Submitted:
29 August 2023
Posted:
30 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
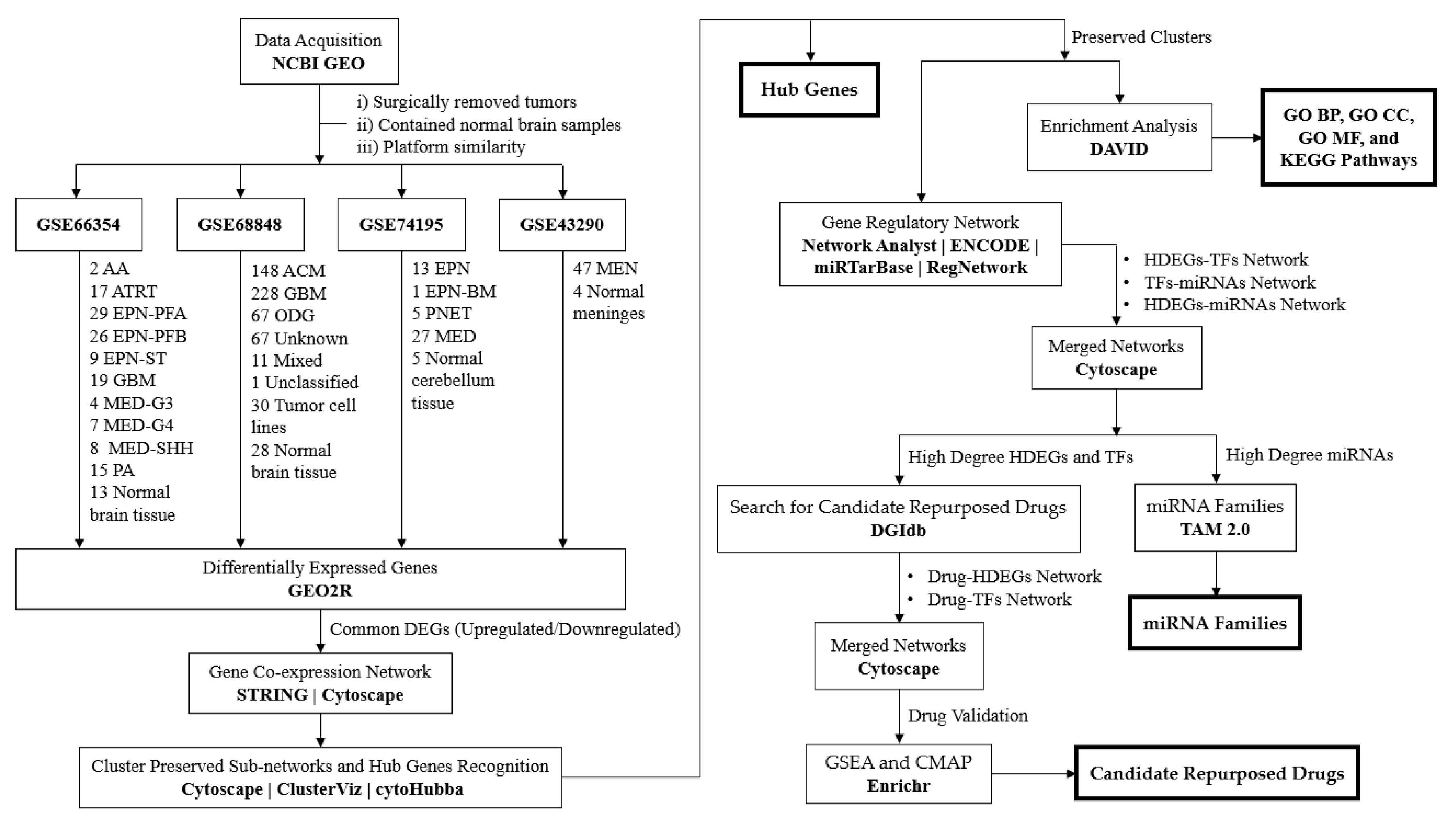
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Acquiring and Preprocessing Microarray Datasets
2.1.1. Microarray Expression Profiles Acquisition
2.1.2. Differentially Expressed Genes
2.2. Gene Co-Expression Network and Hub Genes Identification
2.2.1. Protein-Protein Interaction Network
2.2.2. Clusters and Hub Genes Network
2.3. Enrichment and Pathway Analysis
2.4. Gene Regulatory Network
2.5. Screening of Candidate Repurposed Drugs
2.6. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis and Connectivity Mapping for Validation of Repurposed Candidate Drugs
2.7. MicroRNAs Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
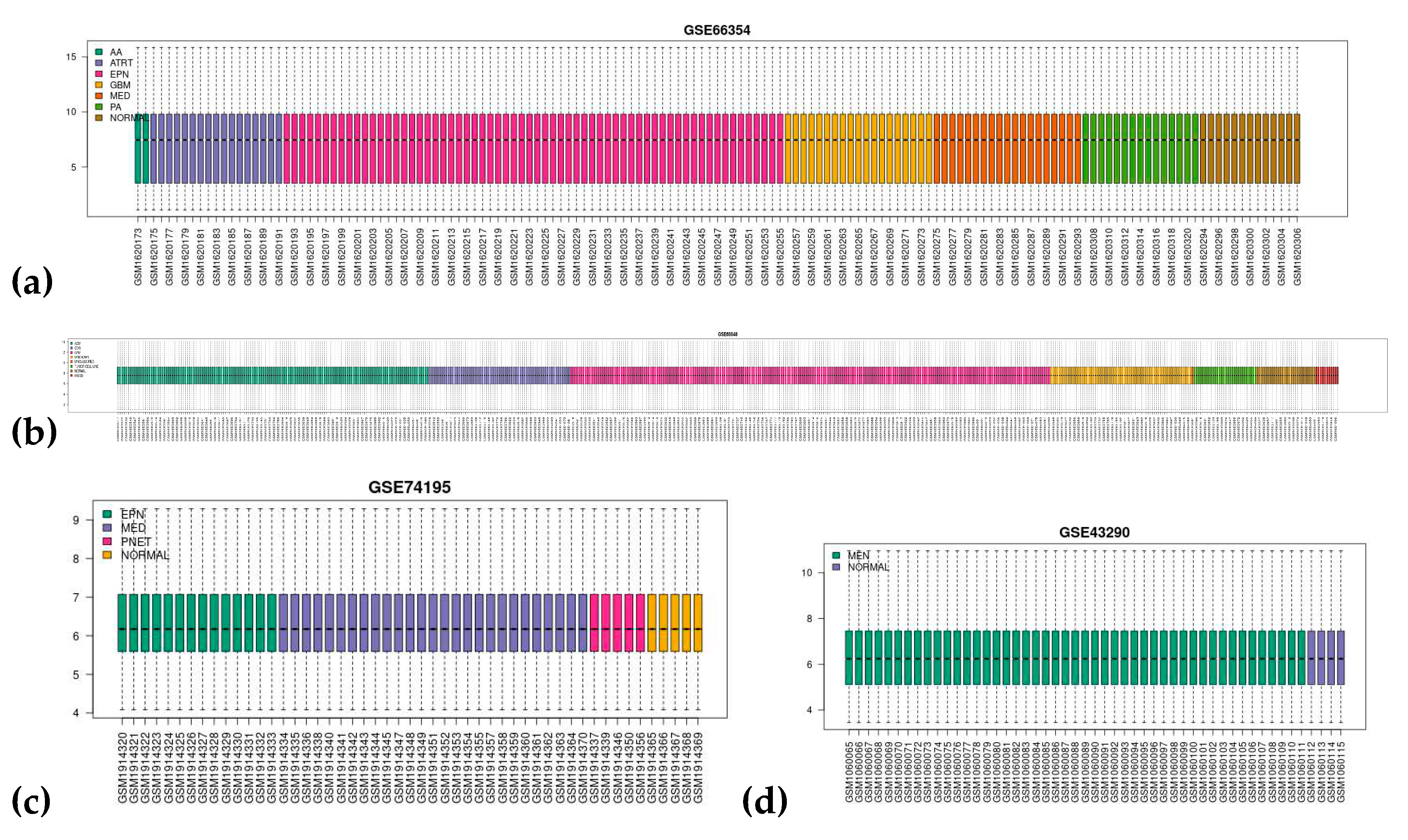
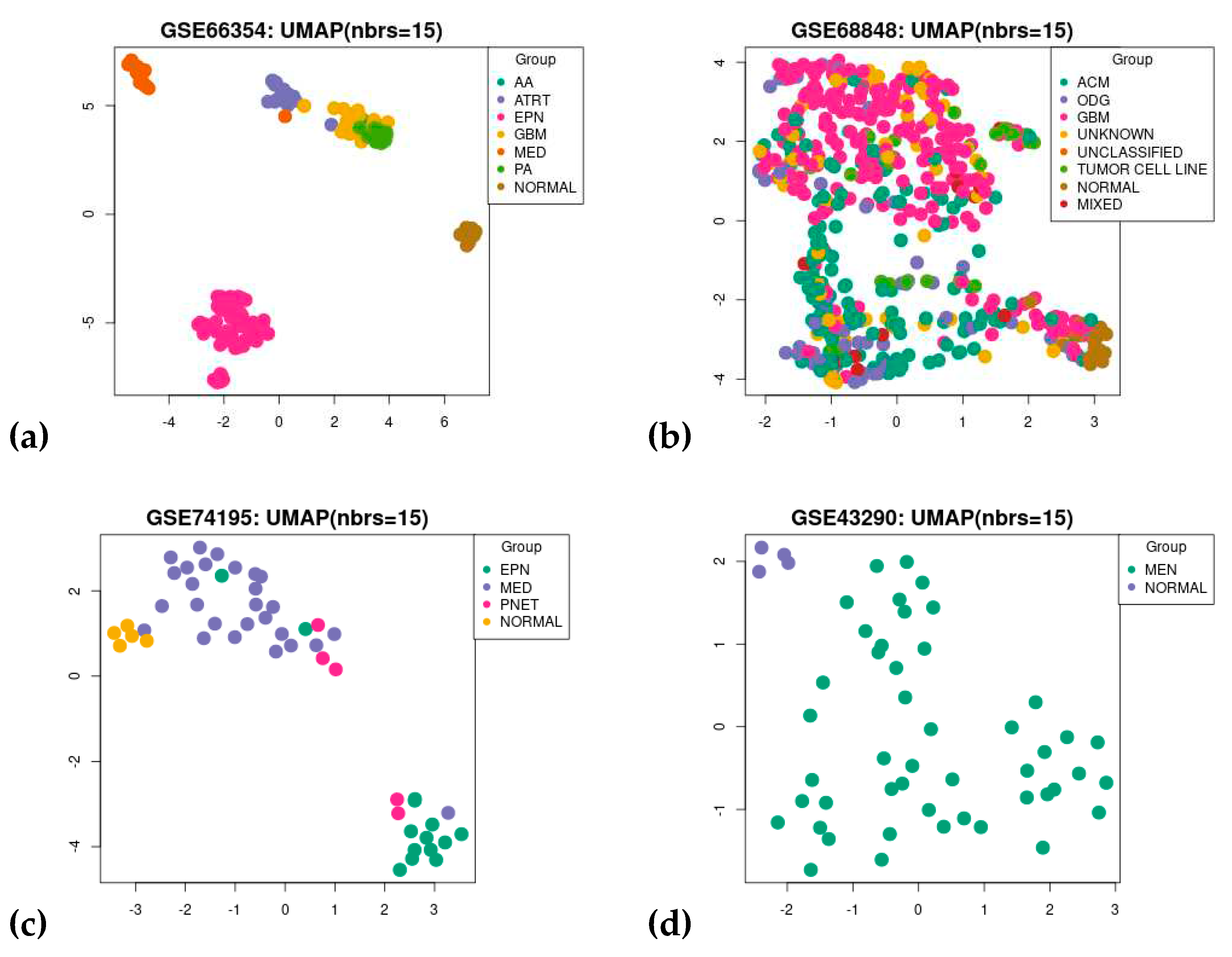
3.1. Dataset Search and Selection
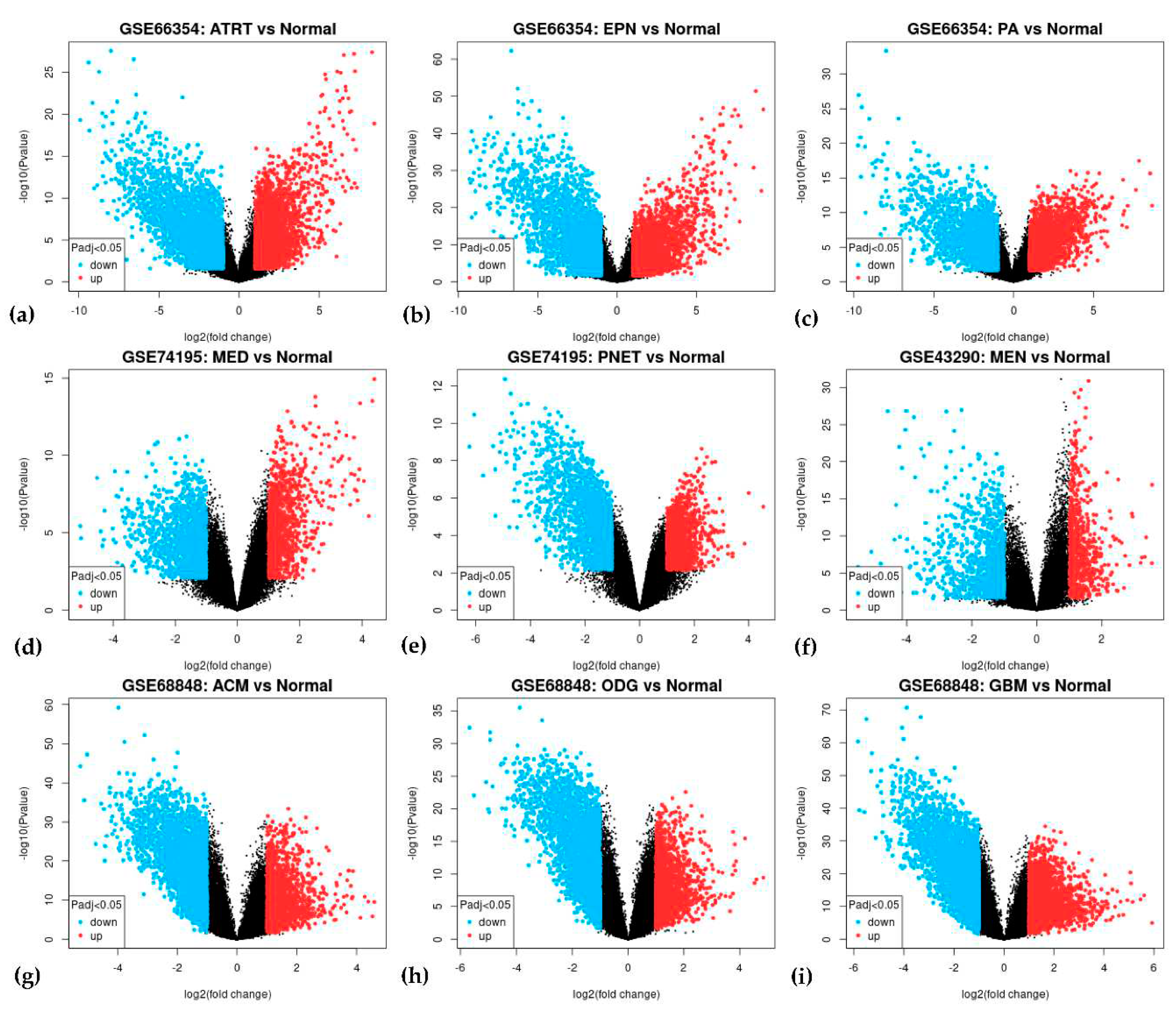
3.2. Differentially Expressed Genes
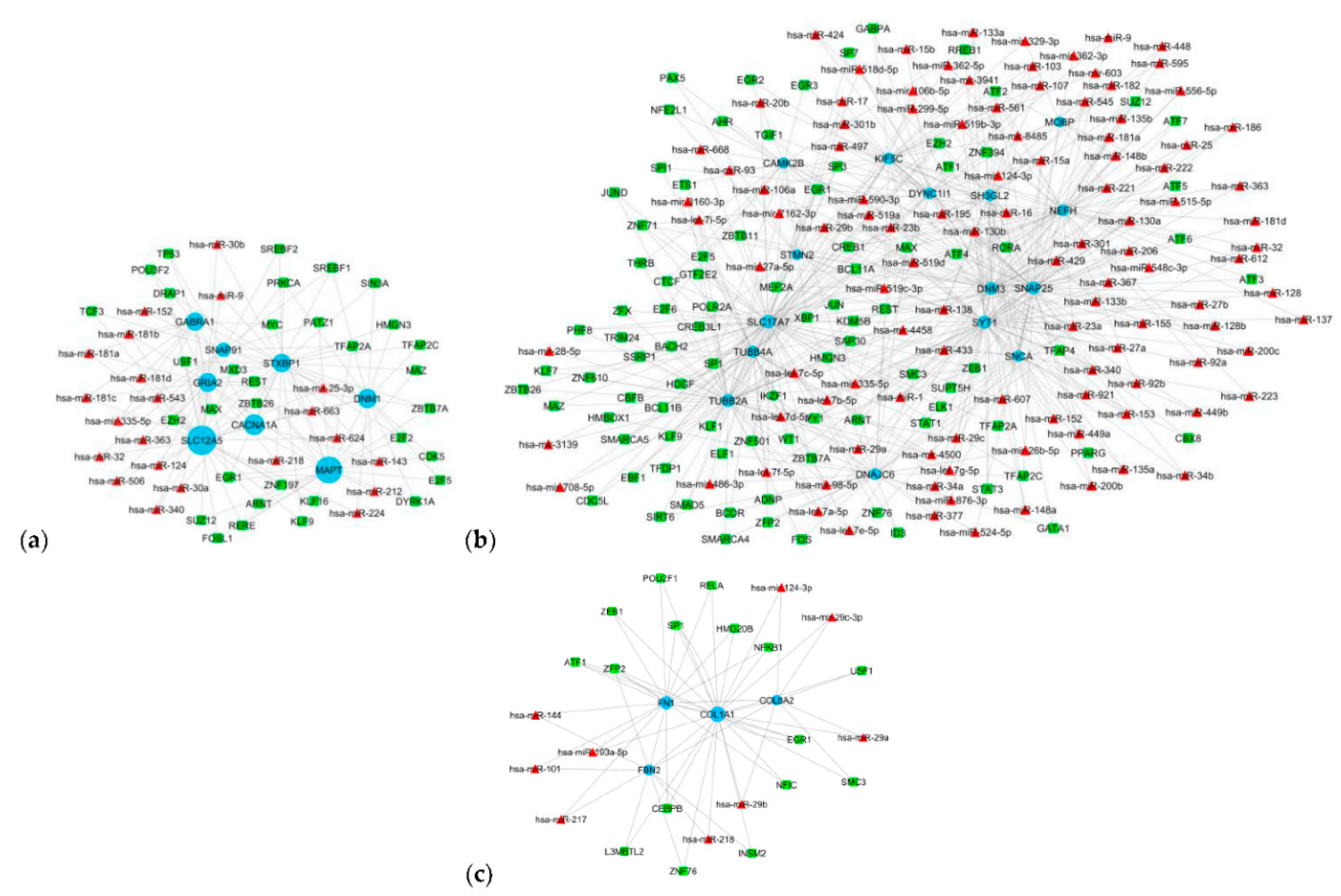
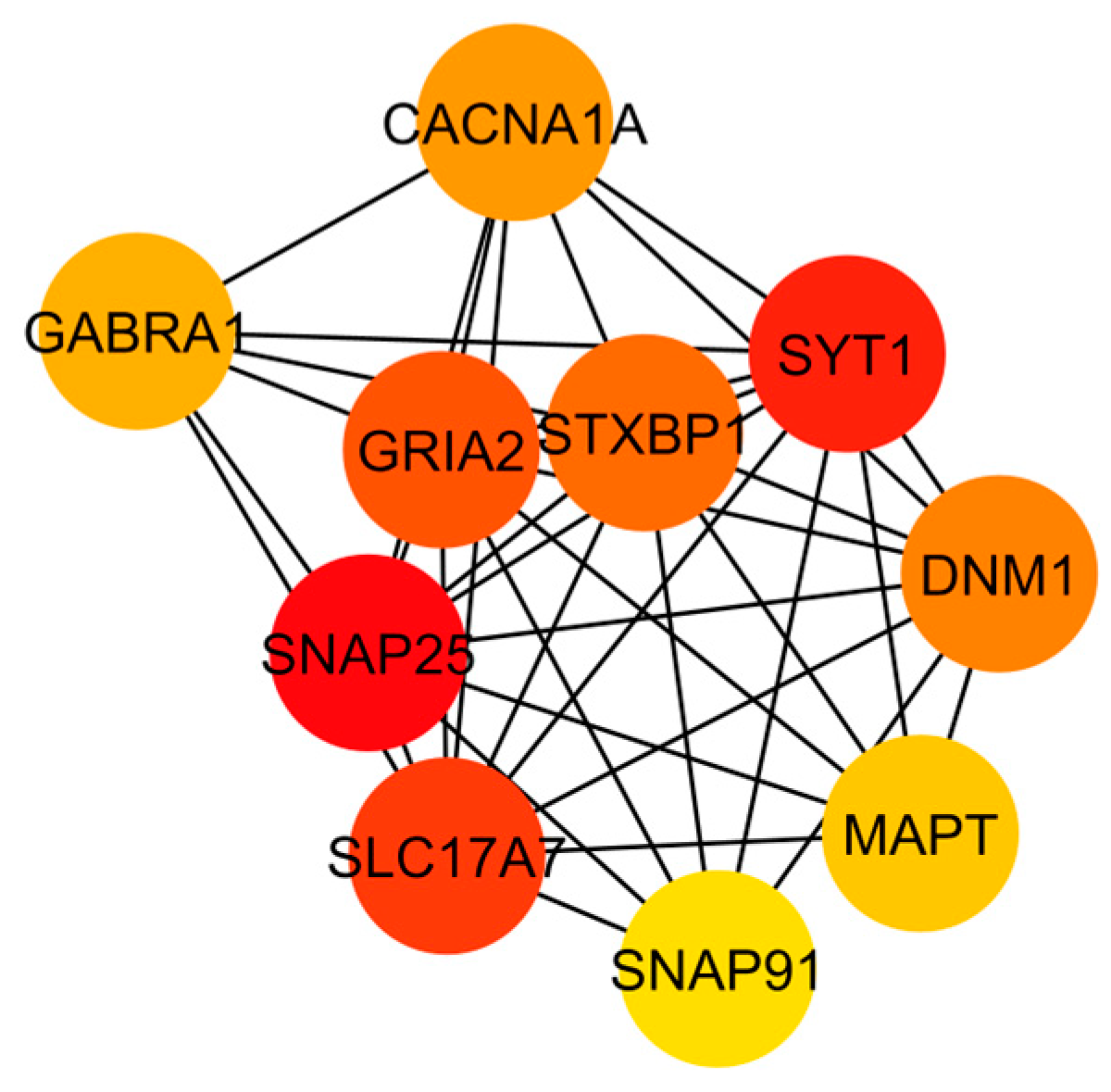
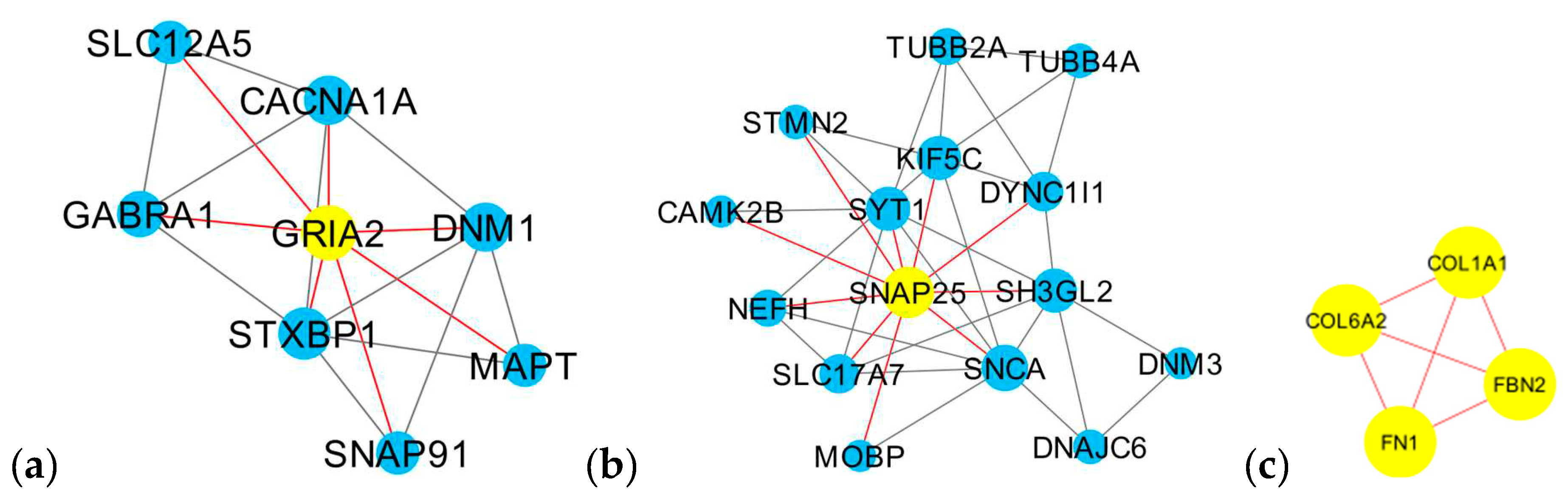
3.3. Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis
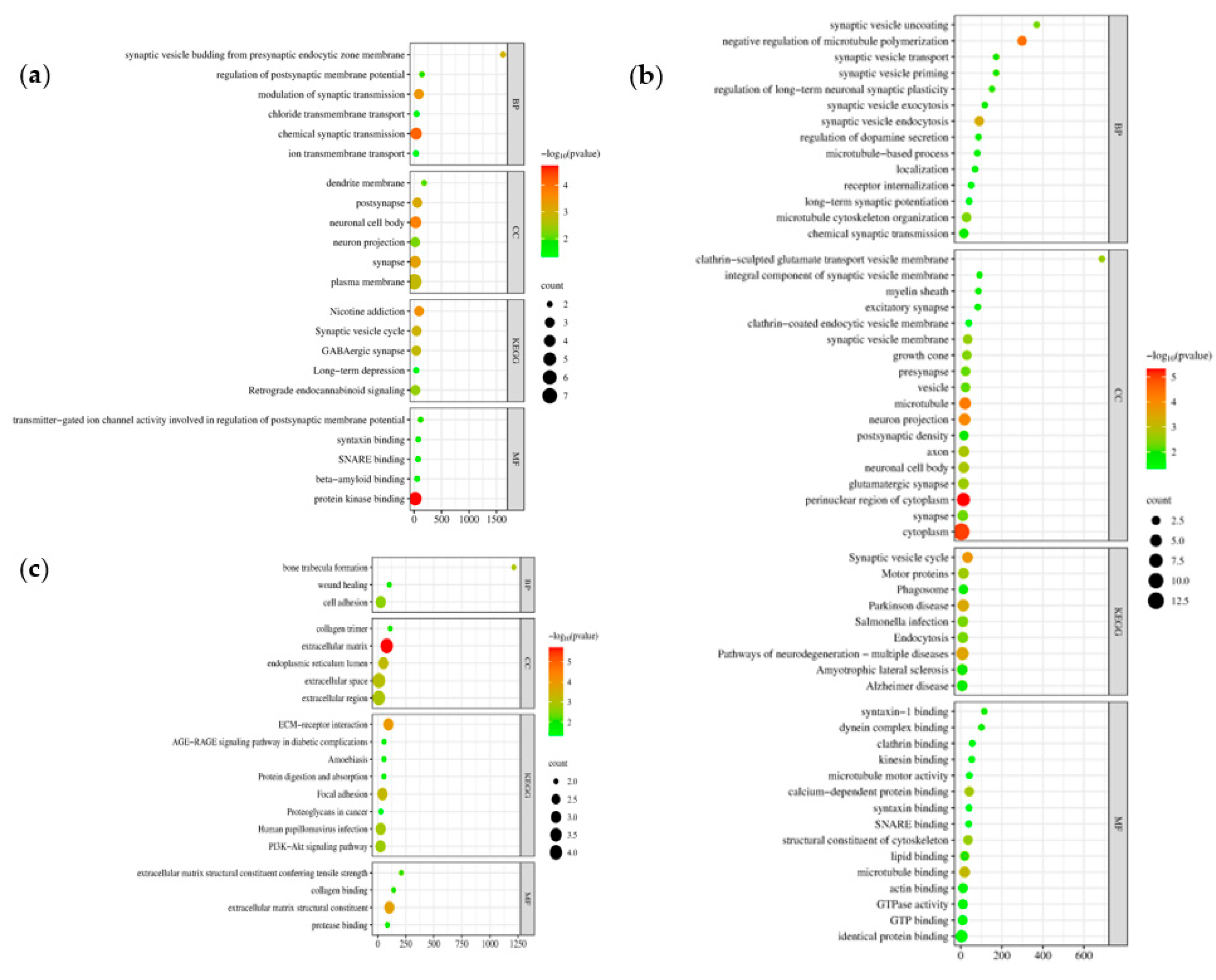
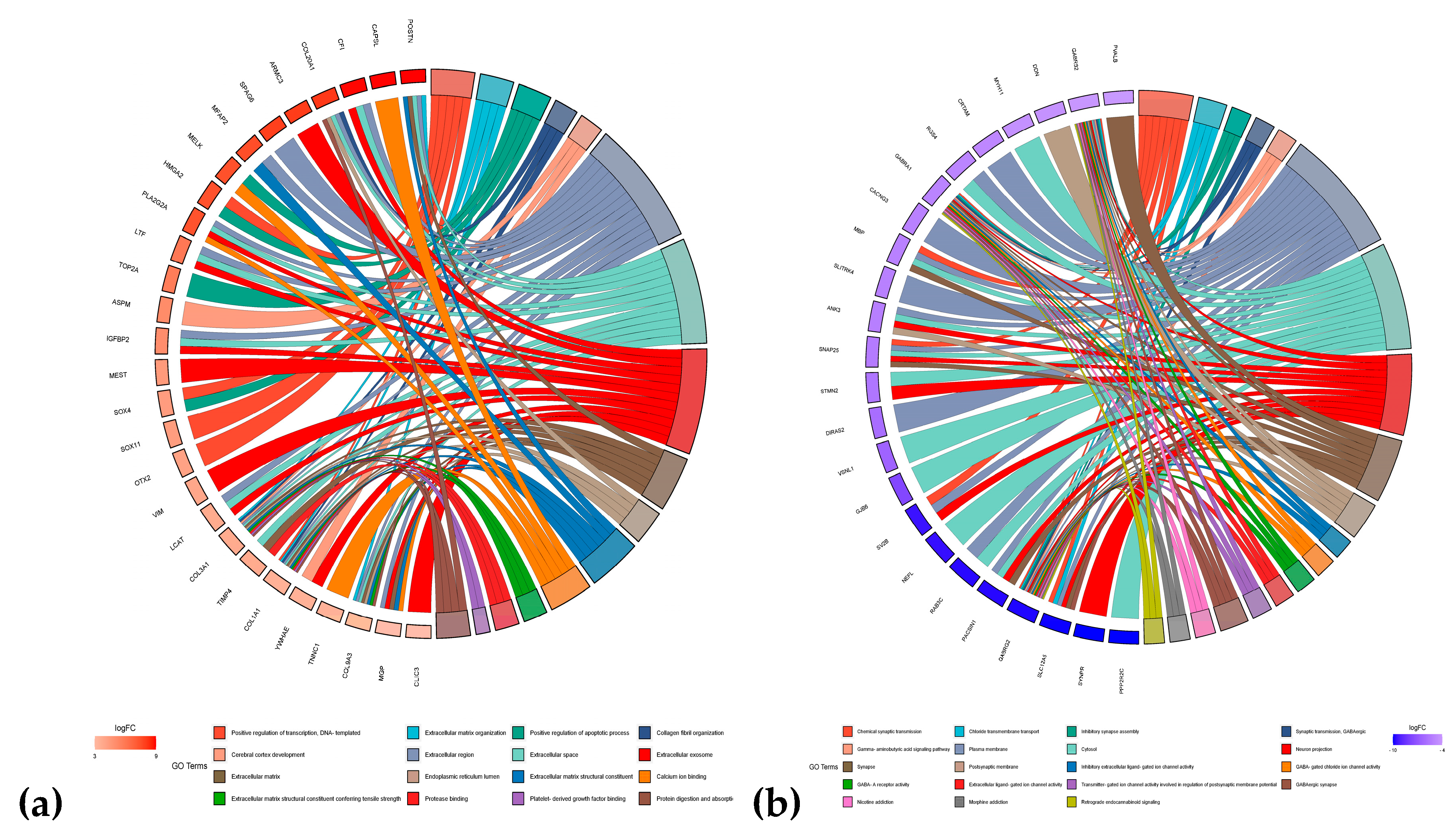
3.4. Enrichment Analysis
3.5. Gene Regulatory Network
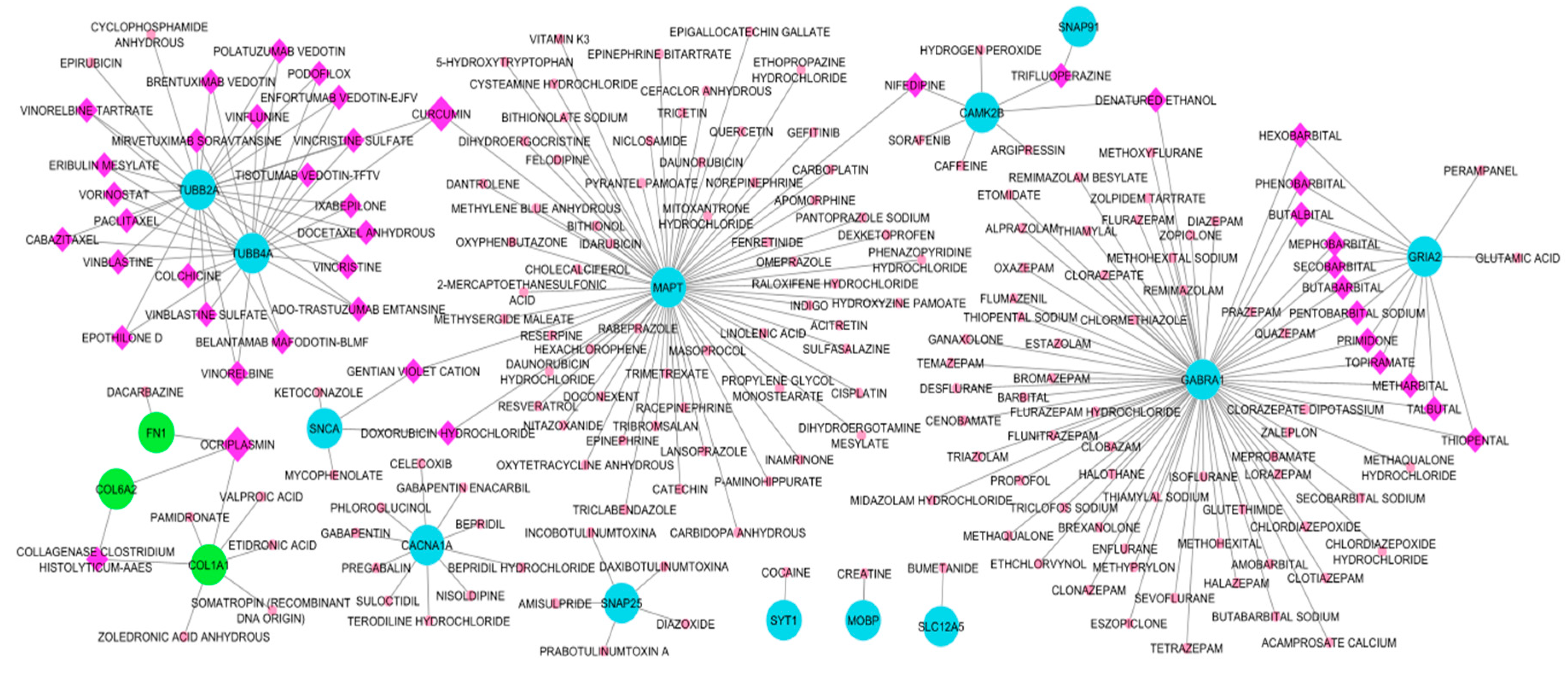
3.6. Drug repurposing candidates
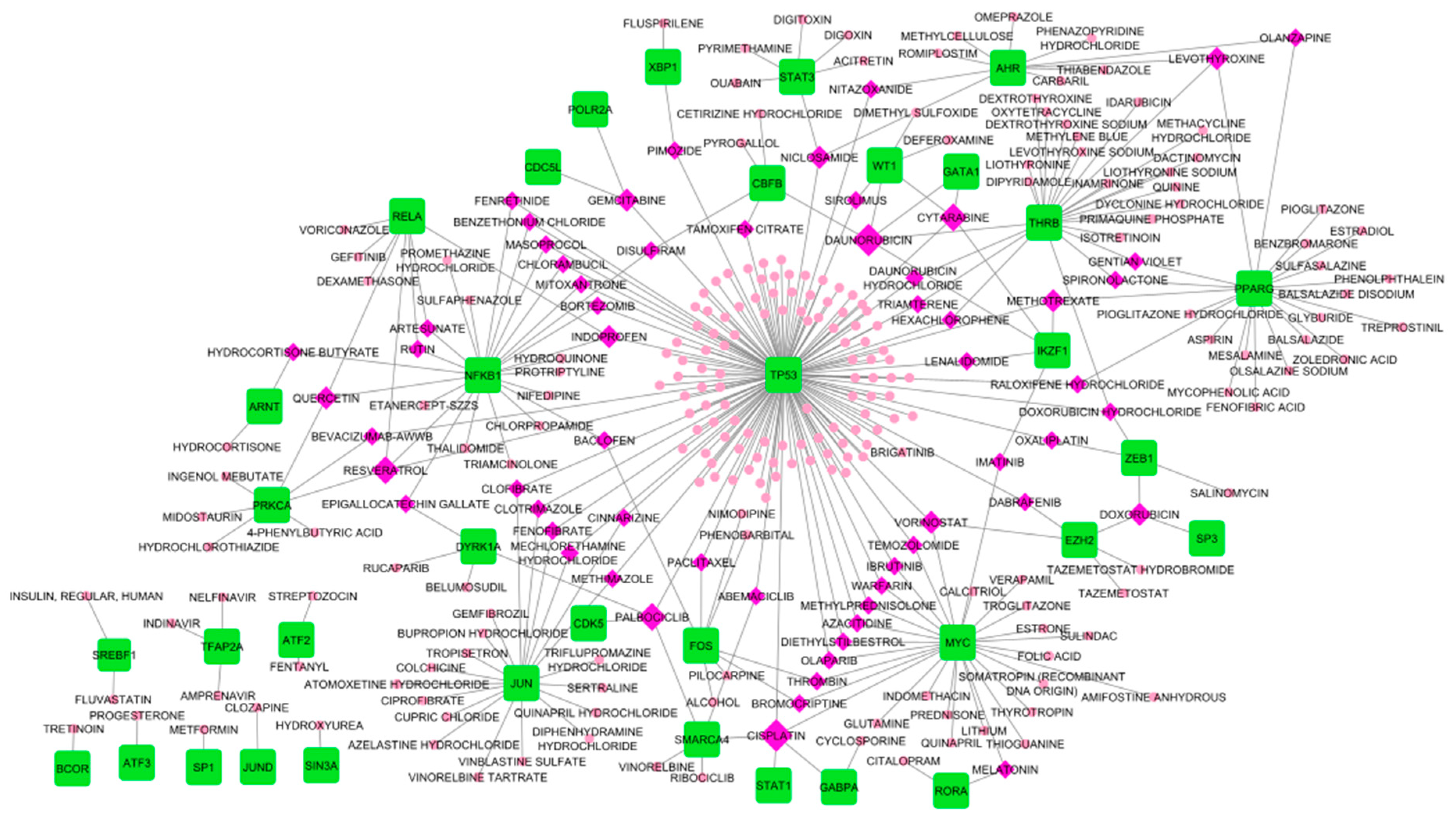
3.6.1. Drug-Hub Differentially Expressed Genes Network
3.6.2. Drug-Transcription Factors Networks
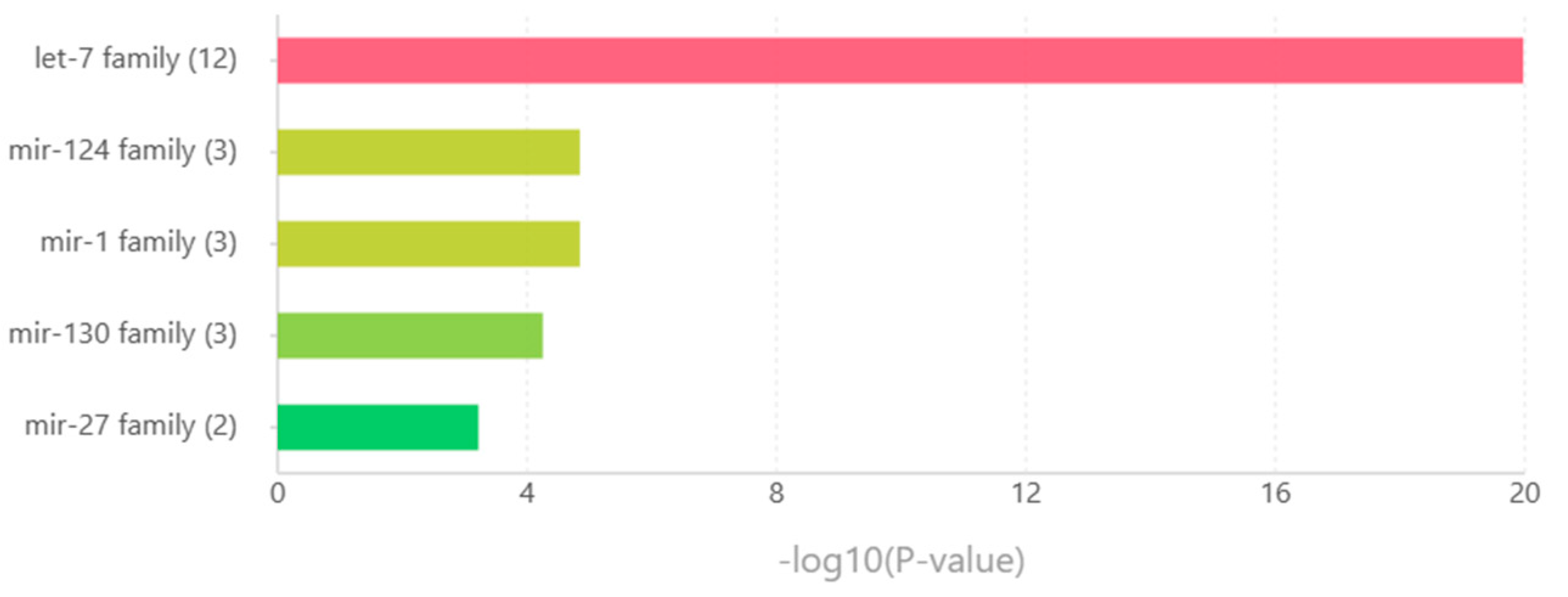
3.7. MicroRNA families
3.8. Gene set enrichment analysis and connectivity map for drug validation
4. Discussion
| Drug | HDEG | TF | Upregulated gene | Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quercetin | MAPT | NFKB1, PRKCA, RELA | SNCA | Kinase inhibitors |
| Vorinostat | TUBB2A, TUBB4A | EZH2, MYC, TP53 | DNAJC6, DNM3, KIF5C, SLC17A7, STXBP1, SYT1, TUBBA2A | Antineoplastic agents |
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgment
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Girardi, F.; Matz, M.; Stiller, C.; You, H.; Gragera, R.M.; Valkov, M.Y.; Bulliard, J.L.; De, P.; Morrison, D.; Wanner, M.; et al. Global Survival Trends for Brain Tumors, by Histology: Analysis of Individual Records for 556,237 Adults Diagnosed in 59 Countries during 2000–2014 (CONCORD-3). Neuro Oncol 2023, 25, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilic, I.; Ilic, M. International Patterns and Trends in the Brain Cancer Incidence and Mortality: An Observational Study Based on the Global Burden of Disease. Heliyon 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.D.; Ostrom, Q.T.; Kruchko, C.; Patil, N.; Tihan, T.; Cioffi, G.; Fuchs, H.E.; Waite, K.A.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L.; et al. Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumor Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 2021, 71, 381–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronica, E.; Ciusani, E.; Coppola, A.; Costa, C.; Russo, E.; Salmaggi, A.; Perversi, F.; Maschio, M. Epilepsy and Brain Tumors: Two Sides of the Same Coin. J Neurol Sci 2023, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slegers, R.J.; Blumcke, I. Low-Grade Developmental and Epilepsy Associated Brain Tumors: A Critical Update 2020. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandini, C.; Garofalo, M.; Rey, F.; Garau, J.; Zucca, S.; Sproviero, D.; Bordoni, M.; Berzero, G.; Davin, A.; Poloni, T.E.; et al. MINCR: A Long Non-Coding RNA Shared between Cancer and Neurodegeneration. Genomics 2021, 113, 4039–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audrey, C.; Lim, K.S.; Ahmad Zaki, R.; Fong, S.L.; Chan, C.Y.; Sathis Kumar, T.; Narayanan, V.; Tan, C.T. Prevalence of Seizures in Brain Tumor: A Meta-Analysis. Epilepsy Res 2022, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, U.; Gudigar, A.; Paul, A.; Goutham, T.S.; Inamdar, M.A.; Hegde, A.; Devi, A.; Ooi, C.P.; Deo, R.C.; Barua, P.D.; et al. Brain Tumor Detection and Screening Using Artificial Intelligence Techniques: Current Trends and Future Perspectives. Comput Biol Med 2023, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Neuro Oncol 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Fahmideh, M.A.; Cote, D.J.; Muskens, I.S.; Schraw, J.M.; Scheurer, M.E.; Bondy, M.L. Risk Factors for Childhood and Adult Primary Brain Tumors. Neuro Oncol 2019, 21, 1357–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kentsis, A. Why Do Young People Get Cancer? Pediatr Blood Cancer 2020, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Shen, Y.; Liang, T. Oncolytic Virotherapy: Basic Principles, Recent Advances and Future Directions. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2023, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gao, C.; Jiang, S.; Wu, H.; Liu, Z.; Dou, T. Burden and Trends of Brain and Central Nervous System Cancer from 1990 to 2019 at the Global, Regional, and Country Levels. Archives of Public Health 2022, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocarnik, J.M.; Compton, K.; Dean, F.E.; Fu, W.; Gaw, B.L.; Harvey, J.D.; Henrikson, H.J.; Lu, D.; Pennini, A.; Xu, R.; et al. Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life Years for 29 Cancer Groups From 2010 to 2019 A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. JAMA Oncol 2022, 8, 420–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.A.; Chu, K.C.; Hankey, B.F.; Ries, L.A.G. Cancer Incidence and Mortality Patterns among Specific Asian and Pacific Islander Populations in the U.S. Cancer Causes and Control 2008, 19, 227–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, K.A.; Scott, S.; Firth, A.U.; Sung, H.; Henley, S.J.; Sherman, R.L.; Siegel, R.L.; Anderson, R.N.; Kohler, B.A.; Benard, V.B.; et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, Part 1: National Cancer Statistics. Cancer 2022, 128, 4251–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, M.; Subramani, V. Rare Pediatric Brain Tumors. Pediatric Hematology Oncology Journal 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Klockow, J.L.; Zhang, M.; Lafortune, F.; Chang, E.; Jin, L.; Wu, Y.; Daldrup-Link, H.E. Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM): An Overview of Current Therapies and Mechanisms of Resistance. Pharmacol Res 2021, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caccese, M.; Padovan, M.; D’Avella, D.; Chioffi, F.; Gardiman, M.P.; Berti, F.; Busato, F.; Bellu, L.; Bergo, E.; Zoccarato, M.; et al. Anaplastic Astrocytoma: State of the Art and Future Directions. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2020, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santino, S.F.; Salles, D.; Stávale, J.N.; Malinverni, A.C.M. Pathophysiological Evaluation of Pilocytic Astrocytoma in Adults: Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Analysis. Pathol Res Pract 2023, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, D.; Santino, S.F.; Ribeiro, D.A.; Malinverni, A.C.M.; Stávale, J.N. The Involvement of the MAPK Pathway in Pilocytic Astrocytomas. Pathol Res Pract 2022, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, M. Imaging of Oligodendroglioma. British Journal of Radiology 2016, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesseling, P.; van den Bent, M.; Perry, A. Oligodendroglioma: Pathology, Molecular Mechanisms and Markers. Acta Neuropathol 2015, 129, 809–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hägerstrand, D.; Smits, A.; Eriksson, A.; Sigurdardottir, S.; Olofsson, T.; Hartman, M.; Nistér, M.; Kalimo, H.; Östman, A. Gene Expression Analyses of Grade II Gliomas and Identification of RPTPβ/ζ as a Candidate Oligodendroglioma Marker. Neuro Oncol 2008, 10, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griesinger, A.M.; Josephson, R.J.; Donson, A.M.; Levy, J.M.M.; Amani, V.; Birks, D.K.; Hoffman, L.M.; Furtek, S.L.; Reigan, P.; Handler, M.H.; et al. Interleukin-6/STAT3 Pathway Signaling Drives an Inflammatory Phenotype in Group an Ependymoma. Cancer Immunol Res 2015, 3, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukaka, R.G.; Szathmari, A.; Di Rocco, F.; Leblond, P.; Faure-Conter, C.; Claude, L.; Vasiljevic, A.; Beuriat, P.A.; Mottolese, C. Posterior Fossa Ependymoma in Children: A Long-Term Single-Center Experience. Neurochirurgie 2023, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korones, D.N. Pediatric Ependymomas: Something Old, Something New. Pediatric Hematology Oncology Journal 2023, 8, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, J.A.; Hawkins, C. Medulloblastoma: WHO 2021 and Beyond. Pediatric and Developmental Pathology 2022, 25, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morfouace, M.; Cheepala, S.; Jackson, S.; Fukuda, Y.; Patel, Y.T.; Fatima, S.; Kawauchi, D.; Shelat, A.A.; Stewart, C.F.; Sorrentino, B.P.; et al. ABCG2 Transporter Expression Impacts Group 3 Medulloblastoma Response to Chemotherapy. Cancer Res 2015, 75, 3879–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, M.; Koster, J.; Bunt, J.; Hasselt, N.E.; Lakeman, A.; van Sluis, P.; Troost, D.; Schouten-van Meeteren, N.; Caron, H.N.; Cloos, J.; et al. Integrated Genomics Identifies Five Medulloblastoma Subtypes with Distinct Genetic Profiles, Pathway Signatures and Clinicopathological Features. PLoS One 2008, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Rodríguez, R.A.; Dávila-Borja, V.M.; Juárez-Méndez, S. Data Mining of Pediatric Medulloblastoma Microarray Expression Reveals a Novel Potential Subdivision of the Group 4 Molecular Subgroup. Oncol Lett 2018, 15, 6241–6250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabernero, M.D.; Maillo, A.; Gil-Bellosta, C.J.; Castrillo, A.; Sousa, P.; Merino, M.; Orfao, A. Gene Expression Profiles of Meningiomas Are Associated with Tumor Cytogenetics and Patient Outcome. Brain Pathology 2009, 19, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birks, D.K.; Donson, A.M.; Patel, P.R.; Dunham, C.; Muscat, A.; Algar, E.M.; Ashley, D.M.; Kleinschmidt-DeMasters, B.K.; Vibhakar, R.; Handler, M.H.; et al. High Expression of BMP Pathway Genes Distinguishes a Subset of Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumors Associated with Shorter Survival. Neuro Oncol 2011, 13, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birks, D.K.; Donson, A.M.; Patel, P.R.; Sufit, A.; Algar, E.M.; Dunham, C.; Kleinschmidt-Demasters, B.K.; Handler, M.H.; Vibhakar, R.; Foreman, N.K. Pediatric Rhabdoid Tumors of Kidney and Brain Show Many Differences in Gene Expression but Share Dysregulation of Cell Cycle and Epigenetic Effector Genes. