Submitted:
01 August 2023
Posted:
02 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
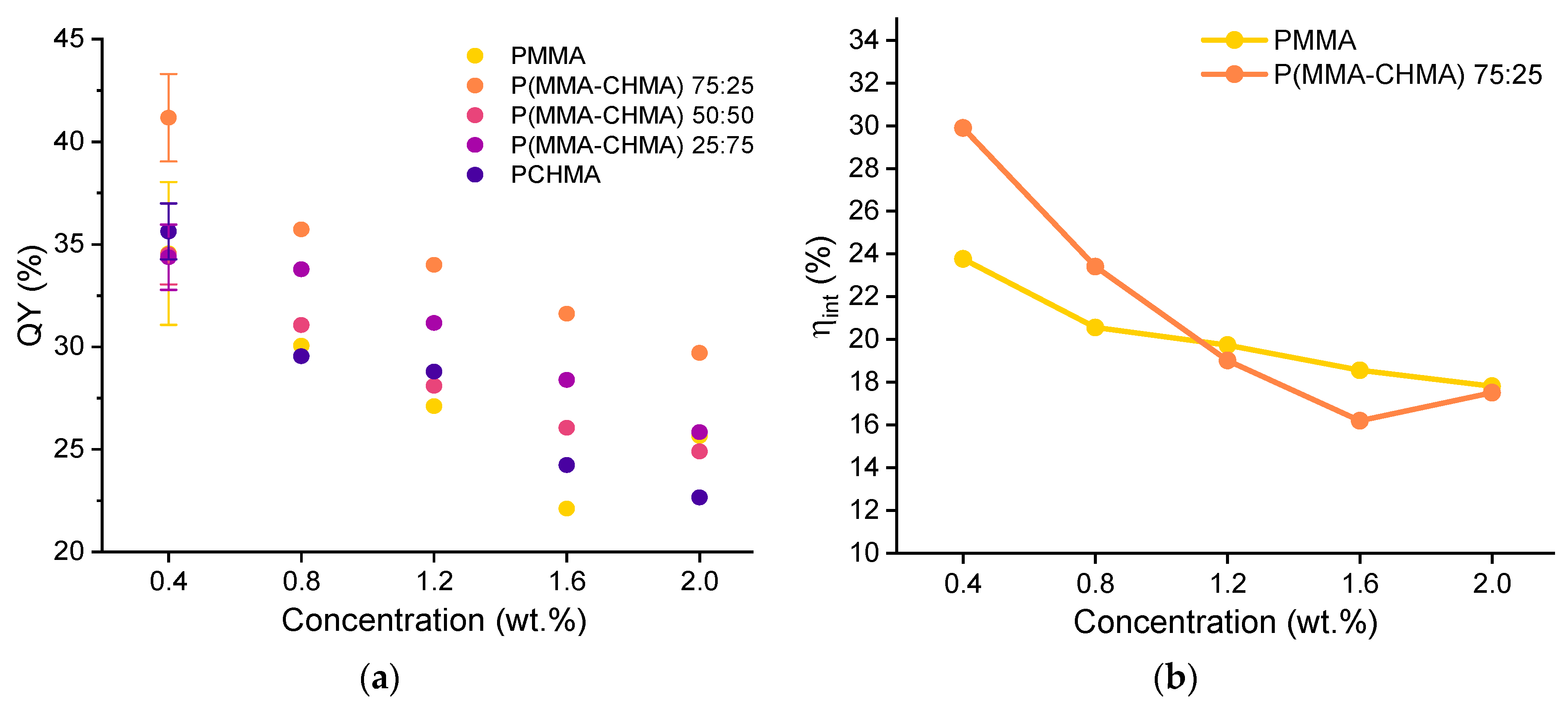
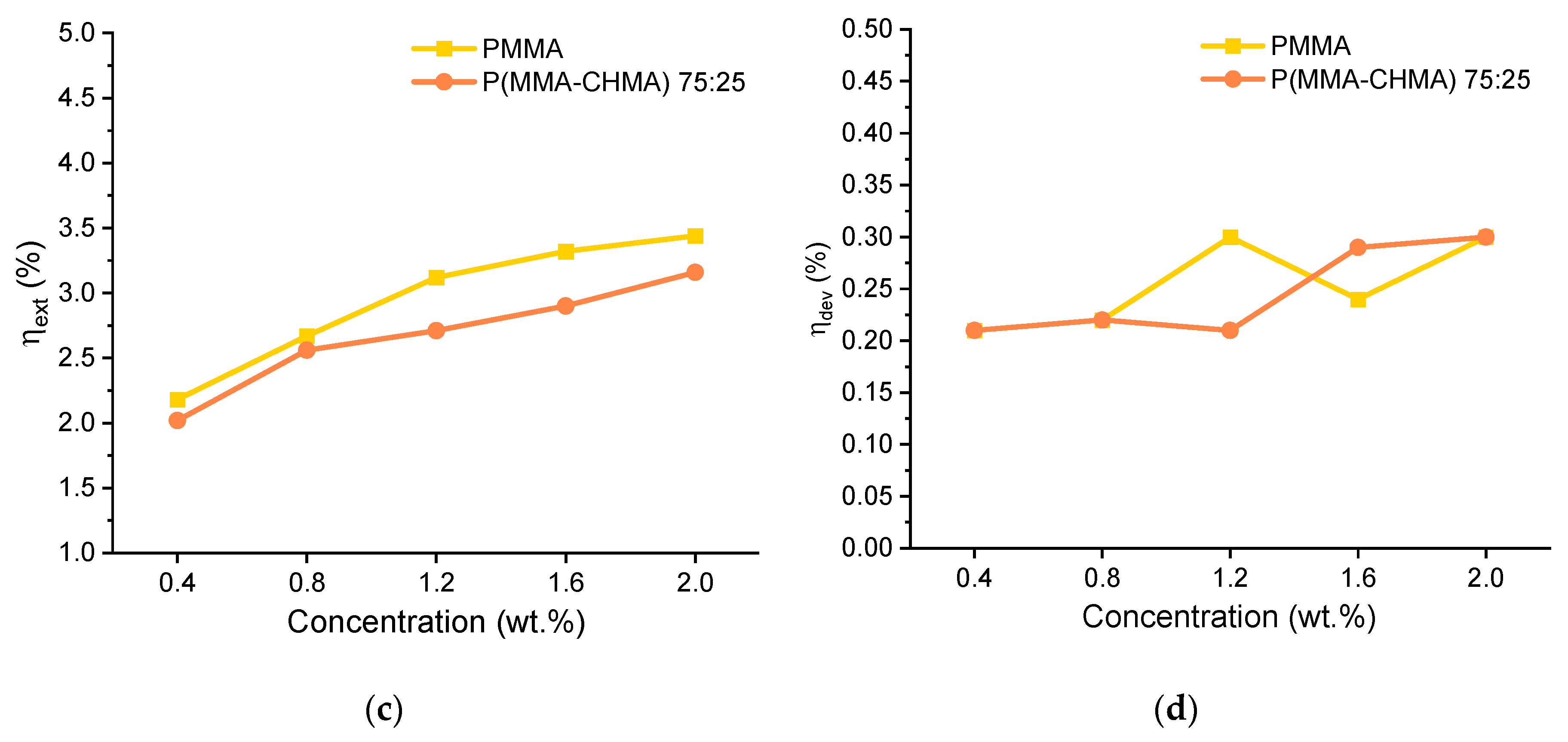
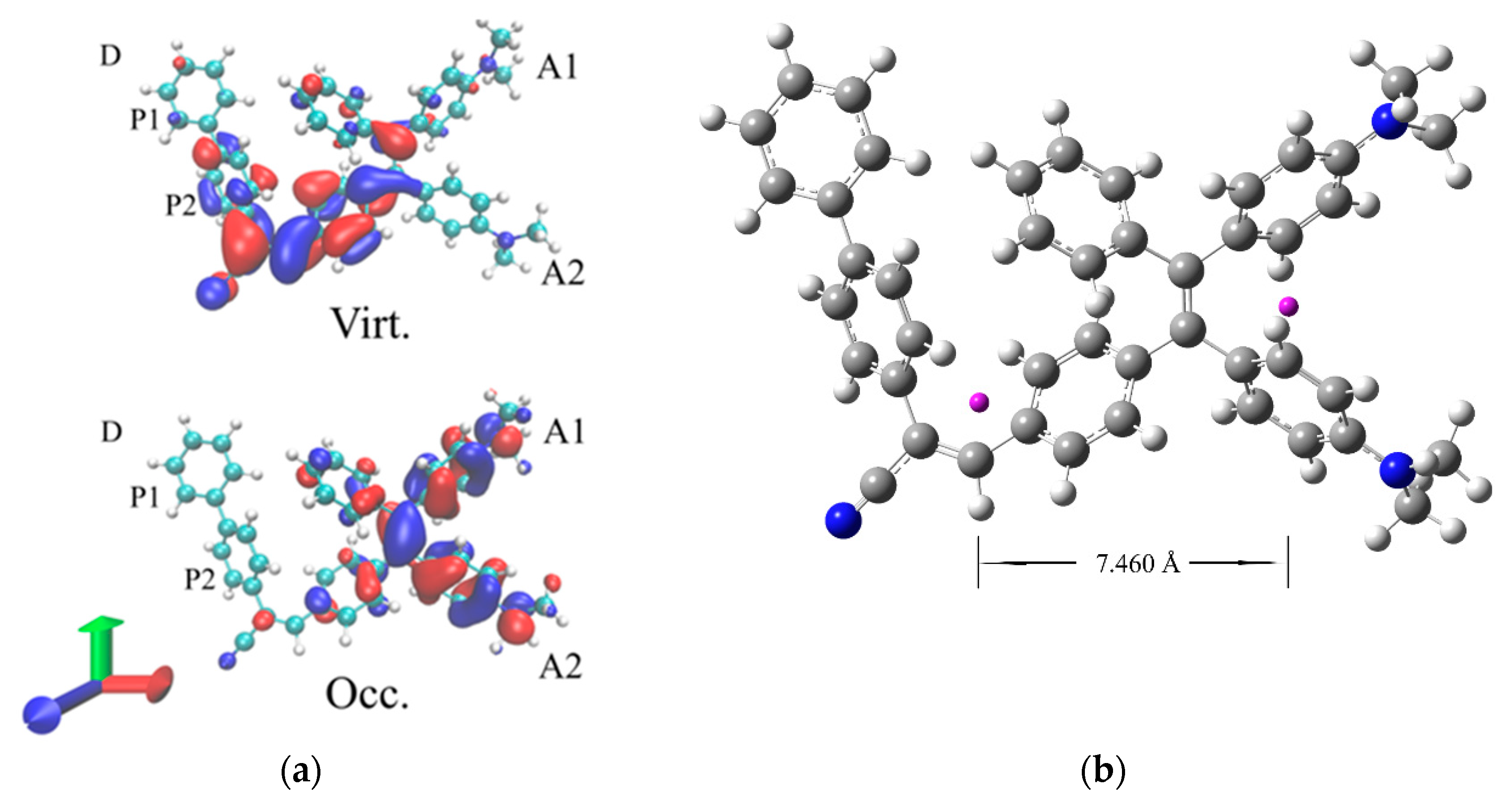
3. Results and Discussion
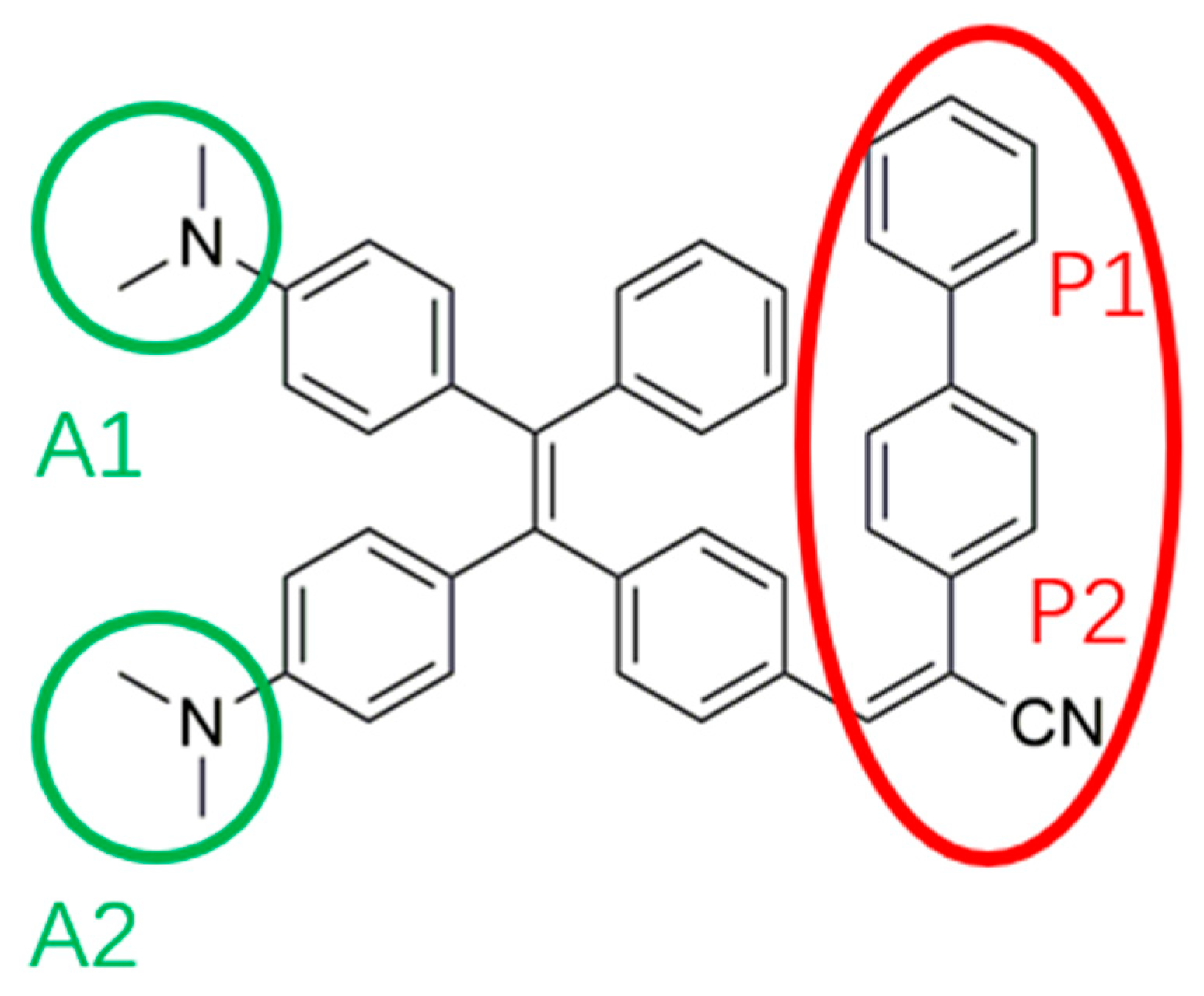
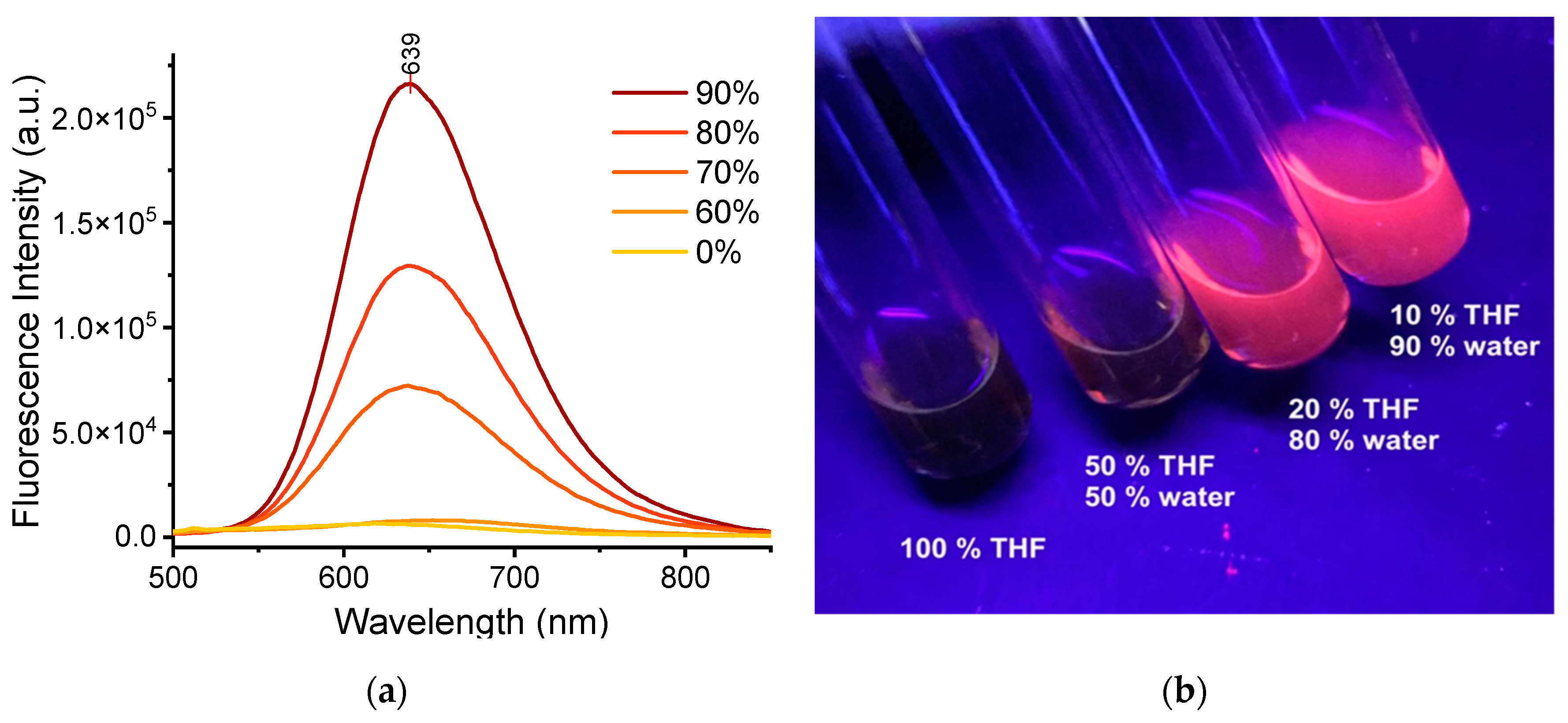
3.1. TPE-BPAN in solution
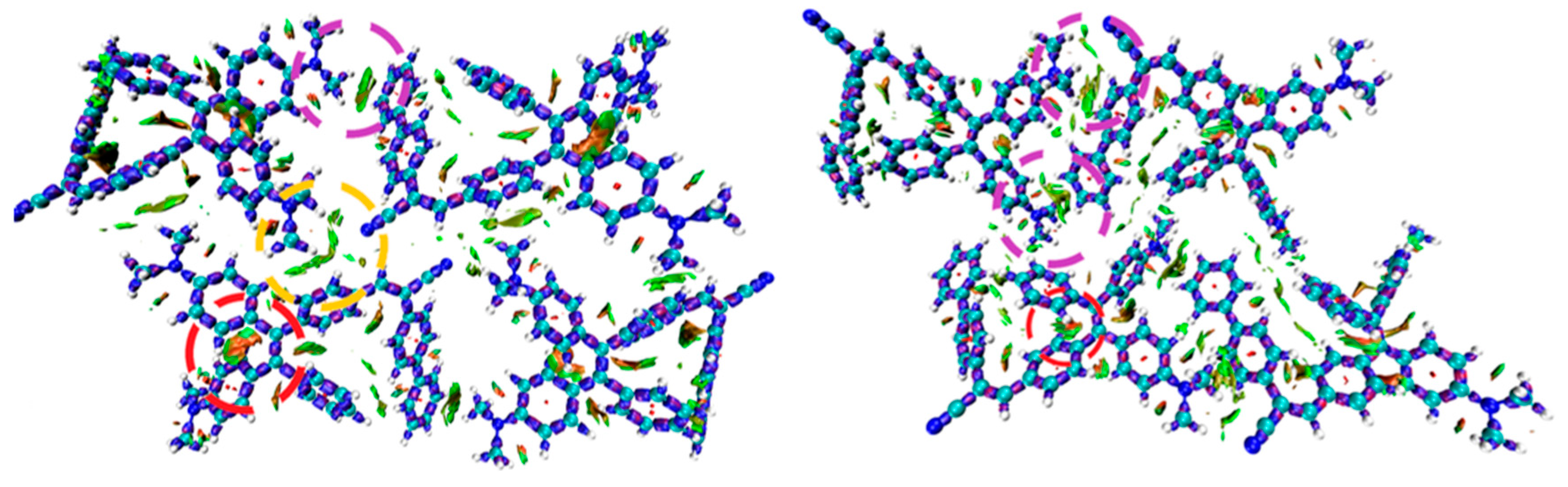
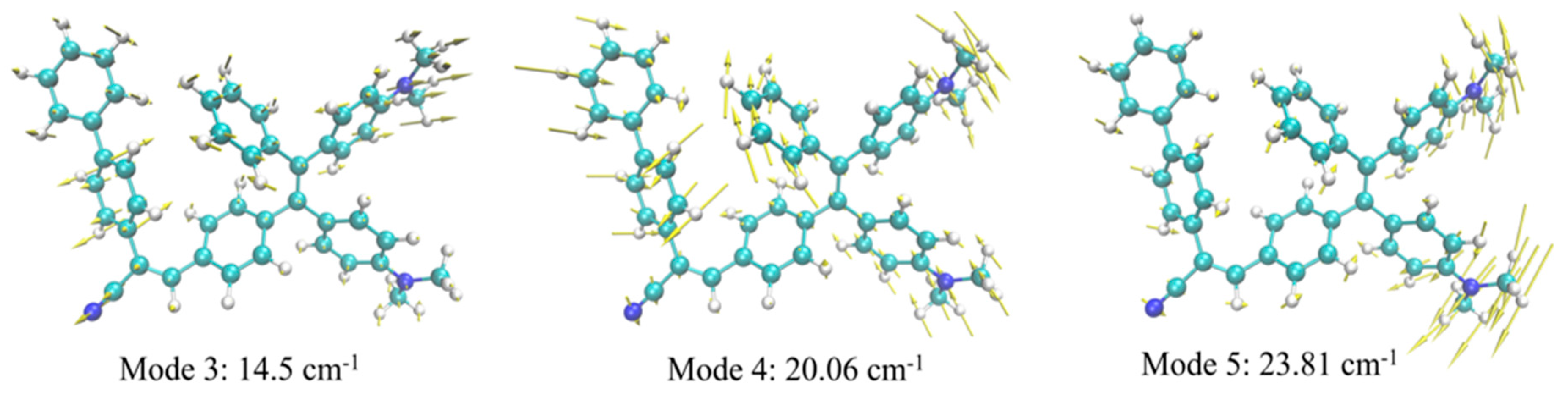
3.2. TPE-BPAN crystalline aggregates
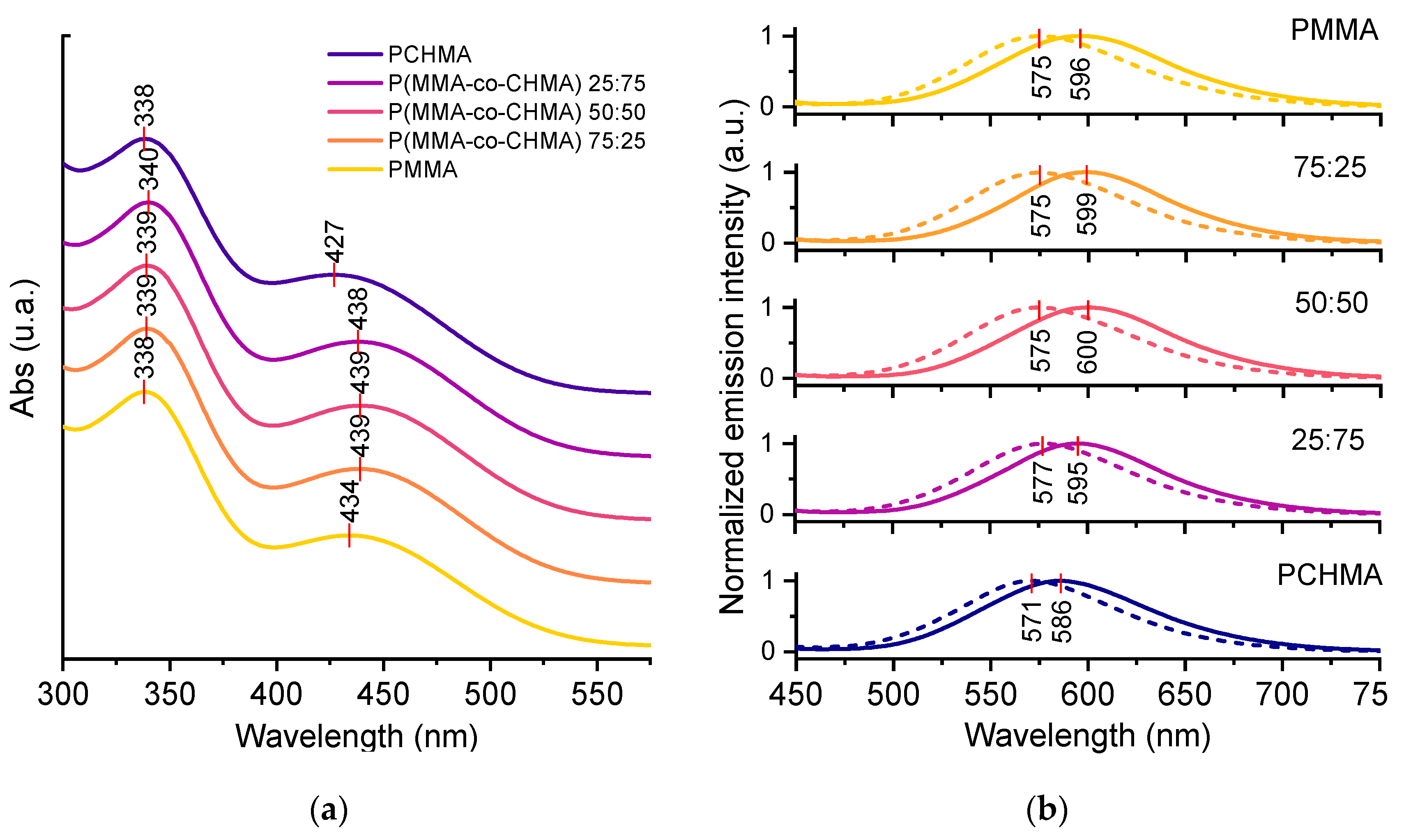
3.2. TPE-BPAN in polymeric thin films
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laveyne, J.I.; Bozalakov, D.; Van Eetvelde, G.; Vandevelde, L. Impact of Solar Panel Orientation on the Integration of Solar Energy in Low-Voltage Distribution Grids. Int. J. Photoenergy 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, B.S.; Howard, I.A. Luminescent Solar Concentrators for Building Integrated Photovoltaics: Opportunities and Challenges. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Hong, Y.; Dong, Y.; Ren, Y.; Haussie, M.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Wong, K.S.; Tang, B.Z. Color-Tunable, Aggregation-Induced Emission of a Butterfly-Shaped Molecule Comprising a Pyran Skeleton and Two Cholesteryl Wings. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 2000–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, A. Luminescent Solar Concentrators Based on Aggregation Induced Emission. Isr. J. Chem. 2018, 58, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Qin, A.; Tang, B.Z. AIE Polymers: Synthesis and Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 100, 101176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Hong, Y.; Dong, Y.; Häußler, M.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, Z.; Guo, Z.; Tang, B.Z. Fluorescent “Light-up” Bioprobes Based on Tetraphenylethylene Derivatives with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics. Chem. Commun. 2006, 3705–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geervliet, T.A.; Gavrila, I.; Iasilli, G.; Picchioni, F.; Pucci, A. Luminescent Solar Concentrators Based on Renewable Polyester Matrices. Chem. - An Asian J. 2019, 14, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidugli, N.; Mori, R.; Bellina, F.; Tang, B.Z.; Pucci, A. Aggregation-Induced Emission: New Emerging Fluorophores for Environmental Sensing. Princ. Appl. Aggregation-Induced Emiss. 2018, 335–349. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Banal, J.L.; Jones, D.J.; Tang, B.Z.; Ghiggino, K.P.; Wong, W.W.H. Aggregation-Induced Emission-Mediated Spectral Downconversion in Luminescent Solar Concentrators. Mater. Chem. Front. 2018, 2, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, G.; Kendall, J.; Meazzini, I.; Preis, E.; Bayseç, S.; Scherf, U.; Clément, S.; Evans, R.C. Luminescent Solar Concentrators Based on Energy Transfer from an Aggregation-Induced Emitter Conjugated Polymer. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 3039–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Compaan, A.; Ren, T.; Dong, W.J. Increasing the Power Output of a CdTe Solar Cell via Luminescent down Shifting Molecules with Intramolecular Charge Transfer and Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 2907–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ren, T.; Dong, W.-J. Tuning Photophysical Properties of Triphenylamine and Aromatic Cyano Conjugate-Based Wavelength-Shifting Compounds by Manipulating Intramolecular Charge Transfer Strength. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2013, 251, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, A. AIE Polymer Films for Optical Sensing and Energy Harvesting. In Handbook of Aggregation-Induced Emission; Wiley, 2022; pp. 57–78.
- Della Latta, E.; Sabatini, F.; Micheletti, C.; Carlotti, M.; Martini, F.; Nardelli, F.; Battisti, A.; Degano, I.; Geppi, M.; Pucci, A.; et al. Performant Flexible Luminescent Solar Concentrators of Phenylpolysiloxanes Crosslinked with Perylene Bisimide Fluorophores. Polym. Chem. 2023, 14, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastelijn, M.J.; Bastiaansen, C.W.M.; Debije, M.G. Influence of Waveguide Material on Light Emission in Luminescent Solar Concentrators. Opt. Mater. (Amst). 2009, 31, 1720–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostos, F.J.; Iasilli, G.; Carlotti, M.; Pucci, A. High-Performance Luminescent Solar Concentrators. Polymers (Basel). 