Submitted:
29 August 2023
Posted:
30 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
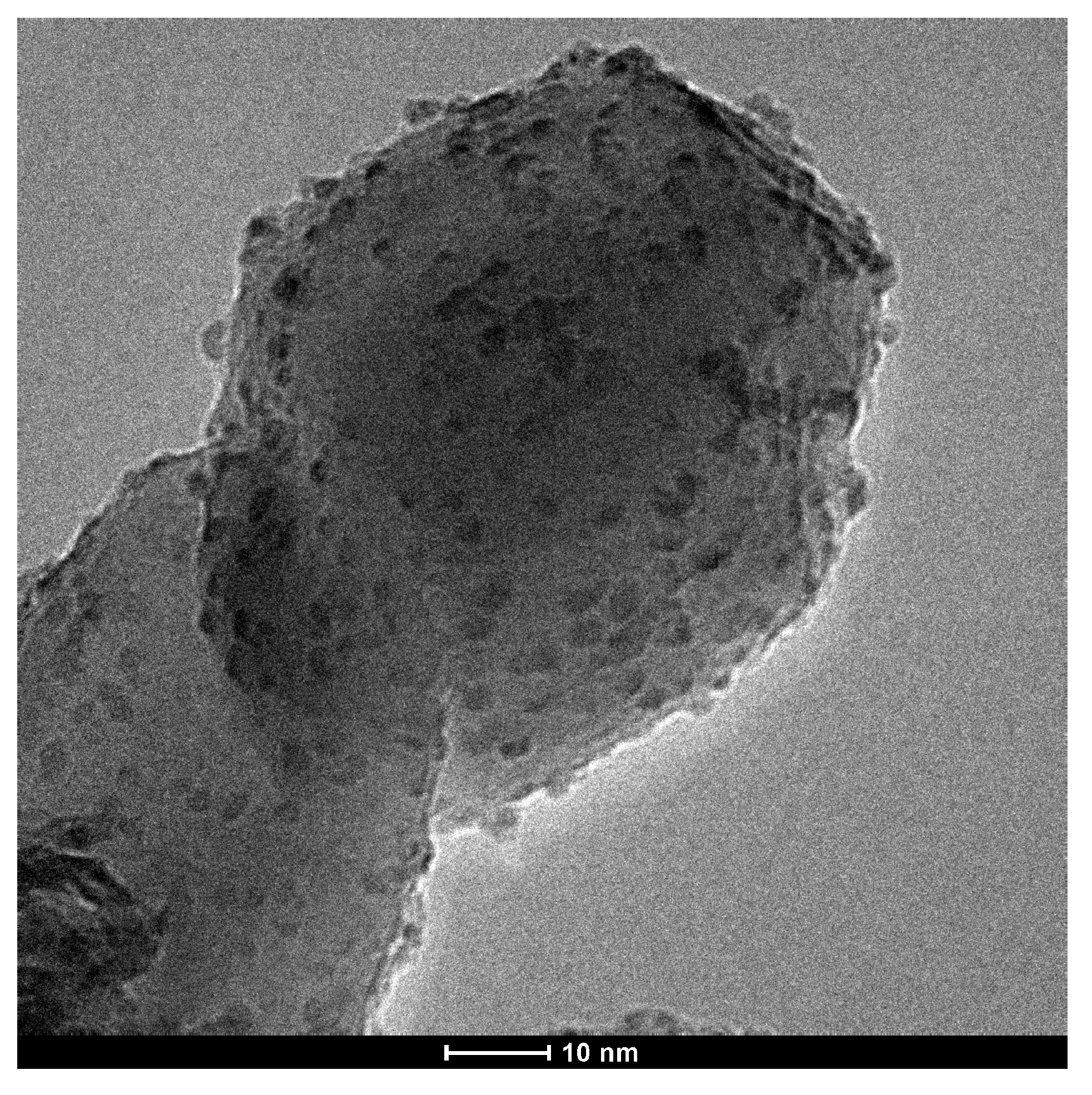
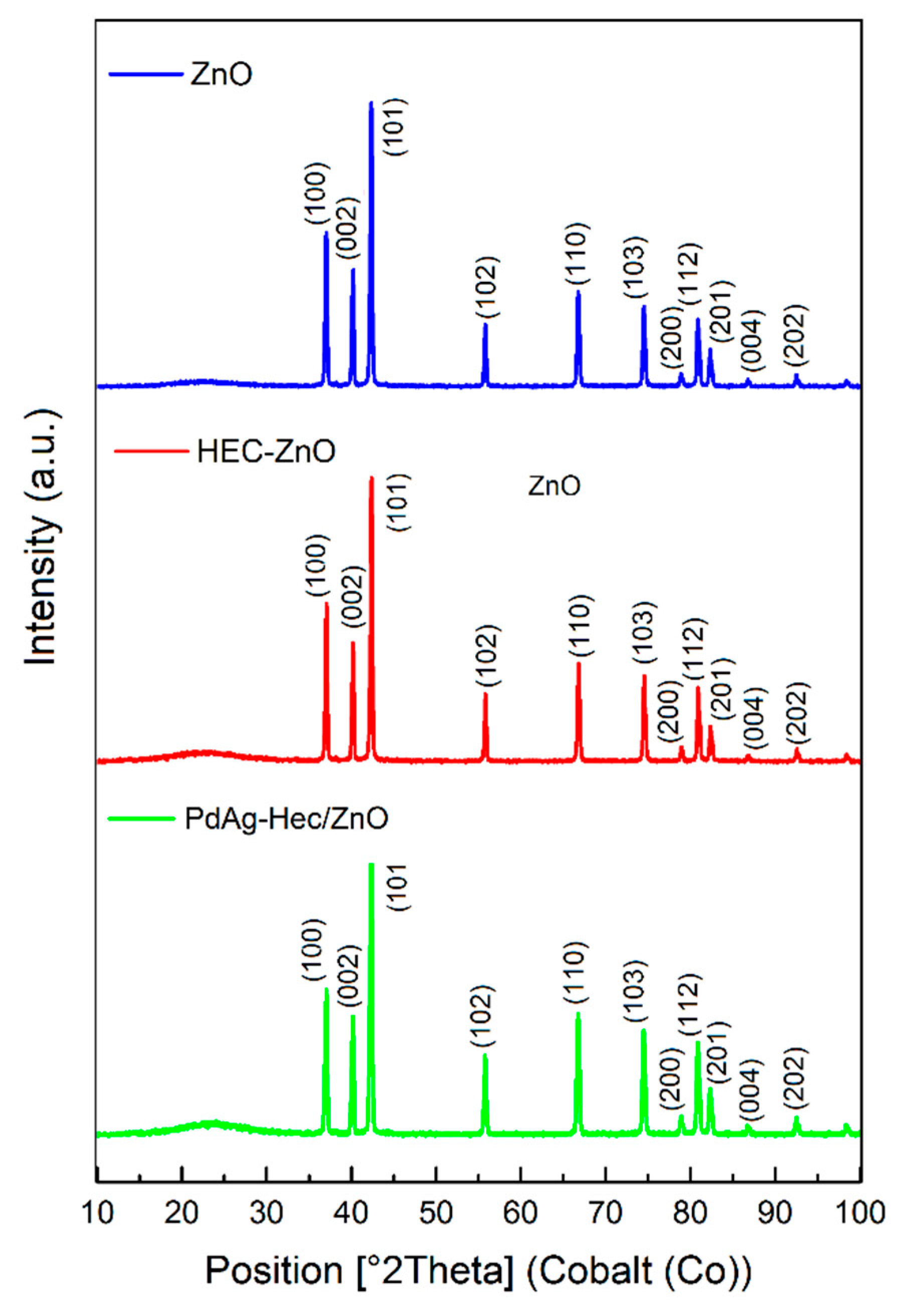
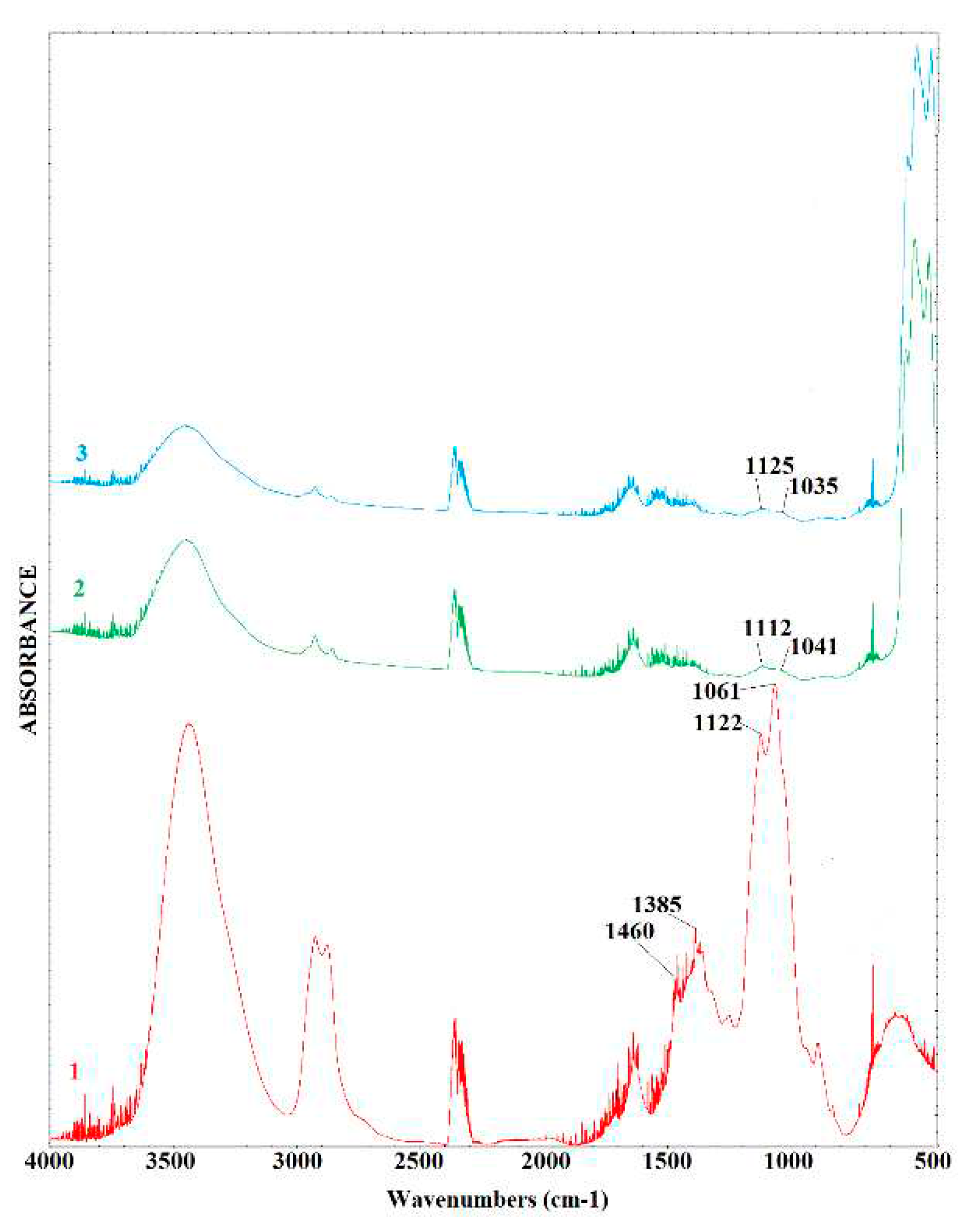
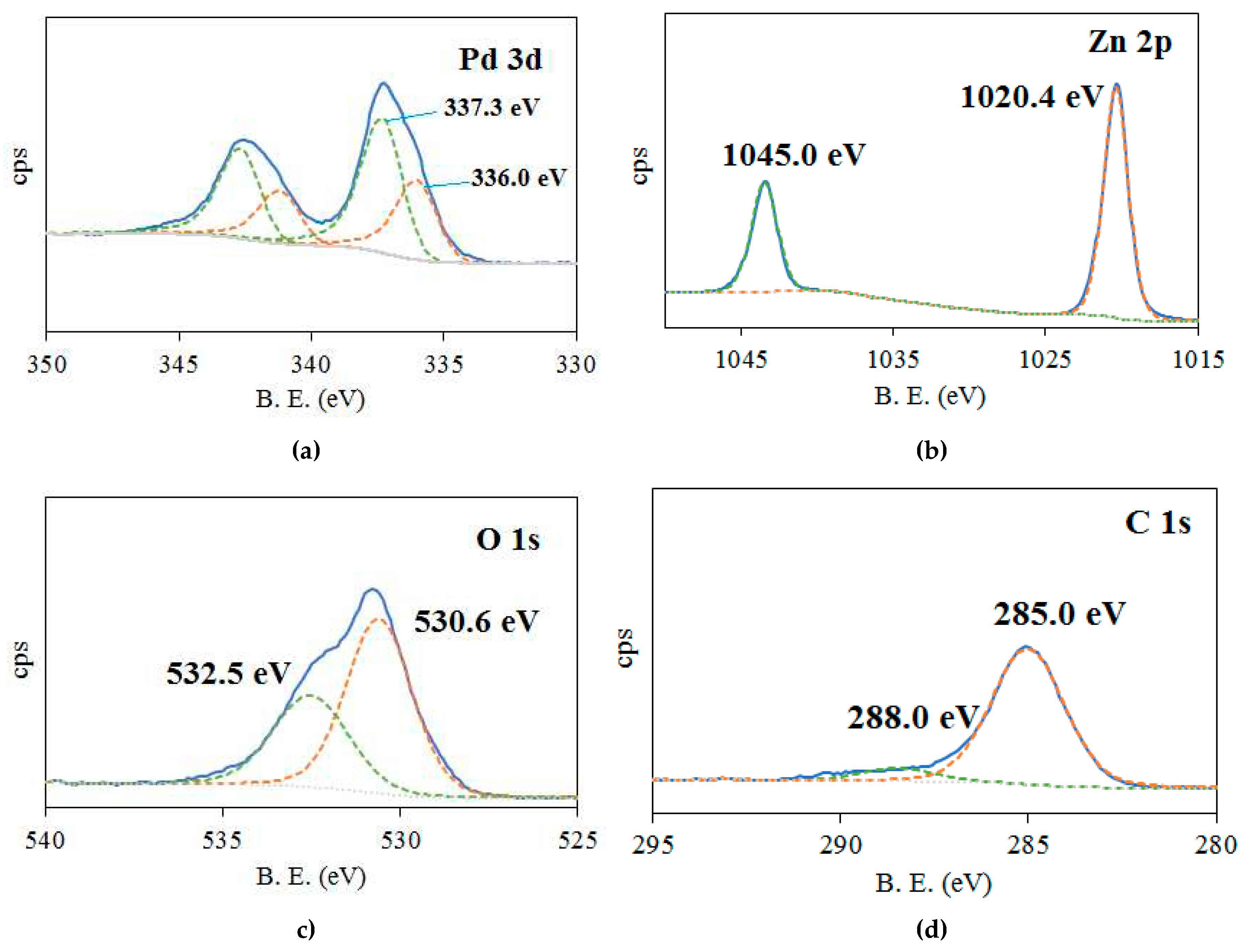
2.1. Characterization of catalysts
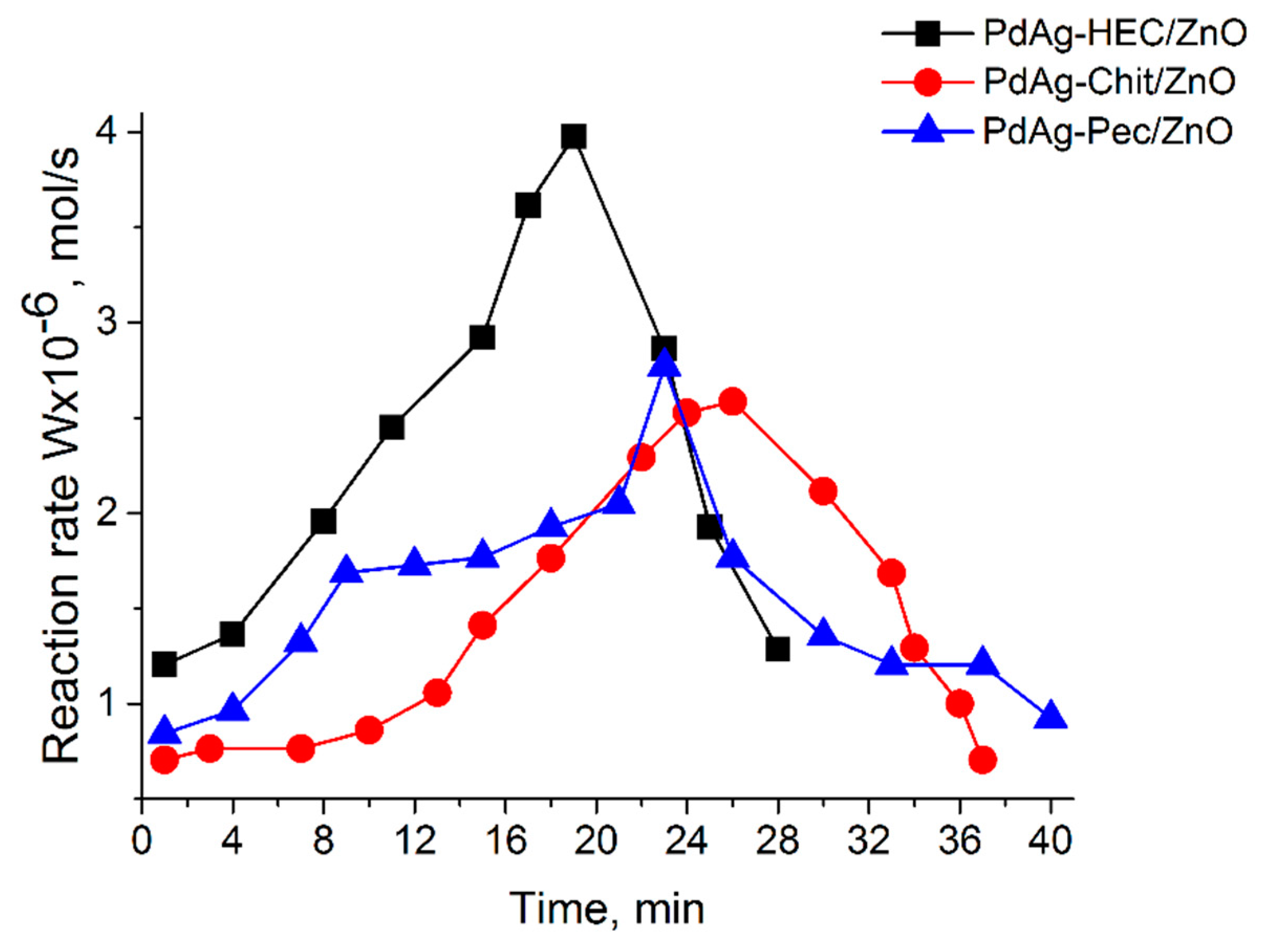
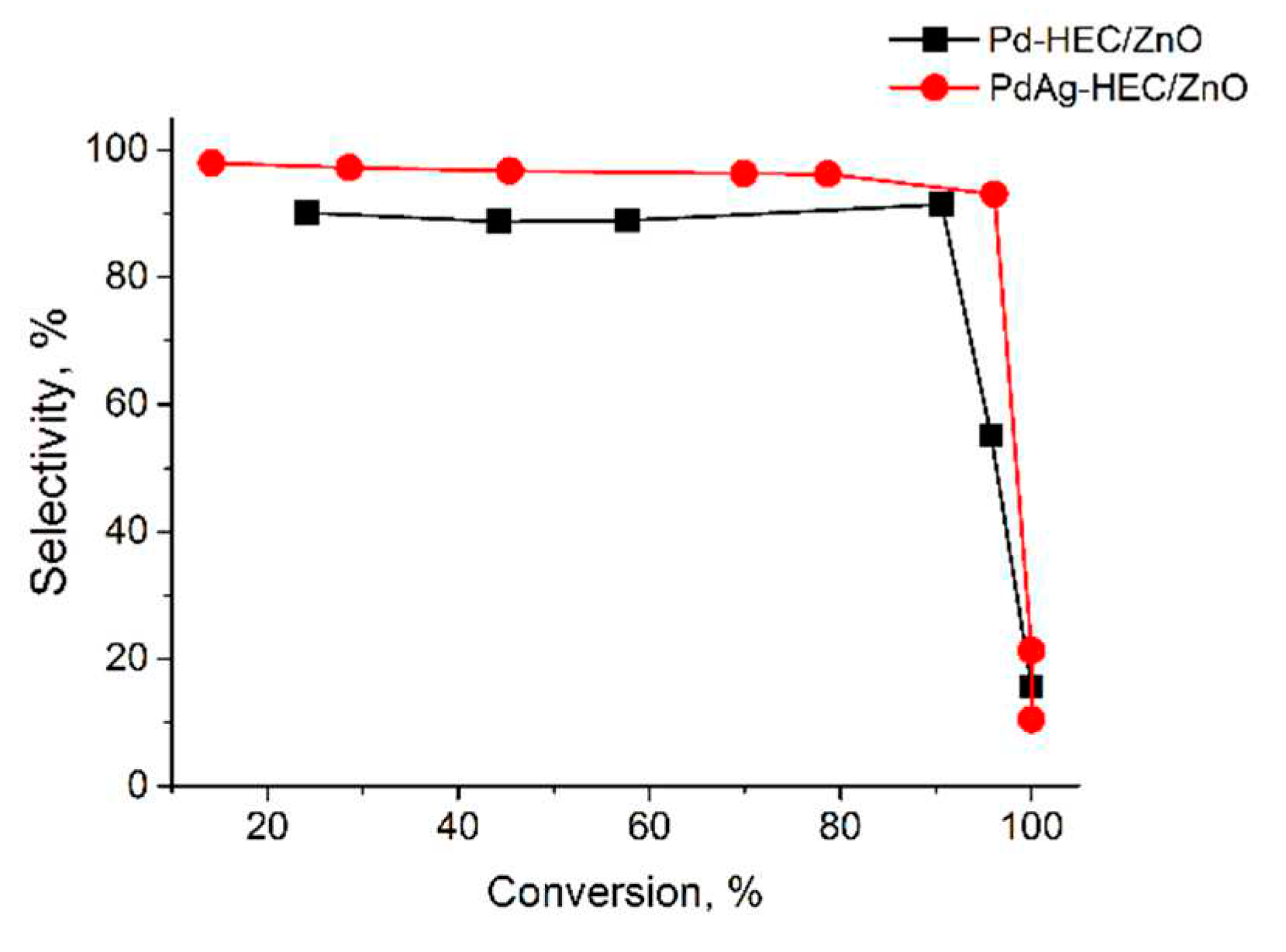
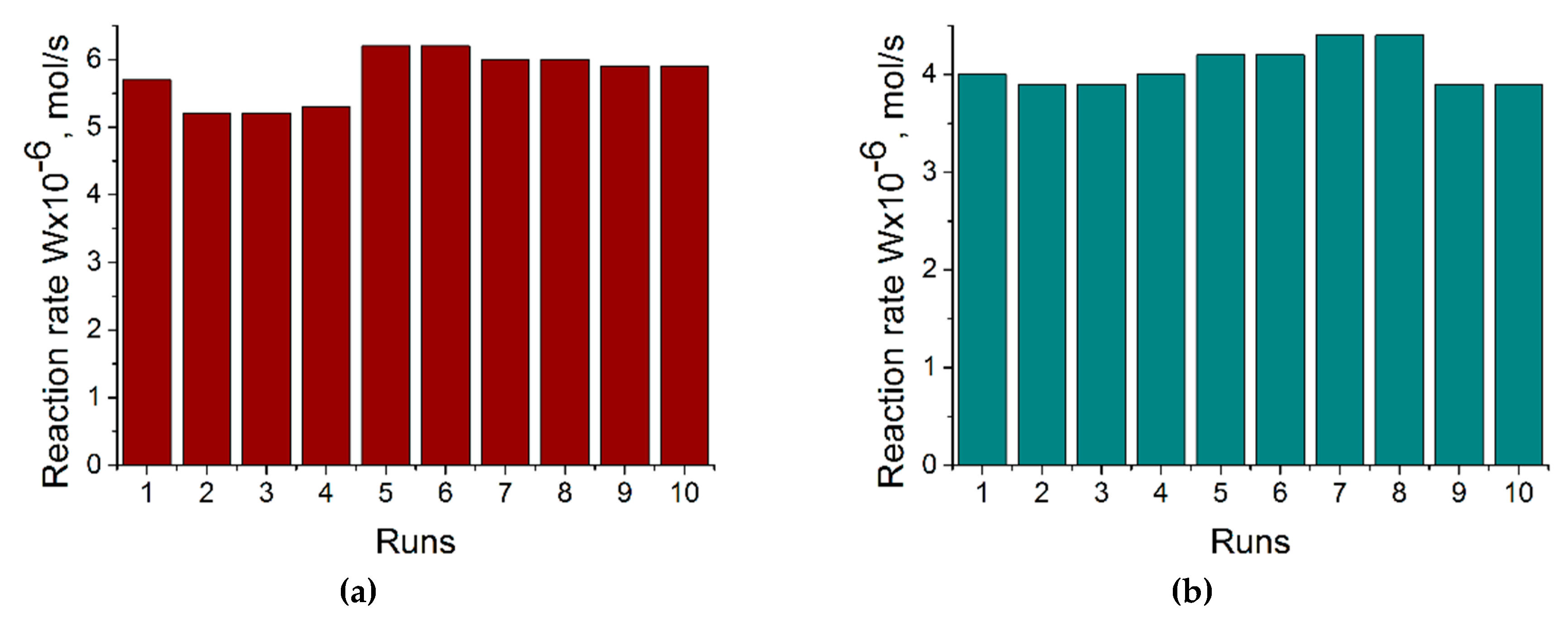
2.2. Catalytic test
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of K2PdCl4 precursor solution
3.3. Synthesis of Pd-HEC/ZnO catalyst
3.4. Synthesis of PdAg-polysaccharide/ZnO catalysts
3.5. Characterization of catalysts [53,56]
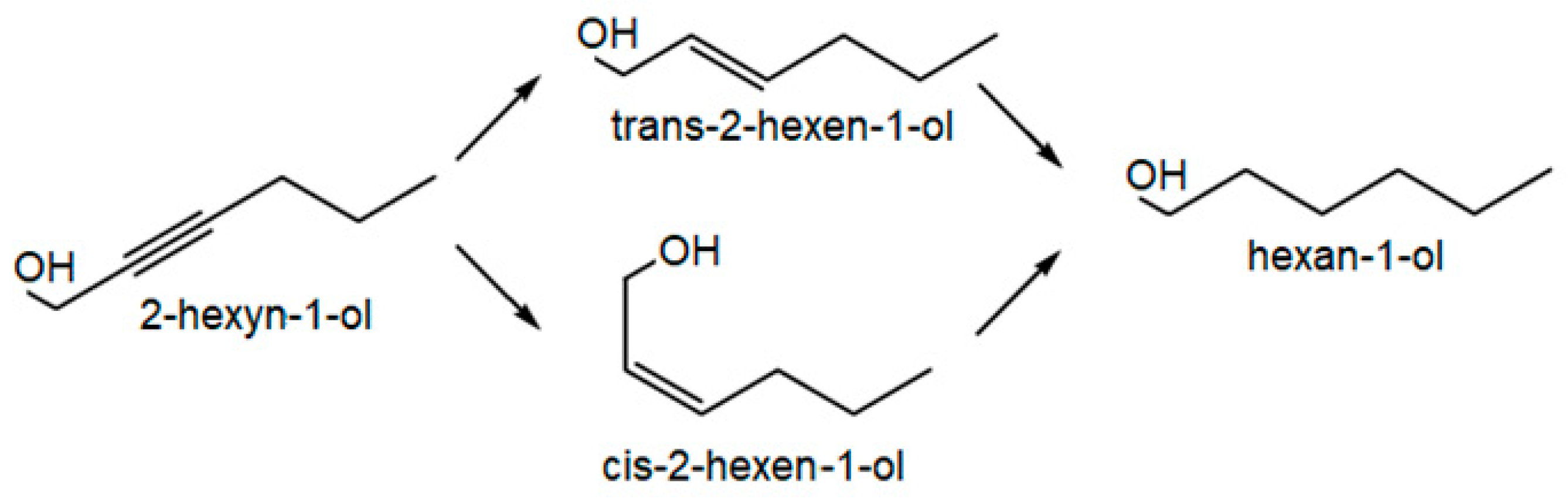
3.6. Hydrogenation of 2-hexyn-1-ol
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, X. , Li, Y., Li, W., Pei, X., Ye, D. Chitosan derived efficient and stable Pd nano-catalyst for high efficiency hydrogenation. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2023, 241, 124615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, T. Pd(0) nanocatalyst stabilized on a novel agar/pectin composite and its catalytic activity in the synthesis of biphenyl compounds by Suzuki-Miyaura cross coupling reaction and reduction of o-nitroaniline. Carbohydrate Polymers 2018, 195, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M. , Shafiei, N., Nezafat, Z., Bidgoli, N.S.S., Soleimani, F. Recent progresses in the application of cellulose, starch, alginate, gum, pectin, chitin and chitosan based (nano)catalysts in sustainable and selective oxidation reactions: A review. Carbohydrate Polymers 2020, 241, 116353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M. , Sajjadi, M., Iravani, S., Varma, R.S. Starch, cellulose, pectin, gum, alginate, chitin and chitosan derived (nano)materials for sustainable water treatment: A review. Carbohydrate Polymers 2021, 251, 116986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y. , Li, Z., Chen, J. Applications of Lignin-Derived Catalysts for Green Synthesis. Green Energy & Environment 2019, 4, 210–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlambi, P.N. , Moloto, M.J. Starch-capped silver oxide (Ag2O) nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity. Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures 2022, 17, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Almeida, D.A. , Sabino, R.M., Souza, P.R., Bonafé, E.G., Venter, S.A.S., Popat, K.C., Martins, A.F., Monteiro, J.P. Pectin-capped gold nanoparticles synthesis in-situ for producing durable, cytocompatible, and superabsorbent hydrogel composites with chitosan. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2020, 147, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, Á. The use of chitosan-based metal catalysts in organic transformations. Coordination Chemistry Reviews 2019, 388, 126–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, A. , Khazaei, M., Rahmati, S. A green method for the synthesis of gelatin/pectin stabilized palladium nanoparticles as efficient heterogeneous catalyst for solvent-free Mizoroki-Heck reaction. J. Mol. Catal. A. 2015, 398, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarzadeh-Moghaddam, M. , Shaddel, R., Peighambardoust, S., Singh, V., Srivastava, P., Singh, A., Singh, D., Malviya, T. Polysaccharide-Silica Hybrids: Design and Applications. Polymer Reviews 2016, 56, 113–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvat, G. , Pantić, M., Knez, Ž., Novak, Z. Preparation and characterization of polysaccharide-silica hybrid aerogels. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 16492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El-Aziz, M.E. , Kamal, K.H., Ali, K.A., Abdel-Aziz, M.S., Kamel, S. Biodegradable grafting cellulose/clay composites for metal ions removal. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2018, 118, 2256–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubakar, Z. , Sirajo, V. Pectin graft copolymer-montmorillonite composite: Synthesis, swelling and divalent metal ion adsorption. Separation Science and Technology 2018, 35, 2170–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesi, A. , Meseldzija, S., Cabrera-Barjas, G., Onjia, A. Novel Biocomposite Films Based on High Methoxyl Pectin Reinforced with Zeolite Y for Food Packaging Applications. Foods 2022, 11, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talgatov, E.T. , Auezkhanova, A.S., Kapysheva, U.N., Bakhtiyrova, S.K., Zharmagambetova, A.K. Synthesis and Detoxifying Properties of Pectin-Montmorillonite Composite. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. , Liang, R., Dai, T.T., Chen, J. Shuai, X., Liu, C. Pectin-based adsorbents for heavy metal ions: A review. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2019, 91, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bok-Badura, J. , Jakóbik-Kolon, A., Karoń, K., Mitko, K. Sorption studies of heavy metal ions on pectin-nano-titanium dioxide composite adsorbent. Separation Science and Technology 2018, 53, 1034–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. , Yang, Z.L., Ding, T., Song, Y.J., Li, H.C., Li, D.Q., Chen, S., Xu, F. The role of surface functional groups of pectin and pectin-based materials on the adsorption of heavy metal ions and dyes. Carbohydr Polym. 2022, 276, 118789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. , Singhal, N., Singh, R.K., Gupta, P., Singh, R., Jain, S.L. Dual catalysis with magnetic chitosan: Direct synthesis of cyclic carbonates from olefins with carbon dioxide using isobutyraldehyde as the sacrificial reductant. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 11860–11866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, R.B.N. , Varma, R.S. Copper on chitosan: A recyclable heterogeneous catalyst for azide-alkyne cycloaddition reactions in water. Green Chem, 1843; 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, S. , Rachayya, N., Hulle, S. Citrus pectins: Structural properties, extraction methods, modifications and applications in food systems – A review. Applied Food Research, 1002; 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnin, E. , Garnier, C., Ralet, M.-C. Pectin-modifying enzymes and pectin-derived materials: Applications and impacts. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2014, 98, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman-Benn, A. , Contador, C.A., Li, M.-W., Lam, H.-M., Ah-Hen, K., Ulloa, P.E., Ravanal, M.C. Pectin: An overview of sources, extraction and applications in food products, biomedical, pharmaceutical and environmental issues. Food Chemistry Advances 2023, 2, 100192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y. , Bi, J., Zhang, S., Zhu, D., Meng, D., Ming, S.,, Qin, K., Liu, Q., Guo, L., Li, T. Palladium supported on N-Heterocyclic carbene functionalized hydroxyethyl cellulose as a novel and efficient catalyst for the Suzuki reaction in aqueous media. Applied Surface Science, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karger-Kocsis, J. , Siengchin, S. Single-polymer composites: Concepts, realization and Outlook. KMUTNB International Journal of Applied Science and Technology 2014, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.B. , Attia, M.A., El-Dars, F.M.S.E., Emam, H.E. Hydroxyethyl cellulose for spontaneous synthesis of antipathogenic nanostructures: (Ag & Au) nanoparticles versus Ag-Au nano-alloy. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2019, 128, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. , Zeng, W., Zhao, J., Qiu, X., Xiong, H., Liang, Y., Xie, Y., Ziqiang, L., Chen, D. Preparation and anti-leakage properties of hydroxyethyl cellulose-g-poly (butyl acrylate-co-vinyl acetate) emulsion. Carbohydrate Polymers, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y. , Song, M., Zhang, Y., Shi, L.Y., Lv, Y., Ran, R. Enzymic degradation of hydroxyethyl cellulose and analysis of the substitution pattern along the polysaccharide chain. Carbohydrate Polymers 2017, 169, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, K. , Amin, M., Hussain, M.A., Sher, M., Bukhari, S.N.A., Jantan, I., Edgar, K.J. Designing novel bioconjugates of hydroxyethyl cellulose and salicylates for potential pharmaceutical and pharmacological applications. International Journal of Biometeorology 2017, 103, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.N. , Christopher, L.P. A novel, cost-effective and eco-friendly method for preparation of textile fibers from cellulosic pulps. Carbohydrate Polymers 2017, 173, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boufi, S. , Gonzalez, I., Delgado-Aguilar, M., Tarres, Q., Pelach, M.A., Mutje, P. Nanofibrillated cellulose as an additive in papermaking process: A review. Carbohydrate Polymers 2016, 154, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H. , Santos, H.A. Khan, T. Applications of bacterial cellulose in food, cosmetics and drug delivery. Cellulose 2016, 23, 2291–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S. , Li, L., Cao, X., Yang, Q. Ni-chitosan/carbon nanotube: An efficient biopolymer-inorganic catalyst for selective hydrogenation of acetylene. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharmagambetova, A.K. , Auyezkhanova, A.S., Talgatov, E.T., Jumekeyeva, A.I. Chitosan-Modified Palladium Catalysts in Hydrogenation of n-Hex-2-yne. Theoretical and Experimental Chemistry 2021, 57, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohendou, M. , Pakzad, K., Nezafat, Z., Nasrollahzadeh, M., Dekamin, M.G. Progresses in chitin, chitosan, starch, cellulose, pectin, alginate, gelatin and gum based (nano)catalysts for the Heck coupling reactions: A review. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2021, 192, 771–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolinska, J. , Holdynski, M., Pieta, P., Lisowski, W., Ratajczyk, T., Palys, B., Jablonska, A., Opallo, M. Noble Metal Nanoparticles in Pectin Matrix. Preparation, Film Formation, Property Analysis, and Application in Electrocatalysis. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 23909–23918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, V.-D., T. Le, C.-H., Chau, V.-T., Le, T.N.-D., Dang, C.-H., Vo, T.T.-N., Nguyen, T.D., Nguyen, T.-D. Palladium nanoparticles in situ synthesized on Cyclea barbata pectin as a heterogeneous catalyst for Heck coupling in water, the reduction of nitrophenols and alkynes. New Journal of Chemistry 2021, 45, 4746–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, S.A. , Villarreal, J.S., Acosta P.I., Noboa J.F., Gallo-Cordova, A., Mora, J.R. Designing an efficient and recoverable magnetic nanocatalyst based on Ca, Fe and pectin for biodiesel production. Fuel 2022, 310, Part. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharmagambetova, A.K. , Seitkalieva, K.S., Talgatov, E.T., Auezkhanova, A.S., Dzhardimalieva, G.I., Pomogailo, A.D. Polymer-modified supported palladium catalysts for the hydrogenation of acetylene compounds. Kinetics and Catalysis 2016, 57, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. , He, G., Huang, J. Self-assembly on natural cellulose: Towards high-efficient catalysts. Current Opinion in Colloid & Interface Science 2023, 63, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Idrissi, N. , Belachemi, L., Merle, N., Zinck, P., Kaddami, H. Comprehensive preparation and catalytic activities of Co/TEMPO-cellulose nanocomposites: A promising green catalyst. Carbohydrate Polymers 2022, 295, 119765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prekob, Á. , Hajdu, V., Muránszky, G., Fiser B., Sycheva A., Ferenczi, T., Viskolcz, B., Vanyorek, L. Application of carbonized cellulose-based catalyst in nitrobenzene hydrogenation. Materials Today Chemistry 2020, 17, 100337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, M. , Li, A.Y., Hudson, R., Masnadi, M., Li, Ch.-J., Moores, A. Reversing aggregation: direct synthesis of nanocatalysts from bulk metal. Cellulose nanocrystals as active support to access efficient hydrogenation silver nanocatalysts. Green Chem. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.B. , Attia, M.A., El-Dars, F.M.S.E., Emam, H.E. Hydroxyethyl cellulose for spontaneous synthesis of antipathogenic nanostructures: (Ag & Au) nanoparticles versus Ag-Au nano-alloy. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2019, 128, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. , Zeng, W., Zhao, J., Qiu, X., Xiong, H., Liang, Y., Xie Y., Ziqiang, L., Chen, D. Preparation and anti-leakage properties of hydroxyethyl cellulose-g-poly (butyl acrylate-co-vinyl acetate) emulsion. Carbohydrate Polymers 2021, 255, 117467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y. , Song, M., Zhang, Y., Shi, L.Y., Lv, Y., Ran, R. Enzymic degradation of hydroxyethyl cellulose and analysis of the substitution pattern along the polysaccharide chain. Carbohydrate Polymers 2017, 169, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y. , Bi J., Zhang, S., Zhu, D., Meng, D., Ming, S., Qin, K., Liu, Q., Guo, L., Li, T. Palladium supported on N-Heterocyclic carbene functionalized hydroxyethyl cellulose as a novel and efficient catalyst for the Suzuki reaction in aqueous media. Applied Surface Science 2020, 531, 147392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C. , Qu L., Yu, H., Yu, F., Yuan B., Yu, S., Nie, S. Synthesis of Ru nanoparticles with hydroxyethyl cellulose as stabilizer for high-efficiency reduction of α-pinene. Cellulose 2019, 26, 8059–8071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharmagambetova, A.K. , Usmanova, M.M., Auyezkhanova, A.S., Akhmetova, S.N., Talgatov, E.T., Tumabayev, N.Zh, Dyusenalin B.K. Synthesis and catalytic properties of composites with Pd-(2-Hydroxyethylcellulose) on bentonite. News of the national academy of sciences of the Republic of Kazakhstan. Series Chemistry and Technology. [CrossRef]
- Devi, P.G. , Velu, A.S. Synthesis, structural and optical properties of pure ZnO and Co doped ZnO nanoparticles prepared by the co-precipitation method. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 2016, 10, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukerabigwi, J. F. , Lei, S., Fan, L., Wang, H., Luo, S., Ma, X., Qin J., Huan X., Cao, Y. Eco-friendly nano-hybrid superabsorbent composite from hydroxyethyl cellulose and diatomite. RSC Advances 2016, 6, 31607–31618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G. K. , Peck, T. C., Roberts, C. A. “PdO vs. PtO”- The Influence