1. Introduction
There are a multitude of uses for plastic products in agriculture (plasticulture) including containers, pots, packaging, tunnel coverings, drip irrigation tubing and mulch films. Large amounts of plastics are used as mulches applied on the soil surface in vegetable production (e.g., tomato, cucumber, watermelon, strawberry, vine, young orchards) to reduce the weed competition, to increase water and fertilizer use efficiency and soil temperature, and to enhance crop yield, especially in arid and semi-arid environments [1-3]. Coloured plastic mulches have been widely accepted and utilized by farmers to solve above-lined problems [
2], and residual film can affect soil organisms and various physicochemoical properties of soil and plant performance [
2], [
4]. Often, plastic mulch is composed of polyethylene, PE [
5] that degrades slowly in soil, with an incomplete recovery of the used plastic film producing a large quantity of residues left in soils with negative impact in the environment [
4], [
6]. Around 25.8 Mt of plastic waste are yearly generated in Europe [
7], but the percentage of mulch films that remain in the soil in Europe is based on experts’ opinion, rather than collected data. France, Spain, Germany, Italy and UK are the main European users of plastic mulch [
8]. Portugal uses around 4,500 t/year of plastic to cover approximately 23,000 ha of agricultural land, and only a small part of this is recovered for recycling or secondary uses because of issues of contamination with soil, vegetation, pesticide, fertilizers. To comply with the European legislation and the circular economy transition for agricultural plastics it is necessary to take the necessary measures to facilitate the recycling of plastics and promote the use of materials with less negative impact in the environment, such as the biopolymers.
Blueberry (Vaccinium sp.) is a perennial flowering plant with blue or purple berries. It belongs to the Ericaceae Family, prized for their sweet edible fruits rich of vitamin C, minerals, and a number of antioxidants. Blueberries are commonly eaten fresh, but can be baked in a variety of pastries. Portuguese blueberry production is mainly exported to The Netherlands, France, Spain, Belgium, UK and Germany [
9].
Long-term studies on the effects of plastic mulch on soil characteristics are scarce. The aims of present work were to assess the impact of a long-term production system using a green high density plastic (HDPE) mulching a) on chemical and biological properties of topsoil cultivated with blueberry (Vaccinium sp.) at Southern Portugal, and b) on the accumulation of phtalate esters (PAEs), namely the di(2-Ethylhexyl) phtalate (DEHP) in cultivated soil.
