Submitted:
28 July 2023
Posted:
02 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- To add the perspective of service quality to construct an evaluation index system that is more complete and comprehensive;
- To integrate the fuzzy theory into the evaluation method to make the evaluation results closer to the real life situation;
- To Evaluate the performance of humanitarian supply chain resilience using an ensemble ANP-fuzzy VIKOR method.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Definition of indicators
2.1.1. Organizational involvement
2.1.2. Reliability
2.1.3. Agility
2.1.4. Cost Factor
2.1.5. Quality of service
| Standard | Indicator | Descriptions |
|---|---|---|
| Organizational involvement AReliability B | Active government involvement (F1) | Government plays a major role in the humanitarian supply chain |
| Active participation of NGOs (F2) | NGOs are gaining ground in the humanitarian supply chain | |
| Coordination among participating organizations (F3) | Coordination among supply chain members is important for humanitarian supply chain resilience | |
| Logistics provider reliability (F4) | Logistics providers can accelerate the relief process and improve the resilience of the humanitarian supply chain | |
| Agility C | Material supplier reliability (F5) | Timely supply of materials helps to speed up the rescue process and enhance rescue efficiency |
| Responsiveness (F6) | Rapid supply chain response enhances supply chain agility | |
| Resource Scheduling Capability (F7) | Having the ability to quickly dispatch resources makes the humanitarian supply chain more resilient | |
| Cost Factor D Quality of service E |
Timeliness of transportation (F8) | Timely transportation allows for smooth relief efforts and further improves supply chain resilience performance |
| Transportation Costs (F9) | Lower transportation costs can lead to increased supply chain revenue and increased supply chain operability | |
| Inventory costs (F10) Material Mobilization and Procurement Costs (F11) |
Reducing inventory costs contributes to a sustainable supply chain, thereby increasing its resilience Lower material raising and procurement costs allow for more material to be raised on the same budget, and increased material availability helps improve supply chain performance |
|
| Supply of necessities of life (F12) | The main function of the humanitarian supply chain is to provide the necessities of life to the relief workers | |
| Timely arrival of rescue supplies (F13) | The timely arrival of relief supplies can protect the lives and livelihoods of those waiting for help |
2.2. Review of humanitarian supply chain assessment methods
| References | Description | Method |
|---|---|---|
| [54] | A combination of pre-positioning relief items in the mainland and anticipating them on board ships and at terminals is proposed to help improve the efficiency of disaster relief operations as well as the resilience of the supply chain. | Goal Planning |
| [55] | The impact of supply chain agility (SCAG) and supply chain resilience (SCRES) on performance, mediated by organizational culture, was investigated | DCV |
| [56] | Fuzzy MICMAC methodology was used to identify and analyze the factors that develop resilience in humanitarian supply chains | Fuzzy-MICMAC |
| [60] | Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) to assess the barriers in the humanitarian supply chain in coastal Bangladesh under the influence of cyclones | ISM |
| [61] | Use a dynamic systems model approach to compare centralized and decentralized supply chain configurations and apply them to humanitarian supply chains | Dynamic System Model |
