Submitted:
08 August 2023
Posted:
08 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Field measurements of over-track buildings in metro depots
2.1. Site introductions
2.2. Field measurement setups
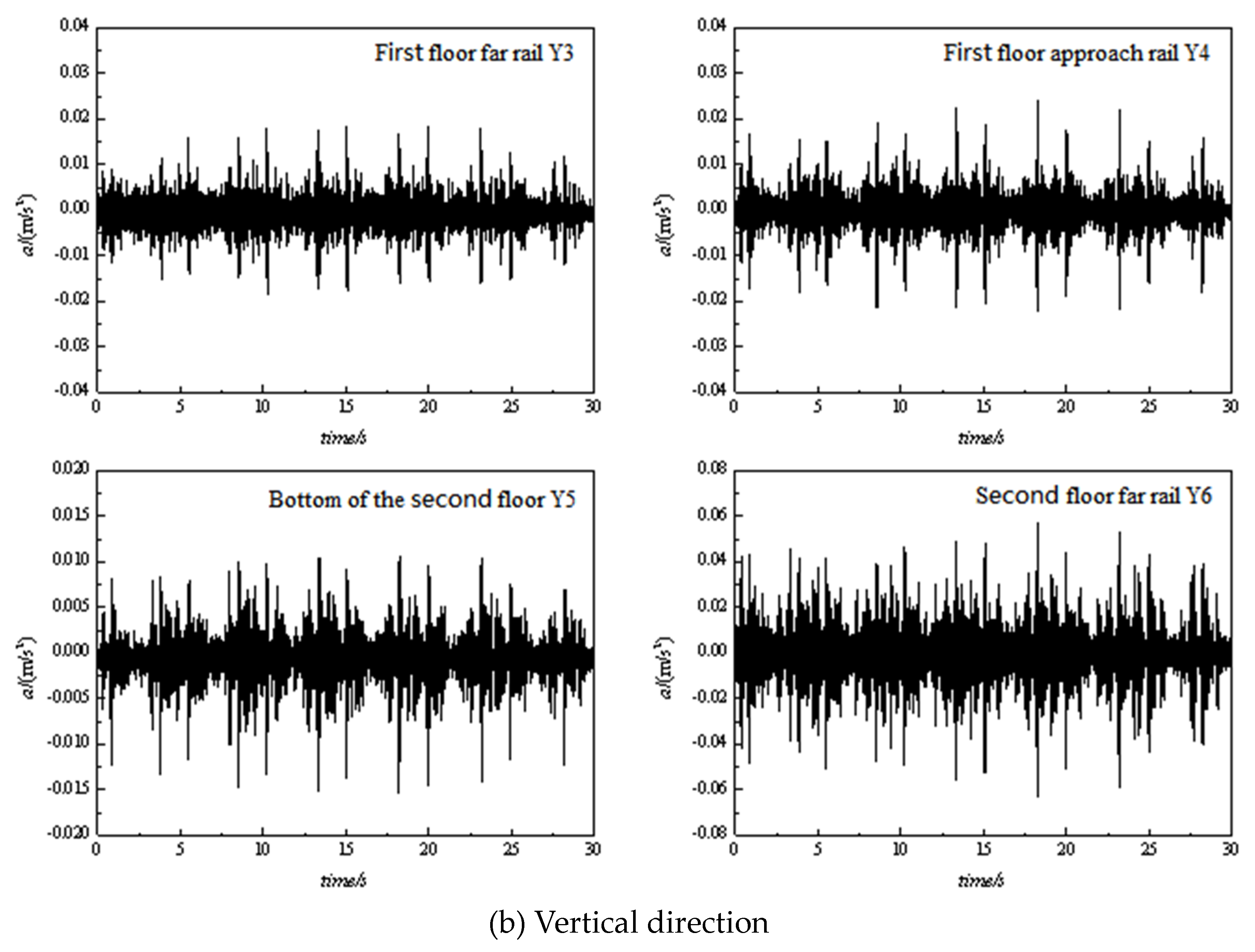
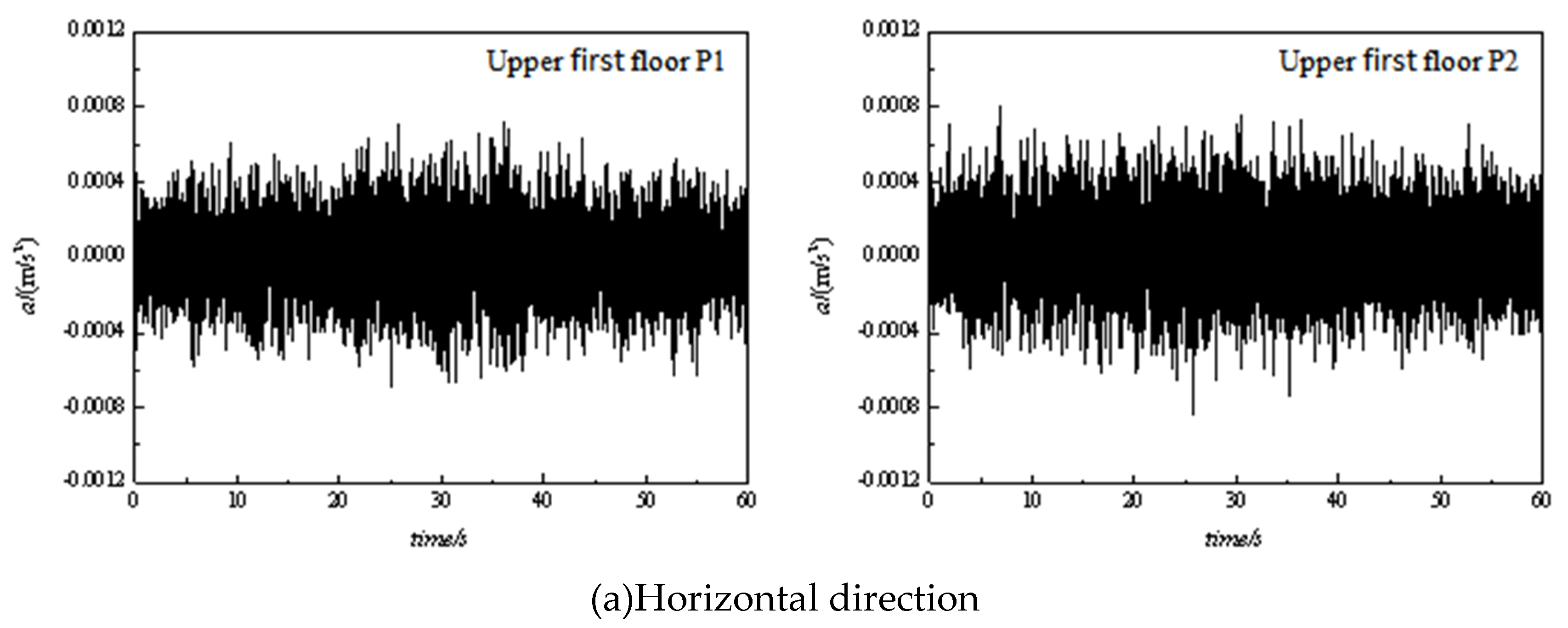
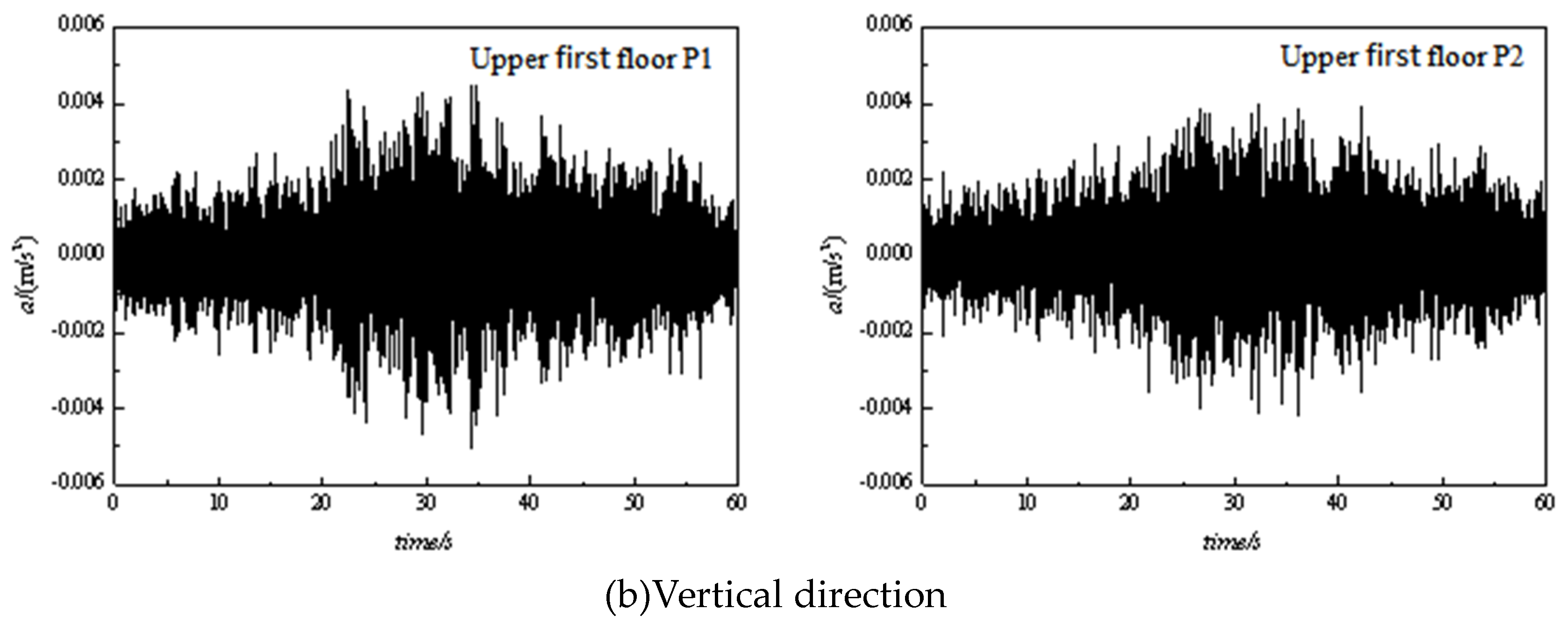
