- I.
Introduction
Religions were something that humans held as principles in their life. It’s been evolving for centuries and there are so many religions in the world. One of the most-followed religions in the world is Islam. Islam is a religion that was brought by Prophet Muhammad PBUH in the early 600 (DC). PEW Research Center suggests that in 2020, the numbered of Muslims reach approximately 1.9 billion followers in the entire world.
For such a huge number of followers, there must be something that keeps them in line, or else there will be a lot of chaos occur in the world we know of. Apparently, in Islam, there is a concept called pillars of Islam, where these pillars are the main obligations that must be carried out by Muslims so they can live a life filled with kindness and virtue. In the pillars of Islam, there is something called zakat. According to The Hanafi Mazhab — a school of thought attributed to Imam Abu Hanifah, one of the most respected Muslim theologists — zakat is an obligation to give a certain portion of certain wealth to certain people who were destined by Allah Azza Wa Jalla to seek His pleasure. [1] The objective of zakat, as emphasized in the Qur’an, is a glorious objective of purification and upliftment (At-Taubah 9:103). Before the collected portion of wealth is given to certain people, zakat must be managed systematically and transparently by Islamic law.
According to Indonesian Law No. 23rd of 2011 about Zakat Management, the management of zakat includes the activities of compiling, implementing, and managing the collection, distribution, and use of zakat. [1] Usually, zakat is managed by mosque administrators in each region. The management of zakat in several mosques is still carried out using a manual system, which can cause the loss of some zakat recipient data and the calculation of funds that have been received by zakat recipients. [2] The manual system is also considered less efficient for managing large amounts of data. To overcome this renowned problem, a Zakat management information system was designed. Agile methods are used in system development. It is hoped that this system will provide convenience to mosque administrators in managing zakat.
This paper’s remainder is structured as follows: Section I introduces the credit scoring and background. Section II related work. Section III are methods. Section IV result and discussion. Section V concludes this paper.
- II.
Related Work
In this section, we review articles, journals, and former research that were conducted about information systems, agile software development lifecycle, and previous research efforts on combining the two technologies.
- A.
Information System
Information Systems was a common topic that has been always the subject of much research. This academic field has always been aiming at systematizing the design of data processing applications in organizations to respond to the challenge of continuous innovation and communication tech- nologies. [3] To put it simply, an information system is created to simplify the process of data processing which saves humans a lot of work.
- B.
Agile Software Development
Embodied in the pillars of Islam, zakat is a pillar that must be run. Zakat is one obligation such as prayer and fasting. Rejecting paying for it on purpose is just the same as denying the pillars of Islam. Zakat got done by channeling it directly to recipients in need. Zakat got It is also channeled through management institutions/agencies zakat. Management and distribution of zakat through institutions/bodies have been done since ancient times The Prophet is usually called bait mal. Lifecycle [4].
Researchers plan to have an Information System Zakat management that can replace the system Zakat which is still operating manually. The method to be used is agile because this method is based on iterative work consisting of rules and solutions that have been agreed upon and is very efficient for making this application. This desire arises because researchers are involved directly on the part of this institution. Institution zakat experience problems in managing zakat, such as prob- lems in recording Muzakki data, Mustahik data, zakat income data, and data distribution of zakat to Mustahik and inside making reports that still use the method manuals. Identify the weaknesses of the online zakat application, there is no transparency so the zakat payer still feels that the funds that have been zakat are going to be distributed or not and maybe it is more of dhol to be paid directly so that there is a contract that is carried out in an orderly manner. The problem encountered in this zakat application is controversy among the public who ask about the law regarding paying zakat using the application online. The secretary of the Indonesian Council of Fatwa Commission (MUI) explained that paying zakat fitrah online is permissible. ”zakat payments do not have to be met physically. In fiqh statements, there is no physical consent granted (to meet)”.
- III.
Methodology
The development method used in making this system is an agile method. The agile methodology is a project management method with fast development cycles, also known as sprints [5]. In the development process, it is divided into several parts so that it runs quickly and this method needs quick adaptation to changes in any form [6].
- 1)
Planning
The initial stage of the agile method is planning to determine system requirements. This stage is divided into two stages, namely the system analysis stage and system requirements specification. [6].
- 2)
Design
The design phase is designing a solution that will meet the needs of the user. Starting from designing the system architecture, user interface, and the necessary software components. [7].
- 3)
Develop
The next step is system implementation and deployment after conducting system analysis and determining device re- quirements. The implementation stage is the stage that turns the plan into a web-based application based on the application prototype that was made before [7].
- 4)
Testing
At this stage, the software created at the implementation stage is tested. Application testing aims to see how well the application program works. Does the application flow match the established business processes and are there any errors in the application being developed [7].
- 5)
Deployment
The steps are taken to ensure the quality of the software created by testing the quality of the system. If the system produced meets the requirements, the software will be ready to be developed later. [7].
- 6)
Review
The review stage is to review the features that have been developed, provide feedback, and identify opportunities for improvement. [7].
- 7)
Launch
The launch stage is when the software product is ready to be officially rolled out to end users. This launch involves the communication, marketing and distribution of the product to the target users. After launch, further development and maintenance of the product can be carried out based on user feedback and changing needs as they arise. [7]
In this context, the survey describes the input features for the accepted samples’ credit scoring. [1,2,4–6,8–10]
- IV.
Result and Discussion
- A.
Project Requirement
Analysis of problem needs Referring to the results of the interviews that were conducted with Mas Amim, Mas Eko, and Mrs. Arofah as Village employees, Katapang on March 17 2020 stated that it was deemed necessary to collect mustahik data and determine priority mustahik because so far the distribution of zakat has not been completely even and data reporting is still manual. Sometimes there are also mustahik who should receive zakat but do not receive zakat. [7].
- B.
Proposal Analysis
Based on the problems raised, the solution obtained in this study is in the form of making applications that can help decide priority mustahik.
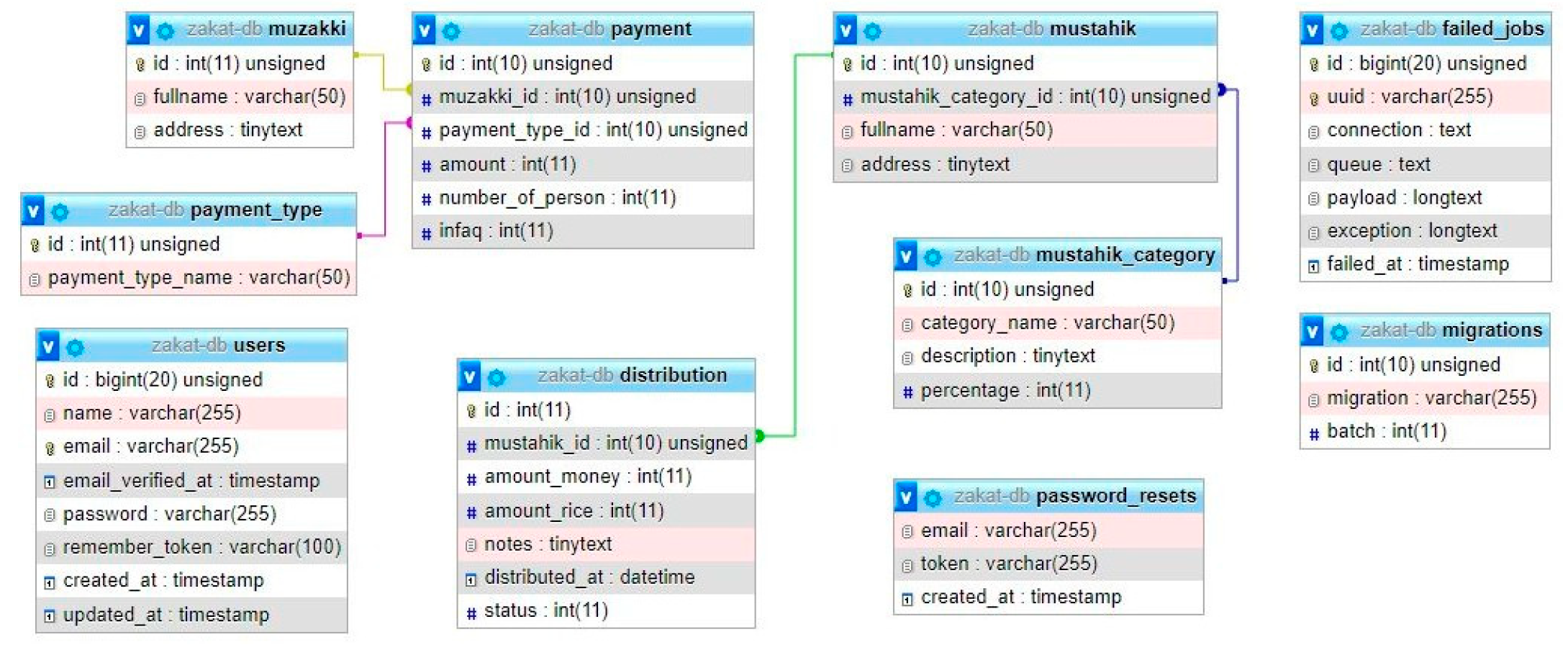
The Zakat Fitrah Information and Management System application was created.
