Submitted:
11 August 2023
Posted:
15 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Genesis of Diagnosis of Diabetes Through Microarray Gene Technology
1.2. Review of literature
2. Methodology
2.1. Role of Diabetic in Micro Array Gene:
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Data set
| Data Set | No of Genes | Class 1 Diabetes |
Class 2 Non-Diabetic |
Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pancreas | 28735 | 20 | 50 | 70 |
4. Need for Dimensionality Reduction Techniques
4.1. Dimensionality Reduction
- Bessel Function as Dimensionality Reduction
- 2.
- Discrete cosine Transform (DCT) as Dimensionality Reduction
- 3.
- Least Square Linear Regression (LSLR) as Dimensionality Reduction
- 4.
- Artificial Algae Algorithm (AAA) as Dimensionality Reduction
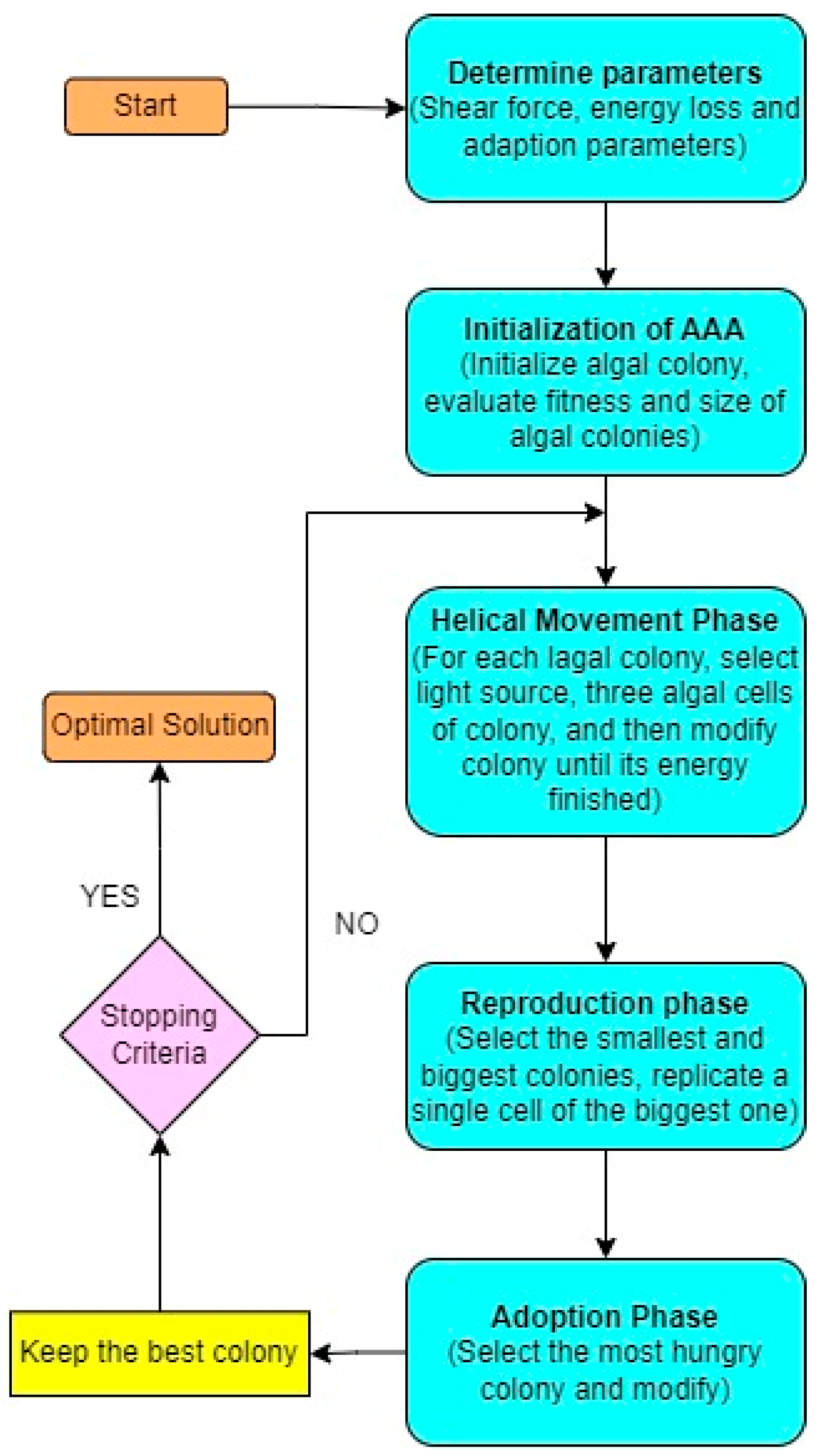
4.2. Statistical Analysis
5. Feature Selection Methods
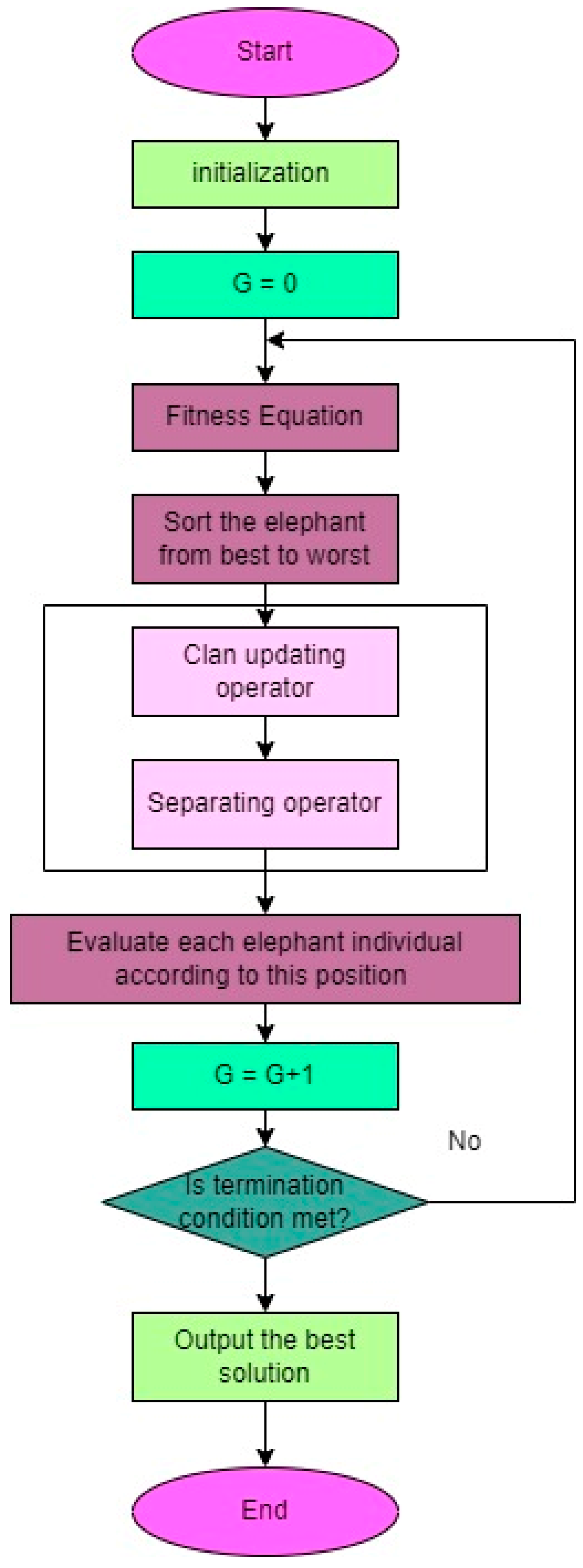
- Elephant Herding Optimization (EHO) algorithm
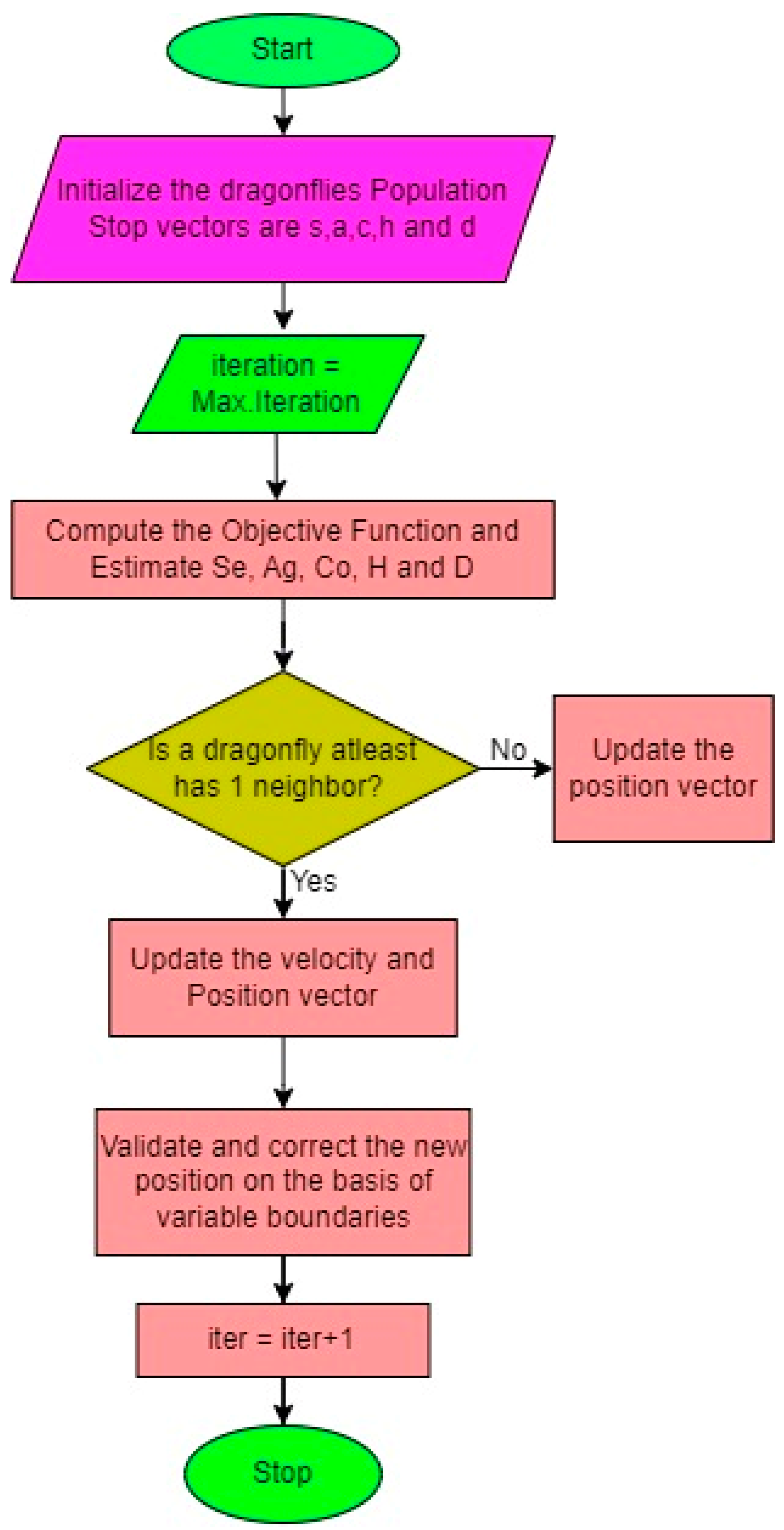
- Dragonfly Optimization Algorithm (DOA)
- Separation: This implies that the static phase of the algorithm focuses on preventing dragonflies from colliding with each other in their vicinity. This calculation aims to ensure the avoidance of collisions among flies.
- 2.
- Alignment: This denotes the synchronization of velocities among dragonflies belonging to the same group. It is represented as.
- 3.
- Cohesiveness: This represents the inclination of individual flies to converge towards the centre of swarms. The calculation for this is given by.
- 4.
- Attraction: The attraction towards the food source is quantified as
- 5.
- Diversion: The diversion from the enemy is determined by the outward distance, which is calculated as.
6. Classification Techniques
- Non-Linear Regression (NLR)
- 2.
- Linear Regression (LR)
- Feature selection parameters, obtained from algorithms such as Bessel Function, DCT, LSLR and AAA, are used as input for classifiers.
- A line represented by is fitted to the data in a linear manner.
- The cost function is defined to minimize the squared error between the observed data and the predictions.
- The solutions are found by equating the derivatives of to zero.
- Steps 2, 3, and 4 are repeated to obtain coefficients that yield the minimum squared error.
- 3.