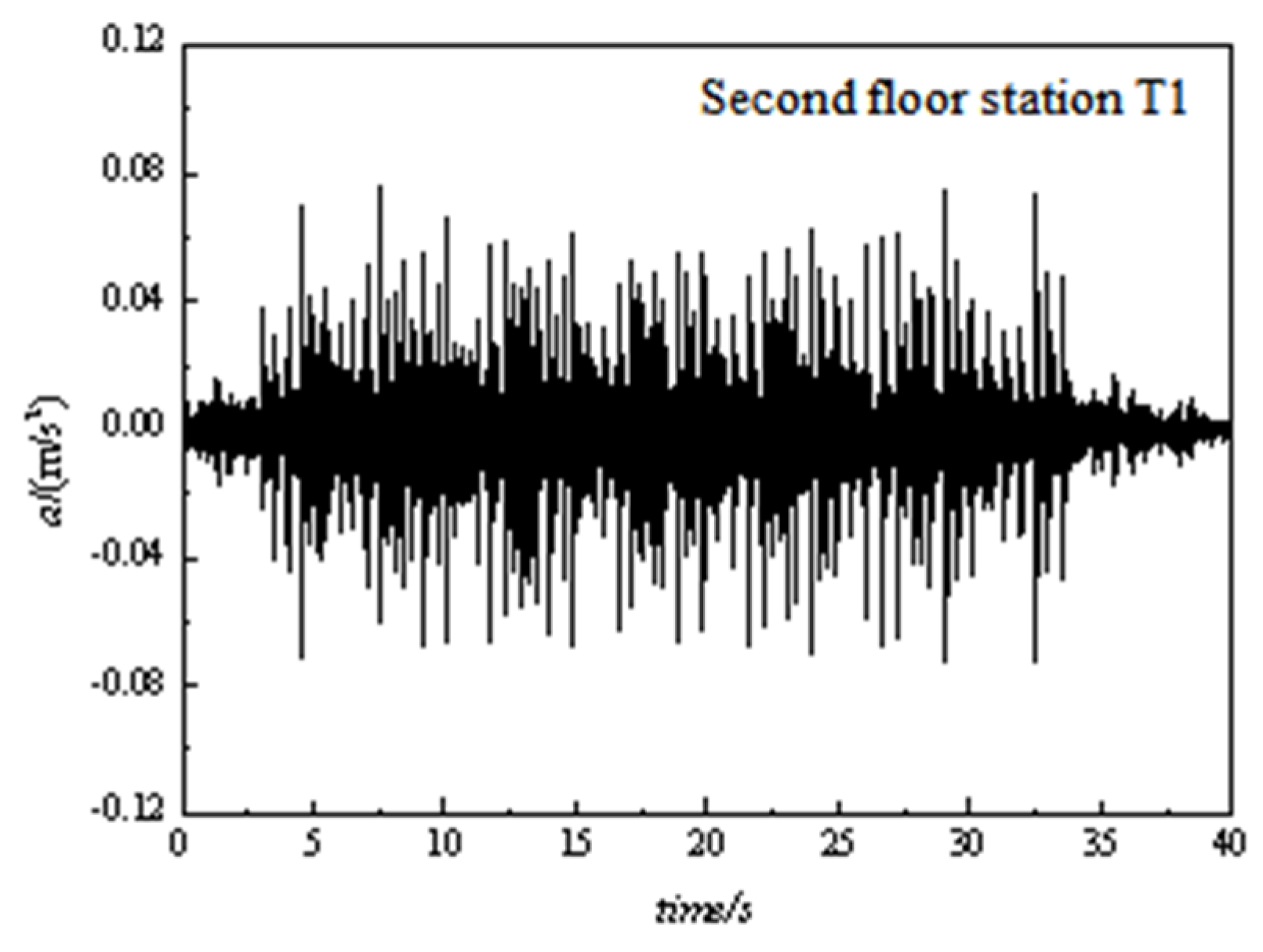
3. Measurement data analysis and comparisons
3.1. Time domain analysis
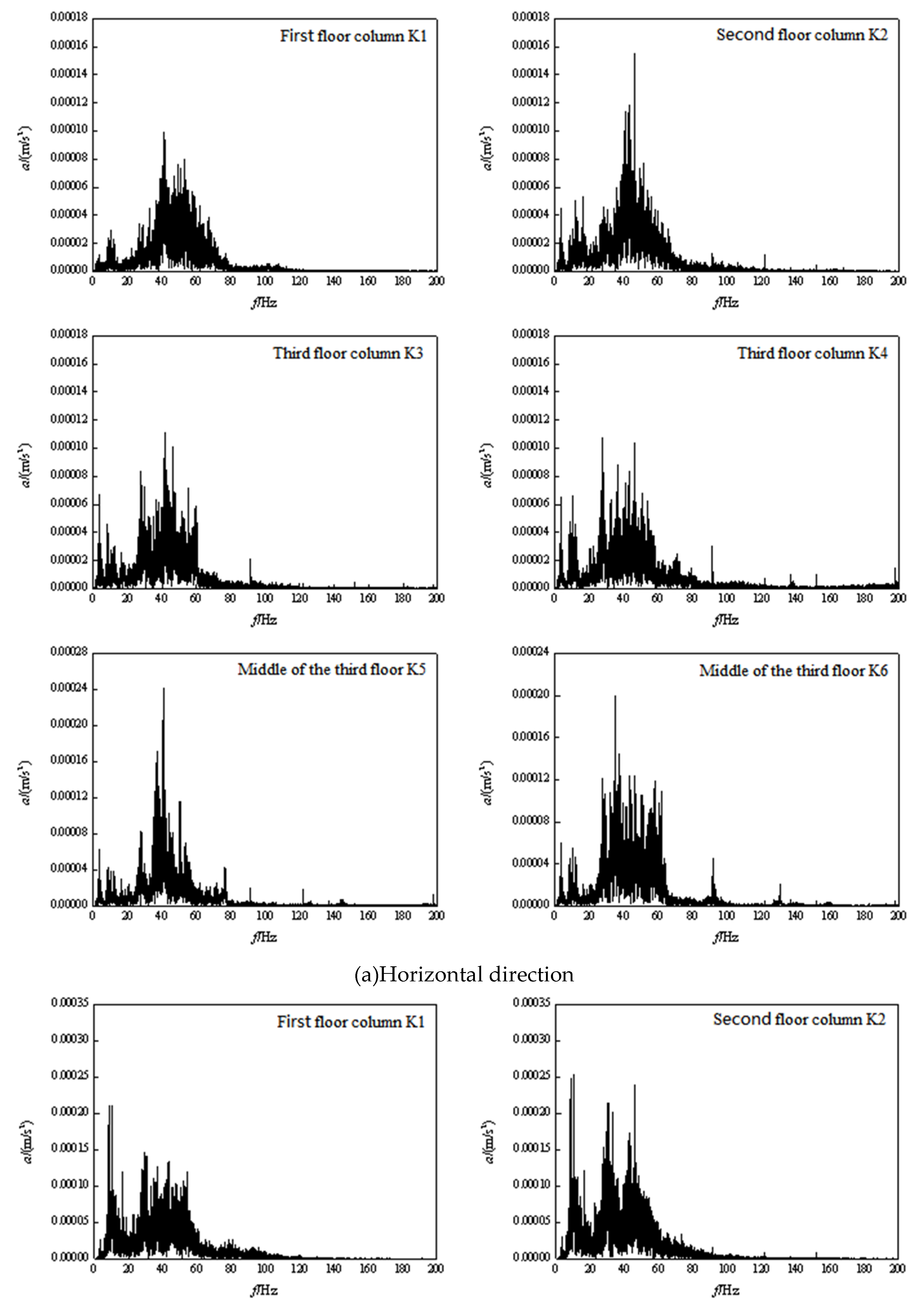
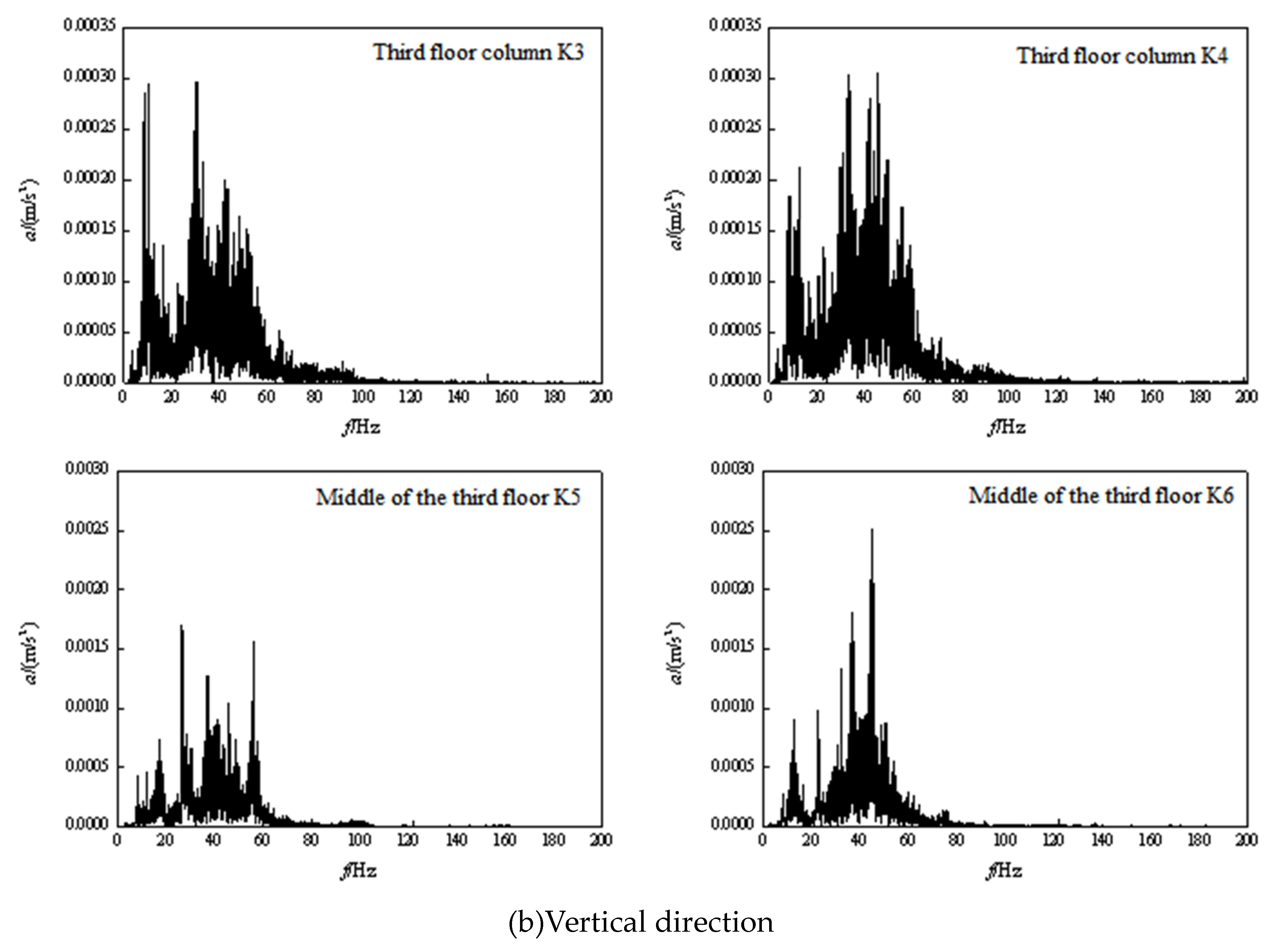
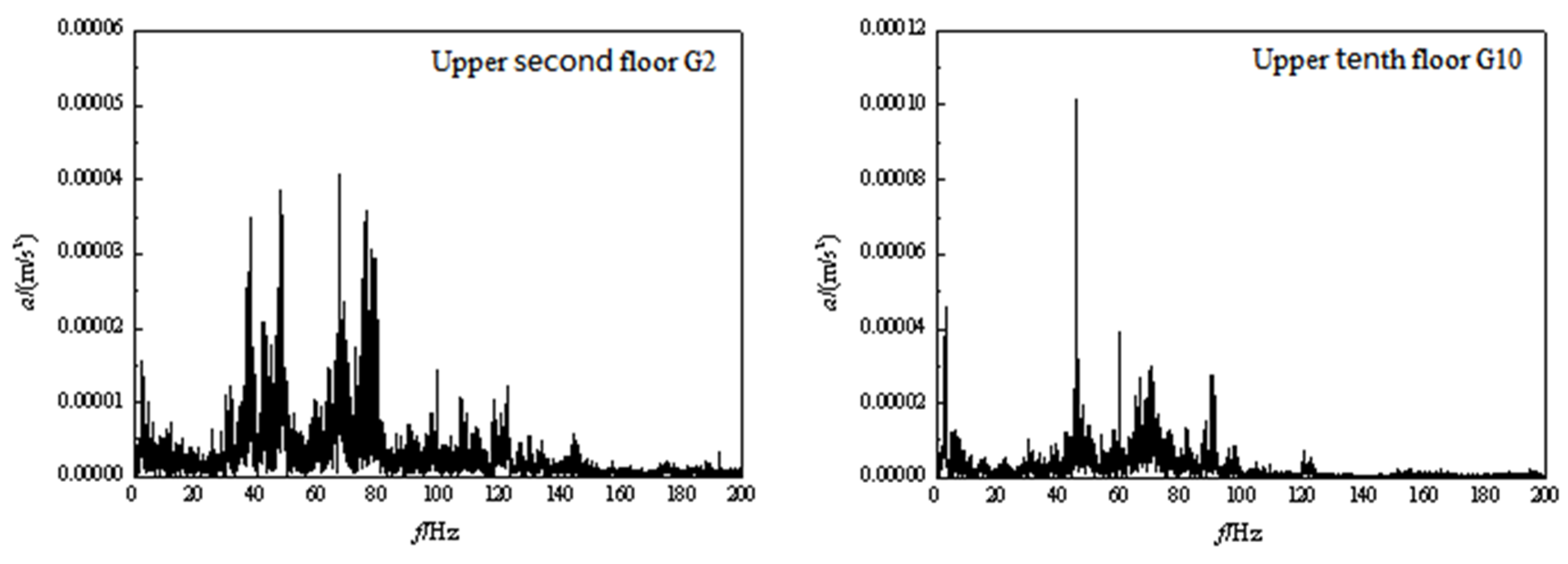
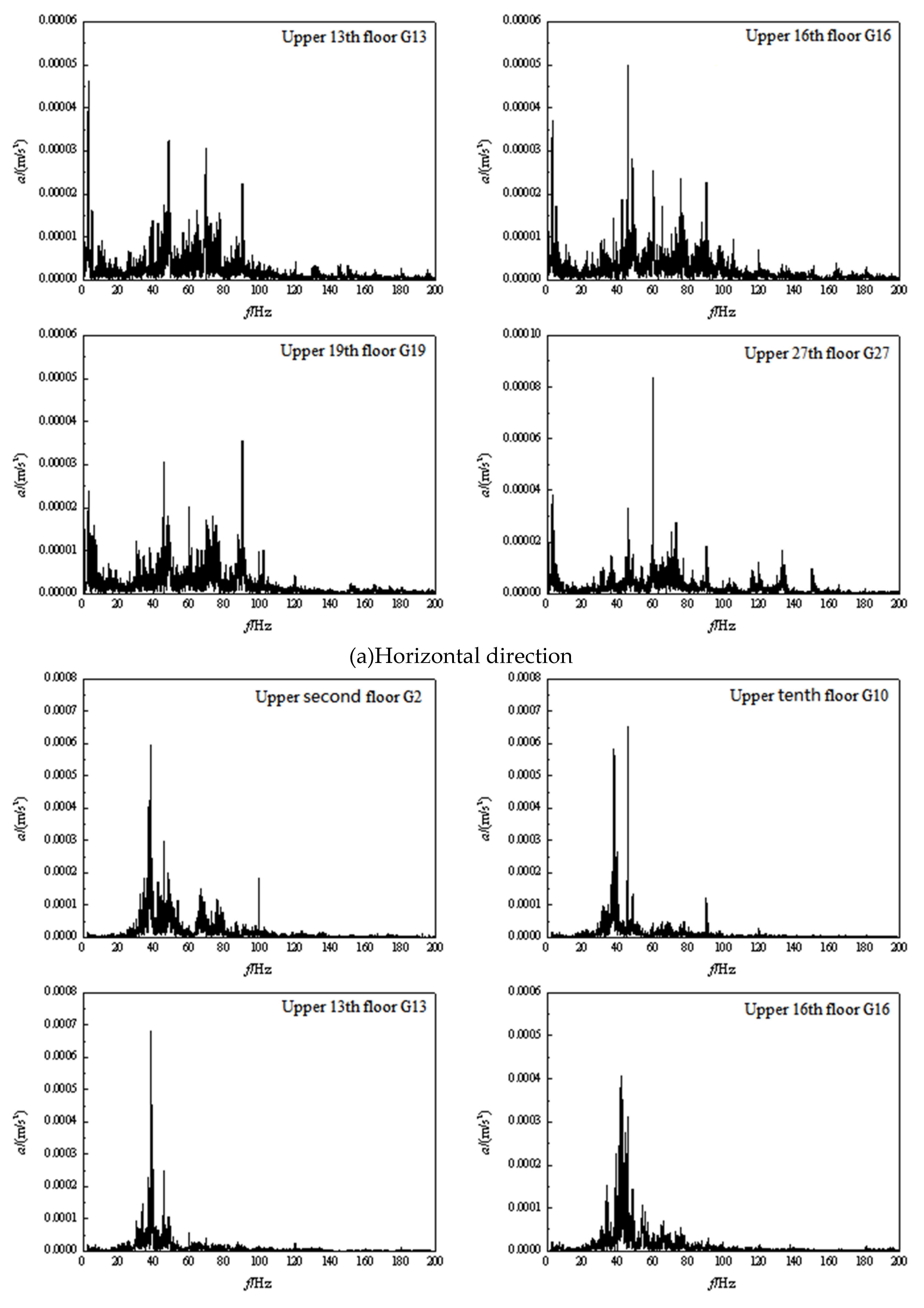