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, H.A.; Ward, J.H.; Miller, S.; Lowe, J.; Coyle, B.; Grundy, R.G. The Role of the WNT/β-Catenin Pathway in Central Nervous System Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumours (CNS PNETs). Br J Cancer 2013, 108, 2130–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez, N. V.; Forshew, T.; Tatevossian, R.; Ellis, M.; Richard-Loendt, A.; Rogers, H.; Jacques, T.S.; Reitboeck, P.G.; Pearce, K.; Sheer, D.; et al. Comparative Expression Analysis Reveals Lineage Relationships between Human and Murine Gliomas and a Dominance of Glial Signatures during Tumor Propagation in Vitro. Cancer Res 2013, 73, 5834–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Yao, R.; Xu, Q.; Ma, L.; Liu, J. Bioinformatics Analysis Identified RGS4 as a Potential Tumor Promoter in Glioma. Pathol Res Pract 2022, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lönnemark, O.; Ryttlefors, M.; Sundblom, J. Cranioplasty in Brain Tumor Surgery: A Single-Center Retrospective Study Investigating Cranioplasty Failure and Tumor Recurrence. World Neurosurg 2023, 170, e313–e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamblin, R.; Vardon, A.; Akpalu, J.; Tampourlou, M.; Spiliotis, I.; Sbardella, E.; Lynch, J.; Shankaran, V.; Mavilakandy, A.; Gagliardi, I.; et al. Risk of Second Brain Tumour after Radiotherapy for Pituitary Adenoma or Craniopharyngioma: A Retrospective, Multicentre, Cohort Study of 3679 Patients with Long-Term Imaging Surveillance. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2022, 10, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giacomo, A.M.; Mair, M.J.; Ceccarelli, M.; Anichini, A.; Ibrahim, R.; Weller, M.; Lahn, M.; Eggermont, A.M.M.; Fox, B.; Maio, M. Immunotherapy for Brain Metastases and Primary Brain Tumors. Eur J Cancer 2023, 179, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Meng, F.; Deng, C.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, J.; Feijen, J.; Zhong, Z. Highly Efficacious and Specific Anti-Glioma Chemotherapy by Tandem Nanomicelles Co-Functionalized with Brain Tumor-Targeting and Cell-Penetrating Peptides. Journal of Controlled Release 2018, 278, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Kong, J.; Huang, X.; Zeng, J.; Du, Q.; Yang, T.; Yue, H.; Bao, Q.; Miao, Y.; Xu, Y.; et al. Targeted Glioblastoma Therapy by Integrating Brain-Targeting Peptides and Corn-Derived Cancer Cell-Penetrating Proteins into Nanoparticles to Cross Blood-Brain Tumor Barriers. Mater Today Nano 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, T.; Hasan, I.; Roy, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Guo, B. Advances in MRNA Nanomedicines for Malignant Brain Tumor Therapy. Smart Mater Med 2023, 4, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anami, Y.; Otani, Y.; Xiong, W.; Ha, S.Y.Y.; Yamaguchi, A.; Rivera-Caraballo, K.A.; Zhang, N.; An, Z.; Kaur, B.; Tsuchikama, K. Homogeneity of Antibody-Drug Conjugates Critically Impacts the Therapeutic Efficacy in Brain Tumors. Cell Rep 2022, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, E.A.; Rechberger, J.S.; Gupta, S.; Schwartz, J.D.; Daniels, D.J.; Khatua, S. Drug Delivery across the Blood-Brain Barrier for the Treatment of Pediatric Brain Tumors – An Update. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2022, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaito, S.; Burnet, N.G.; Aznar, M.C.; Marvaso, G.; Jereczek-Fossa, B.A.; Crellin, A.; Indelicato, D.; Pan, S.; Colaco, R.; Rieu, R.; et al. Proton Beam Therapy in the Reirradiation Setting of Brain and Base of Skull Tumour Recurrences. Clin Oncol 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, S.; Melnick, K.; Rahman, M.; Ghiaseddin, A. Updates on Role for and Efficacy of Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy in the Management of Brain Tumors. Advances in Oncology 2023, 3, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Xie, H.; Zhang, B.; Xia, W.; Guo, B. Multifunctional Nanotheranostics for near Infrared Optical Imaging-Guided Treatment of Brain Tumors. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2022, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukder, M.A.; Islam, M.M.; Uddin, M.A.; Akhter, A.; Pramanik, M.A.J.; Aryal, S.; Almoyad, M.A.A.; Hasan, K.F.; Moni, M.A. An Efficient Deep Learning Model to Categorize Brain Tumor Using Reconstruction and Fine-Tuning. Expert Syst Appl 2023, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvathaneni, V.; Kulkarni, N.S.; Muth, A.; Gupta, V. Drug Repurposing: A Promising Tool to Accelerate the Drug Discovery Process. Drug Discov Today 2019, 24, 2076–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, R. Drug Repurposing for Glioblastoma Based on Molecular Subtypes. J Biomed Inform 2016, 64, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, N.T.; Stathias, V.; Schürer, S.; Dakshanamurthy, S. Machine and Deep Learning Approaches for Cancer Drug Repurposing. Semin Cancer Biol 2021, 68, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, W.; Lin, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. Development of a Machine Learning Classifier for Brain Tumors Diagnosis Based on DNA Methylation Profile. Frontiers in Bioinformatics 2021, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinić, J.; Efferth, T.; García-Sosa, A.T.; Grahovac, J.; Padrón, J.M.; Pajeva, I.; Rizzolio, F.; Saponara, S.; Spengler, G.; Tsakovska, I. Repurposing Old Drugs to Fight Multidrug Resistant Cancers. Drug Resistance Updates 2020, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.E.M.; Kadioglu, O.; Henry, &; Greten, J.; Yildirim, A.; Mayr, K.; Wenz, F.; Giordano, F.A.; Efferth, T. Drug Repurposing Using Transcriptome Sequencing and Virtual Drug Screening in a Patient with Glioblastoma. [CrossRef]