| [62] | Weighting of humanitarian supply chain barriers in a big data-driven context assessed by fuzzy full explanatory structural model (F-T-ISM) | F-T-ISM |
| Proposed method | Thirteen representative indicators were selected to evaluate humanitarian supply chain resilience factors, and the VIKOR evaluation method was used to rank the resilience of humanitarian supply chains in five typical disaster areas | PFs-ANP-VIKOR |
3. Methods
3.1. ANP method
- (1)
- Element normalization process. = ,(i,j=1,2,…..,n)
- (2)
- Summing the normalized matrices by rows: =
- (3)
- For=, normalized, ,(i,j=1,2,…,n)
3.2. Pythagoras (PFs) fuzzy theory
3.2.1. Pythagorean fuzzy set definition
3.2.2. Pythagorean fuzzy set arithmetic rule
3.2.3. Comparison of fuzzy numbers and the Hemming distance
3.2.4. Pythagorean fuzzy weighted averaging
3.2.5. Fuzzy semantic transformation
| Fuzzy Natural Semantics | ) |
|---|---|
| Very low (VL) | (0.15,0.85) |
| Low (L) | (0.25,0.75) |
| Moderately low (ML) | (0.35,0.65) |
| Medium (M) | (0.55,0.45) |
| Moderately high (MH) | (0.65,0.35) |
| High (H) | (0.75,0.25) |
| Very high (VH) | (0.85,0.15) |
3.3. PFs- VIKOR steps
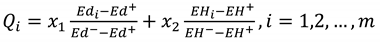
4. Methodological research
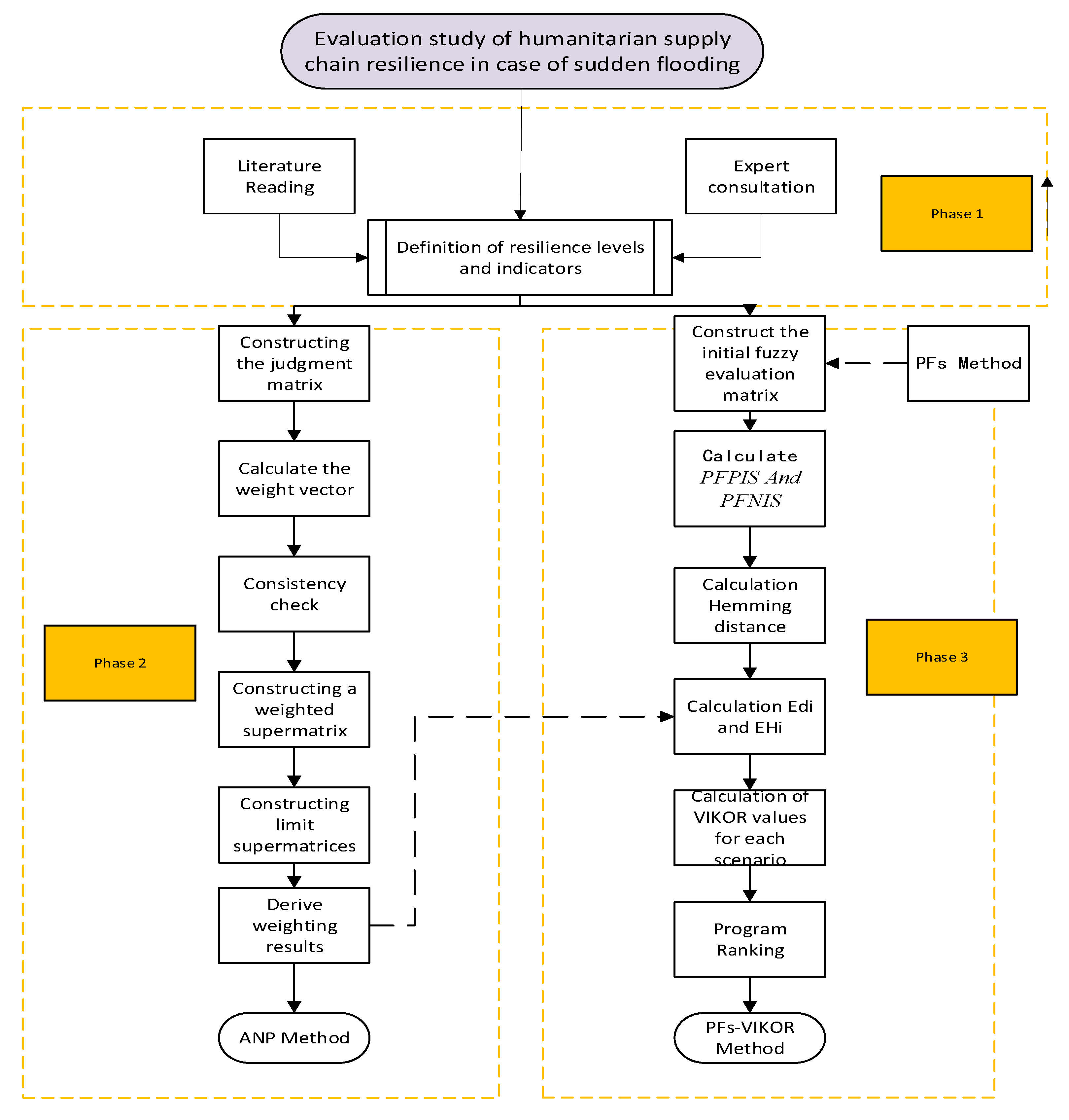
4.1. Study areas
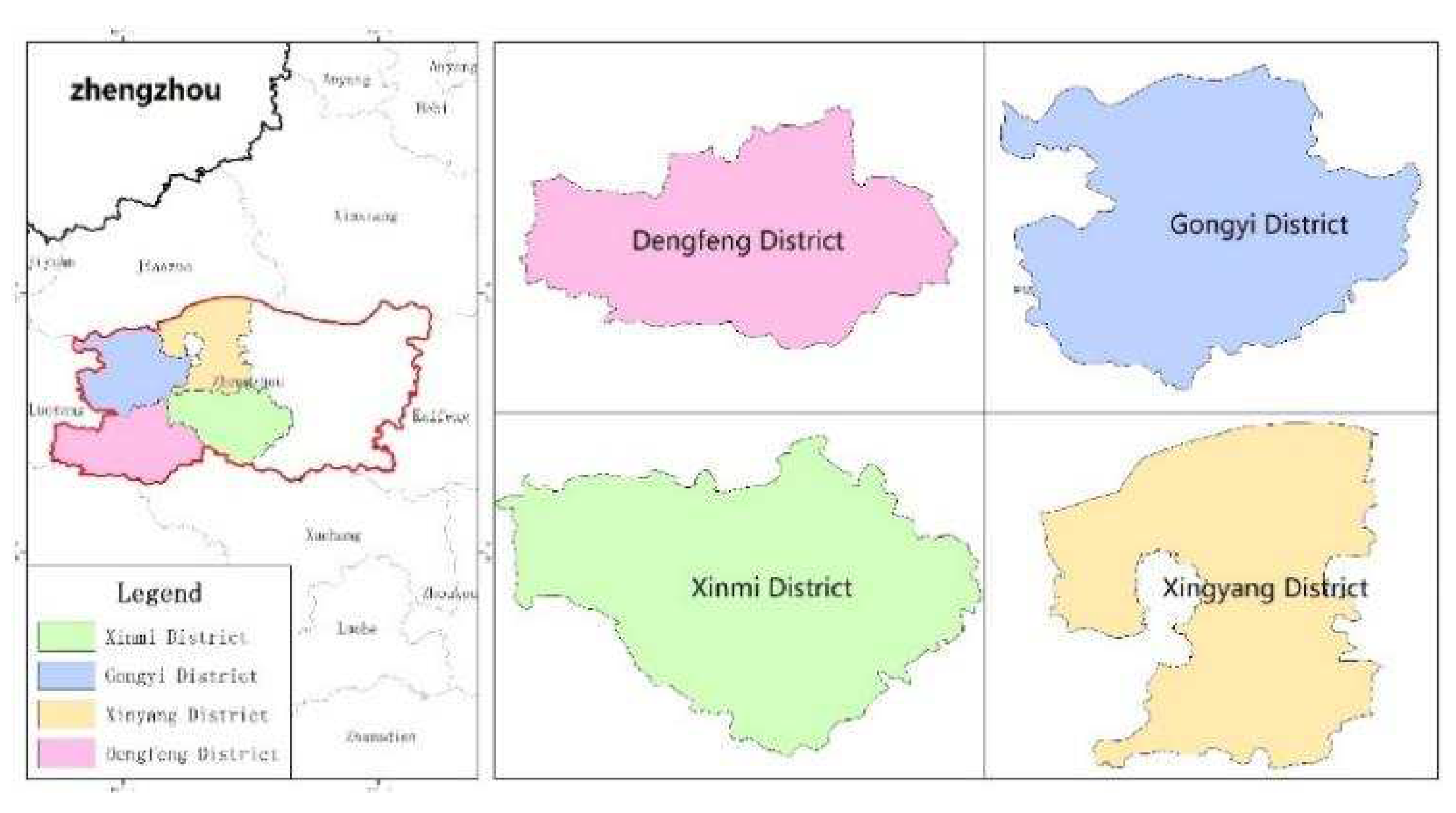
4.2. Data collection
4.3. Modeling based on the ANP-PFs-VIKOR approach
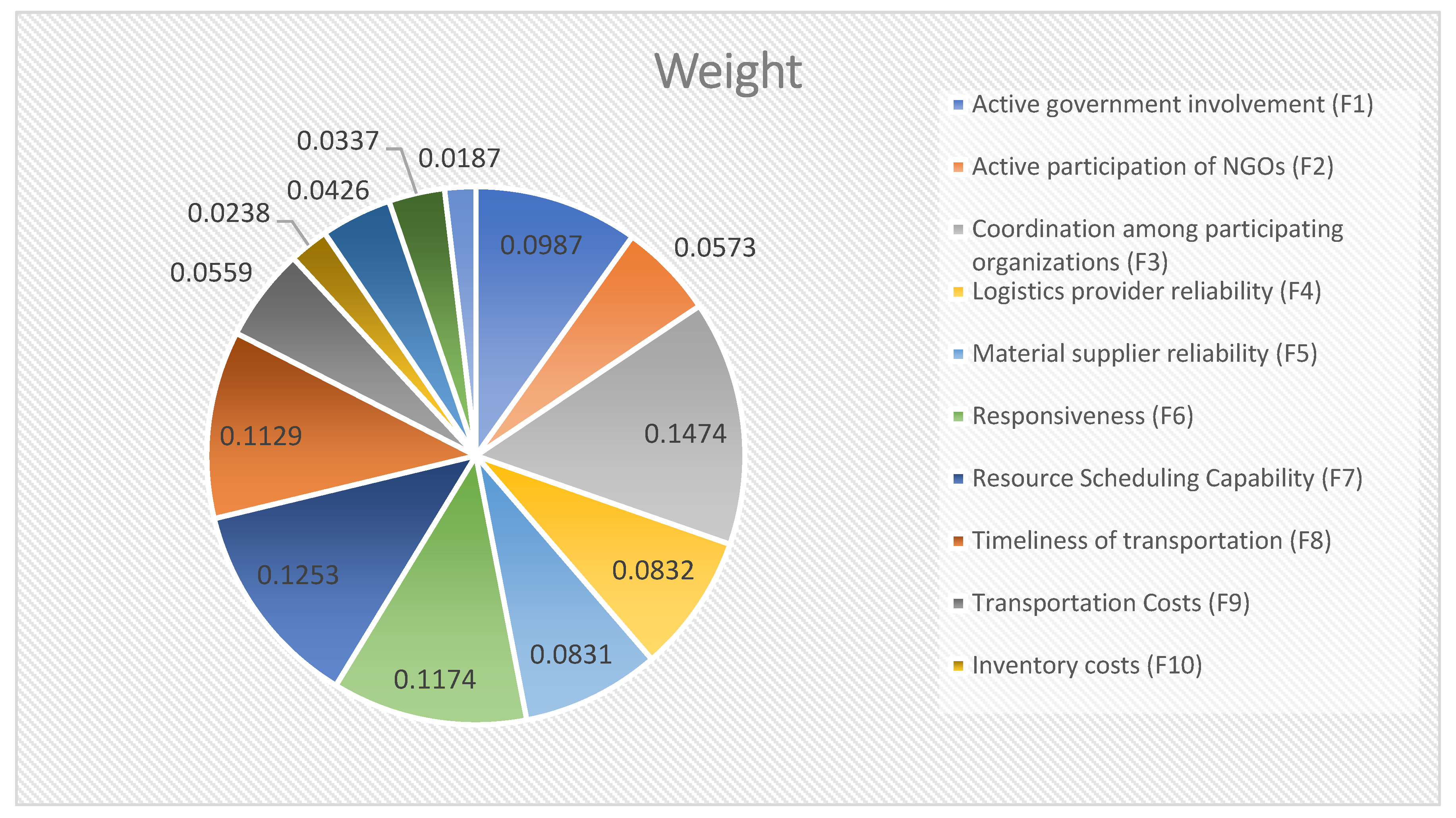
| Standard | Weight | Indicator | Weight | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organizational involvement A | 0.2813 | Active government involvement (F1) | 0.0987 | 5 |
| Active participation of NGOs (F2) Coordination among participating organizations (F3) |
0.05730.1474 | 8 1 |
||
| Reliability B Agility C |
0.1663 0.3777 |
Logistics provider reliability (F4) | 0.0832 | 6 |
| Material supplier reliability (F5) | 0.0831 | 7 | ||
| Responsiveness (F6) | 0.1174 | 3 | ||
| Resource Scheduling Capability (F7) Timeliness of transportation (F8) |
0.1253 0.1129 |
2 4 |
||
| Cost Factor D Quality of service E |
0.1223 0.0524 |
Transportation Costs (F9) | 0.0559 | 9 |
| Inventory costs (F10) Material Mobilization and Procurement Costs (F11) Supply of necessities of life (F12) Timely arrival of rescue supplies (F13) |
0.0238 0.0426 0.0337 0.0187 |
12 10 11 13 |
| Xingyang | Gongyi | Dengfeng | Xinmi | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0.6113 | 0.1521 | 0.5500 | 0.2025 | 0.7500 | 0.0625 | 0.6113 | 0.1521 |
| F2 | 0.5110 | 0.2406 | 0.5500 | 0.2025 | 0.6982 | 0.0917 | 0.5974 | 0.1631 |
| F3 | 0.3973 | 0.3660 | 0.4971 | 0.2546 | 0.6500 | 0.1225 | 0.5500 | 0.2025 |
| F4 | 0.4500 | 0.3025 | 0.5110 | 0.2406 | 0.7500 | 0.0625 | 0.6113 | 0.1521 |
| F5 | 0.4500 | 0.3025 | 0.4971 | 0.2546 | 0.7500 | 0.0625 | 0.6113 | 0.1521 |
| F6 | 0.3973 | 0.3660 | 0.4500 | 0.3025 | 0.6500 | 0.1225 | 0.5110 | 0.2406 |
| F7 | 0.3973 | 0.3660 | 0.4111 | 0.3492 | 0.7500 | 0.0625 | 0.6113 | 0.1521 |
| F8 | 0.5500 | 0.2025 | 0.6500 | 0.1225 | 0.5500 | 0.2025 | 0.6500 | 0.1225 |
| F9 | 0.5974 | 0.1631 | 0.5500 | 0.2025 | 0.7500 | 0.0625 | 0.5500 | 0.2025 |
| F10 | 0.4500 | 0.3025 | 0.5500 | 0.2025 | 0.6500 | 0.1225 | 0.5110 | 0.2406 |
| F11 | 0.6500 | 0.1225 | 0.6500 | 0.1225 | 0.4500 | 0.3025 | 0.6500 | 0.1225 |
| F12 | 0.4500 | 0.3025 | 0.4500 | 0.3025 | 0.6982 | 0.0917 | 0.5500 | 0.2025 |
| F13 | 0.5500 | 0.2025 | 0.4500 | 0.3025 | 0.7500 | 0.0625 | 0.6113 | 0.1521 |
5. Discussion
5.1. ANP Discussion
5.2. PFs-VIKOR discussion
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
Appendix I
