Submitted:
16 August 2023
Posted:
16 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Copepods collection and identification
2.2. DNA Extraction and quality Control
2.3. Library Preparation for mitochondrial genome
2.4. Illumina sequencing and data analysis
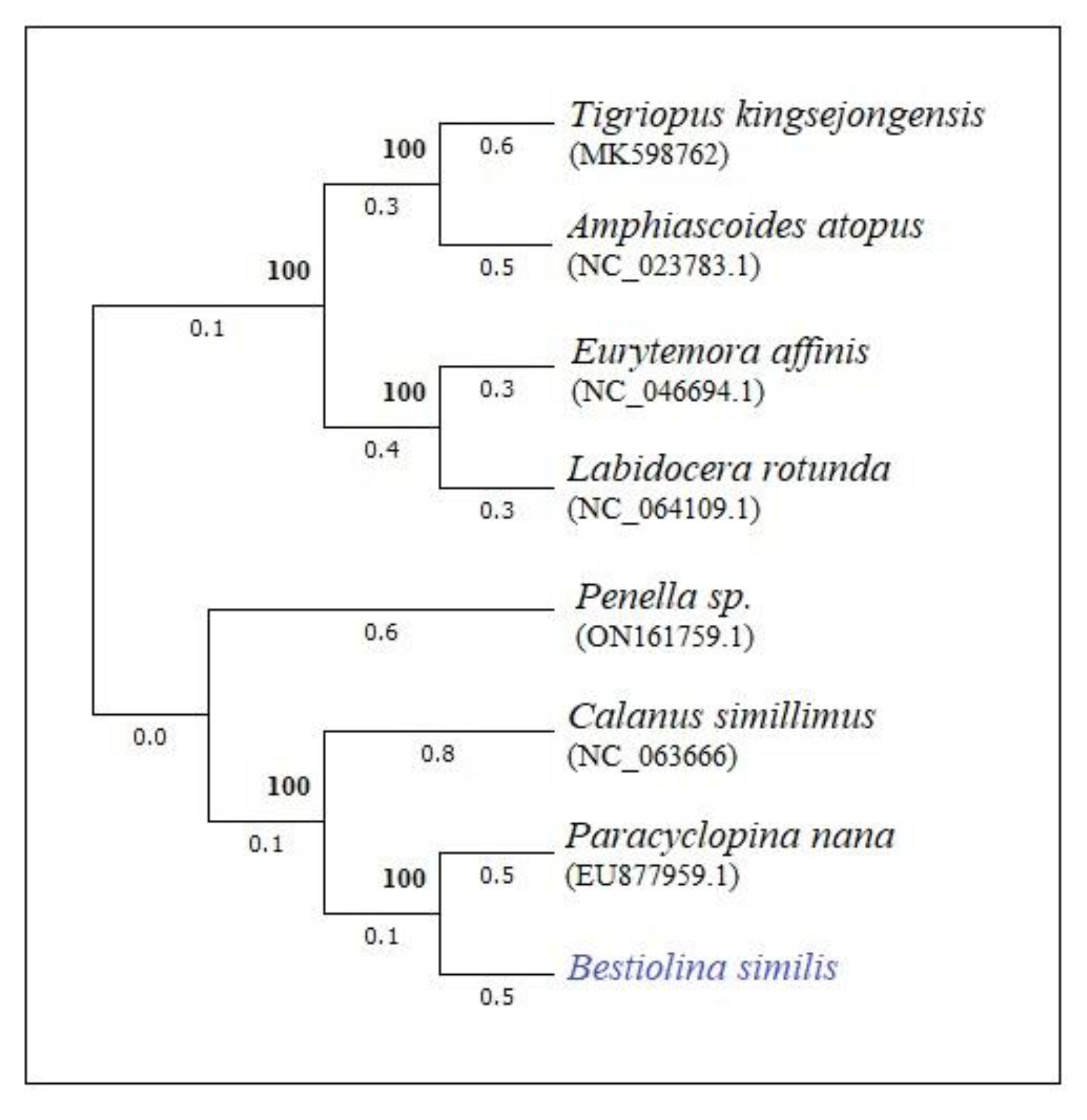
2.5. Phylogenetic tree construction
3. Results
3.1. Overview of the mitochondrial genome of B. similis
3.2. Protein coding regions of the genome
3.3. Regions of tRNA genes
3.4. Phylogenetic tree based on mitochondrial genome of B. similis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huys, R.; Boxshall, G.A. Copepod evolution. The Ray society, London, 2004.