- MotieGhader, H.; Safavi, E.; Rezapour, A.; Amoodizaj, F.F.; Iranifam, R. asl Drug Repurposing for Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) Based on Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis. Sci Rep 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mailem, R.C.; Tayo, L.L. Drug Repurposing Using Gene Co-Expression and Module Preservation Analysis in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS), Sepsis, and COVID-19. Biology (Basel) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhavan, S.; Zenklusen, J.C.; Kotliarov, Y.; Sahni, H.; Fine, H.A.; Buetow, K. Rembrandt: Helping Personalized Medicine Become a Reality through Integrative Translational Research. Molecular Cancer Research 2009, 7, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusev, Y.; Bhuvaneshwar, K.; Song, L.; Zenklusen, J.C.; Fine, H.; Madhavan, S. Data Descriptor: The REMBRANDT Study, a Large Collection of Genomic Data from Brain Cancer Patients. Sci Data 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bont, J.M.; Kros, J.M.; Passier, M.M.C.J.; Reddingius, R.E.; Sillevis Smitt, P.A.E.; Luider, T.M.; Den Boer, M.L.; Pieters, R. Differential Expression and Prognostic Significance of SOX Genes in Pediatric Medulloblastoma and Ependymoma Identified by Microarray Analysis. Neuro Oncol 2008, 10, 648–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, E.; Barrett, T. The Gene Expression Omnibus Database. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press Inc., 2016; Vol. 1418, pp. 93–110.
- Zhou, W.; Han, L.; Altman, R.B. Imputing Gene Expression to Maximize Platform Compatibility. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.; Freudenberg, J.; Thompson, S.; Aronow, B.; Pavlidis, P. Experimental Comparison and Cross-Validation of the Affymetrix and Illumina Gene Expression Analysis Platforms. Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 33, 5914–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; Speed, T.P. A Comparison of Affymetrix Gene Expression Arrays. BMC Bioinformatics 2007, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for Functional Genomics Data Sets - Update. Nucleic Acids Res 2013, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackstadt, A.J.; Hess, A.M. Filtering for Increased Power for Microarray Data Analysis. BMC Bioinformatics 2009, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Robinson, D.G.; Storey, J.D. The Functional False Discovery Rate with Applications to Genomics. Biostatistics 2021, 22, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. G:Profiler: A Web Server for Functional Enrichment Analysis and Conversions of Gene Lists (2019 Update). Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING Database in 2023: Protein-Protein Association Networks and Functional Enrichment Analyses for Any Sequenced Genome of Interest. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhong, J.; Chen, G.; Li, M.; Wu, F.X.; Pan, Y. ClusterViz: A Cytoscape APP for Cluster Analysis of Biological Network. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform 2015, 12, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wu, H.H.; Ho, C.W.; Ko, M.T.; Lin, C.Y. CytoHubba: Identifying Hub Objects and Sub-Networks from Complex Interactome. BMC Syst Biol 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. DAVID: A Web Server for Functional Enrichment Analysis and Functional Annotation of Gene Lists (2021 Update). Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.A.; Clark, J.; Ireland, A.; Lomax, J.; Ashburner, M.; Foulger, R.; Eilbeck, K.; Lewis, S.; Marshall, B.; Mungall, C.; et al. The Gene Oncology (GO) Database and Informatics Resource. Nucleic Acids Res 2004, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; 2000; Vol. 28;
- Zhou, G.; Soufan, O.; Ewald, J.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Basu, N.; Xia, J. NetworkAnalyst 3.0: A Visual Analytics Platform for Comprehensive Gene Expression Profiling and Meta-Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47, W234–W241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abascal, F.; Acosta, R.; Addleman, N.J.; Adrian, J.; Afzal, V.; Aken, B.; Akiyama, J.A.; Jammal, O. Al; Amrhein, H.; Anderson, S.M.; et al. Expanded Encyclopaedias of DNA Elements in the Human and Mouse Genomes. Nature 2020, 583, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, H.; Ma, J.; Zang, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Tang, Q.; Meyer, C.A.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.S. Target Analysis by Integration of Transcriptome and ChIP-Seq Data with BETA. Nat Protoc 2013, 8, 2502–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.Y.; Lin, Y.C.D.; Cui, S.; Huang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Xu, J.; Bao, J.; Li, Y.; Wen, J.; Zuo, H.; et al. MiRTarBase Update 2022: An Informative Resource for Experimentally Validated MiRNA-Target Interactions. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50, D222–D230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.P.; Wu, C.; Miao, H.; Wu, H. RegNetwork: An Integrated Database of Transcriptional and Post-Transcriptional Regulatory Networks in Human and Mouse. Database 2015, 2015, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The GTEx Consortium Atlas of Genetic Regulatory Effects across Human Tissues The GTEx Consortium*;
