1. Introduction
Organic molecules containing phosphonic and phosphinic acidic groups are unusual, though naturally occurring compounds [1-6]. They are unusual because they characterized by the presence of a carbon-phosphorous (C-P) bond. In particular, phosphonates contain a single C-P bond, whereas phosphinates contain either two such bonds (i.e. C-P-C) or C-P-H bonds. For both types of compounds the rest of the valences on the phosphorous atom are engaged in bonding oxygen. The C-P bond, unlike the C-O-P bonds (such as those occurring in the more common organic phosphate esters and anhydrides) has unique features, including a remarkable stability against enzymatic (i.e., cannot be cleaved by hydrolyses) or chemical cleavage, such as acid/base hydrolysis. Notably, the phosphinic and phosphonic moieties structurally mimic phosphate esters, carboxylates and tetrahedral intermediates occurring during carboxyl group transformations [
3,
4]. This also explains why many of these compounds act as substrates or competitive inhibitors of enzymes the natural substrates of which possess the above functional groups. Prominent examples of these class of molecules include compounds of natural origin, such as the antibiotics fosfomycin [
6], dehydrophos and plumbemycin, the antimalarial compounds fosmidomycin and FR-900098, the antifungals rhizocticins, the herbicide phosphinothricin (PT; also known as glufosinate) [
3,
4], as well as chemically synthesized antivirals Adefovir and Tenofovir, which are successfully employed to treat hepatitis B infections [
7]. Examples of such molecules are shown in
Figure 1a.
Given that some of the natural compounds mentioned above may be toxic also to the producing micro-organism, they are naturally synthetized as di- or tri-peptide precursors, which then enter the target cell through dipeptide or oligopeptide permeases, Dpp and Opp, respectively [
3,
4,
8,
9]. Once internalized, they are cleaved by cytosolic peptidases that cause the release of the active C-P-containing amino acid. This mechanism has been referred as a “Trojan horse” or pro-drug strategy [
3,
4,
8,
9]. A remarkable example is phosphinothricin (PT; glufosinate; Fig. 1a), a non-proteinogenic amino acid, which was initially isolated as a bioactive component of the tripeptide Bialaphos, phosphinothricyl-
L-alanyl-
L-alanine. PT is a phosphinic analogue of
L-glutamate, with a phosphinic moiety (C-PO
2HCH
3) replacing the glutamate γ-carboxyl group. PT was demonstrated to act as a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme glutamine synthetase (GS), which catalyzes the ATP-dependent formation of glutamine starting from glutamate and ammonia, by mimicking the γ-phosphorylated intermediate of glutamate formed during the first step of the reaction [
10,
11]. In plants, the inhibition of GS leads to a rapid accumulation of intracellular ammonium ion (NH
4+), which perturbs pH homeostasis and leads to cell death. Hence, PT and the PT-containing tripeptides, Bialaphos or Phosalacine (i.e.
L-alanyl-
L-leucyl-PT), exhibit strong herbicidal activity [
3,
5,
12,
13]. In addition to the well-established herbicidal effect, Bialaphos and a PT-containing dipeptide,
L-Leu-
L-PT, were remarkably effective on clinical isolates of
Klebsiella pneumoniae, which displayed resistance to more than 20 commercial antibiotics belonging to different classes [
14].
Less investigated than PT and Bialaphos is the PT desmethylated on the phosphinic moiety (
L-2-amino-4-(hydroxy)-phosphinylbutyric acid; hereafter
L-Glu-γ-P
H; Fig. 1b), which is also an analogue of
L-glutamate, that carries the more rarely occurring
H-phosphinic group, i.e. C-P(O)(OH)H.
L-Glu-γ-P
H was originally isolated as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of Bialaphos in
Streptomyces hygroscopicus [
15] and more recently in the free form in
Nonomureae sp. NRRL B-24552 [
1]. In
S. hygroscopicus L-Glu-γ-P
H was shown to accumulate and inhibit growth in the mutant form of this micro-organism where the Bialaphos biosynthetic pathway was blocked [
16]. To protect themselves from the action of the antibiotics they synthetize, the producer organisms (i.e.
Streptomyces) inactivate PT by acetylation [
17] and then incorporation into Bialaphos, which is then released in the environment. To date the mechanism of antibacterial activity of
L-Glu-γ-P
H remains unknown. However, we demonstrated that the
H-phosphinic group of
L-Glu-γ-P
H is a bioisostere of carboxylates, and that the desmethylated phosphinic compounds derived from it (i.e. the
H-phosphinic analogues of GABA and succinate) can be recognized and metabolized just as the substrate by the relevant enzymes [
18]. We also found that only the
L-isomer of Glu-γ-P
H displays an antibacterial activity, which implies that the compound is indeed metabolized and leads to the formation of intermediate(s) that are eventually responsible for the observed antibacterial activity [
18].
