Submitted:
21 August 2023
Posted:
22 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
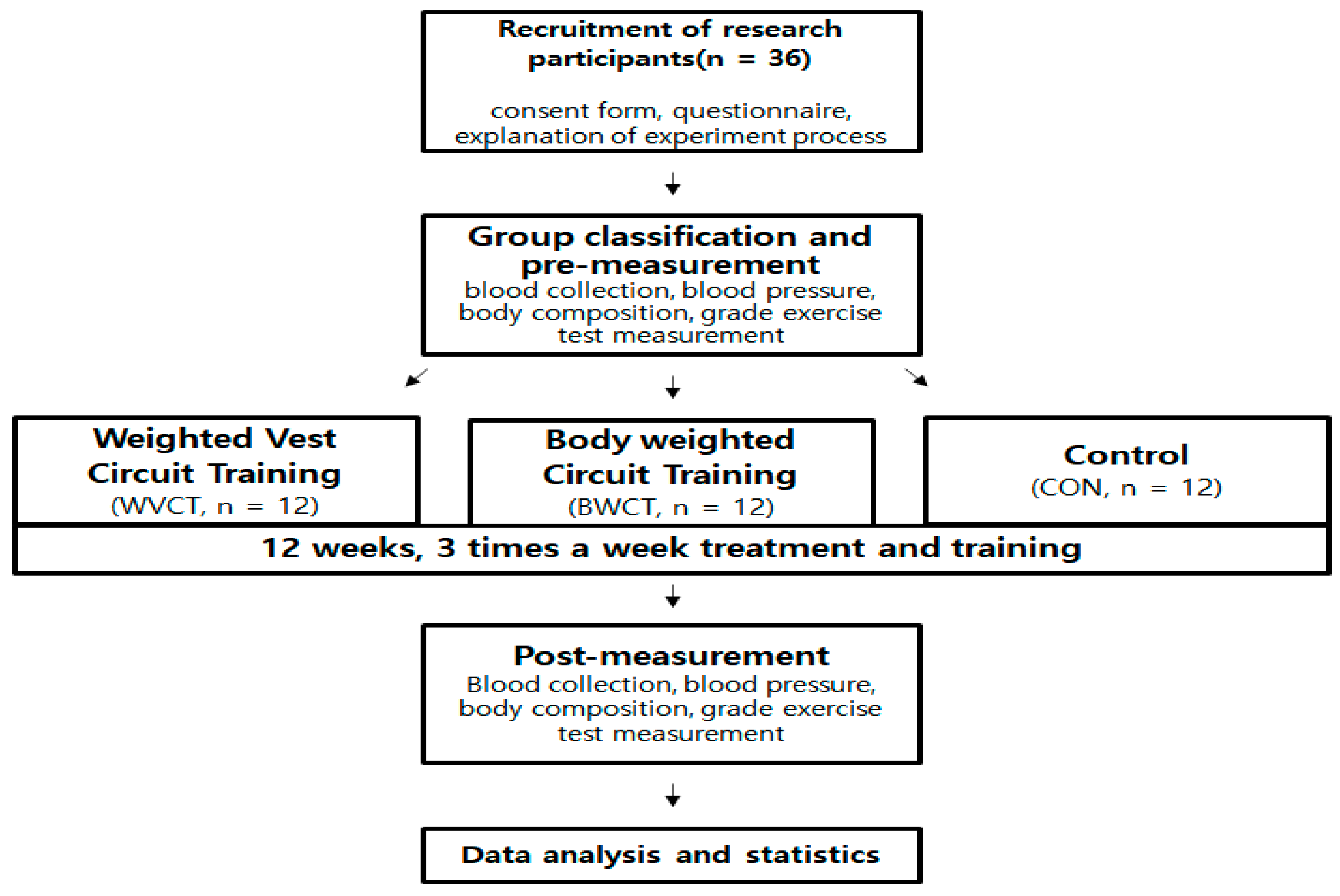
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement
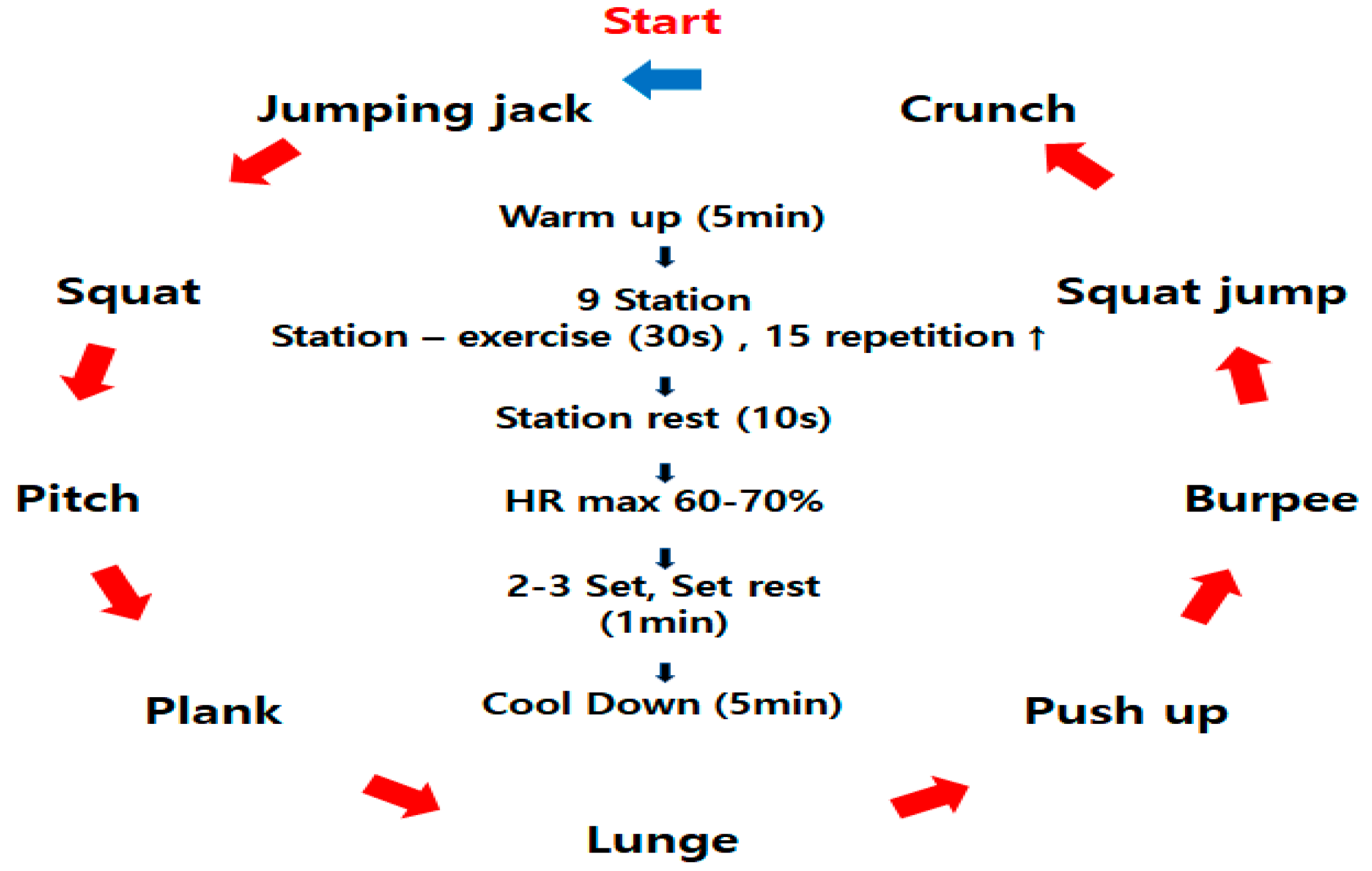
2.4. Training Protocol
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Body Composition
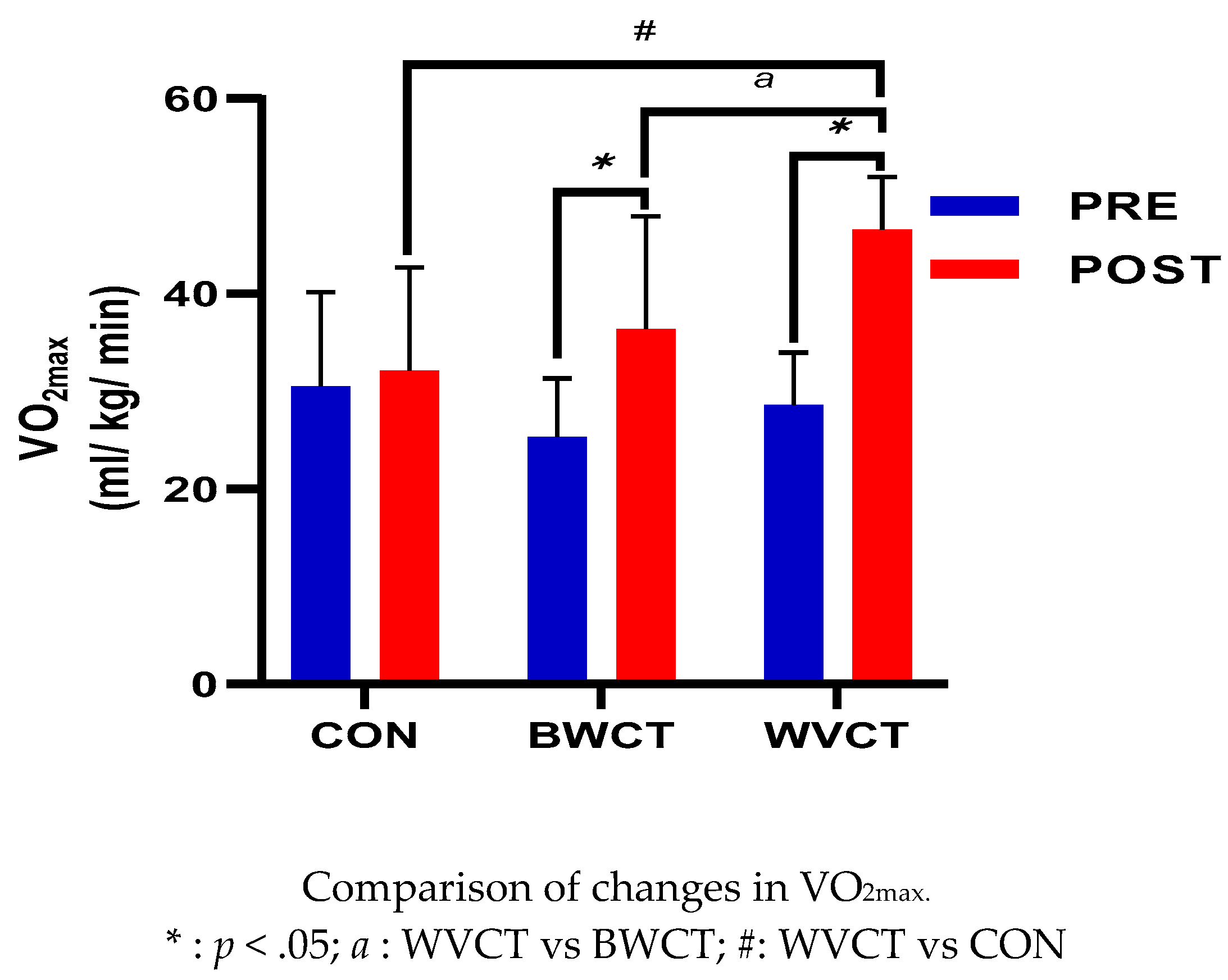