Web-based Zakat Fitrah Information and Management system application.
The Village Party inputs data on mustahik candidates into the system.
Table I.
Access Rights.
| No. |
User |
Description |
| 1 |
Admin |
Admin is a person who has the
authority to be able to manipulate zakat and mustahik payment data |
1) Design stage:
- C.
Identifikasi Use Case
In this application the design processes are stated in a use case. Below is a use case identification table.
Table II.
Access Rights.
| Menu |
Function |
Access Rights |
| Login |
Use case which describes the
activity of entering a user- name and password to be able to access the menu in the MyZakat system. |
Admin |
| Input Zakat Payment Data |
Use case that describes the ac-
tivity of inputting zakat pay- ment data. |
Admin |
| Edit Zakat Payment Data |
Use case that describes the ac-
tivity of changing zakat pay- ment data |
Admin |
| Delete Zakat Payment Data |
Use case that describes the
activity of deleting zakat pay- ment data |
Admin |
Mustahik Data Input
Delete Mustahik Data Edit Mustahik Data |
Use case that describes the
activity of inputting mustahik data
UUse case that describes the activity of deleting mustahik data
Use case that describes the activity of changing mustahik data |
Admin
Admin Admin |
- D.
Implementation stage
The system requirements specifications needed in making this application are
Table III.
Technical Requirement.
Table III.
Technical Requirement.
| 1 |
Platform |
Web Application |
| 2 |
Stacks |
Laravel 8.*, PHP |
| 3 |
