Submitted:
11 September 2023
Posted:
13 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Variability of conductance change.
Thermal versus voltage controlled switching.
The effect of device structure
3. The influence of the substrate
4. Influence of additives
5. The mechanism of conductance change.
6. Conclusions and outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ekanayaka, T.K.; Hao, G.; Mosey, A.; Dale, A.S.; Jiang, X.; Yost, A.J.; Sapkota, K.R.; Wang, G.T.; Zhang, J.; N’Diaye, A.T.; et al. Nonvolatile Voltage Controlled Molecular Spin-State Switching for Memory Applications. Magnetochemistry 2021, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotaru, A.; Gural’skiy, I.A.; Molnár, G.; Salmon, L.; Demont, P.; Bousseksou, A. Spin State Dependence of Electrical Conductivity of Spin Crossover Materials. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 4163–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosey, A.; Dale, A.S.; Hao, G.; N’Diaye, A.; Dowben, P.A.; Cheng, R. Quantitative Study of the Energy Changes in Voltage-Controlled Spin Crossover Molecular Thin Films. J. Phys. Chem. Let.t 2020, 11, 8231–8237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, E. Charge Transport Properties of Spin Crossover Systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, E.; Ekanayaka, T.K.; McElveen, K.A.; Lai, R.Y.; Dowben, P.A. Evidence for Long Drift Carrier Lifetimes in [Fe(Htrz)2(trz)](BF4)], plus Polyaniline Composites. Org. Electron. 2022, 105, 106516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.; Mosey, A.; Jiang, X.; Yost, A.J.; Sapkota, K.R.; Wang, G.T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; N’Diaye, A.T.; Cheng, R.; et al. Nonvolatile Voltage Controlled Molecular Spin State Switching. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 114, 032901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamachi, T.; Gruber, M.; Davesne, V.; Bowen, M.; Boukari, S.; Joly, L.; Scheurer, F.; Rogez, G.; Yamada, T.K.; Ohresser, P.; et al. Robust Spin Crossover and Memristance across a Single Molecule. Nature Commun. 2012, 3, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopakumar, T.G.; Matino, F.; Naggert, H.; Bannwarth, A.; Tuczek, F.; Berndt, R. Electron-Induced Spin Crossover of Single Molecules in a Bilayer on Gold. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2012, 51, 6262–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulmann, C.; Jacob, K.; Dorbes, S.; Lampert, S.; Malfant, I.; Doublet, M.-L.; Valade, L.; Real, J.A. Electrical Conductivity and Spin Crossover: A New Achievement with a Metal Bisdithiolene Complex. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 8548–8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisenda, R.; Harzmann, G.D.; Celis Gil, J.A.; Thijssen, J.M.; Mayor, M.; van der Zant, H.S.J. Stretching-Induced Conductance Increase in a Spin-Crossover Molecule. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 4733–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvachko, Y.N.; Starichenko, D. V.; Korolyov, A. V.; Yagubskii, E.B.; Kotov, A.I.; Buravov, L.I.; Lyssenko, K.A.; Zverev, V.N.; Simonov, S. V.; Zorina, L. V.; et al. The Conducting Spin-Crossover Compound Combining Fe(II) Cation Complex with TCNQ in a Fractional Reduction State. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 9121–9130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Giménez, V.; Tatay, S.; Martí-Gastaldo, C. Electrical Conductivity and Magnetic Bistability in Metal–Organic Frameworks and Coordination Polymers: Charge Transport and Spin Crossover at the Nanoscale. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 5601–5638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Li, Z.-Y.; Ishikawa, R.; Yamashita, M. Spin Crossover and Valence Tautomerism Conductors. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 435, 213819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Cui, H.-B.; Okano, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Einaga, Y.; Sato, O. Electrical Conductivity Modulation Coupled to a High-Spin−Low-Spin Conversion in the Molecular System [FeIII(qsal)2][Ni(dmit)2]3·CH3CN·H2O. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 5739–5741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosey, A.; Dale, A.S.; Hao, G.; N’Diaye, A.; Dowben, P.A.; Cheng, R. Correction to “Quantitative Study of the Energy Changes in Voltage-Controlled Spin Crossover Molecular Thin Films. ” J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 