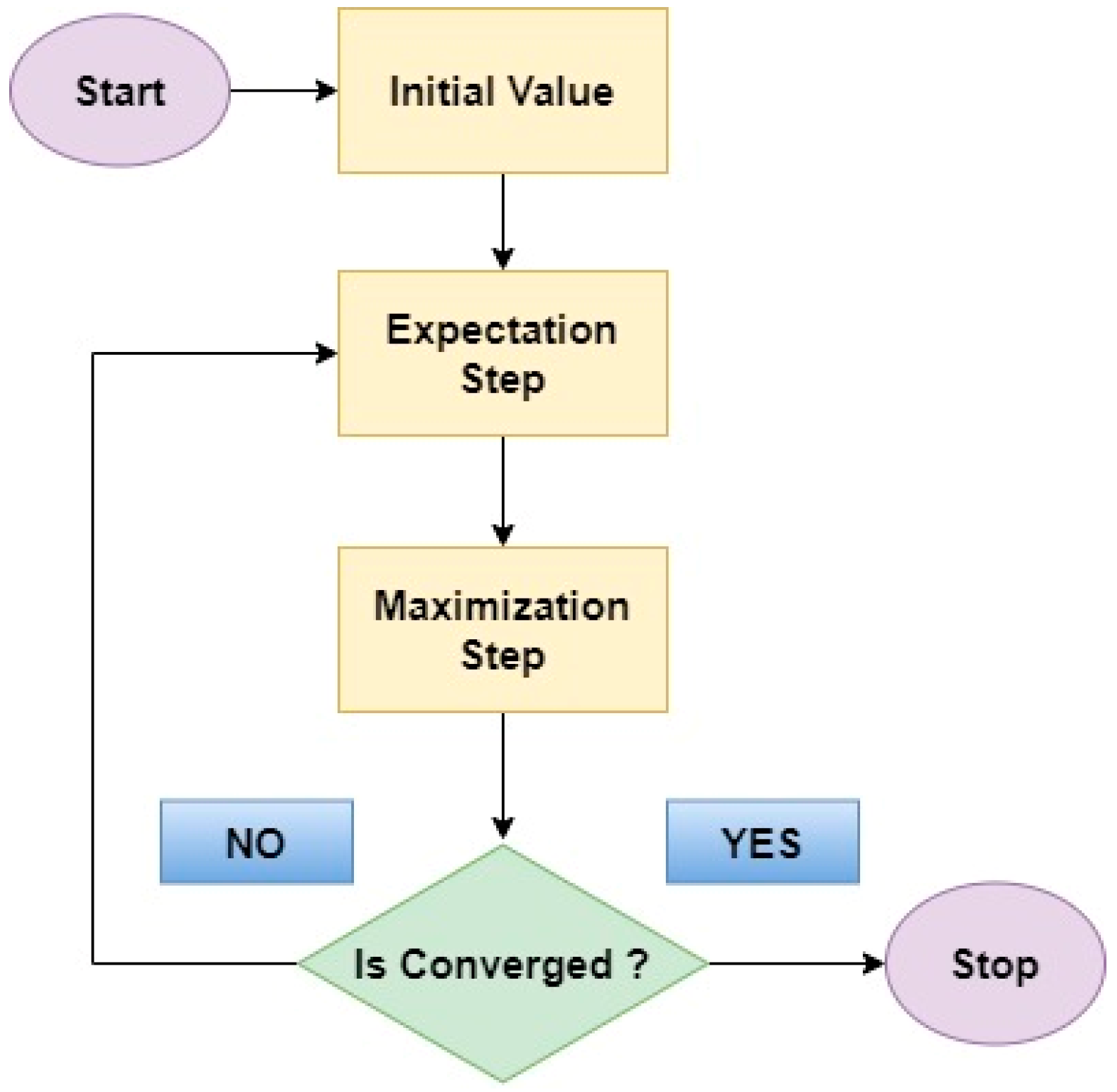
- Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM)
- 4.
- Expectation Maximum (EM)
- 5.
- Bayesian Linear Discriminant Classifier (BLDC)
- 6.
- Logistic Regression (LoR)
- 7.
- Softmax Discriminant Classifier (SDC)
- 8.
- SVM - Linear: This method utilizes a linear kernel to classify the data.
- 9.
- SVM - Polynomial: This approach involves the use of a polynomial kernel for data classification.
- 10.
- SVM - Radial Basis Function (RBF): The RBF kernel is employed in this method for classifying the data.
6.1. Training and Testing of Classifiers
| Truth of Clinical Situation | Predicted Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Diabetic | Normal | ||
| Actual Values | Diabetic | TP | FN |
| Normal | FP | TN | |
6.2. Selection of target
| Classifiers | Description |
|---|---|
| NLR | Uniform weight w=0.4, bias b=0.001, iteratively modified sum of Least square Error, Criterion: MSE |
| Linear Regression | Uniform weight w=0.451, bias b=0.003, Criterion: MSE |
| GMM | Mean, Covariance of the input samples and tuning parameter is EM steps. Criterion: MSE |
| EM | test point likelihood probability 0.13,cluster Probability of 0.45, with convergence rate of 0.631, Criterion: MSE |
| BDLC | P(y), Prior probability: 0.5, Class mean: 0.85,0.1; Criterion: MSE |
| Logistic regression | Threshold H𝞱(x) <0.48 with Criterion: MSE |
| SDC | γ=0.5 along with mean of each class target values as 0.1, and 0.85 |
| SVM (linear) | C (Regularization Parameter): 0.85, Class Weights: 0.4, Convergence Criteria: MSE |
| SVM(Polynomial) | C: 0.76, Coefficient of the kernel function (gamma): 10, Class weights: 0.5, Convergence Criteria: MSE |
| SVM(RBF) | C: 1, Coefficient of the kernel function (gamma): 100, Class weights: 0.86, Convergence Criteria: MSE |
- Results and Discussion
6.3. Computational Complexity
6.4. Limitation and Major Outcomes
6.5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- "Facts & Figures," International Diabetes Federation. [Online]. Available: https://idf.org/about-diabetes/facts-figures/.
- Pradeepa R, Mohan V. Epidemiology of type 2 diabetes in India. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021 Nov;69(11):2932-2938. [CrossRef]
- Chockalingam, Sriram, Maneesha Aluru, and Srinivas Aluru. "Microarray data processing techniques for genome-scale network inference from large public repositories." Microarrays 5.3 (2016): 23. [CrossRef]
- Herman, W. H., Ye, W., Griffin, S. J., Simmons, R. K., Davies, M. J., Khunti, K., & Wareham, N. J. (2015). Early detection and treatment of type 2 diabetes reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality: a simulation of the results of the Anglo-Danish-Dutch study of intensive treatment in people with screen-detected diabetes in primary care (ADDITION-Europe). Diabetes care, 38(8), 1449-1455. [CrossRef]
- Strianese, O., Rizzo, F., Ciccarelli, M., Galasso, G., D’Agostino, Y., Salvati, A., &Rusciano, M. R. (2020). Precision and personalized medicine: how genomic approach improves the management of cardiovascular and neurodegenerative disease. Genes, 11(7), 747. [CrossRef]
- Abul-Husn, N. S., & Kenny, E. E. (2019). Personalized medicine and the power of electronic health records. Cell, 177(1), 58-69. [CrossRef]
- Schnell, O., Crocker, J. B., & Weng, J. (2017). Impact of HbA1c testing at point of care on diabetes management. Journal of diabetes science and technology, 11(3), 611-617. [CrossRef]
- Lu, H., Chen, J., Yan, K., Jin, Q., Xue, Y., & Gao, Z. (2017). A hybrid feature selection algorithm for gene expression data classification. Neurocomputing, 256, 56-62. [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2022. Diabetes Care 1 January 2022; 45 (Supplement_1): S17–S38. [CrossRef]
- Jakka A, Jakka VR. Performance evaluation of machine learning models for diabetes prediction. International Journal Innovation Technology Explore Eng Regular Issue. 2019; 8 (11):1976–80. [CrossRef]
- Radja M, Emanuel AWR. Performance evaluation of supervised machine learning algorithms using different data set sizes for diabetes prediction. In: 2019 5th international conference on science in information technology (ICSITech). 2019. [CrossRef]
- Dinh A, Miertschin S, Young A, Mohanty SD. A data-driven approach to predicting diabetes and cardiovascular disease with machine learning BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019;19(1):1–15. [CrossRef]
- Yang T, Zhang L, Yi L, Feng H, Li S, Chen H, Zhu J, Zhao J, Zeng Y, Liu H, et al. Ensemble learning models based on noninvasive features for type 2 diabetes screening: model development and validation. JMIR Med Inform. 2020;8(6):e15431. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad LJ, Algehyne EA, Usman SS. Predictive supervised machine learning models for diabetes mellitus. SN Comput Sci. 2020;1(5):1–10. [CrossRef]
- Kim H, Lim DH, Kim Y. Classification and prediction on the effects of nutritional intake on overweight/obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus using deep learning model: 4–7th Korea national health and nutrition examination survey. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(11):5597. [CrossRef]
- Lawi, A., & Syarif, S. (2019, October). Performance evaluation of naive Bayes and support vector machine in type 2 diabetes Mellitus gene expression microarray data. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1341, No. 4, p. 042018). IOP Publishing.
- Ciaramella, A., &Staiano, A. (2019). On the role of clustering and visualization techniques in gene microarray data. Algorithms, 12(6), 123. [CrossRef]
- Velliangiri, S., &Alagumuthukrishnan, S. J. P. C. S. (2019). A review of dimensionality reduction techniques for efficient computation. Procedia Computer Science, 165, 104-111. [CrossRef]
- Parand, K., &Nikarya, M. (2019). New numerical method based on generalized Bessel function to solve nonlinear Abel fractional differential equation of the first kind. Nonlinear Engineering, 8(1), 438-448. [CrossRef]
- Bell, W. W. (1967). Special Functions For Scientists And Engineers, Published simultaneously in Canada by D.
- Kalaiyarasi, M., &Rajaguru, H. (2022). Performance Analysis of Ovarian Cancer Detection and Classification for Microarray Gene Data. BioMed Research International, 2022. [CrossRef]
- N. Ahmed, T. Natarajan, and K. R. Rao,“Discrete cosine transform,” IEEE Transactions on Computers, vol. C-23, no. 1, pp. 90–93, 1974.
- J. Epps and E. Ambikairajah, Use of the discrete cosine transform for gene expression data analysis, 2004.
- Hotelling, H. (1933). Analysis of a complex of statistical variables into principal components. Journal of Educational Psychology, 24(6), 417–441. [CrossRef]
- Hastie, Trevor, et al. The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference, and prediction. Vol. 2. New York: springer, 2009.
- Uymaz, S. A., Tezel, G., &Yel, E. (2015). Artificial algae algorithm (AAA) for nonlinear global optimization. Applied soft computing, 31, 153-171. [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, S. K., & Lee, S. W. (2020). An integrated approach for ovarian cancer classification with the application of stochastic optimization. IEEE access, 8, 127866-127882. [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. G., Deb, S., & Coelho, L. D. S. (2015, December). Elephant herding optimization. In 2015 3rd international symposium on computational and business intelligence (ISCBI) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
- Bharanidharan, N., &Rajaguru, H. (2021). Dementia MRI image classification using transformation technique based on elephant herding optimization with Randomized Adam method for updating the hyper-parameters. International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology, 31(3), 1221-1245. [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. (2016). Dragonfly algorithm: a new meta-heuristic optimization technique for solving single-objective, discrete, and multi-objective problems. Neural compu ting and applications, 27, 1053-1073. [CrossRef]
- Bharanidharan N, Rajaguru H. Performance enhancement of swarm intelligence techniques in dementia classification using dragonfly-based hybrid algorithms. Int J Imaging Syst Technol. 2019;1–18. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Guanglu, Douglas Allaire, and Jonathan Cagan. "Reducing the Search Space for Global Minimum: A Focused Regions Identification Method for Least Squares Parameter Estimation in Nonlinear Models." Journal of Computing and Information Science in Engineering 23.2 (2023): 021006. [CrossRef]
- Draper, Norman R., and Harry Smith. Applied regression analysis. Vol. 326. John Wiley & Sons, 1998.
- Llaha and A. Rista, "Prediction and Detection of Diabetes using Machine Learning," in Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Real-Time Applications in Computer Science and Information Technology (RTA-CSIT), May 2021, pp. 94-102.
- Prabhakar, Sunil Kumar, HarikumarRajaguru, and Seong-Whan Lee. "A comprehensive analysis of alcoholic EEG signals with detrend fluctuation analysis and post classifiers." 2019 7th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI). IEEE, 2019.
- Liu, S., Zhang, X., Xu, L., & Ding, F. (2022). Expectation–maximization algorithm for bilinear systems by using the Rauch–Tung–Striebel smoother. Automatica, 142, 110365.
- Zhou, Weidong, et al. "Epileptic seizure detection using lacunarity and Bayesian linear discriminant analysis in intracranial EEG." IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering 60.12 (2013): 3375-3381. [CrossRef]
- Hamid, Imad Yagoub. "Prediction of Type 2 Diabetes through Risk Factors using Binary Logistic Regression." Journal of Al-Qadisiyah for computer science and mathematics 12.3 (2020): Page-1.
- Adiwijaya K, Wisesty UN, Lisnawati E, Aditsania A, Kusumo DS. Dimensionality reduction using principal component analysis for cancer detection based on microarray data classification. J Comput Sci. 2018; 14:1521-1530. https://doi.org/ 10.3844/jcssp.2018.1521.1530.
- F Zang, JS Zhang, "Softmax Discriminant Classifier", 3rd International Conference on Multimedia Information Networking and Security, pp. 16-20, 2011.
- Yao, X. J., et al. "Comparative classification study of toxicity mechanisms using support vector machines and radial basis function neural networks." Analytica Chimica Acta 535.1-2 (2005): 259-273. [CrossRef]
- Fushiki, Tadayoshi. "Estimation of prediction error by using K-fold cross-validation." Statistics and Computing 21 (2011): 137-146. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z., & Bovik, A. C. (2009). Mean squared error: Love it or leave it? A new look at signal fidelity measures. IEEE signal processing magazine, 26(1), 98-117.