Text Editor |
Visual Studio Code |
| 4 |
Database |
MySQL |
| 5 |
Browser |
Google Chrome |
- E.
Page View
- 1)
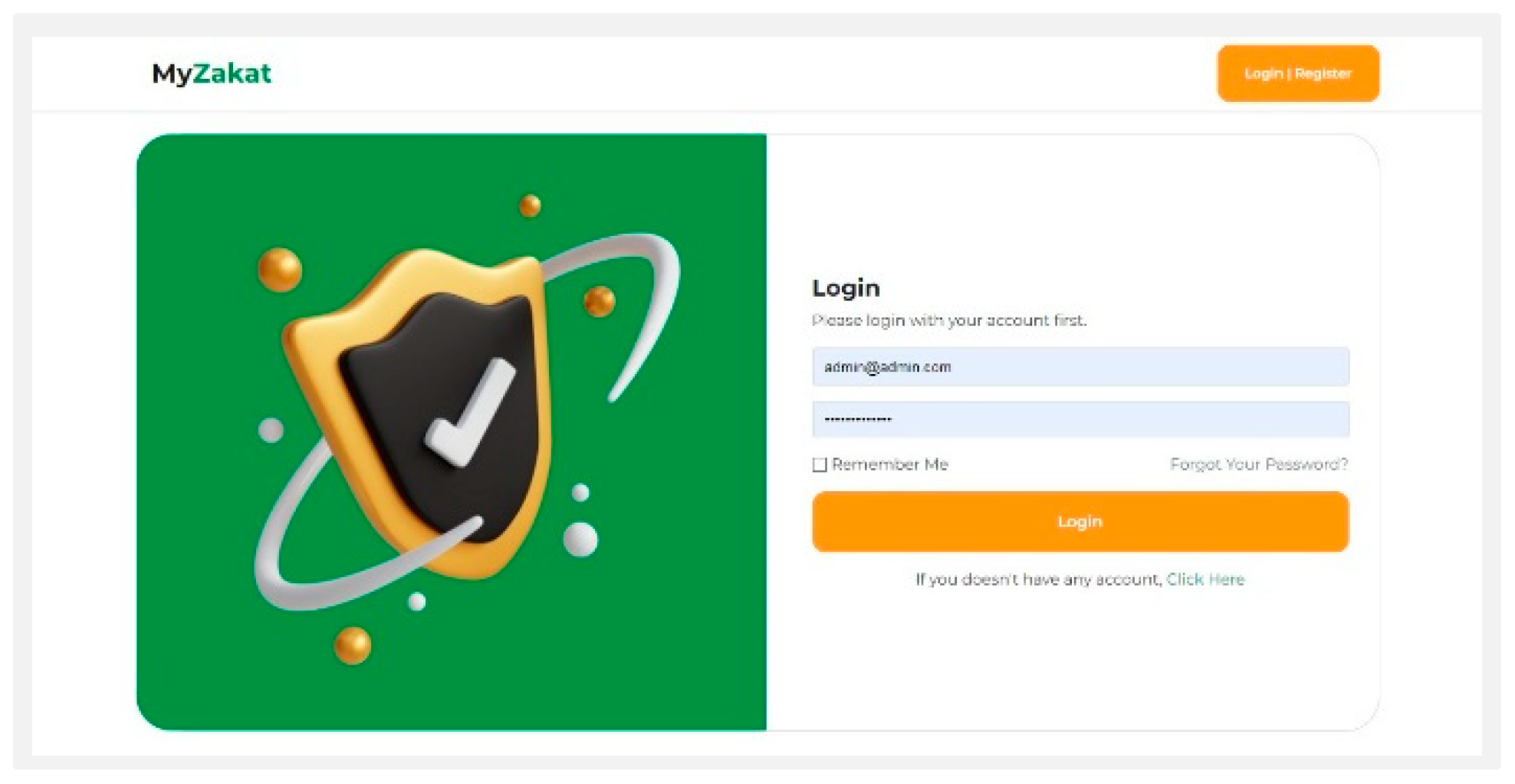
Login: The login page is the page used by the user to enter the main system
- 2)
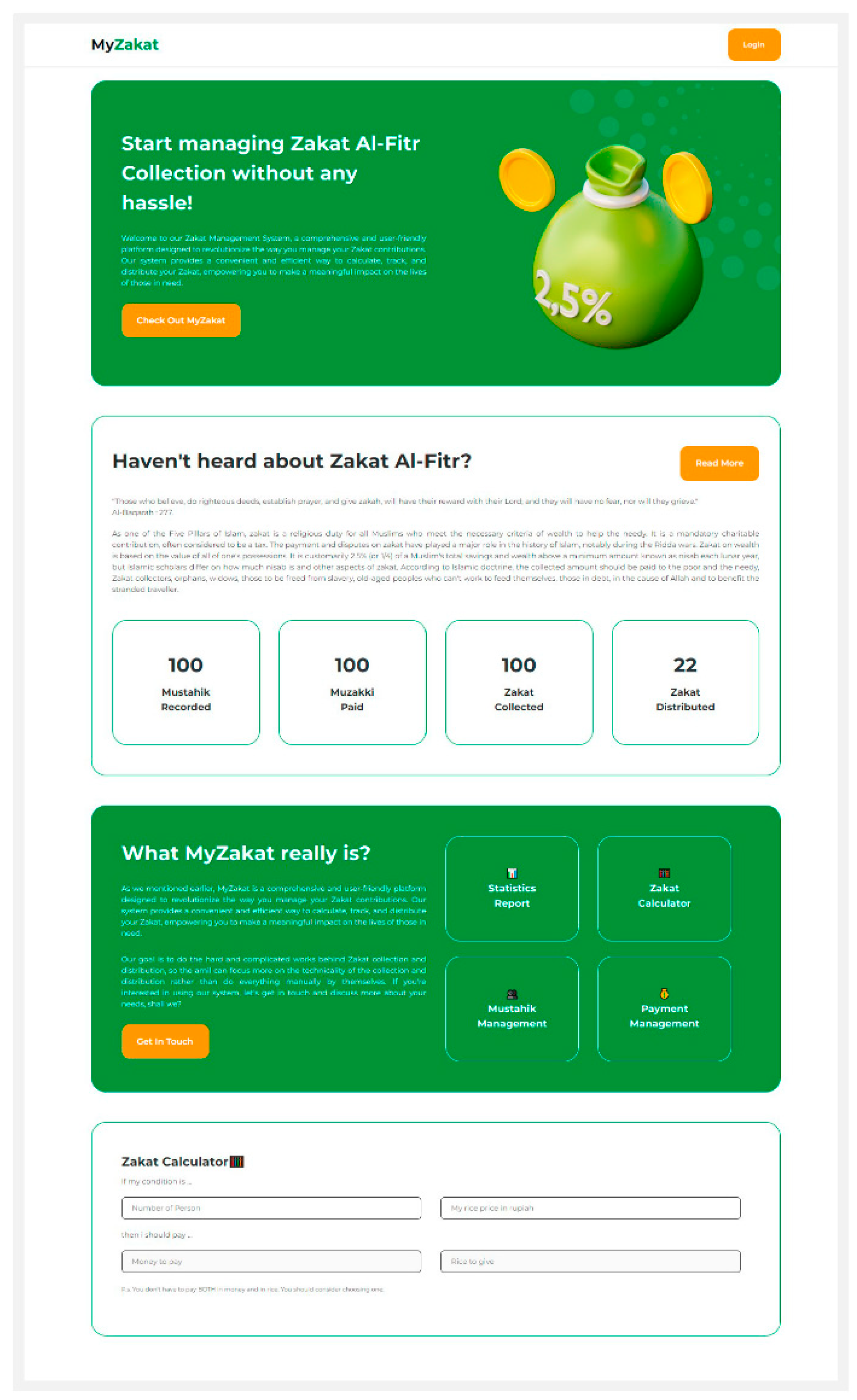
Landing: Landing is a page that contains information about zakat, procedures for paying zakat and calculations if you want to pay zakat using money or rice
- 3)
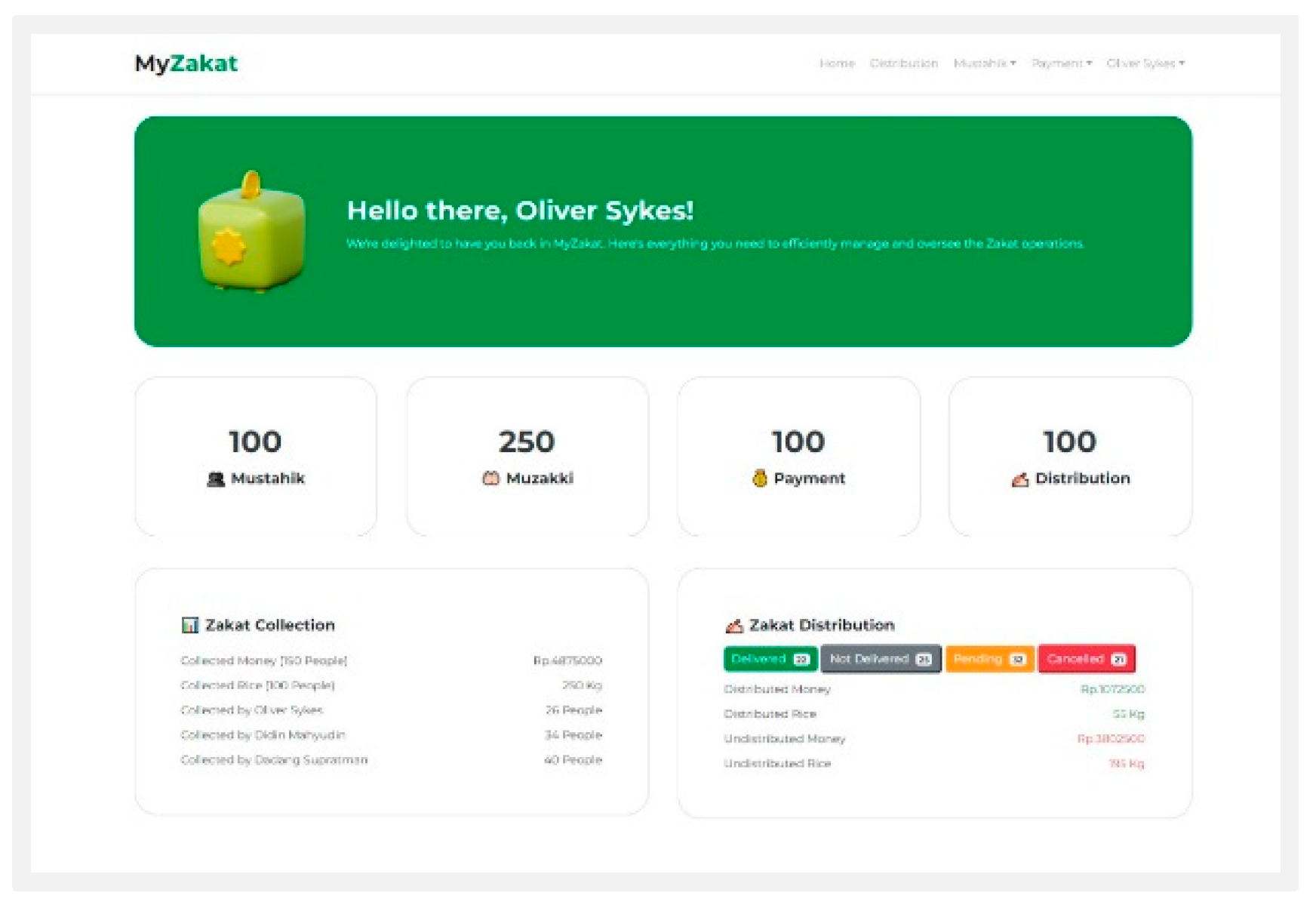
Dashboard: Dashboard is the first page that displays after logging in, which contains muzakki data
- 4)
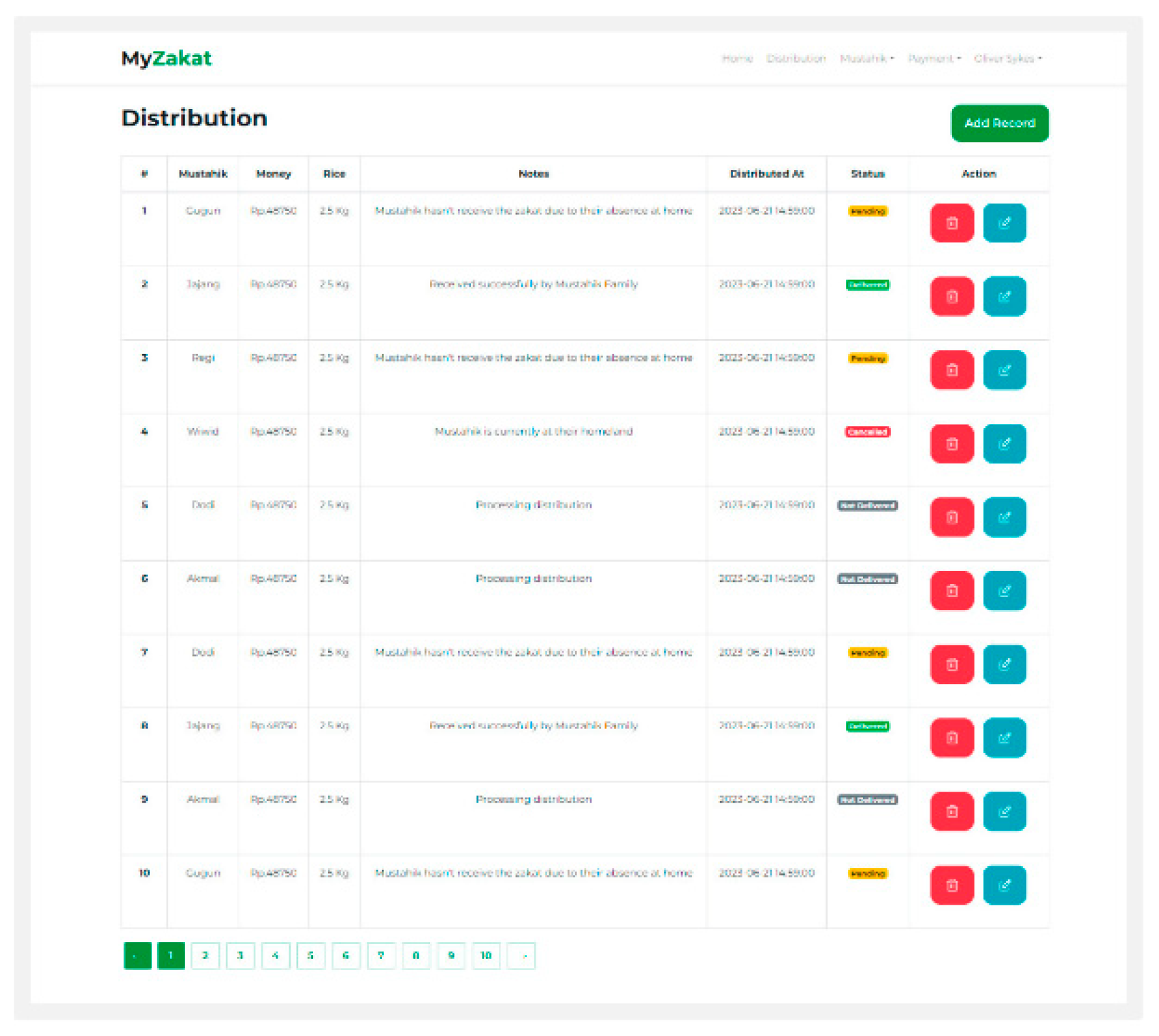
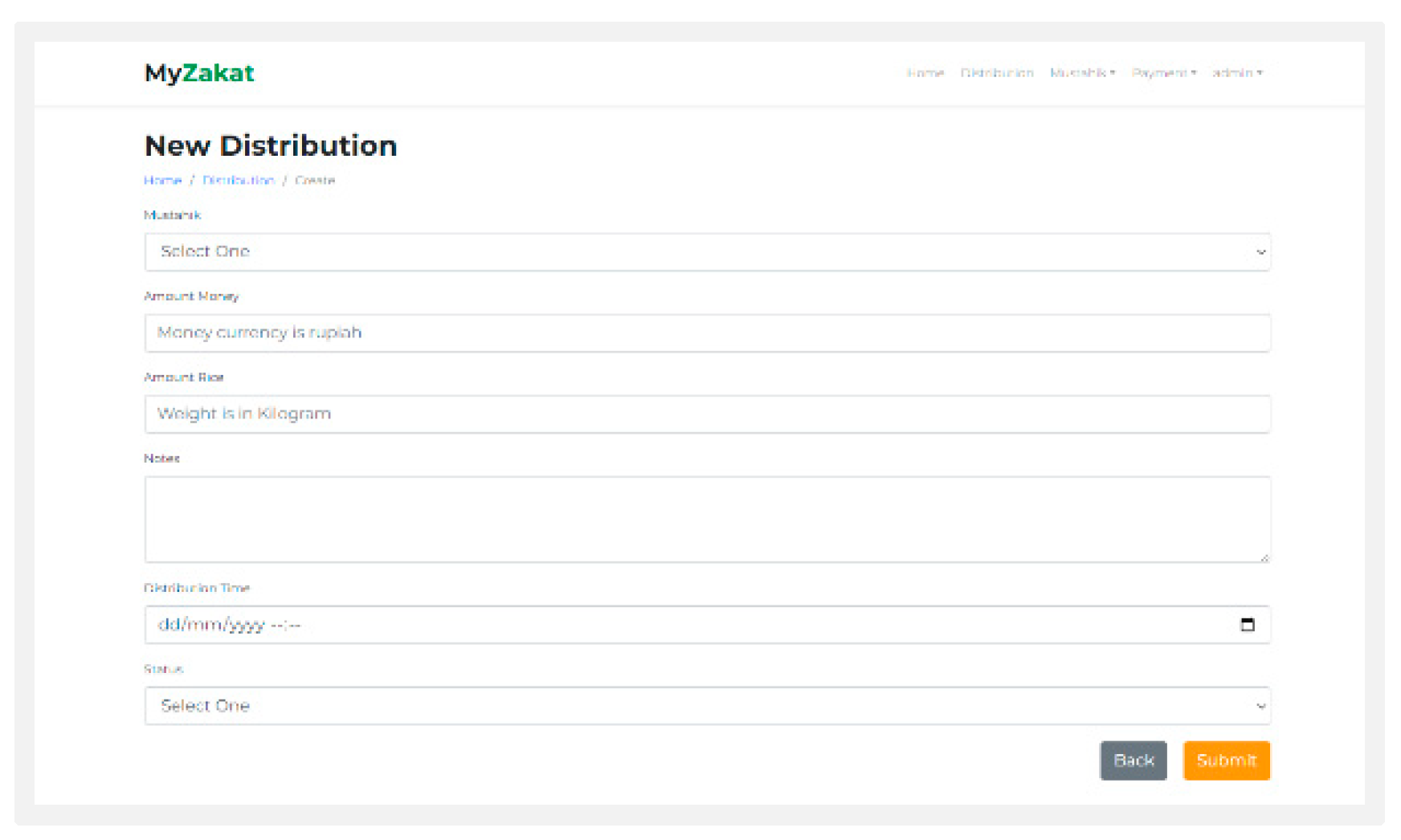
Distribution: Dustribution is a page of distribution, and distribution of zakat to zakat recipients.