- Freshour, S.L.; Kiwala, S.; Cotto, K.C.; Coffman, A.C.; McMichael, J.F.; Song, J.J.; Griffith, M.; Griffith, O.L.; Wagner, A.H. Integration of the Drug-Gene Interaction Database (DGIdb 4.0) with Open Crowdsource Efforts. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, D1144–D1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshov, M. V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A Comprehensive Gene Set Enrichment Analysis Web Server 2016 Update. Nucleic Acids Res 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Han, X.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, R.; Cui, Q.; Zhou, Y. TAM 2.0: Tool for MicroRNA Set Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, W180–W185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, Y. ping; Qian, Y. wen; Yu, L. xing; Wen, W.; Cui, X. liang; Wang, H. yang Identification of Important Genes and Drug Repurposing Based on Clinical-Centered Analysis across Human Cancers. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2021, 42, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoloso, M.S.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNA Involvement in Brain Tumors: From Bench to Bedside. In Proceedings of the Brain Pathology; January 2008; Vol. 18; pp. 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Giannopoulou, A.I.; Kanakoglou, D.S.; Piperi, C. Transcription Factors with Targeting Potential in Gliomas. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Lemus, E.; Martínez-García, M. Pathway-Based Drug-Repurposing Schemes in Cancer: The Role of Translational Bioinformatics. Front Oncol 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damodharan, S.; Puccetti, D. Pediatric Central Nervous System Tumor Overview and Emerging Treatment Considerations. Brain Sci 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maarif, R.; Kubota, Y.; Chernov, M.F. Early Tumor-Related Hemorrhage after Stereotactic Radiosurgery of Brain Metastases: Systematic Review of Reported Cases. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience 2023, 115, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottensmeier, H.; Zimolong, B.; Wolff, J.E.; Ehrich, J.; Galley, N.; Von Hoff, K.; Kuehl, J.; Rutkowski, S. Neuropsychological Short Assessment of Disease- and Treatment-Related Intelligence Deficits in Children with Brain Tumours. European Journal of Paediatric Neurology 2015, 19, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, N.N.; Wang, C.Y.; Chen, C.F.; Sun, Z.; Lai, M.D.; Lin, Y.C. Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels: Novel Targets for Cancer Therapy. Oncol Lett 2017, 14, 2059–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DNM1 Encephalopathy A New Disease of Vesicle Fission; 2017;
- Hu, M.; Gu, J.; Su, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Wang, Q.; Xing, C. DNM1: A Prognostic Biomarker Associated with Immune Infiltration in Colon Cancer - A Study Based on TCGA Database. Biomed Res Int 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belotti, Y.; Tolomeo, S.; Yu, R.; Lim, W.T.; Lim, C.T. Prognostic Neurotransmitter Receptors Genes Are Associated with Immune Response, Inflammation and Cancer Hallmarks in Brain Tumors. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, K.; Martirosian, V.; Nakamura, B.N.; Iyer, M.; Julian, A.; Eisenbarth, R.; Shao, L.; Attenello, F.; Neman, J. Neuronal Exposure Induces Neurotransmitter Signaling and Synaptic Mediators in Tumors Early in Brain Metastasis. Neuro Oncol 2022, 24, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.H.; Choi, J.J.; Park, Y.A.; Lee, Y.Y.; Song, S.Y.; Sung, C.O.; Song, T.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, T.J.; Lee, J.W.; et al. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes According to Chemosensitivity in Advanced Ovarian Serous Adenocarcinomas: Expression of GRIA2 Predicts Better Survival. Br J Cancer 2012, 107, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, S.; Chobrutskiy, B.I.; Sikaria, D.; Blanck, G. MAPT (Tau) Expression Is a Biomarker for an Increased Rate of Survival for Low-Grade Glioma. Oncol Rep 2019, 41, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, B.; Lee, H.; Yoon, J.-G.; Madan, A.; Wayner, E.; Tonning, S.; Hothi, P.; Schroeder, B.; Ulasov, I.; Foltz, G.; et al. Global Analysis of H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 Profiles in Glioblastoma Stem Cells and Identification of SLC17A7 as a Bivalent Tumor Suppressor Gene; Vol. 6;
- Huang, Q.; Lian, C.; Dong, Y.; Zeng, H.; Liu, B.; Xu, N.; He, Z.; Guo, H. SNAP25 Inhibits Glioma Progression by Regulating Synapse Plasticity via GLS-Mediated Glutaminolysis. Front Oncol 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.-F.; Mao, X.-Y.; Zhu, T.; Mao, C.-X.; Liu, Z.-X.; Wang, Z.-B.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Yin, J.-Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Oncotarget 70494 Www.Impactjournals.Com/Oncotarget COL3A1 and SNAP91: Novel Glioblastoma Markers with Diagnostic and Prognostic Value; Vol. 7;
- Abramov, D.; Guy, N.; Guiberson, L.; Burré, J. STXBP1 Encephalopathies: Clinical Spectrum, Disease Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Strategies; C.