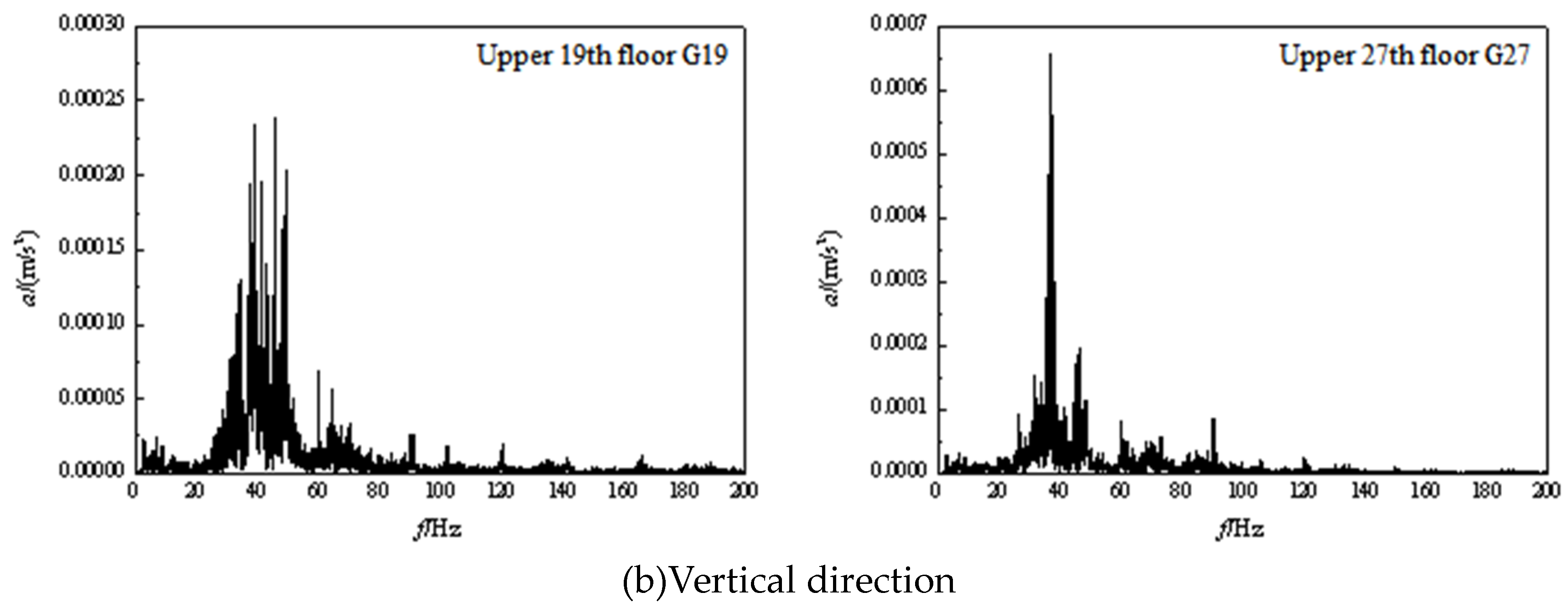
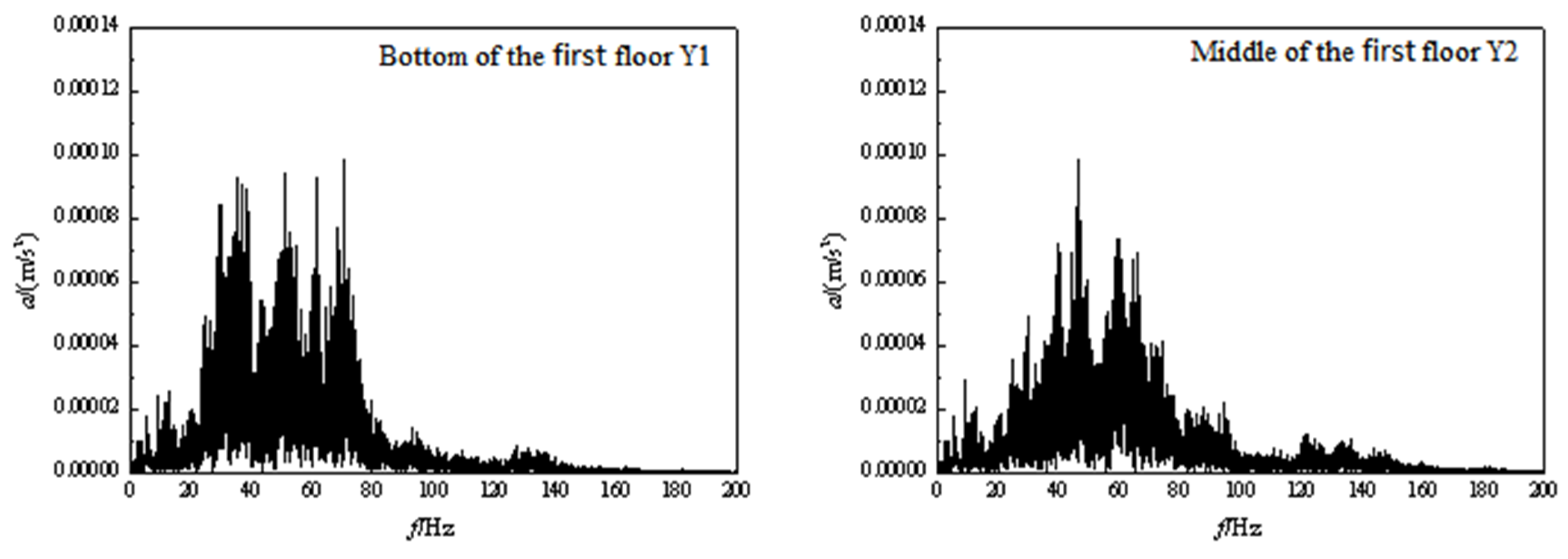
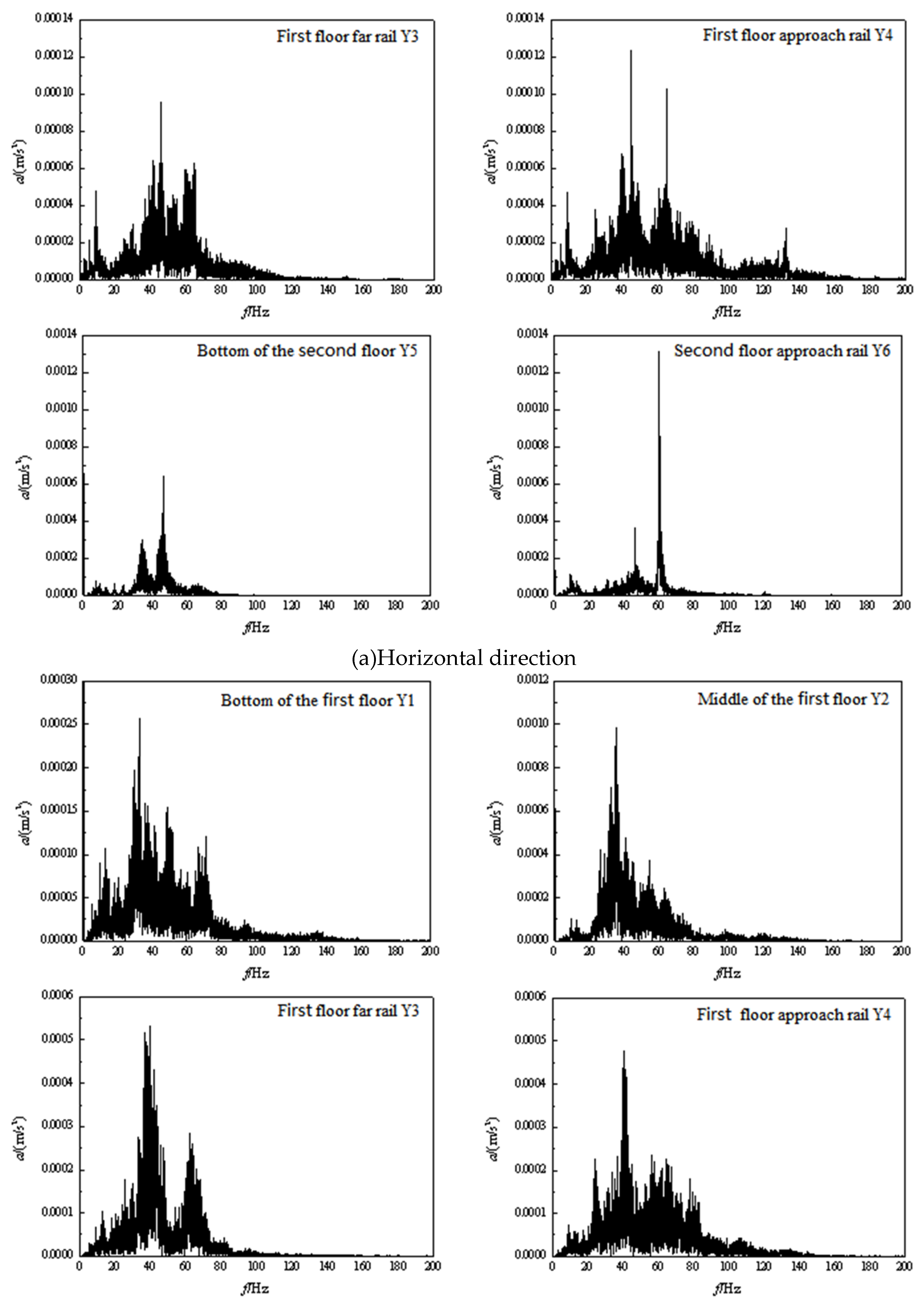
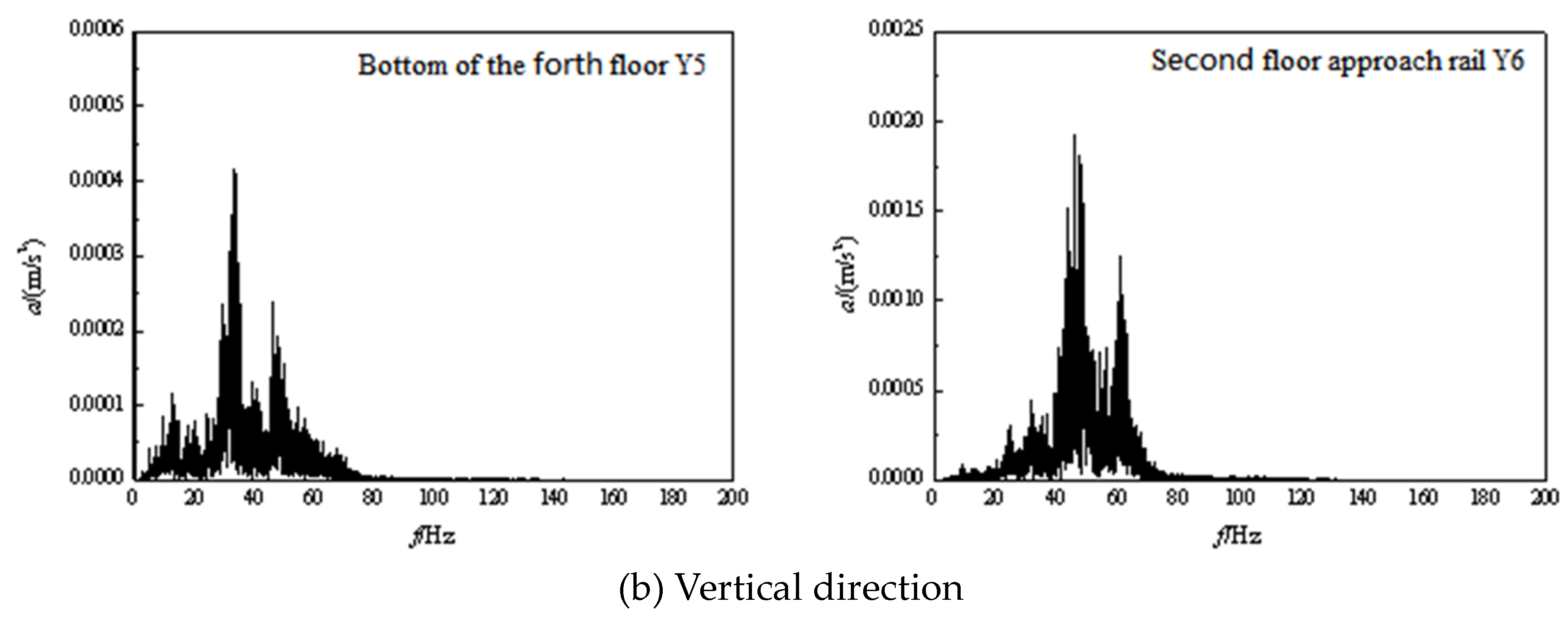
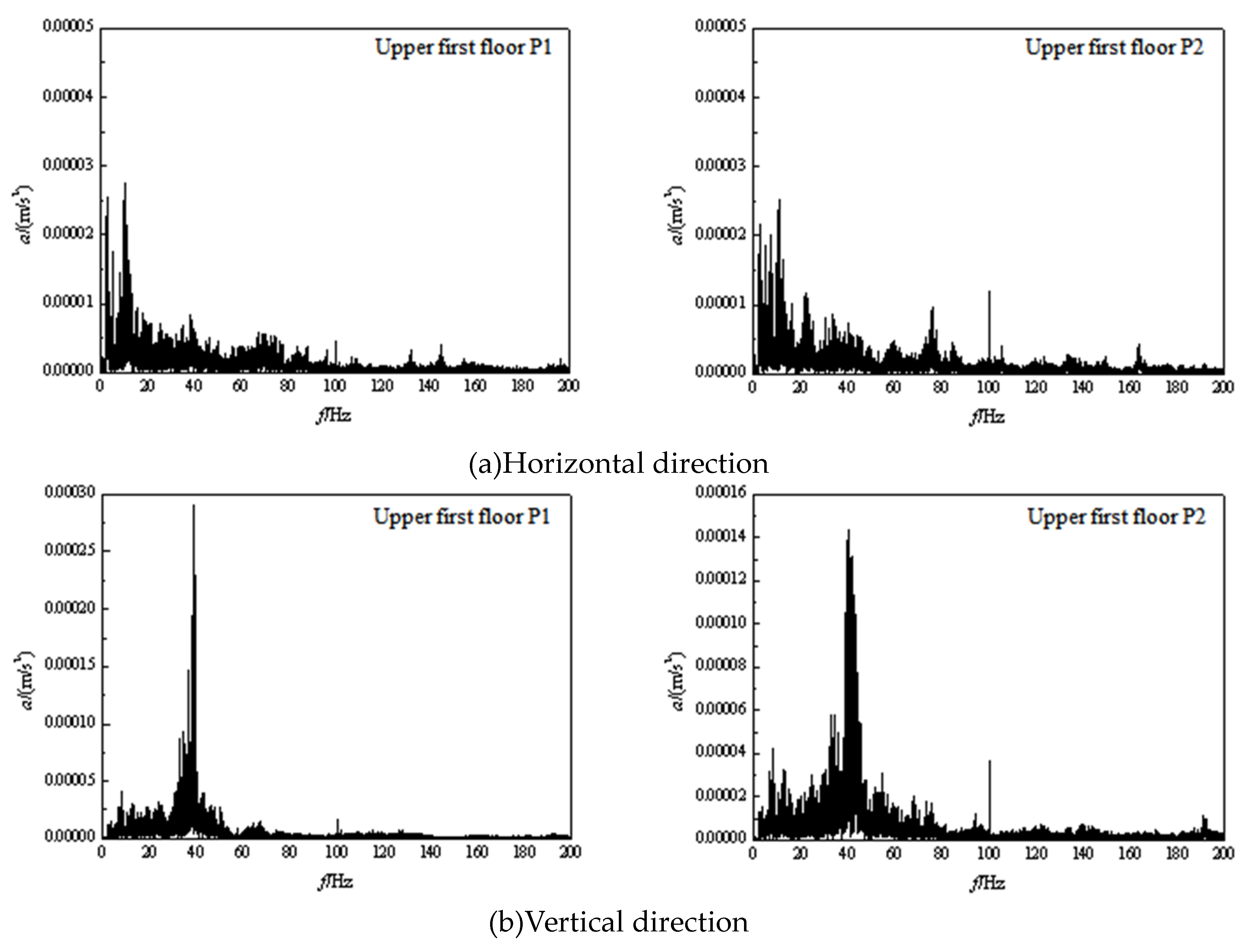
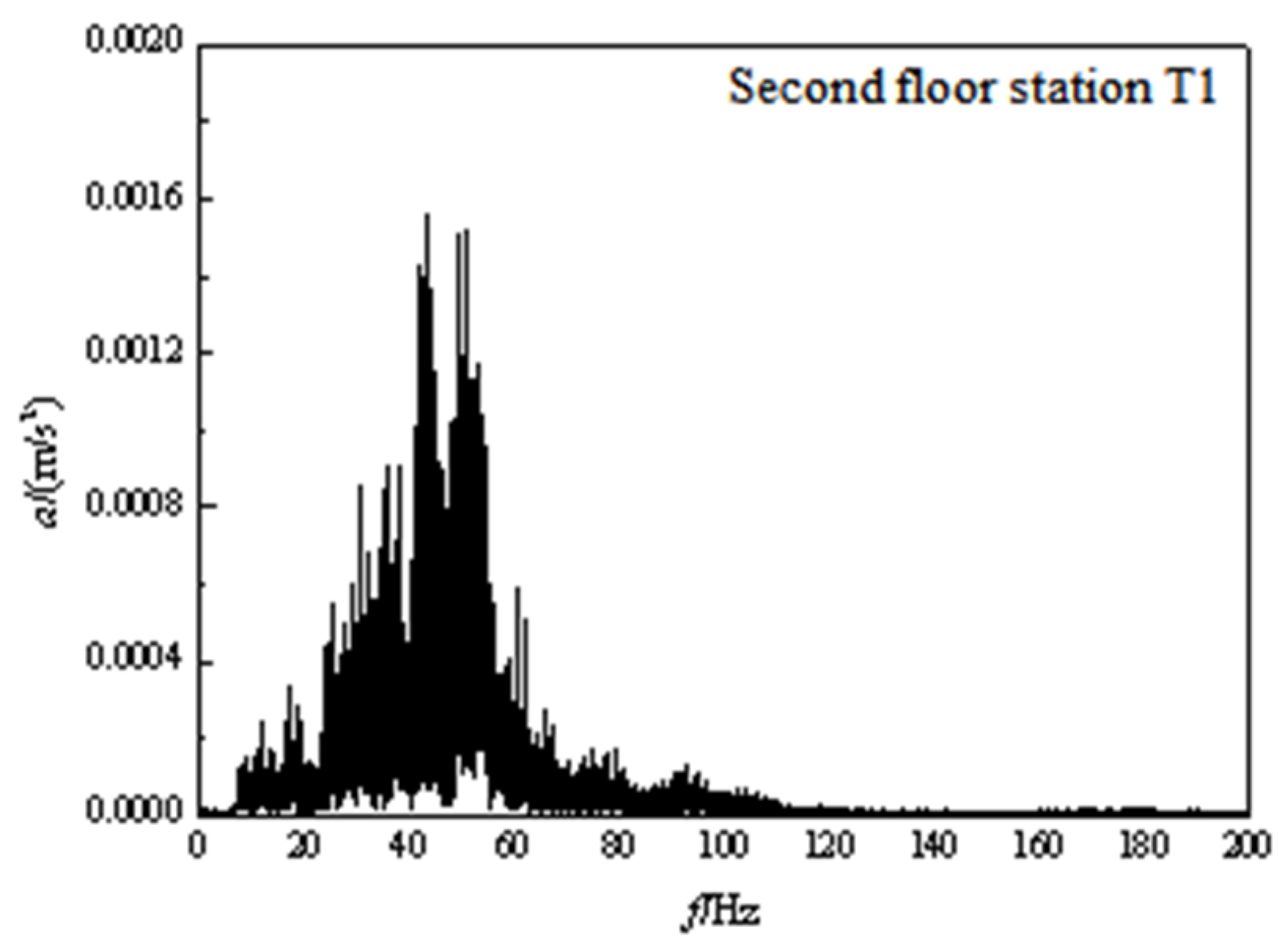
3.2. Frequency domain analysis
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lundqvist A, Dahlberg T. Dynamic train/track interaction including model for track settlement evolvement [J]. Vehicle system dynamics, 2004, 41: 667-676. Thompson D, Thompson D J. Railway Noise and Vibration: Mechanisms, Modelling and Means of Control[M]. Holland: Elsevier Science & Technology, 2009.