of PGM Oxide Promotion of Co3O4 Spinel on Direct NO Decomposition Activity. Catalysts 2019, 9(1), 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talgatov, E.T. , Auyezkhanova, A.S., Zharmagambetova, A.K., Tastanova, L.K., Bukharbayeva F.U., Jumekeyeva, A.I., Aubakirov, T.A. The Effect of Polymer Matrix on the Catalytic Properties of Supported Palladium Catalysts in the Hydrogenation of Alkynols. Catalysts 2023, 13, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajaber M., A. , Anjum M. N., Ibrahim M., Farooq T., Ahmad M. N., Abideen Z. Synthesis and Characterization of Hydroxyethyl Cellulose Grafted with Copolymer of Polyaniline and Polypyrrole Biocomposite for Adsorption of Dyes. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Idrissi, A. , El Barkany, S., Amhamdi, H., Maaroufi, A.-K. Physicochemical characterization of celluloses extracted from Esparto “Stipa tenacissima” of Eastern Morocco. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 128, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharmagambetova, A. , Auyezkhanova, A., Talgatov, E., Jumekeyeva, A., Buharbayeva, F., Akhmetova, S., Myltykbayeva, Zh., Lopez Nieto, J. M. Synthesis of polymer protected Pd–Ag/ZnO catalysts for phenylacetylene hydrogenation. Journal of Nanoparticle Research. [CrossRef]
- Parambhath, V.B. , Nagarm, R., Ramaprabhum, S. Effect of Nitrogen Doping on Hydrogen Storage Capacity of Palladium Decorated Graphene. Langmuir 2012, 28, 7826–7833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusinque, B. , Escobedo, S., de Lasa, H. Photoreduction of a Pd-Doped Meso-porous TiO2 Photocatalyst for Hydrogen Production under Visible Light. Catalysts 2020, 10, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. , Shi, C. , Wang, X.B., Li, W-Y., Liangm, C. Intermetallic PdZn nanoparticles catalyze the continuous-flow hydrogenation of alkynols to cis-enols. Commun. Chem. 2021, 4, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintcheva, N. , Aljulaih, A.A., Wunderlich, W., Kulinich, S.A., Iwamori, S. Laser-Ablated ZnO Nanoparticles and Their Photocatalytic Activity toward Organic Pollutants. Materials 2018, 11, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claros, M. , Setka, M., Jimenez, Y.P., Vallejos, S. AACVD Synthesis and Characterization of Iron and Copper Oxides Modified ZnO Structured Films. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, L.