Submitted:
26 July 2023
Posted:
27 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.2. Study Object
2.2. Study Area and Field Sampling
2.3. Laboratory analyses
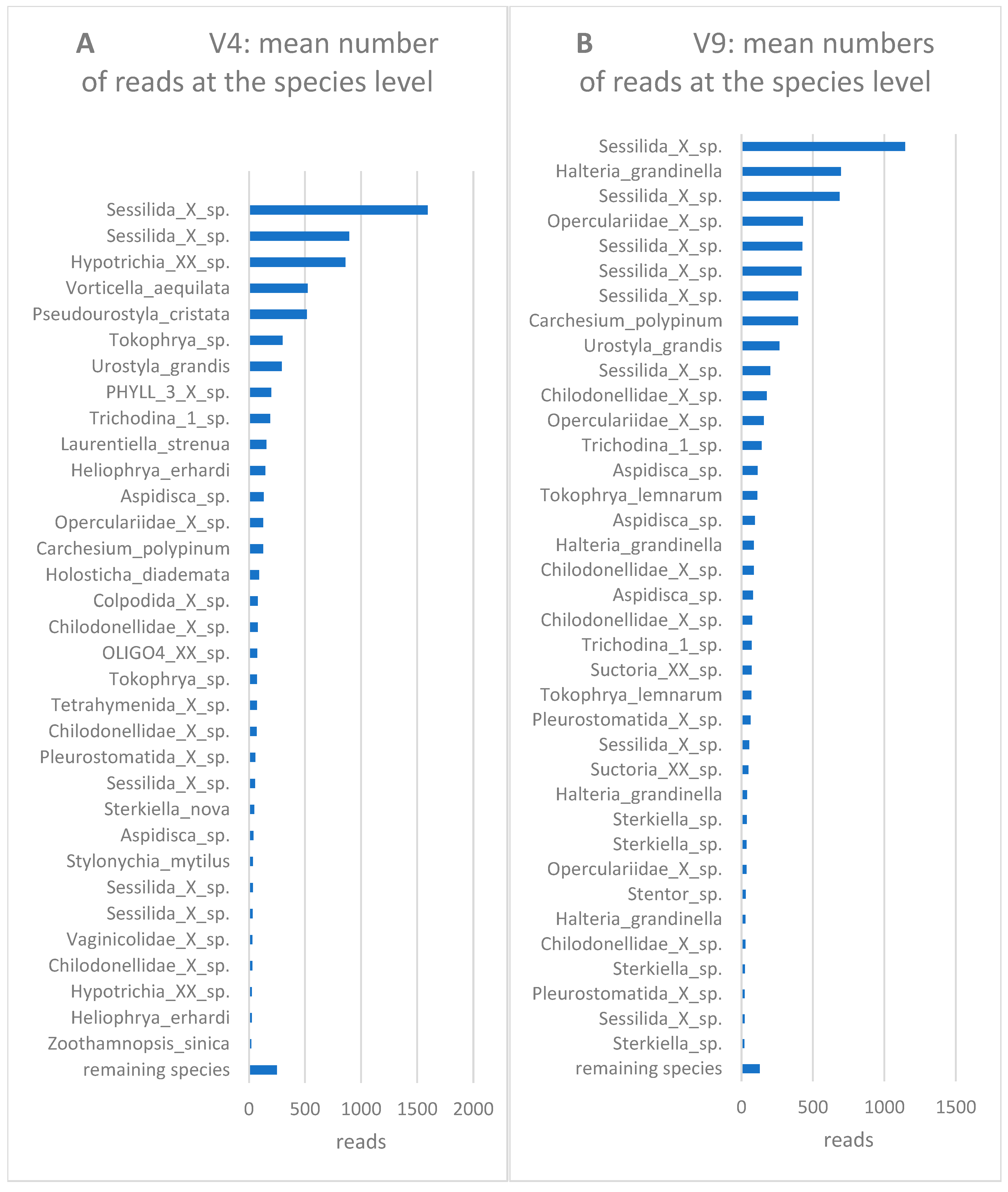
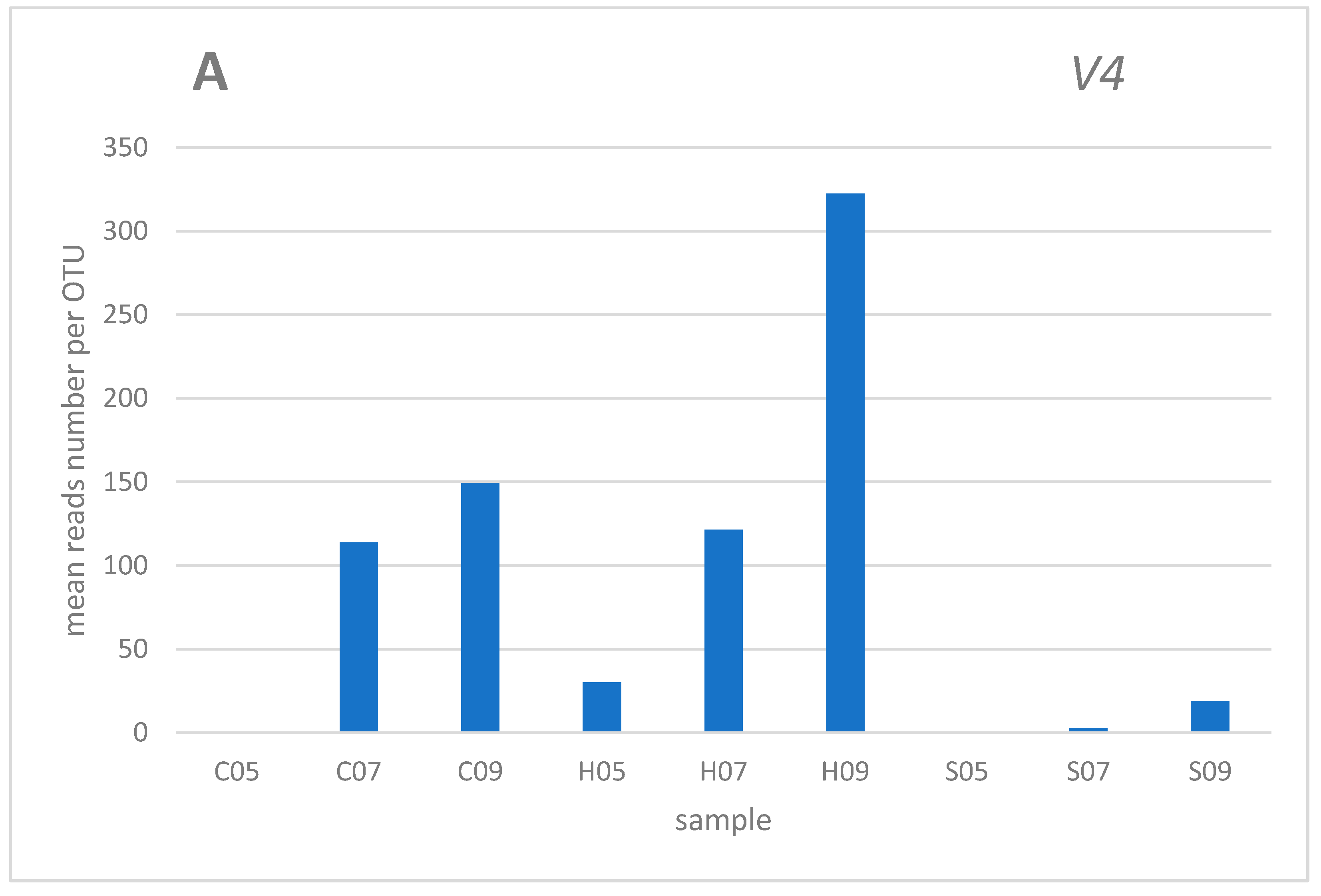
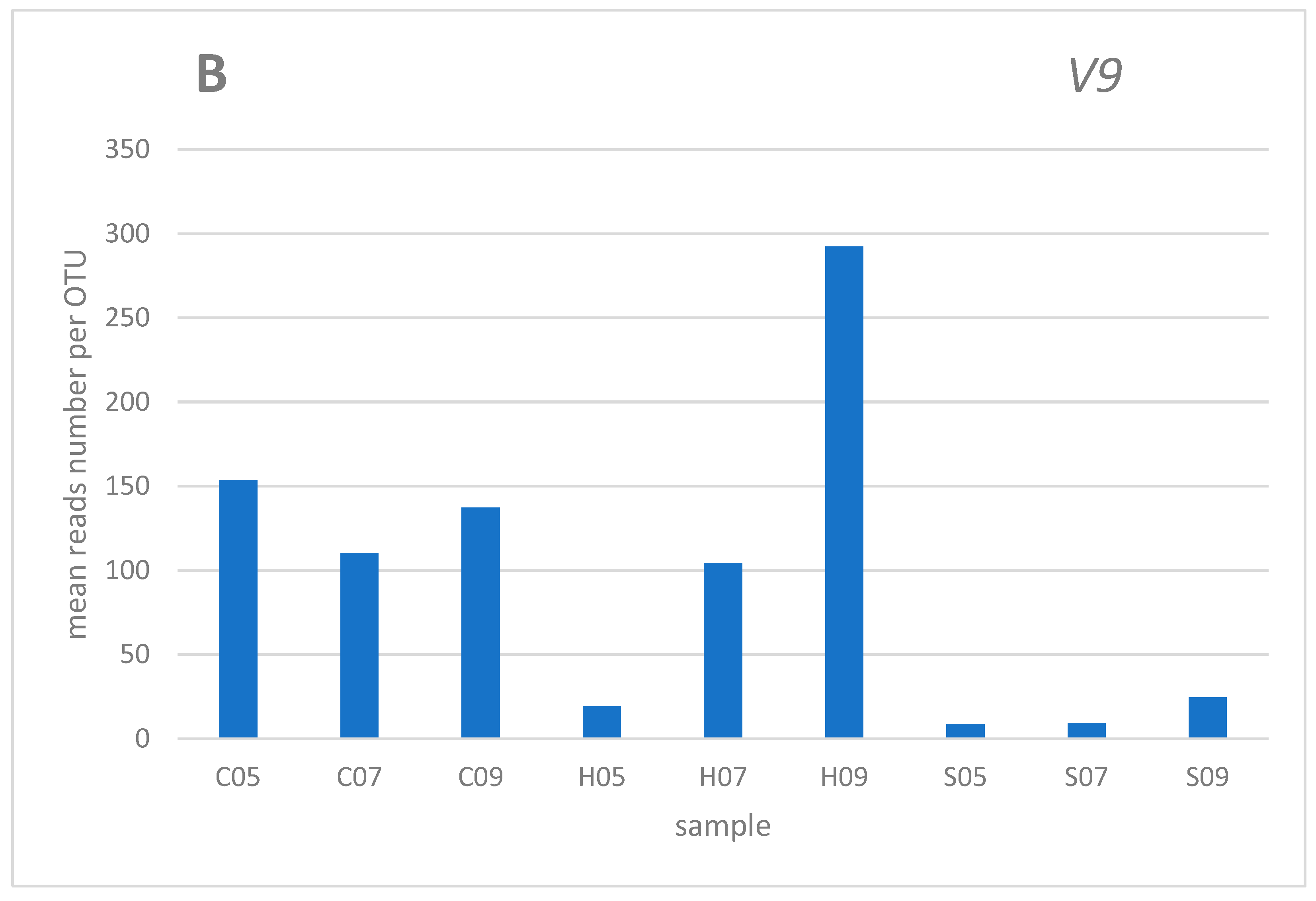
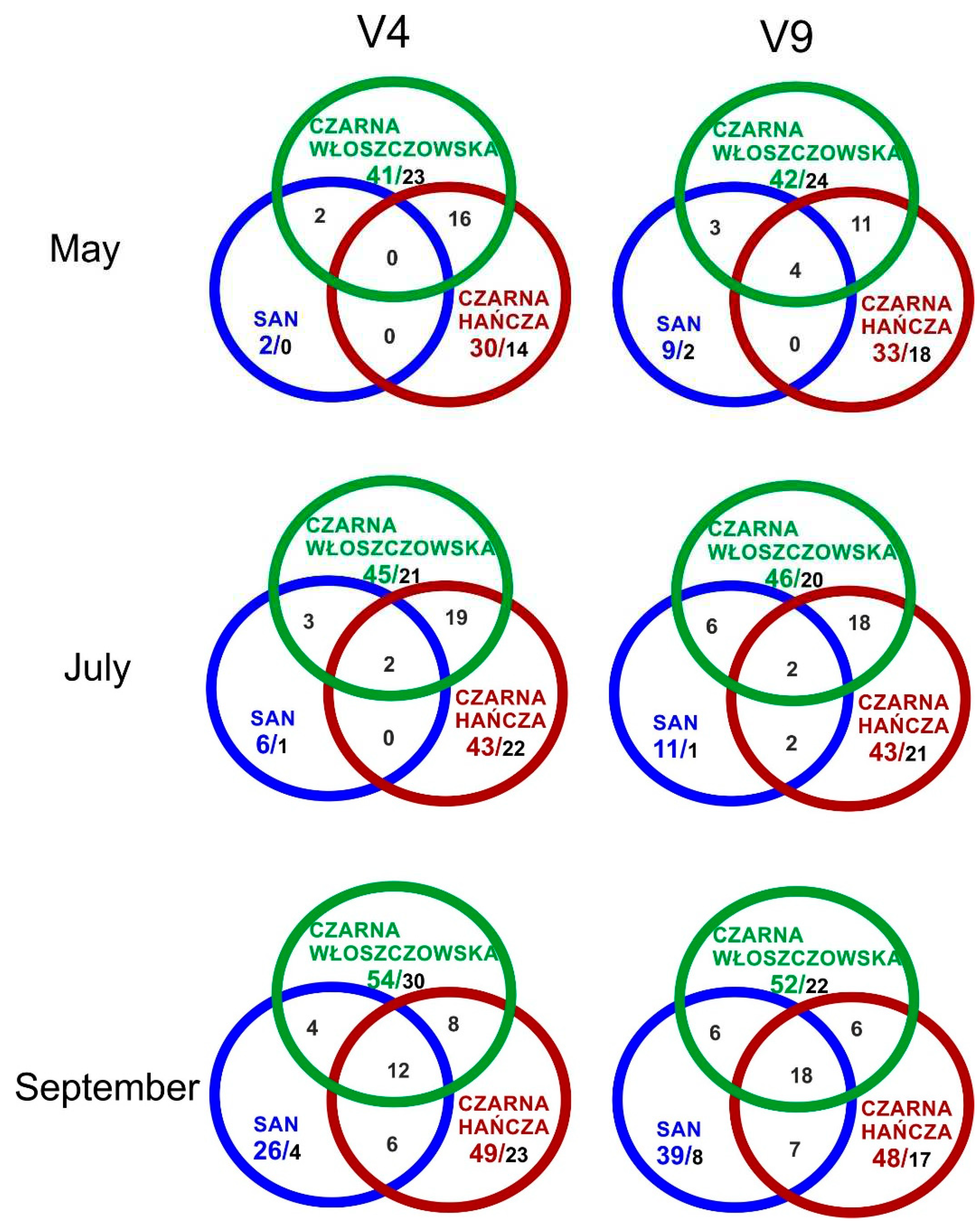
3. Results and discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, E.O., The current state of biological diversity. Biodiversity, 1988, 521(1), 3-18.
- McArthur, W.H. Observations of the enteric protozoa of Rana pipiens during larval development and metamorphosis. Proceedings of the Iowa Academy of Science (Iowa Acad Sci), 1955, 62: 640-651.