3.2. Changes in Cardiorespiratory Fitness
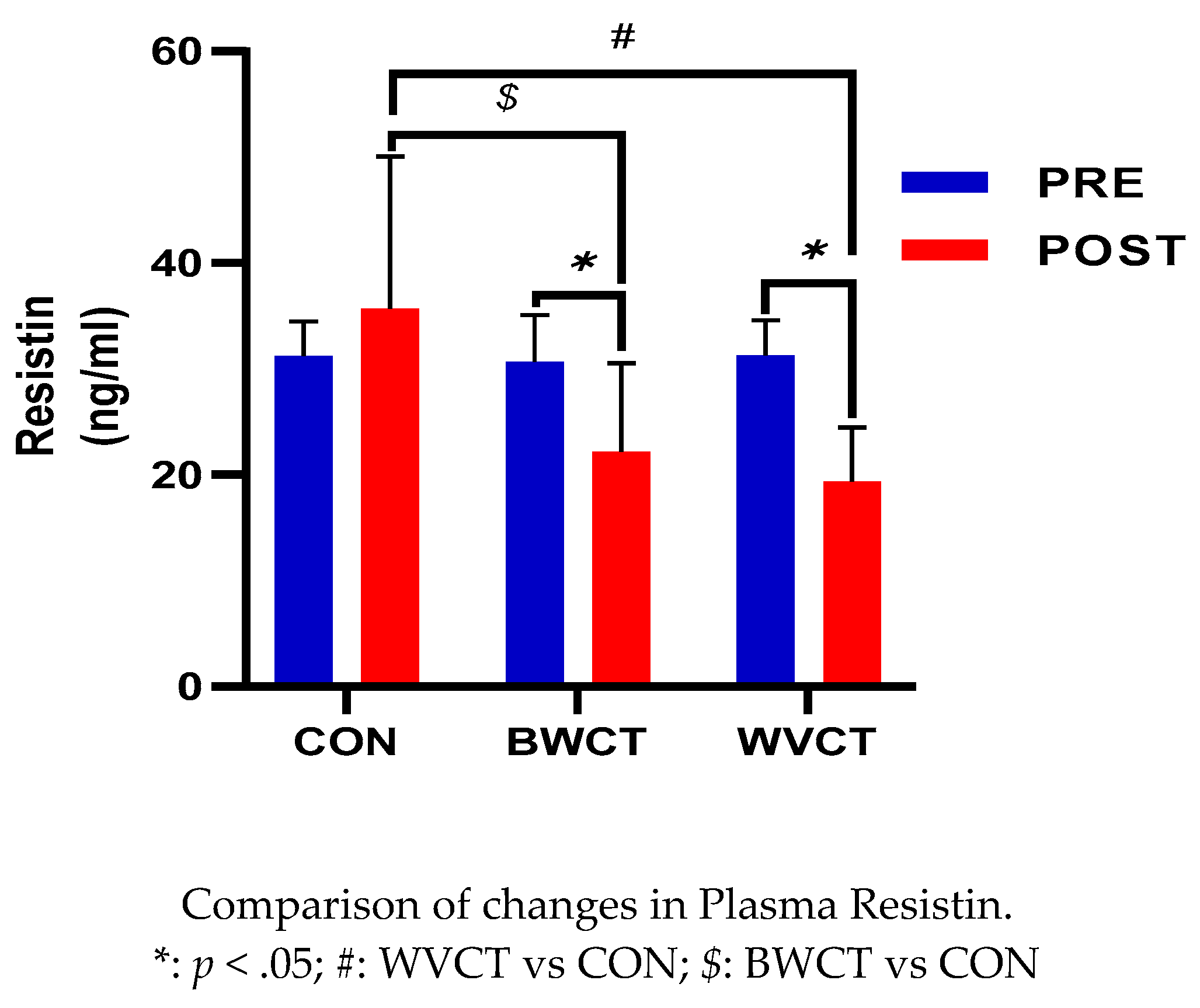
3.3. Changes in Plasma Resistin.
3.4. Changes in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
3.5. Changes in Rate of Improvement in Normal-Weight Obesity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Organization, W.H. Obesity and overweight. 2017.