To the best of our knowledge, peptides containing amino acids with a
H-phosphinic group in distal position from the carboxyl group have never been investigated as antibacterials. Herein, to evaluate the potential of Glu-γ-P
H as an effective antibacterial, we studied the inhibition of growth caused by the dipeptide
L-Leu-
D,L-Glu-γ-P
H on both
Escherichia coli and
Bacillus subtilis, as representatives of Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, respectively. We compared its activity with that of
D,L-PT and
L-Leu-
D,L-PT, its dipeptide derivative, as well as with the corresponding phosphonic analogues of glutamate (i.e., Glu-γ-P
5 and
L-Leu-
D,L-Glu-γ-P
5; Fig. 1b). Our data suggest that the incorporation of Glu-γ-P
H in a dipeptide significantly improves the penetration of the molecule, thus enhancing its antibacterial activity and potential use for treating bacterial infections caused by different microorganisms. This work represents another piece of evidence that phosphinic compounds can be regarded as interesting molecules with antibacterial activity, as recently proposed for the PT-derived dipeptide on multidrug resistant clinical isolates of
K. pneumoniae [
14].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
D,L-Glu-γ-P
H was synthesized as described in [
19];
N-(benzyloxycarbonyl)-
L-leucine
N-hydroxysuccinimide ester (Z-
L-Leu-OSu) was prepared according to [
20] and was recrystallized from
i-PrOH before use.
L-2-Amino-4-phosphonobutyric acid (L-AP4) was obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnology and was recrystallized from H
2O-EtOH before use; Amoxicillin (2.0 μg per disk) – from Becton, Dickinson & Co (USA).
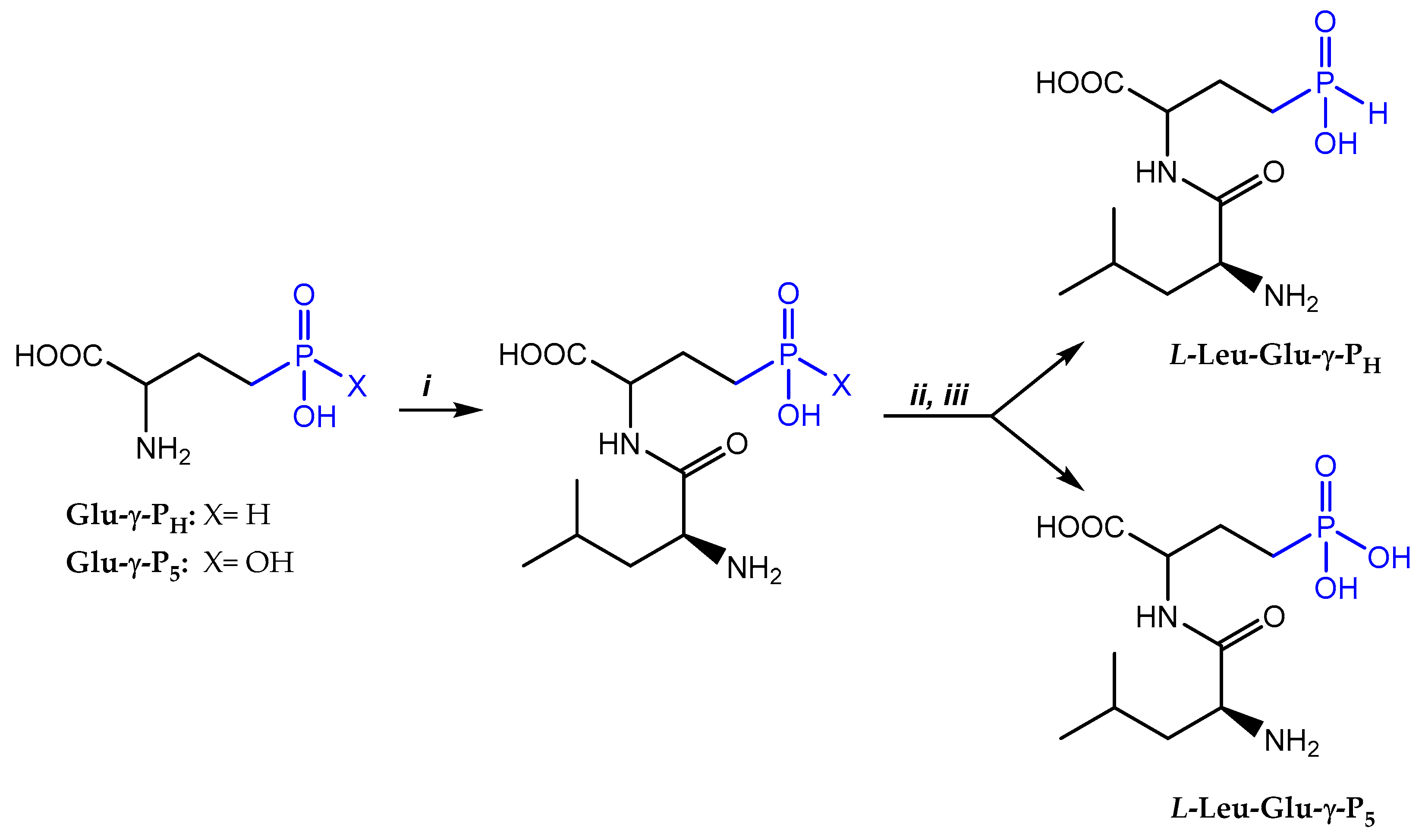
Synthesis of
L-Leucyl-
D,L-Glu-γ-P
H is described in detail elsewhere [
14].