2463–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefter, C.; Rat, S.; Costa, J.S.; Manrique-Juárez, M.D.; Quintero, C.M.; Salmon, L.; Séguy, I.; Leichle, T.; Nicu, L.; Demont, P.; et al. Current Switching Coupled to Molecular Spin-States in Large-Area Junctions. Advanced Materials 2016, 28, 7508–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalabaeva, V.; Ridier, K.; Rat, S.; Manrique-Juarez, M.D.; Salmon, L.; Séguy, I.; Rotaru, A.; Molnár, G.; Bousseksou, A. Room Temperature Current Modulation in Large Area Electronic Junctions of Spin Crossover Thin Films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggini, L.; Gonidec, M.; Canjeevaram Balasubramanyam, R.K.; Squillantini, L.; Pecastaings, G.; Caneschi, A.; Rosa, P. Temperature-Induced Transport Changes in Molecular Junctions Based on a Spin Crossover Complex. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 5343–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggini, L.; Gonidec, M.; González-Estefan, J.H.; Pecastaings, G.; Gobaut, B.; Rosa, P. Vertical Tunnel Junction Embedding a Spin Crossover Molecular Film. Adv. Electron Mater. 2018, 4, 1800204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schleicher, F.; Studniarek, M.; Kumar, K.S.; Urbain, E.; Katcko, K.; Chen, J.; Frauhammer, T.; Hervé, M.; Halisdemir, U.; Kandpal, L.M.; et al. Linking Electronic Transport through a Spin Crossover Thin Film to the Molecular Spin State Using X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Operando Techniques. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 31580–31585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotaru, A.; Dugay, J.; Tan, R.P.; Guralskiy, I.A.; Salmon, L.; Demont, P.; Carrey, J.; Molnár, G.; Respaud, M.; Bousseksou, A. Nano-Electromanipulation of Spin Crossover Nanorods: Towards Switchable Nanoelectronic Devices. Advanced Materials 2013, 25, 1745–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugay, J.; Giménez-Marqués, M.; Kozlova, T.; Zandbergen, H.W.; Coronado, E.; van der Zant, H.S.J. Spin Switching in Electronic Devices Based on 2D Assemblies of Spin-Crossover Nanoparticles. Advanced Materials 2015, 27, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Cavanillas, R.; Sanchis-Gual, R.; Dugay, J.; Coronado-Puchau, M.; Giménez-Marqués, M.; Coronado, E. Design of Bistable Gold@Spin-Crossover Core–Shell Nanoparticles Showing Large Electrical