- Boxshall, G.A.; Defaye, D. Global diversity of copepods (Crustacea: Copepoda) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 2008, 595, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, B.; Fleminger, A. A revision of the genus Clausocalanus (Copepoda:Calanoida) with remarks on distributional patterns in diagnostic characters. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1968; 1–235. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, M.A.; Sivakumar, K.; Baskar, G.; Vijayaraj, R. Diversity rhythm in pontellid copepods (Pontellidae: Copepoda) from the Covelong coast pre- and post-COVID-19 lockdown, Bay of Bengal. Turk. J. Zoo. 2023, 47, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Bercial, L.; Cornils, A.; Copley, N.; Bucklin, A. DNA barcoding of marine copepods: assessment of analytical approaches to species identification. PLoS Curr 2014, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucklin, A.; Frost, B.W.; Bradford-Grieve, J.; Allen, L.D.; Copley, N.J. Molecular systematic and phylogenetic assessment of 34 calanoid copepod species of the Calanidae and Clausocalanidae. Mar. Bio. 2003, 142, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elías-Gutiérrez, M.; Valdez-Moreno, M.; Topan, J.; Young, MR.; Cohuo-Colli, JA. Improved protocols to accelerate the assembly of DNA barcode reference libraries for freshwater zooplankton. Ecol Evol. 2018, 8, 3002–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefébure, T.; Douady, C.J.; Gouy, M.; Gibert, J. Relationship between morphological taxonomy and molecular divergence within Crustacea: Proposal of a molecular threshold to help species delimitation. Mol. Phylo. Evo. 2006, 40, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanin, A. Phylogeny of Arthropoda inferred from mitochondrial sequences: strategies for limiting the misleading effects of multiple changes in pattern and rates of substitution. Mol. Phylo. Evo. 2006, 38, 100–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.T.; Hwang, U.W. The complete mitochondrial genome of Pollicipes mitella (Crustacea, Maxillopoda, Cirripedia): non-monophylies of maxillopoda and crustacea. Mol.&cells 2006, 22, 314–322. [Google Scholar]
- Nawaz, M.A.; Sivakumar, K.; Baskar, G. Impact of variation in environmental parameters on the abundance of Paracalanidae (Calanoida: Copepoda) from the stressed tropical coast of India, Bay of Bengal. Russ. J. Mar. Bio, (Accepted for publication). 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hani, P.M.; Jayalakshmi, K.J. Temporal variation in diversity, abundance, and size class structure of planktonic copepods from a tropical estuary. Aquat. Ecol. 2023, 57, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Register of Marine Species. Available from https://www.marinespecies.org at VLIZ. Accessed 2023-07-24.
- Kasturirangan, L.R. A Key for identification of The most common planktonic copepod of Indian coastal water (N.K. Panikkar, Ed.). Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, New Delhi, 1963.
- Ali, M.; Al-Yamani, F.; Prusova, I. Bestiolina arabica sp. nov. (Copepoda, Calanoida, Paracalanidae), a new species from the Northwestern Arabian Gulf. Crustaceana 2007, 80, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.Y.; Lee, W.; Soh, H.Y. A new species of Bestiolina (Crustacea: Copepoda: Calanoida) from the Yellow Sea, with notes on the zoogeography of the genus. Proceed. of Bio. Soc. of Washington 2010, 123, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyadi, M. Calanoid Copepods in Indonesian Waters. Research Center for Biology, Indonesia Institute of Sciences, Bogor, 2004.