Agar agar powder No. 1 for bacteriology was from LobaChemie. All other reagents, salts and solvents were of the highest purity and used as supplied by Sigma-Aldrich and Acros.
TLC was carried out on plastic sheet Cellulose F254 (Merck, Germany) in i-PrOH‒25% NH4OH‒H2O = 7:1:2. L-Leu-D,L-Glu-γ-PH and L-Leu-D,L-Glu-γ-P5 were detected on TLC plates following staining with ninhydrin (0.4% in acetone).
Ion-exchange chromatography was carried out on Dowex 50WX8, H+-form, 100-200 mesh (BioRad) using water for elution.
NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker AM-300 (300.13 MHz for 1H, 75.43 MHz for 13C, and 121.44 MHz for 31P) using D2O as a solvent with sodium 3-trimethyl-1-propanesulfonate (DSS) as internal, or 85% H3PO4 as external standards. Chemical shifts are given in parts per million (ppm), the letter “J” indicates spin-spin coupling constants which are given in Hertz (Hz).
2.2. Synthesis of L-Leucyl-D,L-Glu-γ-PH
To a solution containing D,L-Glu-γ-PH (500 mg, 3.0 mmol), NaHCO3 (127 mg, 1.5 mmol), Na2CO3 (158 mg, 1.5 mmol) in 1.0 M NaOH (6 mL), water (1 mL), and 1,2-dimethoxyethane (1 mL), a solution of N-Cbz-L-Leu-OSu (1.08 g, 3.0 mmol) in 1,2-dimethoxyethane (5 mL) was added, and the reaction mixture was stirred overnight at 20°C. The reaction mixture was concentrated in vacuo, the residue was then dissolved in water (15 mL), acidified with 37% HCl to pH=1.0, and the separated oil was extracted with EtOAc (3 x 7 mL). The combined EtOAc extracts were washed with water (3.0 mL), brine (2 x 5 mL) and dried (MgSO4). The solvent was removed in vacuo and the residue was dried in vacuo at 1.0 Torr at 40°C for 1 h. The obtained foam was dissolved in glacial AcOH (3 mL), then anisole (0.2 mL) and 35% HBr/AcOH (2.2 mL) were added. The reaction mixture was incubated at 20°C for 1.5 h (until the end of the evolution of CO2), pooled into abs. Et2O (60 mL) and left overnight at -20°C. Solvents were decantated, the residual oil was co-evaporated in vacuo with water (2 x 10 mL), the residue was dissolved in water (10 mL) and applied on a Dowex 50WX8 column (V= 12 mL). Column was eluted with water (600 mL), collecting 10 mL fractions, and then ninhydrin-positive fractions (from 15 to 50) were combined, evaporated to dryness in vacuo, and the residue was dried in vacuo over P2O5 to give L-Leu-D,L-Glu-γ-PH (640 mg, yield 76% for two steps) as a colorless solid, Rf 0.66. 1H NMR (300.13 MHz, D2O): δ = 7.02 (dm, 1H, 1JHP 514.1 Hz, H-P), 4.57-4.47 (m, 1H, CH-COOH), 4.17-4.09 (m, 1H, CH-NH2), 2.24-2.12 (m, 1H, CHa-P), 2.09-1.95 (m, 1H, CHb-P), 1.90-1.62 (m, 5H, CH2-CH2-P, CH2-CH-NH2, CH-(CH3)2), 1.10-1.00 (m, 6H, CH-(CH3)2). 13C NMR (75.43 MHz, D2O): δ = 177.81 and 177.31 (2×s, COOH), 173.31 and 173.20 (2×s, CONH), 56.52 and 56.26 (2×d, 3JPC 16.5 Hz and 3JPC 16.4 Hz, CH-COOH), 54.79 and 54.61 (2×s, CH-NH2), 42.59 (s, CH2-CH-NH2), 30.25 and 30.05 (2×d, 1JPC 89.3 Hz, 1JPC 89.4 Hz, CH2-P), 26.71 and 26.50 (2×s, CH2-CH2-P), 25.82 and 25.79 (2×s, CH-(CH3)2), 24.39 and 24.35 and 23.94 and 23.91 (4×s, CH3).31P NMR (121.44 MHz, D2O): δ = 29.34 and 29.17 (2×s). Symbol “×” indicate differences of the same signals and coupling constants of L,L- and L,D-diastereomers. HRMS (ESI-MS): found m/z 281.1261; calc. forC10H21N2O5P [M+H]+ 281.1266.
