Submitted:
30 August 2023
Posted:
05 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Review of Previous Work
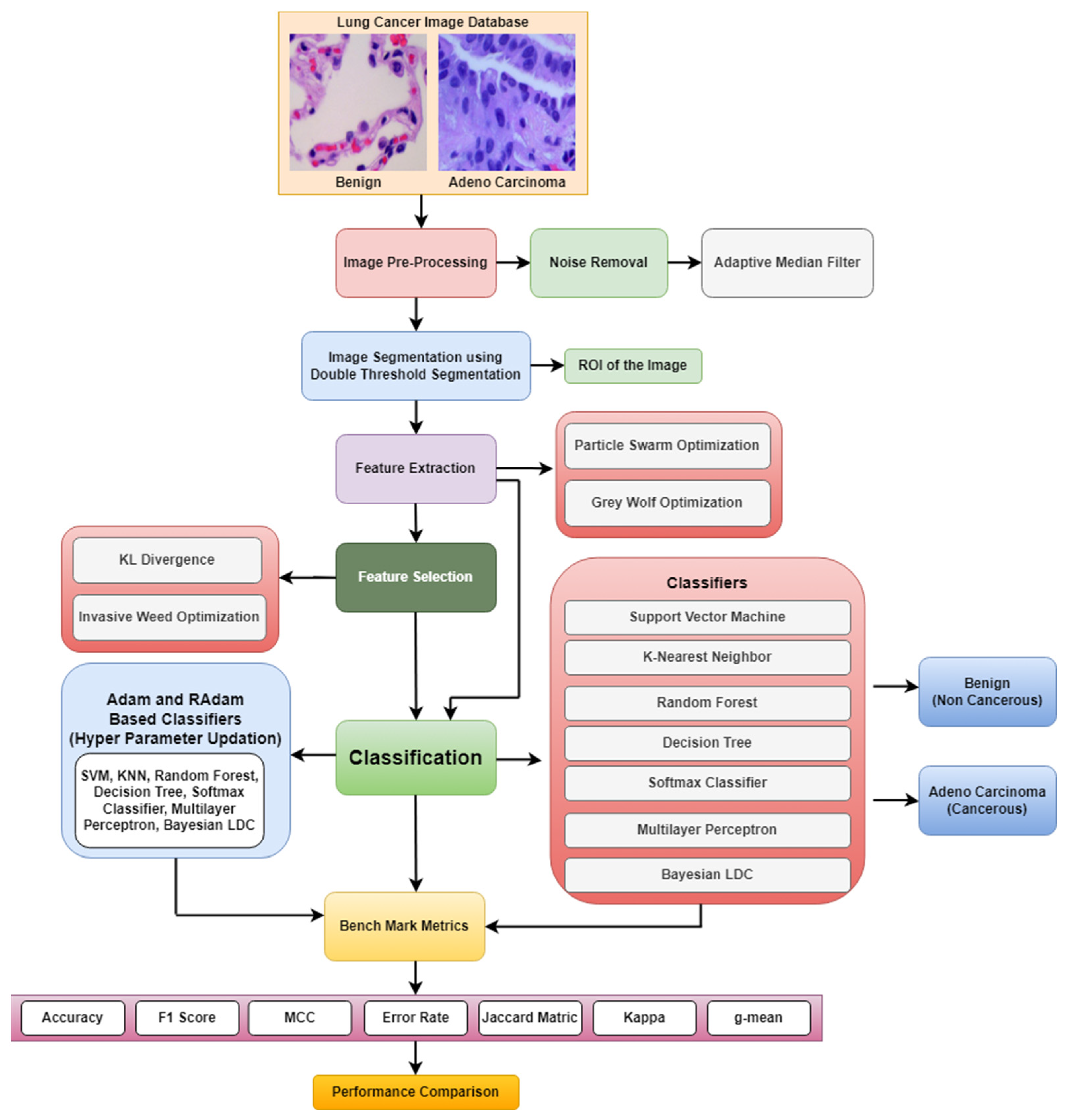
2. Methodology for Lung Cancer Detection
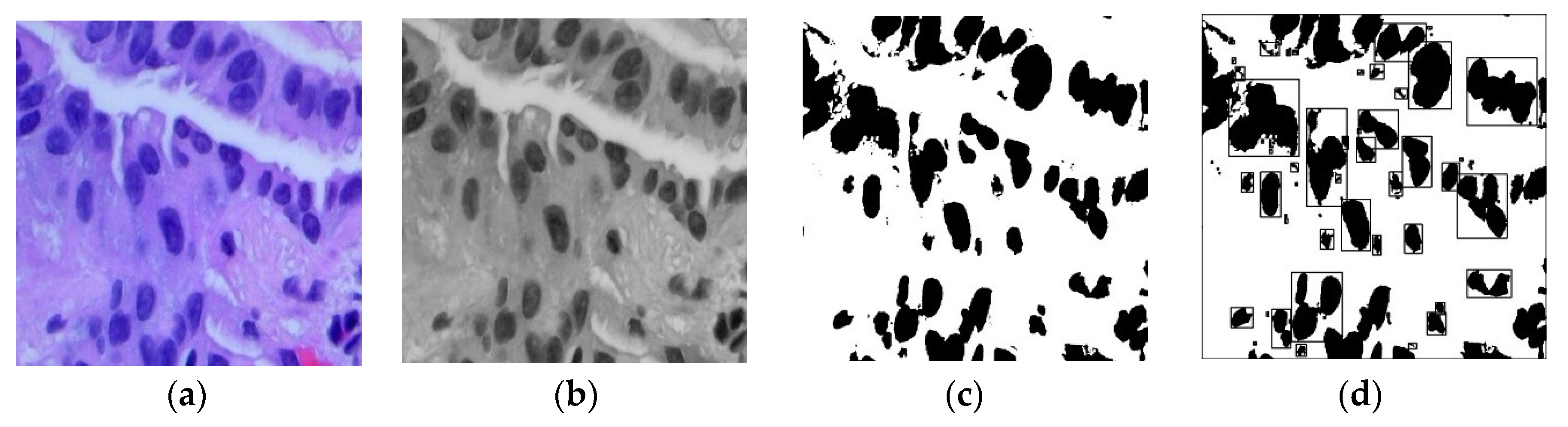
2.1. Preprocessing and Segmentation
3. Feature Extraction
3.1. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
3.2. Grey Wolf Optimization (GWO)
3.3. Statistical Analysis
4. Feature Selection
4.1. KL Divergence
4.2. Invasive Weed Optimization
- Primary Population Initialization: A few seeds are dispersed to start the search.
- Reproduction process: Seeds have the potential to grow into flowering plants, which then choose and spread the fittest seeds for survival and reproduction. The quantity of grass grain grains decreases in a linear fashion from to as follows:
- Spectral Spread Method: The group's seeds are distributed normally with a mean planting position and standard deviation (SD) determined by the equation below.
- Competitive Deprivation: If the colony has more grasses than the maximum limit (Smax), the grass with the lowest fitness is eliminated to maintain a consistent number of herbs.
- The process continues until the maximum iteration is reached, keeping the lowest cost value of the grasses.
5. Classifiers for the detection of Lung Cancer
5.1. Support Vector Machine
5.2. K-Nearest Neighbor
5.3. Random Forest
- Randomly select M samples from X using the Bootstrap method.
- Choose n random features (where n<N) to split a decision tree node. Determine the split criterion by selecting the feature with the lowest Gini value. Gini is computed using the formula:Where represents the relative frequency of dataset features and represents the number of classes.
- Generate M decision trees by repeating steps 1 and 2, M times.
- Create a random forest by combining the decision trees and utilize voting to determine the classification outcome.
5.4. Decision Tree
5.5. Softmax Discriminant Classifier
5.6. Multilayer Perceptron
5.7. Bayesian Linear Discriminant Classifier
5.8. Methods for Updating Hyperparameters in Various Classifiers
5.8.1. Adam Approach
-
Initialization: Set initial values for hyperparameters:Target value, maximum iterations, maximum depth and criterion for Decision Tree, maximum iterations for Adam, , , , .
-
Hyperparameter Tuning Loop:
- a)
-
For = 1 to maximum iterations for Adam
- Calculate maximum depth
- Determine the criterion
- b)
-
For =1 to maximum iterations for Decision Tree
- Update values for maximum depth
- Criterion is set to MSE.
-
Determine the optimal values for maximum depthend for.
- Formulate a confusion matrix and compute the error rate (ER).
- Compute the loss gradient using Equation 36.
-
Establish new optimal hyperparameter values using Equation 30 through 34.end for.
5.8.2. RAdam’s Approach
-
Initialization: Set initial values for hyperparameters:Target value, maximum iterations, maximum depth and criterion for Decision Tree, maximum iterations for Adam, , , , , solution considering rate, solution adjusting rate and bandwidth.
-
Hyperparameter Tuning Loop:
- a)
-
For = 1 to maximum iterations for Adam
- Calculate maximum depth
- Determine the criterion
- b)
-
For =1 to maximum iterations for Decision Tree
- Update values for maximum depth
- Criterion is set to MSE.
-
Determine the optimal values for maximum depthend for.
- Formulate a confusion matrix and compute the error rate (ER).
- Compute the loss gradient using Equation 36.