- Suárez-Morales, E.; Almeyda-Artigas, R.J. A new species of Bestiolina (Copepoda: Calanoida: Paracalanidae) from the Northwestern Atlantic with comments on the distribution of the genus. Revista Mexicana de Biodiversidad 2016, 87, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorado-Roncancio, J.; Gaviria, S.; Bernal-De La Torre, L.; Ahrens, M.J. A new species of Bestiolina (Crustacea, Copepoda, Calanoida, Paracalanidae) from coastal waters of the Colombian Pacific, including a worldwide key for the identification of the species. ZooKeys 2019, 2019 846, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razouls, C.; Desreumaux, N.; Kouwenberg, J.; Bovée, F. Biodiversity of Marine Planktonic Copepods (morphology, geographical distribution and biological data). Sorbonne University, CNRS, 2022. http://copepodes.obs-banyuls.fr/en.
- Boxshall, G.; Halsey, S. An introduction to copepod diversity. The Ray Society London, 2004.
- Kumar, S.; Tamura, K.; Nei, M. MEGA: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis. Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, 1993.
- Felsenstein, J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: An approach using the bootstrap. Evolution, 1985, 39, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grauer, D.; Li, W.H. Fundamentals of molecular evolution, 2nd Edn. Sinauer Associates, 2000.
- Pattengale, N.D.; Alipour, M.; Bininda-Emonds, O.; Moret, B.; Stamatakis, A. How many bootstrap replicates are necessary? J. Comp. Bio. 2010, 17, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andronov, V.N. Veslonogie rachki Bestiola gen. n. (Copepoda, Paracalanidae). Zoologicheskii Zhurnal 1972, 51, 290–292. [Google Scholar]
- Cornils, A.; Blanco-Bercial, L. Phylogeny of the Paracalanidae Giesbrecht, 1888 (Crustacea: Copepoda: Calanoida). Mol. Phylo. Evo. 2013, 69, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, K.; Nawaz, M.A.; Saboor, A. Population composition of calanoid copepods of the Chennai coast, Tamil Nadu. Ind. J.Geo-Mar. Sci. 2021, 50, 693–700. [Google Scholar]
- Umer, K.S.; Ebenezer, V.; Subramoniam, T. A short-term study on the effect of environmental factor variation on a zooplankton community. Ind. J.Geo-Mar. Sci 2020, 49, 1158–1164. [Google Scholar]
- Dilshad, B. I. Diversity and biology of calanoid copepods of Chennai coast India. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Madras, 2006.
- Santhi, M; Ramanibai, R. Studies on Copepods from Chennai Coast (Cooum and Adyar), Bay of Bengal-During the Cruise. Curr. Res. J. Bio. Sci. 2011, 3, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Rajthilak, C.; Perumal, P.; Santhanam, P.; Nandakumar, R.; Ananth, S. Spatial and temporal distributions of calanoid copepods (Crustacea; Arthropoda) along the Tamil Nadu coast (Southeast India). Ind. J.Geo-Mar. Sci. 2016, 45, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, B.D.; Bhattacharya, A.; Rakshit, D.; Sarkar, S. Impact of the tropical cyclonic storm 'Aila' on the water quality characteristics and mesozooplankton community structure of Sundarban mangrove wetland, India. Ind. J.Geo-Mar. Sci. 2014, 43, 216–223. [Google Scholar]
- Crease, T.J. The complete sequence of the mitochondrial genome of Daphnia pulex (Cladocera: Crustacea). Gene 1999, 233, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadel, G.S.; Clayton, D.A. Mitochondrial DNA maintenance in vertebrates. Annual Review of Biochemistry 1997, 66, 409–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Comparative analysis of the complete mitochondrial genomes of two species of Clupeiformes and the phylogenetic implications for Clupeiformes. J. Mar. Bio. Asso. of. Uni. King. 2022, 102, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S. , Lim, B. J., Min, G. S., & Choi, H. G. The complete mitochondrial genome of Arctic Calanus hyperboreus (Copepoda, Calanoida) reveals characteristic patterns in calanoid mitochondrial genome. Gene, 2013, 520, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, B. S.; Han, J.; Hwang, D. S.; Souissi, S.; Hagiwara, A.; Lee, J. S. Complete mitochondrial genome of the calanoid copepod Eurytemora affinis (Calanoida, Temoridae). Mito. DNA Part B 2019, 4, 2731–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Fu, Z.; Zhou, S.; Hu, J.; Yang, R.; Yu, G.; Ma, Z. The Complete Mitochondrial Genome of Pennella sp. Parasitizing Thunnus albacares. Front. Cell. and Infec. Microbio. 2022, 12, 945152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrov, D.V. Mitochondrial Genomes in Invertebrate Animals. In: Wells, R.D., Bond, J.S., Klinman, J., Masters, B.S.S. (eds) Molecular Life Sciences. Springer, New York, NY, 2018.