2.3. Synthesis of L-Leucyl-D,L-Glu-γ-P5
This dipeptide was prepared as described for L-Leu-D,L-Glu-γ-PH (see section 2.2) starting from D,L-AP4 (366 mg, 2.0 mmol) and N-Cbz-L-Leu-OSu (716 mg, 2.0 mmol) in H2O-1,2-dimethoxyethane mixture. After the deprotection of the crude N-Cbz-dipeptide with 35% HBr/AcOH and the removal of the access of HBr/AcOH as descibed in section 2.2, the residue was dissolved in H2O (10 mL) and applied on a Dowex 50WX8 column (V= 12 mL). Column was eluted with water (700 mL), collecting 10 mL fractions, and then ninhydrin-positive fractions (from 25 to 60) were combined, evaporated to dryness in vacuo and the residue was dried in vacuo over P2O5 to afford L-Leucyl-D,L-Glu-γ-P5 (320 mg, yield 54% for two steps): Rf 0.29. 1Н NMR (300.13 MHz, D2O): δ = 4.44-4.32 (m, 1H, CH-COOH), 4.00 (dd, 1H, 3JHHa 7.5 & 7.4 Hz, 3JHHb 7.4 & 6.7 Hz, CH-NH2), 2.15-2.01 (m, 1H, CHa-P), 2.00-1.85 (m, 1H, CHb-P), 1.77-1.54 (m, 5H, CH2-CH2-P, CH2-CH-NH2, CH-(CH3)2), 0.98-0.85 (m, 6H, CH-(CH3)2). 13С NMR (75.43 MHz, D2O): δ = 178.12 and 177.55 (2×s, COOH), 173.30 and 173.19 (2×s, CONH), 56.84 and 56.50 (2×d, 3JPC 17.5 Hz and 3JPC 17.3 Hz, CH-COOH), 54.81 and 54.62 (2×s, CH-NH2), 42.58 (s, CH2-CH-NH2), 27.90 and 27.88 (2×s, CH-(CH3)2), 26.94 and 26.68 (2×d, 1JPC 134.5 Hz and 1JPC 134.7 Hz, CH2-P), 26.70 and 26.50 (2×s, CH2-CH2-P), 24.39 and 24.35 and 23.93 and 23.91 (4×s, CH3). 31P NMR (121.44 MHz, D2O): δ = 24.93. HRMS (ESI-MS): found m/z 297.1210; calc. for C10H21N2O6P [M+H]+ 297.1215.
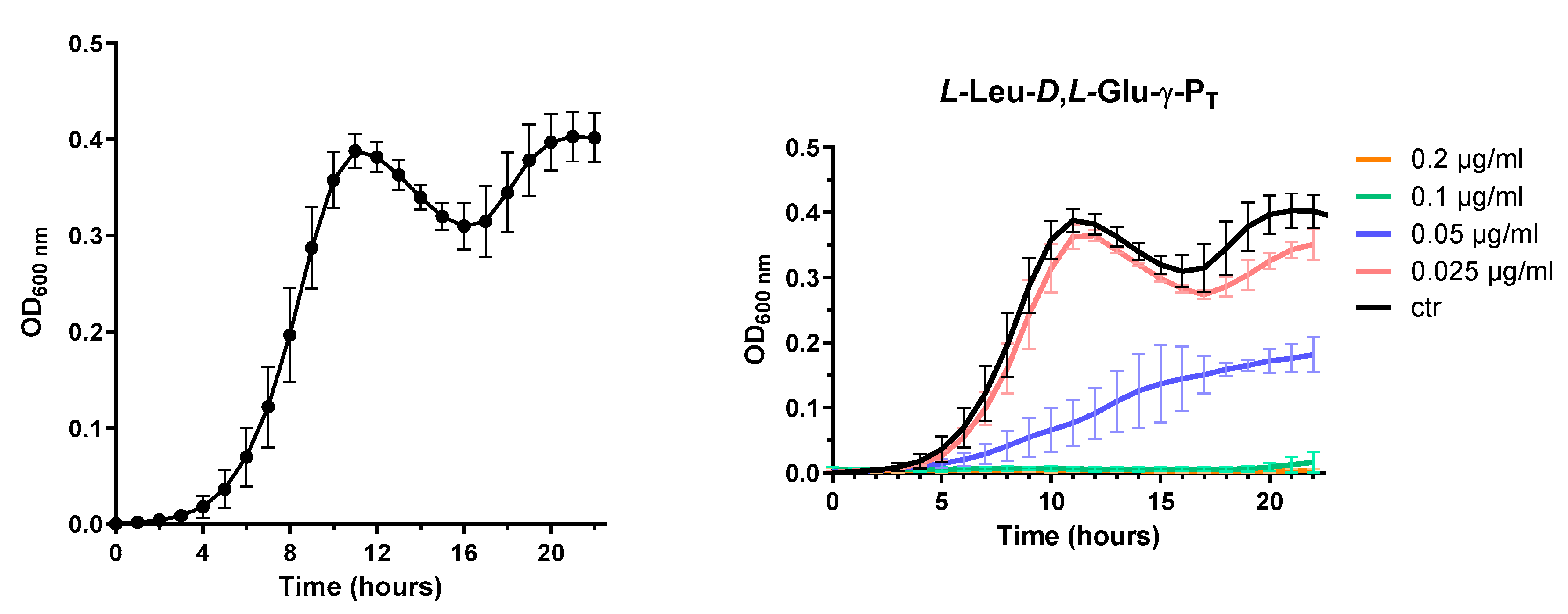
2.4. The microdilution method to determine the antimicrobial activity of tested compounds against Escherichia coli
The minimum inhibitory concentration able to inhibit 90% (MIC
90) of the the growth of the bacterial population of the test strain E. coli K12 MG1655 was calculated using the broth microdilution method in the minimal medium EG containing MgSO
4•7H
2O (0.2 g), citric acid•H
2O (2.0 g), anhydrous K
2HPO
4 (10.0 g), NaNH
4HPO
4•H
2O (3.5 g), and glucose (4.0 g), milliQ water (1.0 L), at final pH 7.0 as described elsewhere [
18]. Briefly,overnight cultures (2 mL) of E. coli K12 strain MG1655 grown in LB (lysigeny broth) medium were centrifuged at 3500 rpm for 15 min at 15°C and the bacterial cellular pellets resuspended in an isovolume of saline solution (9 g/L NaCl). The OD
