1. Introduction
The production of high-quality water is one of the primary targets of environmental sustainability. This can be achieved using an efficient treatment process for industrial wastewater to provide a healthy ecosystem [
1,
2,
3]. All industrial wastewater treatment processes focus on reducing waste-producing pollutants. Managing the treatment processes of wastewater and effluent is the key factor in providing a high-performance treatment process. Most petroleum refineries and petrochemical plants produce a high range of hydrocarbons in wastewater [
4,
5,
6,
7]. All of these materials cause fatal problems for humans and the environment. Phenol is one of the dangerous materials that is produced within effluent wastewater and requires efficient treatment techniques to be removed [
8,
9,
10]. The hydrocarbon materials can be removed from wastewater using various industrial reactors, such as membrane reactors, fluidized bed reactors, trickle bed reactors, and bubble column reactors (BCRs). BCRs are one of the most applied gas-liquid and gas-liquid-solid multiphase reactors in industrial processes. They are characterized by many benefits such as easy operation, efficient mixing, high heat and mass transfer rates, low maintenance costs, and low energy consumption [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15].
In a BCR, the movement of bubbles inside the reactor induces liquid mixing (i.e., effective hydrodynamic performance) so that high mass transfer and heat transfer can be achieved. Additionally, the evaluation of the hydrodynamic behaviors of the bubble column reactor will determine the extent of a chemical reaction as well as the reactor's performance [
16]. The main hydrodynamic parameters in a BCR are the reactor height-to-diameter ratio, superficial gas velocity, gas holdup, bubble size, gas-liquid interfacial area, flow patterns, and gas distributor design [
17,
18,
19,
20,
21]. The use of bubble columns in wastewater treatment is highly dependent on the mass transfer mechanism between the gas and liquid phases. Thus, understanding the operational parameters of the diffusion process will provide a clear picture delineating an effective process for the removal of hydrocarbons in a BCR [
4,
22]. The degradation of various hydrocarbon contaminants from the effluent streams of wastewater employing BCRs must provide effective contact between the reaction mixtures. The degradation process of hydrocarbons occurs in the liquid phase, and gas bubbles encourage an efficient mass transfer, with the pollutant materials included in the system before the oxidation reaction [
23,
24,
25,
26].
The addition of packing materials inside a BCR will enhance the reaction mechanism due to the increased contact surface area between the gas and liquid phases [
8,
27]. Therefore, a high chemical reaction rate will be achieved with a short residence time. The packing material supports the formation of a thin film over the packing surfaces. This thin film is characterized by a low resistance to mass transfer such that a high chemical reaction rate can be attained. Moreover, the ozonation reaction kinetics indicate that the chemical reaction usually produces hydroxyl radicals [
21,
26]. These free radicals are highly volatile in the reaction media in converting organic material (e.g., phenol) into simple compounds (e.g., water and carbon dioxide) [
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33]. Furthermore, the flow regime inside the BCR plays a critical role in determining the reactor’s performance. Due to the difficulty of predicting the flow behavior in a BCR, evaluation of the superficial gas velocity can contribute to the determination of the flow patterns as well as the exact hydrodynamic behavior. Therefore, more extensive work is needed to reveal the relationship between the gas-liquid-solids, in a BCR in removing phenol from wastewater [
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39].
Ghaisani et al. [
40] applied a semicontinuous, multi-injection BCR in the degradation of phenolic compounds in the presence of ozone gas. They achieved the highest removal efficiency of 99.48 and 99.83% using ozonation and catalytic ozonation methods, respectively, at an operating time of 60 min. Also, they indicated that the degradation process was highly influenced by the activity of hydroxyl radicals in the reactor. Wei et al. [
41] used a rotating packed bed reactor in the presence of a Fe–Mn–Cu/γ–Al
2O
3 catalyst to enhance phenol removal from wastewater, which was 96.42% effective at 30 min. Al-Ezzi [
42] employed a pulsed BCR and loop reactor to treat phenol using activated carbon as an adsorbent media in the reactor and found that about a 90% phenol removal efficiency was achieved. Honarmandrad et al. [
43] investigated the reaction of phenol in wastewater in the presence of CaO
2 and ozone as a gas phase. They noted that the chemical reaction was endothermic with the highest reaction yield being 97.8% for a synthetic sample of wastewater at 90 min. Jothinathan et al. [
44] treated petrochemical wastewater using an ozonation process in the presence of an Fe/GAC catalyst in micro-bubble and macro-bubble operations. They noted that the highest chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal efficiency was 88%, which was 18 and 43% greater than the micro-bubble and macro-bubble ozonation reactions, respectively. Alattar et al. [
45] studied the removal of phenol from wastewater using an ozonized packed BCR, finding a removal efficiency of 100% of phenol after 30 min. This study showed that the packing material was a key factor in increasing the contact surface area between the gas and liquid phases, which also affected the phenol degradation rate. Bhosale et al. [
46] evaluated the scale-up requirements of ozonation reactors to remove phenolic compounds from wastewater. From the results of the reaction kinetics analysis, the authors noted that the reaction rates of the phenolic compounds were highly influenced by the mass transfer mechanism and ozonation reaction.
The literature demonstrates that it is still difficult to understand how hydrodynamic parameters influence the mass transfer mechanism in a BCR using ozone gas in the presence of packing materials. Also, the ozonation reaction usually exhibits poor solubility and a fast decomposition of the ozone molecules [
14,
30]. All of these factors provide limited mass transfer in the liquid phase reaction inside a BCR. Hence, it is necessary to identify various superficial ozone gas velocities and evaluate their effect on the reactor’s performance [
47,
48,
49,
50,
51,
52,
53,
54]. Therefore, the main objective of the present work is to enhance the ozonation reaction to attain high phenol removal from wastewater using an ozonized packed BCR and to evaluate the influence of the hydrodynamic behavior and packing material on the reactor’s performance.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Many chemicals were utilized in the experiential runs, including the phenol compound (C6H5OH, 99.8% purity) purchased from Gryfskand (Poland), sodium thiosulfate (99.86% purity), potassium iodide (99.42% purity), and sulfuric acid (99.55% purity) obtained from Sigma (USA). Moreover, α-Al2O3 was used as a packing material and a ZnO NPs nanocatalyst and both were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (USA).
2.2. Reaction Apparatus
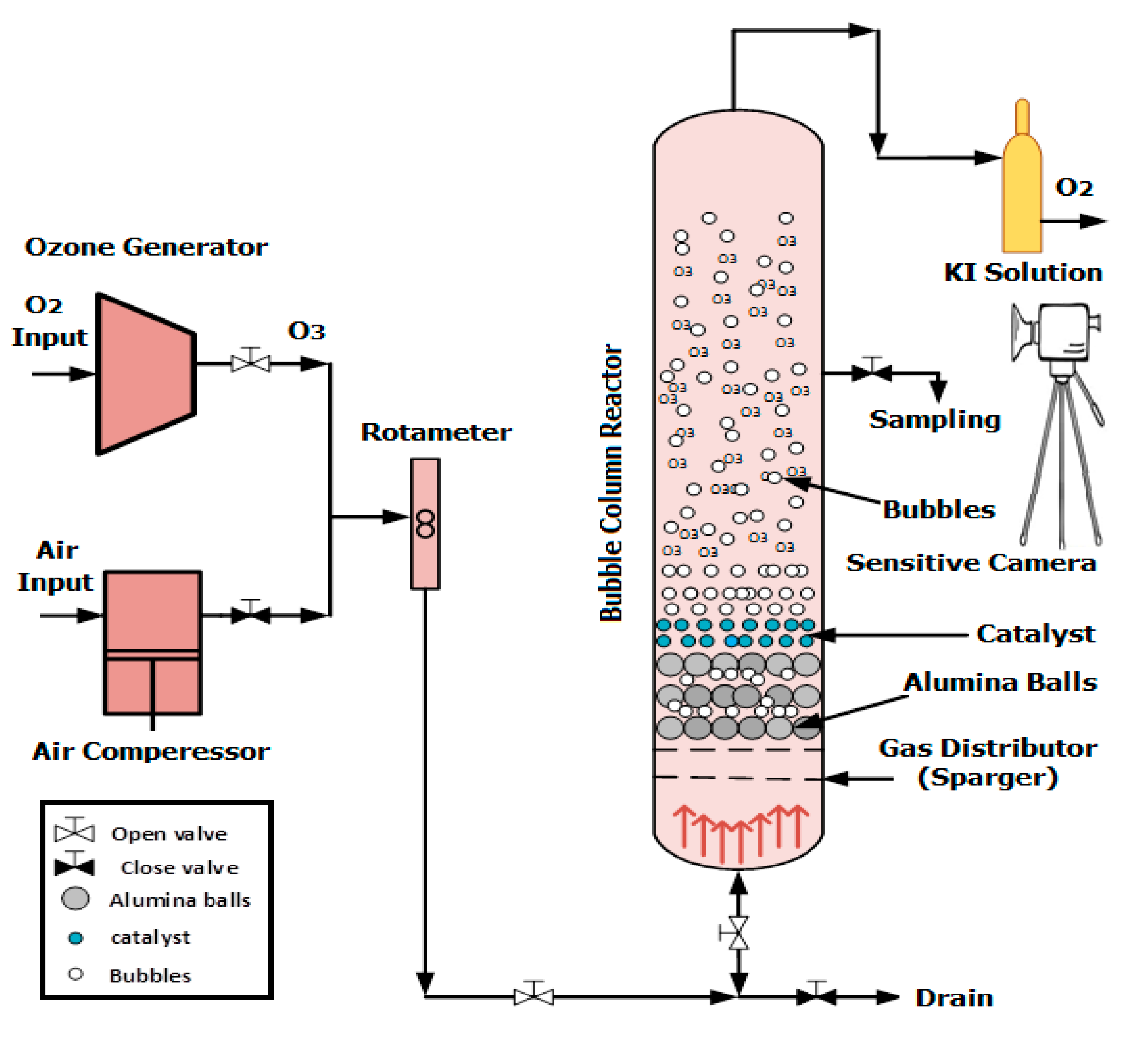
The reaction apparatus consisted of a packed bubble column reactor (BCR). The reactor operated in semi-batch mode, in which the liquid phase (i.e., polluted wastewater) was stationary, while the gas phase (i.e., ozone gas) entered the reactor continuously in the upward flow direction. All of the treatment experiments were achieved at a constant operating temperature of 25
ºC. The interaction between the gas phase and the liquid phase produced gas bubbles depending on the applied superficial gas velocity and other hydrodynamic parameters. These ozone bubbles were highly dispersed in the wastewater inside the reactor.
Figure 1 illustrates the schematic diagram of the reaction apparatus of a BCR. The system contained a cylindrical column with an inner diameter of 8 cm and a height of 180 cm. The air and ozone gas were supplied from an air compressor and ozone generator systems, respectively. Sensitive gas flow meters were employed in the apparatus to measure the gas flow rate into the BCR. The bottom section of the BCR contained a gas distributor manufactured from stainless steel (i.e., perverted plate) with 52 holes 0.5 mm in size, distributed in cycles in all of the plate areas.