- Oliveros, E.; Somers, V.K.; Sochor, O.; Goel, K.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. The concept of normal weight obesity. Progress in cardiovascular diseases 2014, 56, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.A.; Tao, C.; Gupta, R.K.; Scherer, P.E. Tracking adipogenesis during white adipose tissue development, expansion and regeneration. Nature medicine 2013, 19, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J. Risk stratification of metabolic syndrome according to obesity, abdominal obesity and gender in Korean adults [dissertation]. Seoul: Korea University. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Flegal, K.M.; Shepherd, J.A.; Looker, A.C.; Graubard, B.I.; Borrud, L.G.; Ogden, C.L.; Harris, T.B.; Everhart, J.E.; Schenker, N. Comparisons of percentage body fat, body mass index, waist circumference, and waist-stature ratio in adults. The American journal of clinical nutrition 2009, 89, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Corral, A.; Somers, V.K.; Sierra-Johnson, J.; Thomas, R.J.; Collazo-Clavell, M.; Korinek, J.; Allison, T.G.; Batsis, J.; Sert-Kuniyoshi, F.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Accuracy of body mass index in diagnosing obesity in the adult general population. International journal of obesity 2008, 32, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lorenzo, A.; Martinoli, R.; Vaia, F.; Di Renzo, L. Normal weight obese (NWO) women: an evaluation of a candidate new syndrome. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases 2006, 16, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lorenzo, A.; Del Gobbo, V.; Premrov, M.G.; Bigioni, M.; Galvano, F.; Di Renzo, L. Normal-weight obese syndrome: early inflammation? The American journal of clinical nutrition 2007, 85, 40–45. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, K.; Yang, S.; Kim, T.; Yoo, H.; Kang, H.; Song, W.; Baik, S.-H.; Choi, D.; Choi, K.M. The association between the ratio of visceral fat to thigh muscle area and metabolic syndrome: the Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study (KSOS). Clinical endocrinology 2010, 73, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, T.; Ryan, A.S.; Nicklas, B.J. The metabolic syndrome in obese postmenopausal women: relationship to body composition, visceral fat, and inflammation. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2004, 89, 5517–5522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez, R.; Seidell, J.; Ahn, Y.I.; Weiss, K.M. A new index of abdominal adiposity as an indicator of risk for cardiovascular disease. A cross-population study. International journal of obesity and related metabolic disorders: journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity 1993, 17, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Corral, A.; Somers, V.K.; Sierra-Johnson, J.; Korenfeld, Y.; Boarin, S.; Korinek, J.; Jensen, M.D.; Parati, G.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Normal weight obesity: a risk factor for cardiometabolic dysregulation and cardiovascular mortality. European heart journal 2010, 31, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.R.; Rangwala, S.M.; Shapiro, J.S.; Rich, A.S.; Rhoades, B.; Qi, Y.; Wang, J.; Rajala, M.W.; Pocai, A.; Scherer, P.E. Regulation of fasted blood glucose by resistin. Science 2004, 303, 1195–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benomar, Y.; Gertler, A.; De Lacy, P.; Crépin, D.; Ould Hamouda, H.; Riffault, L.; Taouis, M. Central resistin overexposure induces insulin resistance through Toll-like receptor 4. Diabetes 2013, 62, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari, R.; Raghunath, V. Obesity and Type II diabetes mellitus: Is resistin the link? Journal of Diabetes and Endocrine Practice 2018, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; He, J.; Ding, H.; Yan, L.; Cheng, H. Resistin induces insulin resistance by both AMPK-dependent and AMPK-independent mechanisms in HepG2 cells. Endocrine 2009, 36, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, G.T.; Morgan, R. Circuit training. Journal of the Physical Education Association 1954, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haennel, R.; Teo, K.