Responses for the Spin Switching. Advanced Materials 2019, 31, 1900039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prins, F.; Monrabal-Capilla, M.; Osorio, E.A.; Coronado, E.; van der Zant, H.S.J. Room-Temperature Electrical Addressing of a Bistable Spin-Crossover Molecular System. Advanced Materials 2011, 23, 1545–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dugay, J.; Aarts, M.; Giménez-Marqués, M.; Kozlova, T.; Zandbergen, H.W.; Coronado, E.; van der Zant, H.S.J. Phase Transitions in Spin-Crossover Thin Films Probed by Graphene Transport Measurements. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holovchenko, A.; Dugay, J.; Giménez-Marqués, M.; Torres-Cavanillas, R.; Coronado, E.; van der Zant, H.S.J. Near Room-Temperature Memory Devices Based on Hybrid Spin-Crossover@SiO2 Nanoparticles Coupled to Single-Layer Graphene Nanoelectrodes. Advanced Materials 2016, 28, 7228–7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Séguy, I.; Ridier, K.; Shalabaeva, V.; Piedrahita-Bello, M.; Rotaru, A.; Salmon, L.; Molnár, G.; Bousseksou, A. Resistance Switching in Large-Area Vertical Junctions of the Molecular Spin Crossover Complex [Fe(HB(tz)3)2]: ON/OFF Ratios and Device Stability. J. Physics: Condensed Matter 2020, 32, 214010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etrillard, C.; Faramarzi, V.; Dayen, J.-F.; Letard, J.-F.; Doudin, B. Photoconduction in [Fe(Htrz)2(trz)](BF4). H2O Nanocrystals. Chemical Communications 2011, 47, 9663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Meng, Y.; Ni, Z.-P.; Tong, M.-L. Synergistic Electrical Bistability in a Conductive Spin Crossover Heterostructure. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, D.; Aketa, N.; Tanaka, H.; Horike, S.; Fukumori, M.; Tamaki, T.; Inose, T.; Akai, T.; Toyama, H.; Sakata, O.; et al. Facile Preparation of Hybrid Thin Films Composed of Spin-Crossover Nanoparticles and Carbon Nanotubes for Electrical Memory Devices. Dalton Transactions 2019, 48, 7074–7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Domanov, O.; Schafler, E.; Vejpravova, J.; Shiozawa, H. Synthesis and Size-Dependent Spin Crossover of Coordination Polymer [Fe(Htrz)2(trz)](BF4)]. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefter, C.; Gural’skiy, I.A.; Peng, H.; Molnár, G.; Salmon, L.; Rotaru, A.; Bousseksou, A.; Demont, P. Dielectric and Charge Transport Properties of the Spin Crossover Complex [Fe(Htrz)2(trz)](BF4)]. Physica Status Solidi - Rapid Research Letters (RRL) 2014, 8, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekanayaka, T.K.; Üngör, Ö.; Hu, Y.; Mishra, E.; Phillips, J.P.; Dale, A.S.; Yazdani, S.; Wang, P.; McElveen, K.A.; Zaz, M.Z.; et al. , Perturbing the Spin State and Conduction of Fe (II) Spin Crossover Complexes with TCNQ. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 296, 127276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, N.A.A.M.; Said, S.M.; Salleh, M.F.M.; Afifi, A.M.; Ibrahim, N.M.J.N.; Hasnan, M.M.I.M.; Tahir, M.; Hashim, N.Z.I. Review of Fe-Based Spin Crossover Metal Complexes in Multiscale Device Architectures. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2023, 544, 121168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Castro, D.; Garcés-Pineda, F.A.; Moneo-Corcuera, A.; Sánchez-Molina, I.; Galán-Mascarós, J.R. Mechanochemical Processing of Highly Conducting Organic/Inorganic Composites Exhibiting Spin Crossover–Induced Memory Effect in Their Transport Properties. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2102469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üngör, Ö.; Choi, E.S.; Shatruk, M. Optimization of Crystal Packing in Semiconducting Spin-Crossover Materials with Fractionally Charged TCNQδ– Anions (0 < δ < 1). Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 10765–10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Y. N. Shvachko, D.V. Starichenko, A.V. Korolyov, A.I. Kotov, L.I. Buravov, V. N. Zverev, S.V. Simonov, L.V. Zorina, E.B. Yagubskii, The highly conducting spincrossover compound combining Fe(III) cation complex with TCNQ in a fractional reduction state. Synthesis, structure, electric and magnetic properties, Magnetochemistry 2017, 3, 9. [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.; Benjamin, S.M.; Steven, E.; Brooks, J.S.; Shatruk, M. Photomagnetic Response in Highly Conductive Iron(II) Spin-Crossover Complexes with TCNQ Radicals. Angewandte Chemie 2015, 127, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, S.; Collier, K.; Yang, G.; Phillips, J.; Dale, A.; Mosey, A.; Grocki, S.; Zhang, J.; Shanahan, A.E.; Cheng, R.; et