Submitted:
09 August 2023
Posted:
10 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Wild Mallards Fecal Sample Collection
2.2. Domestic Mallards Fecal Sample Collection
2.3. Fecal DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.4. Mixing and Purification of PCR Products
2.5. Libraries Generated and IIIumina NovaSeq Sequencing
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. 16S rRNA Gene Data
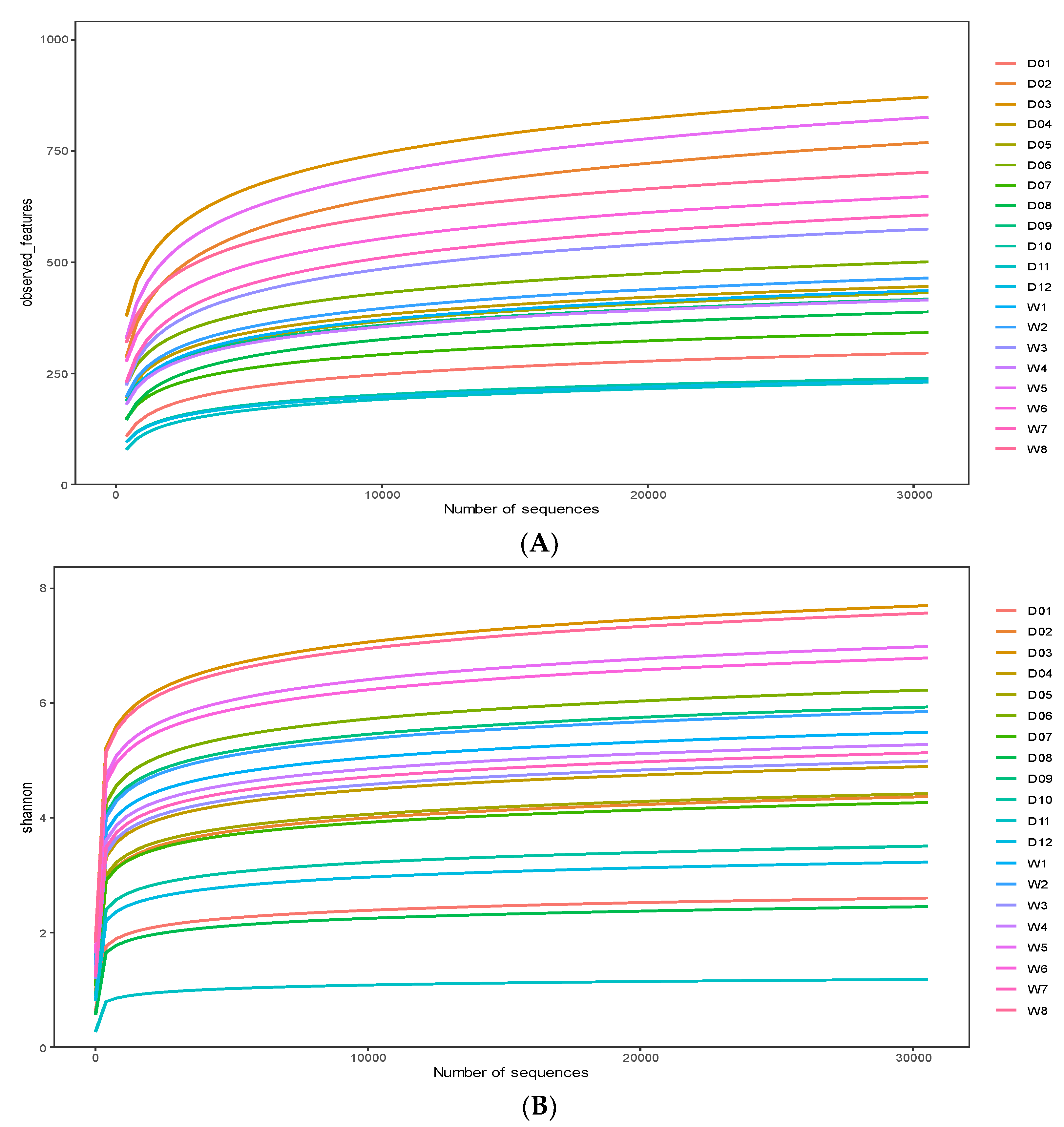
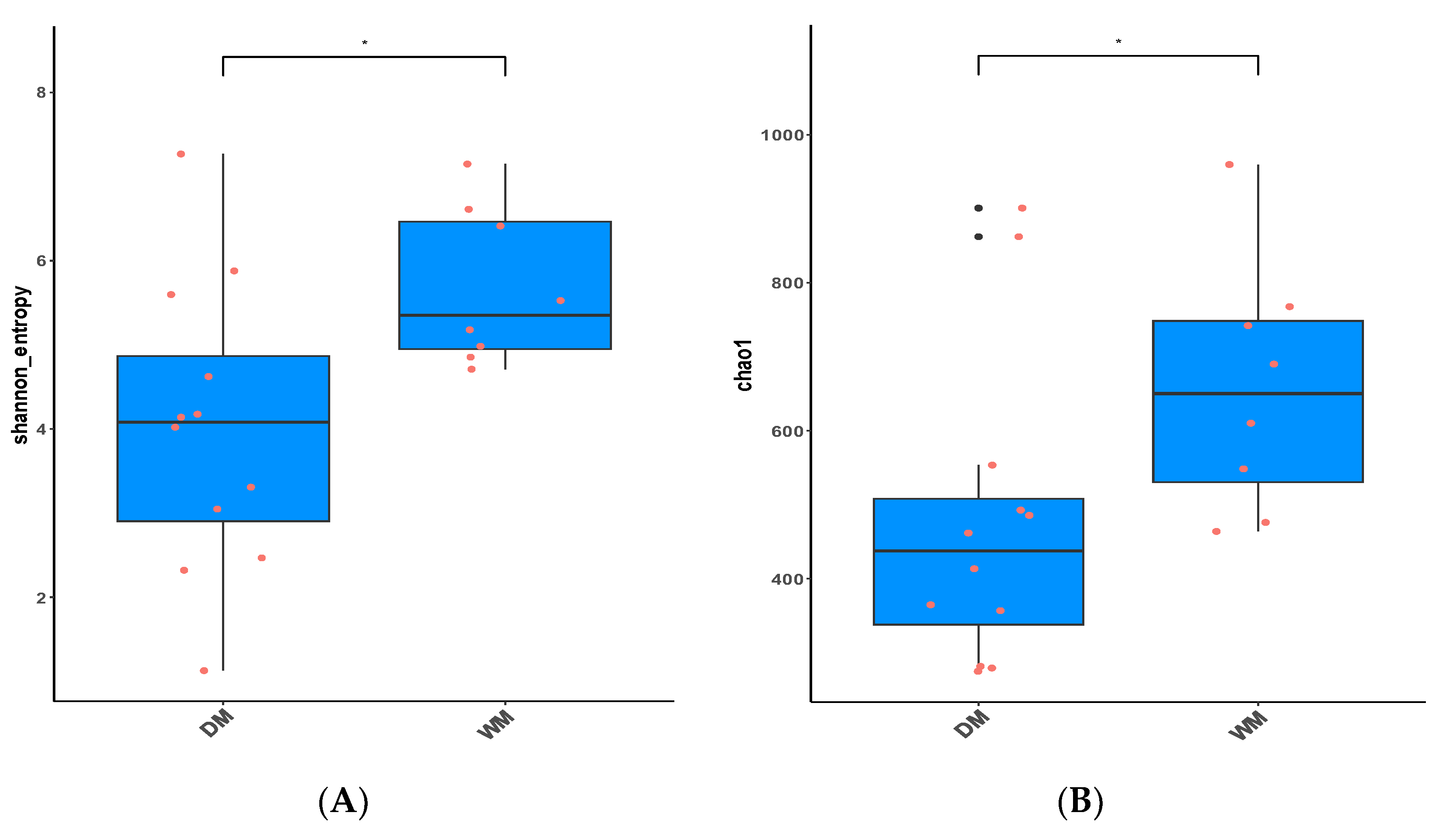
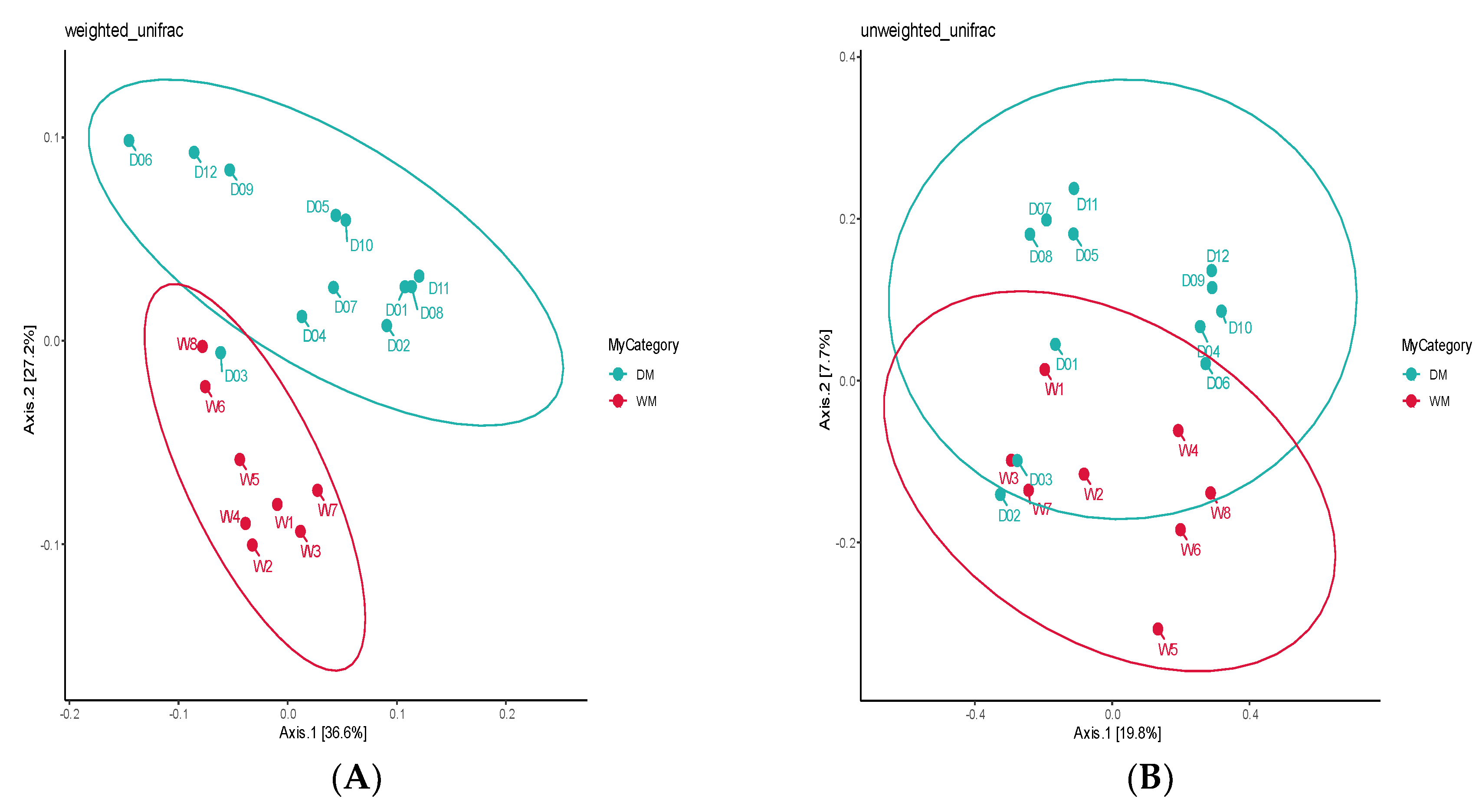
3.2. Alpha Diversity and Beta Diversity Analyses
3.3. Comparison of The Intestinal Microflora of Two Groups of Mallards at The Phylum and Genus Levels
3.4. Prediction of Gut Microbiome Function
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grond, K.; Sandercock, B.K.; Jumpponen, A.; Zeglin, L.H. The avian gut microbiota: community, physiology and function in wild birds. J. Avian Biol. 2018, 49, e01788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, Peter J.; Gordon, Jeffrey I. The core gut microbiome, energy balance and obesity. Journal of Physiology-London 2009, 587, 4153–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolis, K.G.; Gershon, M.D.; Bogunovic, M. Cellular Organization of Neuroimmune Interactions in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahern, P.P.; Faith, J.J.; Gordon, J.I. Mining the Human Gut Microbiota for Effector Strains that Shape the Immune System. Immunity 2014, 40, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanmiguel, C.; Gupta, A.; Mayer, E.A. Gut Microbiome and Obesity: A Plausible Explanation for Obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pevsner-Fischer, M.; Tuganbaev, T.; Meijer, M.; Zhang, S.-H.; Zeng, Z.-R.; Chen, M.-H.; Elinav, E. Role of the microbiome in non-gastrointestinal cancers. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 7, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forslund, K.; Hildebrand, F.; Nielsen, T.; Falony, G.; Le Chatelier, E.; Sunagawa, S.; Prifti, E.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Pedersen, H.K.; et al. Disentangling type 2 diabetes and metformin treatment signatures in the human gut microbiota. Nature 2015, 528, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montiel-Castro, A.J.; González-Cervantes, R.M.; Bravo-Ruiseco, G.; Pacheco-López, G. The microbiota-gut-brain axis: neurobehavioral correlates, health and sociality. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prum, R.O.; Berv, J.S.; Dornburg, A.; Field, D.J.; Townsend, J.P.; Lemmon, E.M.; Lemmon, A.R. A comprehensive phylogeny of birds (Aves) using targeted next-generation DNA sequencing. Nature 2015, 526, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Amado, M.A.; Shin, H.; Sanz, V.; Lentino, M.; Martínez, L.M.; Contreras, M.; Michelangeli, F.; Domínguez-Bello, M.G. Comparison of gizzard and intestinal microbiota of wild neotropical birds. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0194857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Rodriguez, Magdalena. ; Martin-Vivaldi, Manuel.; Martinez-Bueno, Manuel.; Jose Soler, Juan. Gut Microbiota of Great Spotted Cuckoo Nestlings is a Mixture of Those of Their Foster Magpie Siblings and of Cuckoo Adults. Genes 2018, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Eckburg, P.B.; Bik, E.M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Purdom, E.; Dethlefsen, L.; Sargent, M.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Relman, D.A. Diversity of the Human Intestinal Microbial Flora. Science 2005, 308, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Cao, L. Characterising the interspecific variations and convergence of gut microbiota in Anseriformes herbivores at wintering areas. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Xue, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, G.; Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Cao, H.; et al. A phylo-functional core of gut microbiota in healthy young Chinese cohorts across lifestyles, geography and ethnicities. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, D.C.; Tun, H.M.; Kim, J.E.; Leung, F.C.; Cheng, K.M. Characterization of cecal microbiota of the emu (Dromaius novaehollandiae). Veter- Microbiol. 2013, 166, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zheng, S.; Sharshov, K.; Cao, J.; Sun, H.; Yang, F.; Wang, X.; Li, L. Distinctive gut microbial community structure in both the wild and farmed Swan goose (Anser cygnoides). J. Basic Microbiol. 2016, 56, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Cao, J.; Li, J.-R.; Yang, F.; Li, Z.; Li, L.-X. Comparative analysis of the gastrointestinal microbial communities of bar-headed goose (Anser indicus) in different breeding patterns by high-throughput sequencing. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 182, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; He, X.; Valitutto, M.; Chen, L.; Xu, Q.; Yao, Y.; Hou, R.; Wang, H. Gut microbiota composition and metabolomic profiles of wild and captive Chinese monals (Lophophorus lhuysii). Frontiers in Zoology. 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Xia, P.; Wang, H.; Yu, H.; Giesy, J.P.; Zhang, Y.; Mora, M.A.; Zhang, X. Effects of captivity and artificial breeding on microbiota in feces of the red-crowned crane (Grus japonensis). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-F.; Zhu, W.-Q.; Song, W.-T.; Shu, J.-T.; Han, W.; Chen, K.-W. Origin and genetic diversity of Chinese domestic ducks. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2010, 57, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, V.L.; Tan, C.L.; Knight, R.; Amato, K.R. Effect of preservation method on spider monkey (Ateles geoffroyi) fecal microbiota over 8weeks. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 113, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterino, M.S.; Cho, S.; Sperling, F.A.H. The Current State Of Insect Molecular Systematics: A Thriving Tower of Babel. Annu. Rev. Èntomol. 2000, 45, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grond, K.; Lanctot, R.B.; Jumpponen, A.; Sandercock, B.K. Recruitment and establishment of the gut microbiome in arctic shorebirds. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hird, S.M.; Carstens, B.C.; Cardiff, S.W.; Dittmann, D.L.; Brumfield, R.T. Sampling locality is more detectable than taxonomy or ecology in the gut microbiota of the brood-parasitic Brown-headed Cowbird (Molothrus ater). PeerJ 2014, 2, e321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; Hussain, R.; Lu, H.; Ye, Y.; Mehmood, K.; Zhang, H.; Shang, P. First Report of Fecal Microflora of Wild Bar-Headed Goose in Tibet Plateau. Front. Veter- Sci. 2022, 8, 791461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, G. Comparative Analysis of the Fecal Bacterial Microbiota of Wintering Whooper Swans (Cygnus Cygnus). Front. Veter- Sci. 2021, 8, 670645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, F.; Li, L.; Wang, A.; Sharshov, K.; Druzyaka, A.; Lancuo, Z.; Wang, S.; Shi, Y. Characterization of the gut microbiome of black-necked cranes (Grus nigricollis) in six wintering areas in China. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy-Vitorino, F.; Ley, R.E.; Gao, Z.; Pei, Z.; Ortiz-Zuazaga, H.; Pericchi, L.R.; Garcia-Amado, M.A.; Michelangeli, F.; Blaser, M.J.