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartolini, M.; Micheletti, C.; Picchi, A.; Coppola, C.; Sinicropi, A.; Di Donato, M.; Foggi, P.; Mordini, A.; Reginato, G.; Pucci, A.; et al. Orange/Red Benzo[1,2- B :4,5- b ′]Dithiophene 1,1,5,5-Tetraoxide-Based Emitters for Luminescent Solar Concentrators: Effect of Structures on Fluorescence Properties and Device Performances. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2023, 6, 4862–4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheletti, C.; Wang, Q.; Ventura, F.; Turelli, M.; Ciofini, I.; Adamo, C.; Pucci, A. Red-emitting Tetraphenylethylene Derivative with Aggregation-induced Enhanced Emission for Luminescent Solar Concentrators: A Combined Experimental and Density Functional Theory Study. Aggregate 2022, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papucci, C.; Charaf, R.; Coppola, C.; Sinicropi, A.; Di Donato, M.; Taddei, M.; Foggi, P.; Battisti, A.; De Jong, B.; Zani, L.; et al. Luminescent Solar Concentrators with Outstanding Optical Properties by Employment of D-A-D Quinoxaline Fluorophores. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 15608–15621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tummeltshammer, C.; Taylor, A.; Kenyon, A.J.; Papakonstantinou, I. Losses in Luminescent Solar Concentrators Unveiled. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2016, 144, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Zhao, E.; Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. A Highly Selective AIE Fluorogen for Lipid Droplet Imaging in Live Cells and Green Algae. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, R.; Iasilli, G.; Lessi, M.; Muñoz-García, A.B.; Pavone, M.; Bellina, F.; Pucci, A. Luminescent Solar Concentrators Based on PMMA Films Obtained from a Red-Emitting ATRP Initiator. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papakonstantinou, I.; Portnoi, M.; Debije, M.G. The Hidden Potential of Luminescent Solar Concentrators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, X.; Gong, X. Boosting Efficiency of Luminescent Solar Concentrators Using Ultra-Bright Carbon Dots with Large Stokes Shift. Nanoscale Horizons 2022, 8, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernzerhof, M.; Scuseria, G.E. Assessment of the Perdew–Burke–Ernzerhof Exchange-Correlation Functional. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 5029–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, C.; Barone, V. Toward Reliable Density Functional Methods without Adjustable Parameters: The PBE0 Model. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 6158–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasi, J.; Mennucci, B.; Cammi, R. Quantum Mechanical Continuum Solvation Models. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 2999–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.L. Natural Transition Orbitals. J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 4775–4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamo, C.; Le Bahers, T.; Savarese, M.; Wilbraham, L.; García, G.; Fukuda, R.; Ehara, M.; Rega, N.; Ciofini, I. Exploring Excited States Using Time Dependent Density Functional Theory and Density-Based Indexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 304–305, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bahers, T.; Adamo, C.; Ciofini, I. A Qualitative Index of Spatial Extent in Charge-Transfer Excitations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 2498–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, A.H. ; Rhys Theory of Light Absorption and Non-Radiative Transitions in F -Centres. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A. Math. Phys. Sci. 1950, 204, 406–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klintenberg, M.; Derenzo, S.E.; Weber, M.J. Accurate Crystal Fields for Embedded Cluster Calculations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2000, 131, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbraham, L.; Adamo, C.; Labat, F.; Ciofini, I. Electrostatic Embedding To Model the Impact of Environment on Photophysical Properties of Molecular Crystals: A Self-Consistent Charge Adjustment Procedure. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 3316–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derenzo, S.E.; Klintenberg, M.K.; Weber, M.J. Determining Point Charge Arrays That Produce Accurate Ionic Crystal Fields for Atomic Cluster Calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 2000, 112, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbraham, L.; Louis, M.; Alberga, D.; Brosseau, A.; Guillot, R.; Ito, F.; Labat, F.; Métivier, R.; Allain, C.; Ciofini, I. Revealing the Origins of Mechanically Induced Fluorescence Changes in Organic Molecular Crystals. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1800817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presti, D.; Wilbraham, L.; Targa, C.; Labat, F.; Pedone, A.; Menziani, M.C.; Ciofini, I.; Adamo, C. Understanding Aggregation-Induced Emission in Molecular Crystals: Insights from Theory. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 5747–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, Q. Interaction Region Indicator: A Simple Real Space Function Clearly Revealing Both Chemical Bonds and Weak Interactions**. Chemistry–Methods 2021, 1, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Chen, F. Multiwfn: A Multifunctional Wavefunction Analyzer. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 33, 580–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butty, E.; Suppan, P. Solvatochromic Effects in Mixed Polymers. Polym. Photochem. 1984, 5, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Atwater, H.A.; Baldo, M.A.; Baran, D.; Barile, C.J.; Barr, M.C.; Bates, M.; Bawendi, M.G.; Bergren, M.R.; Borhan, B.; et al. Consensus Statement: Standardized Reporting of Power-Producing Luminescent Solar Concentrator Performance. Joule 2022, 6, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debije, M.G.; Evans, R.C.; Griffini, G. Laboratory Protocols for Measuring and Reporting the Performance of Luminescent Solar Concentrators. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheletti, C.; Dini, V.A.; Carlotti, M.; Fuso, F.; Genovese, D.; Zaccheroni, N.; Gualandi, C.; Pucci, A. Blending or Bonding? Mechanochromism of an Aggregachromic Mechanophore in a Thermoplastic Elastomer. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, D.; Lunt, R.R. How to Accurately Report Transparent Luminescent Solar Concentrators. Joule 2019, 3, 2871–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Eabs (eV) |
Eem (eV) |
Emi. Intensity (au) |
Stokes Shift (eV) |
|
| THFcalc | 2.281 | 1.578 | 13677 | 0.71 |
| H2Ocalc | 2.281 | 1.547 | 14413 | 0.734 |
| gas phasecalc | 2.460 | 1.789 | 8675 | 0.671 |
| THFexp. | 2.793 | 2.006 | 6650 | 0.787 |
| Eabs (eV) | fabs (a.u.) | Eemi (eV) | femi (a.u.) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBE0-D3 | Pol_1 | 2.526 | 0.255 | 2.524 | 0.255 |
| Pol_2 | 2.380 | 0.195 | 1.767 | 0.192 | |
| Pol_3 | 2.459 | 0.199 | 1.605 | 0.154 | |
| Exp. 10% THF | - | 2.695 | 1.947 | ||
|
PBE0 |
THF sol |
2.281 | 0.290 | 1.578 |
0.338 |
| Exp THF solution | -- | 2.793 | 2.006 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