2.3. Operating Procedure
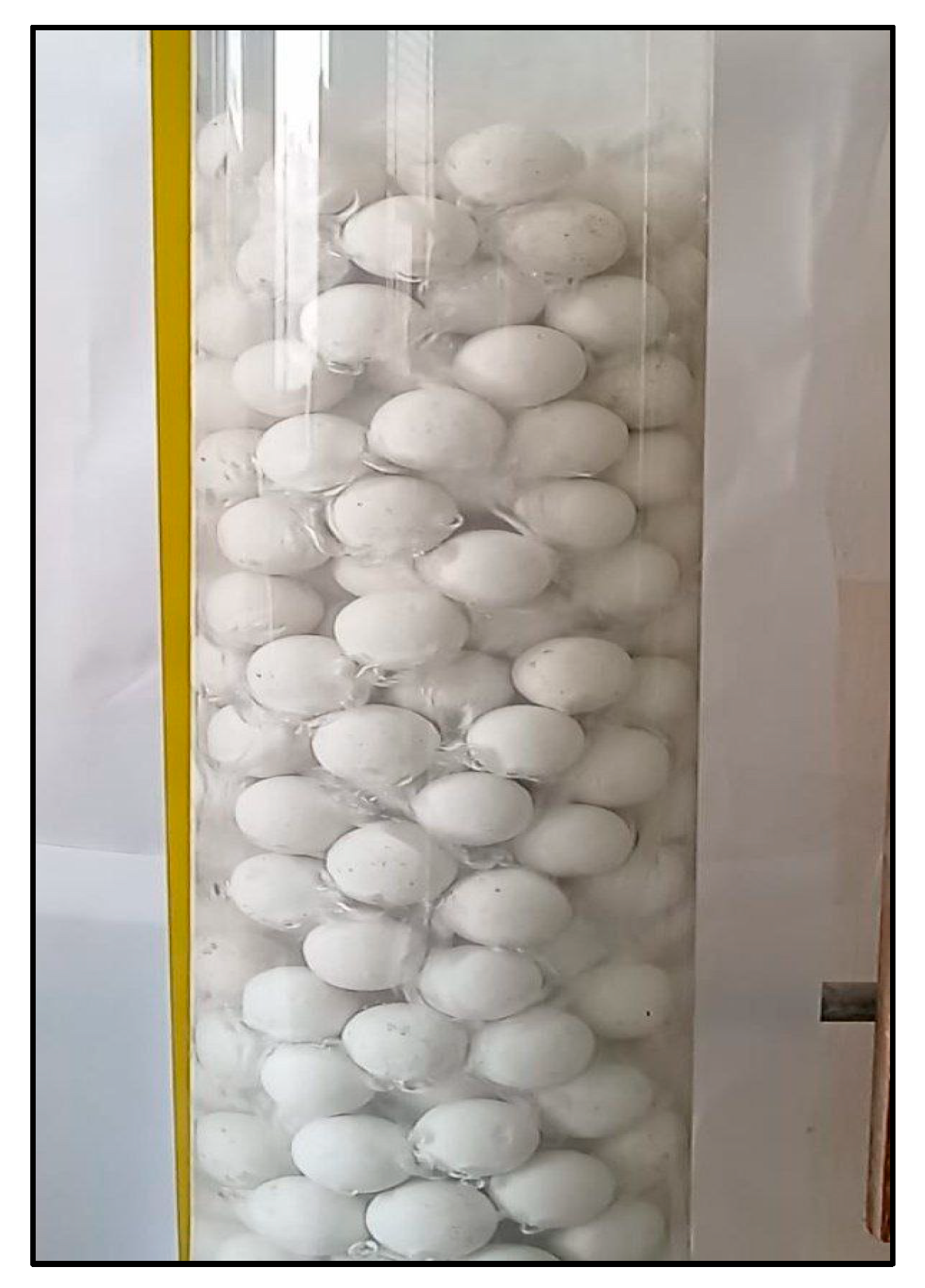
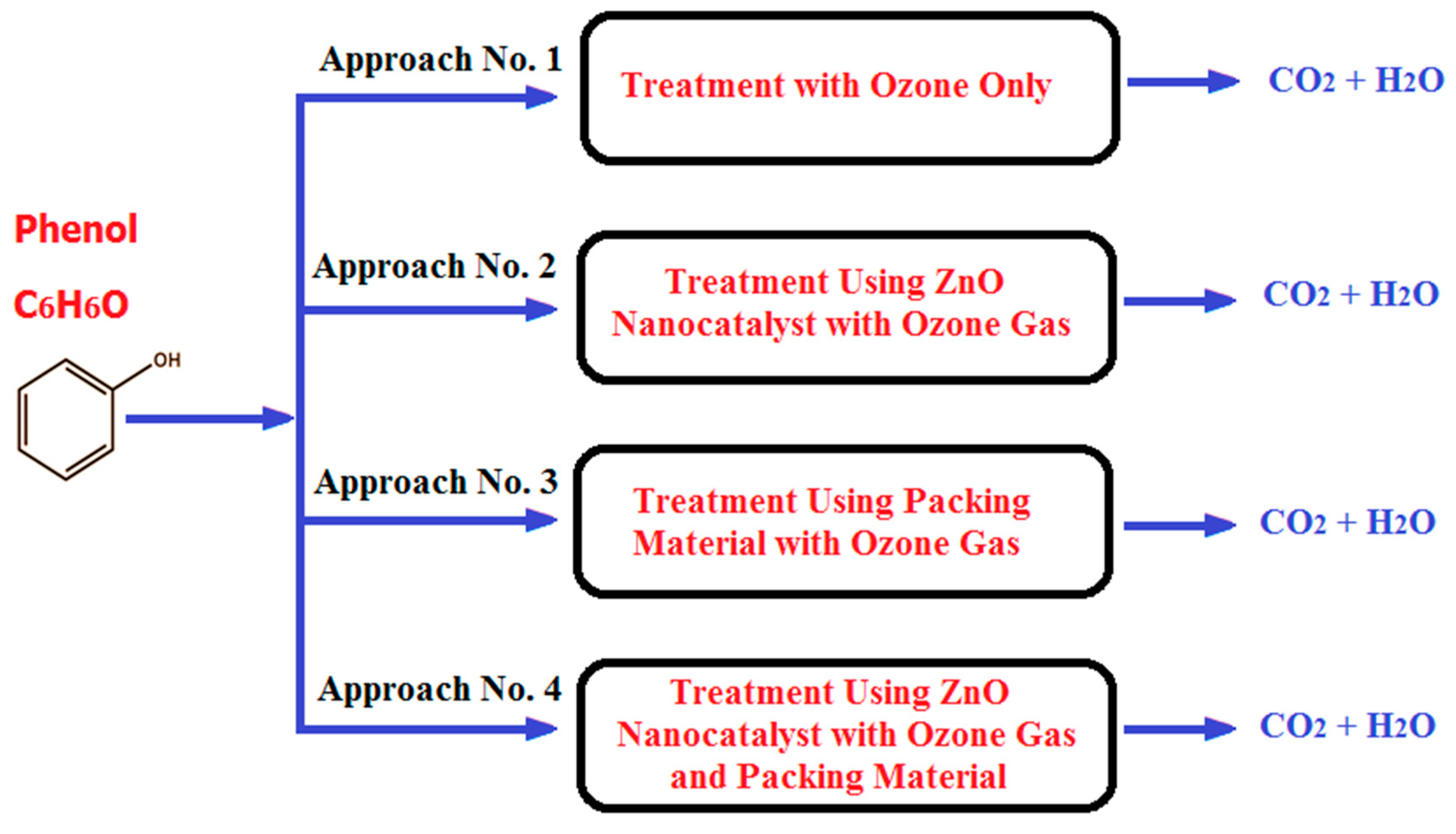
In the present investigation, the ozonation reaction for phenol removal was achieved using four treatment approaches in the BCR. The first approach was carried out in the BCR in the presence of ozone gas only. The second approach of phenol removal was achieved using alumina balls (α-Al
2O
3 of approximately zero surface area with no porosity) in the reactor with ozone gas, as shown in
Figure 2. The third treatment included the use of ZnO nanoparticles (NPs) as a nanocatalysts with ozone, while the fourth combined the packing material and ZnO nanocatalyst with ozone gas.
Figure 3 summarizes the four operating approaches in the BCR. Different concentrations of phenol in wastewater were used (i.e., 10, 15, 20, and 25 ppm). Dry air was fed to an ozone generator apparatus to produce high-purity ozone gas at a constant rate. The applied treatment time for the phenol material in the reactor was 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, and 100 min. The operating temperature and operating pressure were kept constant in the bubble column reactor at 25ºC and 1 bar, respectively, for all experiments. During each experiment, a sample from the reaction mixture was drawn from the sampling valve. The phenol concentration was measured using a total organic carbon (TOC) analyzer (E200, Shimadzu Company, Japan).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Flow Behavior in the BCR
The hydrodynamic characterization of the BCR has an impact on its performance. It is well-known from the literature that the flow regimes in the BCR are highly dependent on the gas velocity, pressure drop, gas holdup, and physical properties of the mixture [
8,
43,
47].
Figure 4 shows the relationship between the superficial gas velocity and the gas holdup in the presence of ozone gas alone and in the presence of ozone plus a ZnO nanocatalyst in the BCR. The majority of the flow at the applied gas velocity (less than 0.05 cm/s) was homogeneous bubbly flow. Also, the bubble size distribution was uniform, with a low bubble rise velocity. The ozone gas superficial velocity was able to positively affect the BCR’s performance. Additionally, it was found that the superficial gas velocity had a significant impact on the performance of the BCR due to its direct effect on the hydrodynamic parameters such as gas holdup, bubble size, and rising velocity.
Figure 4 shows that there was a slight variation in the gas holdup results when using ozone with a ZnO nanocatalyst in comparison with using ozone gas alone in the BCR. This variation is attributed to the change in the hydrodynamic behavior due to the presence of the ZnO nanocatalyst.