Figure 6.
New Distribution.
Figure 6.
New Distribution.
- 5)
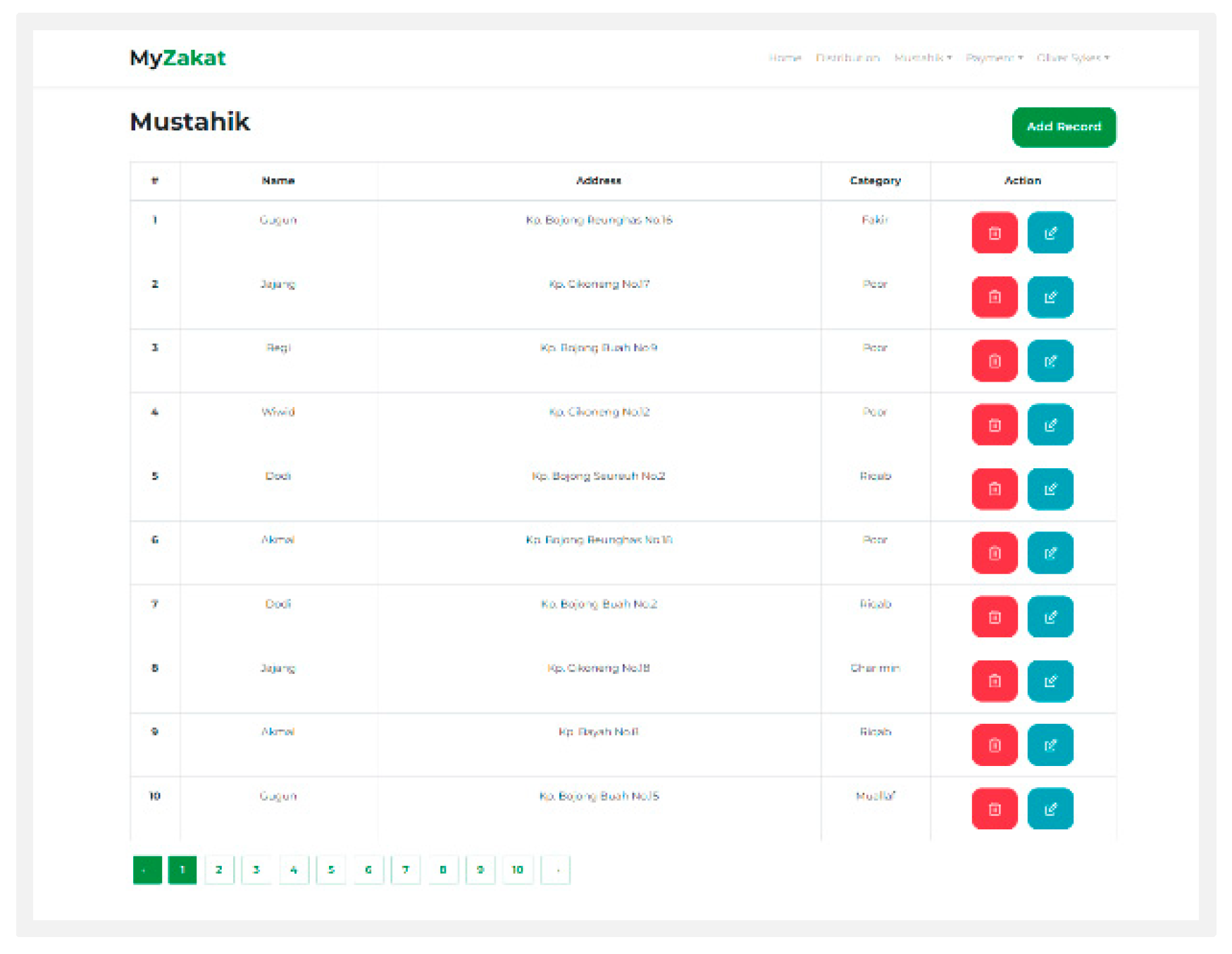
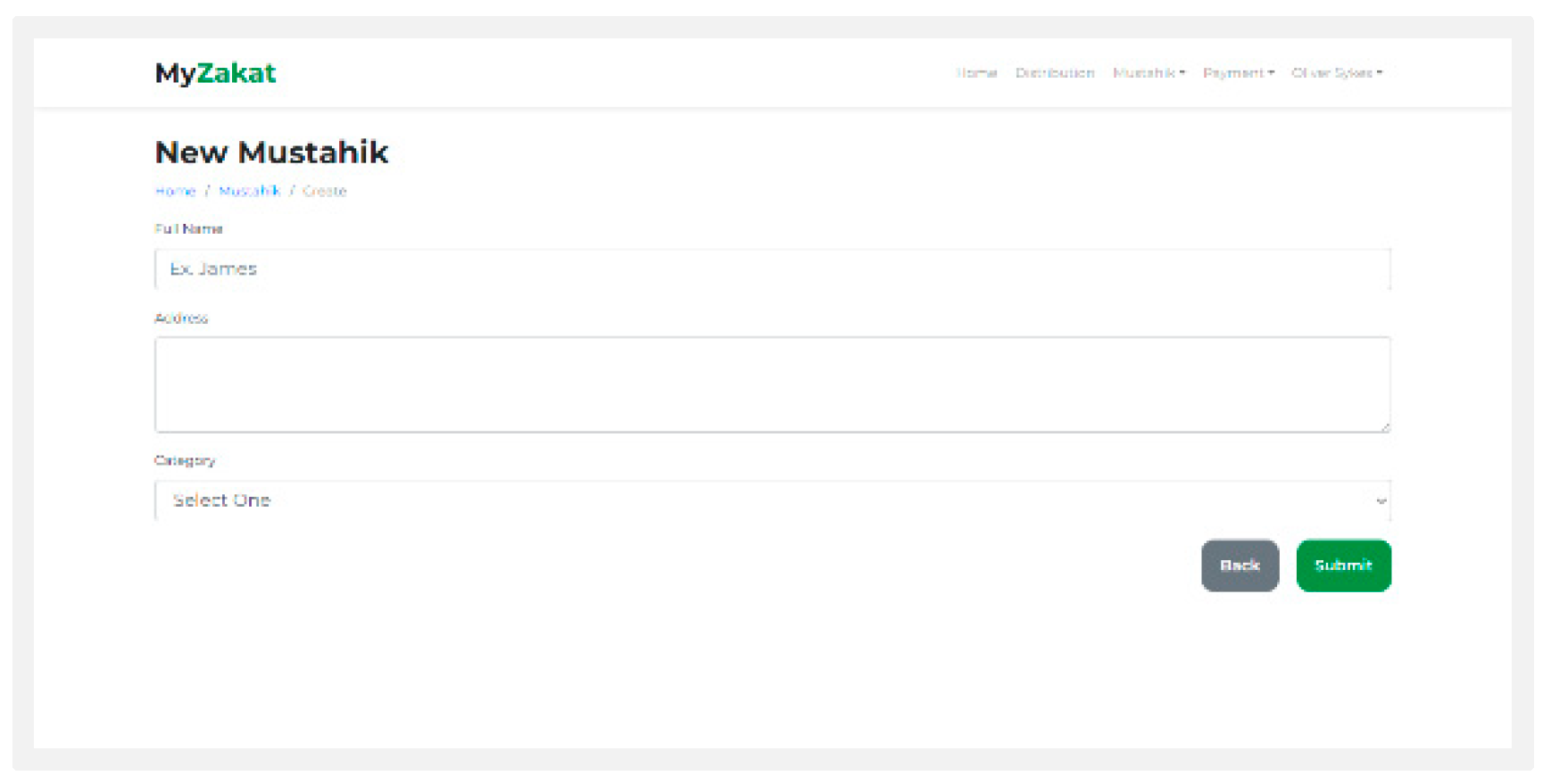
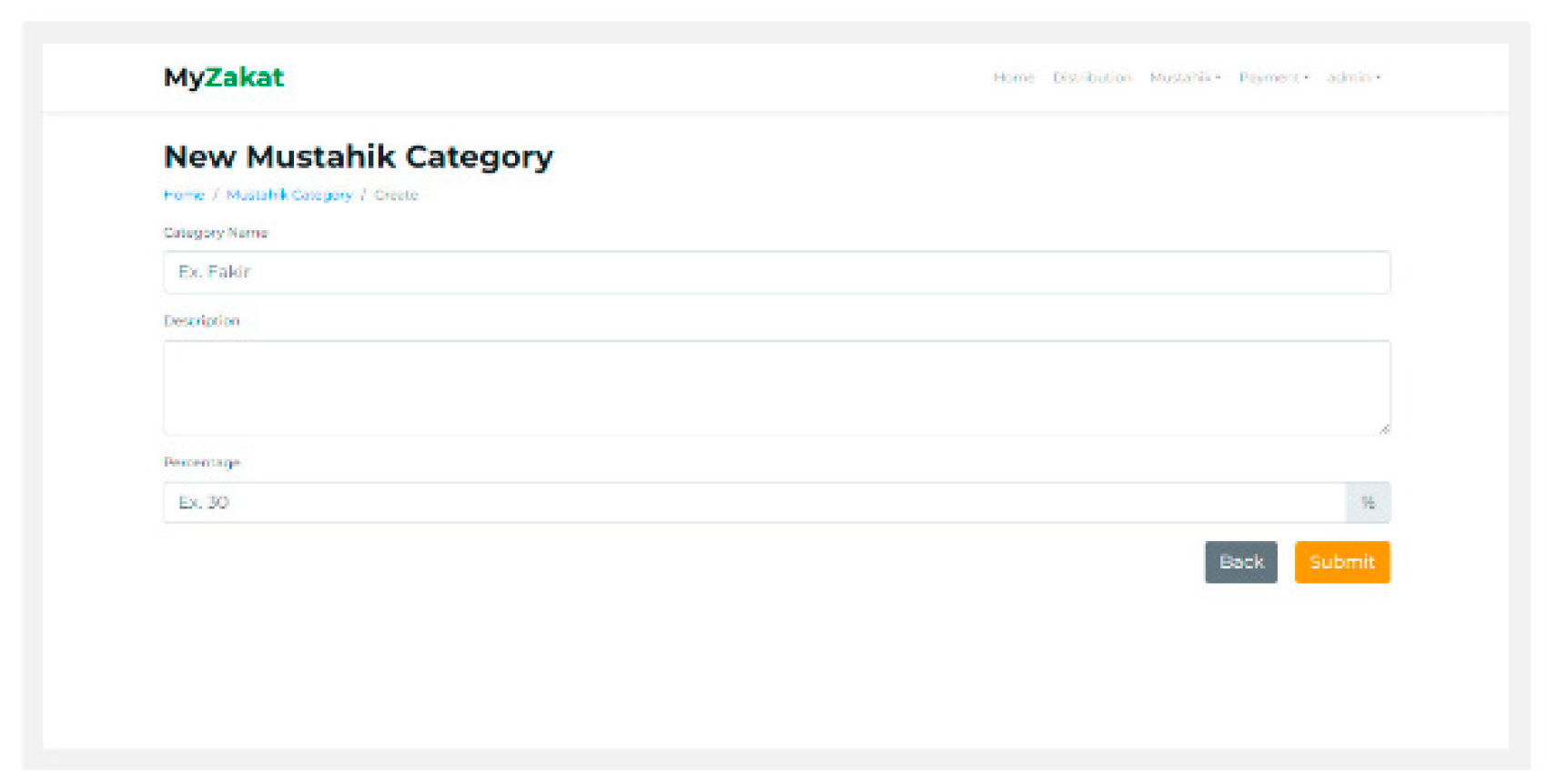
Mustahik: On this page you can add the name, address, and category mustahik.