2. Material and methods
2.1. Environmental conditions and experimental layout
The study was run at Fataca Experimental Farm, Odemira, Southern Portugal, Lat: 37.5903, Lng: -8.7403. In a 30-year period, the annual temperature in the region varied from a mean minimum of 7 ºC to a maximum of 31 ºC (average of 19 ºC), and rainfall varied from a mean 3 mm in July and August to 75 mm in December (average annual rainfall of 437.0 mm).
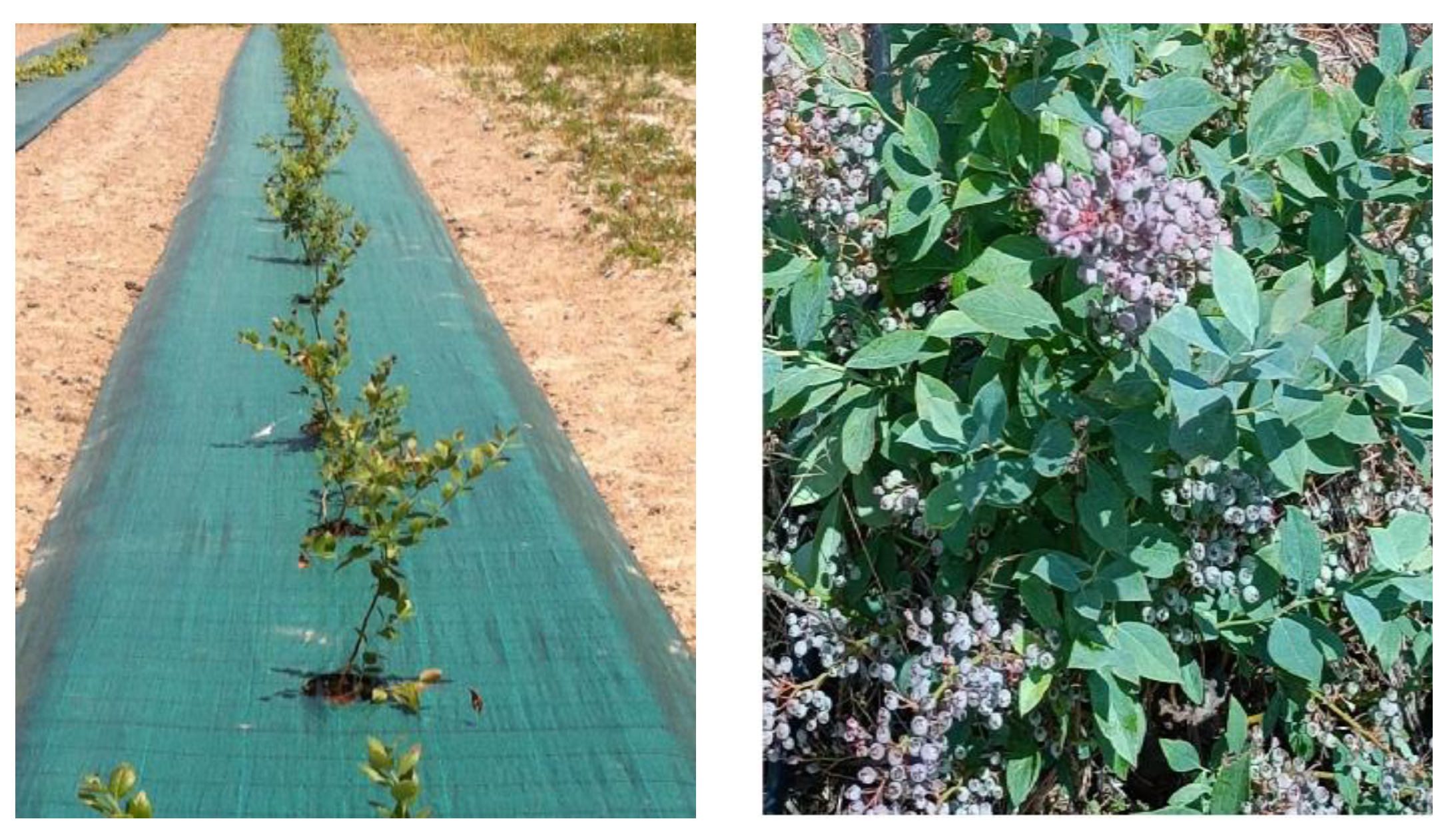
Two-years-old blueberry plantlets (Vaccinium cv. Centra Blue) were transplanted from nursery to the field in summer 2013 and were maintained for 10 years. The soil was amended with composted pinus bark to improve soil structure and organic matter concentration. In the open-field, inter-row spacing was 2.50 m. Planting rows were covered with a permeable green high density plastic (100%HDPE) mulch (Fig. 1) to control weeds emergence and increase soil moisture. Plastic labelling did not indicate its thickness, but could last on the soil surface for 10 years. In each planting row. two lines for drip fertigation was used, with emiters of 2.0 L h-1 placed each 30 cm. Fertilization was applied according to plants needs, i.e, ammonium, potassium, phosphorus and magnesium sulphate. Electric conductivity (EC) of fertigation solution was set to a maximum of 1.2 mS cm-1. A contiguous bare soil, without mulching and planting, was separated from cultivated soil with plastic mulching for about 5 m, and was used as a control treatment (CK).
The experimental layout included two treatments: a control (bare) soil with no planting and no mulching, and a cultivated soil covered with green high density plastic (HDPE) mulch, and three replicates (5 plants each).
Figure 1.
Soil covered with conventional green high density plastic mulch in blueberry (Vaccinium cv. Centra Blue) plantation, at Fataca Experimental Farm (Odemira, south Portugal).
Figure 1.
Soil covered with conventional green high density plastic mulch in blueberry (Vaccinium cv. Centra Blue) plantation, at Fataca Experimental Farm (Odemira, south Portugal).
2.2. Soil sampling and chemical and biological determinations
In June 2023, soil samples were taken at 0-20 cm depth for both treatments during the vegetative phase of 10-yr-old blueberry plants in the planting rows with green plastic mulching. Fresh soil samples were sieved (<2 mm) and used to evaluate the ezymatic activity and the population of nematodes present; other sub-samples were air-dried and sieved (<2 mm) to evaluate the changes of chemical composition after 10 years cultivation of blueberries, using green plastic mulch on planting row.