-
Establish new optimal hyperparameter values using Equation 30 through 34.end for.
-
For each iteration: current iterations for randomization = 1 to maximum iterations for randomizationIf randomization 1 < solution considering rate.Set for this iteration as Set for this iteration as If randomization 2 < solution adjusting rate.Set for this iteration as + bandwidth * randomization 3.Set for this iteration as = + bandwidth * randomization 4.end if.If for this iteration is less than the lower bound, set it to the lower bound.end if.If for this iteration is less than the lower bound, set it to the lower boundend if.If for this iteration is less than the upper bound, set it to the upper bound.end if.If for this iteration is less than the upper bound, set it to the upper boundend if.Set for this iteration as lower bound + (bandwidth * randomization 5).Set for this iteration as lower bound + (bandwidth * randomization 6).end if.
-
Repeat.
- Calculate maximum depth
- Determine the criterion
-
For each iteration from 1 to maximum iterations for Decision Tree
- Update the values of maximum depth
- Set the criterion to MSE.
-
Determine the optimal values for maximum depthend for.
- Formulate a confusion matrix and compute the error rate (ER).
-
Compute the ER using & as hyperparameters.end for.
6. Results and Discussion
6.1. Training and Testing of the classifiers
6.2. Selection of the Optimal Parameters for the Classifiers
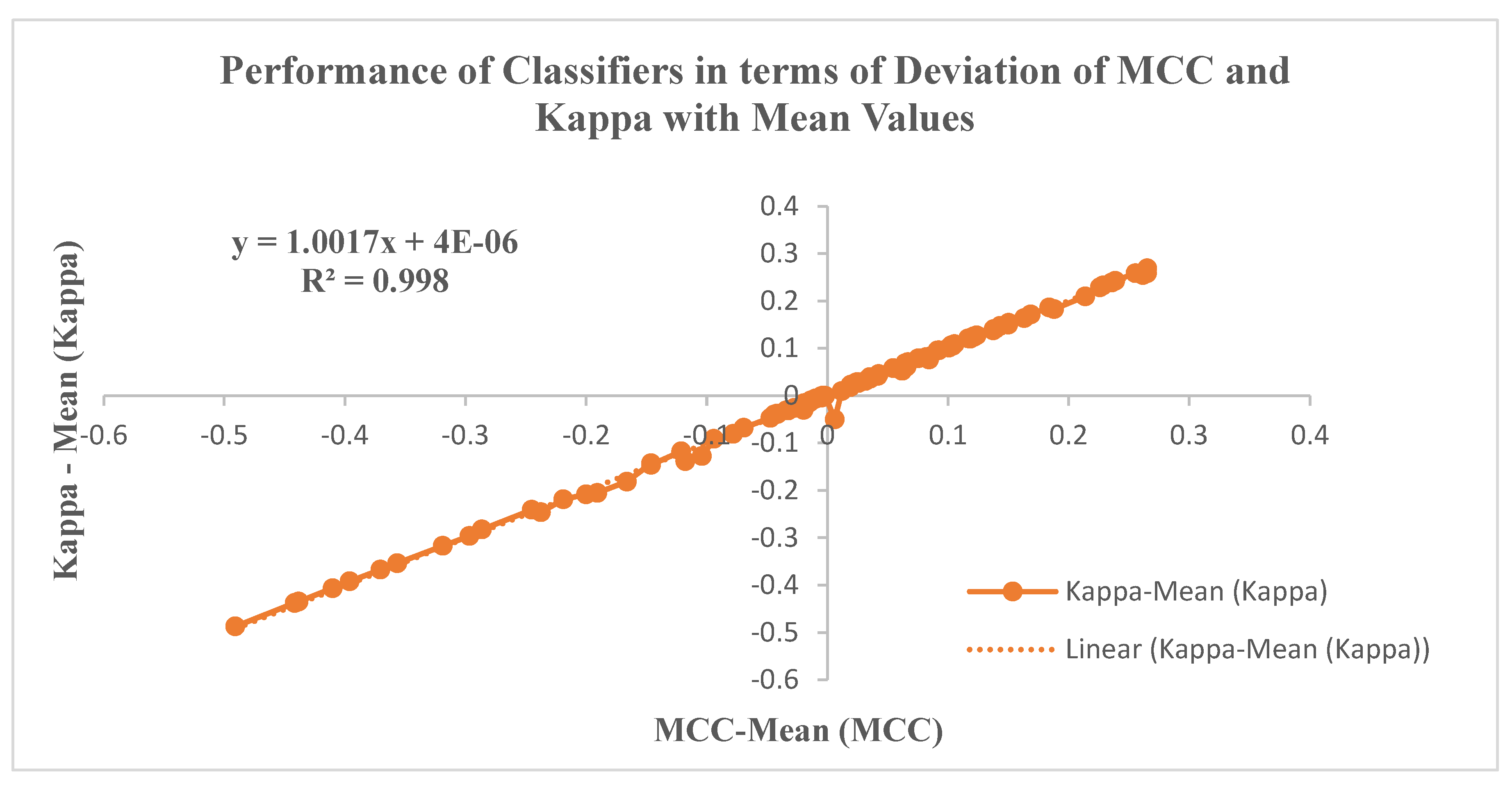
6.3. Performance metrics of the Classifiers
| Feature Selection |
Classifiers | Accuracy (%) | Error Rate (%) | F1 Score (%) | MCC | Jaccard Index (%) |
g-mean (%) |
Kappa |
|
KL Divergence |
SVM | 82.24 | 17.76 | 80.89 | 0.65 | 67.91 | 82.77 | 0.64 |
| KNN | 91.07 | 8.94 | 90.30 | 0.82 | 82.31 | 91.61 | 0.82 | |
| Random Forest | 81.56 | 18.44 | 81.62 | 0.63 | 68.95 | 81.56 | 0.63 | |
| Decision Tree | 77.35 | 22.66 | 76.80 | 0.55 | 62.34 | 77.39 | 0.55 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 79.67 | 20.33 | 78.31 | 0.60 | 64.35 | 80.05 | 0.59 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 79.44 | 20.56 | 78.97 | 0.59 | 65.25 | 79.49 | 0.59 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 80.42 | 19.58 | 79.96 | 0.61 | 66.61 | 80.47 | 0.61 | |
| IWO | SVM | 91.06 | 8.94 | 90.86 | 0.82 | 83.24 | 91.13 | 0.82 |
| KNN | 85.50 | 14.51 | 85.36 | 0.71 | 74.46 | 85.50 | 0.71 | |
| Random Forest | 90.26 | 9.74 | 90.35 | 0.81 | 82.39 | 90.27 | 0.81 | |
| Decision Tree | 91.57 | 8.43 | 91.71 | 0.83 | 84.70 | 91.87 | 0.83 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 85.13 | 14.87 | 85.71 | 0.70 | 75.00 | 85.32 | 0.70 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 85.21 | 14.79 | 85.77 | 0.71 | 75.09 | 85.39 | 0.70 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 88.62 | 11.38 | 89.38 | 0.78 | 80.80 | 89.25 | 0.77 |
6.4. Computational complexity analysis of the Classifiers
7. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prabhakar, S.K.; Lee, S.-W. An Integrated Approach for Ovarian Cancer Classification With the Application of Stochastic Optimization. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 127866–127882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, A.; Ward, EM.; Johnson, CJ.; Cronin, KA.; Ma, J.; Ryerson, AB.; et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, 1975-2014, Featuring Survival. J Natl Cancer Inst. Oxford University Press; 2017.
- Miki, T.; Yano, S.; Hanibuchi, M.; Sone, S. Bone Metastasis Model With Multiorgan Dissemination of Human Small-Cell Lung Cancer (SBC-5) Cells in Natural Killer Cell-Depleted SCID Mice [Internet]. Oncol Res. 2018. Available from: www.cognizantcommunication.com.
- Draelos, R.L.; Dov, D.; Mazurowski, M.A.; Lo, J.Y.; Henao, R.; Rubin, G.D.; Carin, L. Machine-learning-based multiple abnormality prediction with large-scale chest computed tomography volumes. Med Image Anal. 2020, 67, 101857–101857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabó, M.; Bozó, A.; Darvas, K.; Soós, S.; Őzse, M.; Iványi, Z.D. The role of ultrasonographic lung aeration score in the prediction of postoperative pulmonary complications: an observational study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2021, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirinukunwattana, K.; Snead, D.; Epstein, D.; Aftab, Z.; Mujeeb, I.; Tsang, Y.W.; Cree, I.; Rajpoot, N. Novel digital signatures of tissue phenotypes for predicting distant metastasis in colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, J.G.; Longton, G.M.; Carney, P.A.; Geller, B.M.; Onega, T.; Tosteson, A.N.A.; Nelson, H.D.; Pepe, M.S.; Allison, K.H.; Schnitt, S.J.; et al. Diagnostic Concordance Among Pathologists Interpreting Breast Biopsy Specimens. JAMA 2015, 313, 1122–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foran, D.J.; Yang, L.; Chen, W.; Hu, J.; A Goodell, L.; Reiss, M.; Wang, F.; Kurc, T.; Pan, T.; Sharma, A.; et al. ImageMiner: a software system for comparative analysis of tissue microarrays using content-based image retrieval, high-performance computing, and grid technology. J. Am. Med Informatics Assoc. 2011, 18, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozekes, S.; Camurcu, AY. Automatic lung nodule detection using template matching. 4th International Conference on Advances in Information Systems. ADVIS. 2006; 4243:247-253.