- Tilman, D., Isbell, F., Cowles, J.M. Biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Annual review of ecology, evolution, and systematics, 2014, 45, 471-493. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1064088. [CrossRef]
- Baird Callicott, J., Rozzi, R., Delgado, L., Monticino, M., Acevedo, M. and Harcombe, P. Biocomplexity and conservation of biodiversity hotspots: three case studies from the Americas. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2007, 362(1478), 321-333. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2006.1989. [CrossRef]
- Dybas, C.L., From Biodiversity to Biocomplexity: A Multidisciplinary Step toward Understanding Our Environment: Highlights of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the American Institute of Biological Sciences, 24–26 March 2001, Washington, DC. BioScience, 2001, 51(6), 426-430. https://doi.org/10.1641/0006-3568(2001)051[0426:FBTBAM]2.0.CO;2. [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D. Multiple threats imperil freshwater biodiversity in the Anthropocene. Current Biology, 2019, 29(19), R960-R967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2019.08.002. [CrossRef]
- Strayer, D.L., Hunter, D.C., Smith, L.C., Borg, C.K. Distribution, abundance, and roles of freshwater clams (Bivalvia, Unionidae) in the freshwater tidal Hudson River. Freshwater Biology 1994, 3, 239–248. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.1994.tb00858.x. [CrossRef]
- Newton, T.J., Zigler, S.J., Rogala, J.T., Gray, B.R. and Davis, M. Population assessment and potential functional roles of native mussels in the Upper Mississippi River. Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems, 2011, 21(2), 122-131. https://doi.org/10.1002/aqc.1170. [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, C. C. Ecosystem services provided by freshwater mussels. Hydrobiologia, 2018, 810 (1), 15–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750- 0 17-31. [CrossRef]
- Zieritz, A., Sousa, R., Aldridge, D. C., Douda, K., Esteves, E., Ferreira-Rodríguez, N., Mageroy, J. H., Nizzoli, D., Osterling, M., Reis, J., Riccardi, N., Daill, D., Gumpinger, C., & Vaz, A. S. A global synthesis of ecosystem services provided and disrupted by fresh-water bivalve molluscs. Biological Reviews, 2022, 97, 1967–1998. https://doi.org/10.1111/BRV.12878. [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R., Zając, T., Halabowski, D., Aksenova, O.V., Bespalaya, Y.V., Carvalho, F., Castro, P., Douda, K., da Silva, J.P., Ferreira-Rodríguez, N. and Geist, J. A roadmap for the conservation of freshwater mussels in Europe. Conservation Biology, 2023, 37(2), p.e13994. https://doi.org/10.1111/cobi.13994. [CrossRef]
- Hudson, P.J., Dobson, A.P. and Lafferty, K.D. Is a healthy ecosystem one that is rich in parasites? Trends in ecology & evolution, 2006, 21(7), 381-385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2006.04.007. [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R. R., Harris, N. C., Colwell, R. K., Koh, L. P., Sodhi, N. S. The sixth mass coextinction: are most endangered species parasites and mutualists? Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2009, 276(1670), 3037-3045. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2009.0413. [CrossRef]
- Brian, J.I., Aldridge, D.C. Mussel parasite richness and risk of extinction. Conservation Biology, 2022, 36(6), p.e13979. https://doi.org/10.1111/cobi.13979. [CrossRef]
- Jokela, J., Uotila, L., Taskinen, J. Effect of the castrating trematode parasite Rhipidocotyle fennica on energy allocation of fresh-water clam Anodonta piscinalis. Functional Ecology 1993, 7, 332-338. https://doi.org/10.2307/2390213. [CrossRef]
- McElwain, A. Are parasites and diseases contributing to the decline of freshwater mussels (Bivalvia, Unionida)?. Freshwater Mollusk Biology and Conservation, 2019, 22(2), 85-89. https://doi.org/10.31931/fmbc.v22i2.2019.85–89. [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, C. C., Nichols, S. J., Spooner, D. E. Community and foodweb ecology of freshwater mussels. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 2008, 27(2), 409-423. https://doi.org/10.1899/07-058.1. [CrossRef]
- Kat, P.W. Parasitism and the Unionacea (bivalvia). Biological Reviews, 1984, 59(2), 189-207, https://doi.org/1111/j.1469-185X.1984.tb00407.x. [CrossRef]
- Tatoj, K., Ćmiel, A. M., Kwaśna, D., Lipińska, A. M., Zając, K., Zając, T. The endangered thick-shelled river mussel (Unio crassus): a new host species for the European bitterling (Rhodeus amarus). Biodiversity and Conservation, 2017, 26, 1217-1224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10531-017-1295-y. [CrossRef]
- Mioduchowska, M., Konecka, E., Gołdyn, B., Pinceel, T., Brendonck, L., Lukić, D., Kaczmarek, Ł., Namiotko T., Zając K., Zając T., Jastrzębski J. P., Bartoszek, K. Playing Peekaboo with a Master Manipulator: Metagenetic Detection and Phylogenetic Analysis of Wolbachia Supergroups in Freshwater Invertebrates. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2023, 24(11), 9400. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119400. [CrossRef]