In each soil sample, pH was determined in 1:2.5 soil:water ratio, the electric conductivity (EC) was measured by potentiometry. Total nitrogen (N) was determined by dry combustion and organic carbon (C) was estimated by sodium dichromate digestion and measured by UV-Vis spectrophotometry. The extractable P and K was determined by Egnér-Riehm method [
10], the exchangeable bases were extracted by 1M ammonium acetate (CH
3COONH
4) solution at pH 7.0 [
11], the micronutrients (Cu, Zn, Fe, Mn) were extracted according to [
12], and extracted boron (B) was estimated by hot water method. The di(2-Ethylhexyl) phtalate (DEHP) was determined by GC-MS.
In each fresh soil sample, the dehydrogenase activity was evaluated by spectrophotometryic quantification of the triphenyl formazan formed from reduction of 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride, using a modification of the method of Casida et al. [
13] as described by Menino et al. [
14]. The populations of nematodes present were extracted from 500 mL subsamples using the tray method [
15]. The suspensions were observed under a stereomicroscope (Nikon SMZ1500, Tokyo, Japan), and specimens of each trophic group (plant parasites, bacterial feeders, fungivorous, omnivores and predators) were counted, followed by observation using a brightfield light microscope (Olympus BX-51, Hamburg, Germany) for identification.
2.3. Statistical analysis
Changes of chemical properties, enzymatic activity, and nematode communities in the topsoil of planting rows after 10-years cultivation of blueberry with green plastic (PE) mulch in comparison with a bare control soil (non-mulching, without planting). Values were presented as means and coefficient of variation or standard deviation (n=3).
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Changes in soil chemical composition
After 10 years’ cultivation of blueberry ‘Centra Blue’, in the open-field and covered with green plastic (PE) mulch, some changes in soil chemical properties were observed (
Table 1 and
Table 2) compared with the control (CK) bare soil. The green HDPE mulch was designed to alter the microclimate at the plant and soil levels and was mainly formulated with role in light absorption and crop physiology. Considering the best chemical indicators of soil quality, the organic C, CEC and EC were slightly reduced in the planting row covered with plastic mulching in the long-term comparing to bare soil (
Table 1). Indicators of soil quality are defined as those soil properties that display the greatest sensitivity to changes in soil function. The same tendency as above happened with soil total N, with a lower value in the long-term planting soil with mulching (0.84 g kg
-1) compared to uncovered CK soil (1.08 g kg
-1), but the C/N ratio in both soils was kept similar (11.9), appropriate for mineralization process. The organic C in cultivated soil (10.03 g kg
-1) was low for blueberry growth (optimal value of 23 g C kg
-1; [
16] even lower than the CK soil (
Table 1). Comparing with a black polypropylene (PP) non-woven mulch, Domagała-Świątkiewicz and Siwek [
17] found an opposite result in raspberry cultivation soil. The lowest organic C and total N concentrations in present soil with HDPE film could be explained by a fast mineralization rate by a possible higher soil temperature and moisture due to mulching, but contradict the observed by Muñoz et al. [
18] with black PE film of 50 µm in strawberry production in high tunnels, showing that other factors could also affect the soil organic matter status in the planting row with mulching. The present reduction of EC with mulching to 0.07 mS cm
-1 was more favorable for plant growth, and had the same tendency as raspberry soil using a polylactic acid-based (PLA) biopolymer [
17]. The pH-value in cultivated soil (5.7) was above the optimum range of values (4.0-5.5) for blueberry growth [
16], [
19], but slightly lower than the CK soil (
Table 1). These authors referred that when the soil pH exceeds that range, blueberries may show adverse symptoms, such as nutrients deficiency, delay of flower bud differentiation and flowering, growth inhibition, low photosynthetic intensity, and reduced fruit yield and quality (e.g., increase of titratable acid concentration).
