012, 63, 201–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salthouse, T.A. When Does Age-Related Cognitive Decline Begin? Neurobiol Aging 2009, 30, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh-Manoux, A.; Kivimaki, M.; Glymour, M.M.; Elbaz, A.; Berr, C.; Ebmeier, K.P.; Ferrie, J.E.; Dugravot, A. Timing of Onset of Cognitive Decline: Results from Whitehall II Prospective Cohort Study. BMJ 2012, 344, d7622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedden, T.; Gabrieli, J.D.E. Insights into the Ageing Mind: A View from Cognitive Neuroscience. Nat Rev Neurosci 2004, 5, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freemantle, E.; Vandal, M.; Tremblay-Mercier, J.; Tremblay, S.; Blachère, J.-C.; Bégin, M.E.; Brenna, J.T.; Windust, A.; Cunnane, S.C. Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Energy Substrates, and Brain Function during Aging. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2006, 75, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andlin-Sobocki, P.; Jönsson, B.; Wittchen, H.-U.; Olesen, J. Cost of Disorders of the Brain in Europe. Eur J Neurol 2005, 12 Suppl 1, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, C.N.; Natelson Love, M.C.; Triebel, K.L. Normal Cognitive Aging. Clin Geriatr Med 2013, 29, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarmeas, N.; Anastasiou, C.A.; Yannakoulia, M. Nutrition and Prevention of Cognitive Impairment. Lancet Neurol 2018, 17, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tönnies, E.; Trushina, E. Oxidative Stress, Synaptic Dysfunction, and Alzheimer’s Disease. J Alzheimers Dis 2017, 57, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrattan, A.M.; McGuinness, B.; McKinley, M.C.; Kee, F.; Passmore, P.; Woodside, J.V.; McEvoy, C.T. Diet and Inflammation in Cognitive Ageing and Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr Nutr Rep 2019, 8, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Vorburger, R.; Scarmeas, N.; Luchsinger, J.A.; Manly, J.J.; Schupf, N.; Mayeux, R.; Brickman, A.M. Circulating Inflammatory Biomarkers in Relation to Brain Structural Measurements in a Non-Demented Elderly Population. Brain Behav Immun 2017, 65, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swomley, A.M.; Butterfield, D.A. Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment: Evidence from Human Data Provided by Redox Proteomics. Arch Toxicol 2015, 89, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valls-Pedret, C.; Sala-Vila, A.; Serra-Mir, M.; Corella, D.; de la Torre, R.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Martínez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Fitó, M.; Pérez-Heras, A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; et al. Mediterranean Diet and Age-Related Cognitive Decline: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern Med 2015, 175, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, T.J.; Katuwal, S.; Anderson, G.A.; Gu, L.; Zhou, R.; Gibbons, W.R. Photobioreactor Cultivation Strategies for Microalgae and Cyanobacteria. Biotechnol Prog 2018, 34, 811–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delbrut, A.; Albina, P.; Lapierre, T.; Pradelles, R.; Dubreucq, E. Fucoxanthin and Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Co-Extraction by a Green Process. Molecules 2018, 23, E874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, N.; Vandal, M.; Calon, F. The Benefit of Docosahexaenoic Acid for the Adult Brain in Aging and Dementia. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2015, 92, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurko-Mauro, K.; McCarthy, D.; Rom, D.; Nelson, E.B.; Ryan, A.S.; Blackwell, A.; Salem, N.; Stedman, M. MIDAS Investigators Beneficial Effects of Docosahexaenoic Acid on Cognition in Age-Related Cognitive Decline. Alzheimers Dement 2010, 6, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, E.; Batool, R.; Akhtar, W.; Rehman, S.; Shahzad, T.; Malik, A.; Shariati, M.A.; Laishevtcev, A.; Plygun, S.; Heydari, M.; et al. Xanthophyll: Health Benefits and Therapeutic Insights. Life Sci 2020, 240, 117104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Chen, W.; Tian, F.; Yuan, C.; Wang, H.; Yue, H. Neuroprotective Role of Fucoxanthin against Cerebral Ischemic/Reperfusion Injury through Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 2018, 106, 1484–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Cheng, W.; Liu, T. Combined Production of Fucoxanthin and EPA from Two Diatom Strains Phaeodactylum Tricornutum and Cylindrotheca Fusiformis Cultures. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 2018, 41, 1061–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minghetti, L.; Salvi, R.; Lavinia Salvatori, M.; Ajmone-Cat, M.A.; De Nuccio, C.; Visentin, S.; Bultel-Poncé, V.; Oger, C.; Guy, A.; Galano, J.-M.; et al. Nonenzymatic Oxygenated Metabolites of α-Linolenic Acid B1- and L1-Phytoprostanes Protect Immature Neurons from Oxidant Injury and Promote Differentiation of Oligodendrocyte Progenitors through PPAR-γ Activation. Free Radic Biol Med 2014, 73, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotuhi, M.; Mohassel, P.; Yaffe, K. Fish Consumption, Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Risk of Cognitive Decline or Alzheimer Disease: A Complex Association. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2009, 5, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyall, S.C. Long-Chain Omega-3 Fatty Acids and the Brain: A Review of the Independent and Shared Effects of EPA, DPA and DHA. Front Aging Neurosci 2015, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Li, L.; Song, Q.; Ai, H.; Chu, J.; Li, W. Behavioural Study of the D-Galactose Induced Aging Model in C57BL/6J Mice. Behav Brain Res 2005, 157, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shan, Q.; Ma, D. Purple Sweet Potato Color Repairs D-Galactose-Induced Spatial Learning and Memory Impairment by Regulating the Expression of Synaptic Proteins. Neurobiol Learn Mem 2008, 90, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimmig, B.; Hudson, C.; Moss, L.; Peters, M.; Subbarayan, M.; Weeber, E.J.; Bickford, P.C. Astaxanthin Supplementation Modulates Cognitive Function and Synaptic Plasticity in Young and Aged Mice. Geroscience 2019, 41, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yook, J.S.; Okamoto, M.; Rakwal, R.; Shibato, J.; Lee, M.C.; Matsui, T.; Chang, H.; Cho, J.Y.; Soya, H. Astaxanthin Supplementation Enhances Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Spatial Memory in Mice. Mol Nutr Food Res 2016, 60, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farr, S.A.; Niehoff, M.L.; Ceddia, M.A.; Herrlinger, K.A.; Lewis, B.J.; Feng, S.; Welleford, A.; Butterfield, D.A.; Morley, J.E. Effect of Botanical Extracts Containing Carnosic Acid or Rosmarinic Acid on Learning and Memory in SAMP8 Mice. Physiol Behav 2016, 165, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmeguid, N.E.; Khalil, M.I.M.; Elhabet, R.; Sultan, A.S.; Salam, S.A. Combination of Docosahexaenoic Acid and Ginko Biloba Extract Improves Cognitive Function and Hippocampal Tissue Damages in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J Chem Neuroanat 2021, 116, 101995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Sun, J.; Xu, D.; Xie, H.; Ye, M.; Zhao, Y. A Dietary Supplement Containing Micronutrients, Phosphatidylserine, and Docosahexaenoic Acid Counteracts Cognitive Impairment in D-Galactose-Induced Aged Rats. Frontiers in Nutrition 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Gao, Z.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Teng, H.; Hou, L.; Yin, Y.; Zou, X. Protective Effects of Fucoidan on Aβ25–35 and d-Gal-Induced Neurotoxicity in PC12 Cells and d-Gal-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction in Mice. Mar Drugs 2017, 15, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Xuan, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yan, S.; Zhou, D.; Naman, C.B.; Zhang, J.; He, S.; Yan, X.; Cui, W. Fucoxanthin Has Potential for Therapeutic Efficacy in Neurodegenerative Disorders by Acting on Multiple Targets. Nutritional Neuroscience 2022, 25, 2167–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Kukreti, R.; Saso, L.; Kukreti, S. Oxidative Stress: A Key Modulator in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Molecules 2019, 24, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andronie-Cioara, F.L.; Ardelean, A.I.; Nistor-Cseppento, C.D.; Jurcau, A.; Jurcau, M.C.; Pascalau, N.; Marcu, F. Molecular Mechanisms of Neuroinflammation in Aging and Alzheimer’s Disease Progression. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.M.; Hill, K.E.; Burk, R.F.; Weeber, E.J. Altered Hippocampus Synaptic Function in Selenoprotein P Deficient Mice. Molecular Neurodegeneration 2006, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, L.; Vizi, E.S.; Sperlágh, B. P2X7 Receptor Mediated Phosphorylation of p38MAP Kinase in the Hippocampus. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2007, 355, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, F.; Taniyama, Y.; Muratsu, J.; Otsu, R.; Shimizu, H.; Rakugi, H.; Morishita, R. Source of Chronic Inflammation in Aging. Front Cardiovasc Med 2018, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobylarek, D.; Iwanowski, P.; Lewandowska, Z.; Limphaibool, N.; Szafranek, S.; Labrzycka, A.; Kozubski, W. Advances in the Potential Biomarkers of Epilepsy. Front Neurol 2019, 10, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koyama, A.; O’Brien, J.; Weuve, J.; Blacker, D.; Metti, A.L.; Yaffe, K. The Role of Peripheral Inflammatory Markers in Dementia and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2013, 68, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Processes: From Molecules to Man. Biochem Soc Trans 2017, 45, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Ding, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Fucoxanthin Provides Neuroprotection in Models of Traumatic Brain Injury via the Nrf2-ARE and Nrf2-Autophagy Pathways. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 46763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Liu, F.; Lin, J.; Chen, H.; Huang, C.; Chen, L.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, L.; Zhang, K.; Jin, J.; et al. Fucoxanthin Inhibits β-Amyloid Assembly and Attenuates β-Amyloid Oligomer-Induced Cognitive Impairments. J Agric Food Chem 2017, 65, 4092–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-N.; Heo, S.-J.; Yoon, W.-J.; Kang, S.-M.; Ahn, G.; Yi, T.-H.; Jeon, Y.-J. Fucoxanthin Inhibits the Inflammatory Response by Suppressing the Activation of NF-κB and MAPKs in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol 2010, 649, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhramanyam, C.S.; Wang, C.; Hu, Q.; Dheen, S.T. Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2019, 94, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dighriri, I.M.; Alsubaie, A.M.; Hakami, F.M.; Hamithi, D.M.; Alshekh, M.M.; Khobrani, F.A.; Dalak, F.E.; Hakami, A.A.; Alsueaadi, E.H.; Alsaawi, L.S.; et al. Effects of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Brain Functions: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e30091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, M.; Maury, J.; Dickerson, B.; Gonzalez, D.E.; Kendra, J.; Jenkins, V.; Nottingham, K.; Yoo, C.; Xing, D.; Ko, J.; et al. Effects of Dietary Supplementation of a Microalgae Extract Containing Fucoxanthin Combined with Guarana on Cognitive Function and Gaming Performance. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhri, S.; Yarmohammadi, A.; Yarmohammadi, M.; Farzaei, M.H.; Echeverria, J. Marine Natural Products: Promising Candidates in the Modulation of Gut-Brain Axis towards Neuroprotection. Mar Drugs 2021, 19, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yue, J.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Lin, X.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, H.; et al. Gut Microbiota Interact With the Brain Through Systemic Chronic Inflammation: Implications on Neuroinflammation, Neurodegeneration, and Aging. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 796288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiramatsu, M.; Inoue, K. Nociceptin/Orphanin FQ and Nocistatin on Learning and Memory Impairment Induced by Scopolamine in Mice. Br J Pharmacol 1999, 127, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermes-Lima, M.; Willmore, W.G.; Storey, K.B. Quantification of Lipid Peroxidation in Tissue Extracts Based on Fe(III)Xylenol Orange Complex Formation. Free Radic Biol Med 1995, 19, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Concentration | |
|---|---|
| Chlorophylls (g equivalent chloropyll A/100g) | |
| Chlorophyll C | 3.46 ± 0.45 |
| Σ Chlorophyll B | ND |
| Σ Chlorophyll A | 0.24 ± 0.25 |
| Total carotenoids | |
| Β-carotene (g equivalent Β-carotene / 100g) | 0.09 ± 0.08 |
| All trans Fucoxanthin (g equivalent fucoxanthin/100g) | 1.99 ± 1.01 |
| Total unsaturated fatty acids omega 3 (g/100g of product) | 6.51 ± 1.17 |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) | 7.99 ± 6.14 |
| Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) | 0.23 ± 0.20 |
| Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) | 0.24 ± 0.17 |
| Stearidonic acid (SDA) | 0.07 ± 0.08 |
| Total unsaturated fatty acids omega 6 (g/100g of product) | 2.56 ± 0.19 |
| Hexadecadienoic acid | 2.01 ± 1.38 |
| Linoleic acid | 0.83 ± 0.66 |
| Arachidonic acid | 0.52 ± 0.44 |
| Eicosatetraenoic acid | 0.14 ± 0.12 |
| Total saturated fatty acids (g/100g of product) | 45.42 ± 8.49 |
| Caprylic acid | 23.24 ± 5.35 |
| Capric acid | 18.23 ± 4.06 |
| Palmitic acid | 2.53 ± 0.60 |
| Myristic acid | 0.90 ± 0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