- 6)
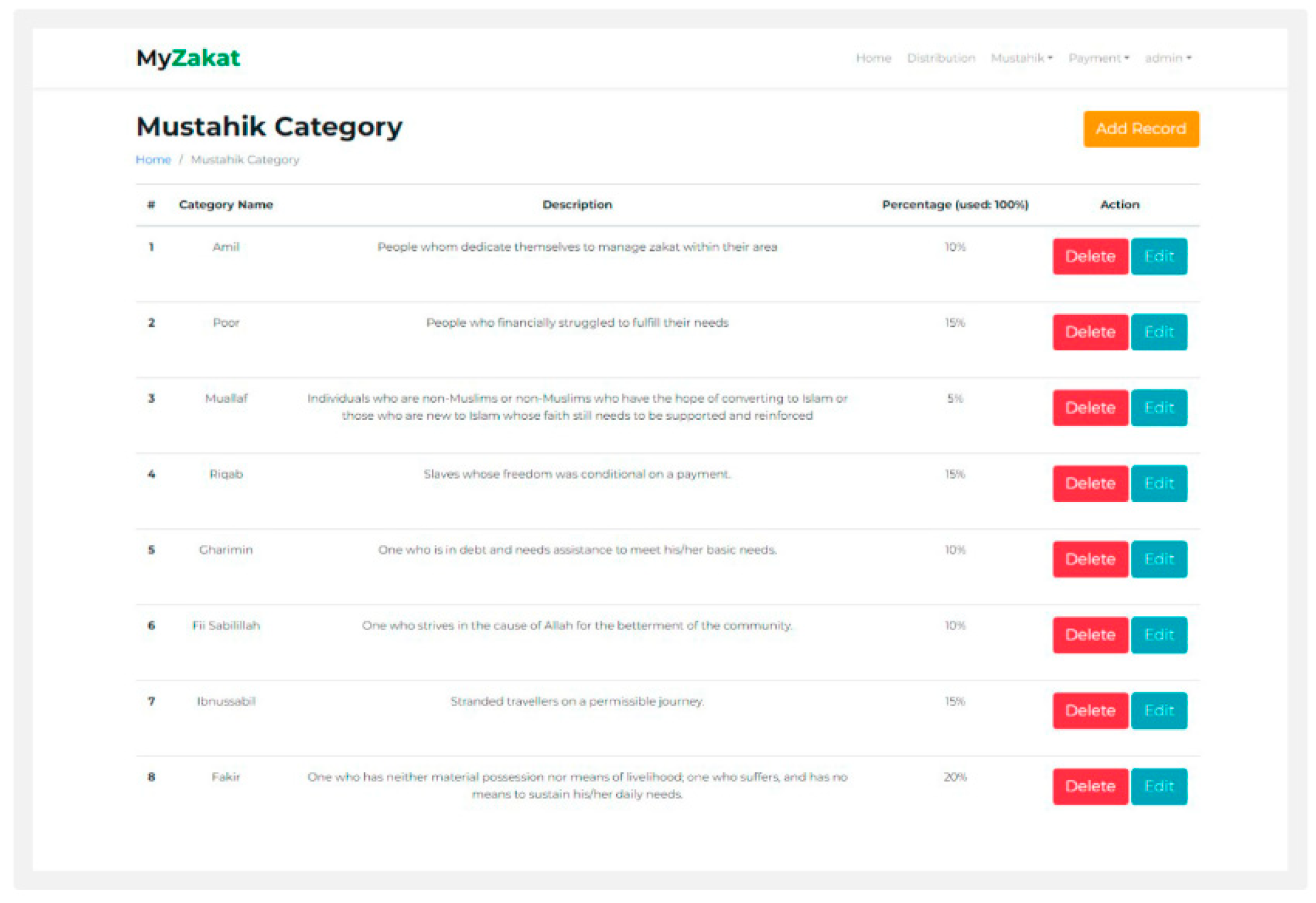
Mustahik Category: The category mustahik page dis- plays data that has been input on the mustahik page, and displays the percentage of zakat receipts
Figure 9.