- Schilham, AM.; van Ginneken, B.; Loog, M. A computer-aided diagnosis system for detection of lung nodules in chest radiographs with an evaluation on a public database. Med Image Anal. 2006 Apr;10(2):247-58.
- Wang, S.; Wang, T.; Yang, L.; Yang, D.M.; Fujimoto, J.; Yi, F.; Luo, X.; Yang, Y.; Yao, B.; Lin, S.; et al. ConvPath: A software tool for lung adenocarcinoma digital pathological image analysis aided by a convolutional neural network. EBioMedicine 2019, 50, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehmeshki, J.; Ye, X.; Lin, X.; Valdivieso, M.; Amin, H. Automated detection of lung nodules in CT images using shape-based genetic algorithm. Comput. Med Imaging Graph. 2007, 31, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Cuenca, J.J.; Tahoces, P.G.; Souto, M.; Lado, M.J.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Remy, J.; Vidal, J.J. Application of the iris filter for automatic detection of pulmonary nodules on computed tomography images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2009, 39, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.; van Ginneken, B.; Schilham, A.; de Hoop, B.; Gietema, H.; Prokop, M. A large-scale evaluation of automatic pulmonary nodule detection in chest CT using local image features and k-nearest-neighbour classification. Med Image Anal. 2009, 13, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.W.; Tafe, L.J.; Linnik, Y.A.; Vaickus, L.J.; Tomita, N.; Hassanpour, S. Pathologist-level classification of histologic patterns on resected lung adenocarcinoma slides with deep neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jabbar, M.; Alshahrani, M.; Senan, E.M.; Ahmed, I.A. Histopathological Analysis for Detecting Lung and Colon Cancer Malignancies Using Hybrid Systems with Fused Features. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teramoto, A.; Tsukamoto, T.; Kiriyama, Y.; Fujita, H. Automated Classification of Lung Cancer Types from Cytological Images Using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 4067832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapcott, M.; Hewitt, K.J.; Rajpoot, N. Deep Learning With Sampling in Colon Cancer Histology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.; Hoogi, A.; Depeursinge, A.; Rubin, D.L. Automated classification of brain tumor type in whole-slide digital pathology images using local representative tiles. Med Image Anal. 2016, 30, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojansivu, V.; Linder, N.; Rahtu, E.; Pietikäinen, M.; Lundin, M.; Joensuu, H.; Lundin, J. Automated classification of breast cancer morphology in histopathological images. Diagn. Pathol. 2013, 8, S29–S29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficsor, L.; Varga, V.S.; Tagscherer, A.; Tulassay, Z.; Molnar, B. Automated classification of inflammation in colon histological sections based on digital microscopy and advanced image analysis. Cytom. Part A 2008, 73, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, M.; Hamer, G.; Son, S.H.; Shin, S.Y. Automated Single and Multi-Breast Tumor Segmentation Using Improved Watershed Technique in 2D MRI Images. 2016, 61–66. [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.-W.; Lai, Y.-H. Effective segmentation and classification for HCC biopsy images. Pattern Recognit. 2010, 43, 1550–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessert, N.; Bengs, M.; Wittig, L.; Drömann, D.; Keck, T.; Schlaefer, A.; Ellebrecht, D.B. Deep transfer learning methods for colon cancer classification in confocal laser microscopy images. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, N.; Ramakrishnan, AG. Automation of differential blood count. TENCON 2003. Conference on Convergent Technologies for Asia-Pacific Region, Bangalore, India, 2003; 2:547-551.
- Fauziah, K.; Anton, S.P.; Abdullah, A. Detection of leukemia in human blood sample based on microscopic images: A study. Journal of theoretical and applied information technology. 2012; 46: 579-586.
- Chen, C.-H.; Lee, Y.-W.; Huang, Y.-S.; Lan, W.-R.; Chang, R.-F.; Tu, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Liao, W.-C. Computer-aided diagnosis of endobronchial ultrasound images using convolutional neural network. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 177, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoirunnisa, A.; Adiwijaya; Adytia, D. Implementation of CRNN Method for Lung Cancer Detection based on Microarray Data. JOIV : Int. J. Informatics Vis. 2023, 7, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehmood, S.; Ghazal, T.M.; Khan, M.A.; Zubair, M.; Naseem, M.T.; Faiz, T.; Ahmad, M. Malignancy Detection in Lung and Colon Histopathology Images Using Transfer Learning With Class Selective Image Processing. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 25657–25668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumaraf, S.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, X.; Ferkous, C. A new transfer learning based approach to magnification dependent and independent classification of breast cancer in histopathological images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2020, 63, 102192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Fernández, A; Gómez Río, M.; Llamas Elvira, JM.; Sánchez-Palencia Ramos, A.; Bellón Guardia, M.; Ramos Font, C.; Torné Poyatos, P.; Pedraza Muriel, V. Diagnosis efficacy of structural (CT) and functional (FDG-PET) imaging methods in the thoracic and extrathoracic staging of non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2007, 9, 32–39. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanhol, F.A.; Oliveira, L.S.; Cavalin, P.R.; Petitjean, C.; Heutte, L. Deep features for breast cancer histopathological image classification. IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC). 2017, 1868–1873. [CrossRef]
- Ciompi, F.; Geessink, O.; Bejnordi, B.E.; De Souza, G.S.; Baidoshvili, A.; Litjens, G.; Van Ginneken, B.; Nagtegaal, I.; Van Der Laak, J. The importance of stain normalization in colorectal tissue classification with convolutional networks. 2017 IEEE 14th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2017), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 18–21 April 2017, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 18–21 April 2017; pp. 160–163. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Bai, J.; Liao, G. Fine-tuning Pre-trained Convolutional Neural Networks for Gastric Precancerous Disease Classification on Magnification Narrow-band Imaging Images. Neurocomputing 2019, 392, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Xu, A.; Liu, D.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, F.; Ding, W. Deep Learning-Based Classification of Liver Cancer Histopathology Images Using Only Global Labels. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Informatics 2020, 24, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ztürk, Ş.; Akdemir, B. Application of Feature Extraction and Classification Methods for Histopathological Image using GLCM, LBP, LBGLCM, GLRLM and SFTA. Procedia Computer Science. 2018; 132:40-46.
- Alinsaif, S.; Lang, J. Texture features in the Shearlet domain for histopathological image classification. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2020 Dec 15; 20(Suppl 14):312.
- Sujin, PR.; Prakash, TR.; & Linda, MM. Particle Swarm Optimization Based Reactive Power Optimization. ArXiv, abs/1001.3491. 2010.
- Saremi, S.; Mirjalili, SZ.; Mirjalili, SM. Evolutionary population dynamics and grey wolf optimizer. Neural Comput Appl. 2015; 26:1257–63.
- Prabhakar, S.K.; Rajaguru, H. Alcoholic EEG signal classification with Correlation Dimension based distance metrics approach and Modified Adaboost classification. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadalipour, B.; Mallahzadeh, A.R.; Davoodi-Rad, Z. Application of the invasive weed optimization technique for antenna configurations. Progress In Electromagnetics Research, PIER. 2008, 425–428. [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Huang, Q.; Wu, D. Decision Tree-Based Contextual Location Prediction from Mobile Device Logs. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Rath, N.K.; Swain, A.; Rath, S.K. Feature Selection and Classification of Microarray Data using MapReduce based ANOVA and K-Nearest Neighbor. Procedia Comput. Sci. Elsevier; 2015, 54, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.; Danaher, T.; Hehir, W.; Collins, L. A remote sensing approach to mapping fire severity in south-eastern Australia using sentinel 2 and random forest. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2020, 240, 111702-715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, F.; Zhang, J. Softmax Discriminant Classifier. Third International Conference on Multimedia Information Networking and Security, 2011; 16-19.
- Smith, K.A.; Gupta, J.N. Neural networks in business: techniques and applications for the operations researcher. Comput. Oper. Res. 2000, 27, 1023–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybenko, G. Approximation by superpositions of a sigmoidal function. Math. Control. Signals, Syst. 1989, 2, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, P.; Teuling, N.D.; Long, X.; Aarts, R.M. Cardiorespiratory Sleep Stage Detection Using Conditional Random Fields. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Informatics 2017, 21, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesen, M.; Moor, BD. Hyperparameter Search in Machine Learning. ArXiv, abs/1502.02127. 2015.