-S. , Campbell, J.M., Rojas, O.J. Cellulose as the in situ reference for organic XPS. Why? Because it works. Surface and Interface Analysis 2020, 52, 1134–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Catalysts | Concentration of metal ions in mother liquor C(Me)×10-6, mol L-1 | Degree of adsorption, % | Pd and Ag content in catalyst, % | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before adsorption | After adsorption | ||||||||
| Pd2+ | Ag+ | Pd2+ | Ag+ | Pd2+ | Ag+ | Pd2+ | Ag+ | Total | |
| Pd-HEC/ZnO | 1889.14 | - | 164.36 | - | 91.3 | - | 0.4565 | - | 0.46 |
| PdAg-HEC/ZnO | 1416.86 | 465.85 | 98.58 | 0.0020 | 93.0 | 100.0 | 0.3489 | 0.1250 | 0.47 |
| PdAg-Chit/ZnO | 1416.86 | 465.85 | 21.16 | 0.0016 | 98.5 | 100.0 | 0.3694 | 0.1250 | 0.49 |
| PdAg-Pec/ZnO | 1416.86 | 465.85 | 45.07 | 1.25 | 96.8 | 99.7 | 0.3631 | 0.1247 | 0.49 |
| Sample | Elemental composition of the catalyst, wt% | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pdcalcd/detd | Agcalcd/detd | Zncalcd/detd | |
| Pd-HEC/ZnO | 0.50/0.49 | - | 79.0/77.8 |
| PdAg-HEC/ZnO | 0.37/0.36 | 0.13/0.18 | 79.0/81.5 |
| PdAg-Chit/ZnO | 0.37/0.44 | 0.13/0.15 | 79.0/81.6 |
| PdAg-Pec/ZnO | 0.37/0.48 | 0.13/0.16 | 79.0/82.0 |
| Sample | Surface area, m2 g-1 |
|---|---|
| ZnO | 8.7 |
| HEC/ZnO | 1.1 |
| PdAg-HEC/ZnO | 5.2 |
| Catalysts | Wmax·10-6 (mol s-1) | Maximum yield of cis-hexen-1-ol, % | Scis-hexen-1-ol,% | Conversion, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd-HEC/ZnO | 4.3 | 82.8 | 90.6 | 91.4 |
| PdAg-HEC/ZnO | 4.0 | 89.4 | 97.2 | 93.0 |
| PdAg-Chit/ZnO | 2.6 | 85.9 | 92.3 | 93.1 |
| PdAg-Pec/ZnO | 2.8 | 86.4 | 93.5 | 92.4 |
| Reactionparameters | Catalysts | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PdAg-Chit/ZnO | PdAg-HEC/ZnO | |||||
| Wmax·10−6 (mol s−1) | Maximum yield of cis-hexen-1-ol, % | Scis-hexen-1-ol, % | Wmax·10−6 (mol s−1) | Maximum yield of cis-hexen-1-ol, % | Scis-hexen-1-ol, % | |
| Temperature, °C | ||||||
| 20 | 0.6 | 84.0 | 91.8 | 0.4 | 77.0 | 93.0 |
| 30 | 2.3 | 76.4 | 93.5 | 1.3 | 75.6 | 84.9 |
| 40 | 2.6 | 85.9 | 92.3 | 4.0 | 89.4 | 97.2 |
| 50 | 2.3 | 79.3 | 79.8 | 1.6 | 76.2 | 86.7 |
| Catalyst loading, g | ||||||
| 0.01 | 0.6 | 62.0 | 67.8 | 0.5 | 58.4 | 63.2 |
| 0.03 | 1.9 | 71.8 | 84.7 | 2.5 | 88.2 | 89.8 |
| 0.05 | 2.6 | 85.9 | 92.3 | 4.0 | 89.4 | 97.2 |
| 0.10 | 2.8 | 83.5 | 89.9 | 4.4 | 87.6 | 94.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