Mustahik Category.
Figure 9.
Mustahik Category.
Figure 10.
Mustahik Category.
Figure 10.
Mustahik Category.
- 7)
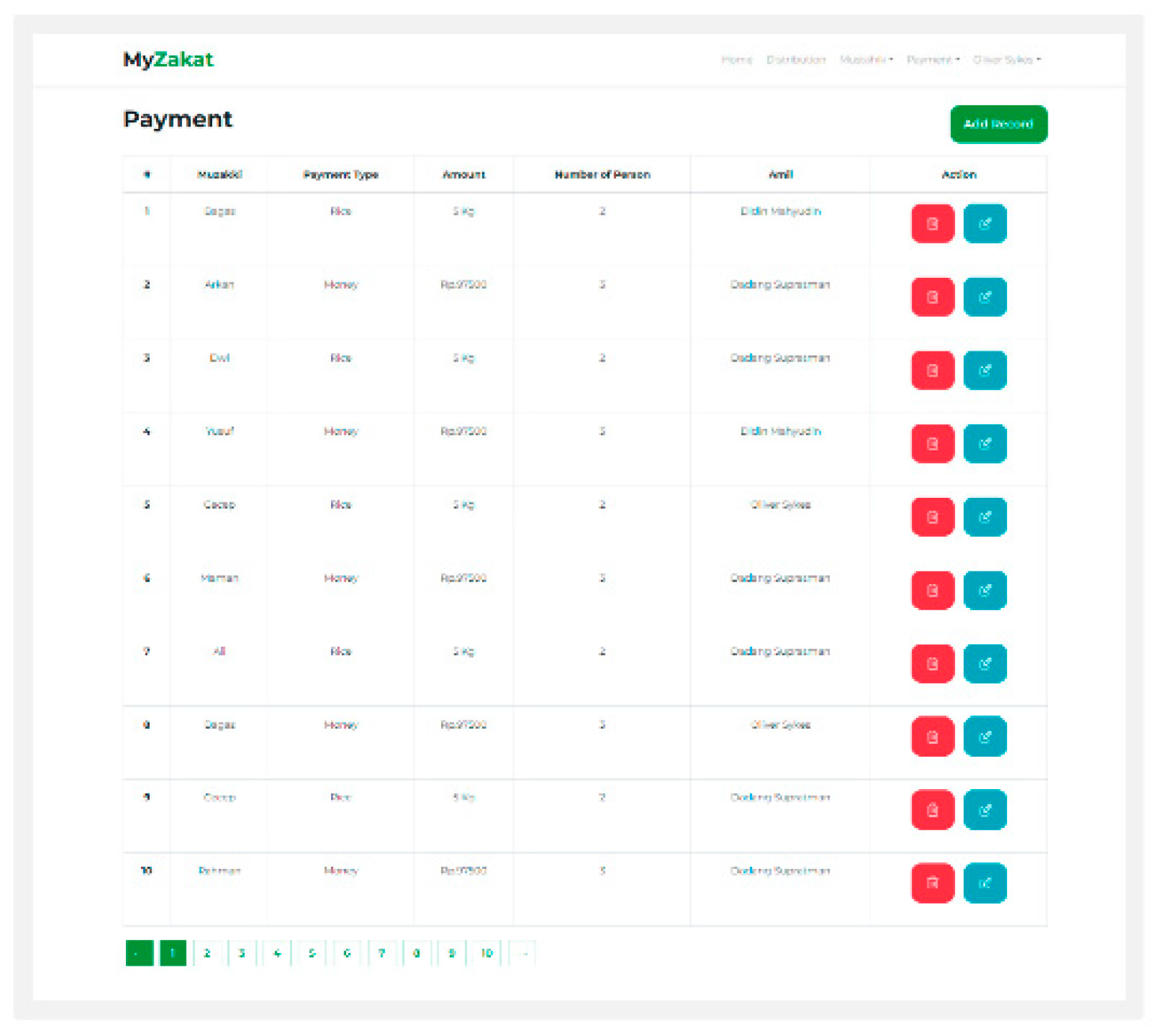
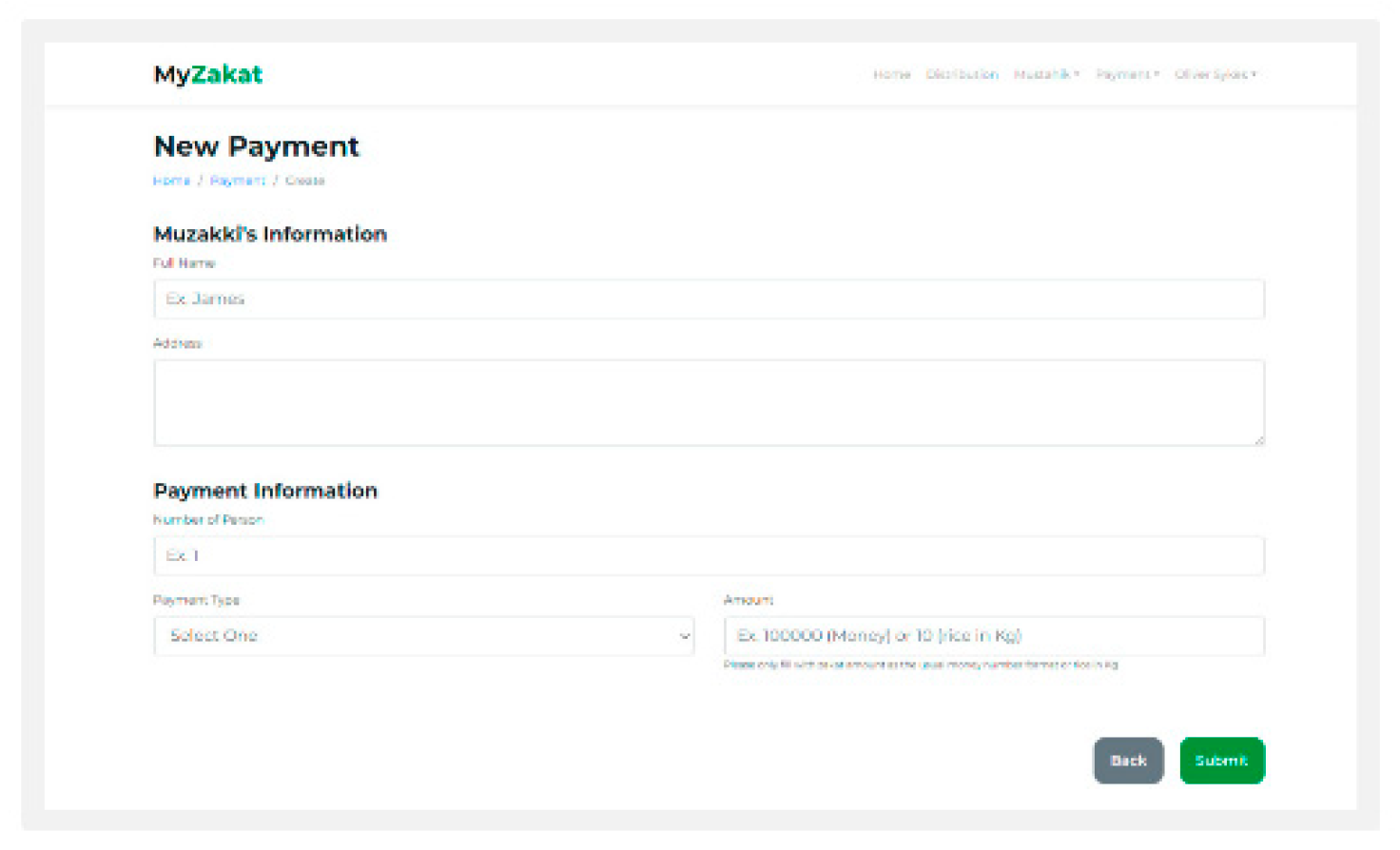
Payment: On the Payment page the admin can input muzzaki information
- 8)
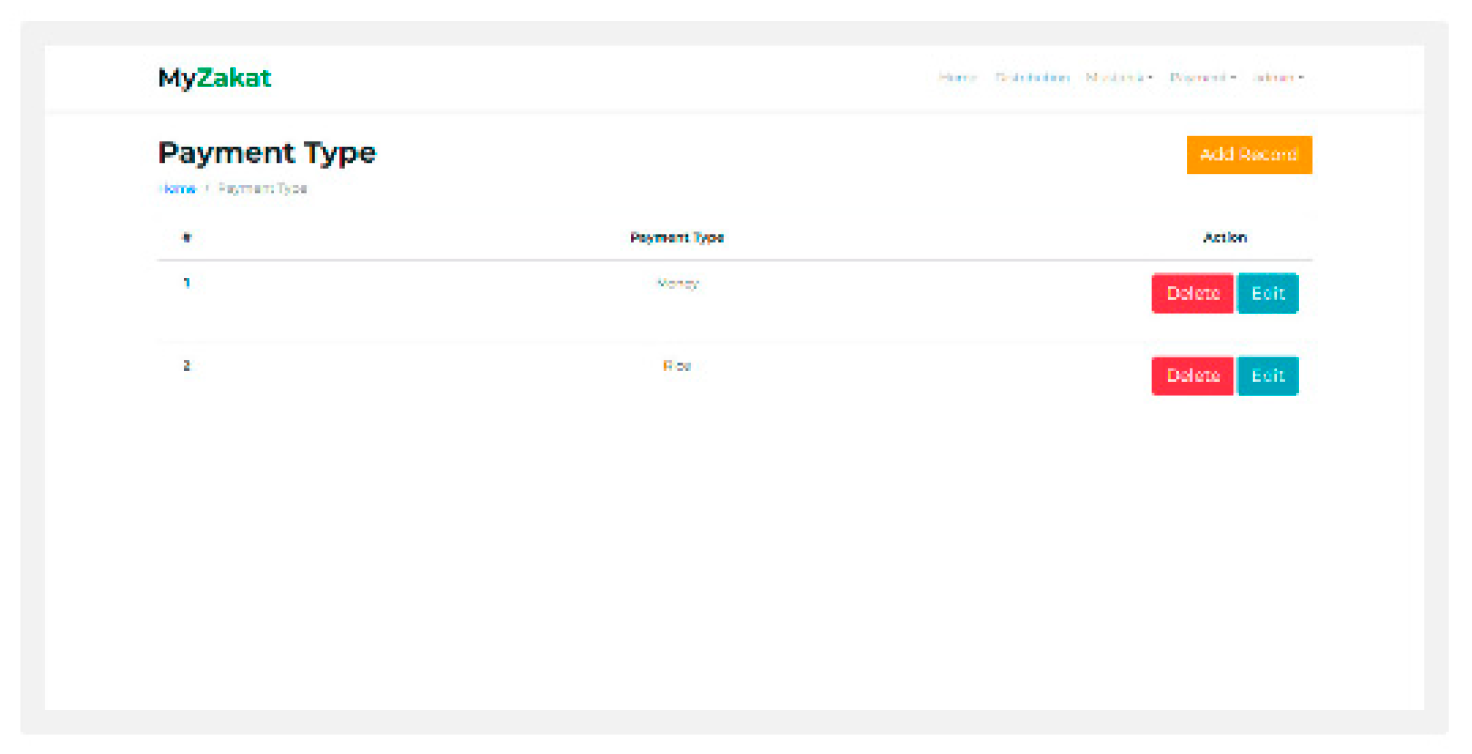
Payment type: This page contains payment types in the form of money or rice.
Figure 14.
Figure 14. payment type.
Figure 14.
Figure 14. payment type.
- V.
Conclusion
Based on the research that has been carried out on a design basis, namely designing an application system that can process zakat data on the web-based amil zakat agency in Bayah Timur village, it can be concluded that the system built provides facilities for administrators (processing section) to input data, perform change data and delete the data entered, With this research, data related to the processing of zakat is no longer stored in files but stored in a database to avoid loss or damage to the stored data. To increase the effectiveness and efficiency compared to the old system. The built system also provides a calculator facility to calculate how much zakat must be paid in the form of money or rice. With this application, it can provide more convenience for zakat managers.
Acknowledgment
The author’s wishes to acknowledge the Informatics De- partment UIN Sunan Gunung Djati Bandung, which partially supports this research work.
References
- Furqon, A. Manajemen zakat. Semarang: CV Karya Abadi Jaya, 2015.