- Rossi F, Nicolini A. A simple model to predict train-induced vibration: Theoretical formulation and experimental validation[J]. Environmental Impact Assessment Review, 23(3): 305-322,2003. [CrossRef]
- Auersch L. Dynamic interaction of various beams with the underlying soil–finite and infinite, half-space and Winkler models [J]. European Journal of Mechanics-A/Solids, 2008, 27(5): 933-958. [CrossRef]
- Meng Ma, Weining Liu, Chunyu Qian, Guohua Deng, Yudong Li, “Study of the train-induced vibration impact on a historic Bell Tower above two spatially overlapping metro lines,” Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, vol. 81, pp. 58-74, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Kouroussis G, Gazetas G, Anastasopoulos I; et al. Discrete modelling of vertical track–soil coupling for vehicle–track dynamics [J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2011, 31(12): 1711-1723. [CrossRef]
- Chao Zou, Yimin Wang, James A. Moore, Masoud Sanayei, “Train-induced field vibration measurements of ground and over-track buildings,” Science of the Total Environment, vol. 575, pp. 1339-1351, 2017. [CrossRef]
- X. Lei and C. Jiang, “Analysis of vibration reduction effect of steel spring floating slab track with finite elements,” Journal of Vibration and Control, Vol. 22, pp. 1462–1471, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Masoud Sanayei, Anish Kayiparambil P., James A. Moore, Cory R. Brett, “Measurement and prediction of train-induced vibrations in a full-scale building,” Engineering Structures, vol. 77, pp. 119-128, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Meng Ma, Weining Liu, Chunyu Qian, Guohua Deng, Yudong Li, “Study of the train-induced vibration impact on a historic Bell Tower above two spatially overlapping metro lines,” Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, vol. 81, pp. 58-74, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Zhai W, Wang K. Lateral hunting stability of railway vehicles running on elastic track structures [J]. Journal of Computational and Nonlinear Dynamics, 2010, 5(4): 041009. [CrossRef]