- Ki, J. S.; Park, H. G.; Lee, J. S. The complete mitochondrial genome of the cyclopoid copepod Paracyclopina nana: a highly divergent genome with novel gene order and atypical gene numbers. Gene 2009, 435, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
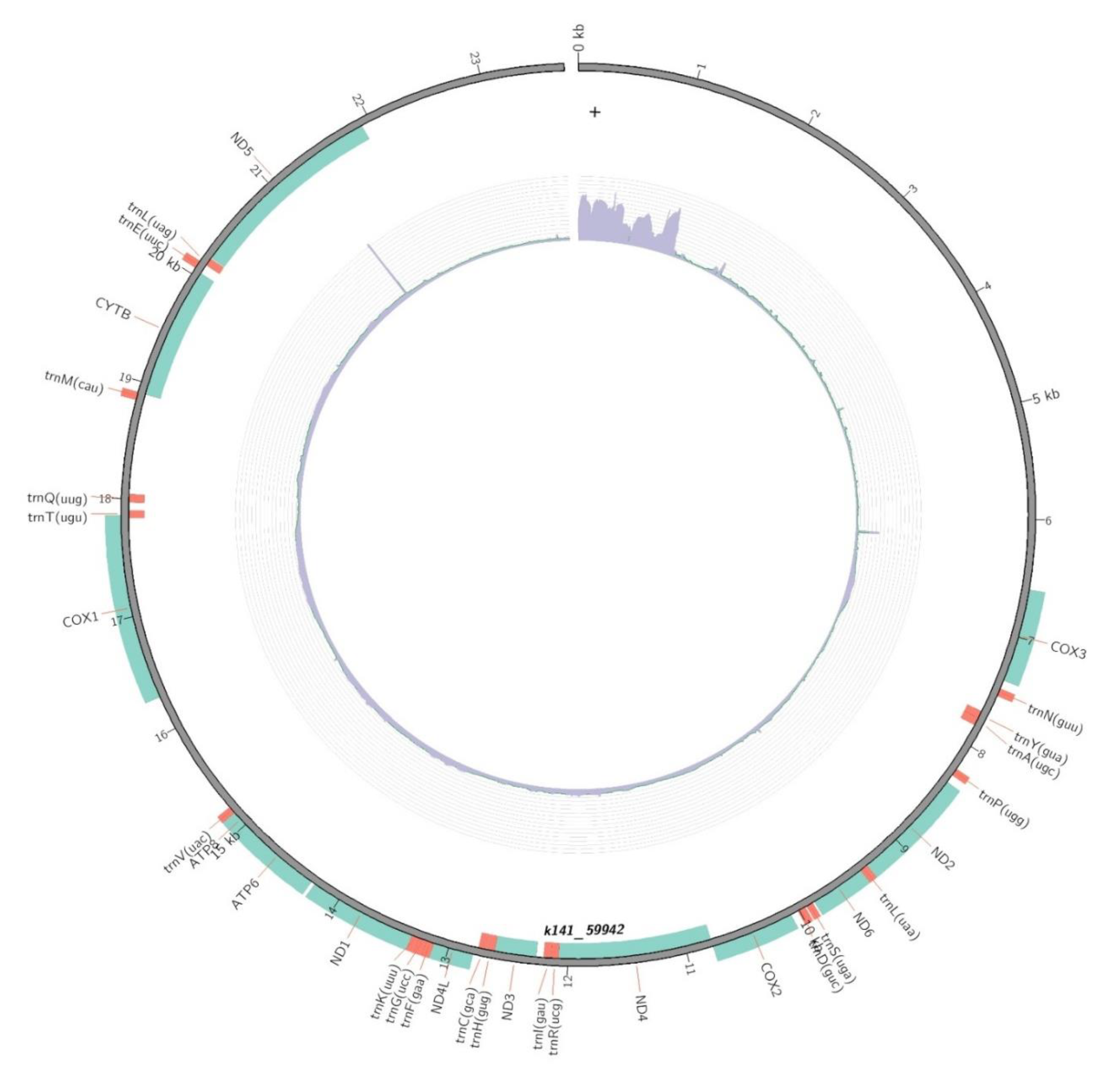
| Start | End | Length(bp) | Gene name | Gene product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6591 | 7382 | 792 | COX3 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit III |
| 8357 | 9325 | 969 | ND2 | NADH dehydrogenase subunit 2 |
| 9394 | 9855 | 462 | ND6 | NADH dehydrogenase subunit 6 |
| 10079 | 10777 | 699 | COX2 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit II |
| 10780 | 12078 | 1299 | ND4 | NADH dehydrogenase subunit 4 |
| 12267 | 12620 | 354 | ND3 | NADH dehydrogenase subunit 3 |
| 12794 | 13129 | 336 | ND4L | NADH dehydrogenase subunit 4L |
| 13327 | 14238 | 912 | ND1 | NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1 |
| 14271 | 14984 | 714 | ATP6 | ATP synthase F0 subunit 6 |
| 14981 | 15136 | 156 | ATP8 | ATP synthase F0 subunit 8 |
| 16292 | 17863 | 1572 | COX1 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit I |