-K.; Quinney, A.; Kappagoda, T. Effects of hydraulic circuit training on cardiovascular function. Medicine and science in sports and exercise 1989, 21, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, R.; Bhise, A.; Shukla, Y.; Prabhakar, M. Effects of high intensity circuit training using body weight on aerobic fitness and muscular endurance in college students. Physiotherapy 2015, 101, e1418–e1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klika, B.; Jordan, C. High-intensity circuit training using body weight: Maximum results with minimal investment. ACSM’s Health & Fitness Journal 2013, 17, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bocalini, D.S.; Lima, L.S.; de Andrade, S.; Madureira, A.; Rica, R.L.; Dos Santos, R.N.; Serra, A.J.; Silva Jr, J.A.; Rodriguez, D.; Figueira Jr, A. Effects of circuit-based exercise programs on the body composition of elderly obese women. Clinical interventions in aging 2012, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potteiger, J.A.; Kirk, E.P.; Jacobsen, D.J.; Donnelly, J.E. Changes in resting metabolic rate and substrate oxidation after 16 months of exercise training in overweight adults. International journal of sport nutrition and exercise metabolism 2008, 18, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvao, D.A.; Taaffe, D.R. Resistance exercise dosage in older adults: single-versus multiset effects on physical performance and body composition. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 2005, 53, 2090–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macadam, P.; Cronin, J.B.; Feser, E.H. Acute and longitudinal effects of weighted vest training on sprint-running performance: A systematic review. Sports Biomechanics 2022, 21, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roghani, T.; Torkaman, G.; Movasseghe, S.; Hedayati, M.; Goosheh, B.; Bayat, N. Effects of short-term aerobic exercise with and without external loading on bone metabolism and balance in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. Rheumatology international 2013, 33, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnis, K.; Balady, G.J. Comparison of submaximal exercise responses using the Bruce vs modified Bruce protocols. Medicine and science in sports and exercise 1994, 26, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, E.; Schwarzkopf, R. Effects of Standard Set and Circuit Weight Training on Excess Post-exercise Oxygen. Journal of Applied Sport Science Research 1992, 6, 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Contrò, V.; Bianco, A.; Cooper, J.; Sacco, A.; Macchiarella, A.; Traina, M.; Proia, P. Effects of different circuit training protocols on body mass, fat mass and blood parameters in overweight adults. Journal of Biological Research-Bollettino della Società Italiana di Biologia Sperimentale 2017, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juffer, P.; Jaspers, R.T.; Lips, P.; Bakker, A.D.; Klein-Nulend, J. Expression of muscle anabolic and metabolic factors in mechanically loaded MLO-Y4 osteocytes. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism 2012, 302, E389–E395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juffer, P.; Bakker, A.D.; Klein-Nulend, J.; Jaspers, R.T. Mechanical loading by fluid shear stress of myotube glycocalyx stimulates growth factor expression and nitric oxide production. Cell biochemistry and biophysics 2014, 69, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanchi, N.E.; Lancha, A.H. Mechanical stimuli of skeletal muscle: implications on mTOR/p70s6k and protein synthesis. European journal of applied physiology 2008, 102, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyfe, J.J.; Bishop, D.J.; Stepto, N.K. Interference between concurrent resistance and endurance exercise: molecular bases and the role of individual