| Active government involvement (F1) | Active participation of NGOs (F2) | Coordination among participating organizations (F3) | Logistics provider reliability (F4) | Supply of necessities of life (F12) | Timely arrival of rescue supplies (F13) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organizational involvement A | Active government involvement (F1) | 0 | |||||||
| Active participation of NGOs (F2) | 0 | ||||||||
| Coordination among participating organizations (F3) | 0 | ||||||||
| Reliability B | Logistics provider reliability (F4) | ||||||||
| Material supplier reliability (F5) | |||||||||
| Agility C | Responsiveness (F6) | ||||||||
| Resource Scheduling Capability (F7) | |||||||||
| Timeliness of transportation (F8) | |||||||||
| Cost Factor D | Transportation Costs (F9) | ||||||||
| Inventory costs (F10) | |||||||||
| Material Mobilization and Procurement Costs (F11) | |||||||||
| Quality of service E | Supply of necessities of life (F12) | 0 | |||||||
| Timely arrival of rescue supplies (F13) | 0 |
Appendix Ⅱ
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | F9 | F10 | F11 | F12 | F13 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 | 0.49 |
| F2 | 0.27 | 0.11 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.11 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.26 |
| F3 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 |
| F4 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.47 | 0.42 | 0.42 |
| F5 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.41 | 0.42 | 0.43 | 0.48 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.44 | 0.43 |
| F6 | 0.61 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.61 | 0.51 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.63 | 0.62 | 0.54 | 0.61 |
| F7 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.80 | 0.82 | 0.81 | 0.82 | 0.83 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.83 |
| F8 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| F9 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.12 | 0.11 |
| F10 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| F11 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.23 | 0.29 |
| F12 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| F13 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | F9 | F10 | F11 | F12 | F13 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 5 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| F2 8 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07 |
| F3 2 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.13 |
| F4 6 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| F5 7 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08 |
| F6 3 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.11 |
| F7 1 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| F8 4 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| F9 9 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| F10 12 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| F11 10 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| F12 11 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| F13 13 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | F9 | F10 | F11 | F12 | F13 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| F2 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.07 |
| F3 | 0.13 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.12 |
| F4 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| F5 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.08 |
| F6 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.12 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.11 |
| F7 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.15 |
| F8 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.10 |
| F9 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
