Submitted:
05 December 2023
Posted:
07 December 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
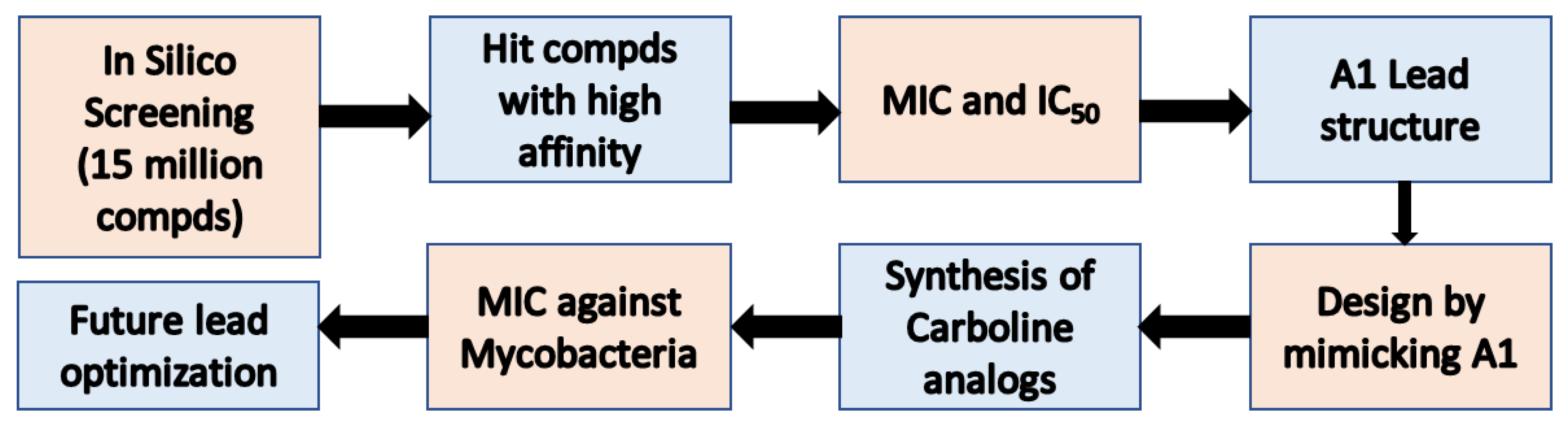
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Strains
2.2. General Synthesis
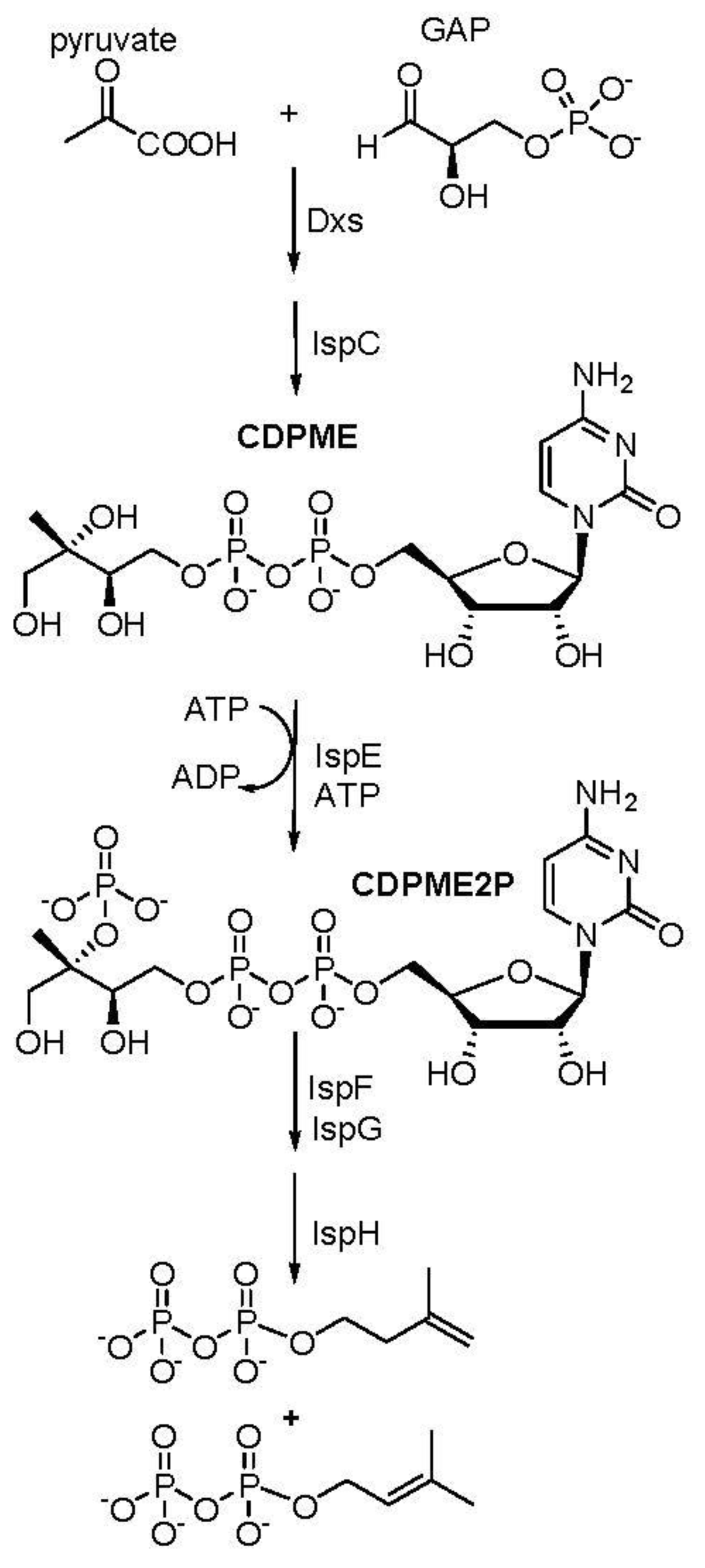
2.3. CDPME Synthesis
2.4. Determination of IC50 assay
2.4.1. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against M. avium.
2.4.2. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against M. abscessus.
2.4.3. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against M. tuberculosis H37Ra.
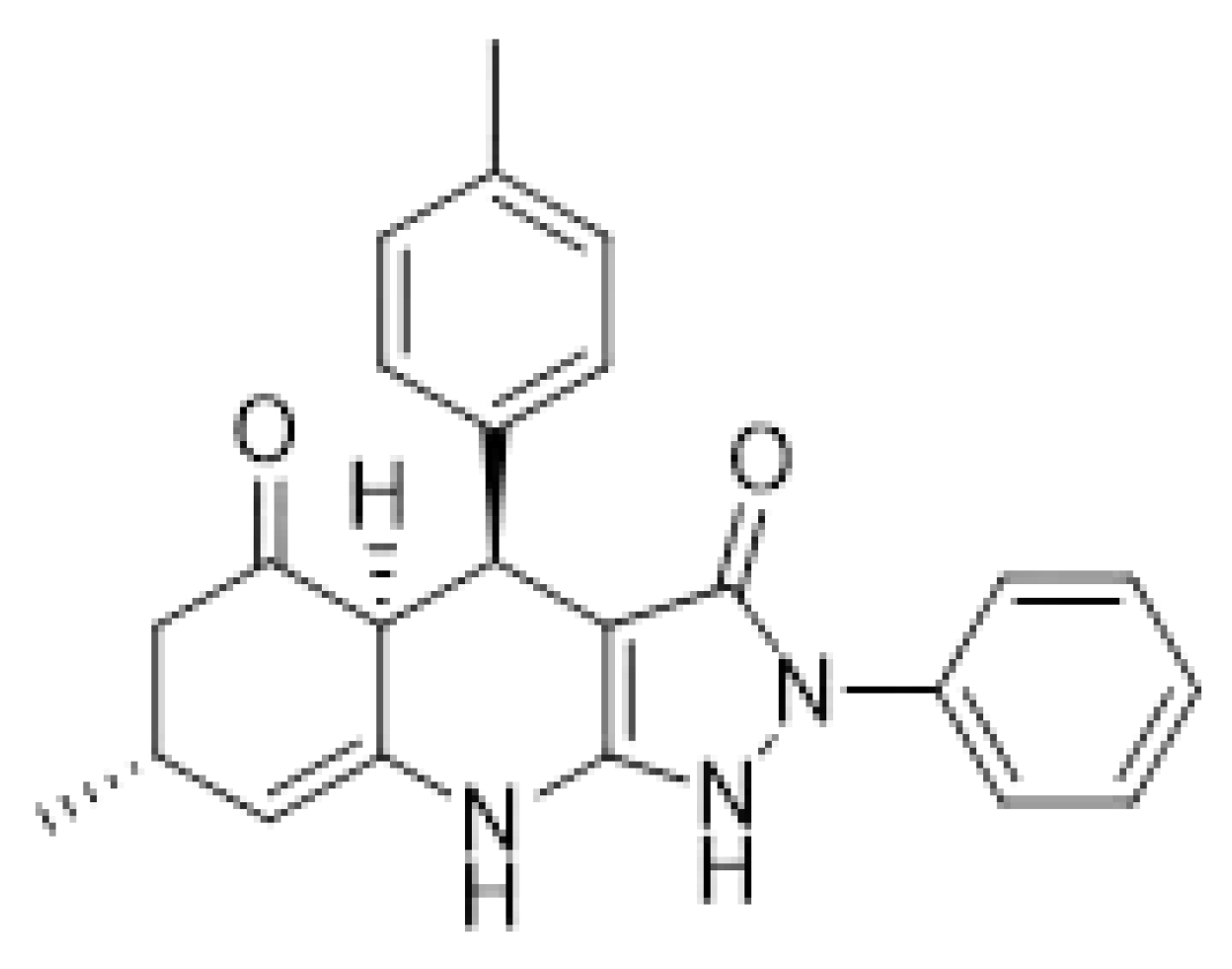
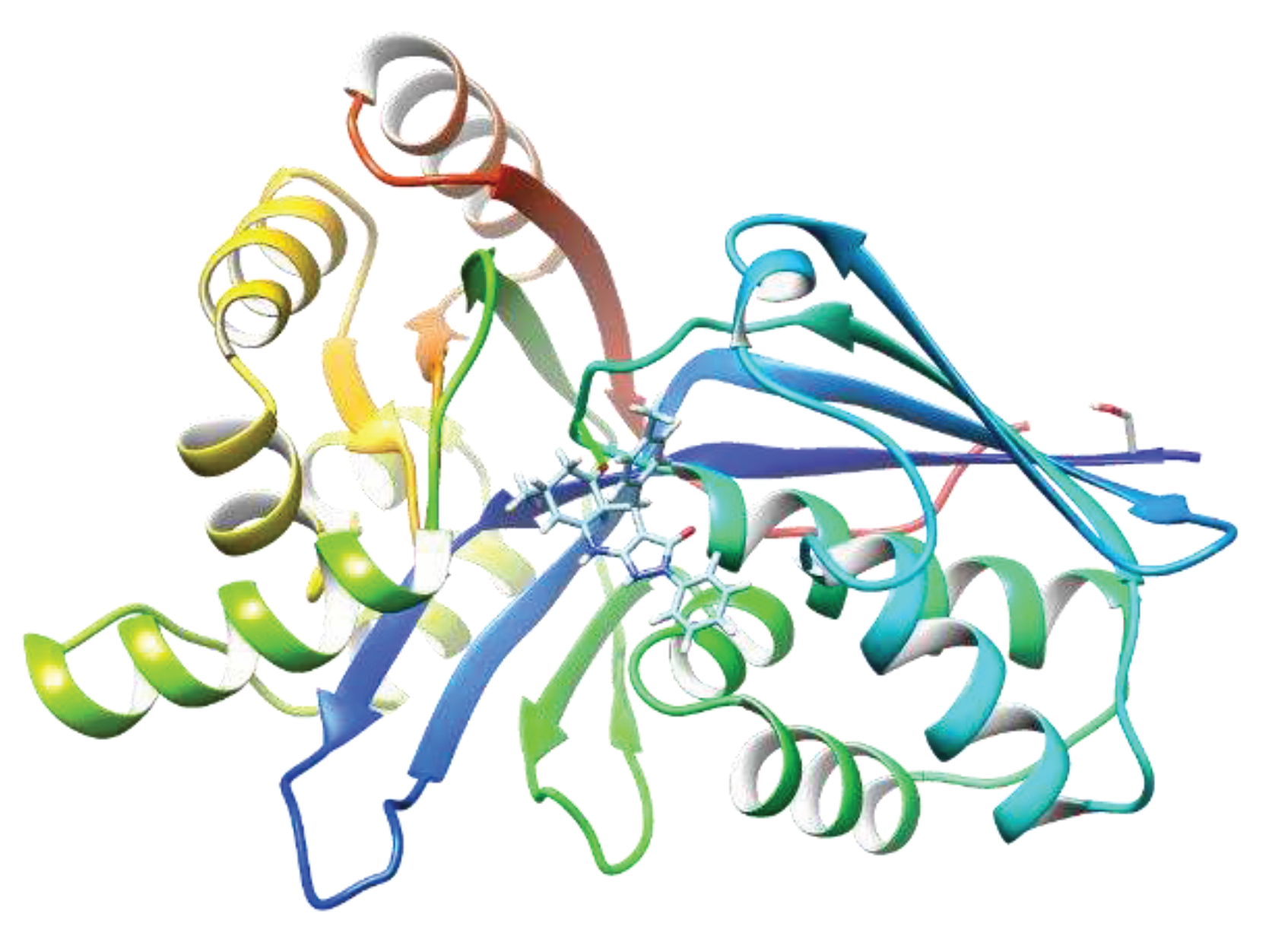
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Competing financial interests
References
- Brennan PJ, Crick DC. 2007. The cell-wall core of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the context of drug discovery. Curr Top Med Chem 7:475-88. [CrossRef]
- Hunter WN, Bond CS, Gabrielsen M, Kemp LE. 2003. Structure and reactivity in the non-mevalonate pathway of isoprenoid biosynthesis. Biochem Soc Trans 31:537-42. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Concepcion, M. 2004. The MEP pathway: a new target for the development of herbicides, antibiotics and antimalarial drugs. Curr Pharm Des 10:2391-400. [CrossRef]