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. Bacterial Community in the Crop of the Hoatzin, a Neotropical Folivorous Flying Bird. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 5905–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D'Andreano, S.; Bonastre, A.S.; Francino, O.; Marti, A.C.; Lecchi, C.; Grilli, G.; Giovanardi, D.; Ceciliani, F. GENETICS AND GENOMICS Gastrointestinal microbial population of turkey (Meleagris gallopavo) affected by hemorrhagic enteritis virus. Poultry Science. 2017, 96, 3550–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumpertz, R.; Le, D.S.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Trinidad, C.; Bogardus, C.; Gordon, J.I.; Krakoff, J. Energy-Balance Studies Reveal Associations between Gut Microbes, Caloric Load, and Nutrient Absorption in Humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Bäckhed, F.; Fulton, L.; Gordon, J.I. Diet-Induced Obesity Is Linked to Marked but Reversible Alterations in the Mouse Distal Gut Microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.D.; Ma, G.; Cai, J.; Fu, Y.; Yan, X.Y.; Wei, X.B.; Zhang, R.J. Effects of Clostridium butyricum on growth performance, antioxidation, and immune function of broilers. Poultry Science. 2015, 94, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Yun, T.T.; Qi, W.T.; Liang, X.X.; Wang, Y.W.; Li, A.K. Effects of pre-encapsulated and pro-encapsulated Enterococcus faecalis on growth performance, blood characteristics, and cecal microflora in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 2821–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.-P.; Wang, Y.-B.; Huang, S.-W.; Lin, C.-Y.; Wu, M.; Hsieh, C.-H.; Yu, H.-T. Metagenomic analysis reveals a functional signature for biomass degradation by cecal microbiota in the leaf-eating flying squirrel (Petaurista alborufus lena). BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 466–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.K.; Torok, V.A.; Percy, N.J.; Abimosleh, S.M.; Howarth, G.S. Microbial fingerprinting detects unique bacterial communities in the faecal microbiota of rats with experimentally-induced colitis. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Lifeng.; Wu, Qi.; Dai, Jiayin.; Zhang, Shanning.; Wei, Fuwen. Evidence of cellulose metabolism by the giant panda gut microbiome. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2011. 108(43): p. 17714-17719.