- Lynn, D. H., Doerder, F. P., Gillis, P. L., Prosser, R. S. Tetrahymena glochidiophila n. sp., a new species of Tetrahymena (Ciliophora) that causes mortality to glochidia larvae of freshwater mussels (Bivalvia). Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 2018, 127(2), 125-136. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao03188. [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Lima , M., Kebapçı, U., Van Damme, D. Unio crassus. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2014: e.T22736A42465628. Accessed on 10 July 2023. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2014-1.RLTS.T22736A42465628.en. [CrossRef]
- Cuttelod, A., Seddon, M. and Neubert, E. European Red List of Non-marine Molluscs. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union, 2011, https://doi.org/10.2779/84538. [CrossRef]
- Mioduchowska, M., Zając, K., Bartoszek, K., Madanecki, P., Kur, J., Zając, T. 16S rRNA-based metagenomic analysis of the gut microbial community associated with the DUI species Unio crassus (Bivalvia: Unionidae). Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research 2020, 58: 615–623. https://doi.org/10.1111/jzs.12377. [CrossRef]
- Tragin M., Zingone A., Vaulot D. Comparison of coastal phytoplankton composition estimated from the V4 and V9 regions of the 18S rRNA gene with a focus on photosynthetic groups and especially Chlorophyta. Environmental Microbiology, 2017, 20, 506–520. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13952. [CrossRef]
- Amaral-Zettler, L.A., McCliment, E.A., Ducklow, H.W., Huse, S.M. A method for studying protistan diversity using massively parallel sequencing of V9 hypervariable regions of small-subunit ribosomal RNA genes. PLoS One 2009, 4 (7), e6372. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0006372. [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G., Kuczynski, J., Stombaugh, J., Bittinger, K., Bushman, F.D., Costello, E.K., Fierer, N., Gonzalez Pena, A., Goodrich, J.K., Gordon, J.I., Huttley, G.A., Kelley, S.T., Knights, D., Koenig, J.E., Ley, R.E., Lozupone, C.A., McDonald, D., Muegge, B.D., Pirrung, M., Reeder, J., Sevinsky, J.R., Turnbaugh, P.J., Walters, W.A., Widmann, J., Yatsunenko, T., Zaneveld, J., Knight, R. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature Methods 2010, 7(5), 335- 336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.f.303. [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet. journal, 2011, 17(1), 10-12. https://doi.org/10.14806/ej.17.1.200. [CrossRef]
- Aronesty. ea-utils: “Command-line tools for processing biological sequencing data”, 2011 http://code.google.com/p/ea-utils.
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics, 2010, 26(19), 2460-2461. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq461 0. [CrossRef]
- Lewisch, E., Arnold, F., Fuehrer, H.P., Harl, J., Thielen, F. and El-Matbouli, M. Parasites and their impact on thick-shelled river mussels Unio crassus from two populations in Luxembourg. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 2023, 153, 31-43. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao03718. [CrossRef]
- Brian, J.I., Aldridge, D.C. Abundance data applied to a novel model invertebrate host shed new light on parasite community assembly in nature. Journal of Animal Ecology, 2021, 90(5), 1096-1108. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2656.13436. [CrossRef]
- Bruno, D. W., Nowak, B., Elliott, D. G. Guide to the identification of fish protozoan and metazoan parasites in stained tissue sections. Diseases of aquatic organisms, 2006, 70(1-2), 1-36. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao070001. [CrossRef]
- Taskinen, J., Urbańska, M., Ercoli, F., Andrzejewski, W., Ożgo, M., Deng, B., Choo, J. M., Riccardi, N. Parasites in sympatric populations of native and invasive freshwater bivalves. Hydrobiologia, 2021, 848, 3167-3178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04284-0. [CrossRef]
- Grzybkowska, M., Szczerkowska-Majchrzak, E., Dukowska, M., Leszczyńska, J., & Przybylski, M. Ephemera danica (Ephemeroptera: Ephemeridae) as a resource for two commensals: ciliated protozoans (Sessilida) and chironomids (Diptera). Journal of Insect Science, 2016, 16(1), 67. https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/iew050. [CrossRef]
- Dobrzycka-Krahel, A., Rolbiecki, L., Karczewski, J., & Skóra, M. E. Variations in host surfaces morphology and biology of ciliate epibionts explaining distribution pattern of epibionts in the invasive signal crayfish Pacifastacus leniusculus (Dana, 1852). Journal of Zoology, 2022, 316 (4), 282-295. https://doi.org/10.1111/jzo.12953. [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Lateif, R. S. Torra, D. E., El Sherry, Y. M. Infestation of External Ciliated Protozoan in Red Swamp Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Journal of Advanced Veterinary Research, 2023, 13(2), 197-206.