- Koppisch AT, Fox DT, Blagg BS, Poulter CD. 2002. E. coli MEP synthase: steady-state kinetic analysis and substrate binding. Biochemistry 41:236-43. [CrossRef]
- Rekittke I, Wiesner J, Rohrich R, Demmer U, Warkentin E, Xu W, Troschke K, Hintz M, No JH, Duin EC, Oldfield E, Jomaa H, Ermler U. 2008. Structure of (E)-4-hydroxy-3-methyl-but-2-enyl diphosphate reductase, the terminal enzyme of the non-mevalonate pathway. J Am Chem Soc 130:17206-7. [CrossRef]
- Steinbacher S, Kaiser J, Eisenreich W, Huber R, Bacher A, Rohdich F. 2003. Structural basis of fosmidomycin action revealed by the complex with 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate synthase (IspC). Implications for the catalytic mechanism and anti-malaria drug development. J Biol Chem 278:18401-7. [CrossRef]
- Bjorkelid C, Bergfors T, Henriksson LM, Stern AL, Unge T, Mowbray SL, Jones TA. 2011. Structural and functional studies of mycobacterial IspD enzymes. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 67:403-14. [CrossRef]
- Gao P, Yang Y, Xiao C, Liu Y, Gan M, Guan Y, Hao X, Meng J, Zhou S, Chen X, Cui J. 2012. Identification and validation of a novel lead compound targeting 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methylerythritol synthetase (IspD) of mycobacteria. Eur J Pharmacol 694:45-52. [CrossRef]
- Narayanasamy P, Eoh H, Crick DC. 2008. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol: A substrate for IspE. Tetrahedron Lett 49:4461-4463. [CrossRef]
- Eoh H, Narayanasamy P, Brown AC, Parish T, Brennan PJ, Crick DC. 2009. Expression and characterization of soluble 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase from bacterial pathogens. Chem Biol 16:1230-9. [CrossRef]
- Narayanasamy P, Eoh H, Brennan PJ, Crick DC. 2010. Synthesis of 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 2-phosphate and kinetic studies of Mycobacterium tuberculosis IspF. Chem Biol 17:117-22. [CrossRef]
- Narayanasamy P, Crick DC. 2008. Enantiomeric Synthesis of 2-C-Methyl-D-Erythritol 2, 4-Cyclodiphosphate. Heterocycles 76:243-247. [CrossRef]
- Eoh H, Brennan PJ, Crick DC. 2009. The Mycobacterium tuberculosis MEP (2C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate) pathway as a new drug target. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 89:1-11. [CrossRef]