| F10 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 |
| F11 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| F12 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| F13 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
Appendix III
| F1 | 0.7500 | 0.0625 | 0.5500 | 0.2025 |
| F2 | 0.6982 | 0.0917 | 0.5110 | 0.2406 |
| F3 | 0.6500 | 0.1225 | 0.3973 | 0.3660 |
| F4 | 0.7500 | 0.0625 | 0.4500 | 0.3025 |
| F5 | 0.7500 | 0.0625 | 0.4500 | 0.3025 |
| F6 | 0.6500 | 0.1225 | 0.3973 | 0.3660 |
| F7 | 0.7500 | 0.0625 | 0.3973 | 0.3660 |
| F8 | 0.6500 | 0.1225 | 0.5500 | 0.2025 |
| F9 | 0.5500 | 0.2025 | 0.7500 | 0.0625 |
| F10 | 0.4500 | 0.3025 | 0.6500 | 0.1225 |
| F11 | 0.4500 | 0.3025 | 0.6500 | 0.1225 |
| F12 | 0.6982 | 0.0917 | 0.4500 | 0.3025 |
| F13 | 0.7500 | 0.0625 | 0.4500 | 0.3025 |
| Xingyang | Gongyi | Dengfeng | Xinmi | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0.0848 | 0.1115 | 0.0000 | 0.0848 | 0.1115 |
| F2 | 0.0884 | 0.0762 | 0.0000 | 0.0562 | 0.0884 |
| F3 | 0.0729 | 0.0628 | 0.0000 | 0.0470 | 0.0729 |
| F4 | 0.1362 | 0.1237 | 0.0000 | 0.0848 | 0.1362 |
| F5 | 0.1362 | 0.1272 | 0.0000 | 0.0848 | 0.1362 |
| F6 | 0.0729 | 0.0718 | 0.0000 | 0.0592 | 0.0729 |
| F7 | 0.1373 | 0.1377 | 0.0000 | 0.0848 | 0.1373 |
| F8 | 0.0470 | 0.0000 | 0.0470 | 0.0000 | 0.0470 |
| F9 | 0.0200 | 0.0000 | 0.1115 | 0.0000 | 0.1115 |
| F10 | 0.0000 | 0.0248 | 0.0718 | 0.0125 | 0.0718 |
| F11 | 0.0718 | 0.0718 | 0.0000 | 0.0718 | 0.0718 |
| F12 | 0.1009 | 0.1009 | 0.0000 | 0.0762 | 0.1009 |
| F13 | 0.1115 | 0.1362 | 0.0000 | 0.0848 | 0.1362 |
| Xingyang | Gongyi | Dengfeng | Xinmi | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 0.7610 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.7610 |
| F2 | 0.9998 | 0.8615 | 0.0000 | 0.6354 |
| F3 | 1.0003 | 0.8618 | 0.0000 | 0.6451 |
| F4 | 1.0000 | 0.9081 | 0.0000 | 0.6227 |
| F5 | 1.0000 | 0.9342 | 0.0000 | 0.6227 |
| F6 | 1.0003 | 0.9849 | 0.0000 | 0.8130 |
| F7 | 1.0001 | 1.0029 | 0.0000 | 0.6177 |
| F8 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 |
| F9 | 0.1794 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 |
| F10 | 0.0000 | 0.3449 | 1.0000 | 0.1745 |
| F11 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 |
| F12 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.7548 |
| F13 | 0.8183 | 1.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.6227 |
References
- The official website of the World Meteorological Organization.
- National Disaster Reduction Center of the Ministry of Water Resources and the Ministry of Emergency Management.
- Howe, N.P.; Bundell, S. Flood risk rises as people surge into vulnerable regions. Nature 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J. New field of GS1:Humanitarian relief logistics. Barcode and Information System, (In Chinese). 2017; 28. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Z. Research on humanitarian supply chain for post-disaster relief. Jiangsu business theory (In Chinese). 2012, 8, 147–149. [Google Scholar]
- Jinglei, Y.; Linli, X. Comparative analysis of humanitarian logistics and commercial logistics. Port Economy (In Chinese). 2009, 7, 45–47. [Google Scholar]
- Dian'an, J. From Epidemic Shock: Supply Chain Resilience is the Key to Recovery - An Interview with Mr. Jia Dian'an of Baker & McKenzie Beijing. China Money Market 2020, 5, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, Z. Enhancing resilience is the key to ensure the stability of industrial chain supply chain. Economic Daily News (In Chinese). 2020, 10, 20(011). [Google Scholar]