After 10 years’ cultivation of blueberries with green plastic mulch, the concentrations of micronutrients in soil at 0-20 cm depth like the extractable copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn) and B were slightly lower than those in control (bare) soil (
Table 2). Nevertheless, in both soils, the extractable Cu was in the medium range of values and the extractable Fe was very high. As to the extractable Zn, its concentration in the control soil was in the medium range but decreased to a low value in cultivated soil with mulching. The extractable Mn was very low, which is overall good for agricultural purposes, but Fe and Mn are important nutrients for blueberry fruits and their concentrations in plant should be further monitored. Finally, the extractable B had a low concentration in the control (bare) soil and decreased to a very low level under cultivation with plastic mulching. Boron is an essential micronutrient required for physiological and biochemical processes in fruit crops such as blueberry (
Vaccinium sp.), a plant species well adapted to acidic soils (pH
(H2O)≤ 5.5) with low B availability. According to the literature [20-21], the critical range of low and high B levels in plant tissues is narrow, and B requirement is highly variable among plant species and genotypes, with an optimum value for one cultivar being either insufficient or toxic for other species or cultivar. There is little information regarding deficiency and excess of B in fruit plants grown in acidic soils like the blueberry therefore, under the present conditions the evaluation of nutritional status of plant (leaf, fruit) is recommended.
Surprisingly, the cultivated soil did not show contamination with di(2-Ethylhexyl) phtalate (DEHP) by using the green HDPE mulch in the long-term (<2.7 kg kg-1 dry matter), similar to the control soil.
3.2. Effect of long-term cultivation with green HDPE mulch on soil enzymatic activity
Dehydrogenases are intracellular enzymes that are involved in microbial oxidoreductase metabolism. The activity of enzyme dehydrogenases is among the most appropriate, crucial and responsive soil biological indicators, responding immediately to changes in soil systems, cropping and conditions. The soil dehydrogenase activity (DHA) has been recognized as an indicator of the metabolic status of the soil microbiota and of the viable microbial activity [
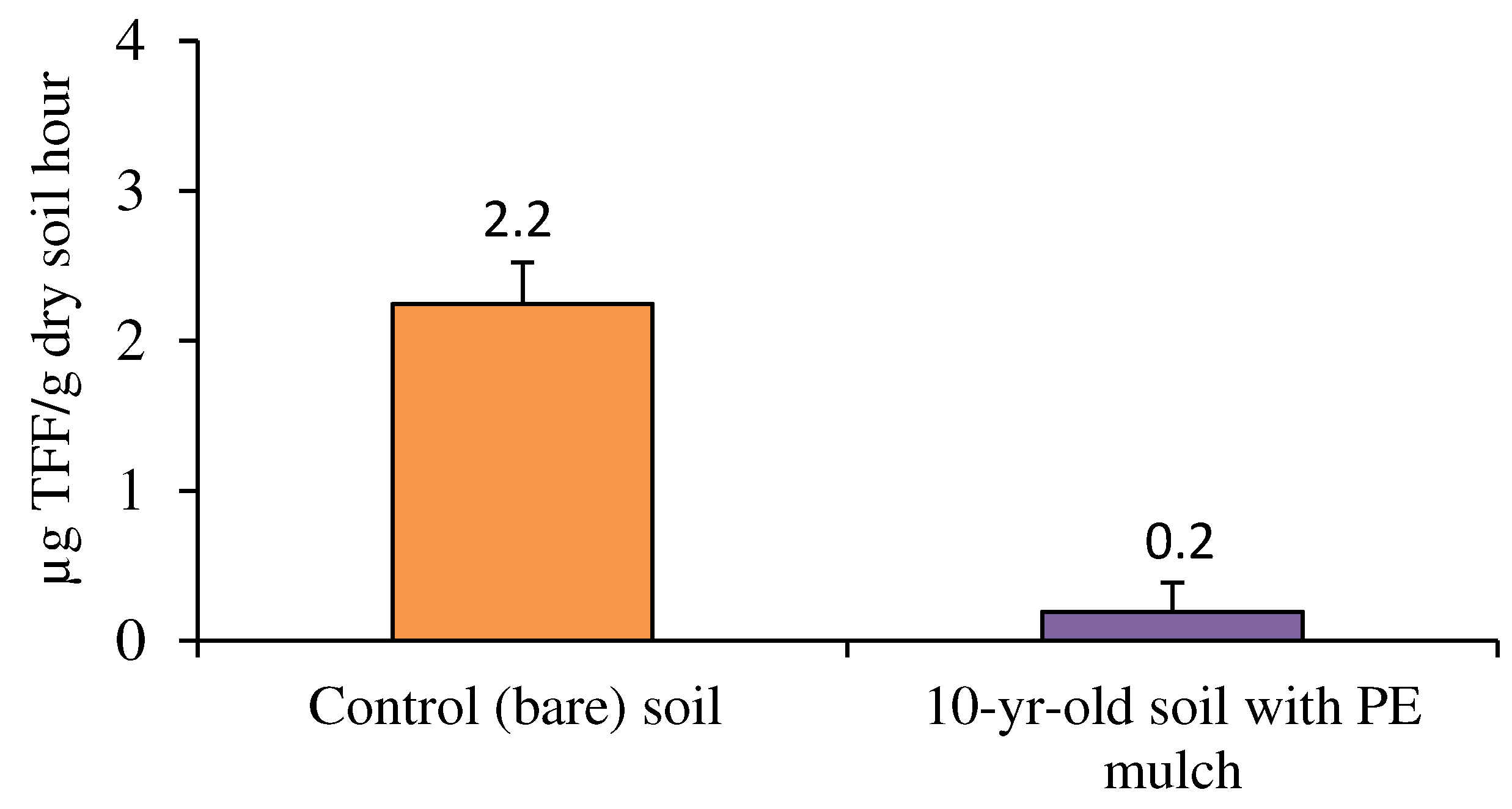