- Maniruzzaman M, Kumar N, Abedin MM, Islam MS, Suri HS, El-Baz AS, Suri JS. Comparative approaches for classification of diabetes mellitus data: machine learning paradigm. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2017;152:23–34. [CrossRef]
- Pham T, Tran T, Phung D, Venkatesh S. Predicting healthcare trajectories from medical records: a deep learning approach. J Biomed Inform. 2017;69:218–29. [CrossRef]
- Hertroijs DFL, Elissen AMJ, Brouwers MCGJ, Schaper NC, Köhler S, Popa MC, Asteriadis S, Hendriks SH, Bilo HJ, Ruwaard D, et al. A risk score including body mass index, glycated hemoglobin and triglycerides predicts future glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017;20(3):681–8. [CrossRef]
- Arellano-Campos O, Gómez-Velasco DV, Bello-Chavolla OY, Cruz-Bautista I, Melgarejo-Hernandez MA, Muñoz-Hernandez L, Guillén LE, Garduño-Garcia JDJ, Alvirde U, Ono-Yoshikawa Y, et al. Development and validation of a predictive model for incident type 2 diabetes in middleaged Mexican adults: the metabolic syndrome cohort. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019;19(1):1–10. [CrossRef]
- Deo R, Panigrahi S. Performance assessment of machine learning based models for diabetes prediction. In: 2019 IEEE healthcare innovations and point of care technologies, (HI-POCT). 2019. [CrossRef]
- Choi BG, Rha S-W, Kim SW, Kang JH, Park JY, Noh Y-K. Machine learning for the prediction of new-onset diabetes mellitus during 5-year follow-up in non-diabetic patients with cardiovascular risks. Yonsei Med J. 2019;60(2):191. [CrossRef]
- Akula R, Nguyen N, Garibay I. Supervised machine learning based ensemble model for accurate prediction of type 2 diabetes. In: 2019 Southeast Con. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Xie Z, Nikolayeva O, Luo J, Li D. Building risk prediction models for type 2 diabetes using machine learning techniques. Prev Chronic Dis. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Bernardini M, Morettini M, Romeo L, Frontoni E, Burattini L. Early temporal prediction of type 2 diabetes risk condition from a general practitioner electronic health record: a multiple instance boosting approach. ArtifIntell Med. 2020;105:101847. [CrossRef]
- Zhang L, Wang Y, Niu M, Wang C, Wang Z. Machine learning for characterizing risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a rural Chinese population: the Henan rural cohort study. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):1–10. [CrossRef]
- Jain S. A supervised model for diabetes divination. BiosciBiotechnol Res Commun. 2020;13(14, SI):315–8. [CrossRef]
- Kalagotla SK, Gangashetty SV, Giridhar K. A novel stacking technique for prediction of diabetes. Comput Biol Med. 2021;135:104554. [CrossRef]
- Haneef R, Fuentes S, Fosse-Edorh S, Hrzic R, Kab S, Cosson E, Gallay A.Use of artifcial intelligence for public health surveillance: a case study to develop a machine learning-algorithm to estimate the incidence of diabetes mellitus in France. Arch Public Health. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Deberneh HM, Kim I. Prediction of Type 2 diabetes based on machine learning algorithm. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(6):3317. [CrossRef]
- Zhang L, Wang Y, Niu M, Wang C, Wang Z. Nonlaboratory based risk assessment model for type 2 diabetes mellitus screening in Chinese rural population: a joint bagging boosting model. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2021;25(10):4005–16. [CrossRef]
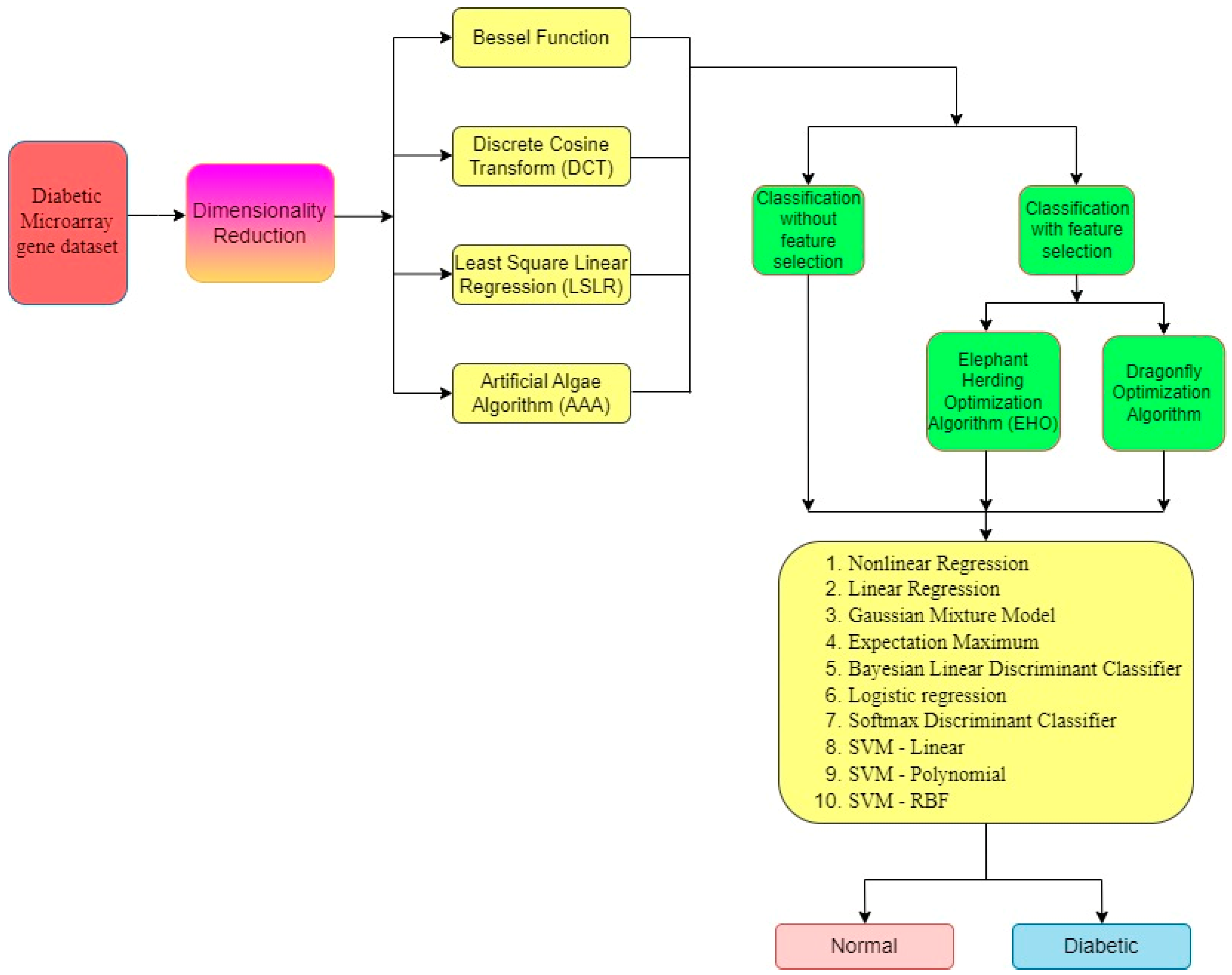
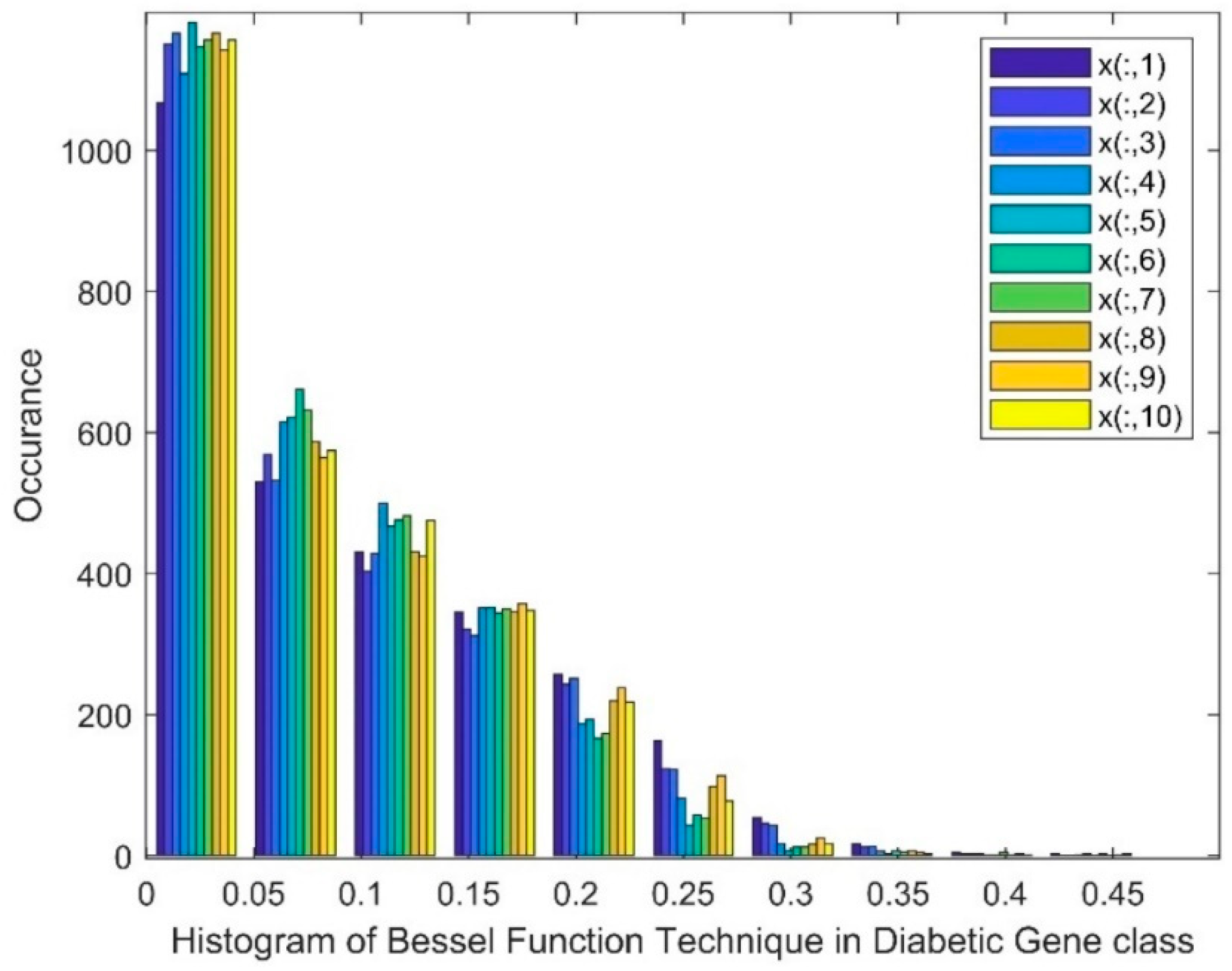
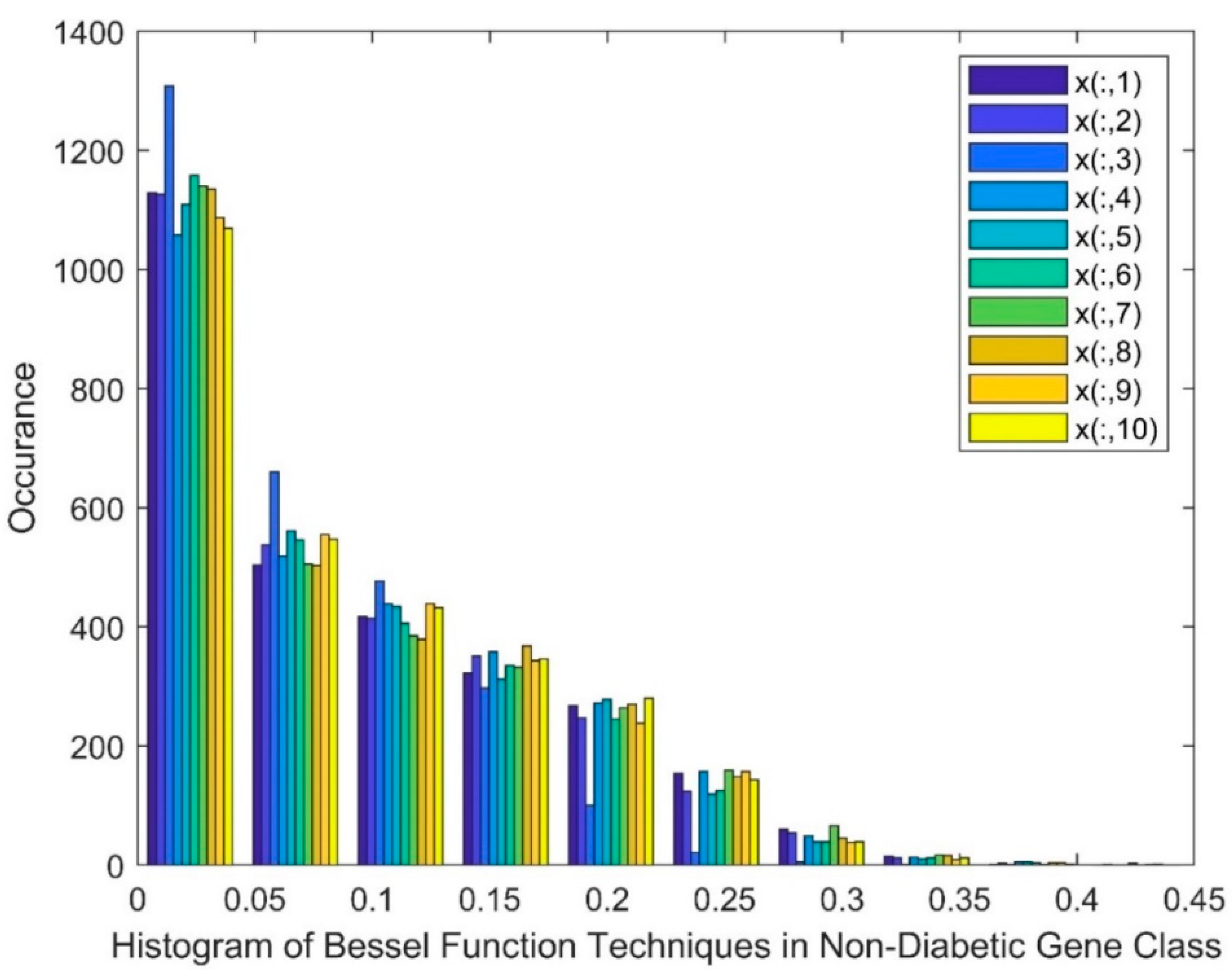
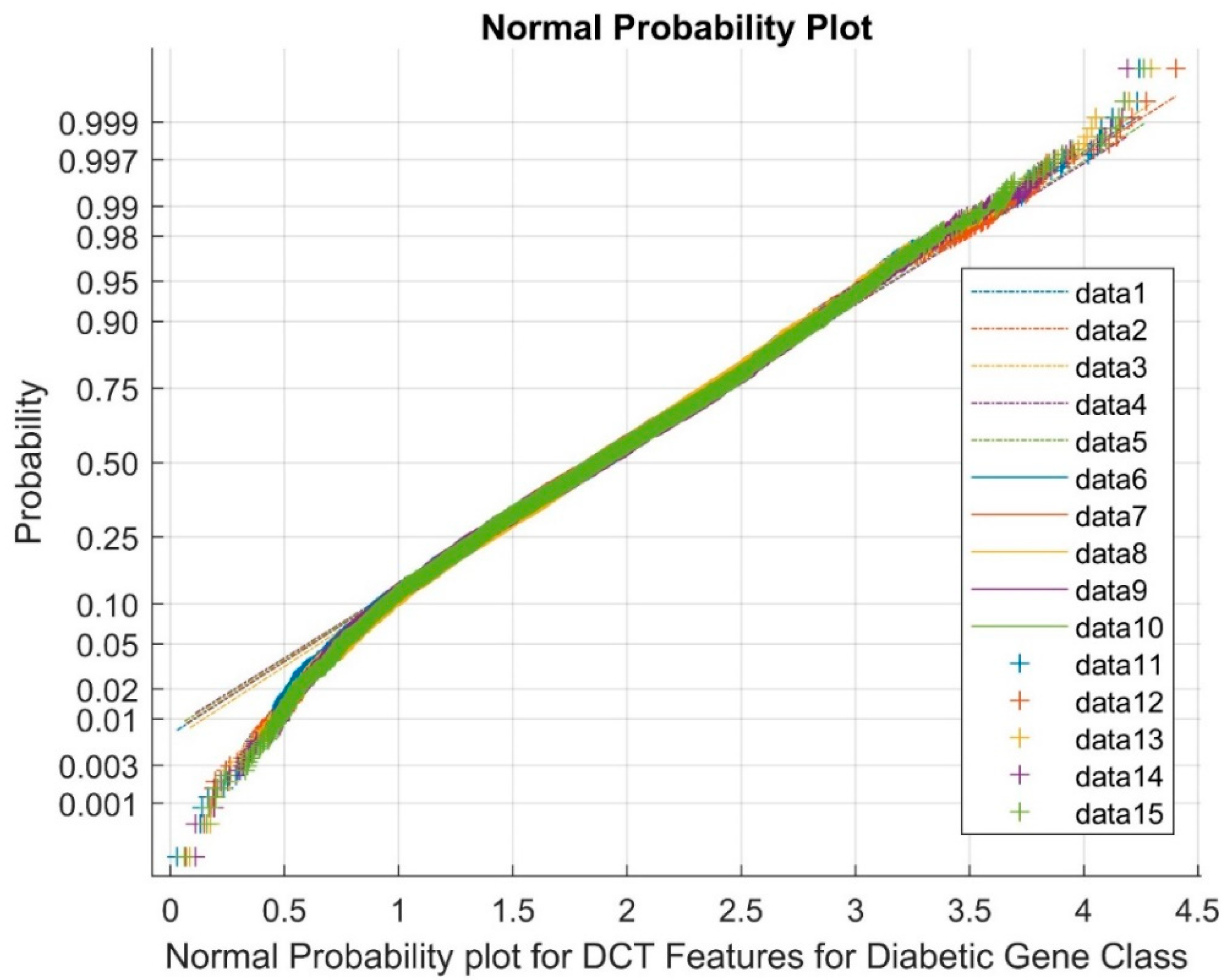
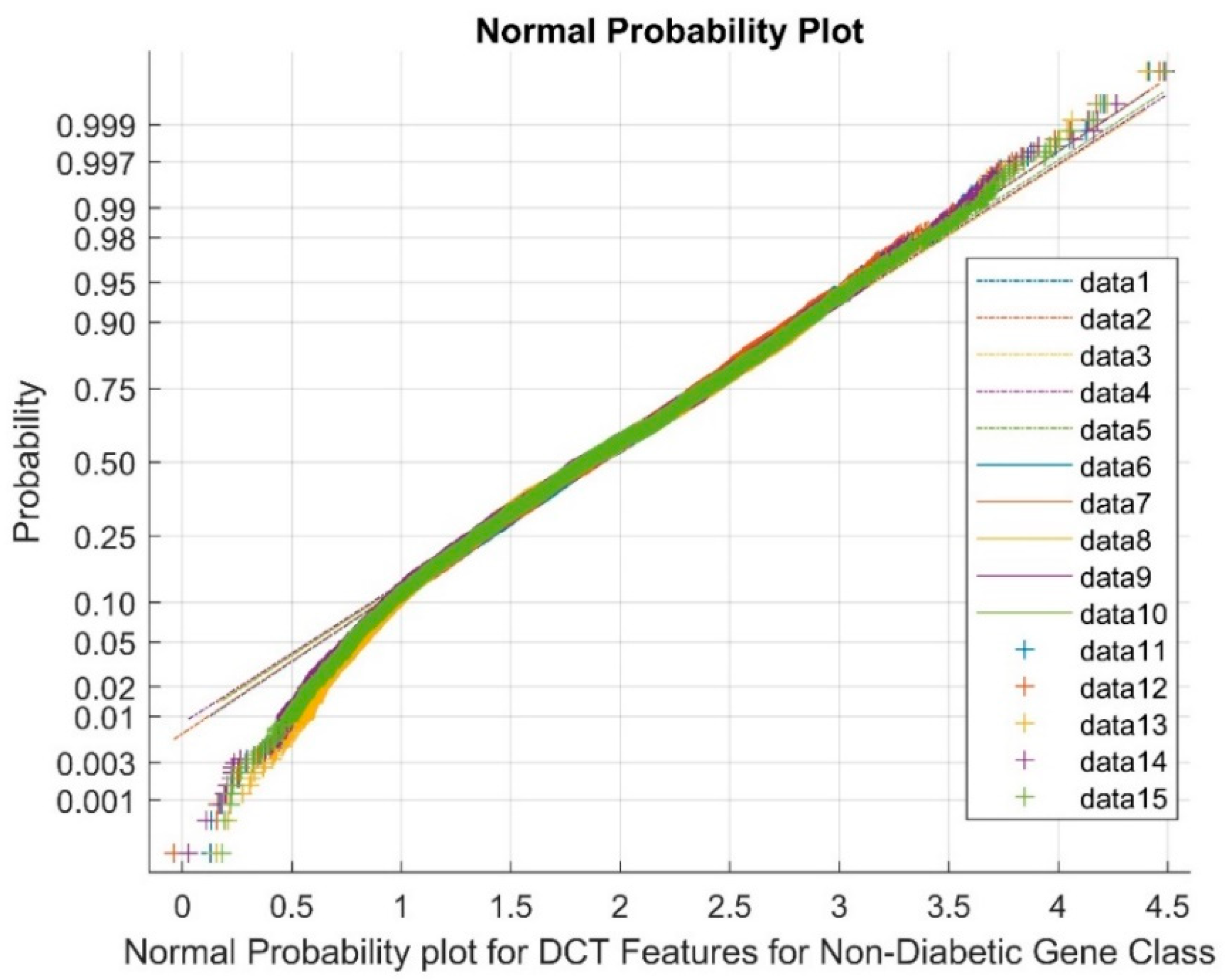
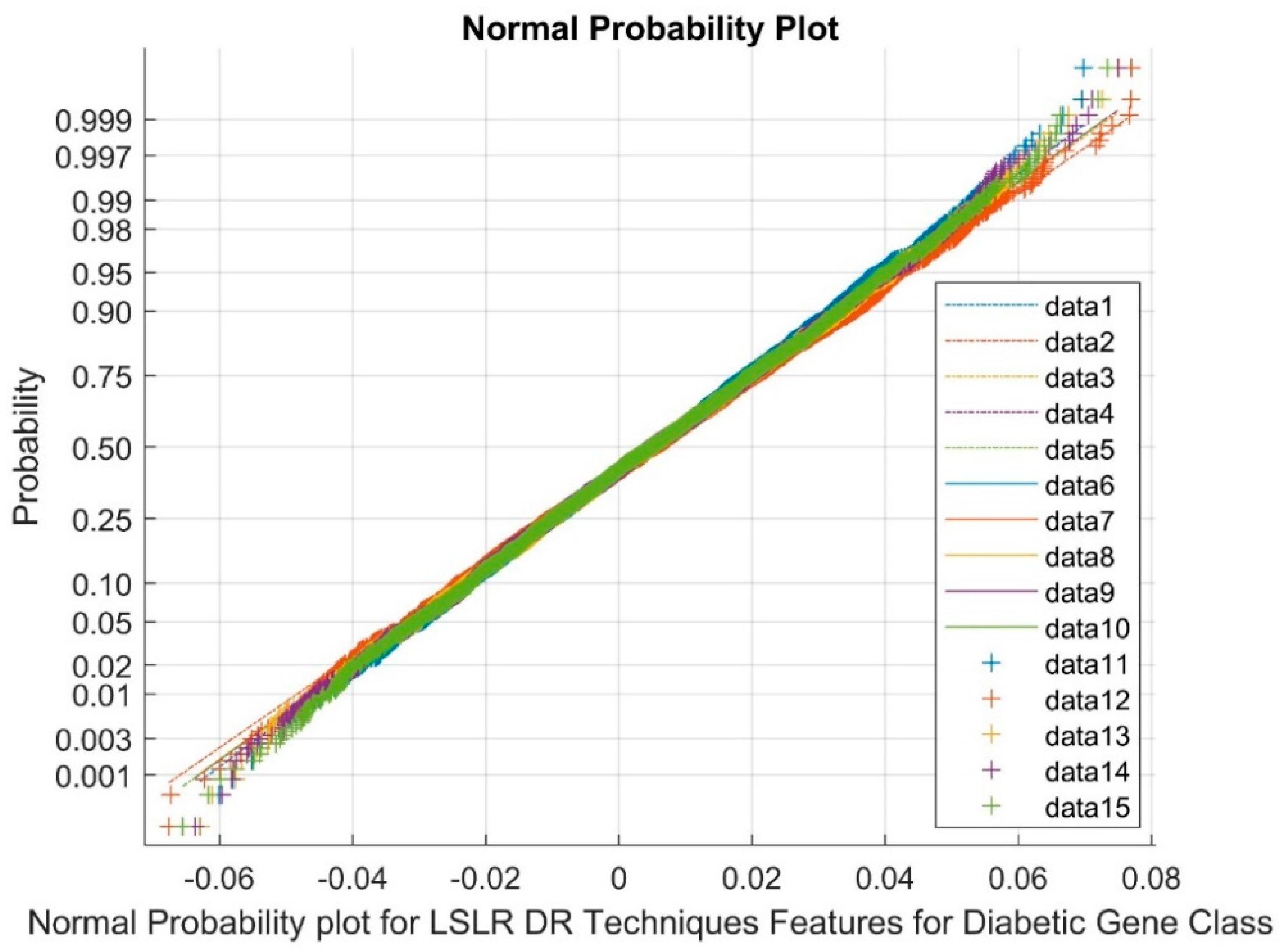
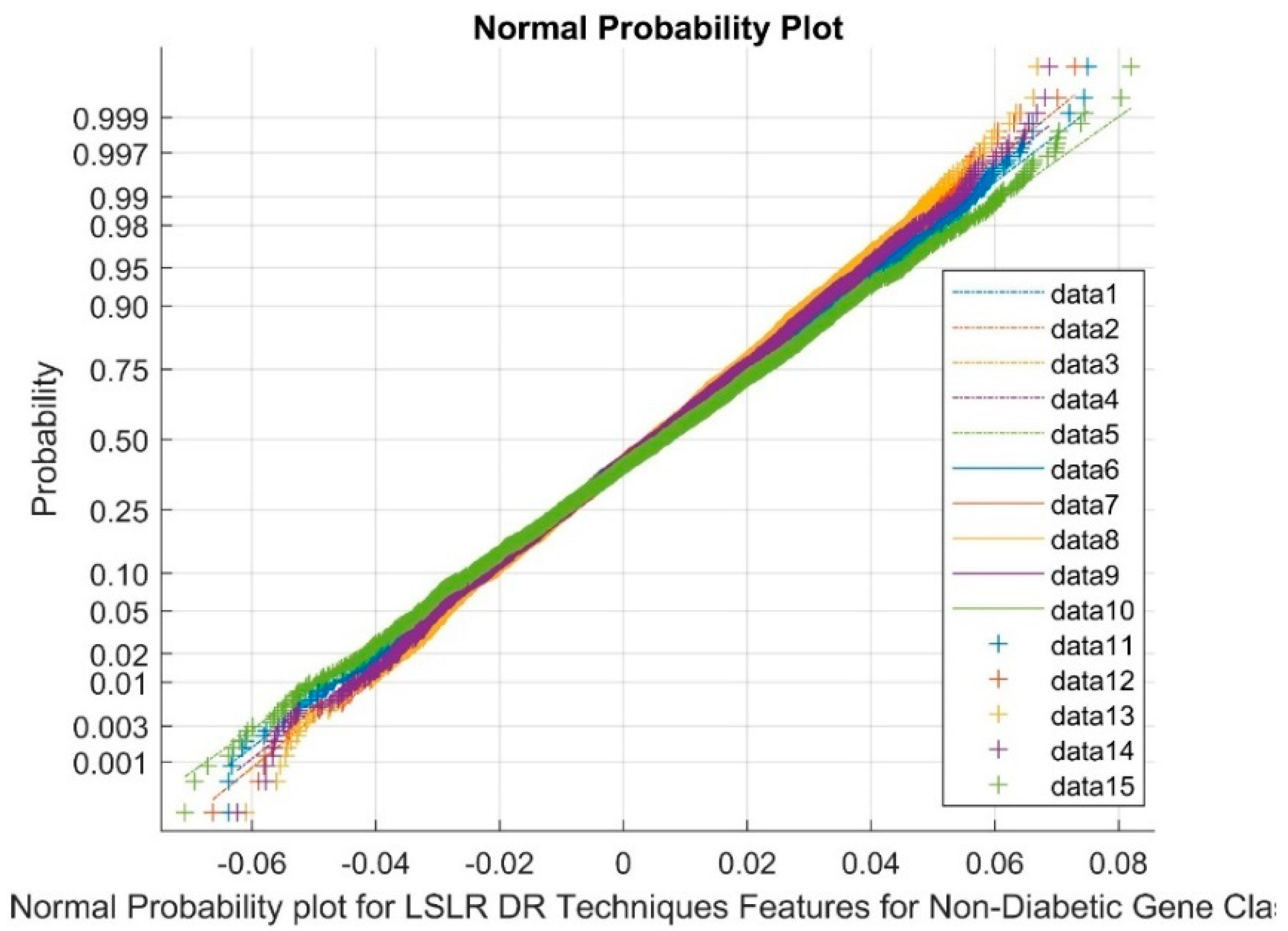
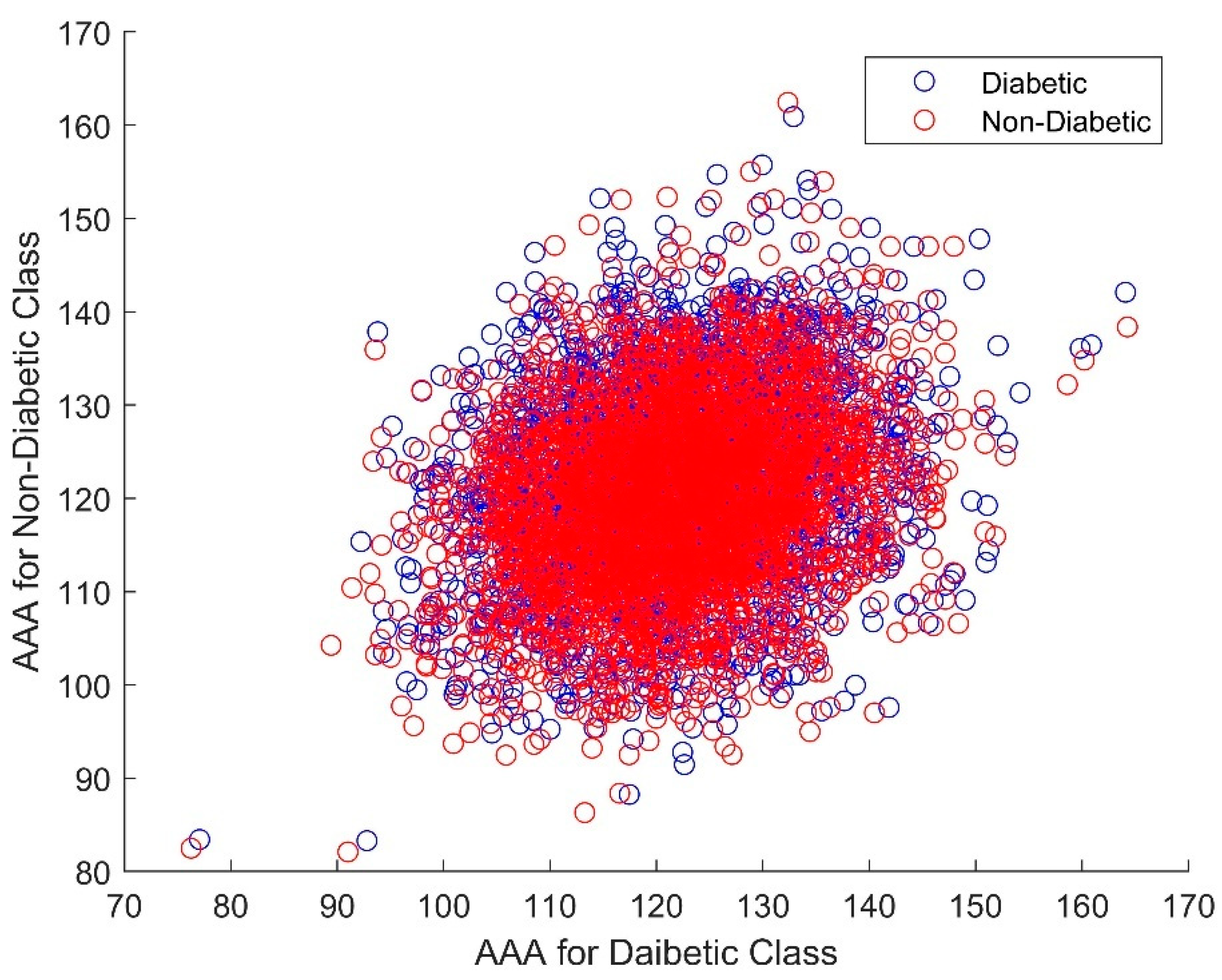
| Statistical Parameters | Bessel Function | Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) | Least Square Linear Regression (LSLR) | Artificial Algae Algorithm (AAA) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DP | NDP | DP | NDP | DP | NDP | DP | NDP | ||||