- Riggs, E.; Shakkour, Z.; Anderson, C.L.; Carney, P.R. SYT1-Associated Neurodevelopmental Disorder: A Narrative Review. Children 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lin, Q.; Zheng, H.; Rao, Y.; Ji, T. The Pro-Invasive Factor COL6A2 Serves as a Novel Prognostic Marker of Glioma. Front Oncol 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Da, J.; Hu, N. Identification of COL1A1 Associated with Immune Infiltration in Brain Lower Grade Glioma. PLoS One 2022, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loon, K.; Yemelyanenko-Lyalenko, J.; Margadant, C.; Griffioen, A.W.; Huijbers, E.J.M. Role of Fibrillin-2 in the Control of TGF-β Activation in Tumor Angiogenesis and Connective Tissue Disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 2020, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B. Prediction and Analysis of Hub Genes between Glioblastoma and Low-Grade Glioma Using Bioinformatics Analysis. Medicine (United States) 2021, 100, E23513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, Z.; Xue, X. TOP2A Correlates with Poor Prognosis and Affects Radioresistance of Medulloblastoma. Front Oncol 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, Y.; Qian, D.; Liang, Q.; Wang, B. Over-Expression of TOP2A as a Prognostic Biomarker in Patients with Glioma; 2018; Vol. 11;
- Sánchez, O.F.; Rodríguez, A. V.; Velasco-España, J.M.; Murillo, L.C.; Sutachan, J.J.; Albarracin, S.L. Role of Connexins 30, 36, and 43 in Brain Tumors, Neurodegenerative Diseases, and Neuroprotection. Cells 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataramani, V.; Tanev, D.I.; Kuner, T.; Wick, W.; Winkler, F. Synaptic Input to Brain Tumors: Clinical Implications. Neuro Oncol 2021, 23, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.L.; Kavallaris, M.; McCarroll, J.A. Microtubules and Their Role in Cellular Stress in Cancer. Front Oncol 2014, 4 JUN.
- Walker, C.; Mojares, E.; Del Río Hernández, A. Role of Extracellular Matrix in Development and Cancer Progression. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isakov, N. Protein Kinase C (PKC) Isoforms in Cancer, Tumor Promotion and Tumor Suppression. Semin Cancer Biol 2018, 48, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, P.J.; Lovinger, D.M. Retrograde Endocannabinoid Signaling in a Postsynaptic Neuron/Synaptic Bouton Preparation from Basolateral Amygdala. Journal of Neuroscience 2005, 25, 6199–6207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benowitz, N.L.; Hukkanen, J.; Jacob, P. Nicotine Chemistry, Metabolism, Kinetics and Biomarkers. Handb Exp Pharmacol 2009, 192, 29–60. [Google Scholar]
- Savaskan, N.E.; Fan, Z.; Broggini, T.; Buchfelder, M.; Eyüpoglu, I.Y. Send Orders for Reprints to Reprints@benthamscience.Ae Neurodegeneration in the Brain Tumor Microenvironment: Glutamate in the Limelight; 2015; Vol. 13;
- Cao, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, D. quan; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Liu, S.X.; Wang, P. Identification of Hub Genes and Potential Molecular Mechanisms in Gastric Cancer by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. PeerJ 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Shen, N.; Wicha, M.S.; Luo, M. The Roles of the Let-7 Family of Micrornas in the Regulation of Cancer Stemness. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.T.; Zhang, G.X.; Gao, S.S. The Potential Diagnostic Accuracy of Let-7 Family for Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2021, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanuki, R.; Yamamura, T. Tumor Suppressive Effects of Mir-124 and Its Function in Neuronal Development. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Wang, Y.; Sims, M.; Cai, C.; Pfeffer, L.M. MicroRNA-1 Suppresses Glioblastoma in Preclinical Models by Targeting Fibronectin. Cancer Lett 2019, 465, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Song, J. MicroRNA-103 Suppresses Glioma Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Targeting the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor. Mol Med Rep 2018, 17, 4083–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, M.; Ding, L.; Tang, J. MiR-27a: A Novel Biomarker and Potential Therapeutic Target in Tumors. J Cancer 2019, 10, 2836–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shala, A.L.; Arduino, I.; Salihu, M.B.; Denora, N. Quercetin and Its Nano-Formulations for Brain Tumor Therapy—Current Developments and Future Perspectives for Paediatric Studies. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, D.; Lockman, P.R.; Thomas, F.C.; Hua, E.; Herring, J.; Hargrave, E.; Johnson, M.; Flores, N.; Qian, Y.; Vega-Valle, E.; et al. Vorinostat Inhibits Brain Metastatic Colonization in a Model of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer and Induces DNA Double-Strand Breaks. Clinical Cancer Research 2009, 15, 6148–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richon, V.M. Cancer Biology: Mechanism of Antitumour Action of Vorinostat (Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid), a Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor. In Proceedings of the British Journal of Cancer; December 2006; Vol. 95.
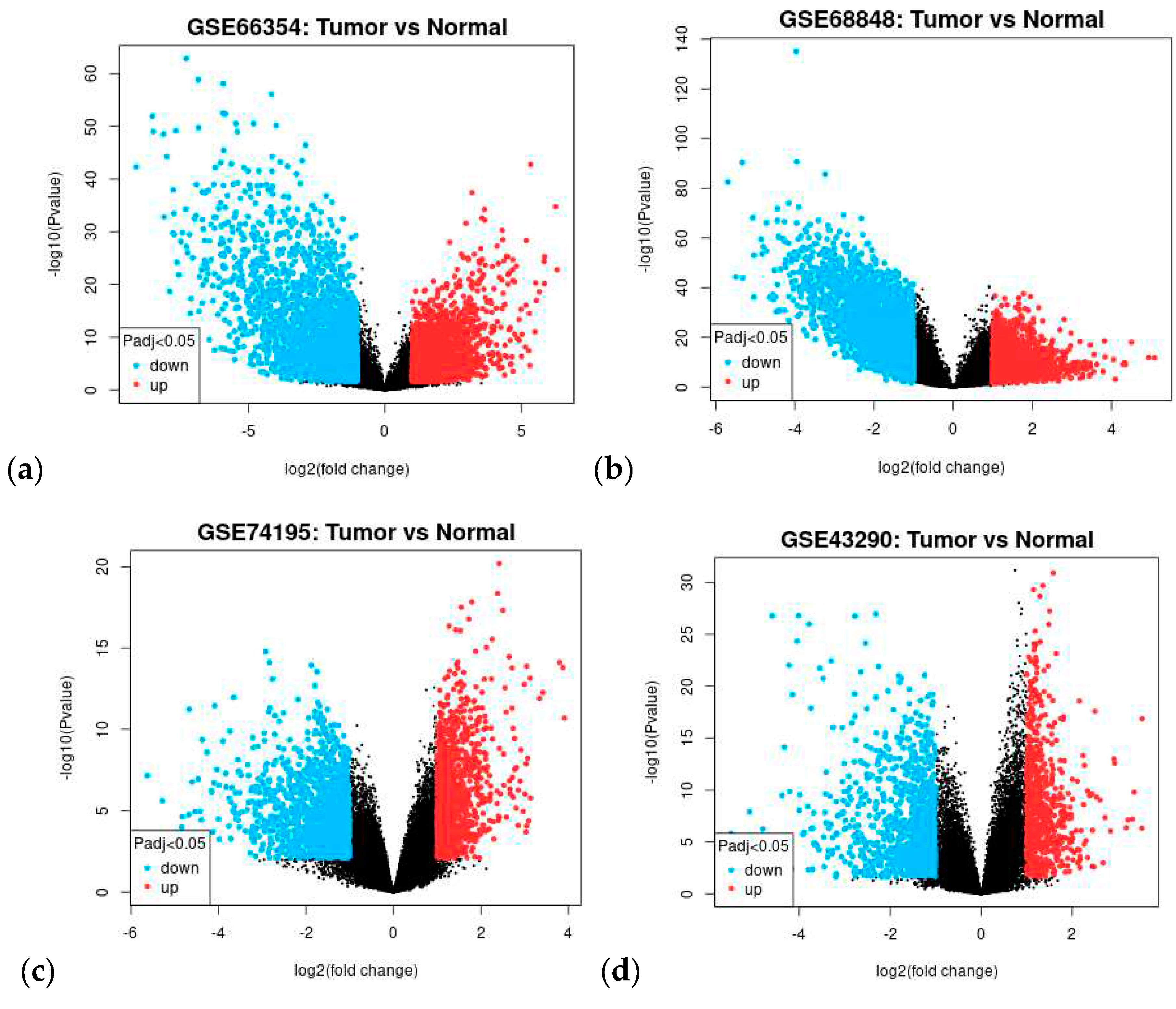
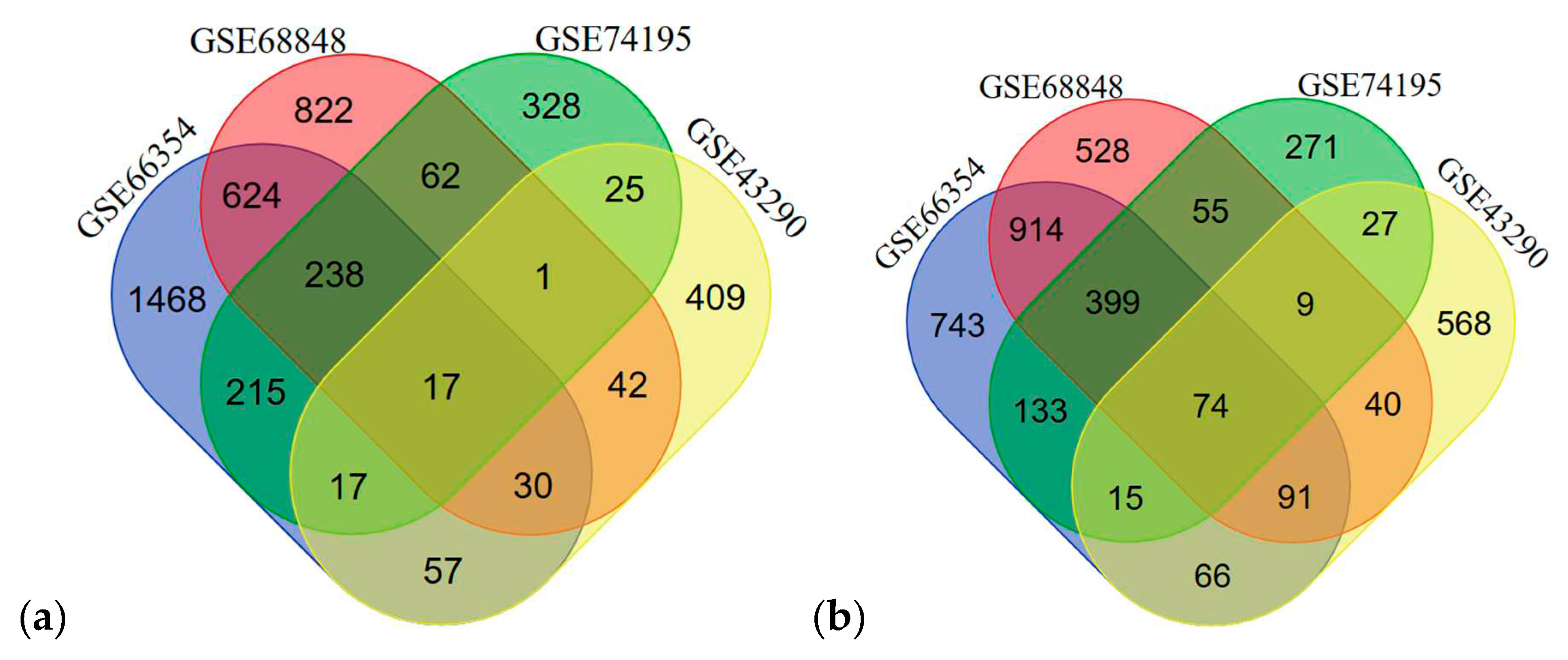

| NCBI GEO Accession | GSE66354 a | GSE68848 b | GSE74195 c | GSE43290 d |
| Published | February 27, 2015 | May 14, 2015 | October 21, 2015 | January 05, 2013 |
| Type | Expression profiling by array | |||
| Conditions | 2 AA 17 ATRT 29 EPN-PFA 26 EPN-PFB 9 EPN-ST 19 GBM 4 MED-G3 7 MED-G4 8 MED-SHH 15 PA 13 normal brain tissue |
148 ACM 228 GBM 67 ODG 67 unknown 11 mixed 1 unclassified 30 tumor cell lines 28 normal brain tissue |
13 EPN 1 EPN-BM 5 PNET 27 MED 5 normal cerebellum tissue |
47 MEN 4 normal meninges |
| Platform | GPL570 [HG-U133_Plus_2] Affymetrix Human Genome U133 Plus 2.0 Array | GPL96 [HG-U133A] Affymetrix Human Genome U133A Array | ||