- Torstensson P T, Nielsen J C O. Simulation of dynamic vehicle–track interaction on small radius curves [J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2011, 49(11): 1711-1732. [CrossRef]
- Handy, S. Smart growth and the transportation-land use connection: What does the research tell us? [J] International Regional Science Review, 2005, 28 (2): 146-167. [CrossRef]
- P. Galvín, D.López Mendoza, D.P. Connolly, G. Degrande, G. Lombaert, A. Romero, “Scoping assessment of free-field vibrations due to railway traffic.” Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, vol. 114, pp. 598-614, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Sheng X, Jones C J C, Thompson D J. A theoretical study on the influence of the track on train-induced ground vibration [J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 2004, 272(3): 909-936. [CrossRef]
- C. Madshus, B. Bessason, L. Hårvik, “PREDICTION MODEL FOR LOW FREQUENCY VIBRATION FROM HIGH SPEED RAILWAYS ON SOFT GROUND,” Journal of Sound and Vibration, vol. 193, no. 1, pp. 195-203, 1996. [CrossRef]
- Zhai W, Wang K, Cai C. Fundamentals of vehicle–track coupled dynamics [J]. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2009, 47(11): 1349-1376. [CrossRef]
- M.F.M. Hussein, H.E.M. Hunt, “A numerical model for calculating vibration from a railway tunnel embedded in a full-space,” Journal of Sound and Vibration, vol. 305, no. 3, pp. 401-431, 2007. [CrossRef]
- X. Sheng, C.J.C. Jones, D.J. Thompson, “A theoretical model for ground vibration from trains generated by vertical track irregularities,” Journal of Sound and Vibration, vol. 272, no. 3, pp. 937-965, 2004. [CrossRef]
- Costa P A, Calcada R, Cardoso A S. Influence of train dynamic modelling strategy on the prediction of track–ground vibrations induced by railway traffic [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F: Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Kouroussis G, Verlinden O, Conti C. A two-step time simulation of ground vibrations induced by the railway traffic [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C: Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2012, 226(2): 454-472. [CrossRef]