| Mean | 0.082961 | 0.084162 | 1.882012 | 1.883618 | 0.00467 | 0.00457 | 121.664 | 120.5492 | |||
| Variance | 0.005165 | 0.005378 | 0.50819 | 0.506957 | 0.000432 | 0.000417 | 101.6366 | 103.0168 | |||
| Skewness | 0.865169 | 0.856162 | 0.187903 | 0.228924 | 0.003787 | -0.0315 | 0.042744 | 0.054472 | |||
| Kurtosis | 0.180926 | 0.135504 | -0.34524 | -0.40687 | -0.16576 | -0.08667 | 0.152272 | 0.091169 | |||
| Pearson CC | 0.866264 | 0.859211 | 0.98138 | 0.983118 | 0.975446 | 0.977318 | 0.9826 | 0.985246 | |||
| CCA | 0.05904 | 0.260275 | 0.090825 | 0.082321 | |||||||
| Feature selection | DR Techniques | Bessel Function | Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) | Least Square Linear Regression (LSLR) | Artificial Algae Algorithm (AAA) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class | DP | NDP | DP | NDP | DP | NDP | DP | NDP | |
| EHO | P value <0.05 |
0.9721 | 0.9998 | 0.994 | 0.9996 | 0.9961 | 0.9999 | 0.9466 | 0.9605 |
| Dragon Fly | P value <0.05 |
0.99985 | 0.876 | 0.9956 | 0.998 | 0.9951 | 0.99931 | 0.9936 | 0.9977 |
| Classifiers | Bessel Function | Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) | Least Square Linear Regression (LSLR) | Artificial Algae Algorithm (AAA) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training MSE |
Testing MSE |
Training MSE |
Testing MSE |
Training MSE | Testing MSE |
Training MSE |
Testing MSE |
|
| NLR | 0.0000023 | 0.000176 | 6.41E-06 | 2.48E-05 | 7.75E-06 | 5.12E-05 | 2.91E-07 | 1.6E-05 |
| LR | 2.41E-05 | 9.51E-05 | 7.52E-06 | 3.11E-05 | 2.18E-07 | 4.66E-05 | 3.67E-08 | 1.45E-05 |
| GMM | 0.0000021 | 0.000175 | 5.72E-07 | 6.8E-06 | 3.09E-07 | 1.11E-05 | 3.76E-06 | 5.33E-06 |
| EM | 1.62E-07 | 9.87E-06 | 2.71E-06 | 1.3E-05 | 9.87E-07 | 1.99E-05 | 8.97E-09 | 7.3E-06 |
| BLDC | 0.0000014 | 0.000253 | 2.86E-07 | 3.94E-05 | 4.74E-06 | 5.28E-05 | 1.43E-07 | 1.64E-05 |
| LoR | 0.0000012 | 0.000289 | 9.47E-06 | 3.58E-05 | 8.69E-06 | 4.54E-05 | 9.26E-08 | 1.45E-05 |
| SDC | 0.0000019 | 0.000203 | 3.66E-06 | 1.07E-05 | 2.47E-06 | 1.86E-05 | 2.31E-09 | 5E-06 |
| SVM (L) | 0.0000031 | 0.00027 | 8.92E-06 | 2.89E-05 | 1.09E-05 | 4.01E-05 | 4.13E-09 | 8.2E-06 |
| SVM (Poly) | 0.0000036 | 0.000211 | 3.36E-07 | 2.11E-05 | 1.29E-06 | 2.85E-05 | 7.84E-09 | 4.69E-06 |
| SVM (RBF) | 4.16E-07 | 8.3E-05 | 1.57E-08 | 2.41E-06 | 3.22E-08 | 5.64E-06 | 1.93E-10 | 1.77E-08 |
| Classifiers | Bessel Function | Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) | Least Square Linear Regression (LSLR) | Artificial Algae Algorithm (AAA) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training MSE |
Testing MSE | Training MSE | Testing MSE |
Training MSE |
Testing MSE |
Training MSE |
Testing MSE |
|
| NLR | 4.85× 10−6 | 2.64× 10−5 | 4.13× 10−5 | 2.88× 10−5 | 1.21× 10−6 | 3.64× 10−5 | 7.21× 10−7 | 9.53× 10−6 |
| LR | 3.62× 10−6 | 4.79× 10−5 | 6.92× 10−6 | 1.35× 10−5 | 7.72× 10−6 | 1.96× 10−5 | 6.98× 10−7 | 4.23× 10−6 |
| GMM | 6.13× 10−6 | 2.26× 10−4 | 7.63× 10−7 | 9.22× 10−6 | 4.57× 10−6 | 1.39× 10−5 | 3.81× 10−7 | 4.52× 10−6 |
| EM | 2.19× 10−7 | 1.2× 10−6 | 4.39× 10−6 | 2.25× 10−5 | 4.81× 10−6 | 3.92× 10−5 | 4.67× 10−7 | 1× 10−5 |
| BLDC | 4.47× 10−6 | 6.56× 10−5 | 7.94× 10−7 | 5.8× 10−5 | 3.72× 10−6 | 1.56× 10−5 | 3.52× 10−7 | 3.97× 10−6 |
| LoR | 3.24× 10−6 | 2.26× 10−4 | 3.32× 10−6 | 1.09× 10−5 | 8.37× 10−6 | 2.26× 10−5 | 7.61× 10−8 | 3.82× 10−6 |
| SDC | 9.62× 10−6 | 2.31× 10−4 | 9.13× 10−7 | 4.62× 10−5 | 4.87× 10−6 | 1.52× 10−5 | 9.93× 10−8 | 3.84× 10−6 |
| SVM (L) | 4.12× 10−5 | 5.29× 10−4 | 8.47× 10−7 | 4.16× 10−6 | 1.93× 10−8 | 9.61× 10−6 | 1.67× 10−8 | 3.81× 10−6 |
| SVM (Poly) | 6.41× 10−5 | 2.34× 10−4 | 2.19× 10−7 | 6.41× 10−6 | 5.77× 10−8 | 1.24× 10−5 | 1.62× 10−8 | 2.05× 10−6 |
| SVM (RBF) | 3.72× 10−7 | 2.56× 10−5 | 6.17× 10−8 | 1.35× 10−6 | 6.79× 10−9 | 2.42× 10−6 | 1.99× 10−10 | 2.5× 10−8 |
| Classifiers | Bessel Function | Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) | Least Square Linear Regression (LSLR) | Artificial Algae Algorithm (AAA) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training MSE | Testing MSE | Training MSE | Testing MSE | Training MSE | Testing MSE | Training MSE | Testing MSE | |