| 18909 | 20045 | 1137 | CYTB | Cytochrome b |
| 20204 | 21916 | 1713 | ND5 | NADH dehydrogenase subunit 5 |
| Start | End | Length(bp) | Gene name | Gene prodcut |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7457 | 7520 | 64 | trnN(guu) | tRNA-Asn |
| 7697 | 7759 | 63 | trnY(gua) | tRNA-Tyr |
| 7761 | 7823 | 63 | trnA(ugc) | tRNA-Ala |
| 8222 | 8284 | 63 | trnP(ugg) | tRNA-Pro |
| 9326 | 9393 | 68 | trnL(uaa) | tRNA-Leu |
| 9874 | 9930 | 57 | trnS(uga) | tRNA-Ser |
| 9947 | 10011 | 65 | trnD(guc) | tRNA-Asp |
| 12078 | 12139 | 62 | trnR(ucg) | tRNA-Arg |
| 12140 | 12202 | 63 | trnI(gau) | tRNA-Ile |
| 12623 | 12689 | 67 | trnH(gug) | tRNA-His |
| 12695 | 12757 | 63 | trnC(gca) | tRNA-Cys |
| 13130 | 13192 | 63 | trnF(gaa) | tRNA-Phe |
| 13195 | 13260 | 66 | trnG(ucc) | tRNA-Gly |
| 13262 | 13324 | 63 | trnK(uuu) | tRNA-Lys |
| 15137 | 15198 | 62 | trnV(uac) | tRNA-Val |
| 17840 | 17901 | 62 | trnT(ugu) | tRNA-Thr |
| 17974 | 18041 | 68 | trnQ(uug) | tRNA-Gln |
| 18845 | 18908 | 64 | trnM(cau) | tRNA-Met |
| 20062 | 20127 | 66 | trnE(uuc) | tRNA-Glu |
| 20130 | 20196 | 67 | trnL(uag) | tRNA-Leu |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