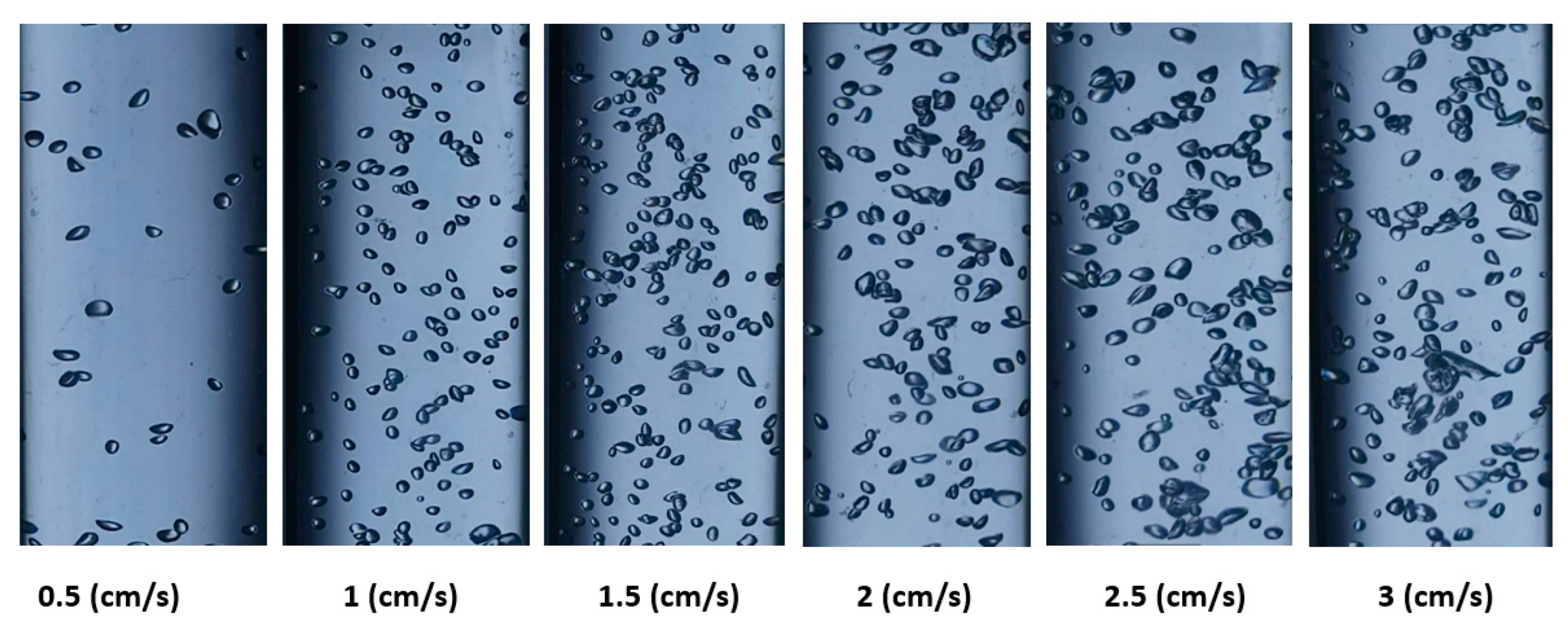
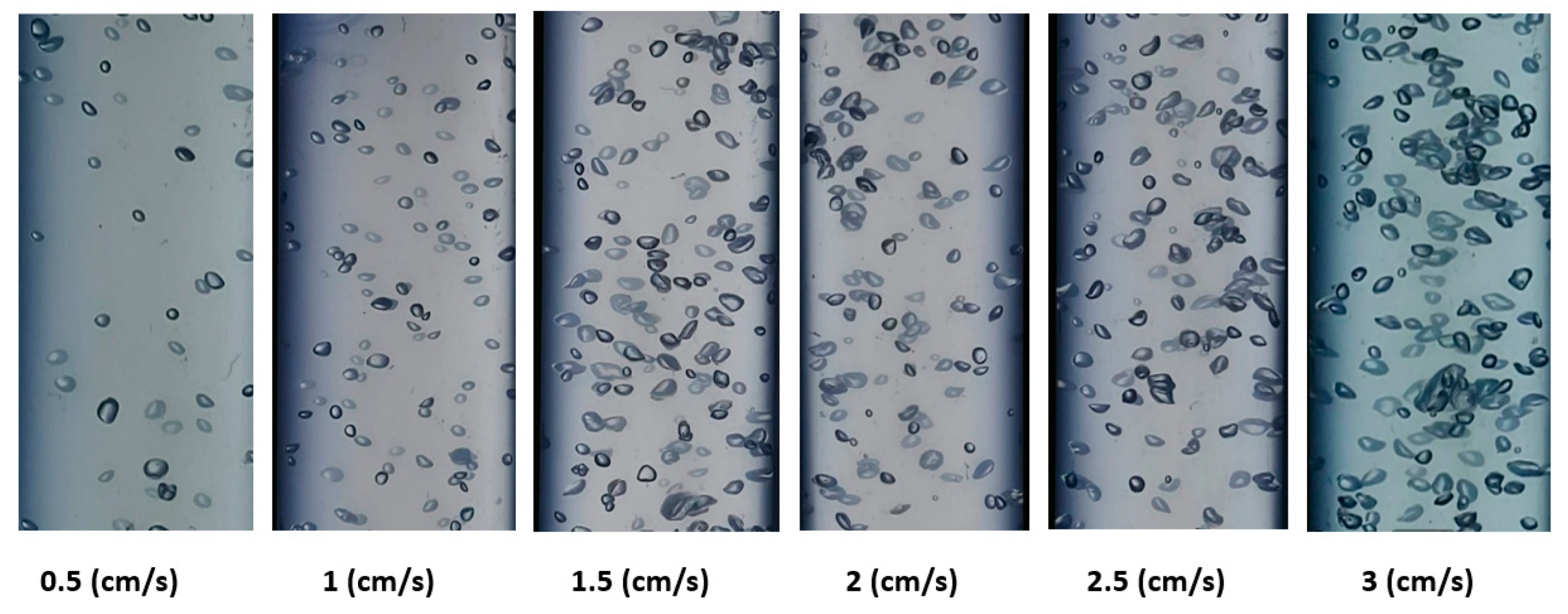
Figure 5 and
Figure 6 show the shapes of the gas bubbles in the BCR employing ozone gas alone and ozone gas with a ZnO nanocatalyst, respectively, at various gas velocities. Both figures demonstrate that as the gas velocity rose, the bubble size increased as the small bubbles aggregated into large ones. Also, the general shape of the bubbles was spherical, with uniform distribution in the reactor at low gas velocities. Accordingly, at higher gas velocities (i.e., 3 cm/s), the bubble size grew and changed, forming ellipsoidal or slug shapes. This behavior can be explained by bubbles congregating and growing into larger bubbles. Numerous authors, including Sharma et al. [
14], Barlak et al. [
29], and Alattar et al. [
31], indicate that the gas velocity has a significant impact on the bubble size and shape in a BCR. A distinct increase in the gas holdup value in the reactor produces an increase in the effective interfacial area, which influences the mass transfer process inside the reactor with the gas velocity.
The result of using ozone gas alone in the BCR can be seen in
Figure 5, where the average bubble diameter was 0.44, 0.49, 0.55, 0.62, 0.68, and 0.72 cm at superficial gas velocities of 0.05, 1, 1.5, 2, 2.5, and 3 cm/s, respectively. Moreover, when using ozone with a ZnO nanocatalyst, the bubble size measured 0.48, 0.54, 0.58, 0.73, and 0.76 cm, respectively, as the same aforementioned velocities. However,
Figure 6 shows that the diameter of the bubbles increased more with the superficial gas velocity in the presence of the ZnO nanocatalyst in comparison with the case of the ozone gas alone. It was observed that the agglomeration processes caused the bubble diameter to grow along with the surface gas velocity, as also indicated by Lucas et al. [
25]. The gas bubble formation mechanism in the BCR and their rising velocities mainly relate to buoyancy phenomena that effectively influence the final hydrodynamic behavior in this type of reactor [
8,
31]. Usually, the rise of a bubble in the two-phase system in the dispersion appears due to coalescence and dispersion. Then, the bubbles can undergo a clear disengagement in the reactor. Malik et al. [
36] and Jothinathan [
46] pointed to the importance of bubble formation and bubble size in determining the effective reaction time between the gas and liquid phases. This phenomenon is the chief factor in determining the interfacial mixing in multiphase systems. Therefore, in the present investigation, it was decided to use a superficial ozone gas velocity of 2.5 cm/s in all experiments due to their appropriate hydrodynamic characteristics for the reaction system in a BCR.
3.2. Characterization of the ZnO Nanocatalyst
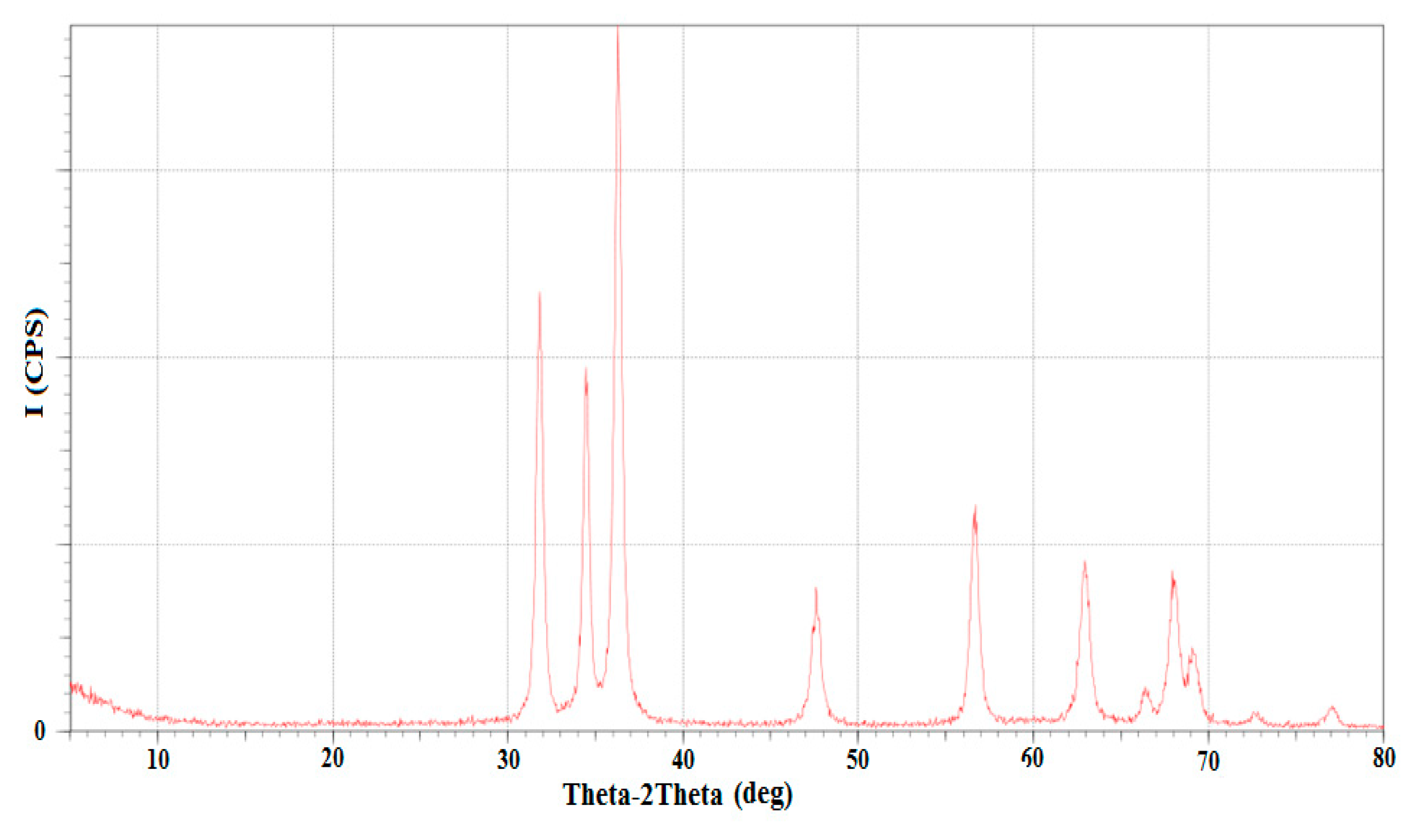
The specifications of the ZnO nanocatalyst were characterized using various testing devices. The structural features of the nanocatalyst was characterized by an X-ray diffractometer to identify the main phases of the material structure.