- Anjomshoae, A.; Banomyong, R.; Mohammed, F.; Kunz, N. A systematic review of humanitarian supply chains performance measurement literature from 2007 to 2021. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 2022, 72, 102852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Peng, Y.; Chen, H. Post-seismic supply chain risk management: A system dynamics disruption analysis approach for inventory and logistics planning. Computers & Operations Research 2014, 42, 14–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.K.; Routroy, S.; Singh, R.K.; Nag, U. Analysis of supply chain vulnerability factors in manufacturing enterprises: a fuzzy DEMATEL approach. International Journal of Logistics Research and Applications 2022, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Bryde, D.J.; Foropon, C.; Graham, G.; Giannakis, M.; Mishra, D.B. Agility in humanitarian supply chain: an organizational information processing perspective and relational view. Ann Oper Res 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Kant, R.; Shankar, R. Evaluating solutions to overcome humanitarian supply chain management barriers: A hybrid fuzzy SWARA. Fuzzy WASPAS approach International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 2020, 51, 101838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Y. A Bayesian Network Method for Humanitarian Supply Chain Performance Evaluation. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 3088–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.; Yue, X. A study of supply chain performance in humanitarian relief - Perspectives on authoritative governance, market competition and partner cooperation. Economic Management, (In Chinese). 2013; 35, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Tatham, P.; Kovács, G. The application of “swift trust” to humanitarian logistics. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2010, 126, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyan, C.; Junwei, L.; Yuhao, Y. An empirical study on the relationship between organizational trust, knowledge sharing and organizational performance. Beijing: Research Management (In Chinese). 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wenhong, Z. HARA Changhong. A study on the relationship between firms' ability to influence government/industry and new product performance. Science Research (In Chinese). 2011, 29, 906–913. [Google Scholar]
- Kai, Y. A preliminary study on the international humanitarian relief coordination mechanism under the framework of the United Nations. In Shanghai: International Outlook; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Roh, S.; Lin, H.H.; Jang, H. Performance indicators for humanitarian relief logistics in Taiwan. Asian J. Shipp. Logist. 2022, 38, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Goh, M.; De Souza, R. De Souza A SCOR framework to measure logistics performance of humanitarian organizations. Journal of Humanitarian Logistics and Supply Chain Management 2016, 6, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Huang, L.; Liang, X. On the simulation-based reliability of complex emergency logistics networks in post-accident rescues. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2018, 15, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larrea, O. Key performance indicators in humanitarian logistics in Colombia. IFAC Proceedings Volumes 2013, 46, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiyun, C. Analysis of international rescue coordination for major natural disasters. Journal of Jinling Institute of Science and Technology (Social Science Edition) 2013, 27, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Larrea, O. Key performance indicators in humanitarian logistics in Colombia. IFAC Proceedings 2013, 46, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, R.; Hanaoka, S. Warehouse location determination for humanitarian relief distribution in Nepal. Transportation Research Procedia 2017, 25, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Agent-based evaluation of humanitarian relief goods supply capability. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 2019, 36, 101105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oloruntoba, R.; Kovács, G. A commentary on agility in humanitarian aid supply chains. Supply Chain Management 2015, 20, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haavisto, I.; Goentzel, J. Measuring humanitarian supply chain performance in a multi-goal context. J. Humanit. Logist. Supply Chain Manag. 2015, 5, 300–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyi, D.G.; Yusuf, Y.; Menhat, M.S.; Abubakar, T.; Ogbuke, N.J. Agile capabilities as necessary conditions for maximising sustainable supply chain performance: An empirical investigation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019, 222, 107501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chern, J.-H. An empirical study on the performance evaluation of indicators for the Nonprofit organizations─an example of 300 major foundations in Taiwan; Nation Defense University, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kazancoglu, I.; Ozbiltekin-Pala, M.; Mangla, S.K.; Kazancoglu, Y.; Jabeen, F. Role of flexibility, agility and responsiveness for sustainable supply chain resilience during COVID-19. J. Clean. Prod. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Rhim, H.; Seog, S.H. Response time and vendor–assembler relationship in a supply chain. European Journal of Operational Research 2008, 184, 652–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fushou, W. Research on supply chain decision making and monitoring based on response time; (In Chinese). Hubei: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sahebjamnia, N.; Torabi, S.A.; Mansouri, S.A. A hybrid decision support system for managing humanitarian relief chain. Decision Support Systems 2017, 95, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingne, H.; Shriram, R. Heuristic deep learning scheduling in cloud for resource-intensive internet of things systems. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2023, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.; Chaba, Y.; Noliya, A. Performance Analysis of Support Vector Machine Learning Based Carrier Aggregation Resource scheduling in 5G Mobile Communication. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 218, 2776–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M; Ramezanian, R. Ghorbani M; Ramezanian, R. Integration of carrier selection and supplier selection problem in humanitarian logistics. Computers & Industrial Engineering 2020, 144, 106473. [Google Scholar]
- Darvishan, A.; Lim, G.J. Dynamic network flow optimization for real-time evacuation reroute planning under multiple road disruptions. Reliability Engineering & System Safety 2021, 214, 107644. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Q. Research on the effectiveness of supply chain cost control of Suning.com based on entropy value method; Hunan Institute of Technology, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whybark, D.C. Issues in managing disaster relief inventories. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2007, 108, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Hanaoka, S. Relief inventory modelling with stochastic lead-time and demand. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 235, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcik, B.; Beamon, B.M. Facility location in humanitarian relief. Int. J. Logist. Res. Appl. 2008, 11, 101–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holguín-Veras, J.; Pérez, N.; Jaller, M.; Van Wassenhove, L.N.; Aros-Vera, F. On the appropriate objective function for post-disaster humanitarian logistics models. J. Oper. Manag. 2013, 31, 262–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Fang, X.; Li, Y.; Ni, S.; Zhang, Q.; Sang, C.K. Three-level multimodal transportation network for cross-regional emergency resources dispatch under demand and route reliability. Reliability Engineering & System Safety 2022, 222, 108461. [Google Scholar]
- Beamon, B.M.; Balcik, B. Performance measurement in humanitarian relief chains. Int. J. Public Sect. Manag. 2008, 21, 4–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Xu, X. Cost allocation model for optimizing supply chain inventory with controllable lead time. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2010, 59, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Murat, A.; Huang, W. Selection of contract suppliers under price and demand uncertainty in a dynamic market. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 198, 830–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merckx, G.; Chaturvedi, A. Short vs. long-term procurement contracts when supplier can invest in cost reduction. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 227, 107652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavamifar, A.; Torabi, S.A.; Moshtari, M. A hybrid relief procurement contract for humanitarian logistics. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review 2022, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W. Research on realization mechanism and management strategy of supply chain low carbon innovation considering consumer preference; Shandong University of Science and Technology, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J. Agent-based evaluation of humanitarian relief goods supply capability. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 2019, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiazhen, H.; Jiawei, Z.; Shiyan, X. Analysis of strategic stockpiling and rotational storage of emergency medical supplies--Taking masks as an example. Shanghai Management Science 2023, 45, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifyazdi, M.; Navangul, K.A.; Gharehgozli, A.; Jahre, M. On- and offshore prepositioning and delivery mechanism for humanitarian relief operations. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2018, 56, 6164–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altay, N.; Gunasekaran, A.; Dubey, R.; Childe, S.J. Agility and resilience as antecedents of supply chain performance under moderating effects of organizational culture within the humanitariansetting: a dynamic capability view. production planning & control 2018, 29, 1158–1174. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, R.K.; Gupta, A.; Gunasekaran, A. Analysing the interaction of factors for resilient humanitarian supply chain. international journal of production research 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhile, W.; Jihai, Z. Agent-based evaluation of humanitarian relief goods supply capability. international journal of disaster risk reduction 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nezhadroshan, A.M.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M. A scenario-based possibilistic-stochastic programming approach to address resilient humanitarian logistics considering travel time and resilience levels of facilities. Int. J. Syst. Sci. Oper. Logist. 