- Sen, S.Y.; Ozkurt, N. Convolutional Neural Network Hyperparameter Tuning with Adam Optimizer for ECG Classification. Proceedings - 2020 Innovations in Intelligent Systems and Applications Conference, ASYU 2020. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc 2020, 1–6. [CrossRef]
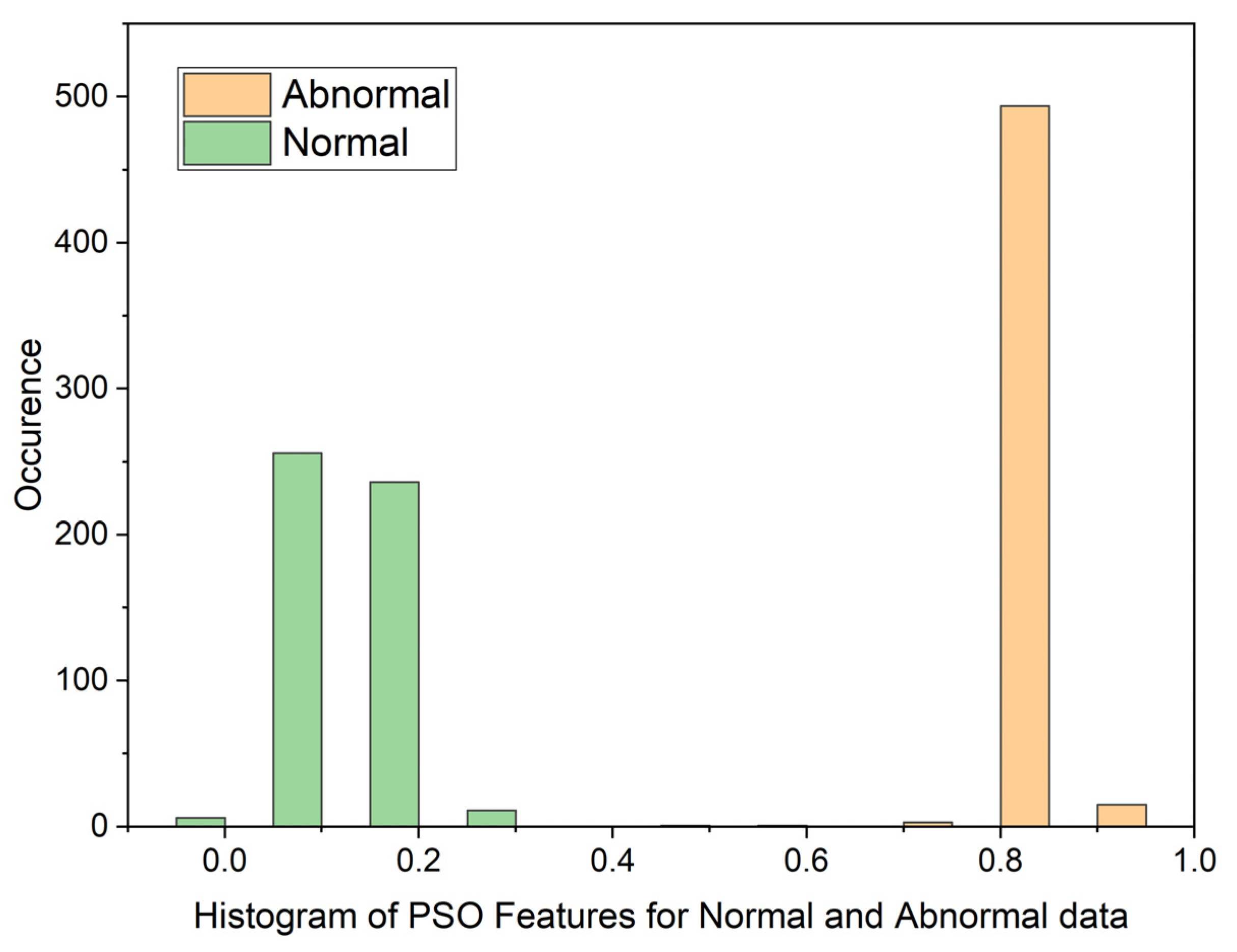
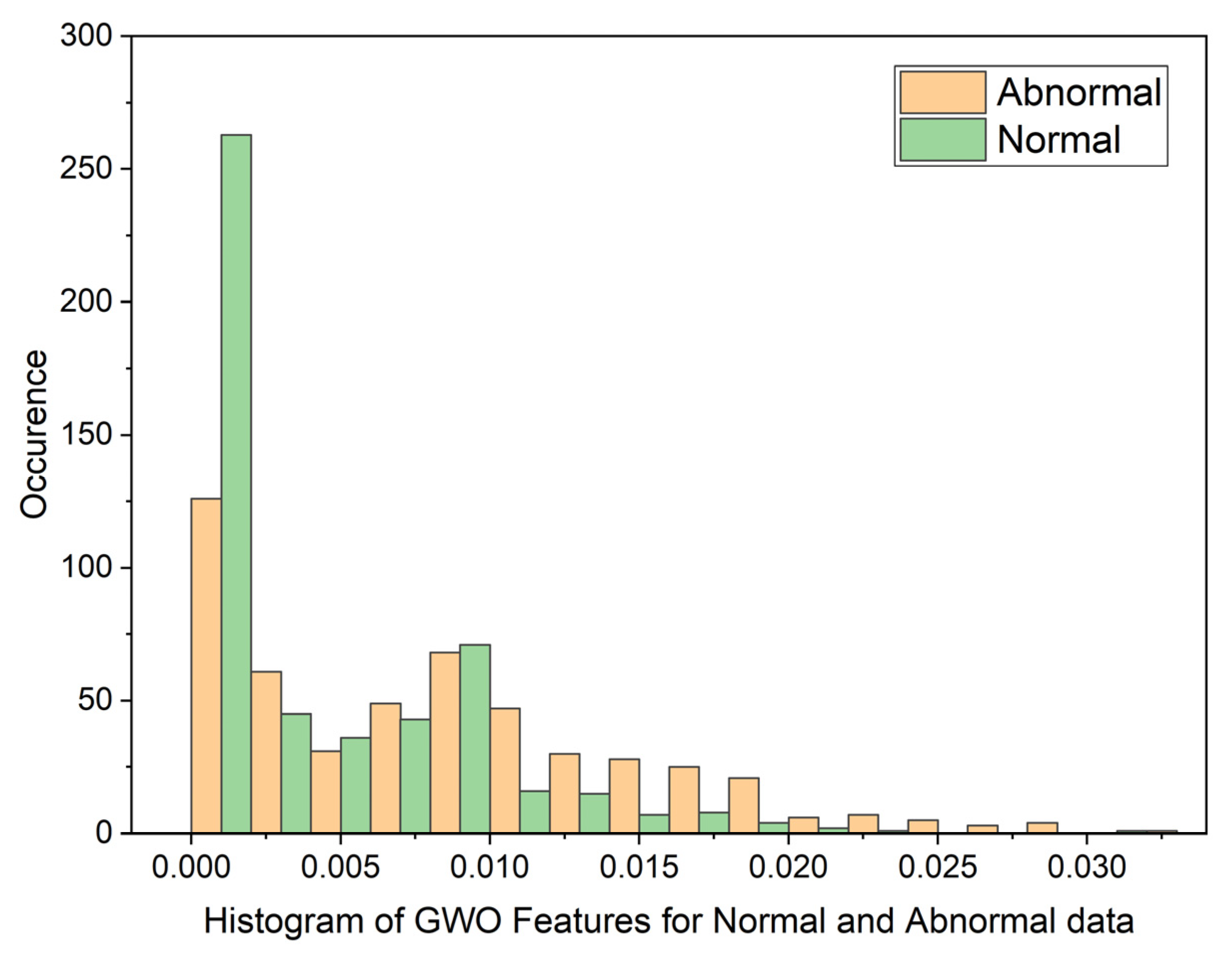
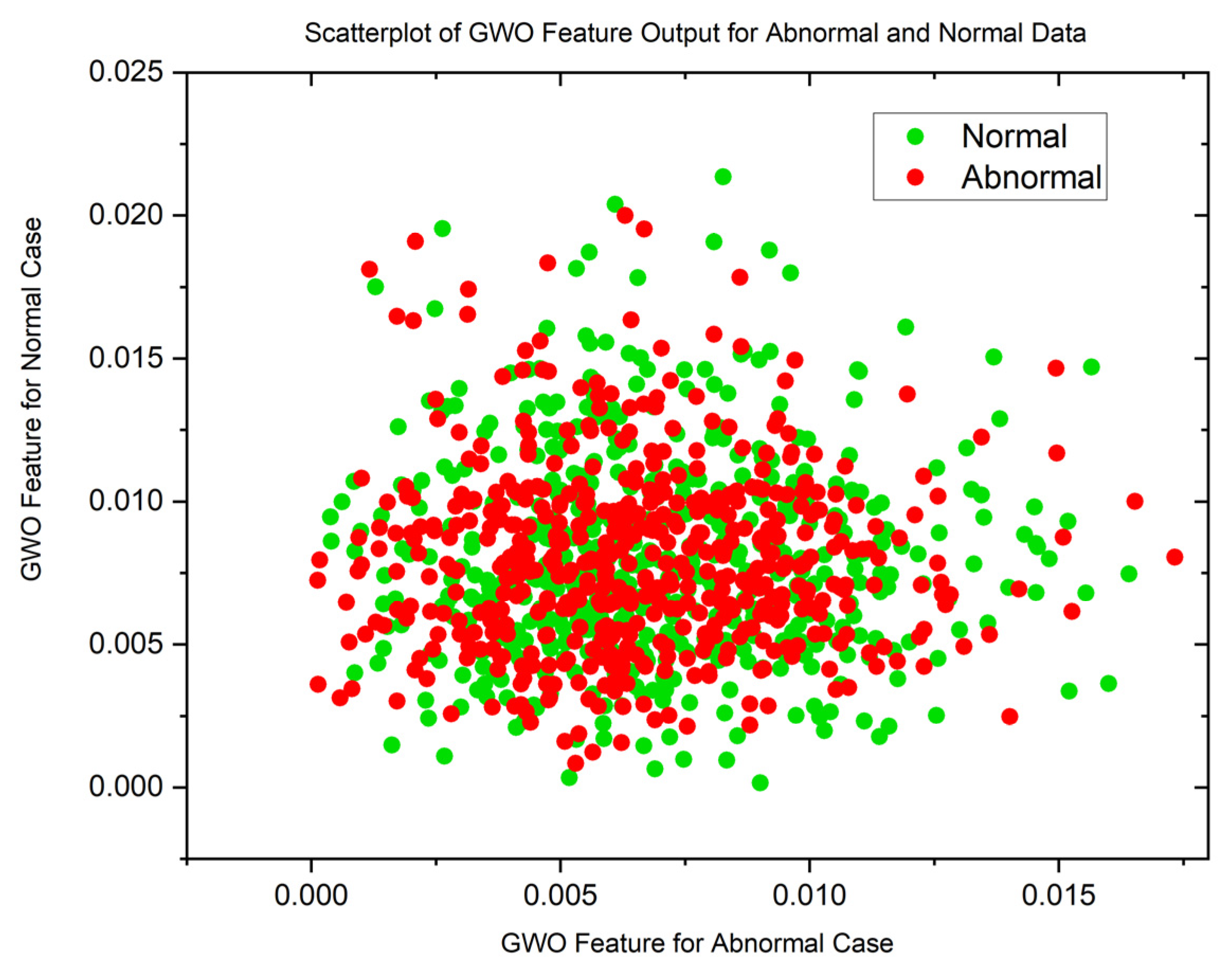
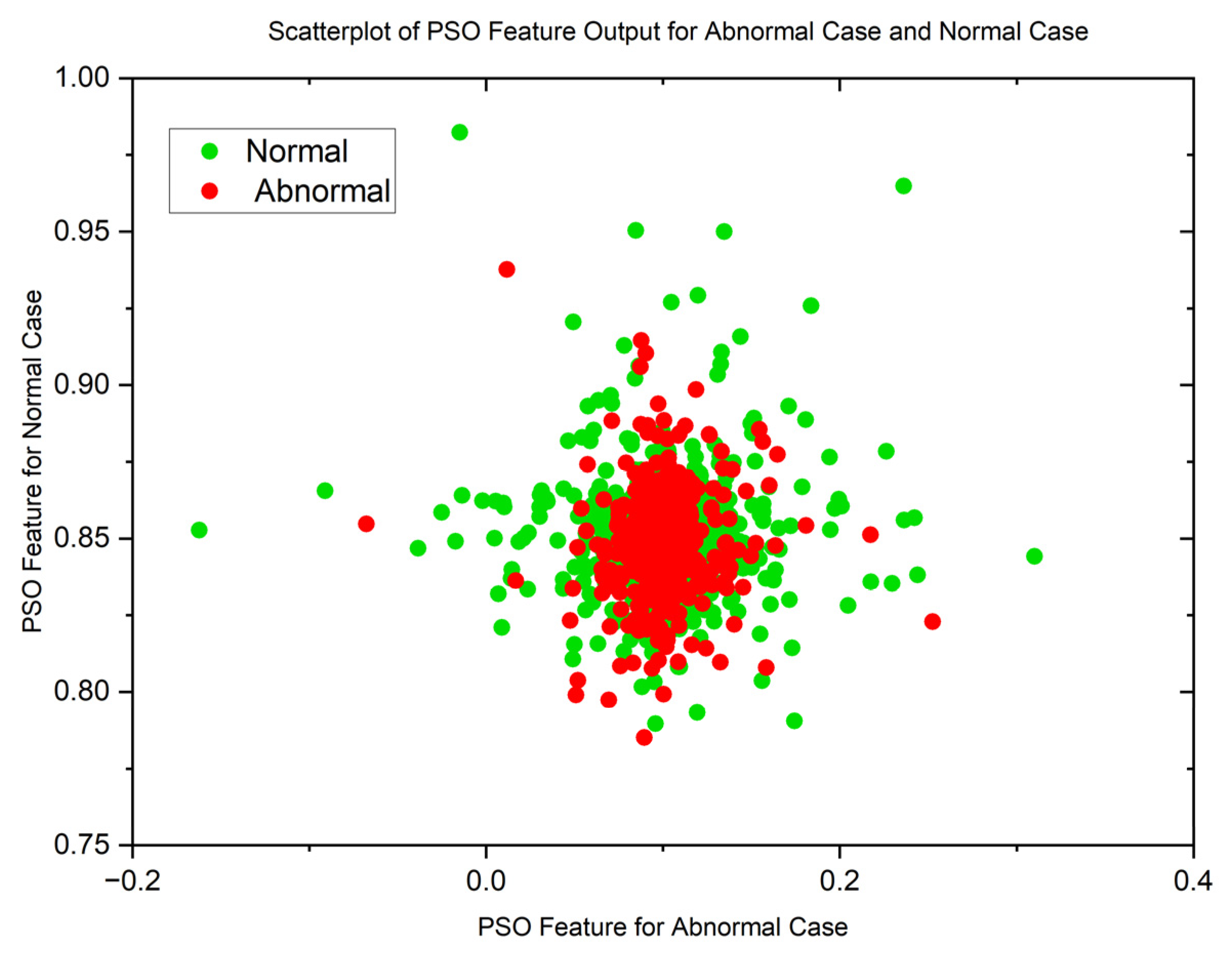
| Statistical Parameters | PSO | GWO | ||
| Malignant | Normal | Malignant | Normal | |
| Mean | 0.8598080214 | 0.1109701363 | 0.01878313748 | 0.01751341349 |
| Variance | 0.05867975074 | 0.07425036326 | 0.07492946326 | 0.07494543857 |
| Skewness | 19.87029488 | 19.83047771 | 22.52231557 | 22.56212107 |
| Kurtosis | 441.8828416 | 444.9961882 | 509.1565306 | 510.3537192 |
| Pearson CC | 0.9019022281 | 0.9269991469 | 0.9985202125 | 0.997858273 |
| CCA | 0.12309 | 0.11291 | ||
| Classifiers | Optimal Parameters of the Classifiers |
| Support Vector Machine | Kernel - RBF; α – 1; Kernel width parameter (σ) – 100; w – 0.85; b - 0.01; Convergence Criterion – MSE. |
| K-Nearest Neighbor | K - 5; Distance Metric – Euclidian; w - 0.5; Criterion – MSE. |
| Random Forest | Number of Trees – 200; Maximum Depth – 10; Bootstrap Sample – 20; Class Weight – 0.45. |
| Decision Tree | Maximum Depth – 20; Impurity Criterion – MSE; Class Weight – 0.4. |
| Softmax Discriminant Classifier | λ = 0.5 along with mean of each class target values as 0.1 and 0.85. |
| Multilayer Perceptron | Learning rate – 0.3; Learning Algorithm – LM; Criterion – MSE. |
| Bayesian Linear Discriminant Classifier | Prior Probability P(x) – 0.5; Class mean = 0.8 and = 0.1, Criterion = MSE. |
| Feature Extraction | Classifiers | Confusion Matrix | MSE | |||
| TP | TN | FP | FN | |||
| PSO | SVM | 3944 | 4009 | 991 | 1056 | 7.29E-06 |
| KNN | 4267 | 3725 | 1275 | 733 | 4.49E-05 | |
| Random Forest | 2692 | 2933 | 2067 | 2308 | 1.60E-05 | |
| Decision Tree | 3184 | 3217 | 1783 | 1816 | 3.60E-07 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 4033 | 3750 | 1250 | 967 | 4.00E-08 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 3425 | 3675 | 1325 | 1575 | 2.25E-06 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 4367 | 3975 | 1025 | 633 | 5.63E-05 | |
| GWO | SVM | 3617 | 4175 | 825 | 1383 | 5.76E-06 |
| KNN | 3500 | 3725 | 1275 | 1500 | 1.44E-05 | |
| Random Forest | 3967 | 3817 | 1183 | 1033 | 3.36E-05 | |
| Decision Tree | 4517 | 3984 | 1016 | 483 | 8.41E-06 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 4083 | 4275 | 725 | 917 | 1.96E-04 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 4050 | 4384 | 616 | 950 | 4.84E-04 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 3967 | 3692 | 1308 | 1033 | 2.50E-07 | |
| Feature Selection |
Classifiers | Confusion Matrix | MSE | |||
| TP | TN | FP | FN | |||
|
KL Divergence |
SVM | 3297 | 2747 | 2253 | 1703 | 3.24E-06 |
| KNN | 3978 | 2605 | 2395 | 1022 | 8.41E-06 | |
| Random Forest | 4115 | 3294 | 1706 | 885 | 2.30E-05 | |
| Decision Tree | 3919 | 4089 | 911 | 1081 | 9.00E-06 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 4089 | 4258 | 742 | 911 | 4.84E-06 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 4271 | 3633 | 1367 | 729 | 2.56E-06 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 3298 | 3311 | 1690 | 1702 | 1.02E-05 | |
| IWO | SVM | 3854 | 3503 | 1497 | 1146 | 2.21E-05 |
| KNN | 3490 | 3985 | 1016 | 1510 | 3.36E-05 | |
| Random Forest | 3574 | 2757 | 2243 | 1426 | 1.94E-05 | |
| Decision Tree | 2982 | 2871 | 2129 | 2018 | 7.84E-06 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 2734 | 3047 | 1953 | 2266 | 1.22E-05 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 3047 | 2592 | 2408 | 1953 | 1.00E-06 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 2681 | 2698 | 2302 | 2319 | 1.85E-05 | |