- Narayanasamy, P. 2015. MEP pathway: A novel Pathway for New antibiotics. Chem Sci J 6. [CrossRef]
- Singh UP, Pathak M, Dubey V, Bhat HR, Gahtori P, Singh RK. 2012. Design, synthesis, antibacterial activity, and molecular docking studies of novel hybrid 1,3-thiazine-1,3,5-triazine derivatives as potential bacterial translation inhibitor. Chem Biol Drug Des 80:572-83. [CrossRef]
- Udaya Pratap Singh, Hans Raj Bhat, Singh RK. 2013. Ceric ammonium nitrate (CAN) catalysed expeditious one-pot synthesis of 1,3-thiazine as IspE kinase inhibitor of Gram-negative bacteria using polyethylene glycol (PEG-400) as an efficient recyclable reaction medium. Comptes Rendus Chimie 16:462-8. [CrossRef]
- Hirsch AK, Alphey MS, Lauw S, Seet M, Barandun L, Eisenreich W, Rohdich F, Hunter WN, Bacher A, Diederich F. 2008. Inhibitors of the kinase IspE: structure-activity relationships and co-crystal structure analysis. Org Biomol Chem 6:2719-30. [CrossRef]
- Hirsch AK, Lauw S, Gersbach P, Schweizer WB, Rohdich F, Eisenreich W, Bacher A, Diederich F. 2007. Nonphosphate inhibitors of IspE protein, a kinase in the non-mevalonate pathway for isoprenoid biosynthesis and a potential target for antimalarial therapy. ChemMedChem 2:806-10. [CrossRef]
- Masini T, Hirsch AK. 2014. Development of inhibitors of the 2C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway enzymes as potential anti-infective agents. J Med Chem 57:9740-63. [CrossRef]
- Choi SR, Britigan BE, Moran DM, Narayanasamy P. 2017. Gallium nanoparticles facilitate phagosome maturation and inhibit growth of virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis in macrophages. PLoS ONE 12:e0177987. [CrossRef]
- Choi SR, Britigan BE, Switzer B, Hoke T, Moran D, Narayanasamy P. 2018. In Vitro Efficacy of Free and Nanoparticle Formulations of Gallium(III) meso-Tetraphenylporphyrine against Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium abscessus and Gallium Biodistribution in Mice. Mol Pharm 15:1215-1225. [CrossRef]
- Choi SR, Switzer B, Britigan BE, Narayanasamy P. 2020. Gallium Porphyrin and Gallium Nitrate Synergistically Inhibit Mycobacterial Species by Targeting Different Aspects of Iron/Heme Metabolism. ACS Infect Dis 6:2582-2591. [CrossRef]