22]. DHA depends on the same factors that affect the abundance and activity of microorganisms. In the present study, DHA in soil collected at 0-20 cm depth at the end of spring and after 10 years’ cultivation of blueberry using a green plastic mulch was significantly lower than the bare soil (Fig. 2). This fact indicates a possible negative effect of green HDPE mulch on the overall soil microbial activity. This fact agrees with Moreno et al. [
23] for organic pepper cultivation, using black PE film, and was explained by a higher temperature and reduction of gas interchange between the soil and the atmosphere under plastic mulching. Nevertheless, the possibility that other factors related to blueberry cultivation may negatively influence soil microbial activity cannot be ruled out.
Figure 2.
Comparison of soil dehydrogenase activity after 10 years’ cultivation of blueberry ‘Centra Blue’ covered with green HDPE mulch, in Fataca Experimental Farm, at Odemira, south Portugal. Values above columns and error bars represent, respectively, the mean and standard deviation of three replicate samples. TFF, triphenyl formazan.
Figure 2.
Comparison of soil dehydrogenase activity after 10 years’ cultivation of blueberry ‘Centra Blue’ covered with green HDPE mulch, in Fataca Experimental Farm, at Odemira, south Portugal. Values above columns and error bars represent, respectively, the mean and standard deviation of three replicate samples. TFF, triphenyl formazan.
3.3. Effect of long-term cultivation with green HDPE mulch on the nematodes communities in soil
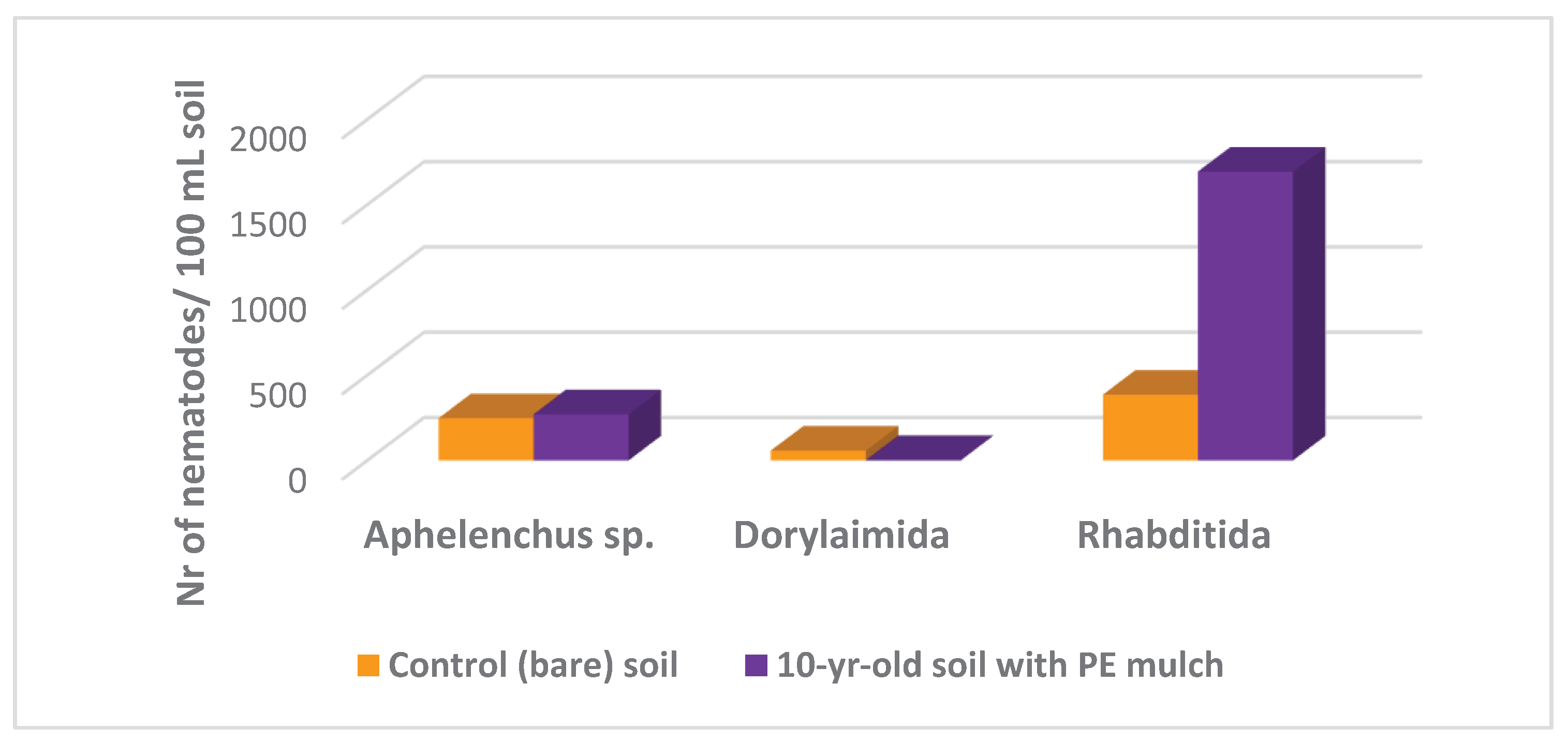
Although this is a preliminary study, discrete shifts of nematode community after 10 years’ cultivation of blueberry ‘Centra Blue’ in the open-field covered with green HDPE mulch were observed in comparison with uncultivated (bare) soil (Fig. 3). The Rhabditida (bacterial feeders) showed a 4-fold increase in cultivated soil compared with the control soil. This huge increase in bacterial-feeder nematodes was probably due to previous soil organic amendment with composted pinus bark, and a possible higher temperature and moisture caused by the plastic film. The presence of higher values of bacterivorous and fungivorous nematodes in cultivated soil indicated that the organic matter mineralization/nitrification was taking place, reducing total organic C and total N in soil, in agreement with
Table 1. Mycophagous nematodes (
Aphelenchus sp.) did not differ between the two treatments, probably because this group of nematodes is less responsive to soil modifications [