| Feature Selection |
Classifiers | Confusion Matrix | MSE | |||
| TP | TN | FP | FN | |||
|
KL Divergence |
SVM | 4029 | 2742 | 2258 | 971 | 1.00E-06 |
| KNN | 3789 | 4147 | 853 | 1211 | 4.90E-05 | |
| Random Forest | 3490 | 4089 | 911 | 1510 | 6.40E-07 | |
| Decision Tree | 3594 | 4147 | 853 | 1406 | 2.50E-07 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 4896 | 2668 | 2333 | 104 | 1.00E-06 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 3737 | 2982 | 2018 | 1263 | 2.03E-05 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 3460 | 2767 | 2233 | 1540 | 1.00E-08 | |
| IWO | SVM | 4401 | 3262 | 1738 | 599 | 4.90E-07 |
| KNN | 3203 | 3880 | 1120 | 1797 | 1.60E-05 | |
| Random Forest | 4440 | 2735 | 2265 | 560 | 1.52E-05 | |
| Decision Tree | 4167 | 2620 | 2380 | 833 | 5.29E-06 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 4219 | 2687 | 2313 | 781 | 2.30E-05 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 4375 | 2747 | 2253 | 625 | 9.61E-06 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 3216 | 2760 | 2240 | 1784 | 6.89E-05 | |
| Feature Selection |
Classifiers | Confusion Matrix | MSE | |||
| TP | TN | FP | FN | |||
|
KL Divergence |
SVM | 4089 | 3568 | 1433 | 911 | 6.61E-04 |
| KNN | 4184 | 4487 | 514 | 817 | 1.44E-05 | |
| Random Forest | 4555 | 3520 | 1480 | 445 | 2.72E-04 | |
| Decision Tree | 3815 | 3809 | 1191 | 1185 | 6.72E-05 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 4392 | 3948 | 1052 | 608 | 2.40E-05 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 3881 | 4048 | 952 | 1119 | 1.96E-06 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 4156 | 3947 | 1053 | 844 | 8.41E-06 | |
| IWO | SVM | 3599 | 4085 | 915 | 1401 | 8.10E-05 |
| KNN | 4058 | 4375 | 625 | 942 | 7.23E-05 | |
| Random Forest | 4129 | 4038 | 962 | 871 | 9.00E-08 | |
| Decision Tree | 3713 | 4308 | 692 | 1288 | 6.40E-05 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 4129 | 4161 | 839 | 871 | 4.00E-04 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 4539 | 4024 | 976 | 461 | 2.50E-05 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 3817 | 3797 | 1203 | 1183 | 1.44E-05 | |
| Feature Selection |
Classifiers | Confusion Matrix | MSE | |||
| TP | TN | FP | FN | |||
|
KL Divergence |
SVM | 3653 | 4466 | 534 | 1347 | 1.23E-05 |
| KNN | 4139 | 4948 | 52 | 862 | 7.23E-05 | |
| Random Forest | 4044 | 3913 | 1088 | 956 | 1.30E-05 | |
| Decision Tree | 3635 | 3985 | 1016 | 1365 | 6.89E-05 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 3565 | 4297 | 703 | 1435 | 1.37E-05 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 3740 | 4034 | 966 | 1260 | 6.40E-07 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 3775 | 3987 | 1013 | 1225 | 4.90E-07 | |
| IWO | SVM | 4339 | 4617 | 383 | 661 | 1.94E-05 |
| KNN | 4129 | 4321 | 680 | 871 | 5.76E-06 | |
| Random Forest | 4509 | 4466 | 534 | 491 | 7.57E-05 | |
| Decision Tree | 4617 | 4390 | 610 | 383 | 6.40E-07 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 4409 | 4005 | 995 | 592 | 1.04E-04 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 4409 | 3913 | 1088 | 592 | 4.49E-05 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 4754 | 3973 | 1027 | 246 | 4.90E-07 | |
| Feature Selection |
Classifiers | Confusion Matrix | MSE | |||
| TP | TN | FP | FN | |||
|
KL Divergence |
SVM | 4144 | 3668 | 1333 | 856 | 6.56E-05 |
| KNN | 4209 | 4537 | 464 | 792 | 2.92E-05 | |
| Random Forest | 4575 | 3620 | 1380 | 425 | 1.09E-05 | |
| Decision Tree | 3950 | 3859 | 1141 | 1050 | 5.93E-05 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 4417 | 4098 | 902 | 583 | 1.60E-05 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 4011 | 4198 | 802 | 989 | 3.03E-05 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 4245 | 4047 | 953 | 755 | 3.97E-05 | |
| IWO | SVM | 3710 | 4235 | 765 | 1290 | 1.37E-05 |