600 then brought to 1.0. The resuspension of the bacterial cells was used to inoculated (1:25) 2 mL of fresh minimal medium EG and bacteria allowed to grow for 6-7 hours at 37°C from a starting OD
600 = 0.04 to a final OD
600 = 0.5 (corresponding to 2.5 x 10
8colony forming units, cfu/mL), then diluted (1:25) to a final OD
600 = 0.02 (corresponding to 1.0 x 10
7 cfu/mL) in the same minimal medium. This dilution was the one used to set up the 96-well microplate containing geometrically increasing concentration of the compounds to be tested. In the microplate, 20 µL of bacterial culture (OD
600 = 0.02) were added to a final volume of 200 µL. Thus, a 1:10 dilution was made and the starting OD
600 in the microplate reader was 0.002, corresponding toa number of cfu/mL at time zero, as assessed by plating on LB-agar, between 0.5-1.0 x 10
6/mL, which corresponds to the optimum starting number of cfu/mL to perform a MIC experiment. The microplate was incubated at 37°C for 24 hours in the microplate reader Varioskan Lux (Thermo Scientific). The OD
600 was recorded automatically every hour. Before each reading, the microplate was set to shake vigorously 10 seconds, to ensure an even distribution of the bacteria in solution. MIC
90 was calculated at 22 hour from the inoculum using the equation: % inhibition = [1-(OD
600treated/OD
600untreated)]×100.
Unless otherwise specified, all the tested compounds were dissolved in Milli-Q water, pH-adjusted to 7-8 by adding 5.0 N NaOH, filtered, dispensed in aliquots and stored at -20°C.
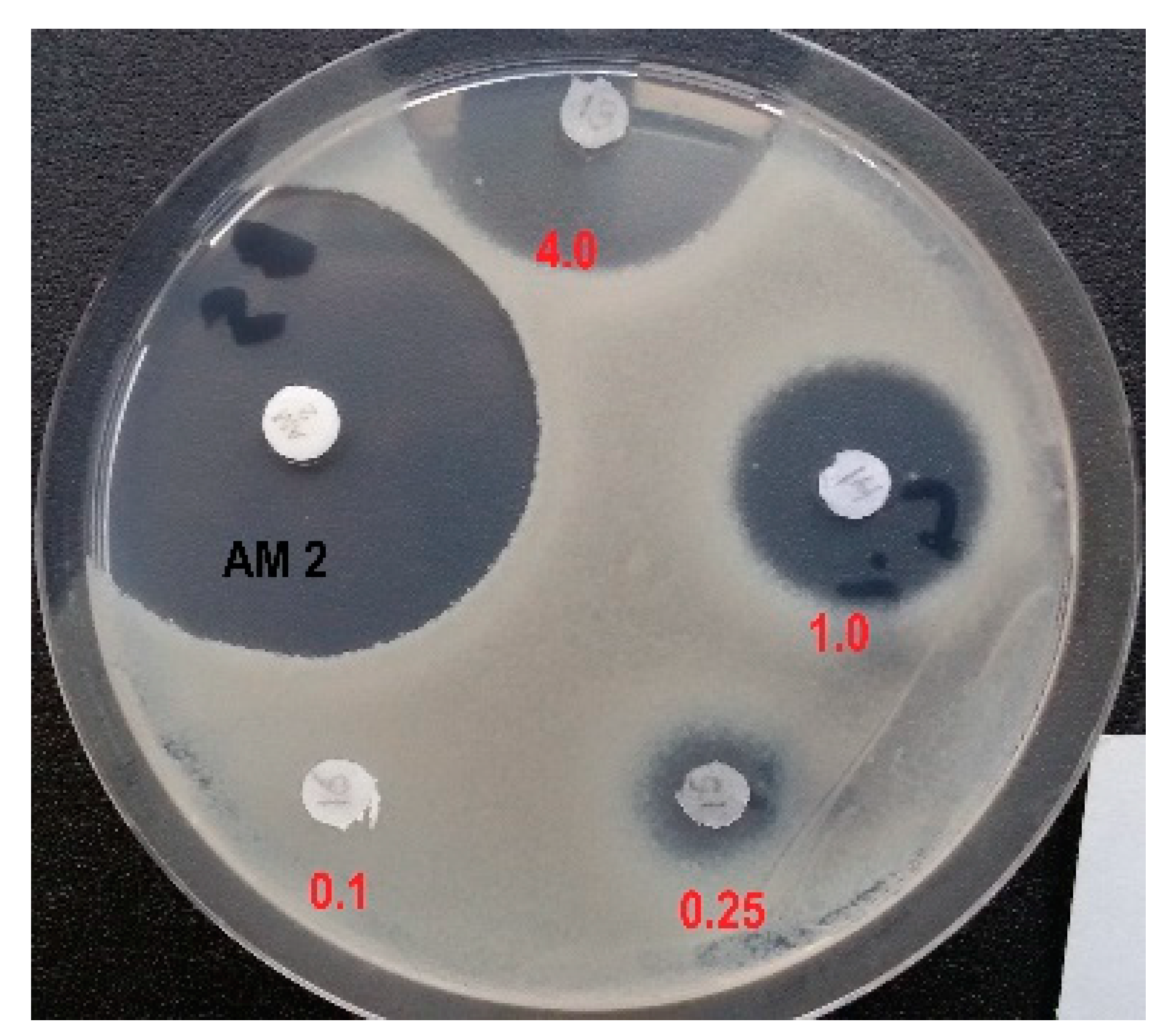
2.5. The agar diffusion method to analyze antimicrobial activity of L-Leucyl-D,L-Glu-γ-PH against Bacillus subtilis АТСС 6633
Different amounts of L-Leu-
D,
L-Glu-γ-P
H were applied to paper disks, the discs were dried in air and placed on the surface of an agar medium for B. subtilis[
21], containing Gibco potato starch (25.0 g), glycerol (2.5 g),
L-Asp (2.0 g),
D,
L-Met (0.4 g), K
2HPO
4 (6.0 g), KH
2PO
4 (2.0 g), NH
4Cl (1.0 g), NH
4NO
3 (0.2 g), Na
2SO
4 (0.2 g), MgSO
4•7H
2O (0.04 g), MnSO
4•4H
2O (0.002 g), FeSO
4•7H
2O (0.002 g), CaCl