- Federal Transit Administration. T ransit Noise and Vibration Impact Assessment Manual; U.S. Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2018.
- Auersch L, “Wave propagation in the elastic half-space due to an interior load and its application to ground vibration problems and buildings on pile foundations,” Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, vol. 30, no. 10, pp. 925-936, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Auersch L, “Dynamic Stiffness of Foundations on Inhomogeneous Soils for a ReaJistic Prediction of Vertical Building,” Resonance, vol. 134, no. 3, pp. 328-340, 2008. [CrossRef]
- S. François, L. Pyl, H.R. Masoumi, G. Degrande, “The influence of dynamic soil–structure interaction on traffic induced vibrations in buildings,” Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 652-664, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Liang Ruihua, Liu Weifeng, Ma Meng, Liu Weining, “An efficient model for predicting the train-induced ground-borne vibration and uncertainty quantification based on Bayesian neural network,” Journal of Sound and Vibration, vol. 495, pp. 115908-, 2020. [CrossRef]
- D. López-Mendoza, A. Romero, D.P. Connolly, P. Galvín, “Scoping assessment of building vibration induced by railway traffic,” Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, vol. 93, pp. 147-161, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Pyl L, Degrande G, Clouteau D. Validation of a Source–Receiver Model for Road Traffic-Induced Vibrations in Buildings. II: Receiver Model[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 2004, 130(12): 1394-1406. [CrossRef]