2020, 8, 321–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, N.; Sonal, C. Operational excellence in humanitarian logistics and supply chain management through leagile framework: a case study from a non-mature economy. production planning & control 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafizur, R.M.; Farah, T.; Mahmuda, M.; Abedin, Z.; Aryal, A.; Raj, K. Assessing Barriers in Humanitarian Supply Chains for Cyclone in Coastal Areas of Bangladesh: An Interpretive Structural Modeling (ISM) Approach. Sustainability 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Giedelmann, L.N; Guerrero, W.J.; Solano-Charris, E.L. System dynamics approach for food inventory policy assessment in a humanitarian supply chain. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, S.; Gupta, S.; Wood, L. Big data analytics in sustainable humanitarian supply chain: barriers and their interactions. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 319, 721–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Wan, C.; Qu, Y.; Cornélissen, G.; Halberg, F. In vitro circadian ANP secretion by gene transferring cells encapsulated in polycaprolactone tubes: gene chronotherapy. Peptides 2004, 25, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Gao, M.; Liang, K. Identification of factors affecting the synergy of multiple subjects in the development and utilization of "urban minerals" based on ANP-BPNN[J]. Management Review 2023, 35, 16–27. [Google Scholar]
- Steurer, J. The Delphi method: an efficient procedure to generate knowledge. Skeletal Radiol 2011, 40, 959–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belton, I.; MacDonald, A.; Wright, G.; Hamlin, I. Improving the practical application of the Delphi method in group-based judgment: A six-step prescription for a well-founded and defensible process. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 2019, 147, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xu, Z.; Xu, J. Large-scale group Delphi method with heterogeneous decision information and dynamic weights. Expert Systems with Application 2023, 213, 118782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Kant, R.; Shankar, R. Evaluating solutions to overcome humanitarian supply chain management barriers: A hybrid fuzzy SWARA – Fuzzy WASPAS approach. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 2020, 51, 101838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, L.; Gurumurthy, A.; Soni, G.; Jain, V. Modelling the inter-relationship between factors affecting coordination in a humanitarian supply chain: a case of Chennai flood relief. Ann Oper Res 2019, 283, 1227–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.-F.; Liu, H.-C. A 2-dimension uncertain linguistic DEMATEL method for identifying critical success factors in emergency managementg. Applied Soft Computin 2018, 71, 386–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Investigation report on the "20 July" exceptionally heavy rainstorm disaster in Zhengzhou.
- John, L.; Gurumurthy, A.; Soni, G.; Jain, V. Modelling the Inter-Relationship between Factors Affecting Coordination in a Humanitarian Supply Chain: A Case of Chennai Flood Relief. Ann. Oper. Res. 2019, 283, 1227–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author (s) and contributor (s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor (s). MDPI and/or the editor (s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
| rank | rank | rank | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xingyang | 0.4986 | 4 | 0.1018 | 4 | 0.5221 | 4 |
| Gongyi | 0.3739 | 3 | 0.0930 | 3 | 0.4365 | 3 |
| Xinmi | 0.2859 | 2 | 0.0811 | 2 | 0.4279 | 2 |
| Dengfeng | 0.2701 | 1 | 0.0605 | 1 | 0.4008 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