2 (0.001 g), agar (15 g), and milliQ water (1.0 L), final pH 6.8, with a seeded lawn of B. subtilis АТСС 6633 strain with a seeding density of 10
6 bacteria per 1 cm
2 of agar surface. Dishes were incubated for 20 h at 37℃. Disk with Amoxicillin (2.0 μg per disk) was used as a control. The antibiotic activity was determined by agar diffusion method based on the presence and size of non-growth zones around the disks [
22].
4. Discussion
The substitution of the carboxyl group of amino acids with a phosphorus-containing group leads to two main families of analogues, the phosphinic and the phosphonic organophosphorous compounds. The latter -P(O)(OH)
2 group has a tetrahedral spatial organization, with a double negative charged at neutral pH, unable to mimic the planar single-charged carboxyl group of the amino acids, as we already demonstrated by modelling studies [
18]. In agreement, in most of the cases aminophosphonic acids are poor inhibitors of the enzymes of amino acid metabolism [
25]. However, among the derivatives of aminophosphonic acids, i.e. esters, amides and the compounds with C-P-C backbone, which are stable mimics of tetrahedral intermediates (or reaction transition states) of the carboxyl group transformations, are not only potent enzyme inhibitors, but even commercial drugs [
9,
25]. Notable examples are the compounds listed in the Introduction (with some depicted in Fig. 1a) including PT which inhibits GS [
10,
11]. Another notable example is a peptidomimetic containing a phosphonate moiety in place of the peptide bond, Fosinopril®, which acts as an inhibitor of the zinc-dependent angiotensin converting enzyme and is used to treat hypertension [
26].
On the contrary, the substitution of one hydroxyl group of aminophosphonic acids with a hydrogen atom eliminates one negative charge as well a bulky atom (i.e. oxygen) and confers to the
H-phosphinic group a flattered tetrahedral geometry as suggested by crystallographic data for β-
H-phosphinic analogue of aspartate [
27]. Respectively, the
H-phosphinic group can be considered as a bioisostere of the carboxyl group, that is confirmed by several substrate-like transformations of α-amino-
H-phosphinic acids ([
18] and ref. therein).