al. Optical Characterization of Isothermal Spin State Switching in an Fe(II) Spin Crossover Molecular and Polymer Ferroelectric Bilayer. J. Physics: Condensed Matter 2023, 35, 365401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Hao, G.; N’Diaye, A.T.; Routaboul, L.; Braunstein, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Doudin, B.; Enders, A.; Dowben, P.A. Perturbing the Spin Crossover Transition Activation Energies in [Fe(H2B(pz)2)2(bipy)] with Zwitterionic Additions. J. Physics: Condensed Matter 2018, 30, 305503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.S.; Hao, G.; N’Diaye, A.T.; Routaboul, L.; Braunstein, P.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Ekanayaka, T.K.; Shi, Q.-Y.; Schlegel, V.; et al. Manipulation of the Molecular Spin Crossover Transition of [Fe(H2B(pz)2)2(bipy)] by Addition of Polar Molecules. J. Physics: Condensed Matter 2020, 32, 034001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Costa, P.S.; Hooper, J.; Miller, D.P.; N’Diaye, A.T.; Beniwal, S.; Jiang, X.; Yin, Y.; Rosa, P.; Routaboul, L.; et al. Locking and Unlocking the Molecular Spin Crossover Transition. Advanced Materials 2017, 29, 1702257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Mu, S.; Chastanet, G.; Daro, N.; Palamarciuc, T.; Rosa, P.; Létard, J.-F.; Liu, J.; Sterbinsky, G.E.; Arena, D.A.; et al. Complexities in the Molecular Spin Crossover Transition. J. Physical Chemistry C 2015, 119, 16293–16302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Palamarciuc, T.; Rosa, P.; Létard, J.-F.; Doudin, B.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Dowben, P.A. Electronic Structure of a Spin Crossover Molecular Adsorbate. J. Physical Chemistry C 2012, 116, 23291–23296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Palamarciuc, T.; Létard, J.-F.; Rosa, P.; Lozada, E.V.; Torres, F.; Rosa, L.G.; Doudin, B.; Dowben, P.A. The Spin State of a Molecular Adsorbate Driven by the Ferroelectric Substrate Polarization. Chemical Comm. 2014, 50, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdani, S.; Phillips, J.; Ekanayaka, T.K.; Cheng, R.; Dowben, P.A. The Influence of the Substrate on the Functionality of Spin Crossover Molecular Materials. Molecules 2023, 28, 