- Chao Zou, Yimin Wang, Xu Zhang, Ziyu Tao, “Vibration isolation of over-track buildings in a metro depot by using trackside wave barriers,” Journal of Building Engineering, vol. 30, pp. 101270, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Connolly D, Giannopoulos A, Forde M C. Numerical modelling of ground borne vibrations from high speed rail lines on embankments[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 2013, 46(0): 13-19. [CrossRef]
- Walker J G, Chan M F K. HUMAN RESPONSE TO STRUCTURALLY RADIATED NOISE DUE TO UNDERGROUND RAILWAY OPERATIONS[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1996. [CrossRef]
- D.P. Connolly, G. Kouroussis, A. Giannopoulos, O. Verlinden, P.K. Woodward, M.C. Forde, “Assessment of railway vibrations using an efficient scoping model,” Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, vol. 58, pp. 37-47, 2014. [CrossRef]
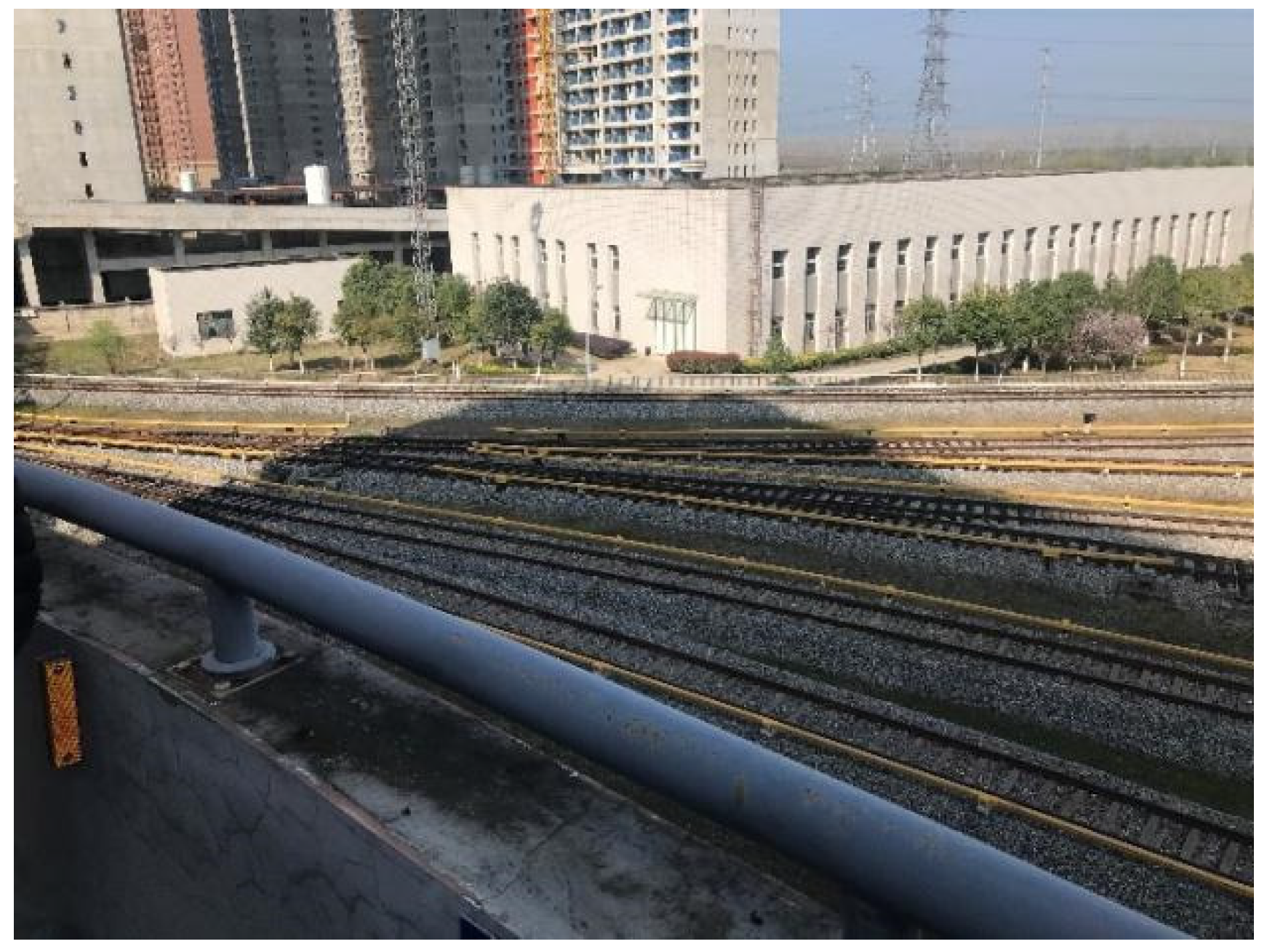
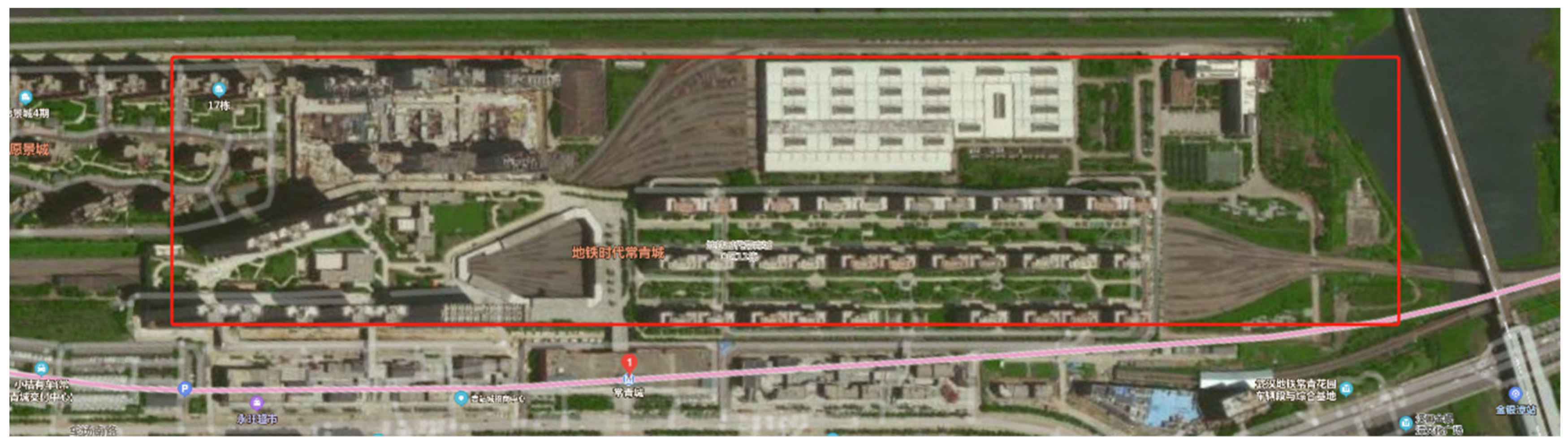
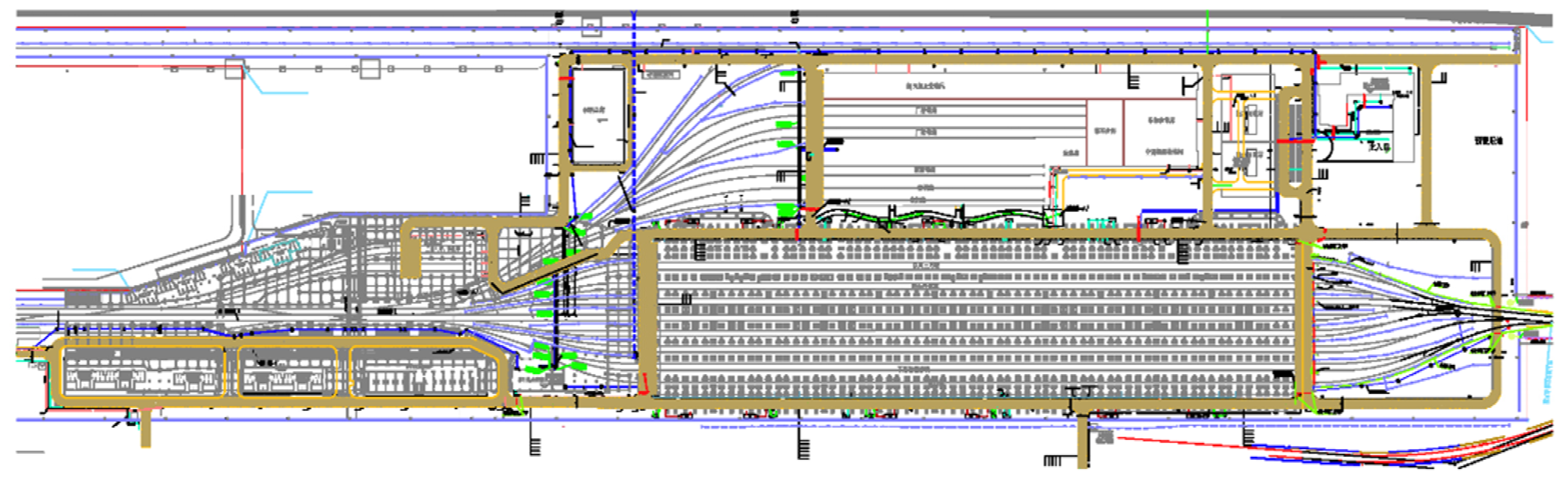

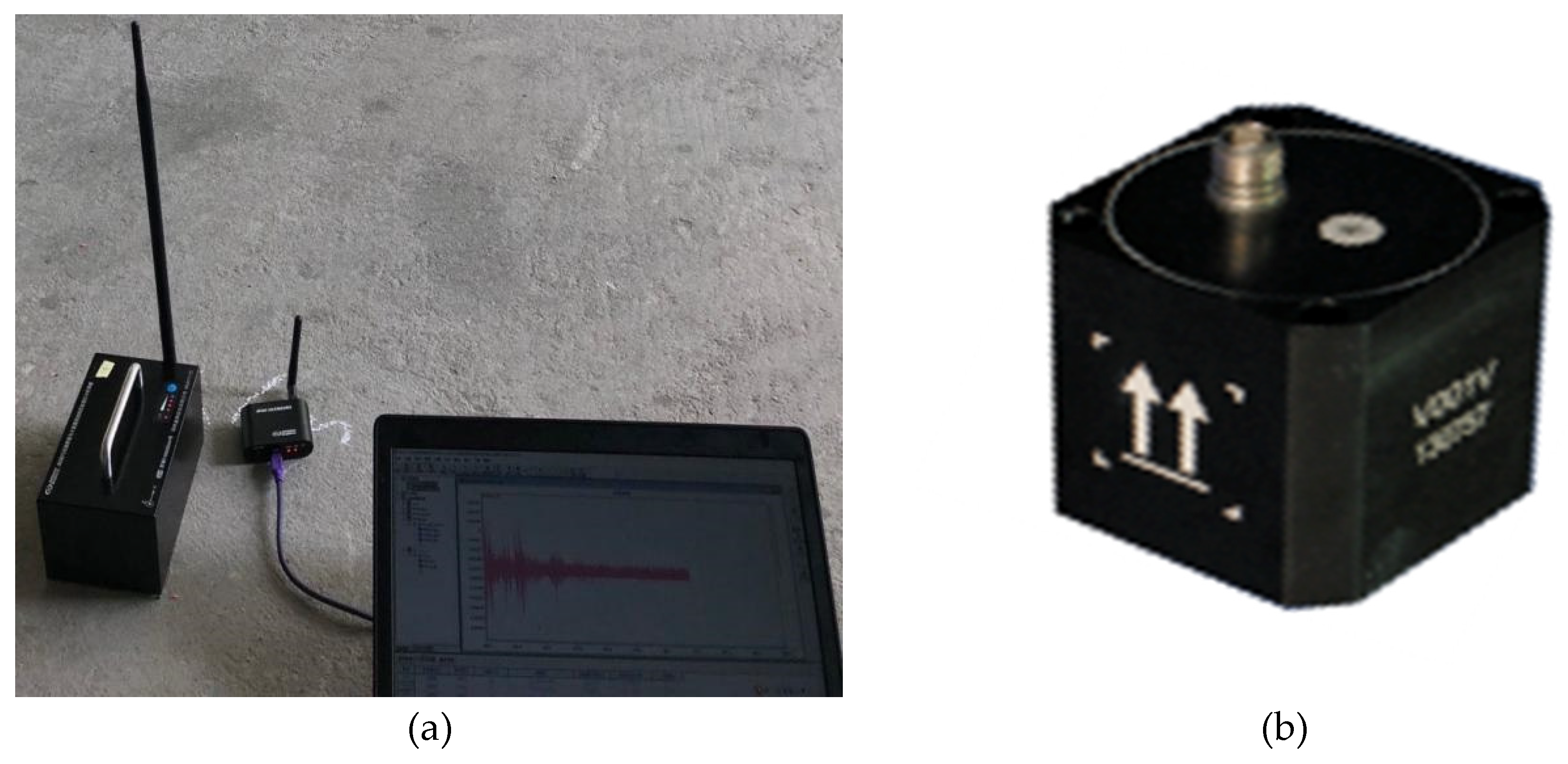
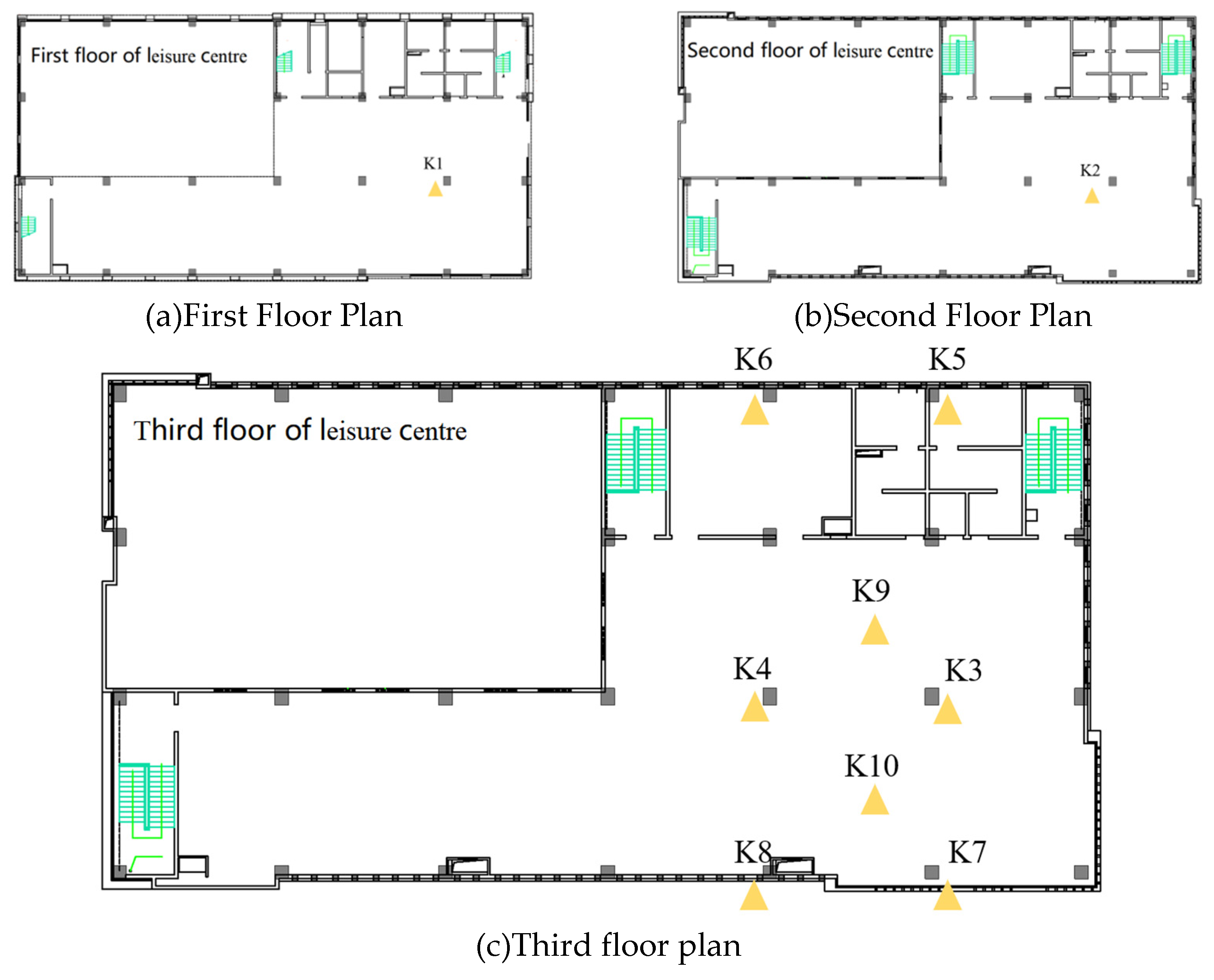
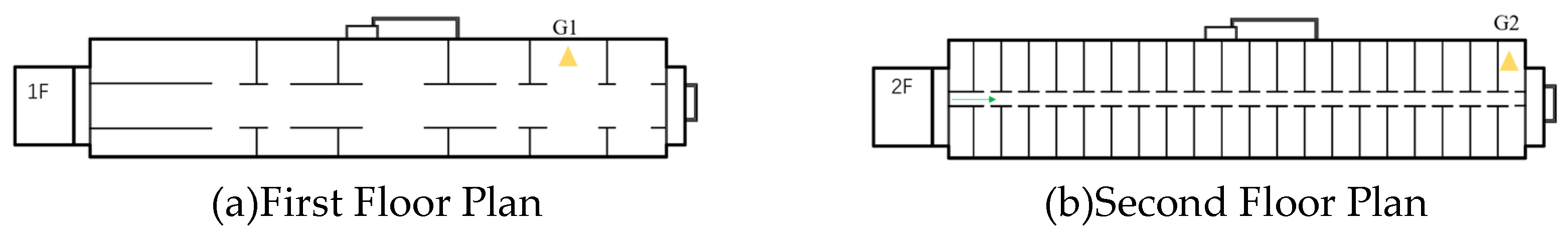
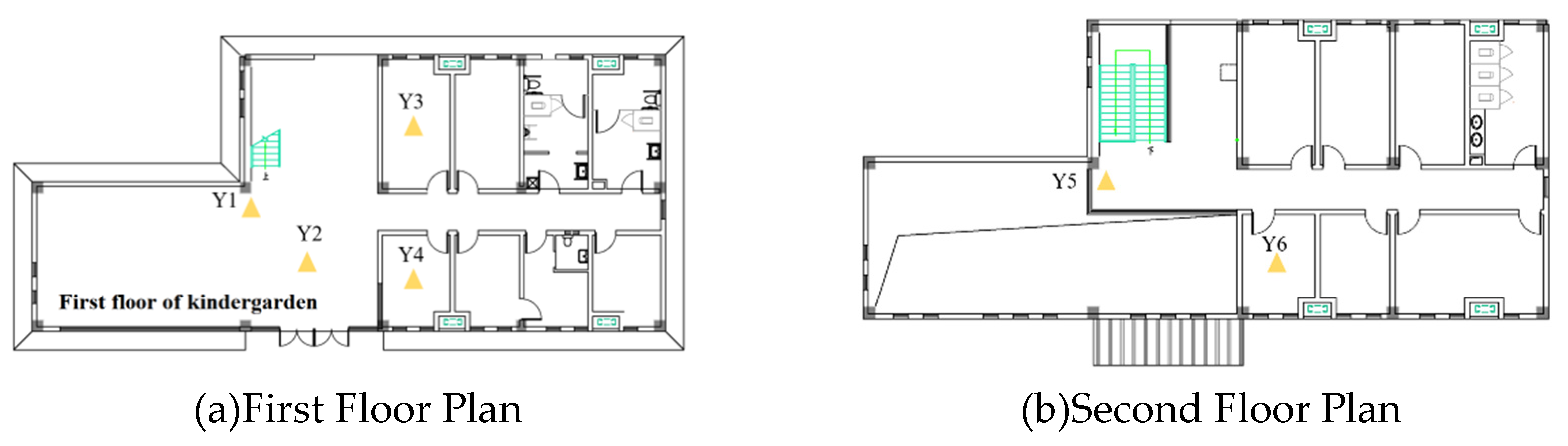
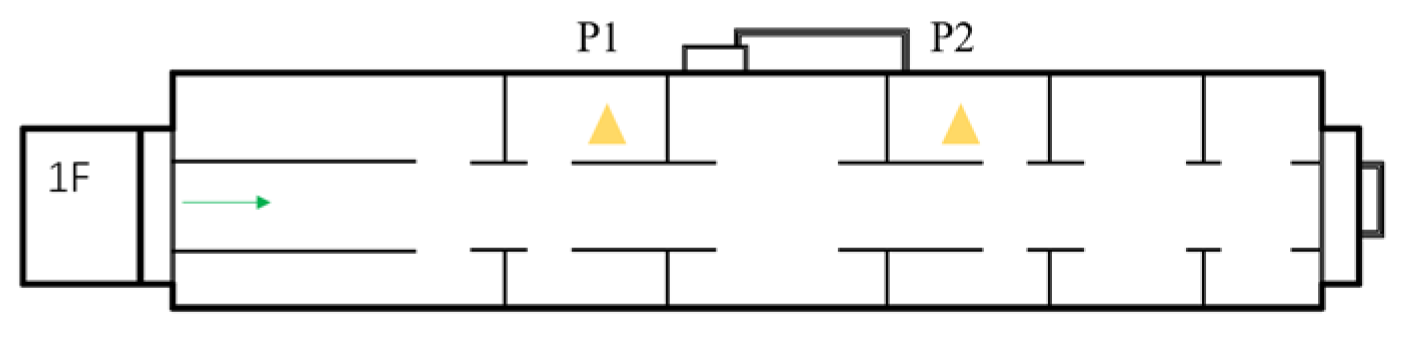
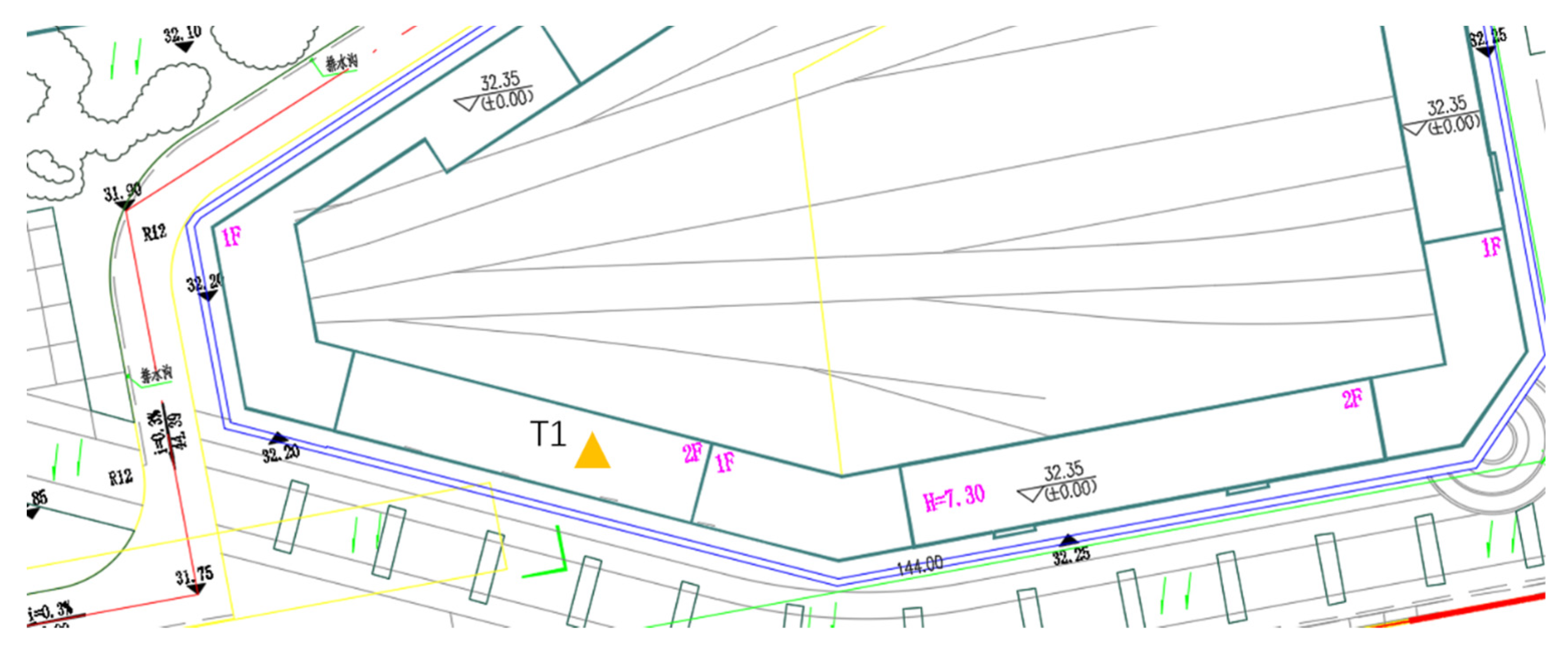
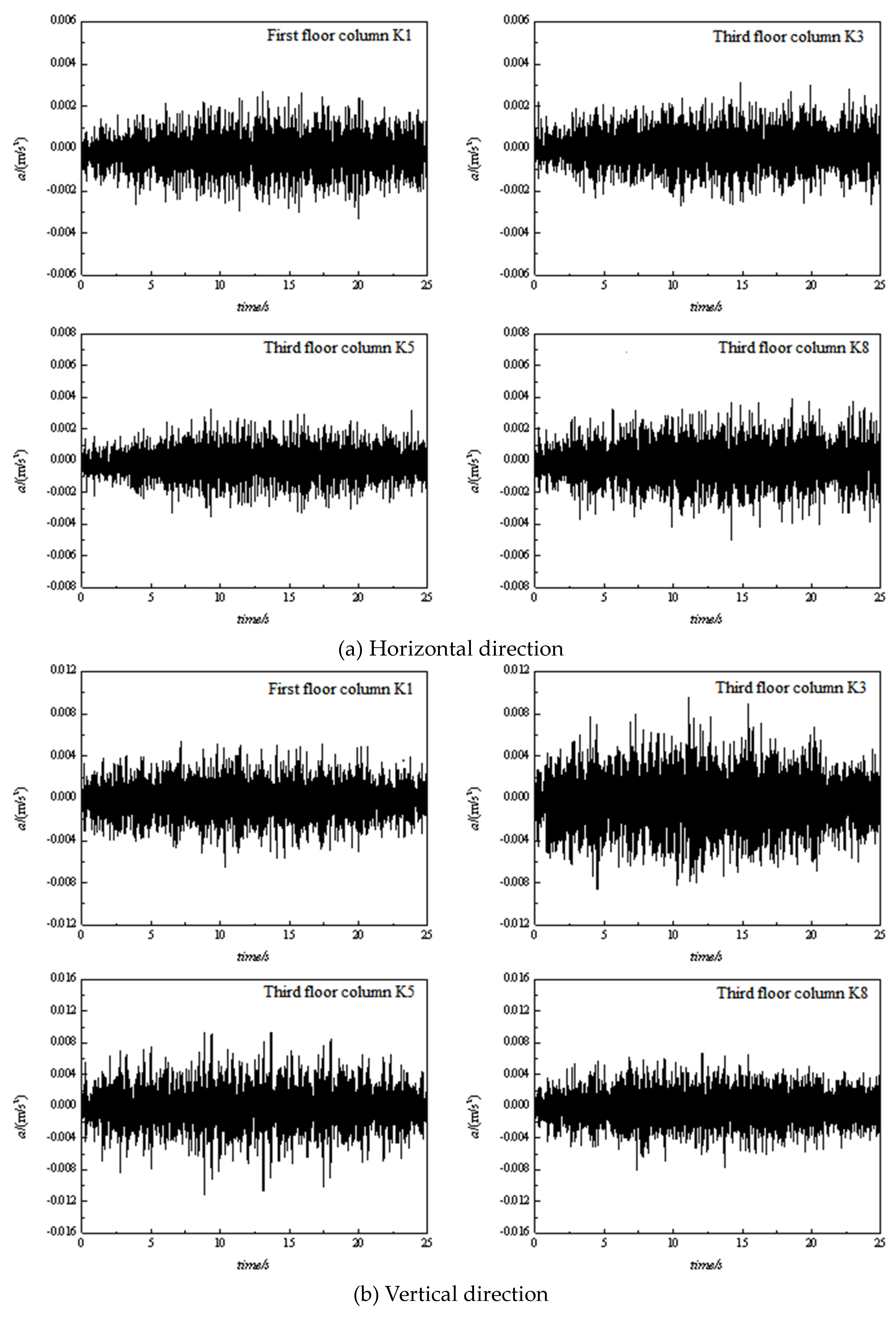
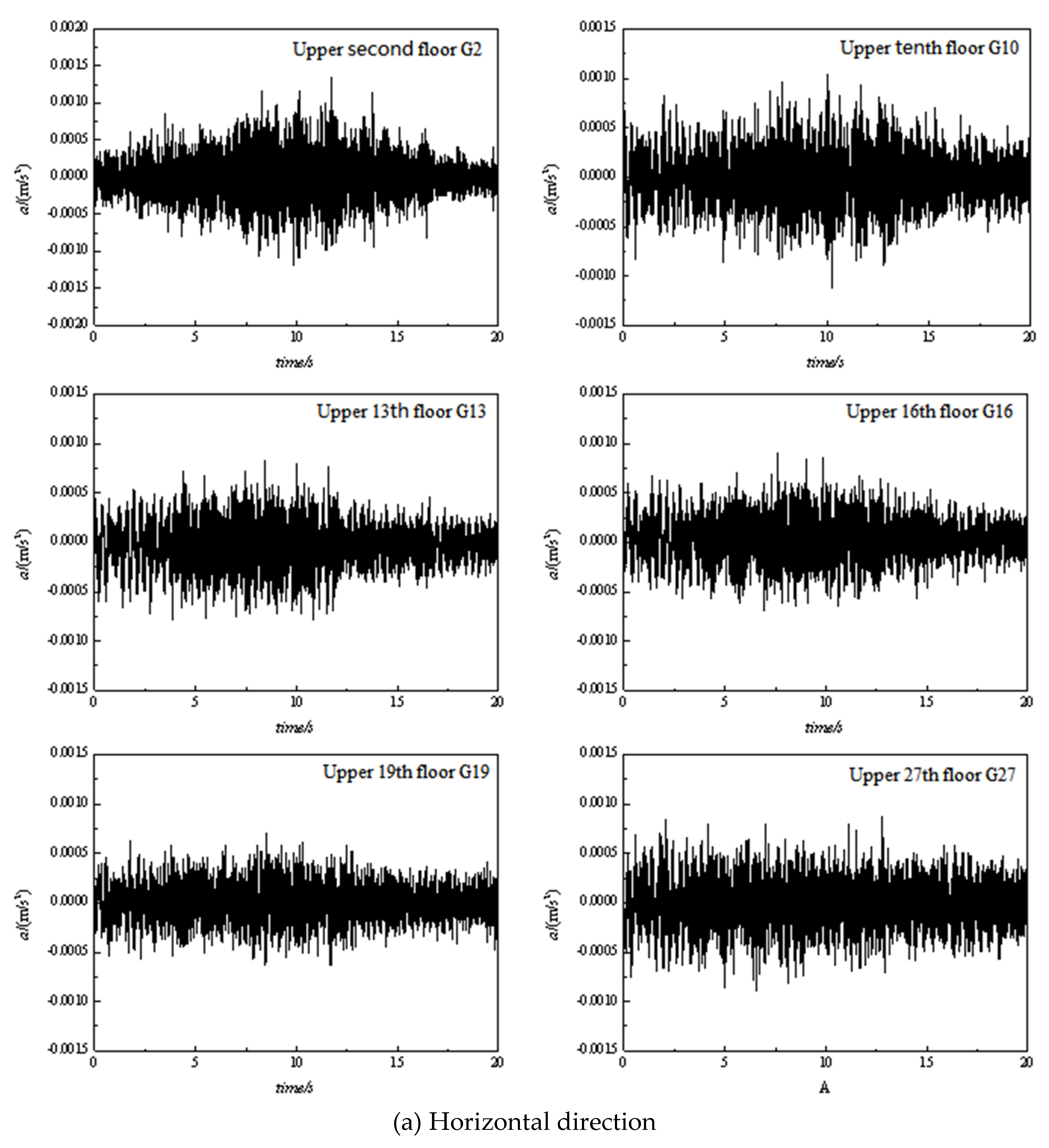
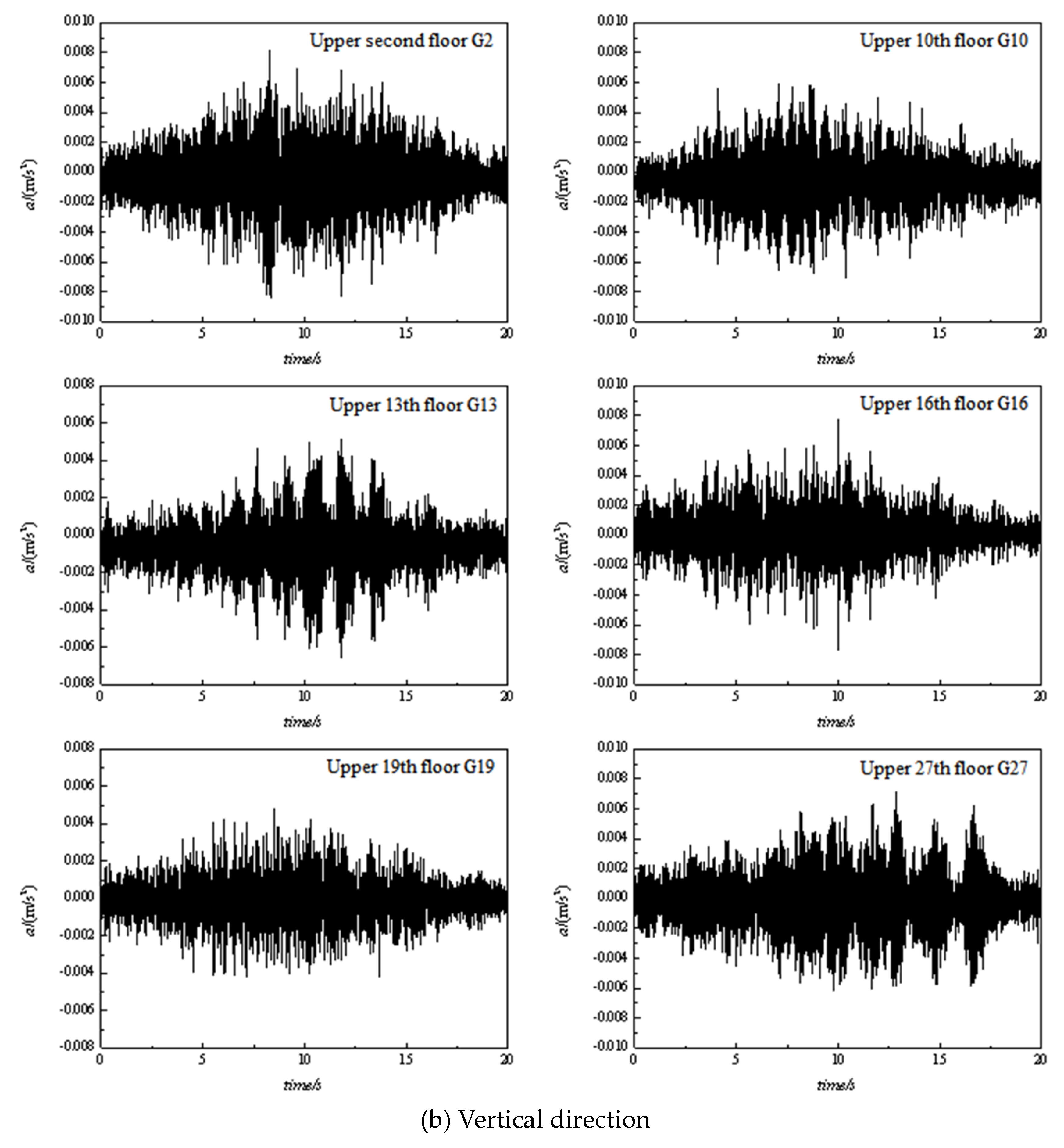
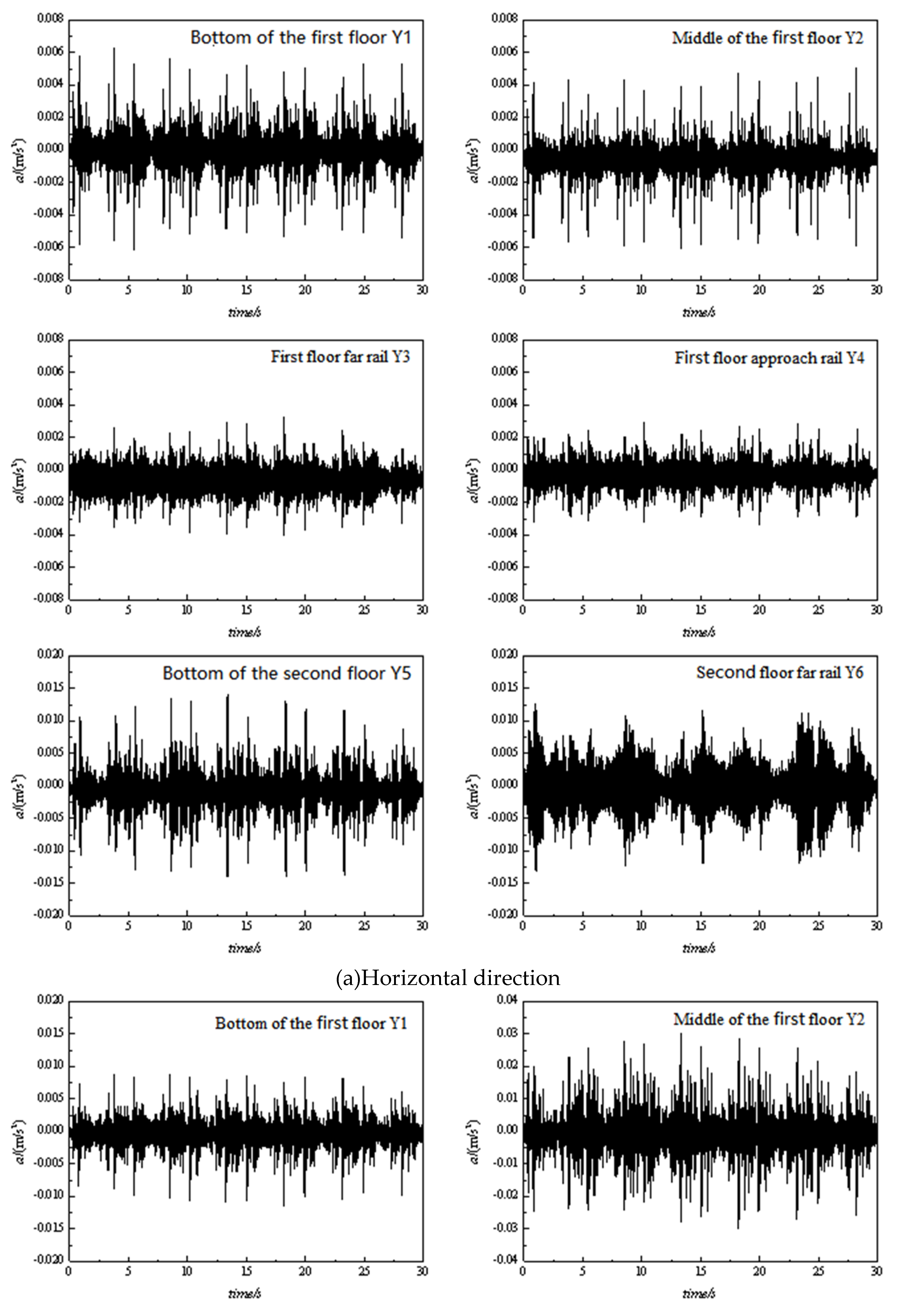
| No. | Location | Vibration source | Speed (km/h) | Track structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Throat area/access section line junction | 3-storey building on the upper cover | 15~20 | Gravel bed, concrete track sleepers |
| 2 | Throat area | 28-storey building on white ground to the south | 15~20 | Gravel bed, concrete sleeper |
| 3 | Throat area | 2 storey kindergarten in the upper building to the north | 10~15 | Gravel bed, concrete sleeper |
| 4 | Parking depot | 11-storey building in the upper cover | 5~10 | Integral bed |
| 5 | Throat area | 2-storey building in the upper cover | 10~15 | Gravel bed, wooden sleepers |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