| NLR | 3.62× 10−6 | 4.54× 10−5 | 4.16× 10−6 | 1.36× 10−5 | 8.21× 10−6 | 2.72× 10−5 | 3.86× 10−6 | 1.28× 10−5 |
| LR | 4.36× 10−6 | 7.12× 10−5 | 2.84× 10−6 | 1.39× 10−5 | 9.4× 10−6 | 3.8× 10−5 | 2.51× 10−8 | 4.32× 10−6 |
| GMM | 7.58× 10−7 | 4.71× 10−5 | 5.66× 10−8 | 7.84× 10−6 | 3.61× 10−6 | 2.09× 10−5 | 4.63× 10−8 | 1.02× 10−5 |
| EM | 4.79× 10−7 | 3.31× 10−5 | 3.79× 10−8 | 1.68× 10−5 | 5.33× 10−6 | 6.12× 10−5 | 3.43× 10−8 | 1.46× 10−5 |
| BLDC | 6.52× 10−7 | 4.16× 10−5 | 2.92× 10−8 | 4.49× 10−5 | 7.54× 10−8 | 9.12× 10−6 | 7.68× 10−8 | 8.1× 10−6 |
| LoR | 6.54× 10−7 | 5.04× 10−5 | 7.23× 10−8 | 6.05× 10−6 | 1.92× 10−7 | 2.23× 10−6 | 4.84× 10−9 | 3.36× 10−6 |
| SDC | 3.86× 10−7 | 2.57× 10−5 | 8.95× 10−7 | 3.08× 10−6 | 7.52× 10−8 | 6.31× 10−6 | 1.63× 10−8 | 2.52× 10−6 |
| SVM (L) | 5.42× 10−7 | 3.51× 10−5 | 8.45× 10−7 | 1.03× 10−5 | 1.41× 10−7 | 2.83× 10−5 | 1.95× 10−7 | 1.7× 10−6 |
| SVM (Poly) | 9.67× 10−7 | 7.23× 10−5 | 6.67× 10−6 | 7.08× 10−6 | 6.3× 10−7 | 1.05× 10−5 | 6.42× 10−8 | 5.33× 10−6 |
| SVM (RBF) | 8.64× 10−8 | 2.72× 10−6 | 1.82× 10−8 | 9.05× 10−7 | 3.4× 10−8 | 1.69× 10−6 | 1.66× 10−8 | 3.25× 10−8 |
| Metrics | Formula | Assessment focus |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Fraction of predictions that are correct | |
| F1 Score | Harmonic mean of precision and recall | |
| Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC) | Correlation between the observed and predicted classifications | |
| Error Rate | Fraction of predictions that are incorrect | |
| FM Metric | Generalization of the F-measure that adds a beta parameter | |
| Kappa |
|
Statistic that measures agreement between observed and predicted classifications, adjusted for chance |
| Dimensionality Reduction | Classifiers | Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) |
F1Score (%) |
MCC | Error Rate (%) |
FM (%) | Kappa | ||
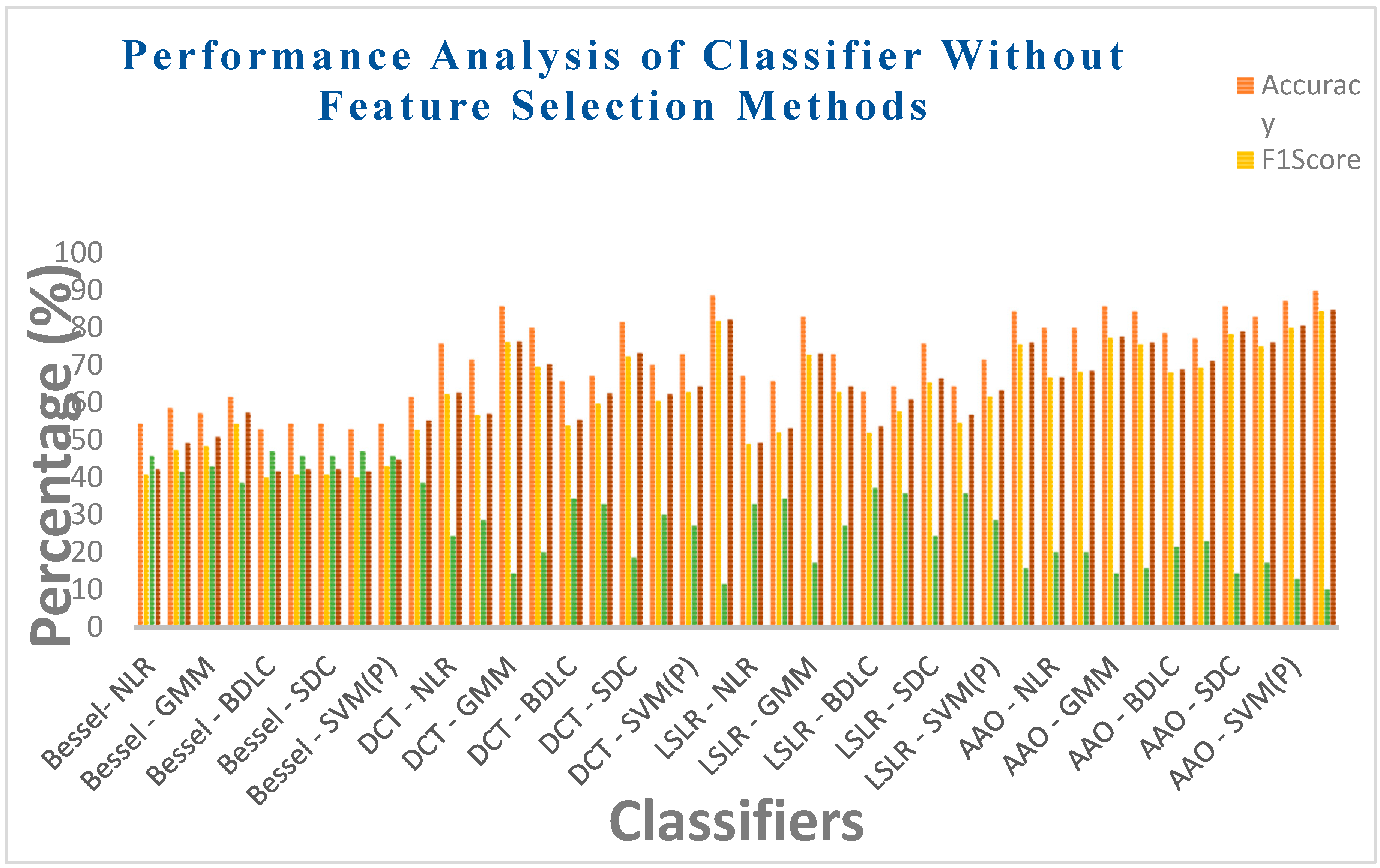
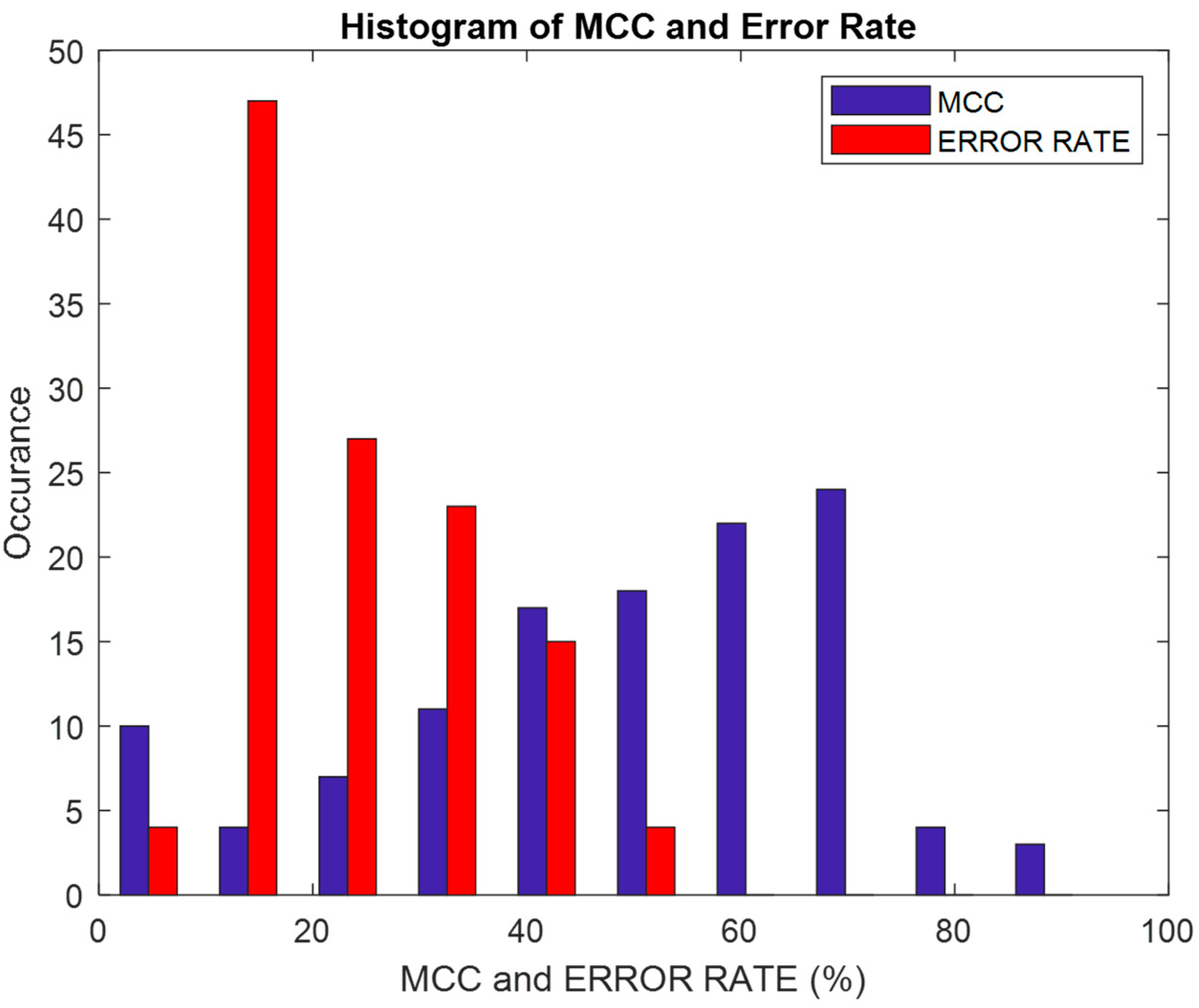
| Bessel Function | NLR | 54.2857 | 40.7407 | 0.0813 | 45.7142 | 42.1831 | 0.0743 |
| LR | 58.5714 | 47.2727 | 0.1897 | 41.4285 | 49.1354 | 0.1714 | |
| GMM | 57.1428 | 48.2758 | 0.1995 | 42.8571 | 50.7833 | 0.1732 | |
| EM | 61.4285 | 54.2372 | 0.3092 | 38.5714 | 57.2892 | 0.2645 | |
| BLDC | 52.8571 | 40 | 0.0632 | 47.1428 | 41.5761 | 0.0571 | |
| LoR | 54.2857 | 40.7407 | 0.0813 | 45.7142 | 42.1831 | 0.0743 | |
| SDC | 54.2857 | 40.7407 | 0.0813 | 45.7142 | 42.1831 | 0.0743 | |
| SVM (L) | 52.8571 | 40 | 0.0632 | 47.1428 | 41.5761 | 0.0571 | |
| SVM (Poly) | 54.2857 | 42.8571 | 0.1084 | 45.7142 | 44.7214 | 0.0967 | |
| SVM (RBF) | 61.4285 | 52.6315 | 0.2805 | 38.5714 | 55.1411 | 0.2470 | |
| Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) | NLR | 75.7142 | 62.2222 | 0.4525 | 24.2857 | 62.6099 | 0.4465 |
| LR | 71.4285 | 56.5217 | 0.3646 | 28.5714 | 57.0088 | 0.3577 | |
| GMM | 85.7142 | 76.1904 | 0.6617 | 14.2857 | 76.277 | 0.6601 | |
| EM | 80 | 69.5652 | 0.5609 | 20 | 70.1646 | 0.5504 | |
| BLDC | 65.7142 | 53.8461 | 0.3083 | 34.2857 | 55.3399 | 0.2881 | |
| LoR | 67.1428 | 59.6491 | 0.4072 | 32.8571 | 62.4932 | 0.3585 | |
| SDC | 81.4285 | 72.3404 | 0.6032 | 18.5714 | 73.1564 | 0.5882 | |
| SVM (L) | 70 | 60.3773 | 0.4162 | 30 | 62.2799 | 0.3849 | |
| SVM (Poly) | 72.8571 | 62.7451 | 0.4547 | 27.1428 | 64.2575 | 0.4291 | |
| SVM (RBF) | 88.5714 | 81.8181 | 0.7423 | 11.4285 | 82.1584 | 0.7358 | |
| Least Square Linear Regression (LSLR) | NLR | 67.1428 | 48.8888 | 0.2545 | 32.8571 | 49.1935 | 0.2511 |
| LR | 65.7142 | 52 | 0.2829 | 34.2857 | 53.0723 | 0.2695 | |
| GMM | 82.8571 | 72.7272 | 0.6091 | 17.1428 | 73.0297 | 0.6037 | |
| EM | 72.8571 | 62.7451 | 0.4547 | 27.1428 | 64.2575 | 0.4291 | |
| BLDC | 62.8571 | 51.8518 | 0.2711 | 37.1428 | 53.6875 | 0.2479 | |
| LoR | 64.2857 | 57.6271 | 0.3728 | 35.7142 | 60.8698 | 0.3190 | |
| SDC | 75.7142 | 65.3061 | 0.4952 | 24.2857 | 66.4364 | 0.4757 | |
| SVM (L) | 64.2857 | 54.5454 | 0.3162 | 35.7142 | 56.6947 | 0.2857 | |
| SVM (Poly) | 71.4285 | 61.5384 | 0.4352 | 28.5714 | 63.2456 | 0.4067 | |