training variables. Sports medicine 2014, 44, 743–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Close, G.L.; Ashton, T.; Cable, T.; Doran, D.; MacLaren, D.P. Eccentric exercise, isokinetic muscle torque and delayed onset muscle soreness: the role of reactive oxygen species. European journal of applied physiology 2004, 91, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, H.; Loenneke, J.P.; Buckner, S.L.; Abe, T. Muscle growth across a variety of exercise modalities and intensities: contributions of mechanical and metabolic stimuli. Medical hypotheses 2016, 88, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, I.N.; Kabakoff, R.C.; Chan, B.; Baker, T.W.; Gurney, A.; Henzel, W.; Nelson, C.; Lowman, H.B.; Wright, B.D.; Skelton, N.J. FIZZ1, a novel cysteine-rich secreted protein associated with pulmonary inflammation, defines a new gene family. The EMBO journal 2000, 19, 4046–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, K.; Katsukawa, F.; Oguchi, S.; Murata, M.; Yamazaki, H.; Shimada, A.; Saruta, T. Correlation between serum resistin level and adiposity in obese individuals. Obesity research 2003, 11, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, X.; Qiu, J.; Gong, L.; Mao, H.; Jia, W.; Guo, J. The relationship between human serum resistin level and body fat content, plasma glucose as well as blood pressure. Zhonghua yi xue za zhi 2002, 82, 1609–1612. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Afshounpour, M.T.; Habibi, A.; Ranjbar, R. Impact of combined exercise training on plasma concentration of Apelin, resistin and insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetics’ male. Hormozgan Medical Journal 2016, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Hejazi, K.; Hosseini, S.R.A.; Fathi, M.; Ziaaldini, M.M. Responses of Visfatin and Resistin Concentration to Different Aerobic Training Intensities Protocols. Annals of Military and Health Sciences Research 2020, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidlamir, A.; Gholamian, S.; Ebrahimi Atri, A.; Seyyedalhoseyni, M.; Hesar Kooshki, M. Effect of regular aerobic exercise on plasma levels of resistin and adiponectin in active young females. Journal of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences 2013, 23, 67–76. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, T.E.; Basilio, J.; Brophy, P.; McCammon, M.; Hickner, R. Long-term exercise training in overweight adolescents improves plasma peptide YY and resistin. Obesity 2009, 17, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Mehta, N.; Reilly, M.P. Adipose inflammation, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular disease. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition 2008, 32, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, C.G.; Seo, T.B.; Kim, H.G.; Yoon, S.J. Effects of 8-week combined training on body composition, isokinetic strength, and cardiovascular disease risk factors in older women. Aging clinical and experimental research 2015, 27, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M.; Rifai, N.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Sacks, F.; Braunwald, E. Long-term effects of pravastatin on plasma concentration of C-reactive protein. Circulation 1999, 100, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, J.; Murano, S.; Kawamura, I.; Nakamura, F.; Murase, Y.; Kawashiri, M.-a.; Nohara, A.; Asano, A.; Inazu, A.; Mabuchi, H. The relationship of percent body fat by bioelectrical impedance analysis with blood pressure, and glucose and lipid parameters. Journal of atherosclerosis and thrombosis 2006, 13, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, E. LDL cholesterol was more strongly associated with percent body fat than body mass index and waist circumference in a health screening population. Obesity research & clinical practice 2018, 12, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.S.; Dhaliwal, S.S.; Hills, A.P.; Pal, S. The effect of 12 weeks of aerobic, resistance or combination exercise training on cardiovascular risk factors in the overweight and obese in a randomized trial. BMC public health 2012, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-W.; Ko, Y.