- Wantoro, A. Sistem informasi berbasis web untuk pengelolaan pener- ima dana zakat, infaq dan sedekah. Jurnal Tekno Kompak 2019, 13, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avgerou, C. Information systems: what sort of science is it? Omega 2000, 28, 567–579. Available online: https://wwwsciencedirectcom/science/article/pii/S0305048399000729. [CrossRef]
- Swara, G.Y.; Kom, M.; Pebriadi, Y. Rekayasa perangkat lunak pemesanan tiket bioskop berbasis web. Jurnal Teknoif Teknik Infor- matika Institut Teknologi Padang 2016, 4, 27–39. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, M.F.; Putro, H.P. Penerapan simple agile methodology dalam pengembangan aplikasi web.
- Muslim, M.A.; Retno, N.A. Implementasi cloud computing menggunakan metode pengembangan sistem agile. Scientific Journal of Informatics 2014, 1, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, I.U. E–commerce perlengkapan haji dan umroh berbasis web menggunakan metode agile software development. in Prosiding Seminar Nasional Mahasiswa Bidang Ilmu Komputer dan Aplikasinya 2020, 1, 432–443. [Google Scholar]
- Abrahamsson, P.; Salo, O.; Ronkainen, J.; Warsta, J. Agile soft- ware development methods: Review and analysis. ArXiv 2017, arXiv:1709.08439. [Google Scholar]
- Salkiawati, R.; Lubis, H.; Yusuf, R.M. Sistem informasi manajemen zakat menggunakan metode prototipe pada masjid agung al barkah. Rekayasa Informasi 2019, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Sulaiman, H.; Jamil, N. Information security governance model to enhance zakat information management in malaysian zakat institutions. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Information Technology and Multimedia. IEEE; 2014; pp. 200–205. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).