3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, R.; Ueno, S.; Nifuku, S.; Horii, Y.; Iguchi, H.; Miyazaki, Y.; Nakano, M.; Hayami, S.; Kumagai, S.; Katoh, K.; et al. Simultaneous Spin-Crossover Transition and Conductivity Switching in a Dinuclear Iron(II) Coordination Compound Based on 7,7′,8,8′-Tetracyano- p -quinodimethane. Chemistry – A European Journal 2020, 26, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- .
- Craze, A.R.; Marjo, C.E.; Li, F. A Complementary Characterisation Technique for Spin Crossover Materials; the Application of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy for Future Device Applications. Dalton Transactions 2022, 51, 428–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spin Crossover in Transition Metal Compounds I; Gütlich, P. , Goodwin, H.A., Eds.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2004; ISBN 978-3-540-40394-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bairagi, K.; Iasco, O.; Bellec, A.; Kartsev, A.; Li, D.; Lagoute, J.; Chacon, C.; Girard, Y.; Rousset, S.; Miserque, F.; et al. Molecular-Scale Dynamics of Light-Induced Spin Cross-over in a Two-Dimensional Layer. Nat Commun 2016, 7, 12212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; N’Diaye, A.T.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yin, Y.; Chen, X.; Hong, X.; Xu, X.; Dowben, P.A. Indications of Magnetic Coupling Effects in Spin Cross-over Molecular Thin Films. Chemical Communications 2018, 54, 944–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beniwal, S.; Zhang, X.; Mu, S.; Naim, A.; Rosa, P.; Chastanet, G.; Létard, J.-F.; Liu, J.; Sterbinsky, G.E.; Arena, D.A.; et al. Surface-Induced Spin State Locking of the [Fe(H2B(Pz)2)2 (Bipy)] Spin Crossover Complex. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 2016, 28, 206002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.; N’Diaye, A.T.; Ekanayaka, T.K.; Dale, A.S.; Jiang, X.; Mishra, E.; Mellinger, C.; Yazdani, S.; Freeland, J.W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Magnetic Field Perturbations to a Soft X-Ray-Activated Fe(II) Molecular Spin State Transition. Magnetochemistry 2021, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, B.; Oberg, J.C.; Gill, T.G.; El Hallak, F.; Hirjibehedin, C.F.; Serri, M.; Heutz, S.; Arrio, M.