Figure 7 displays the X-ray diffraction pattern of the ZnO NPs. This figure clearly shows the presence of a number of peaks at 2θ, such as at 31.74, 34.42, 36.26, 47.57, 56.63, 62.89, 66.43, 67.95, 69.07, 72.69, and 76.86°, corresponding to the Miller indices of the (100), (002), (101), (102), (110), (103), (200), (112), (201), (202), and (004) planes, respectively.
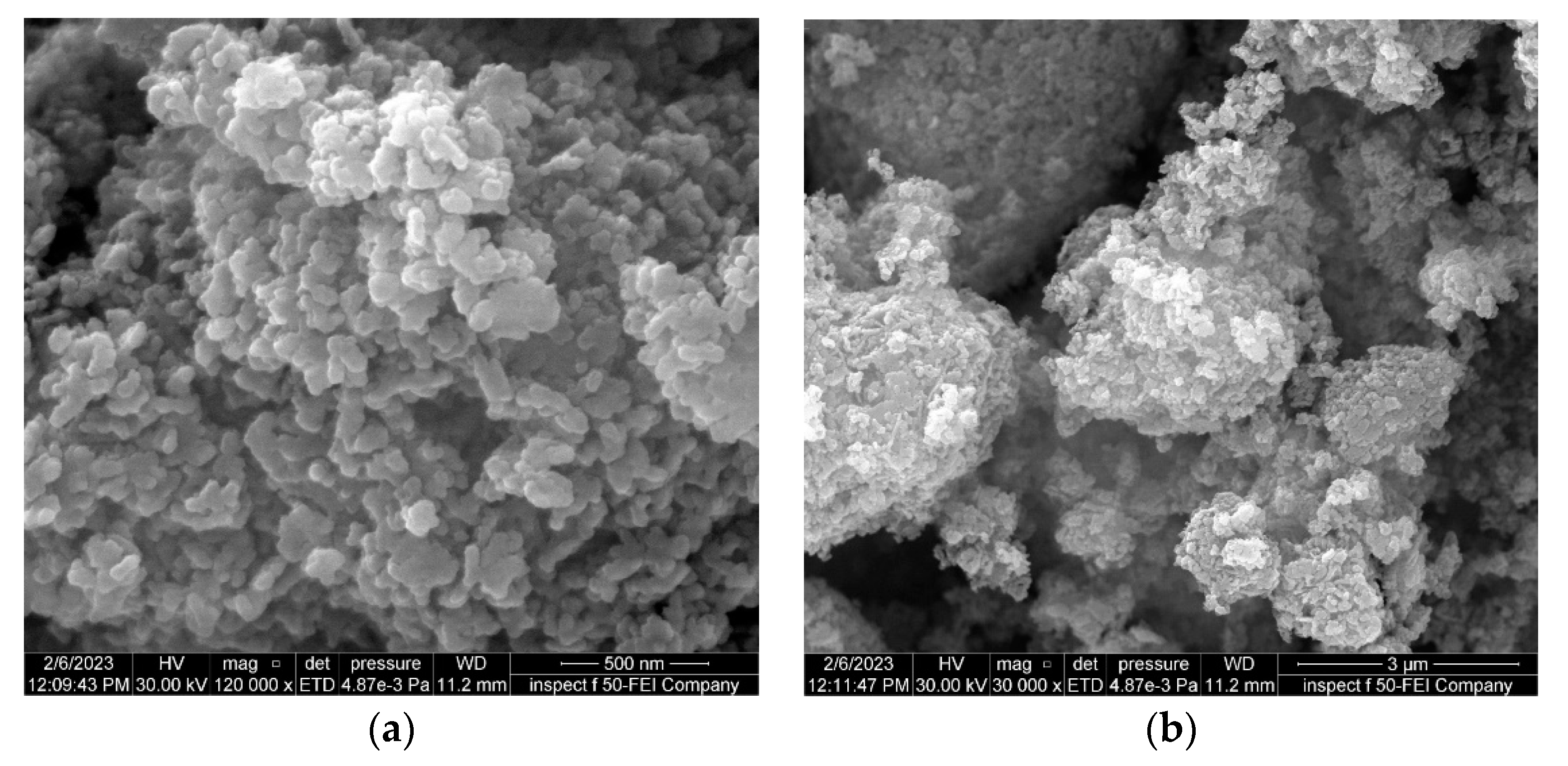
Additionally, the morphological features of the ZnO nanocatalyst were measured using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM).
Figure 8 illustrates the FE-SEM results of the ZnO nanocatalyst at low and high magnifications, respectively. The general shape of the nanocatalyst was spherical, with a particle size of 28 nm. Such a small size is beneficial in dispersing the two-phase mixture in the BCR to provide efficient distribution of the nanocatalyst within a sonication time of 15 min. Also, the FE-SEM results revealed that the ZnO NPs accumulated as clusters. To solve this problem, the ZnO nanocatalyst mixture was subjected to sonication to cause high dispersion inside the BCR.
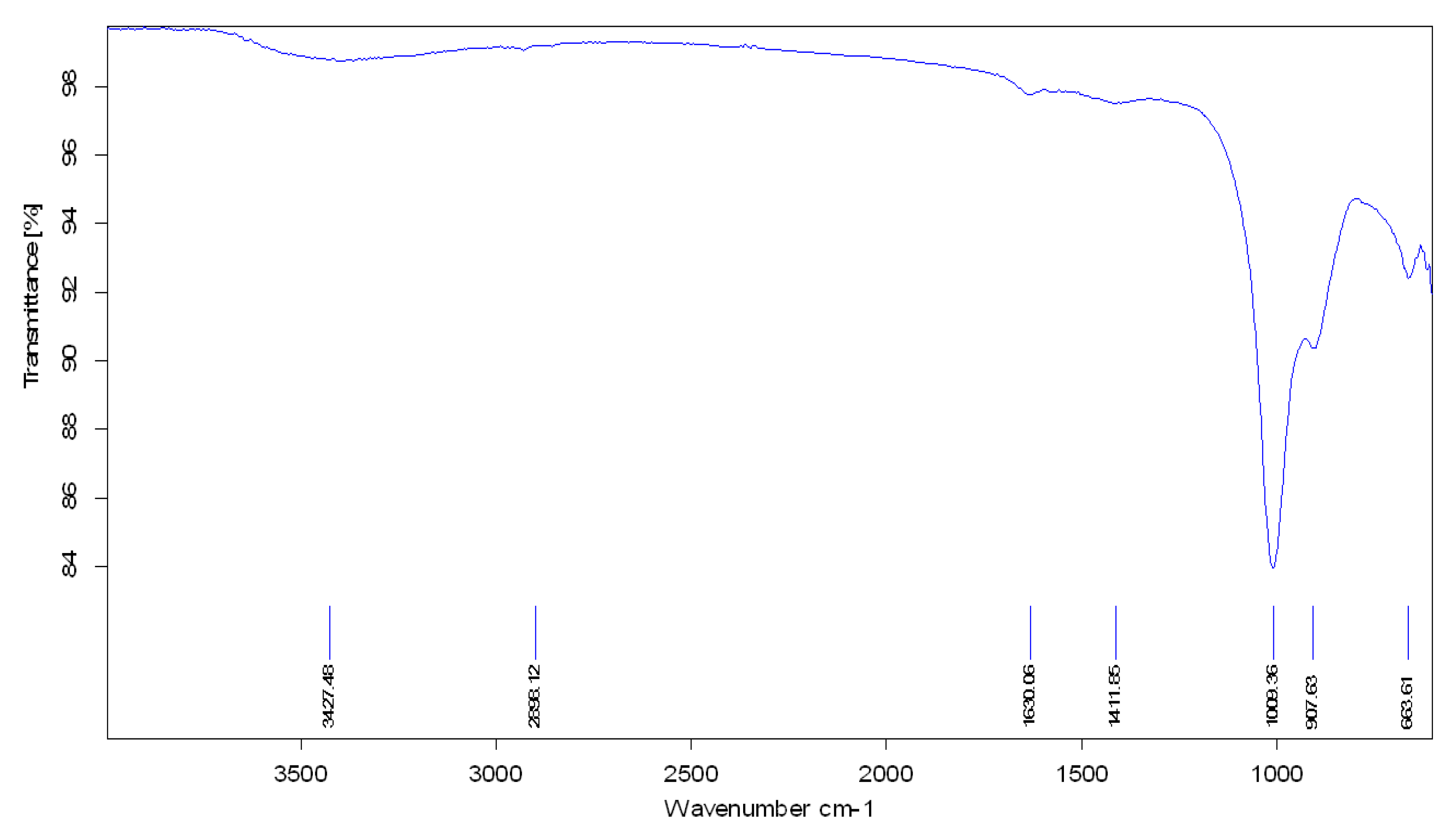
The functional groups associated with the ZnO nanocatalyst were identified using Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy.
Figure 9 shows the main vibrational bands of the ZnO nanocatalyst. The results indicated the presence of absorption bands at 3427.48, 2898.12, 1630.06, 1411.86, 1009.36, 907.63, and 663.61 cm
-1, which represent the main features of the ZnO. A summary of these bands and their positions follows. A clear absorption band was noted at 663.61 cm
-1, which is related to the metal-oxygen vibration (ZnO–stretching), while the band at 907.63 cm
-1 corresponds to the vibration of the C–N or C–O bonds. Moreover, the bands at 1009.36 and 1411.86 cm
-1 are related to oxygen primary and secondary alcohol in-plane vibrations. The peak at 1630.06 cm
-1 is ascribed to aromatic nitro compounds and alkyl vibration. In contrast, the bands at 2898.12 and 3427.48 cm
-1 are ascribed to the stretching vibration of the hydroxyl compound.