| KNN | 4208 | 4375 | 625 | 792 | 4.22E-05 | |
| Random Forest | 4229 | 4188 | 812 | 771 | 4.49E-05 | |
| Decision Tree | 3813 | 4408 | 592 | 1188 | 4.36E-05 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 4229 | 4211 | 789 | 771 | 1.10E-04 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 4558 | 4074 | 926 | 443 | 2.30E-05 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 3917 | 3897 | 1103 | 1083 | 3.02E-05 | |
| Feature Selection |
Classifiers | Confusion Matrix | MSE | |||
| TP | TN | FP | FN | |||
|
KL Divergence |
SVM | 3758 | 4466 | 534 | 1242 | 1.37E-05 |
| KNN | 4159 | 4948 | 52 | 842 | 2.40E-05 | |
| Random Forest | 4094 | 4063 | 938 | 906 | 1.02E-05 | |
| Decision Tree | 3750 | 3985 | 1016 | 1250 | 1.23E-05 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 3670 | 4297 | 703 | 1330 | 4.76E-05 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 3860 | 4084 | 916 | 1140 | 2.12E-05 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 3905 | 4137 | 863 | 1095 | 9.61E-06 | |
| IWO | SVM | 4439 | 4667 | 333 | 561 | 4.36E-05 |
| KNN | 4229 | 4321 | 680 | 771 | 5.48E-05 | |
| Random Forest | 4559 | 4466 | 534 | 441 | 1.90E-04 | |
| Decision Tree | 4667 | 4490 | 510 | 333 | 2.40E-05 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 4459 | 4055 | 945 | 542 | 5.33E-05 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 4459 | 4063 | 938 | 542 | 5.04E-05 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 4789 | 4073 | 927 | 211 | 1.09E-05 | |
| Performance Metrics | Equation | Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) | Average positive-to-negative sample ratio. |
||
| Error Rate | The number of incorrect predictions, based on recorded observations. |
||
| F1 Score (%) | Average of precision and recall to obtain the classification accuracy of a specific class. | ||
| MCC | Pearson correlation between the actual output and the achieved output. |
||
| Jaccard Index (%) | The number of predicted true positives exceeded the number of actual positives, regardless of whether they were real or predicted. |
||
| g-mean (%) | Combination of sensitivity and specificity into a single value that balances both objectives. | ||
| Kappa | Inter-rater agreement measure for assessing agreement between two methods in categorizing cancer cases. | ||
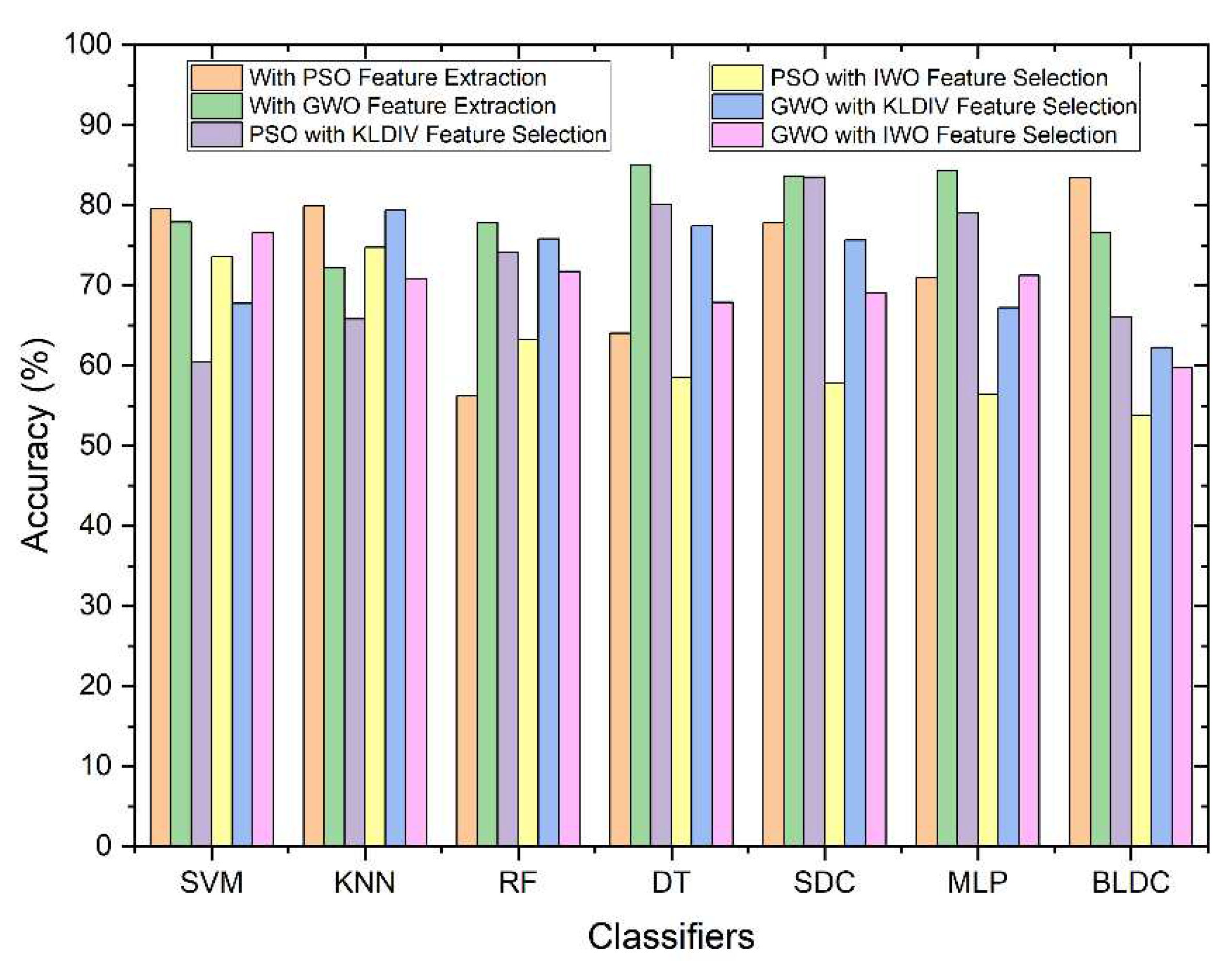
| Feature Extraction | Classifiers | Accuracy (%) | Error Rate (%) | F1 Score (%) | MCC | Jaccard Index (%) | g-mean(%) | Kappa |
| PSO | SVM | 79.53 | 20.47 | 79.40 | 0.59 | 65.83 | 79.53 | 0.59 |
| KNN | 79.92 | 20.08 | 80.95 | 0.60 | 68.00 | 80.21 | 0.60 | |
| Random Forest | 56.25 | 43.75 | 55.17 | 0.13 | 38.09 | 56.26 | 0.13 | |
| Decision Tree | 64.01 | 35.99 | 63.89 | 0.28 | 46.94 | 64.01 | 0.28 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 77.83 | 22.17 | 78.44 | 0.56 | 64.53 | 77.90 | 0.56 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 71 | 29 | 70.26 | 0.42 | 54.15 | 71.04 | 0.42 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 83.42 | 16.58 | 84.05 | 0.67 | 72.48 | 83.59 | 0.67 | |
| GWO | SVM | 77.92 | 22.08 | 76.62 | 0.56 | 62.09 | 78.21 | 0.56 |
| KNN | 72.25 | 27.75 | 71.61 | 0.45 | 55.78 | 72.29 | 0.45 | |
| Random Forest | 77.84 | 22.16 | 78.17 | 0.56 | 64.16 | 77.86 | 0.56 | |
| Decision Tree | 85.01 | 14.99 | 85.77 | 0.70 | 75.08 | 85.33 | 0.70 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 83.58 | 16.42 | 83.26 | 0.67 | 71.32 | 83.62 | 0.67 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 84.34 | 15.66 | 83.80 | 0.69 | 72.12 | 84.46 | 0.69 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 76.59 | 23.41 | 77.22 | 0.53 | 62.89 | 76.66 | 0.53 |
| Feature Selection |
Classifiers | Accuracy (%) | Error Rate (%) | F1 Score (%) | MCC | Jaccard Index (%) |
g-mean (%) |
Kappa |
|
KL Divergence |