-C.; Seo, T.-B.; Kim, Y.-P. Effect of circuit training on body composition, physical fitness, and metabolic syndrome risk factors in obese female college students. Journal of exercise rehabilitation 2018, 14, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, V.L.; Cutler, J.A.; Higgins, M.; Horan, M.J.; Labarthe, D.; Whelton, P.; Brown, C.; Roccella, E.J. Trends in the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in the adult US population: data from the health examination surveys, 1960 to 1991. Hypertension 1995, 26, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbert, J.A.; Silagy, C.A.; Finucane, P.; Withers, R.; Hamdorf, P.; Andrews, G. The effectiveness of exercise training in lowering blood pressure: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials of 4 weeks or longer. Journal of human hypertension 1997, 11, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group | CON (n = 12) | BWCT (n = 12) | WVCT (n = 12) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (yrs) |
27.00 ± 5.38 | 23.00 ± 2.26 | 24.25 ± 4.27 | ns |
| Height (cm) |
161.10 ± 3.56 | 162.3 ± 6.19 | 162.50 ± 5.85 | ns |
| Body Weight (kg) |
55.18 ± 5.93 | 57.56 ± 6.94 | 57.54 ± 8.41 | ns |
| BMI (kg/m2) |
21.20 ± 1.64 | 21.81 ± 1.76 | 21.73 ± 2.10 | ns |
| Skeletal Muscle Mass (kg) |
20.58 ± 2.07 | 21.15 ± 3.04 | 20.99 ± 2.98 | ns |
| Percent Body Fat (%) |
32.19 ± 1.93 | 32.82 ± 2.25 | 32.53 ± 2.40 | ns |
| Variable | CON (n = 12) |
BWCT (n = 12) |
WVCT (n = 12) |
F | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRE | POST | PRE | POST | PRE | POST | ||||
| Body Weight (kg) |
56.76 ± 5.93 | 54.55 ± 3.80 | 57.56 ± 6.94 | 56.50 ± 6.26 | 57.54 ± 8.41 | 55.00 ± 7.19 | Time | 9.567 | .028* |
| Group | .361 | .700 | |||||||
| Time × Group | .892 | .419 | |||||||
| BMI (kg/m2) |
21.58 ± 1.64 | 21.02 ± 1.17 | 21.80 ± 1.76 | 21.42 ± 1.58 | 21.73 ± 2.10 | 21.66 ± 2.59 | Time | 1.192 | .283 |
| Group | .379 | .687 | |||||||
| Time × Group | .238 | .789 | |||||||
| Skeletal Muscle Mass(kg) |
20.58 ± 2.07 | 20.25 ± 1.30 | 21.15 ± 3.04 | 21.52 ± 2.42 | 20.99 ± 2.98 | 22.13 ± 2.99 | Time | 3.012 | .092 |
| Group | .733 | 488 | |||||||
| Time × Group | 3.483 | .042* | |||||||
| Percent Body Fat(%) | 32.19 ± 1.93 | 32.29 ± 1.98 | 32.82 ± 2.25 | 30.21 ± 2.08 | 32.53 ± 2.40 | 29.63 ± 2.11 | Time | 38.194 | .000** |
| Group | .377 | .689 | |||||||
| Time × Group | 10.721 | .000** | |||||||
| Variable | CON (n=12) |
BWCT (n=12) |
WVCT (n=12) |
F | p | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRE | POST | PRE | POST | PRE | POST | ||||
| IL-6 (pg/ml) |
21.20 ± 3.36 | 19.84 ± 5.95 | 20.03 ± 4.04 | 15.14 ± 4.70 | 19.95 ± 3.98 | 13.30 ± 3.72 | Time | 20.649 | .000** |
| Group | 4.458 | .019* | |||||||
| Time × Group | 2.698 | .082 | |||||||
| TC (mg/dL) |
170.75 ± 31.10 | 172.08 ± 28.60 | 183.08 ± 28.05 | 179.42 ± 30.31 | 189.33 ± 32.96 | 169.75 ± 21.41 | Time | 4.433 | .043* |
| Group | .453 | .639 | |||||||
| Time × Group | 3.303 | .049* | |||||||
| LDL-C (mg/dL) |
99.92 ± 28.15 | 101.92 ± 27.93 | 111.33 ± 17.41 | 109.33 ± 13.12 | 109.67 ± 30.69 | 87.75 ± 22.66 | Time | 5.816 | .022* |
| Group | .913 | .411 | |||||||
| Time × Group | 5.962 | .006* | |||||||
| HDL-C (mg/dL) |
61.92 ± 5.92 | 57.33 ± 5.12 | 62.75 ± 16.81 | 59.50 ± 11.55 | 66.25 ± 10.23 | 68.25 ± 8.58 | Time | 1.807 | .188 |
| Group | 2.166 | .131 | |||||||
| Time × Group | 1.930 | .161 | |||||||
| SBP (mmHg) |
112.17 ± 9.73 | 111.33 ± 10.82 | 113.42 ± 9.69 | 111 ± 8.28 | 104.92 ± 11.97 | 101.42 ± 7.42 | Time | 1.577 | .218 |
| Group | 4.679 | .016* | |||||||
| Time × Group | .187 | .831 | |||||||
| DBP (mmHg) |
72.58 ± 3.68 | 76.14 ± 6.63 | 71.75 ± 6.87 | 73.50 ± 5.84 | 70.75 ± 6.40 | 72.58 ± 5.98 | Time | 2.393 | .131 |
| Group | 1.565 | .224 | |||||||
| Time × Group | .150 | .861 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