3.3. Phenol Degradation Using Ozone Gas
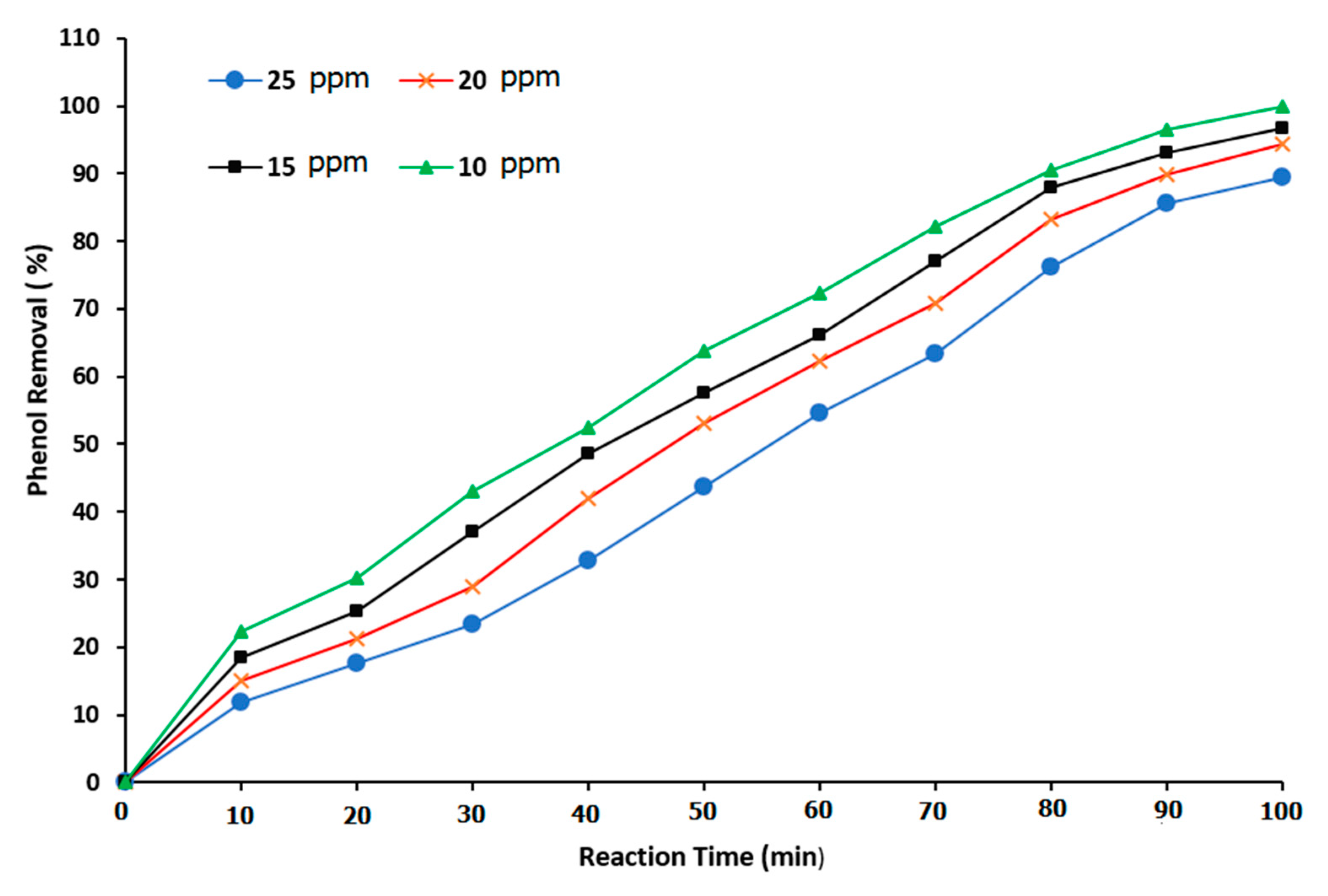
The experiment was achieved using four phenol concentrations of 10, 15, 20, and 25 ppm. For all experimental runs, the pH value was held constant at 7, and the ozone rate was 3 g/h. The phenol degradation reaction was measured as a function of the treatment time in the BCR.
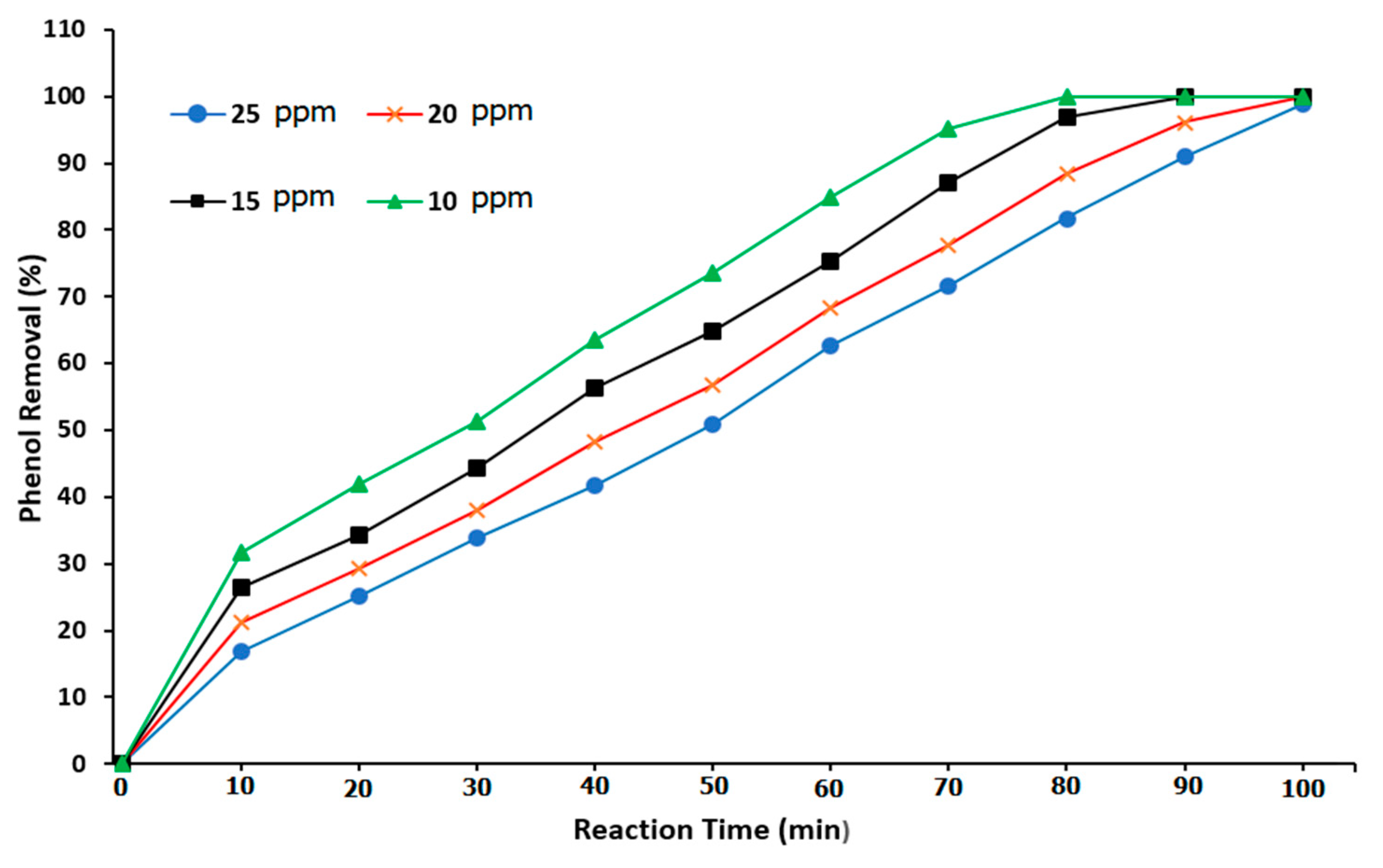
Figure 10 illustrates the relationship between the reaction time and the percentage of phenol removal at various phenol concentrations. At phenol concentrations of 10, 15, 20, and 25 ppm, the phenol removal was 65.82, 57.67, 53, and 43.64%, respectively, at a total reaction time of 50 min. It was noted that at the three phenol concentrations of 10, 15, and 20 ppm, the best reaction times were measured to be 80, 90, and 100 min, respectively. In addition, at an initial phenol concentration (low concentration) of 10 ppm, a reaction time of 100 min was necessary to provide approximately 100% phenol removal. Additionally, as the initial phenol concentration increased, the duration of the reaction time also increased. As a result, the required reaction time was a function of the phenol concentration in the reactor, with this parameter being the main factor that determines BCR performance. Lim et al. [
1], Yamamoto et al. [
15], and Zhou et al. [
53] confirm the importance of the reaction time in phenol degradation.
3.4. Phenol Degradation Using Ozone Gas and a ZnO Nanocatalyst
According to the results of Cheng et al. [
2] and Ratman et al. [
11], the ozonation reaction was slightly low due to a low mass transfer operation. Therefore, more reaction time was required to achieve efficient phenol degradation. As such, the use of heterogeneous catalysts can activate the reaction mechanism of phenol degradation and enhance the ozonation process in the BCR. Accordingly, ZnO NPs were used as the nanocatalyst in the reaction system.
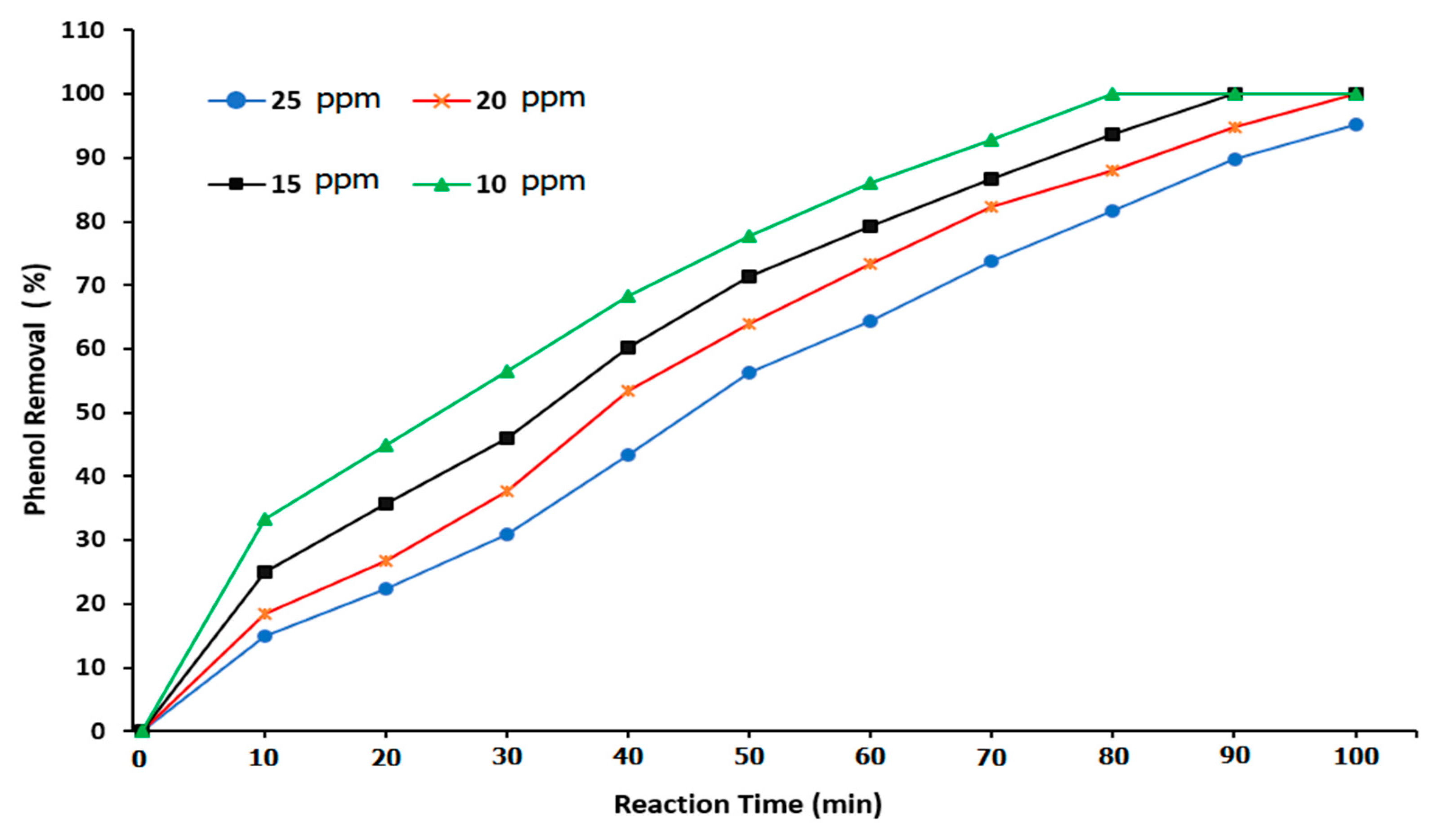
Figure 11 illustrates the influence of the addition of 0.05 g of the ZnO nanocatalyst in the BCR on the phenol removal in relation to the reaction time. The results showed a clear enhancement in the phenol degradation reaction due to the presence of the ZnO nanocatalyst in comparison with the results of using ozone gas alone (
Figure 10). Moreover, at a reaction time of 50 min, the phenol removal values were 73.63, 64.921, 56.697, and 50.861% at phenol concentrations of 10, 15, 20, and 25 ppm, respectively. It was found that the ZnO nanocatalyst worked to initiate the ozonation process to degrade the phenol from wastewater at a high rate. This process exhibited great potential in treating complex hydrocarbons efficiently. The presence of a ZnO nanocatalyst positively affects three factors: (1) active removal of phenol, (2) lowering the amount of consumed treatment energy, and (3) the economic cost [
17,
38,
54].