SVM | 60.44 | 39.56 | 62.51 | 0.21 | 45.46 | 60.56 | 0.21 |
| KNN | 65.83 | 34.17 | 69.96 | 0.33 | 53.79 | 66.96 | 0.32 | |
| Random Forest | 74.09 | 25.91 | 76.05 | 0.49 | 61.36 | 74.65 | 0.48 | |
| Decision Tree | 80.08 | 19.92 | 79.74 | 0.60 | 66.30 | 80.11 | 0.60 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 83.47 | 16.53 | 83.18 | 0.67 | 71.21 | 83.50 | 0.67 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 79.04 | 20.96 | 80.30 | 0.59 | 67.08 | 79.43 | 0.58 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 66.08 | 33.92 | 66.04 | 0.32 | 49.30 | 66.08 | 0.32 | |
| IWO | SVM | 73.57 | 26.43 | 74.47 | 0.47 | 59.32 | 73.67 | 0.47 |
| KNN | 74.74 | 25.26 | 73.43 | 0.50 | 58.01 | 74.95 | 0.49 | |
| Random Forest | 63.31 | 36.69 | 66.09 | 0.27 | 49.35 | 63.64 | 0.27 | |
| Decision Tree | 58.53 | 41.47 | 58.99 | 0.17 | 41.83 | 58.54 | 0.17 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 57.81 | 42.19 | 56.45 | 0.16 | 39.32 | 57.84 | 0.16 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 56.39 | 43.61 | 58.29 | 0.13 | 41.13 | 56.44 | 0.13 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 53.79 | 46.21 | 53.71 | 0.08 | 36.72 | 53.79 | 0.08 |
| Feature Selection |
Classifiers | Accuracy (%) | Error Rate (%) | F1 Score (%) | MCC | Jaccard Index (%) |
g-mean (%) |
Kappa |
|
KL Divergence |
SVM | 67.72 | 32.28 | 71.40 | 0.37 | 55.52 | 68.80 | 0.35 |
| KNN | 79.36 | 20.64 | 78.60 | 0.59 | 64.74 | 79.49 | 0.59 | |
| Random Forest | 75.78 | 24.22 | 74.24 | 0.52 | 59.03 | 76.09 | 0.52 | |
| Decision Tree | 77.41 | 22.59 | 76.09 | 0.55 | 61.41 | 77.69 | 0.55 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 75.64 | 24.37 | 80.08 | 0.57 | 66.77 | 80.74 | 0.51 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 67.19 | 32.81 | 69.49 | 0.35 | 53.25 | 67.54 | 0.34 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 62.27 | 37.73 | 64.72 | 0.25 | 47.84 | 62.49 | 0.25 | |
| IWO | SVM | 76.63 | 23.37 | 79.02 | 0.55 | 65.31 | 77.82 | 0.53 |
| KNN | 70.83 | 29.17 | 68.71 | 0.42 | 52.34 | 71.16 | 0.42 | |
| Random Forest | 71.75 | 28.25 | 75.87 | 0.46 | 61.12 | 74.14 | 0.43 | |
| Decision Tree | 67.87 | 32.13 | 72.18 | 0.38 | 56.47 | 69.50 | 0.36 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 69.06 | 30.94 | 73.17 | 0.40 | 57.69 | 70.74 | 0.38 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 71.22 | 28.78 | 75.25 | 0.45 | 60.32 | 73.33 | 0.42 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 59.76 | 40.24 | 61.52 | 0.20 | 44.42 | 59.84 | 0.20 |
| Feature Selection |
Classifiers | Accuracy (%) | Error Rate (%) | F1 Score (%) | MCC | Jaccard Index (%) |
g-mean (%) |
Kappa |
|
KL Divergence |
SVM | 76.56 | 23.44 | 77.72 | 0.53 | 63.56 | 76.80 | 0.53 |
| KNN | 86.70 | 13.30 | 86.30 | 0.74 | 75.96 | 86.81 | 0.73 | |
| Random Forest | 80.75 | 19.25 | 82.56 | 0.63 | 70.30 | 81.86 | 0.62 | |
| Decision Tree | 76.24 | 23.76 | 76.26 | 0.52 | 61.63 | 76.24 | 0.53 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 83.40 | 16.60 | 84.11 | 0.67 | 72.58 | 83.62 | 0.67 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 79.28 | 20.72 | 78.93 | 0.59 | 65.20 | 79.31 | 0.59 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 81.03 | 18.97 | 81.42 | 0.62 | 68.67 | 81.08 | 0.62 | |
| IWO | SVM | 76.84 | 23.16 | 75.66 | 0.54 | 61.84 | 77.05 | 0.54 |
| KNN | 84.33 | 15.67 | 83.82 | 0.69 | 72.14 | 84.44 | 0.69 | |
| Random Forest | 81.67 | 18.33 | 81.83 | 0.63 | 69.25 | 81.68 | 0.63 | |
| Decision Tree | 80.21 | 19.79 | 78.95 | 0.61 | 65.23 | 80.56 | 0.60 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 82.90 | 17.10 | 82.84 | 0.66 | 70.71 | 82.90 | 0.66 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 85.64 | 14.36 | 86.28 | 0.72 | 75.88 | 85.94 | 0.71 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 76.14 | 23.86 | 76.19 | 0.52 | 61.54 | 76.14 | 0.52 |
| Feature Selection |