24]. Dorylamida (omnivore nematodes) were negligible, especially in cultivated soil, and predators were not found in any treatment. The presence of a green HDPE film apparently did not affect negatively the presence of nematodes, but these results need further confirmation. Moreover, the nematode community structure must be studied using different indices in order to better assess any changes due to soil disturbance [25-26].
Figure 3.
Number of nematodes per 100 mL of bare (control) soil (no mulching, no planting) and soil with 10 years’ cultivation of blueberries ‘Centra Blue’ covered with green HDPE mulch, in Fataca Experimental Farm, at Odemira, south Portugal: Aphelenchus sp. = fungivorous; Dorylaimida = omnivorous; Rhabditida = bacterivorous.
Figure 3.
Number of nematodes per 100 mL of bare (control) soil (no mulching, no planting) and soil with 10 years’ cultivation of blueberries ‘Centra Blue’ covered with green HDPE mulch, in Fataca Experimental Farm, at Odemira, south Portugal: Aphelenchus sp. = fungivorous; Dorylaimida = omnivorous; Rhabditida = bacterivorous.
4. Conclusions
This is a former open-field study on the effects of a long-term cultivation of a perennial plant species, the blueberry, covered with a green high density plastic mulch, in a semi-arid environment at south Portugal. This study revealed that mulching system apparently generated unique soil conditions, mirrored by variations in specific soil parameters. The green polyethylene mulch controlled well the emergence of natural vegetation and did not contribute to increase soil salinity in the topsoil (0-20 cm). However, the long-term cultivation with plastic mulching tended to reduce slightly the soil chemical quality comparing with non-mulching, reducing in particular the organic matter concentration and nitrogen, some base cations and the cation exchange capacity. The soil pH was also slightly reduced to 5.7, but this value was above the recommended values (4.0-5.5) for a good blueberry growth; therefore, monitoring the plant development is recommended. Green plastic mulch did not contribute to di(2-Ethylhexyl) phtalate (DEHP) contamination of topsoil, as well as to copper, iron, zinc and manganese contamination. Manganese and boron were even depleted from soil. Since these micronutrients are important for blueberries nutrition, their concentration in fruits should be further controlled. There is little information regarding boron deficiency in plants grown in acidic soils such as blueberry.