- Liu, Y.-J.; Liu, S.-J.; Drake, H.L.; Horn, M.A. Alphaproteobacteria dominate active 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicide degraders in agricultural soil and drilosphere. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 991–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominianni, C.; Sinha, R.; Goedert, J.J.; Pei, Z.; Yang, L.; Hayes, R.B.; Ahn, J. Sex, Body Mass Index, and Dietary Fiber Intake Influence the Human Gut Microbiome. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0124599–e0124599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Jing, H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Zu, R.; Luo, L.; et al. , Human Streptococcus suis outbreak, Sichuan, China. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 2006, 12, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, C.; Alonso, C.A.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Leon-Sampedro, R.; Del, C.R. .; Coque, T.M. Antimicrobial Resistance in Enterococcus spp. of animal origin. Microbiology spectrum. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, C.A.; Murray, B.E. The rise of the Enterococcus: beyond vancomycin resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, K.; Phillips, C. The ecology, epidemiology and virulence of Enterococcus. Microbiology 2009, 155, 1749–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łopińska, A.; Indykiewicz, P.; Skiebe, E.; Pfeifer, Y.; Trček, J.; Jerzak, L.; Minias, P.; Nowakowski, J.; Ledwoń, M.; Betleja, J.; et al. Low Occurrence of Acinetobacter baumannii in Gulls and Songbirds. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2020, 69, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francey, T.; Gaschen, F.; Nicolet, J.; Burnens, A.P. The Role of Acinetobacter baumannii as a Nosocomial Pathogen for Dogs and Cats in an Intensive Care Unit. J. Veter- Intern. Med. 2000, 14, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardabassi, L.; Dalsgaard, A.; Olsen, J.E. Phenotypic characterization and antibiotic resistance of Acinetobacter spp. isolated from aquatic sources. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 87, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doughari, H.J.; Ndakidemi, P.A.; Human, I.S.; Benade, S. The Ecology, Biology and Pathogenesis of Acinetobacter spp.: An Overview. Microbes Environ. 2011, 26, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Jayasudha, R.; Chakravarthy, S.; Prashanthi, G.S.; Bhargava, A.; Tyagi, M.; Rani, P.K.; Pappuru, R.R.; Sharma, S.; Shivaji, S. Alterations in the gut bacterial microbiome in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus and diabetic retinopathy. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Han, S.; Lu, N.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Xiong, G.; Guo, L. Degradation of Oestrogen and an Oestrogen-like Compound in Chicken Faeces by Bacteria. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opota, O.; Ney, B.; Zanetti, G.; Jaton, K.; Greub, G.; Prod'hom, G. Bacteremia Caused by Comamonas kerstersii in a Patient with Diverticulosis. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 2014, 52, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Ma, R.; Chai, L.; Du, Q.; Yang, R.; Qi, R.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Zhan, K. Determination of bacterial abundance and communities in the nipple drinking system of cascading cage layer houses. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin, P.; Tang, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Xia, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, H.; Zhu, G. Intestinal microbiota mediates Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-induced diarrhea in piglets. BMC Veter- Res. 2018, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales F, Camila, I. ; Colombo F, Alicia, A.; Camara, N.O.S. Inflammatory diseases modelling in zebrafish. World journal of experimental medicine 2016, 6, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Shuling, N.; Kunyuan, T.; Qiuyang, Z.; Hewen, D.; ChenCheng, G.; Tianhe, Y.; Liancheng, L.; Xin, F. Characteristics of the intestinal flora of specific pathogen free chickens with age. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajoka, M.S.R.; Wu, Y.; Mehwish, H.M.; Bansal, M.; Zhao, L. Lactobacillus exopolysaccharides: New perspectives on engineering strategies, physiochemical functions, and immunomodulatory effects on host health. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
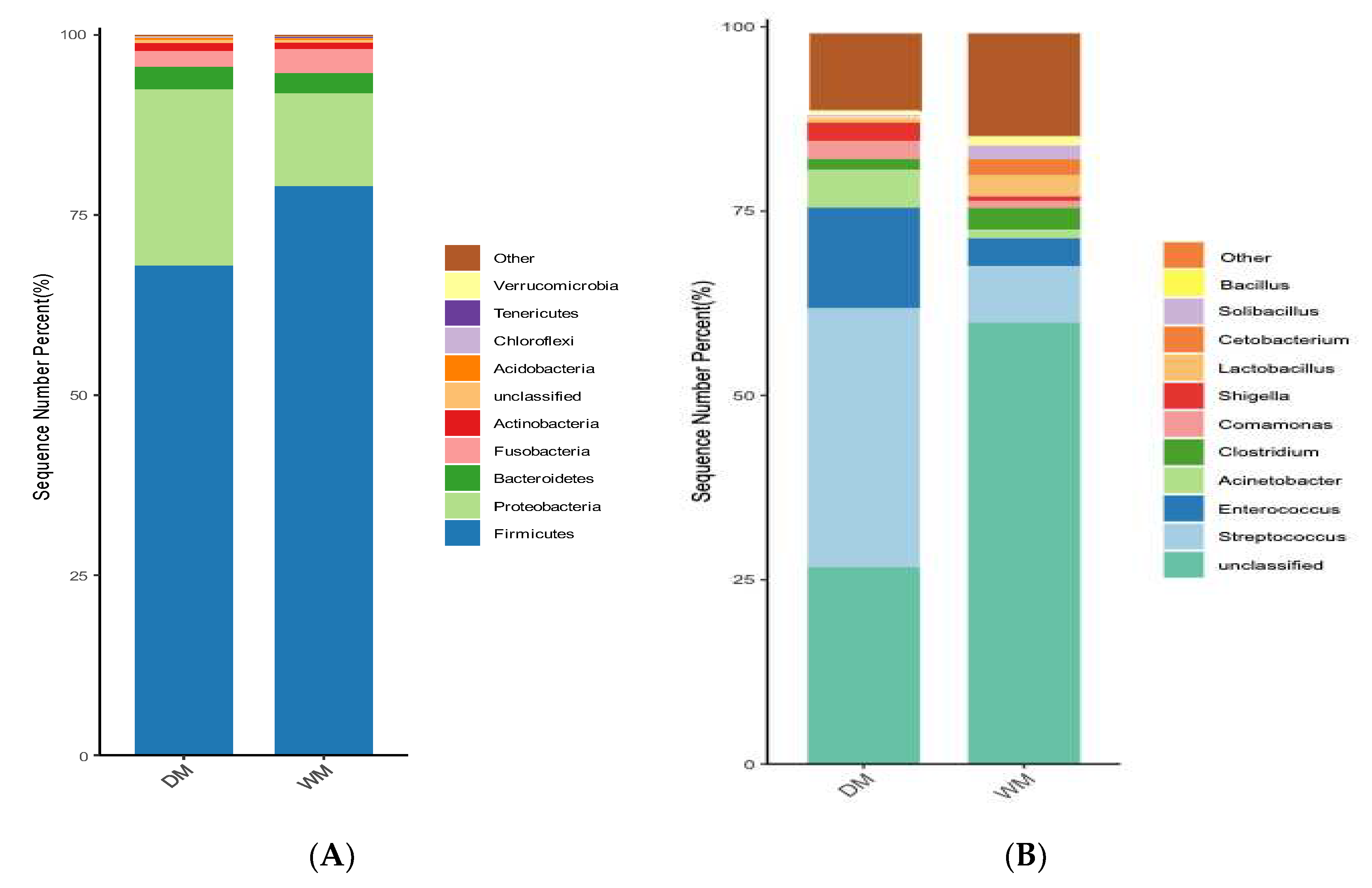
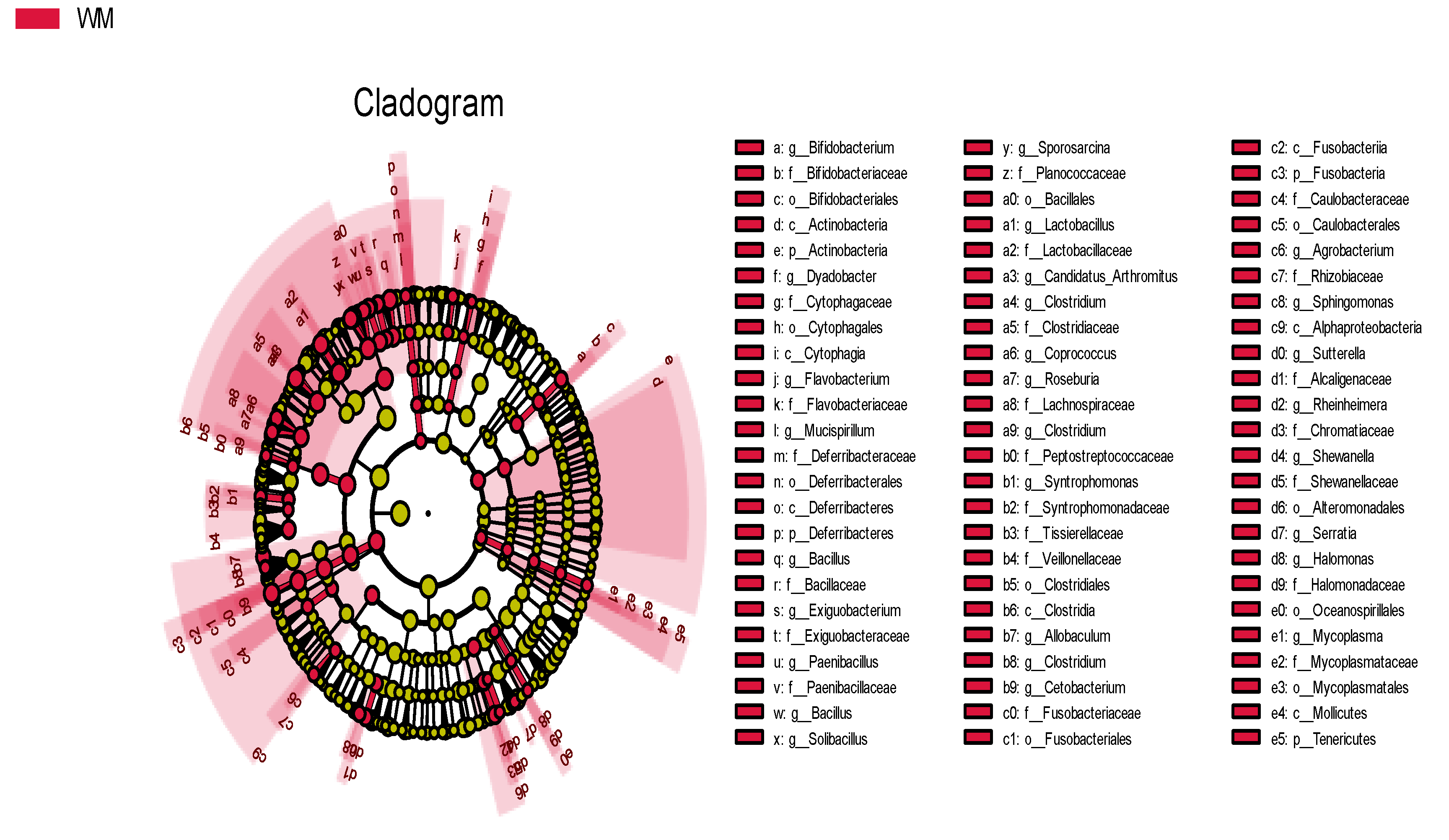
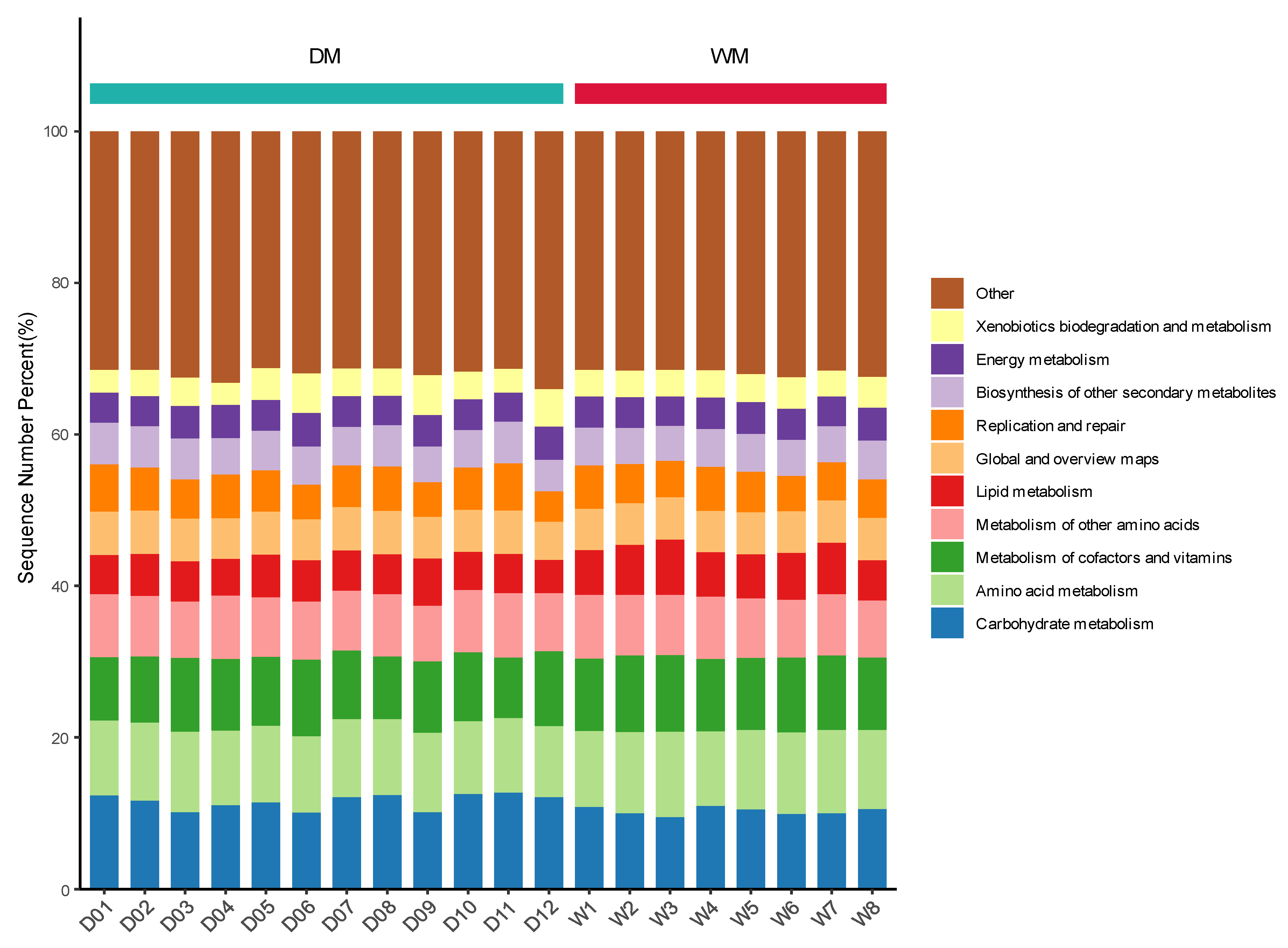
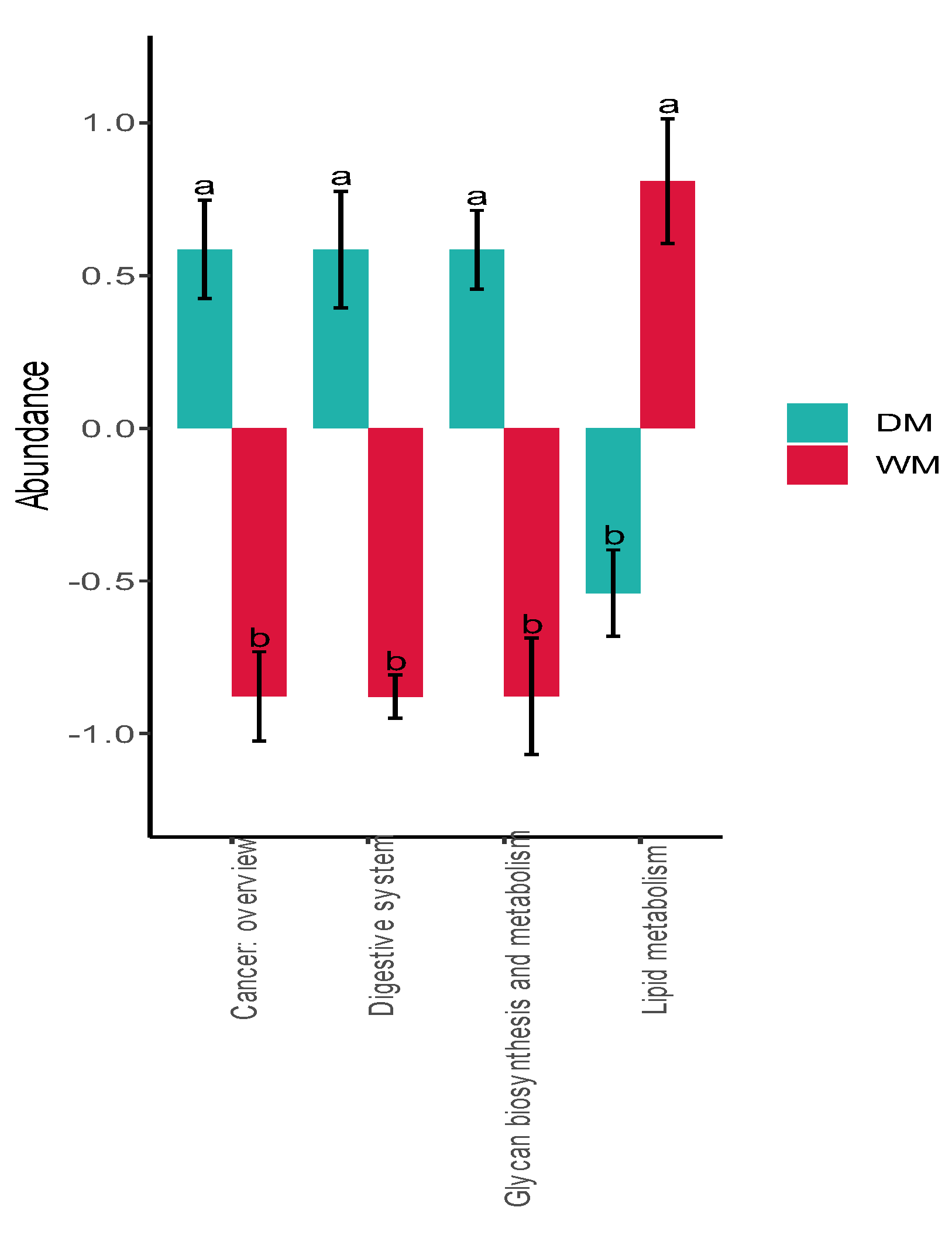
| Category | Firmicutes | Proteobacteria | Bacteroidetes | Fusobacteria | Actinobacteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WM | 79.02% | 12.85% | 2.79% | 3.37% | — |
| DM | 67.97% | 24.48% | 3.13% | 2.21% | 1.10% |
| Phylum | Genus | DM | WM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Firmicutes | Streptococcus | 35.07% | 7.62% |
| Enterococcus | 13.67% | 3.80% | |
| Clostridium | 1.53% | 2.96% | |
| Lactobacillus | — | 2.83% | |
| Solibacillus | — | 1.87% | |
| Bacillus | — | 1.28% | |
| Proteobacteria | Acinetobacter | 5.09% | 1.16% |
| Comamonas | 2.37% | — | |
| Shigella | 2.50% | — | |
| Fusobacteria | Cetobacterium | — | 2.22% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