| SVM (RBF) | 84.2857 | 75.5555 | 0.6505 | 15.7142 | 76.0263 | 0.6418 | |
| Artificial Algae Algorithm (AAA) | NLR | 80 | 66.6666 | 0.5254 | 20 | 66.7424 | 0.5242 |
| LR | 80 | 68.1818 | 0.5424 | 20 | 68.4653 | 0.5377 | |
| GMM | 85.7142 | 77.2727 | 0.6757 | 14.2857 | 77.594 | 0.6698 | |
| EM | 84.2857 | 75.5555 | 0.6505 | 15.7142 | 76.0263 | 0.6418 | |
| BLDC | 78.5714 | 68.0851 | 0.5382 | 21.4285 | 68.853 | 0.5248 | |
| LoR | 77.1428 | 69.2307 | 0.5622 | 22.8571 | 71.1512 | 0.5254 | |
| SDC | 85.7142 | 78.2608 | 0.6918 | 14.2857 | 78.9352 | 0.6788 | |
| SVM (L) | 82.8571 | 75 | 0.6454 | 17.1428 | 76.0639 | 0.625 | |
| SVM (Poly) | 87.1428 | 80 | 0.7165 | 12.8571 | 80.4984 | 0.7069 | |
| SVM (RBF) | 90 | 84.4444 | 0.7825 | 10 | 84.9706 | 0.7720 | |
| Dimensionality Reduction | Classifiers | Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) |
F1 Score (%) |
MCC | Error Rate (%) |
FM (%) | Kappa | ||
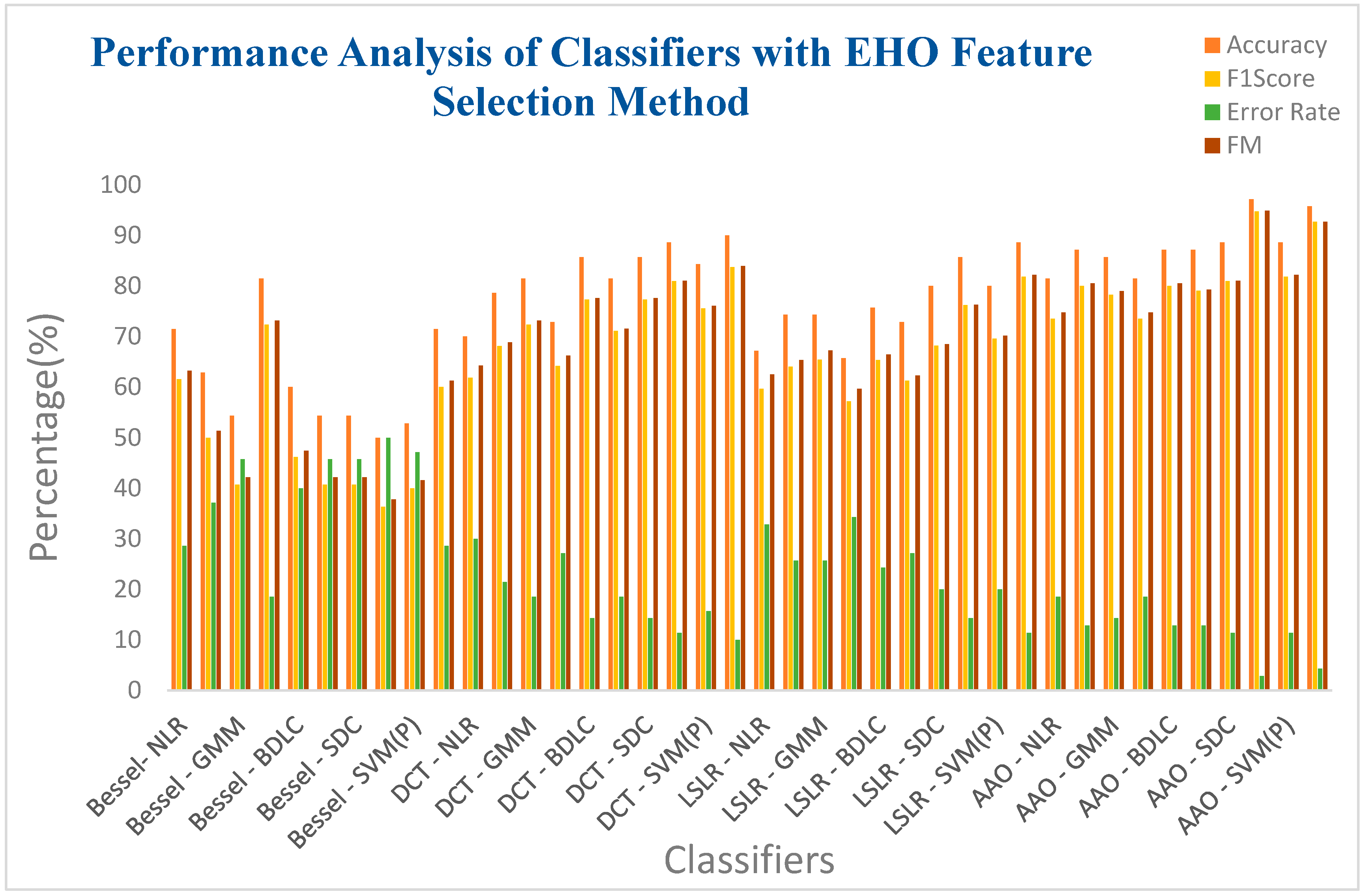
| Bessel Function | NLR | 71.4285 | 61.5384 | 0.4352 | 28.5714 | 63.2456 | 0.4067 |
| LR | 62.8571 | 50 | 0.2448 | 37.1428 | 51.387 | 0.2288 | |
| GMM | 54.2857 | 40.7407 | 0.0813 | 45.7142 | 42.1831 | 0.0743 | |
| EM | 81.4285 | 72.3404 | 0.6032 | 18.5714 | 73.1564 | 0.5882 | |
| BLDC | 60 | 46.1538 | 0.1813 | 40 | 47.4342 | 0.1694 | |
| LoR | 54.2857 | 40.7407 | 0.0813 | 45.7142 | 42.1831 | 0.0743 | |
| SDC | 54.2857 | 40.7407 | 0.0813 | 45.7142 | 42.1831 | 0.0743 | |
| SVM (L) | 50 | 36.3636 | 0 | 50 | 37.7964 | 0 | |
| SVM (Poly) | 52.8571 | 40 | 0.0632 | 47.1428 | 41.5761 | 0.0571 | |
| SVM (RBF) | 71.4285 | 60 | 0.4107 | 28.5714 | 61.2372 | 0.3913 | |
| Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) | NLR | 70 | 61.8181 | 0.4427 | 30 | 64.254 | 0.4 |
| LR | 78.5714 | 68.0851 | 0.5382 | 21.4285 | 68.853 | 0.5248 | |
| GMM | 81.4285 | 72.3404 | 0.6032 | 18.5714 | 73.1564 | 0.5882 | |
| EM | 72.8571 | 64.1509 | 0.4796 | 27.1428 | 66.1724 | 0.4435 | |
| BLDC | 85.7142 | 77.2727 | 0.6757 | 14.2857 | 77.594 | 0.6698 | |
| LoR | 81.4285 | 71.1111 | 0.5845 | 18.5714 | 71.5542 | 0.5767 | |
| SDC | 85.7142 | 77.2727 | 0.6757 | 14.2857 | 77.594 | 0.6698 | |
| SVM (L) | 88.5714 | 80.9523 | 0.7298 | 11.4285 | 81.0443 | 0.7281 | |
| SVM (Poly) | 84.2857 | 75.5555 | 0.6505 | 15.7142 | 76.0263 | 0.6418 | |
| SVM (RBF) | 90 | 83.7209 | 0.7694 | 10 | 83.9254 | 0.7655 | |
| Least Square Linear Regression (LSLR) | NLR | 67.1428 | 59.6491 | 0.4072 | 32.8571 | 62.4932 | 0.3585 |
| LR | 74.2857 | 64 | 0.4746 | 25.7142 | 65.3197 | 0.4521 | |
| GMM | 74.2857 | 65.3846 | 0.4987 | 25.7142 | 67.1984 | 0.4661 | |
| EM | 65.7142 | 57.1428 | 0.3615 | 34.2857 | 59.6285 | 0.3225 | |
| BLDC | 75.7142 | 65.3061 | 0.4952 | 24.2857 | 66.4364 | 0.4757 | |
| LoR | 72.8571 | 61.2244 | 0.4310 | 27.1428 | 62.2841 | 0.4140 | |
| SDC | 80 | 68.1818 | 0.5424 | 20 | 68.4653 | 0.5377 | |
| SVM (L) | 85.7142 | 76.1904 | 0.6617 | 14.2857 | 76.277 | 0.6601 | |
| SVM (Poly) | 80 | 69.5652 | 0.5609 | 20 | 70.1646 | 0.5504 | |
| SVM (RBF) | 88.5714 | 81.8181 | 0.7423 | 11.4285 | 82.1584 | 0.7358 | |
| Artificial Algae Algorithm (AAA) | NLR | 81.4285 | 73.4693 | 0.6236 | 18.5714 | 74.7409 | 0.5991 |
| LR | 87.1428 | 80 | 0.7165 | 12.8571 | 80.4984 | 0.7069 | |
| GMM | 85.7142 | 78.2608 | 0.6918 | 14.2857 | 78.9352 | 0.6788 | |
| EM | 81.4285 | 73.4693 | 0.6236 | 18.5714 | 74.7409 | 0.5991 | |
| BLDC | 87.1428 | 80 | 0.7165 | 12.8571 | 80.4984 | 0.7069 | |
| LoR | 87.1428 | 79.0697 | 0.7021 | 12.8571 | 79.2629 | 0.6985 | |
| SDC | 88.5714 | 80.9523 | 0.7298 | 11.4285 | 81.0443 | 0.7281 | |
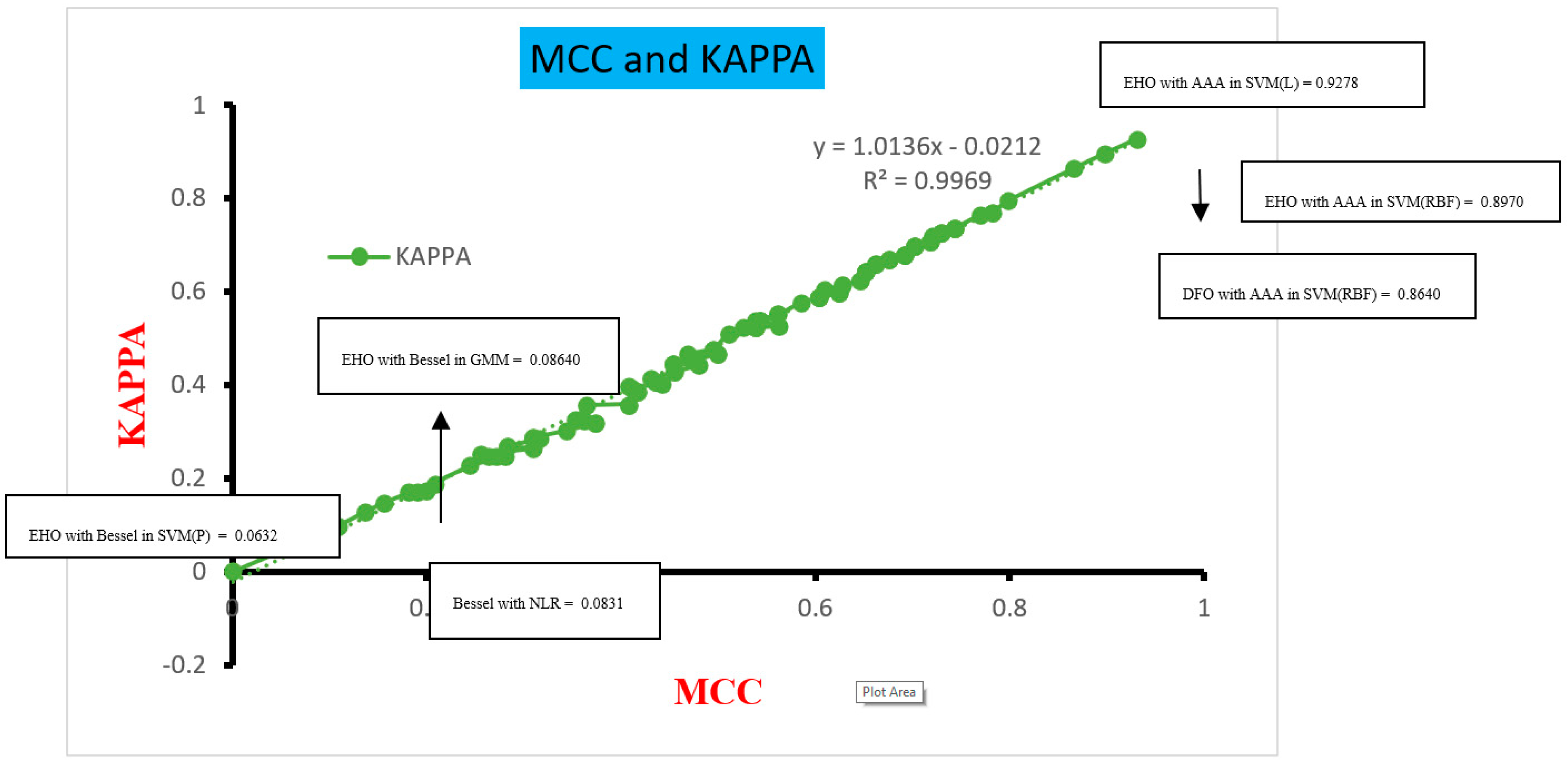
| SVM (L) | 97.1428 | 94.7368 | 0.9302 | 2.85714 | 94.8683 | 0.9278 | |
| SVM (Poly) | 88.5714 | 81.8181 | 0.7423 | 11.4285 | 82.1584 | 0.7358 | |
| SVM (RBF) | 95.7142 | 92.6829 | 0.8970 | 4.28571 | 92.7105 | 0.8965 | |
| Dimensionality Reduction | Classifiers | Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy (%) |
F1Score (%) |
MCC | Error Rate (%) |
FM (%) | Kappa | ||
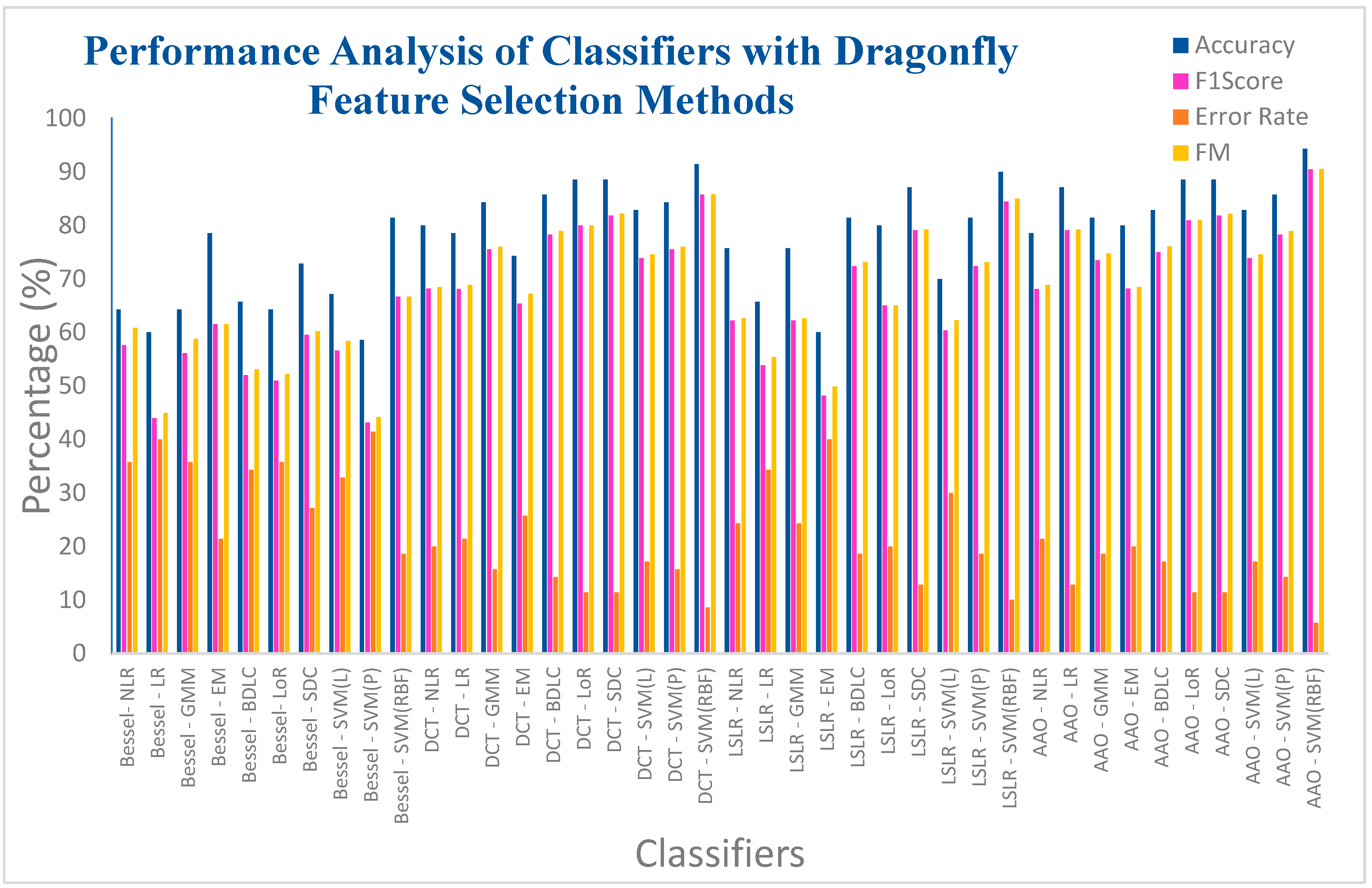
| Bessel Function | NLR | 64.2857 | 57.6271 | 0.3728 | 35.7142 | 60.8698 | 0.3190 |