Furthermore, to achieve the complete degradation of phenol,
Figure 8 shows that reaction times of 80, 90, and 100 min were required at phenol concentrations of 10, 15, and 20 ppm, respectively. However, when using ozone alone without the ZnO nanocatalyst, the required reaction times were longer for the complete removal of phenol. Then, a reaction time of 100 min was required to remove 10 ppm of phenol. The use of the ZnO nanocatalyst provided a high surface area and thus increased the reaction rate within a short reaction time. The increase in the conversion of phenol during the catalyst's ozonation process was mostly due to the effect of free radicals produced by the self-decomposition of ozone on the active site of the ZnO nanocatalyst [
31,
42].
3.5. Phenol Degradation Using Ozone and α-AL2O3 as a Packing Material in a BCR
The low solubility of ozone gas in water remains one of the main challenges in the ozonation reaction. Accordingly, a long reaction time is usually required to overcome this problem. Thus, the use of high surface area packing material in the BCR can greatly increase the mass transfer and reaction rate.
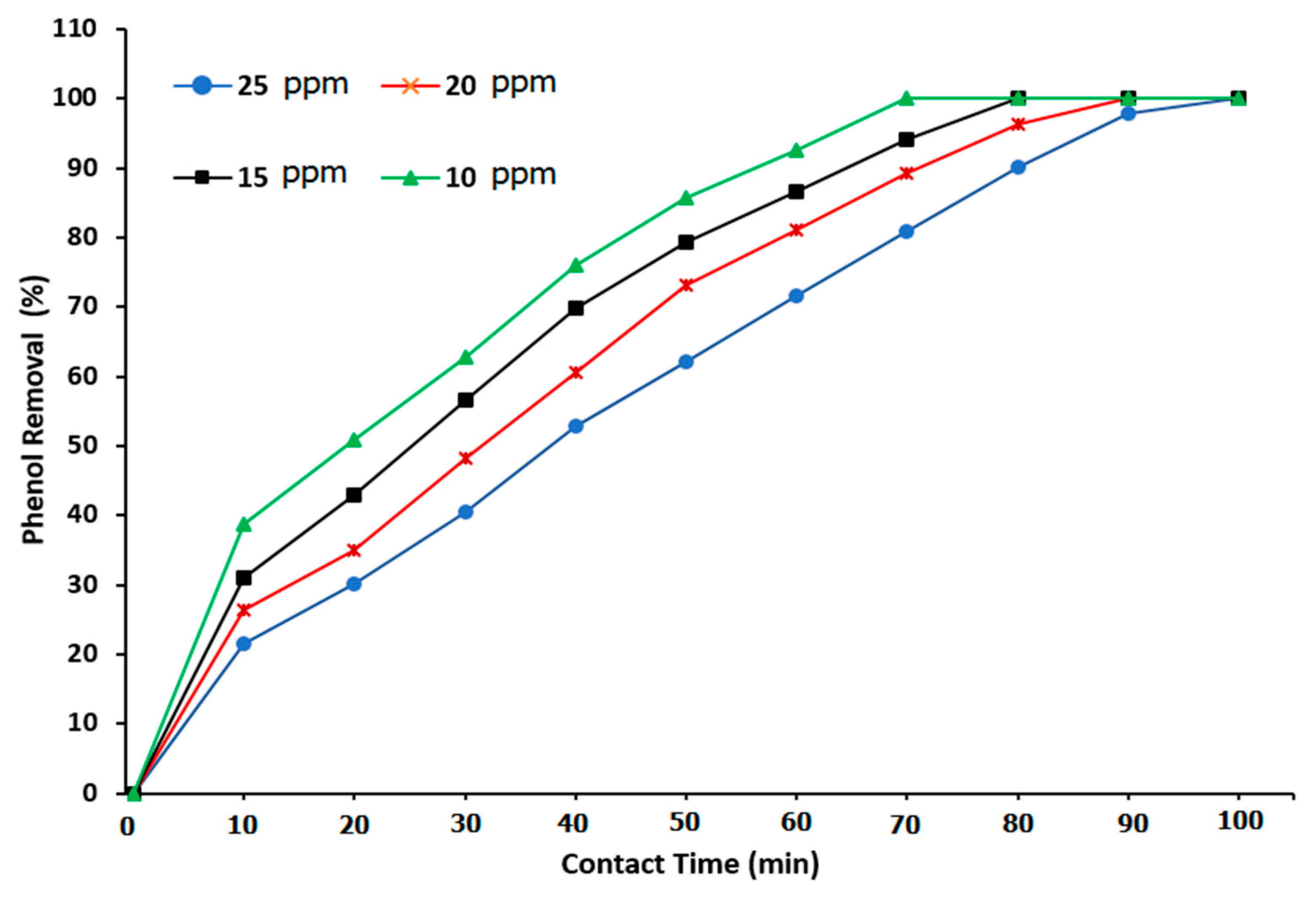
Figure 12 shows the relationship between phenol removal and reaction time in the BCR using ozone and α-AL
2O
3 as a packing material. The degradation rate of phenol removal increased at a low applied phenol concentration. For phenol concentrations of 10, 15, 20, and 25 ppm, the percentage of phenol removal was 77.63, 71.4, 63.99, and 56.38%, respectively. Also, the use of a packing material in the BCR provided a removal of 100% for phenol concentrations of 10, 15, and 20 ppm at reaction times of 80, 90, and 100 min, respectively. Such results contribute to a clear picture of the influence of alumina balls as packing on the ozonation reaction in the BCR.
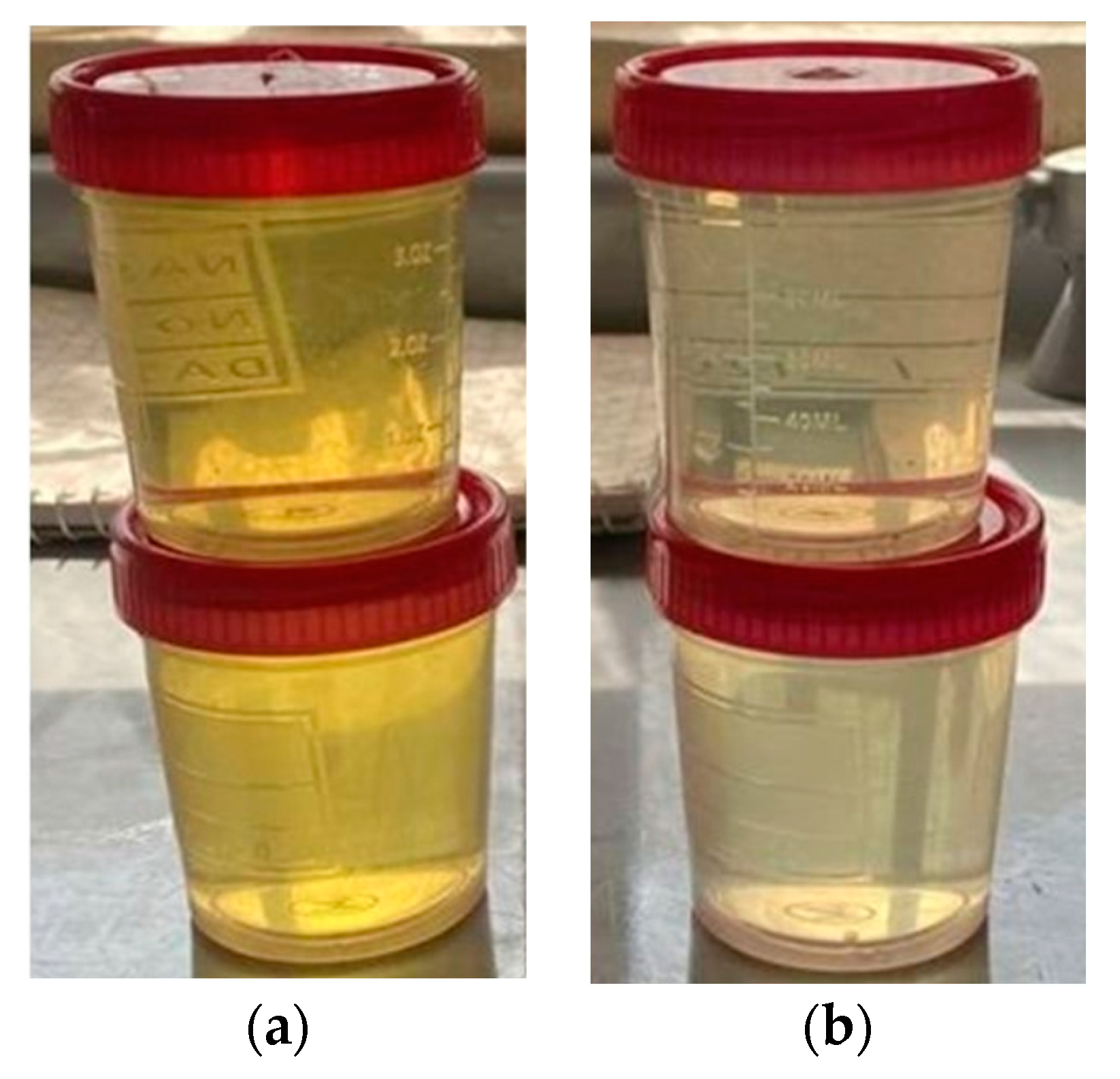
On the other hand, the potassium iodide (KI) of the ozone gas evaluation test demonstrated that the packing had a positive impact on the mass transfer coefficient and contact time. The KI test showed a concentration of 3.5 ppm of produced ozone without packing but only 0.20 ppm in the presence of packing.