Demethylphosphinothricin, Glu-γ-P
H (Fig. 1b), was first discovered and isolated from
Streptomyces hygroscopicus and
S. viridochromogenes [
15] as a key intermediate of the biosynthetic pathway leading to commercial herbicide Bialaphos (a tripeptide containing phosphinothricin, i.e. PT, and two alanyl residues) [
28]The key biochemical peculiarity of Glu-γ-P
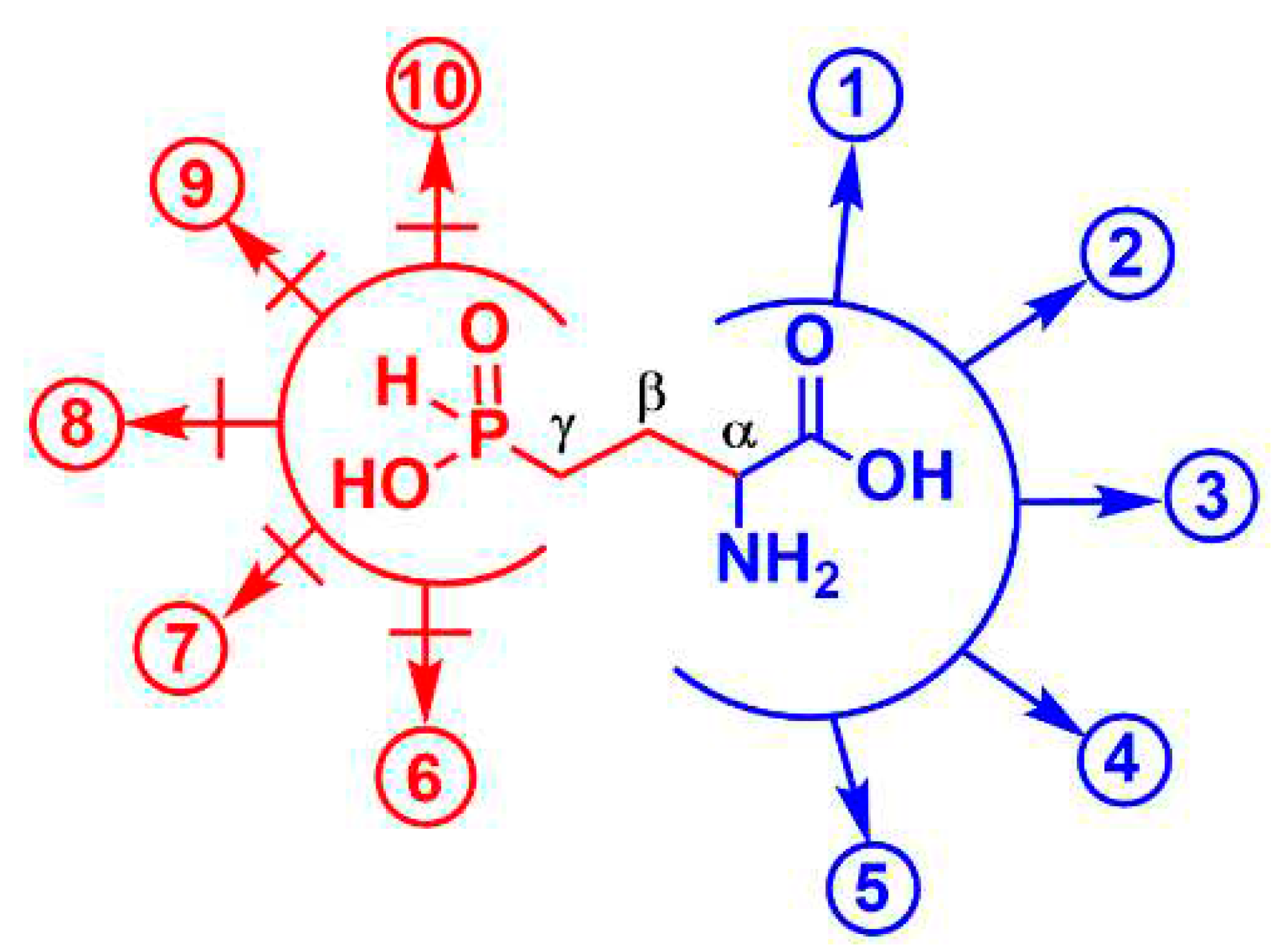
H is the presence of two pharmacophores in its molecule, i.e. the
H-phosphinic group replacing the γ-carboxyl group and the α-amino acid moiety (
Figure 4). This explains the ability of Glu-γ-P
H to undergo some substrate-like transformations
via α-amino acid moiety leading to metabolites containing unusual С-Р-Н bonds (see blue pathways in
Figure 4), as recently demonstrated [
18]. Some of the
de novo synthesized metabolites may eventually be those responsible for the observed antibacterial activity.
It is known that
L-Glu-γ-P
H is a substrate of the PLP-dependent enzyme aspartate aminotransferase, giving rise to
H-phosphinic analogue of α-ketoglutarate, i.e. 2-oxo-4-phosphinobutyric acid (hereafter α-KG-γ-P
H,
Figure 4, reaction 1) [
29].
L-Glu-γ-P
H is a substrate of
E. coli GABA transaminase producing α-KG-γ-P
H [
30]. According to our preliminary observations (unpublished), α-KG-γ-P
H is also formed in NAD-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase reaction (Fig. 4, reaction 2). As a consequence of one of the above reactions, α-KG-γ-P
H may enter the TCA cycle and thereby cause antibacterial activity at some level by acting as an inhibitor of central metabolism.