Biological quality in present cultivated soil requires further developments since the enzymatic activity and nematodes community appear contradictory trends. A negative effect of plastic mulching on the overall soil microbial activity was observed, contradicting the response of nematodes community. Soil dehydrogenase activity and nematode community analysis are valuable tools for assessing the impact of land management practices on soil biology, soil health and overall soil condition. The use of nematodes as soil bio indicators makes ecological sense as they represent a central position in the soil food web and are related to ecological processes such as organic matter mineralization/nitrification, cultural practices and plant growth. Some authors found the nematode community the best biological indicator [24-26].
A more robust experimental design should be put in place and the soil sampling must be repeated with time to confirm present findings. In addition, the diversity of nematodes should be further defined through the identification of key taxa, correlation of key taxa to disturbance, and calibration of indices relative to ecosystem, climate and soil practice (mulching).
Author Contributions
All authors contributed for the study, under the field condition, and for manuscript preparation. Conceptualization of the study was by Filipe Pedra, Maria de Lurdes Inácio, Paula Fareleira, Pedro Oliveira, Pablo Pereira and Corina Carranca; the methodology was planned by Pedro Oliveira and Corina Carranca; formal analysis and measurements were carried out by Filipe Pedra, Maria de Lurdes Inácio and Paula Fareleira; writing the original draft preparation was done by Corina Carranca, Maria de Lurdes Inácio and Paula Fareleira; writing, reviewing and editing were taken by all authrs; supervision was taken by Corina Carranca.
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the Fataca Experimental Farm and BerrySmart company, for supporting the experimental field work and materials. Authors also acknowledge the PRR project: “Agri-Plast-Organização e Inovação para a Redução de Plásticos Agrícolas” and the strategic project UIDB/04551/2020 “GREEN-IT: Bioresources for Sustainability” for funding the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Brodhagen, M.; Peyron, M.; Miles, C. and Inglis, D.A.. Biodegradable plastic agricultural mulches and key features of microbial degradation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2015, 99, 1039–1056. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amare, G. and Desta, B.. Coloured plastic mulches: impact on soil properties and crop productivity. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2021, 8, 4. [CrossRef]
- Carranca, C.; Oliveira, P. e Duarte, E. Estratégias para redução da pegada dos plásticos de cobertura do solo na produção hortícola. Vida Rural 2021, (1866), Ano 68, Abril 2021: 41 – 44. https://www.vidarural.pt/shout_edition/vida-rural-no-1866/.
- Wang, D.; Xi, W.; Shi, X-Y.; Zhong, Y-L.; Guo, C-L.; Han, Y-N. and Li, F-M.. Effect of plastic film mulching and film residues on phthalate esters concentrations in soil and plants, and its risk assessment. Environmental Pollution 2021, 286. [CrossRef]
- Briassoulis, D.; Babou, E.; Hiskakis, M.; Scarascia, G.; Picuno, P.; Guarde, D. and Dejean, C.. Review, mapping and analysis of the agricultural plastic waste generation and consolidation in Europe. Water Management & Research 2013. [CrossRef]
- Barata, M.C.C.F.T. . Estudo da Gestão Eficiente da Água na Cultura do Pimento com Filmes de Cobertura do. Solo. Dissertation, for Master Degree in Environmental Plastics Engineering, pp. 54, ISA/UL, Lisbon, Portugal, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- European Comission.. A European Strategy for Plastics in a Circular, Economy 2018. https://www.europarc.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/Eu-plastics-strategy-brochure.pdf.
- Rondán, C.E. Nuevas Tendencias en Plasticultura, AIMPLAS, 2023, pp. 7.
- GPP – Gabinete de Planeamento, Políticas e Administração Geral. Informação sobre produtos: Mirtilo 2023. https://www.gpp.pt/index.php/produtos/produtos.