Figure 13 explains the change in the appearance of the KI solution, which indicated a higher ozone concentration when packing material was used. Also, this appearance of the KI solution signified the high mass transfer efficiency due to an available high total surface area for the ozonation reaction with packing material.
The presence of packing material provided a higher mass transfer performance [
18,
40]. However, the pressure drops in the BCR that were expected to appear did not due to the large particle size of the α-Al
2O
3 packing, which showed a high void fraction (45%) in the reactor. Accordingly, the expected beneficial influence of the pressure drop on the reactor performance was limited. The use of commercial α-Al
2O
3 packing in the reactor increased the contact surface area between the gas and liquid phases. Fortunately, the enhancement in the mass transfer process made up for the small pressure drop; therefore, the overall mechanism improved the ozonation reaction of phenol. Additionally, a thin film usually formed over the surface of the packing material and played a constant role in enhancing the mass transfer mechanism by improving the liquid distribution, wettability, and ultimately, the reaction rate in the BCR. This aspect is critical in chemical reactions because of the limited reaction rate of the ozonation process. The diffusion mechanism across the thin film provided a clear improvement in the degradation of phenol in wastewater. Moreover, the BCR as a multiphase reactor is usually characterized by efficient mass and heat transfer due to the high efficiency of the hydrodynamic parameters [
8,
14]. As shown in section
3.1, in the present experimental study, the hydrodynamic parameters were evaluated and managed to provide an optimal performance in the BCR.
3.6. Phenol Degradation Using Ozone, α-Al2O3 packing, and the ZnO Nanocatalyst
The fourth experiment included phenol treatment with ozone gas utilizing the ZnO nanocatalyst in the presence of α-Al
2O
3 packing, as shown in
Figure 14. For a phenol concentration of 10 ppm, a conversion rate of 100% was achieved for phenol elimination in the reactor at a reaction time of 70 min, with 0.05 g ZnO nanocatalyst. Accordingly, at phenol concentrations of 15, 20, and 25 ppm, the phenol removal measurements showed values of 94, 89.213, and 80.85%, respectively. Also, the results indicated that phenol concentrations of 25, 20, and 15 ppm required reaction times of 100, 90, and 80 min, respectively, to achieve the complete (100%) degradation of phenol. The development in phenol removal resulted from the hydrodynamic characteristics in the BCR, including the increased interfacial area, low ozone bubble rising velocity, extended gas stagnation time, increased reaction time, and high mass transfer process. All of these parameters reflect the high efficiency of the phenol conversion rate. The presence of packing material and the ZnO nanocatalyst improved the mechanism of the ozonation reaction to provide a high-performance effect in the BCR. These results agree with the results of Li et al. [
7], Gao et al. [
38], and Wei et al. [
43].
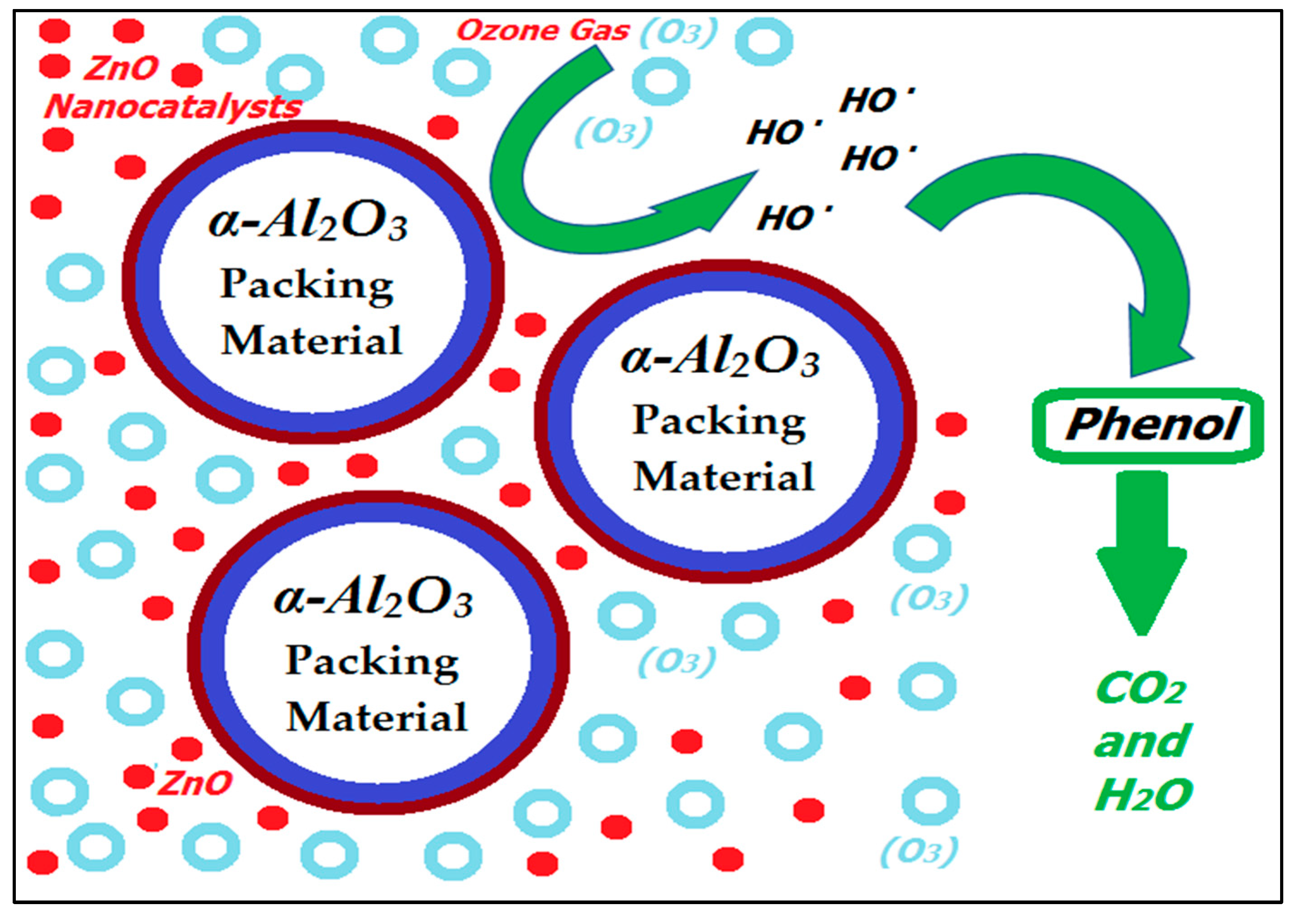
Figure 15 presents a schematic diagram explaining the reaction mechanism of the ozonation reaction in the BCR in the presence of α-Al
2O
3 packing and the ZnO nanocatalyst showing that the nanocatalyst improved the catalytic ozonation process and degraded more phenol by increasing the formation of hydroxyl radicals (OH•). These radicals are strong oxidizing agents used in the phenol degradation process. The hydroxyl radicals increase the catalytic ozonation process to convert more phenol in the reaction system. Moreover, the ZnO nanocatalyst provided an efficient, active catalytic surface for the ozonation reaction by generating more hydroxyl radicals, which boosted the removal efficiency. The presence of nanocatalysts in the ozonation process promote the decomposition of ozone gas into hydroxyl radicals [
17,
34]. Sable et al. [
40] and Honarmandrad et al. [
45] have shown that the catalytic ozonation reaction is a modified oxidation process, including the formation of highly active free radicals that initiate the degradation of organic pollutants at a high rate. Therefore, the present investigation showed a high level of phenol degradation due to the combination of α-Al
2O
3 packing material and the ZnO nanocatalyst in the reaction system.
The addition of the ZnO nanocatalyst to wastewater containing phenol provided a clear increase in the gas holdup and reaction surface area as well as high dispersion of the nanocatalyst particles. All of these factors promoted the consumption of a high quantity of ozone in the reaction mixture, causing the phenol degradation process to improve significantly by forming water and carbon dioxide. Accordingly, a shorter reaction time was required for phenol degradation when applying this method that produced high-performance removal in a BCR [
4,
24,
50].