Classifiers | Accuracy (%) | Error Rate (%) | F1 Score (%) | MCC | Jaccard Index (%) |
g-mean (%) |
Kappa |
|
KL Divergence |
SVM | 78.11 | 21.89 | 79.11 | 0.56 | 65.44 | 78.32 | 0.56 |
| KNN | 87.45 | 12.55 | 87.02 | 0.75 | 77.03 | 87.58 | 0.75 | |
| Random Forest | 81.95 | 18.05 | 83.53 | 0.65 | 71.71 | 82.92 | 0.64 | |
| Decision Tree | 78.09 | 21.91 | 78.19 | 0.55 | 64.19 | 78.10 | 0.54 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 85.15 | 14.85 | 85.61 | 0.70 | 74.84 | 85.27 | 0.70 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 82.09 | 17.91 | 81.75 | 0.64 | 69.13 | 82.12 | 0.64 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 82.92 | 17.08 | 83.25 | 0.66 | 71.31 | 82.96 | 0.66 | |
| IWO | SVM | 79.45 | 20.55 | 78.31 | 0.59 | 64.35 | 79.72 | 0.59 |
| KNN | 85.83 | 14.17 | 85.59 | 0.72 | 74.81 | 85.86 | 0.72 | |
| Random Forest | 84.17 | 15.83 | 84.23 | 0.68 | 72.76 | 84.17 | 0.68 | |
| Decision Tree | 82.21 | 17.79 | 81.08 | 0.65 | 68.18 | 82.58 | 0.64 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 84.40 | 15.60 | 84.43 | 0.69 | 73.05 | 84.40 | 0.69 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 86.32 | 13.68 | 86.95 | 0.73 | 76.91 | 86.59 | 0.73 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 78.14 | 21.86 | 78.29 | 0.56 | 64.21 | 78.14 | 0.56 |
| Feature Selection |
Classifiers | Accuracy (%) | Error Rate (%) | F1 Score (%) | MCC | Jaccard Index (%) |
g-mean (%) |
Kappa |
|
KL Divergence |
SVM | 81.19 | 18.81 | 79.53 | 0.63 | 66.02 | 81.88 | 0.62 |
| KNN | 90.87 | 9.14 | 90.06 | 0.83 | 81.92 | 91.71 | 0.82 | |
| Random Forest | 79.56 | 20.44 | 79.83 | 0.59 | 66.43 | 79.58 | 0.59 | |
| Decision Tree | 76.20 | 23.81 | 75.33 | 0.53 | 60.43 | 76.30 | 0.52 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 78.62 | 21.38 | 76.93 | 0.58 | 62.51 | 79.13 | 0.57 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 77.74 | 22.26 | 77.07 | 0.56 | 62.69 | 77.82 | 0.55 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 77.62 | 22.38 | 77.14 | 0.55 | 62.78 | 77.66 | 0.55 | |
| IWO | SVM | 89.56 | 10.44 | 89.27 | 0.79 | 80.61 | 89.66 | 0.79 |
| KNN | 84.50 | 15.51 | 84.19 | 0.69 | 72.70 | 84.54 | 0.69 | |
| Random Forest | 89.76 | 10.24 | 89.80 | 0.80 | 81.49 | 89.76 | 0.80 | |
| Decision Tree | 90.07 | 9.93 | 90.29 | 0.80 | 81.30 | 90.13 | 0.80 | |
| Softmax Discriminant | 84.13 | 15.87 | 84.75 | 0.68 | 73.54 | 84.31 | 0.68 | |
| Multilayer Perceptron | 83.21 | 16.79 | 84.00 | 0.67 | 72.42 | 83.47 | 0.66 | |
| Bayesian LDC | 87.27 | 12.73 | 88.19 | 0.75 | 78.88 | 88.00 | 0.75 |
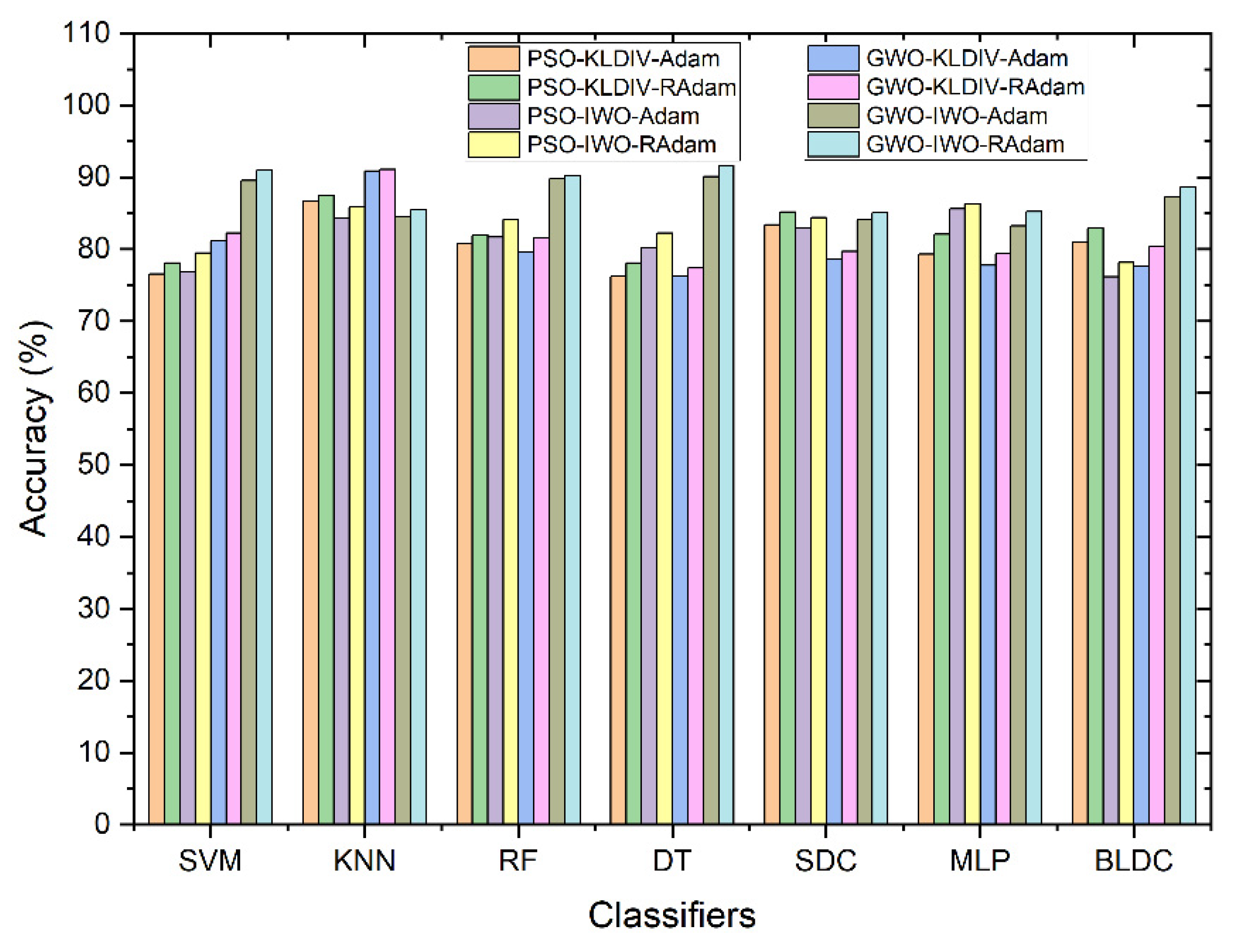
| S No | Feature Extraction | Feature Selection | Classifiers | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PSO | - | Bayesian LDC | 83.42 % |
| 2 | GWO | - | Decision Tree | 85.01 % |
| 3 | PSO | KL Divergence | Softmax Discriminant | 83.47 % |
| 4 | PSO | IWO | KNN | 74.74 % |
| 5 | GWO | KL Divergence | KNN | 79.36 % |
| 6 | GWO | IWO | SVM | 76.63 % |
| 7 | PSO | KL Divergence | KNN with Adam | 86.70 % |
| 8 | PSO | IWO | MLP with Adam | 85.64 % |
| 9 | PSO | KL Divergence | KNN with RAdam | 87.45 % |
| 10 | PSO | IWO | MLP with RAdam | 86.32 % |
| 11 | GWO | KL Divergence | KNN with Adam | 90.87 % |
| 12 | GWO | IWO | Decision Tree with Adam | 90.07 % |
| 13 | GWO | KL Divergence | KNN with RAdam | 91.07 % |
| 14 | GWO | IWO | Decision Tree with RAdam | 91.57 % |
| S No | Classifiers | Without Feature Extraction |
With Feature Extraction | With Feature Selection | With Hyperparameter Tuning of IWO Feature Selection Method |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSO | GWO | KL Divergence |
IWO | Adam | RAdam | |||
| 1 | SVM | |||||||
| 2 | KNN | |||||||
| 3 | RF | |||||||
| 4 | DT | |||||||
| 5 | SDC | |||||||
| 6 | MLP | |||||||
| 7 | BLDC | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