| LR | 60 | 44 | 0.1551 | 40 | 44.9073 | 0.1478 | |
| GMM | 64.2857 | 56.1403 | 0.3438 | 35.7142 | 58.8172 | 0.3027 | |
| EM | 78.5714 | 61.5384 | 0.4673 | 21.4285 | 61.5587 | 0.4670 | |
| BLDC | 65.7142 | 52 | 0.2829 | 34.2857 | 53.0723 | 0.2695 | |
| LoR | 64.2857 | 50.9803 | 0.2637 | 35.7142 | 52.2093 | 0.2489 | |
| SDC | 72.8571 | 59.5744 | 0.4083 | 27.1428 | 60.2464 | 0.3981 | |
| SVM (L) | 67.1428 | 56.6037 | 0.3529 | 32.8571 | 58.3874 | 0.3263 | |
| SVM (Poly) | 58.5714 | 43.1372 | 0.1364 | 41.4285 | 44.1771 | 0.1287 | |
| SVM (RBF) | 81.4285 | 66.6666 | 0.5384 | 18.5714 | 66.6886 | 0.5380 | |
| Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) | NLR | 80 | 68.1818 | 0.5424 | 20 | 68.4653 | 0.5377 |
| LR | 78.5714 | 68.0851 | 0.5382 | 21.4285 | 68.853 | 0.5248 | |
| GMM | 84.2857 | 75.5555 | 0.6505 | 15.7142 | 76.0263 | 0.6418 | |
| EM | 74.2857 | 65.3846 | 0.4987 | 25.7142 | 67.1984 | 0.4661 | |
| BLDC | 85.7142 | 78.2608 | 0.6918 | 14.2857 | 78.9352 | 0.6788 | |
| LoR | 88.5714 | 80 | 0.72 | 11.4285 | 80 | 0.72 | |
| SDC | 88.5714 | 81.8181 | 0.7423 | 11.4285 | 82.1584 | 0.7358 | |
| SVM (L) | 82.8571 | 73.9130 | 0.6264 | 17.1428 | 74.5499 | 0.6146 | |
| SVM (Poly) | 84.2857 | 75.5555 | 0.6505 | 15.7142 | 76.0263 | 0.6418 | |
| SVM (RBF) | 91.4285 | 85.7142 | 0.7979 | 8.57142 | 85.8116 | 0.7961 | |
| Least Square Linear Regression (LSLR) | NLR | 75.7142 | 62.2222 | 0.4525 | 24.2857 | 62.6099 | 0.4465 |
| LR | 65.7142 | 53.8461 | 0.3083 | 34.2857 | 55.3399 | 0.2881 | |
| GMM | 75.7142 | 62.2222 | 0.4525 | 24.2857 | 62.6099 | 0.4465 | |
| EM | 60 | 48.1481 | 0.2078 | 40 | 49.8527 | 0.1900 | |
| BLDC | 81.4285 | 72.3404 | 0.6032 | 18.5714 | 73.1564 | 0.5882 | |
| LoR | 80 | 65 | 0.51 | 20 | 65 | 0.51 | |
| SDC | 87.1428 | 79.0697 | 0.7021 | 12.8571 | 79.2629 | 0.6985 | |
| SVM (L) | 70 | 60.3773 | 0.4162 | 30 | 62.2799 | 0.3849 | |
| SVM (Poly) | 81.4285 | 72.3404 | 0.6032 | 18.5714 | 73.1564 | 0.5882 | |
| SVM (RBF) | 90 | 84.4444 | 0.7825 | 10 | 84.9706 | 0.7720 | |
| Artificial Algae Algorithm (AAA) | NLR | 78.5714 | 68.0851 | 0.5382 | 21.4285 | 68.853 | 0.5248 |
| LR | 87.1428 | 79.0697 | 0.7021 | 12.8571 | 79.2629 | 0.6985 | |
| GMM | 81.4285 | 73.4693 | 0.6236 | 18.5714 | 74.7409 | 0.5991 | |
| EM | 80 | 68.1818 | 0.5424 | 20 | 68.4653 | 0.5377 | |
| BLDC | 82.8571 | 75 | 0.6454 | 17.1428 | 76.0639 | 0.625 | |
| LoR | 88.5714 | 80.9523 | 0.7298 | 11.4285 | 81.0443 | 0.7281 | |
| SDC | 88.5714 | 81.8181 | 0.7423 | 11.4285 | 82.1584 | 0.7358 | |
| SVM (L) | 82.8571 | 73.9130 | 0.6264 | 17.1428 | 74.5499 | 0.6146 | |
| SVM (Poly) | 85.7142 | 78.2608 | 0.6918 | 14.2857 | 78.9352 | 0.6788 | |
| SVM (RBF) | 94.2857 | 90.4761 | 0.8660 | 5.71428 | 90.5789 | 0.8640 | |
| Classifiers | DR Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bessel Function | Discrete Cosine Transform (DST) | Least Square Linear Regression (LSLR) | Artificial Algae Algorithm (AAA) | |
| NLR | O(n2logn) | O(n2logn) | O(n3log2n) | O(n3log4n) |
| LR | O(n2logn) | O(n2logn) | O(n3log2n) | O(n3log4n) |
| GMM | O(n2log2n) | O(n2log2n) | O(n3log2n) | O(n3log4n) |
| EM | O(n3 logn) | O(n3 logn) | O(n3log2n) | O(n3log4n) |
| BLDC | O(n3 logn) | O(n3 logn) | O(2n3 log2n) | O(2n3 log4n) |
| LoR | O(2n2logn) | O(2n2logn) | O(2n4log2n) | O(2n4log4n) |
| SDC | O(n3 logn) | O(n3 logn) | O(n4 log2n) | O(n4 log4n) |
| SVM (L) | O(2n3logn) | O(2n3logn) | O(2n4log2n) | O(2n4log4n) |
| SVM (Poly) | O(2n3log2n) | O(2n3log2n) | O(2n4log4n) | O(2n4log8n) |
| SVM (RBF) | O(2n4log2n) | O(2n4log2n) | O(2n5log4n) | O(2n5log8n) |
| Classifiers | DR Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bessel Function | Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) | Least Square Linear Regression (LSLR) | Artificial Algae Algorithm (AAA) | |
| NLR | O(n4logn) | O(n4logn) | O(n5log2n) | O(n5log4n) |
| LR | O(n4logn) | O(n4logn) | O(n5log2n) | O(n5log4n) |
| GMM | O(n4log2n) | O(n4log2n) | O(n5log2n) | O(n5log4n) |
| EM | O(n5 logn) | O(n5 logn) | O(n5log2n) | O(n5log4n) |
| BLDC | O(n5 logn) | O(n5 logn) | O(2n5 log2n) | O(2n5 log4n) |