L-Glu-γ-P
H was also found to be the substrate of the PLP-dependent enzyme glutamate decarboxylase from
E. coli, yielding the
H-phosphinic analogue of GABA, GABA-P
H (Fig. 4, reaction 3), which then undergoes transamination by GABA-transaminase and the resulting 3-phosphinopropionic aldehyde (the
H-phosphinic analogue of succinic semi-aldehyde) is then oxidized in a NAD-dependent reaction to the
H-phosphinic analogue of succinate by succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase [
18]. Since the
H-phosphinic group is a bioisostere of the carboxyl group, it cannot be excluded that
L-Glu-γ-P
H may be a substrate of glutamyl-tRNA synthetase (Fig. 4, reaction 4) with a subsequent formation of peptides carrying a few
L-Glu-γ-P
H residues (though a high incorporation of
L-Glu-γ-P
H is not expected to occur because of the competition with the much more abundant
L-glutamate in the glutamyl-tRNA synthetase reaction). Finally, it is plausible that
L-Glu-γ-P
H will undergo PLP-dependent racemization to give
D-Glu-γ-P
H (Fig. 4, reaction 5), which will be not involved in the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan (murein), an important component of the bacterial cell wall, due to the different chemistry of the carboxyl and
H-phosphinic groups.
When considering the antibacterial activity of
L-Glu-γ-P
H, the contribution of the second pharmacophore, the distal
H-phosphinic group, must be taken into consideration. Transformations of γ-carboxyl group of glutamate lead to the formation of glutamine (nitrogen assimilation), glutathione (essential antioxidant), dihydrofolate (essential in one-carbon reactions), and are involved in the biosynthesis of proline and ornithine. All these reactions lead to the formation of γ-glutamyl phosphate, or γ-glutamyl adenylate, intermediate through ATP-dependent ligations, key steps in the biosynthesis of the above important metabolites. The intermediate formation of such activated
L-Glu-γ-P
H derivatives is in principle possible, since the
H-phosphinic analogues of methionine and valine were substrates of the ATP-PPi exchange reaction catalyzed by Met- and Val-aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases [
31]. However, the transfer of Met- and Val
H-phosphinic analogues to the 3’-end of tRNA was not observed and is biochemically impossible because the enzymes are highly complementary to the tetrahedral transition state (intermediate compound) of carboxyl group, while the transition state of the
H-phosphinic group is a trigonal bipyramid. These considerations
a priori restrict substrate-like transformations of
L-Glu-γ-P
H via the
H-phosphinic group (Fig. 4, pathways 6-10). Therefore,
L-Glu-γ-P
H may be expected to inhibit glutamine, glutathione, dihydrofolate, proline, and ornithine biosynthetic pathways, but it is difficult to predict how efficient this inhibition would be.
Based on the above, the antibacterial activity of L-Leu-D,L-Glu-γ-PH, which penetrates in bacteria via the peptidyl permease system and upon cleavage via peptidases, releases the antibacterial L-Glu-γ-PH, may be due either to biochemical transformation of its α-amino acid moiety (Fig. 3), giving new biologically active metabolites containing a C-P-H bond, or due to the restriction of metabolically significant transformations at the γ-position of this glutamate analogue – in this case L-Glu-γ-PH would acts as an inhibitor.
In this work we observed that phosphonic dipeptide
L-Leu-
D,
L-Glu-γ-P
5 was significantly less active against
E. coli when compared to
L-Leu-
D,
L-Glu-γ-P
H (
Table 1). It is possible that such a difference may be due to the differences in bioavailability, although phosphonopeptides are known to effectively penetrate bacteria using peptidyl permeases [
9,
30,
32]. More p in our opinion is the assumption that these differences are more likely due to the inability of Glu-γ-P
5, released in the cytosol after dipeptide cleavage, to undergo substrate-like transformations (reactions 1-5 in Fig. 3) that lead to new biologically active phosphonic compounds, unlike what is very likely to occur with
L-Glu-γ-P
H (Fig. 3). This is in line with the inability of
D,
L-Glu-γ-P
5 to act as either a substrate or an inhibitor of
E. coli glutamate decarboxylase [
18,
33] and porcine heart aspartate aminotransferase [
29]. On the other hand, the phosphonic group is a doubly-charged tetrahedral group which mimic the tetrahedral intermediates (or reaction transition states) of the carboxyl group [
9,
25] and this explains the rather high competitive inhibition (K
I 50 µM) of
E. coli glutamine synthetase (GS) with Glu-γ-P
5 [
34]. However, PT (see Introduction and Fig. 1a), a naturally occurring inhibitor of GS, can undergo ATP-dependent ligation, with the formed pyrophosphonate that mimics the phosphorylated intermediate of glutamate occurring in the GS-catalyzed reaction [
10,
11]. Notably, PT has K
I 0.6 µM against the
E. coli GS [
35]. These differences in the inhibitory activities of Glu-γ-P
5 and PT may partly explain the differences observed in the activities of
L-Leu-
D,
L-Glu-γ-P
5 and
L-Leu-
D,
L-PT against
E. coli: the first dipeptide has a MIC
90 = 80 µg/mL, while the second has a MIC
90 = 0.1 µg/mL(
Table 1).