5. Conclusions
In this study, the problem of a limited ozonation reaction rate was solved in a bubble column reactor (BCR). The ozonation reaction of phenol degradation was improved by utilizing α-AL2O3 as a packing material and a ZnO nanocatalyst in a BCR. The results indicated that the presence of packing is suitable for a high mass transfer mechanism due to the high total contact surface area between the gas and liquid phases. Also, the high void fraction of the packing material (45%) maintained the pressure drop inside the reactor within an acceptable limit without influencing the reaction rate. Moreover, it was found that the ZnO nanocatalyst improved the phenol degradation rate dramatically by enhancing the phenol degradation mechanism. The experimental results showed that as the phenol concentration increased in the reaction system, it required additional time for the ozonation reaction. Also, the presence of α-AL2O3 balls and the ZnO nanocatalyst showed the highest phenol removal values. Further, it was observed that the hydrodynamic parameters of the BCR played a major role in determining the BCR’s performance in the reaction process. A phenol concentration of 25, 20, and 15 ppm required a reaction time of 100, 90, and 80 min, respectively, to achieve the complete (100%) degradation of phenol. Additionally, the understanding of the ozonation reaction mechanisms achieved in this work is necessary in order to apply this method in wastewater system treatment at industrial plants.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.A.S.; methodology, A.K.M.; formal analysis, M.A.A.; investigation, K.A.S. and A.K.M.; data curation, M.A.A. and A.K.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K.M.; writing (review and editing), K.A.S.; visualization, M.A.A.; supervision, K.A.S.; project administration, K.A.S. and M.A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Design & Production Research Unit at the Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Technology-Iraq for the scientific support of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lim, S.; Shi, J.L.; von Gunten, U.; McCurry, D.L. Ozonation of organic compounds in water and wastewater: A critical review. Water Res. 2022, 213, 118053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Quan, X.; Li, R.; Wu, J.; Zhao, Q. Ozonation of phenol-containing wastewater using O3/Ca (OH)2 system in a microbubble gas-liquid reactor. Ozone: Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Shang, R.; Wu, W.; Jiao, W.; Liu, Y. Degradation of phenol with Mn-CoOX/γ-Al2O3 catalytic ozonation enhanced by high gravity technology. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 119036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derco, J.; Gotvajn, A.Ž.; Čižmárová, O.; Dudáš, J.; Sumegová, L.; Šimovičová, K. Removal of micropollutants by ozone-based processes. Processes 2021, 9, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, L.; Bazrafshan, E.; Rahdar, A.; Labuto, G.; Kamali, A.R. Nanostructured MgO-enhanced catalytic ozonation of petrochemical wastewater. boletín de la sociedad española de cerámica y vidrio 2021, 60, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wei, C.; Hu, Y.; Wu, H. Zinc ferrite catalysts for ozonation of aqueous organic contaminants: phenol and bio-treated coking wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fu, L.; Chen, F.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, J.; Yin, C. Application of Heterogeneous Catalytic Ozonation in Wastewater Treatment: An Overview. Catalysts 2023, 13, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, V.N.; Rodrigues, C.S.; Sampaio, E.F.; Madeira, L.M. Insights into real industrial wastewater treatment by Fenton's oxidation in gas-bubbling reactors. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 265, 110501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, T.; Jiang, P.; Arowo, M.; Shao, L. Amaranth wastewater treatment by intensified ozonation in a rotating zigzag bed. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 49, 102984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aken, P.; Broeck, R.V.D.; Degrève, J.; Dewil, R. A pilot-scale coupling of ozonation and biodegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol-containing wastewater: The effect of biomass acclimation towards chlorophenol and intermediate ozonation products. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 1432–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratman, I.; Kusworo, T.D.; Utomo, D.P.; Azizah, D.A.; Ayodyasena, W.A. Petroleum Refinery Wastewater Treatment using Three Steps Modified Nanohybrid Membrane Coupled with Ozonation as Integrated Pre-treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, N.E.; Mohammed, S.S.; Shnain, Z.Y.; Abid, M.F.; Alwasiti, A.A.; Sukkar, K.A. Catalytic Photodegradation of Cyclic Sulfur Compounds in a Model Fuel Using a Bench-scale Falling-film Reactor Irradiated by a Visible Light. Bull. Chem. React. Eng. Catal. 2022, 17, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muddemann, T.; Neuber, R.; Haupt, D.; Graßl, T.; Issa, M.; Bienen, F.; Enstrup, M.; Möller, J.; Matthée, T.; Sievers, M.; et al. Improving the Treatment Efficiency and Lowering the Operating Costs of Electrochemical Advanced Oxidation Processes. Processes 2021, 9, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Chokshi, N.; Ruparelia, J.P. Effect of Operating Parameters on O3, O3/UV, O3/UV/PS Process Using Bubble Column Reactor for Degradation of Reactive Dyes. J. Institution of Engineers (India) 2023, Series A, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Iimura, K.; Satone, H.; Itoh, K.; Maeda, K. Ozonation of aqueous phenol using high-silica zeolite in an aerated mixing vessel. Asia-Pacific J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 13, e2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanian, Z.Y.; Abid, M.F.; Suker, K. Photodegradation of mefenamic acid from wastewater in a continuous flow solar falling film reactor. DESALINATION Water Treat. 2021, 210, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedeltchev, S. Unified approach for prediction of the volumetric mass transfer coefficients in a homogeneous and heterogeneous bubble column based on the non-corrected penetration theory: Case studies. Processes, 2022, 10, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flagiello, D.; Tammaro, D.; Erto, A.; Maffettone, P.; Lancia, A.; Di Natale, F. Foamed structured packing for mass-transfer equipment produced by an innovative 3D printing technology. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2022, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Li, X.; Li, G.; Liu, Y.; Rao, P. Preparation of SnOx-MnOx@ Al2O3 for catalytic ozonation of phenol in hypersaline wastewater. Ozone: Sci. Eng. 2023, 45, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.A.; Sukkar, K.A.; Shnain, Z.Y. Effect of graphene and multiwalled carbon nanotube additives on the properties of nano-reinforced rubber. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 3265–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Aken, P.; Broeck, R.V.D.; Degrève, J.; Dewil, R. The effect of ozonation on the toxicity and biodegradability of 2,4-dichlorophenol-containing wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, L.; Li, Z.; Esmailpour, A.A.; Li, K.; Wang, S.; Liu, R.; Li, X.; Yun, J. Efficient Treatment of Phenol Wastewater by Catalytic Ozonation over Micron-Sized Hollow MgO Rods. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 25506–25517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokkiladathu, H.; Farissi, S.; Muthukumar, A.; Muthuchamy, M. Removal of a Contaminant of Emerging Concern by Heterogeneous Catalytic Ozonation Process with a Novel Nano Bimetallic Catalyst Embedded on Activated Carbon. Ozone: Sci. Eng. 2022, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almukhtar, R.; Hammoodi, S.I.; Majdi, H.S.; Sukkar, K.A. Managing Transport Processes in Thermal Cracking to Produce High-Quality Fuel from Extra-Heavy Waste Crude Oil Using a Semi-Batch Reactor. Processes 2022, 10, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, M.S.; Peres, J.A.; Lan, B.Y.; Puma, G.L. Ozonation kinetics of winery wastewater in a pilot-scale bubble column reactor. Water Res. 2009, 43, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Ma, L.; Wang, H.; Fan, J. Industrial wastewater advanced treatment via catalytic ozonation with an Fe-based catalyst. Chemosphere 2018, 195, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothinathan, L.; Cai, Q.; Ong, S.; Hu, J. Organics removal in high strength petrochemical wastewater with combined microbubble-catalytic ozonation process. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajeel, S.A.; Sukkar, K.A.; Zedin, N.K. New magnesia-thermal reduction technique to produce high-purity crystalline nano-silicon via semi-batch reactor. Materials Today: Proceedings 2021, 42, 1966–1972. [Google Scholar]
- Barlak, M.S.; Değermenci, N.; Cengiz, I.; Özel, H.U.; Yildiz, E. Comparison of phenol removal with ozonation in jet loop reactor and bubble column. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wu, C.; Fu, L.; Tian, X.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zuo, J. Development, dilemma and potential strategies for the application of nanocatalysts in wastewater catalytic ozonation: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 124, 330–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alattar, S.A.; Sukkar, K.A.; Alsaffar, M.A. The role of TiO2 NPs catalyst and packing material in removal of phenol from wastewater using an ozonized bubble column reactor. Acta Innov. 2023, 46, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Ye, Y.; Wang, M. Catalytic ozonation of phenol by ZnFe2O4/ZnNCN: performance and mechanism. Environ. Sci. Pollution Res. 2022, 29, 88172–88181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, A.M.; Sukkar, K.A.; Jaed, D.M. Development of an extremely efficient Iraqi nano-lubricating oil (Base-60) employing SiO2 and Al2O3 nanoparticles. In: AIP Conference Proceedings 2022, 2443, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Xie, Y.; Cao, H. Organic pollutants removal in wastewater by heterogeneous photocatalytic ozonation. Chemosphere 2015, 121, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, S.; Dai, X.; Dong, B. Application, mechanism, and prospects of Fe-based/Fe-biochar catalysts in heterogenous ozonation process: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 138018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, S.N.; Ghosh, P.C.; Vaidya, A.N.; Mudliar, S.N. Hybrid ozonation process for industrial wastewater treatment: Principles and applications: A review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 35, 101193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baqur, M.S.; Hamied, R.S.; Sukkar, K.A. An Eco-friendly Process to Produce High-Purity Nano-γ-Al2O3 from Aluminum Scrap Using a Novel Electrolysis Technique for Petroleum Industry Applications. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.; Shao, S.; Li, Z.; Jing, J.; Jiao, W.; Liu, Y. Kinetics of the direct reaction between ozone and phenol by high-gravity intensified heterogeneous catalytic ozonation. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 53, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputera, W.H.; Putrie, A.S.; Esmailpour, A.A.; Sasongko, D.; Suendo, V.; Mukti, R.R. Technology Advances in Phenol Removals: Current Progress and Future Perspectives. Catalysts 2021, 11, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sable, S.S.; Shah, K.J.; Chiang, P.C.; Lo, S.L. Catalytic oxidative degradation of phenol using iron oxide promoted sulfonated-ZrO2 by advanced oxidation processes (AOPs). J. Taiwan Institute Chem. Eng. 2018, 91, 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamied, R.S.; Ali, A.N.M.; Sukkar, K.A. Enhancing Heavy Crude Oil Flow in Pipelines through Heating-Induced Viscosity Reduction in the Petroleum Industry. Fluid Dyn. Mater. Process. 2023, 19, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaisani, S.V.; Wahyudi, D.P.; Enjarlis; Karamah, E.F.; Bismo, S. Performance of phenolic wastewater degradation with ozonation and catalytic ozonation technique in multi injection bubble column reactor. In: AIP Conference Proceedings 2019, 2175, 1. [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Shao, S.; Ding, X.; Jiao, W.; Liu, Y. Degradation of phenol with heterogeneous catalytic ozonation enhanced by high gravity technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman–Al Ezzi, A.A. Phenol removal using pulsation bubble column with inverse fluidization airlift loop reactor. Chem. Industry Chem. Eng. Quarterly 2021, 27, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honarmandrad, Z.; Javid, N.; Malakootian, M. Removal efficiency of phenol by ozonation process with calcium peroxide from aqueous solutions. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothinathan, L.; Cai, Q.; Ong, S.; Hu, J. Organics removal in high strength petrochemical wastewater with combined microbubble-catalytic ozonation process. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alattar, S.A.; Sukkar, K.A.; Alsaffar, M.A. Enhancement of Ozonation Reaction for Efficient Removal of Phenol from Wastewater Using a Packed Bubble Column Reactor. Indones. J. Chem. 2023, 23, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, G.S.; Vaidya, P.D.; Joshi, J.B.; Patil, R.N. Analysis of Reaction Kinetics of the Ozonation of Phenolic Compounds and Assessment of the Role of Mass Transfer in the Overall Rate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2023, 62, 8181–8190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreiro, C.; de Luis, A.; Villota, N.; Lomas, J.M.; Lombraña, J.I.; Camarero, L.M. Application of a Combined Adsorption−Ozonation Process for Phenolic Wastewater Treatment in a Continuous Fixed-Bed Reactor. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.; Mirza, C.R.; Khan, A.H.A.; Khalifa, W.; Achour, B.; Barros, R.; Yousaf, S.; Butt, T.A.; Iqbal, M. Limited Phosphorous Supply Improved Lipid Content of Chlorella vulgaris That Increased Phenol and 2-Chlorophenol Adsorption from Contaminated Water with Acid Treatment. Processes 2022, 10, 2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yoza, B.A.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, Q.X.; Guo, S.; Yan, G. Catalytic ozonation of petroleum refinery wastewater utilizing Mn-Fe-Cu/Al2O3 catalyst. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 5552–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamied, R.S.; Sukkar, K.A.; Majdi, H.S.; Shnain, Z.Y.; Graish, M.S.; Mahmood, L.H. Catalytic-Level Identification of Prepared Pt/HY, Pt-Zn/HY, and Pt-Rh/HY Nanocatalysts on the Reforming Reactions of N-Heptane. Processes 2023, 11, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, R.; Yun, J. Efficient degradation of phenol in aqueous solution by catalytic ozonation over MgO/AC. J. Water Process. Eng. 2020, 36, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Sang, L.; Tu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, N.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J. Rapid degradation of refractory organic pollutants by continuous ozonation in a micro-packed bed reactor. Chemosphere 2021, 270, 128621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).