- Corliss, J.O. Biodiversity, classification, and numbers of species of protists. Nature and human society. The quest for a sustainable world. Proceedings of the 1997 Forum on Biodiversity, Board on Biology, NRC. National Academy Press, Washington, 2000, 130-155.
- Zhang, T., Vďačný, P. Morphological and molecular characterization of the ciliate parasite Tetrahymena rostrata infecting the renal organ of the dusky slug (Arion fuscus). Canadian Journal of Zoology, 2022, 101 (1), 32-45. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjz-2022-0080. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T., & Vďačný, P. A discovery of two new Tetrahymena species parasitizing slugs and mussels: morphology and multi-gene phylogeny of T. foissneri sp. n. and T. unionis sp. n. Parasitology Research, 2021, 120(7), 2595-2616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-021-07152-5. [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.A. Disease outbreaks and mass mortality in cultured Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua L., associated with Trichodina murmanica (Ciliophora). Journal of Fish Diseases, 2004, 27(3), 181-184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2761.2004.00525.x. [CrossRef]
- Madsen, H. C., Buchmann, K., Mellergaard, S. Trichodina sp. (Ciliophora: Peritrichida) in eel Anguilla anguilla in recirculation systems in Denmark: host-parasite relations. Diseases of aquatic organisms, 4, 2000, 2(2), 149-152. https://doi.org/10.3354/dao042149. [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hafez, G., Lahnsteiner, F., Mansour, N., Licek, E. Pathophysiology of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis infection in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and chub (Leuciscus cephalus). Journal of comparative pathology, 151(4), 394-399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcpa.2014.08.003. [CrossRef]
- Gaze, W.H., Wootten, R. Ectoparasitic species of the genus Trichodina (Ciliophora: Peritrichida) parasiting British freshwater fish. Folia Parasitologica, 1998, 45(3), 177-190.
- Karatayev, A.Y., Molloy, D.P., Burlakova, L.E. Seasonal dynamics of Conchophthirus acuminatus (Ciliophora, Conchophthiridae) infection in Dreissena polymorpha and D. bugensis (Bivalvia, Dreissenidae). European Journal of Protistology, 2000, 36(4), 397-404, DOI : 10.1016/S0932-4739(00)80045-0. [CrossRef]
- Blazhekovikj-Dimovska, D., Stojanovski, S. Ectoparasitic species of the genus Trichodina (Ciliophora: Peritrichida) parasitizing Macedonian freshwater fish. Acta Biologica, 2020, 27, 11-20. https://doi.org/10.18276/ab.2020.27-02. [CrossRef]
- Kulaš, A., Gulin, V., Kepčija, R.M., Žutinić, P., Perić, M.S., Orlić, S., Kajan, K., Stoeck, T., Lentendu, G., Čanjevac, I., Martinić, I. Ciliates (Alveolata, Ciliophora) as bioindicators of environmental pressure: A karstic river case. Ecological Indicators, 2021, 124, 107430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.107430. [CrossRef]
- Hajdukiewicz, H., Wyżga, B., Amirowicz, A., Oglęcki, P., Radecki-Pawlik, A., Zawiejska, J., Mikuś, P. Ecological state of a mountain river before and after a large flood: Implications for river status assessment. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 610, 244-257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.07.162. [CrossRef]
| River name | River character | Catchment | GPS of the sampling sites | Dates of sampling |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| San | a dynamic mountainous river in the northern part of the Carpathian Mountains | Vistula | 49.2173 N 22.7174 E |
26.05.2022 |
| 11.07.2022 | ||||
| 13.09.2022 | ||||
| Czarna Włoszczowska | a lowland river flowing through an agricultural landscape | 50.9470 N 19.8464 E |
20.05.2022 | |
| 7.07.2022 22.09.2022 | ||||
| Czarna Hańcza | a pristine lowland river | Neman | 53.9709 N 23.3032 E |
26.05.2022 15.07.2022 14.09.2022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