- Riehm, H. Die ammoniumlaktatessigsaüre–Methodezur Bestimmung der Leichtlöslichen Phosphorsäure in Karbonathaltigen Böden. Agrochimica 1958, 3, 49–65. [Google Scholar]
- Metson, A.J. Methods of chemical analysis for soil survey samples. New Zealand Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, Soil Bureau Bulletin 1961, (12). In: Hazelton P.A.and Murphy, B.W. (Eds). Interpreting Soil Test Results: What Do All the Numbers Mean? 2nd Ed., New South Wales, Department of Natural Resources, Collingwood, Australia, CSIRO Publishing, 168-175.
- Lakanen, E. and Ervio, R.. A comparison of eight extractants for the determination of plant available micronutrients in soils. Acta Agralia Fennica 1971, 123, 223–232.
- Casida Jr., L.E.; Klein, D.A. and Santoro, T. Soil dehydrogenase activity. Soil Science 1964, 98, 371–376. [CrossRef]
- Menino, R.; Felizes, F.; Castelo-Branco, M.A.; Fareleira, P.; Moreira, O.; Nunes, R. and Murta, D. Agricultural value of Black Soldier Fly larvae frass as organic fertilizer on ryegrass. Heliyon 2021, 7, e05855. [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, A.G.; and Hemming, J.R. A comparison of some quantitative methods of extracting small vermiform nematodes from soil. Annals of Applied Biology 1965, 55, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochmian, I.; Malinowskia, R.; Kubusa, M.; Malinowskaa, K. and Sotekb, Z. The feasibility of growing highbush blueberry (V. corymbosum L.) on loamy calcic soil with the use of organic substrates. Scientia Horticulturae 2019, 257. [CrossRef]
- Domagała-Świątkiewicz, I. and Siwek, P.. Effects of plastic mulches and high tunnel raspberry production systems on soil physicochemical quality indicators. International Agrophysics 2018, 32, 39–47. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, K.; Sören, T-B.; Kenngott, K.; Meyer, M.; Diehl, D.; Steinmetz, Z. and Schaumann, G. Effects of plastic versus straw mulching systems on soil microbial community structure and enzymes in strawberry cultivation. Soil Systems 2022, 6, 21. [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wu, W.; Lyu, L. and Li, W. Growth and physiological characteristics of four blueberry cultivars under different high soil pH treatments. Environmental and Experimental Botany 2022, 197. [CrossRef]
- Landi, M.; Degl’Innocenti, E.; Pardossi, A. and Guidi, L.. Antioxidant and photosynthetic responses in plants under boron toxicity: A review. American Journal of Agricultural and Biological Sciences 2012, 7, 255–270. [CrossRef]
- Meriño-Gergichevich, C.; Reyes-Díaz, M.; Guerrero, J. and Ondrasek, G.. Physiological and nutritional responses in two highbush blueberry cultivars exposed to deficiency and excess of boron. Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition 2017, 17, 307–318.
- Alkorta, I.; Aizpurua, A.; Riga, P.; Albizu, I.; Amezaga, I. and Garbisu, C.. Soil enzyme activities as biological indicators of soil health. Reviews on Environmental Health 2003, 18, 65–73. [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.M.; Peco, J.; Campos, J.; Villena, J.; González, S. and Moreno, C.. Effect of different mulch materials on the soil dehydrogenase activity (DHA) in an organic pepper crop. EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts 2016, 18, EGU2016–1581.
- Bongers, T.M.B. Functional diversity of nematodes. Applied Soil Ecology 1998, 10, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongers, T. and Ferris, H.. Nematode community structure as a bioindicator in environmental monitoring. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 1999, 14, 224–228.
- Neher, D. Role of nematodes in soil health and their use as bioindicators. Journal of Nematology 2001, 33, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Chauvin, C.; Trambolho, M.; Hedde, M.; Makowski, D.; Cérémonie, H.; Jimenez, A. and Villenave, C.. Soil nematodes as indicators of heavy metal pollution: A meta-analysis. Open Journal of Soil Science 2020, 10, 579–601. [CrossRef]
- Ferris, H. Form and function: Metabolic footprints of nematodes in the soil food web. European Journal of Soil Biology 2010, 46, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamun, P.; Renco, M.; Kucanova, E.; Brazova, T.; Papajova, I.; Miklisova, D.and Hanzelova, V. Nematodes as bioindicators of soil degradation due to heavy metals. Ecotoxicology 2012, 21, 2319–2330. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).