| RNA Source | Surgical CNS tumors and normal brain tissue | |||
| No. of Samples | 149 | 580 | 51 | 51 |
| Differentially expressed genes | Total | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| Upregulated | 17 | COL1A1, PTBP1, TYMS, KDELR2, SOX4, PDLIM7, FZD2, ZFP36L2, COL6A2, RUVBL1, PPIB, FN1, SLC16A1, FBN2, MDK, GRN, TCF3 |
| Downregulated | 74 | RTN1, PHYHIP, ALDOC, NEFH, PGBD5, CABP1, SYT13, DNM1, IDS, CAMK2B, MAP7, RUNX1T1, KCNAB1, SNCA, EPB41L3, MAGI1, KIF5C, GABRA1, ADARB1, ZNF365, TAGLN3, OPCML, MOBP, PDE4DIP, PEG3, TRPM3, RAPGEF5, NDRG4, STXBP1, NSG1, GABBR2, SH3GL2, EFR3A, PLP1, STMN2, CYFIP2, HSPA12A, MCTP1, SYNGR3, VSNL1, CACNA1A, RCAN2, OLFM1, MAPT, SEPTIN4, GUCY1B3, GABRB1, SNAP25, RIMS3, ITPR1, MYO5A, GABARAPL1, DUSP8, SLC17A7, DNAJC6, DNM3, SYT1, DOCK9, TUBB2A, HOMER1, FAIM2, EHD3, DYNC1I1, SLC12A5, NRIP3, PPP1R16B, GABARAPL1, PCP4, ADAM22, RUNDC3A, SNAP91, TUBB4A, GRIA2, SPOCK1 |
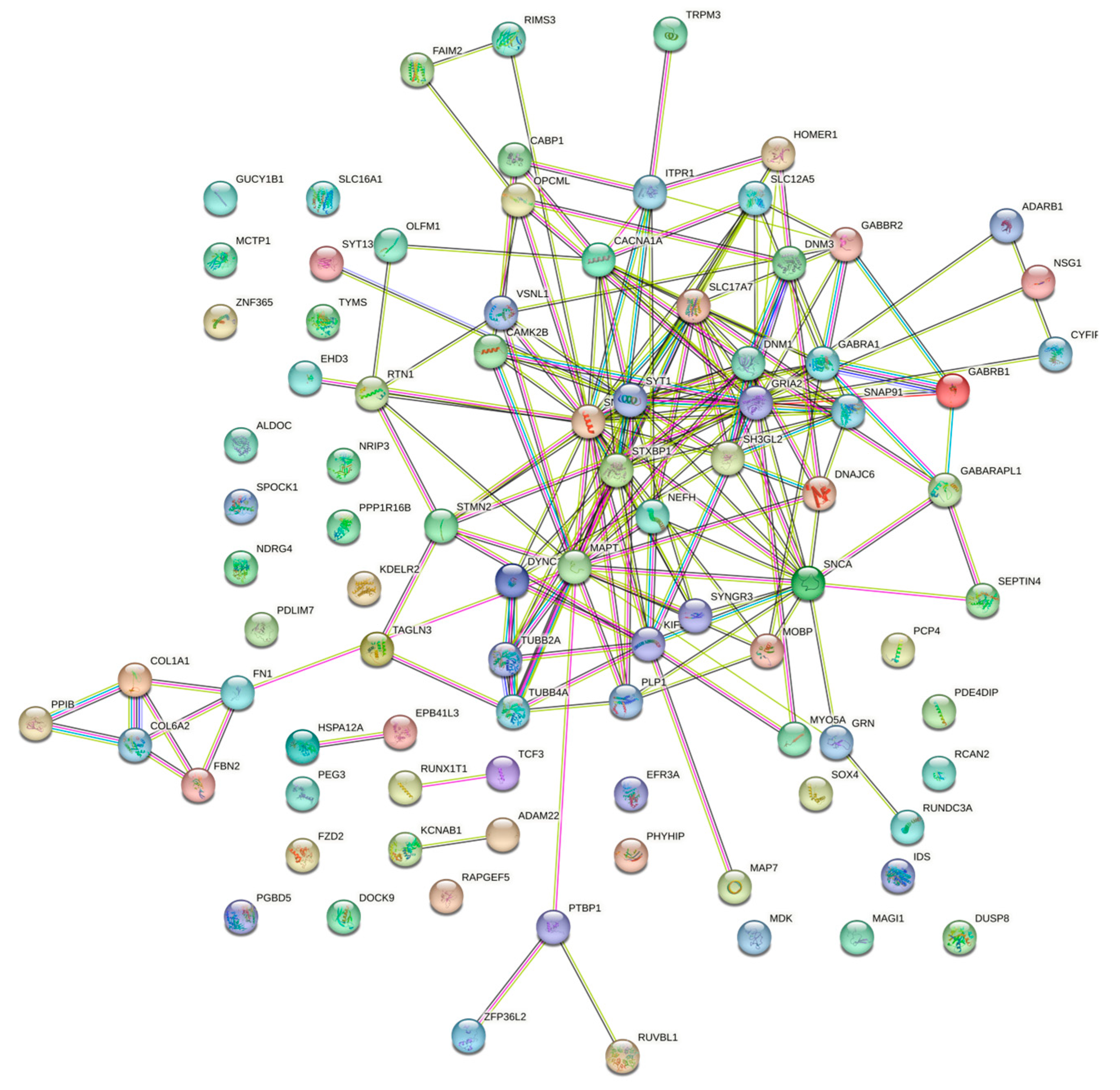
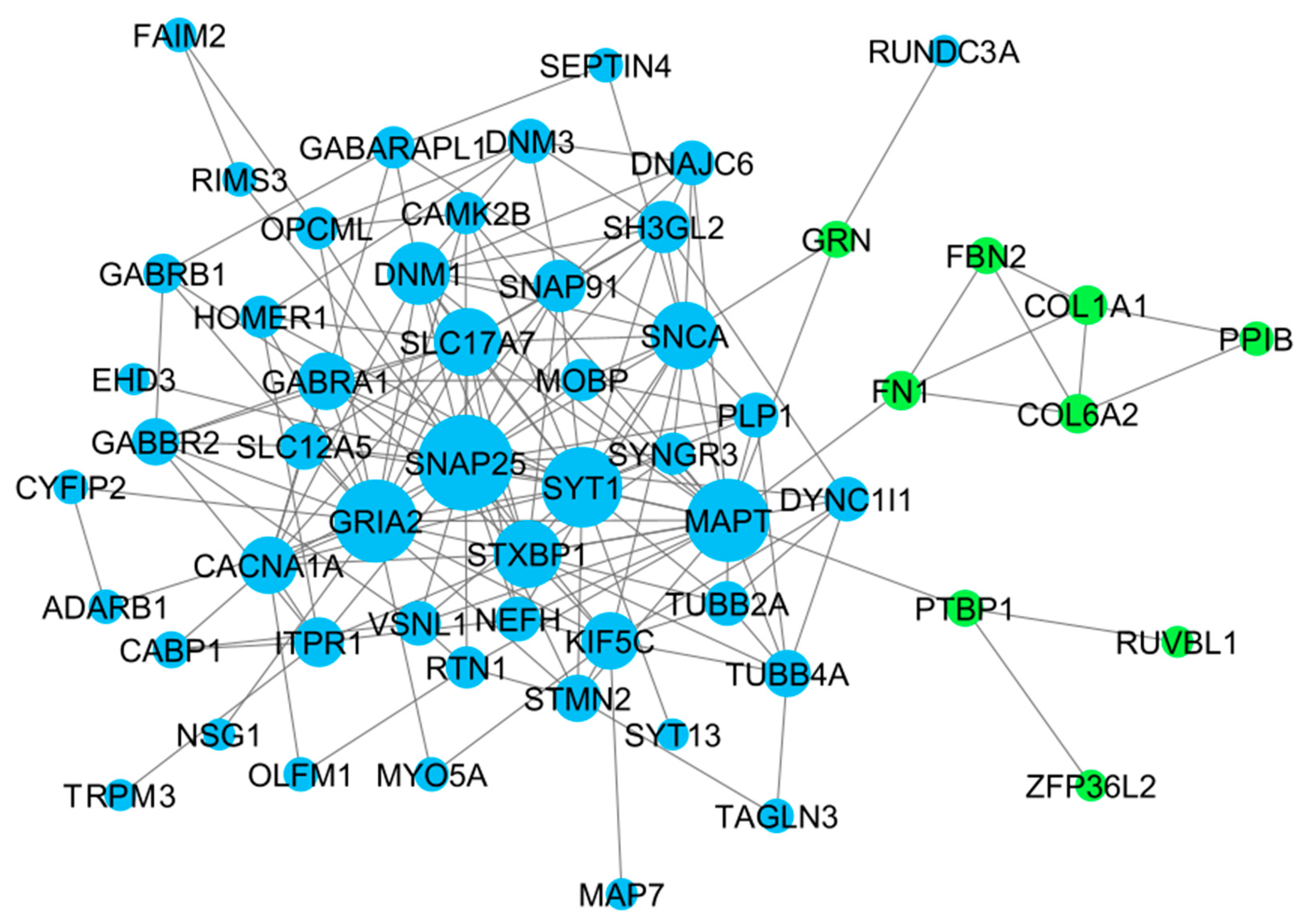
| Cluster | Gene names |
|---|---|
| Cluster 1 (5) | GRIA2 (7), STXBP1 (6), DNM1 (5), CACNA1A (5), GABRA1 (4), MAPT (3), SNAP91 (3), SLC12A5 (3) |
| Cluster 2 (5) | SNAP25 (10), SNCA (8), KIF5C (7), SH3GL2 (7), SYT1 (7), SLC17A7 (5), DYNC1I1 (5), NEFH (4), TUBB2A (4), STMN2 (3), TUBB4A (3), DNAJC6 (3), MOBP (2), CAMK2B (2), DNM3 (2) |
| Cluster 3 (4) | COL1A1 (3), COL6A2 (3), FBN2 (3), FN1 (3) |
| Top 10 | GRIA2 (9), SLC17A7 (9), SNAP25 (9), STXBP1 (9), SYT1 (9), DNM1 (8), CACNA1A (7), GABRA1 (6), MAPT (6), SNAP91 (6) |
| Gene name | Gene description |
|---|---|
| CACNA1A | Calcium voltage-gated channel subunit alpha1 A |
| DNM1 | Dynamin 1 |
| GABRA1 | Gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor subunit alpha1 |
| GRIA2 | Glutamate ionotropic receptor AMPA type subunit 2 |
| MAPT | Microtubule-associated protein tau |
| SLC17A7 | Solute carrier family 17-member 7 |
| SNAP25 | Synaptosome-associated protein 25 |
| SNAP91 | Synaptosome-associated protein 91 |
| STXBP1 | Syntaxin binding protein 1 |
| SYT1 | Synaptotagmin 1 |
| COL1A1 | Collagen type I alpha 1 chain |
| COL6A2 | Collagen type VI alpha 2 chain |
| FBN2 | Fibrillin 2 |
| FN1 | Fibronectin 1 |
| Transcription factors | Gene targets | Cluster |
|---|---|---|
| ARNT | CAMK2B, SLC17A7, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| ATF1 | NEFH, SNAP25, TUBB4A & FN1, COL1A1 | Cluster 2 & Cluster 3 |
| ATF2 | NEFH, SH3GL2, SNAP25 | Cluster 2 |
| ATF4 | CAMK2B, NEFH, SNAP25 | Cluster 2 |
| BCL11A | SNAP25, SLC17A7, TUBB4A | Cluster 2 |
| CREB1 | NEFH, SH3GL2, SLC17A7, SNAP25 | Cluster 2 |
| CTCF | CAMK2B, SLC17A7, TUBB4A | Cluster 2 |
| E2F5 | CAMK2B, SLC17A7, TUBB4A | Cluster 2 |
| EGR1 | GRIA2, MAPT, STXBP1 & CAMK2B, NEFH, SLC17A7, TUBB2A & FN1, COL1A1 | Cluster 1, Cluster 2 & Cluster 3 |
| ELF1 | DNAJC6, SLC17A7, TUBB4A | Cluster 2 |
| ELK1 | DNAJC6, SLC17A7, SNCA | Cluster 2 |
| EZH2 | GRIA2, SNAP91, SLC12A5 & KIF5C, SH3GL2, SLC17A7, STMN2, TUBB4A | Cluster 1 & Cluster 2 |
| KDM5B | DNM3, SLC17A7, TUBB2A | Cluster 2 |
| KLF1 | KIF5C, SLC17A7, TUBB2A | Cluster 2 |
| MAX | GABRA1, MAPT, STXBP1 & DNAJC6, NEFH, SLC17A7 | Cluster 1 & Cluster 2 |
| MEF2A | CAMK2B, SNAP25, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| PHF8 | DNM3, SLC17A7, TUBB2A | Cluster 2 |
| PRKCA | DNM1, GRIA2, STXBP1 | Cluster 1 |
| REST | GRIA2, MAPT, SLC12A5 & DNAJC6, NEFH, SNAP25, STMN2, TUBB2A | Cluster 1 & Cluster 2 |
| RREB1 | CAMK2B, NEFH, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| SAP30 | DNM3, SLC17A7, TUBB2A | Cluster 2 |
| SP1 | CAMK2B, DNAJC6, DYNC1I1, SLC17A7, TUBB2A& FN1, COL1A1 | Cluster 2 & Cluster 3 |
| SP3 | SNAP25, STMN2, TUBB2A | Cluster 2 |
| SREBF1 | DNM1, SNAP91, STXBP1 | Cluster 1 |
| TFAP2A | MAPT, SNAP91, STXBP1 & SLC17A7, SNAP25, SYT1 | Cluster 1 & Cluster 2 |
| TFAP2C | DNAJC6, SNAP25, SLC17A7 | Cluster 2 |
| TFAP4 | DNAJC6, SH3GL2, SNCA | Cluster 2 |
| YY1 | SLC17A7, SNAP25, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| ZBTB7A | DNM1, MAPT, STXBP1 | Cluster 1 |
| ZEB1 | SLC17A7, SNAP25, TUBB2A | Cluster 2 |
| ZFP2 | COL1A1, FBN2, FN1 | Cluster 3 |
| ZNF501 | SLC17A7, SNCA, STMN2 | Cluster 2 |
| ZNF71 | DNM3, DYNC1I1, SLC17A7, TUBB4A | Cluster 2 |
| miRNAs | Gene targets | Cluster |
|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-137 | GABRA1, SNAP91 ,SLC12A5 | Cluster 1 |
| hsa-miR-16 | DYNC1I1, KIF5C, SH3GL2, SNAP25, SNCA | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-181a | GABRA1, GRIA2, SLC12A5 | Cluster 1 |
| hsa-miR-181b | GABRA1, GRIA2, SLC12A5 | Cluster 1 |
| hsa-miR-181c | GABRA1, GRIA2, SLC12A5 | Cluster 1 |
| hsa-miR-181d | GABRA1, GRIA2, SLC12A5 | Cluster 1 |
| hsa-miR-195 | DYNC1I1, KIF5C, SH3GL2, SNAP25, SNCA | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-let-7a-5p | DNAJC6, SYT1, TUBB2A, TUBB4A | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-let-7b-5p | DNM3, SYT1, TUBB2A, TUBB4A | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-let-7c-5p | DNAJC6, SYT1, TUBB2A, TUBB4A | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-let-7d-5p | SYT1, TUBB2A, TUBB4A | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-let-7e-5p | SYT1, TUBB2A, TUBB4A | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-let-7f-5p | SYT1, TUBB2A, TUBB4A | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-let-7g-5p | SYT1, TUBB2A, TUBB4A | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-let-7i-5p | SYT1, TUBB2A, TUBB4A | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-1 | DNM3, SNAP25, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-103 | DYNC1I1, KIF5C, SH3GL2 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-106a | DNM3, KIF5C, SLC17A7 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-107 | DYNC1I1, KIF5C, SH3GL2 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-mir-124-3p | DNM3, KIF5C, TUBB4A & COL1A1, COL6A2 | Cluster 2 & Cluster 3 |