| LoR | O(2n4logn) | O(2n4logn) | O(2n5log2n) | O(2n5log4n) |
| SDC | O(n5 logn) | O(n5 logn) | O(n6 log2n) | O(n6 log4n) |
| SVM (L) | O(2n5logn) | O(2n5logn) | O(2n6log2n) | O(2n6log4n) |
| SVM (Poly) | O(2n5log2n) | O(2n5log2n) | O(2n6log4n) | O(2n6log8n) |
| SVM (RBF) | O(2n6log2n) | O(2n6log2n) | O(2n7log4n) | O(2n7log8n) |
| Classifiers | DR Method | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bessel Function | Discrete Cosine Transform (DST) | Least Square Linear Regression (LSLR) | Artificial Algae Algorithm (AAA) | |
| NLR | O(4n3logn) | O(4n3logn) | O(4n4log2n) | O(4n4log4n) |
| LR | O(4n3logn) | O(4n3logn) | O(4n4log2n) | O(4n4log4n) |
| GMM | O(4n3log2n) | O(4n3log2n) | O(4n4log2n) | O(4n4log4n) |
| EM | O(4n4 logn) | O(4n4 logn) | O(4n4log2n) | O(4n4log4n) |
| BLDC | O(4n4 logn) | O(4n4 logn) | O(8n4 log2n) | O(8n4 log4n) |
| LoR | O(8n3logn) | O(8n3logn) | O(8n5log2n) | O(8n5log4n) |
| SDC | O(4n4 logn) | O(4n4 logn) | O(4n5 log2n) | O(4n5 log4n) |
| SVM (L) | O(8n4logn) | O(8n4logn) | O(8n5log2n) | O(8n5log4n) |
| SVM (Poly) | O(8n4log2n) | O(8n4log2n) | O(8n5log4n) | O(8n5log8n) |
| SVM (RBF) | O(8n5log2n) | O(8n5log2n) | O(8n6log4n) | O(8n6log8n) |
| S.No | Author (with year) | Description of the Population |
Data Sampling |
Machine Learning Parameter |
Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maniruzzaman et al. (2017) [44] | PIDD – (PIMA Indian diabetic dataset) | Cross-validation K2, K4, K5, K10, and JK |
LDA, QDA, NB, GPC, SVM, ANN, AB, LoR, DT, RF |
ACC: 92 | |
| Pham et al. (2017) [45] | Diabetes: 12,000 age between 18–100 Age (Mean): 73 |
Training set - 66% ; tuning set 17% ; test set -17% |
RNN, CLST Memory (C-LSTM) | ACC - 79 | |
| Hertroijs et al. (2018) [46] | Total: 105814 age(mean) : greater than 18 | Training set (90%) test set (10%) 5-fold cross-validation |
Latent Growth Mixture Modelling (LGMM) | ACC: 92.3 | |
| ArellanoCampos et al. (2019) [47] | Base L: 7636 follow: 6144 diabetes: 331 age: 32–54 |
K=10 - Cross-validation and bootstrapping Model | Cox proportional hazard regression | ACC: 75 | |
| Deo et al. (2019) [48] | Total: 140 diabetes: 14 imbalanced age: 12–90 | Training set (70%) test set (30%) fivefold cross-validation, holdout validation |
BT, SVM (L) | ACC: 91 | |
| Choi et al. (2019) [49] | Total: 8454 diabetes: 404 age: 40–72 |
10-fold cross-validation | LoR, LDA, QDA, KNN |
ACC: 78, 77 76, 77 |
|
| Akula et al. (2019) [50] | PIDD Practice Fusion Dataset total: 10,000 Age between : 18–80 |
Training set: 800; test set:10,000 |
KNN, SVM, DT, RF, GB, NN, NB |
ACC: 86 |
|
| Xie et al. (2019) [51] | Total: 138,146 diabetes: 20,467 age: 30–80 |
Training set is around 67% and test set is around 33% |
SVM, DT, LoR, RF, NN, NB | ACC: 81, 74, 81, 79, 82, 78 | |
| Bernardini et al. (2020) [52] | Total: 252 diabetes: 252 age: 54–72 |
10-fold cross-validation | Multiple instance learning boosting |
ACC: 83 |
|
| Zhang et al. (2020) [53] | Total: 36,652 age: 18–79 | 10-fold cross-validation | LoR, classification, and regression tree, GB, ANN, RF, SVM |
ACC : 75, 80, 81, 74, 86, 76 |
|
| Jain et al. (2020) [54] | Control: 500 diabetes: 268 age: 21–81 |
Training set is around 70% test set is around 30% |
SVM, RF, k-NN | ACC: 74, 74, 76 | |
| Kalagotla et al. (2021) [55] | Pima Indian data set | Hold out k-fold cross-validation | Stacking multi-layer perceptron, SVM, LoR | ACC: 78 | |
| Haneef et al. (2021) [56] | Total 44,659 age 18–69 data is imbalanced | Training set (80%) test set (20%) |
LDA | ACC: 67 | |
| Deberneh et al. (2021) [57] | Total: 535,169 diabetes: 4.3% prediabetes: 36% age: 18–108 |
10-fold cross-validation | RF,SVM, XGBoost | ACC: 73, 73, 72 | |
| Zhang et al. (2021) [58] | Total: 37,730 diabetes: 9.4% age: 50–70 Imbalanced |
Training set is around 80% test set is around 20% 10-fold cross-validation |
Bagging boosting, GBT, RF, GBM | ACC: 82 | |
| This article | Nordic islet transplantation programme | 10-fold cross-validation | Bessel Function, DCT, LSLR and AAA | 95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