- Choi SR, Talmon GA, Britigan BE, Narayanasamy P. 2021. Nanoparticulate beta-Cyclodextrin with Gallium Tetraphenylporphyrin Demonstrates in Vitro and in Vivo Antimicrobial Efficacy against Mycobacteroides abscessus and Mycobacterium avium ACS Infect Dis. [CrossRef]
- Tidten-Luksch N, Grimaldi R, Torrie LS, Frearson JA, Hunter WN, Brenk R. 2012. IspE inhibitors identified by a combination of in silico and in vitro high-throughput screening. PLoS One 7:e35792. [CrossRef]
- Zhao X, Vainshtein I, Gellibolian R, Shu Y, Dotimas H, Wang XM, Fung P, Horecka J, Bosano BL, Eglen RM. 2003. Homogeneous assays for cellular protein degradation using beta-galactosidase complementation: NF-kappaB/IkappaB pathway signaling. Assay Drug Dev Technol 1:823-33. [CrossRef]
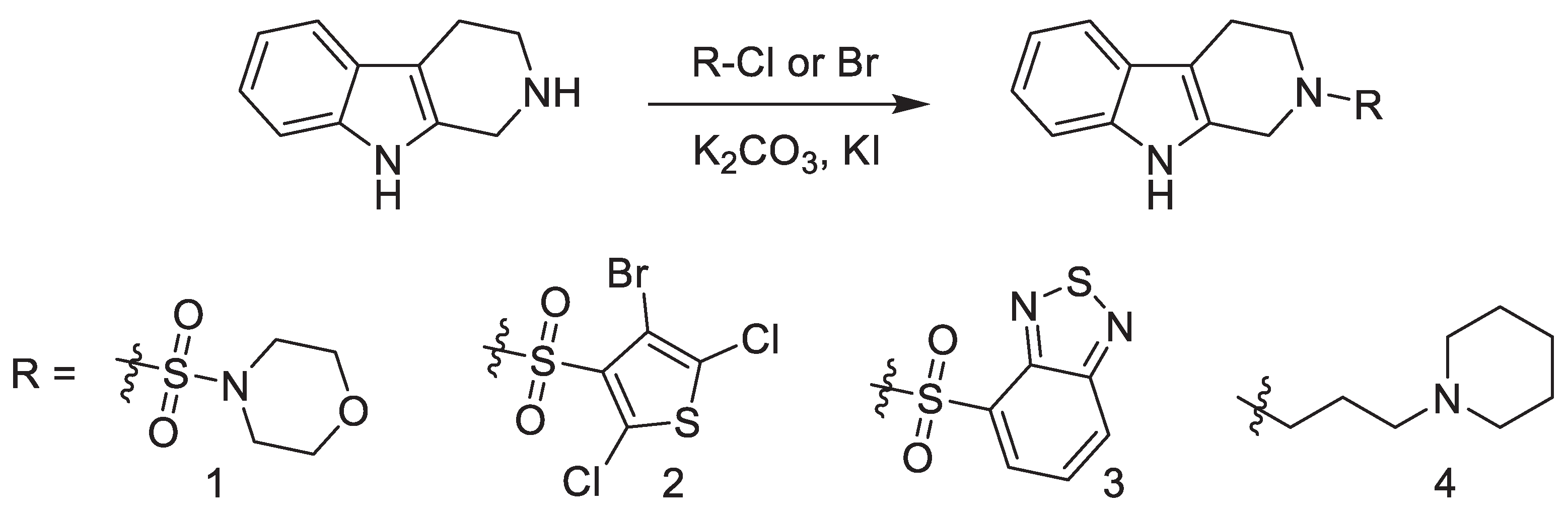
| MIC (µg/mL) | IC50 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | M.tb | M.tb IspE | |
| A1 | 12 | 6 | |
| MIC (µg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | M.avium | M.tb | M.ab |
| 1 | 80 | 128 | 32 |
| 2 | 5 | >128 | 64 |
| 3 | 10 | >128 | 32 |
| 4 | nd | >128 | nd |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