| hsa-miR-130a | DNM3, KIF5C, SNAP25, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-130b | DNM3, KIF5C, SNAP25, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-135b | DNM3, MOBP, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-138 | DNM3, SLC17A7, SNAP25 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-148b | DNM3, MOBP, SYTI | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-153 | DNM3, SNAP25, SNCA, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-15a | DYNC1I1, NEFH, SH3GL2, SNCA | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-206 | DNM3, SNAP25, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-221 | DNM3, MOBP, NEFH | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-222 | DNM3, MOBP, NEFH | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-23a | DNAJC6, DNM3, NEFH, SNAP25 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-23b | DNAJC6, DNM3, NEFH, SNAP25 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-27a | DNM3, SNAP25, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-27b | DNM3, SNAP25, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-301 | DNM3, KIF5C, SNAP25 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-301b | DNM3, KIF5C, SNAP25 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-mir-335-5p | DYNC1I1, NEFH, SLC17A7, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-429 | SNAP25, SYT1, TUBB2A | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-mir-4458 | TUBB2A, TUBB4A, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-mir-4500 | TUBB2A, TUBB4A, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-497 | DYNC1I1, KIF5C, SH3GL2 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-519b-3p | NEFH, SLC17A7, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-519c-3p | KIF5C, NEFH, SLC17A7, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-miR-519d | NEFH, KIF5C, SLC17A7 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-mir-8485 | MOBP, KIF5C, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| hsa-mir-98-5p | TUBB2A, TUBB4A, SYT1 | Cluster 2 |
| Drug | Degree | Target HDEGs |
|---|---|---|
| Curcumin | 3 | MAPT, TUBB2A, TUBB4A |
| Ocriplasmin | 3 | COL1A1, COL6A2, FN1 |
| Drug | Degree | Target TFs | Target HDEGs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cisplatin | 5 | GABPA, MYC, SMARCA4, STAT1, TP53 | MAPT |
| Daunorubicin | 5 | CBFB, GATA1, IKZF1, THRB, WT1 | MAPT |
| Cytarabine | 4 | GATA1, IKZF1, TP53, WT1 | - |
| Palbociclib | 4 | CDK5, DYRK1A, SMARCA4, TP53 | - |
| Resveratrol | 4 | NFKB1, PRKCA, RELA, TP53 | MAPT |
| Doxorubicin hydrochloride | 3 | THRB, TP53, ZEB1 | MAPT, SNCA |
| Doxorubicin | 3 | EZH2, SP3, ZEB1 | - |
| Gemcitabine | 3 | CDC5L, POLR2A, TP53 | - |
| Indoprofen | 3 | NFKB1, RELA, TP53 | - |
| Levothyroxine | 3 | AHR, PPARG, THRB | - |
| Methotrexate | 3 | IKZF1, PPARG, TP53 | - |
| Niclosamide | 3 | AHR, STAT3, TP53 | MAPT |
| Quercetin | 3 | NFKB1, PRKCA, RELA | MAPT |
| Vorinostat | 3 | EZH2, MYC, TP53 | TUBB2A, TUBB4A |
| Drug | Degree | TFs | HDEGs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paclitaxel | 4 | FOS, TP53 | TUBB2A, TUBB4A |
| Colchicine | 3 | JUN | TUBB2A, TUBB4A |
| Daunorubicin hydrochloride | 3 | THRB, TP53 | MAPT |
| Docetaxel anhydrous | 3 | TP53 | TUBB2A, TUBB4A |
| Epigallocatechin gallate | 3 | DYRK1A, NFKB1 | MAPT |
| Fenretinide | 3 | NFKB1, TP53 | MAPT |
| Hexachlorophene | 3 | THRB, TP53 | MAPT |
| Masoprocol | 3 | NFKB1, TP53 | MAPT |
| Nifedipine | 3 | NFKB1 | CAMK2B, MAPT |
| Nitazoxanide | 3 | AHR, TP53 | MAPT |
| Phenobarbital | 3 | FOS | GABRA1, GRIA2 |
| Raloxifene hydrochloride | 3 | PPARG, TP53 | MAPT |
| Trifluoperazine | 3 | TP53 | CAMK2B, SNAP91 |
| Vinblastine sulfate | 3 | JUN | TUBB2A, TUBB4A |
| Vinorelbine | 3 | SMARCA4 | TUBB2A, TUBB4A |
| Vinorelbine tartrate | 3 | JUN | TUBB2A, TUBB4A |
| miRNA Family | miRNAs |
|---|---|
| let-7 family | hsa-let-7a-1, hsa-let-7a-2, hsa-let-7a-3, hsa-let-7b, hsa-let-7c, hsa-let-7d, hsa-let-7e, hsa-let-7f-1, hsa-let-7f-2, hsa-let-7g, hsa-let-7i, hsa-mir-98 |
| mir-124 family | hsa-mir-124-1, hsa-mir-124-2, hsa-mir-124-3 |
| mir-1 family | hsa-mir-1-1, hsa-mir-1-2, hsa-mir-206 |
| mir-103 family | hsa-mir-130a, hsa-mir-130b, hsa-mir-301b |
| mir-27 family | hsa-mir-27a, hsa-mir-27b |
| Drugs | Upregulated gene | Downregulated gene |
|---|---|---|
| Colchicine | - | DNM3, SLC12A5, TUBB2A |
| Doxorubicin | COL1A1, FN1, SNCA | - |
| Indoprofen | COL1A1 | - |
| Levothyroxine | COL1A1, SLC17A7 | - |
| Methotrexate | CAMK2B, KIF5C, SNCA | SLC12A5, STXBP1 |
| Nifedipine | COL1A1, DYNC1I1, FN1, KIF5C | DYNC1I1, STXBP1 |
| Paclitaxel | CAMK2B, DNAJC6, SLC12A5, SLC17A7 | DNM1 |
| Quercetin | SNCA | - |
| Raloxifene | SLC12A5 | DNM1, DNM3 |
| Resveratrol | COL1A1, MAPT, SNCA | - |
| Trifluoperazine | CAMK2B, COL1A1, FN1, TUBB2A | DNM3 |
| Vinblastine | COL1A1, KIF5C | TUBB2A |
| Vorinostat | DNAJC6, DNM3, KIF5C, SLC17A7, STXBP1, SYT1, TUBBA2A | - |
| Regulation | ATRT | EPN | PA | MED | PNET | MEN | ACM | ODG | GBM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upregulated | TOP2A | FAM81B | POSTN | SOX11 | MEST | YWHAE | SOX4 | SOX4 | LTF |
| TMSB15B | CFAP126 | CFI | OTX2 | VIM | TNNC1 | TOP2A | TOP2A | TOP2A | |
| MFAP2 | CAPSL | COL20A1 | DACH1 | COL3A1 | EIF5A | NKAIN4 | HES6 | ASPM | |
| MELK | ARMC3 | TRPM8 | SOX4 | MGP | COL9A3 | HES6 | NDC80 | IGFBP2 | |
| HMGA2 | SPAG6 | PLA2G2A | COL1A1 | COL1A1 | CLIC3 | LCAT | TIMP4 | NDC80 | |
| Downregulated | VSNL1 | RAB3C | SLC12A5 | MBP | SNAP25 | MBP | MFSD4A | MFSD4A | MFSD4A |
| GABRG2 | SLC12A5 | GJB6 | CRTAM | DIRAS2 | CXCL2 | RGS4 | GJB6 | GABRA1 | |
| GJB6 | MYT1L | PPP2R2C | VSNL1 | STMN2 | MAFF | CACNG3 | RGS4 | GJB6 | |
| PACSIN1 | NEFL | SYNPR | GABRB2 | ANK3 | SNAP25 | GABRA1 | GABRA1 | CACNG3 | |
| SV2B | SV2B | PACSIN1 | PVALB | MBP | MYH11 | DDN | VSNL1 | SLITRK4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