-A.; Sainctavit, P.; Mannini, M.; et al. Temperature- and Light-Induced Spin Crossover Observed by X-Ray Spectroscopy on Isolated Fe(II) Complexes on Gold. J Phys Chem Lett 2013, 4, 1546–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, G.; Dale, A.S.; N’Diaye, A.T.; Chopdekar, R. V; Koch, R.J.; Jiang, X.; Mellinger, C.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, R.; Xu, X.; et al. Intermolecular Interaction and Cooperativity in an Fe(II) Spin Crossover Molecular Thin Film System. Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 2022, 34, 295201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, H.; Sugiyama, K.; Ito, E.; Seki, K. Energy Level Alignment and Interfacial Electronic Structures at Organic/Metal and Organic/Organic Interfaces. Advanced Materials 1999, 22, 605–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, S.; Salaneck, W.R.; Fahlman, M. Energy-Level Alignment at Organic/Metal and Organic/Organic Interfaces. Advanced Materials 2009, 21, 1450–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowben, P.A. The Metallicity of Thin Films and Overlayers. Surf Sci Rep 2000, 40, 151–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
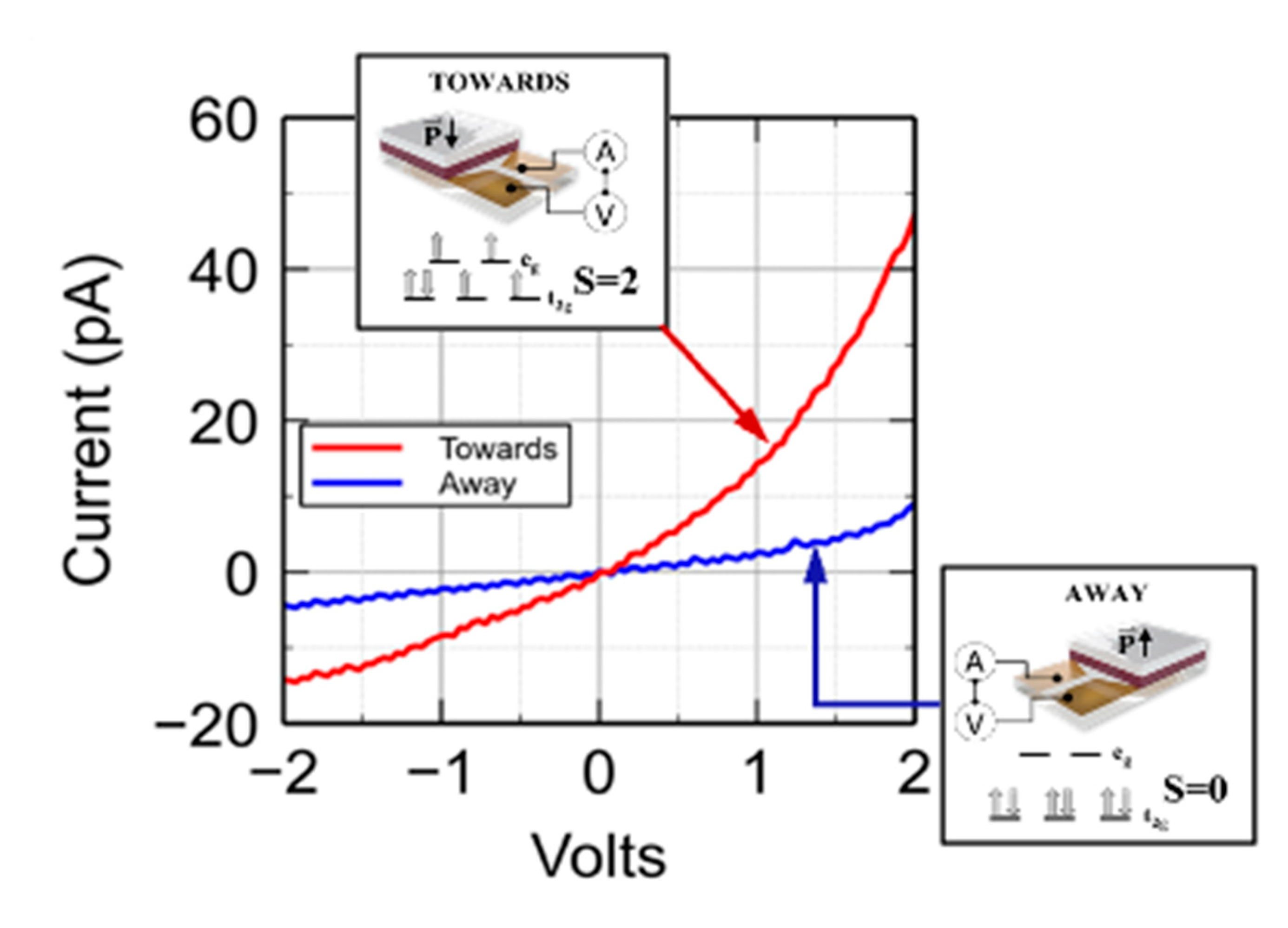
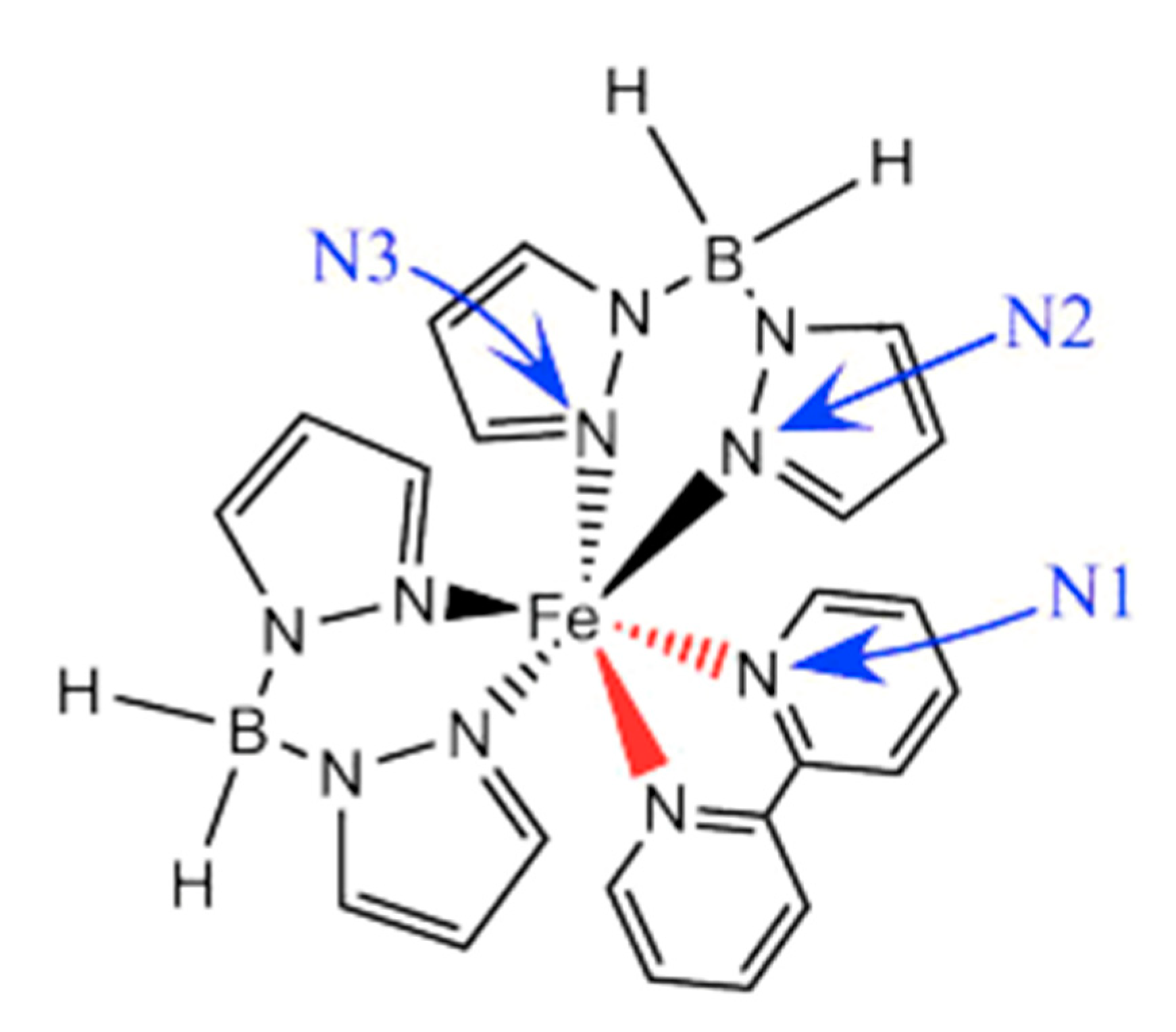
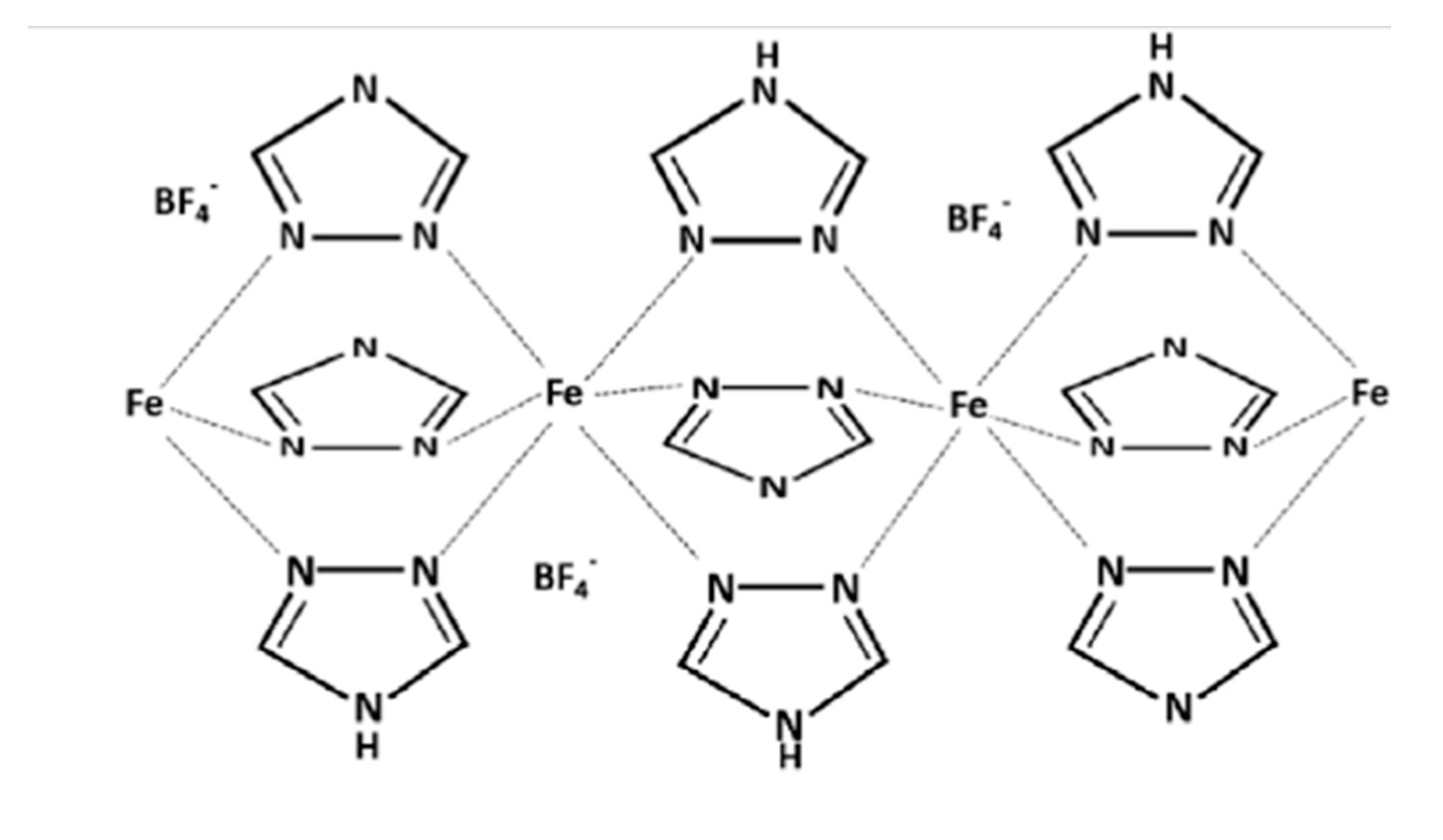
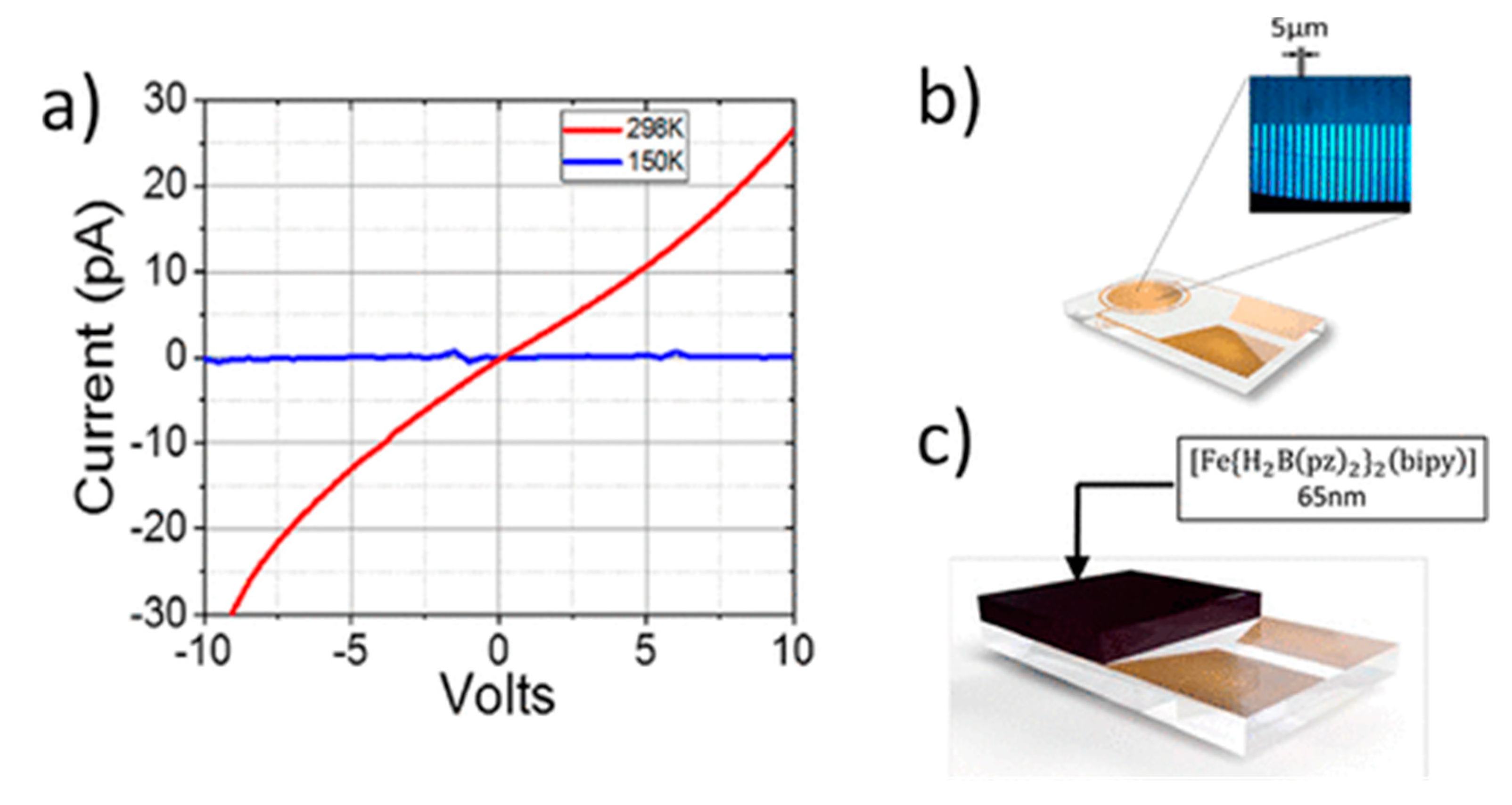
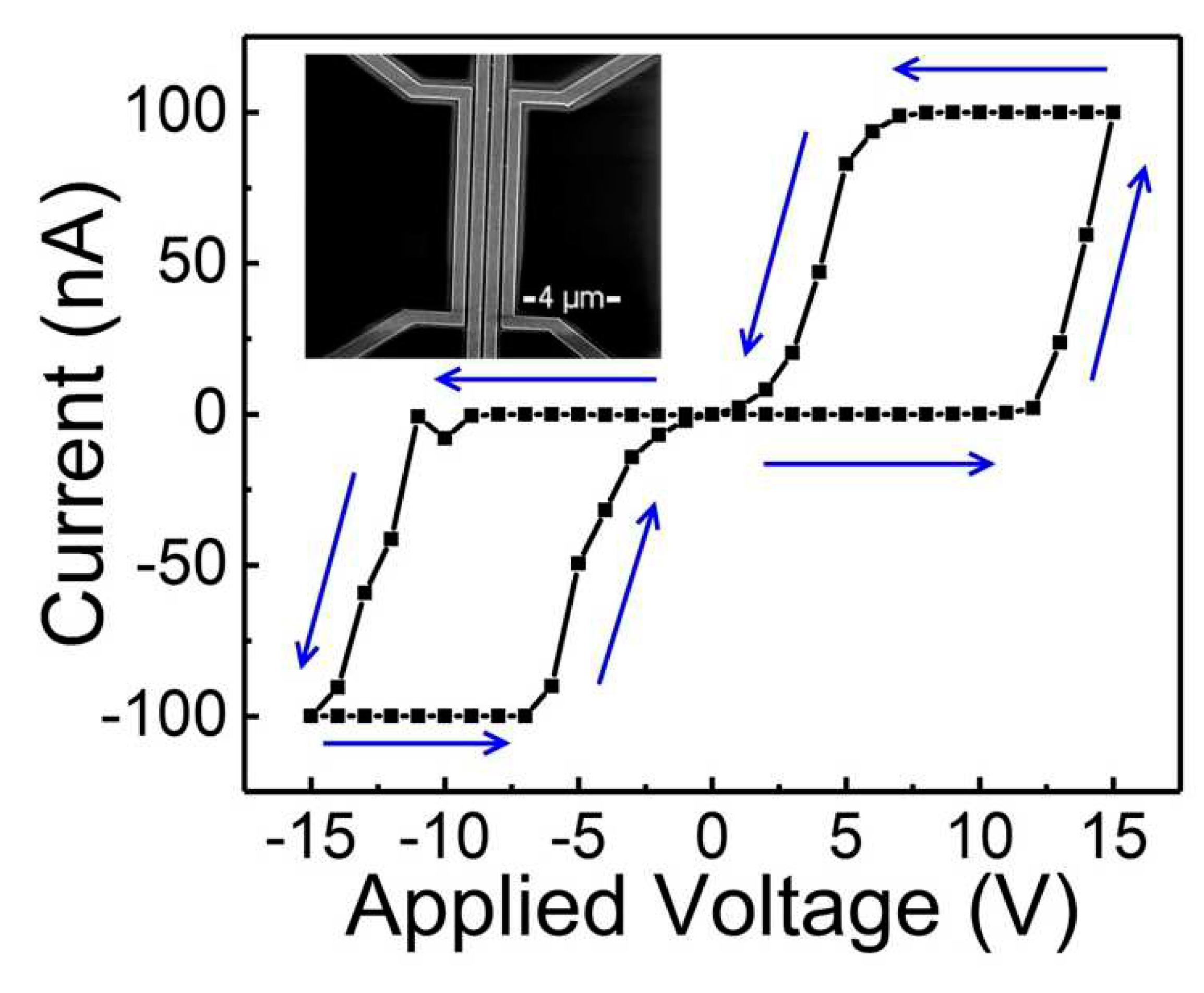
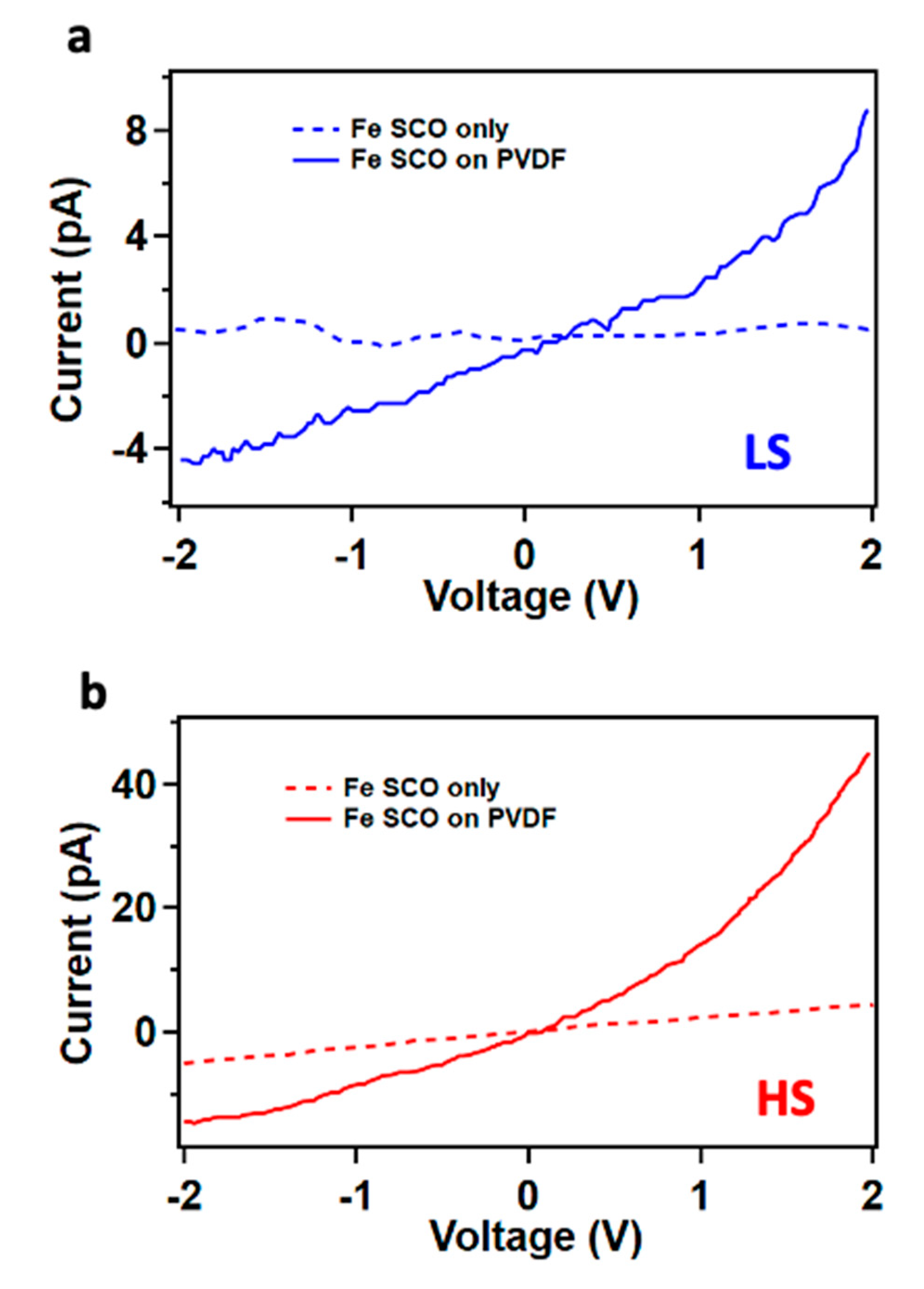
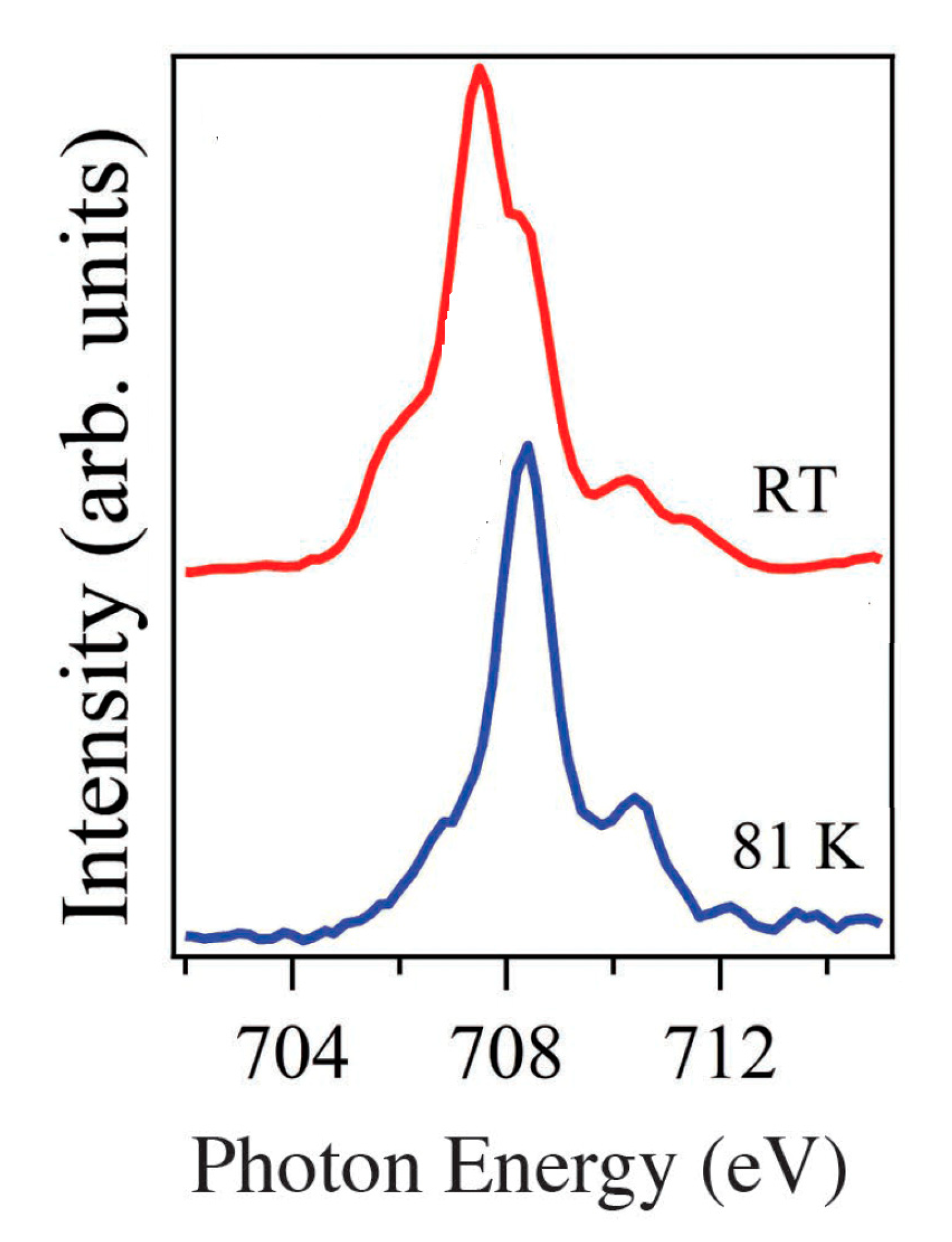
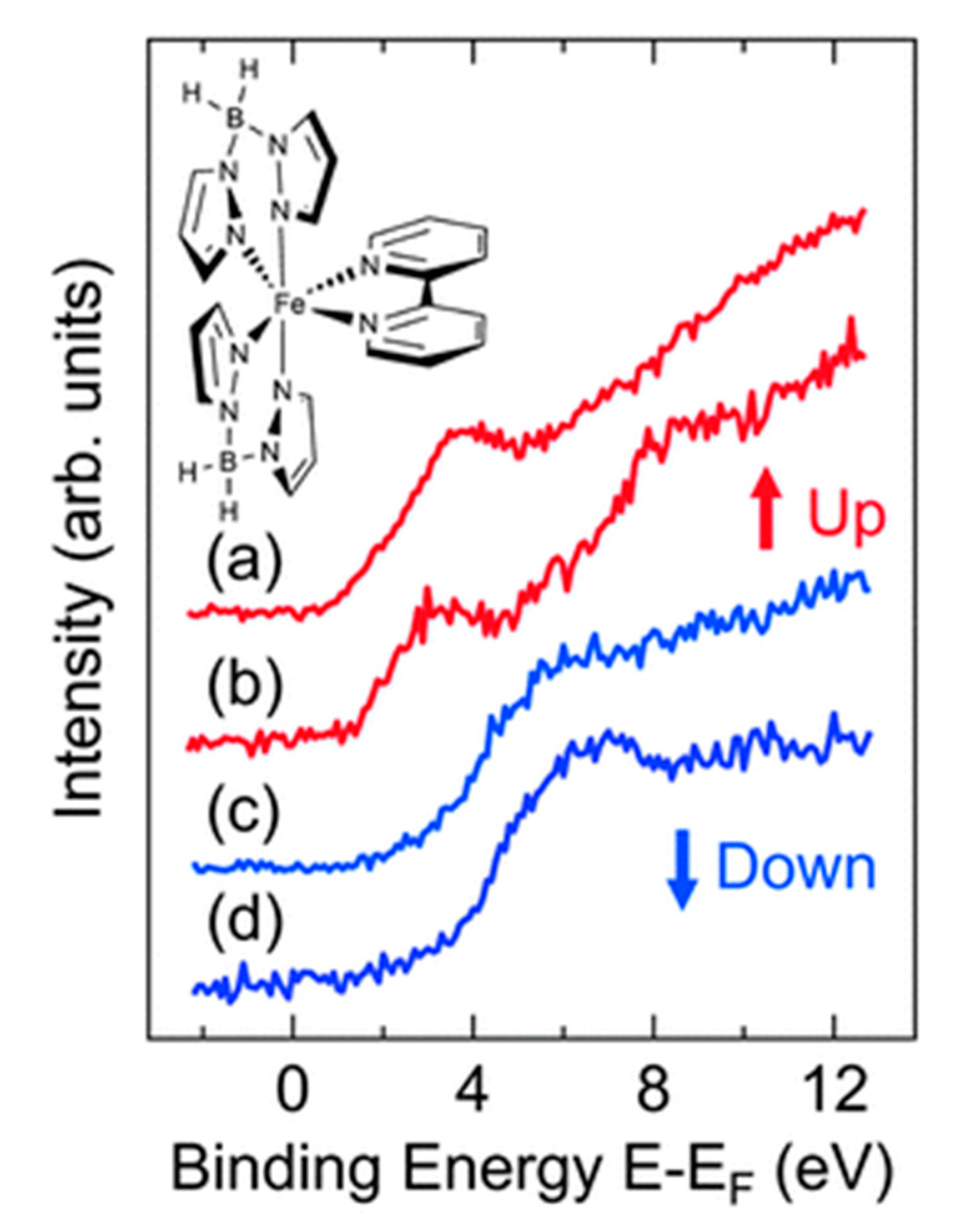
| On state | On/off ratio | On state current (A) | Off state current (A) | Switching mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low spin state | 380 | 1.9x10-9 | 5x10-12 | Temperature controlled | [22] |
| Low spin state | 8 | - | - | Temperature controlled | [29] |
| Low spin state | 2 | 2x10-13 | 1x10-13 | Temperature controlled | [2] |
| Low spin state | 1.6 | 1x10-10 | 0.5x10-10 | Temperature controlled | [26] |
| High spin state | 11 | 5.5x10-9 | 0.5x10-9 | Temperature controlled | [21] |
| High spin state | 6 | 6x10-11 | 1x10-11 | Temperature controlled | [30] |
| High spin state | 1.7 | 9.2x10-10 | 5.2x10-10 | Temperature controlled | [24] |
| High spin state | 1.5 | 6x10-8 | 4x10-8 | Photo induced | [28] |
| High spin state | 1.5 | - | - | Temperature controlled | [31] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





