Submitted:
20 July 2023
Posted:
20 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
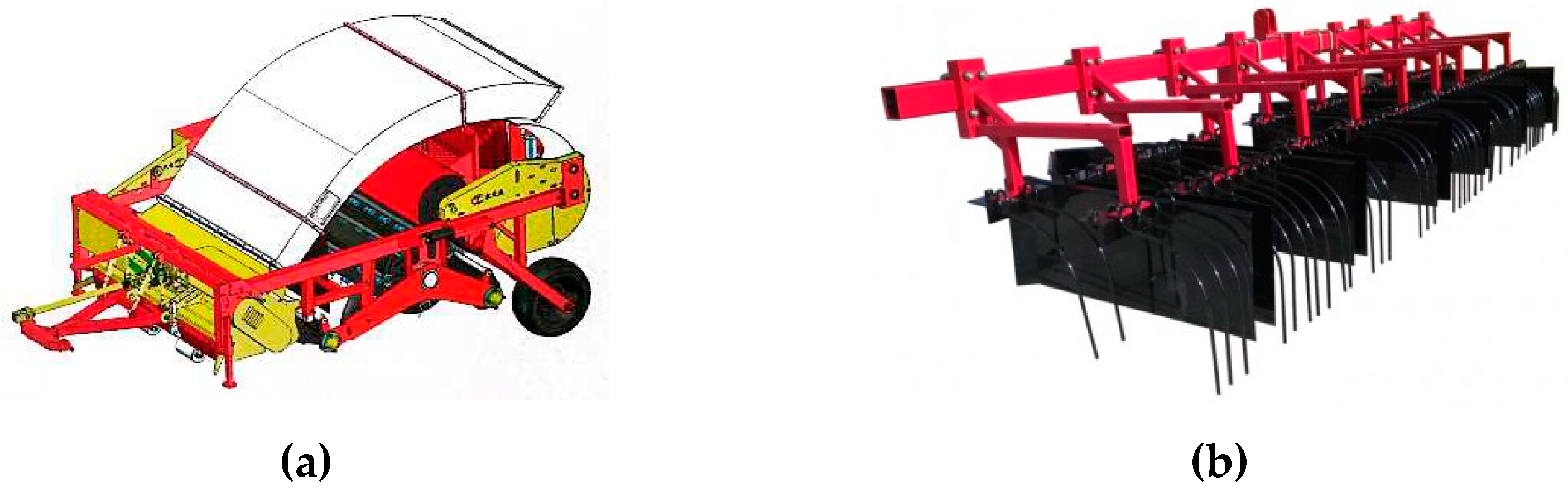
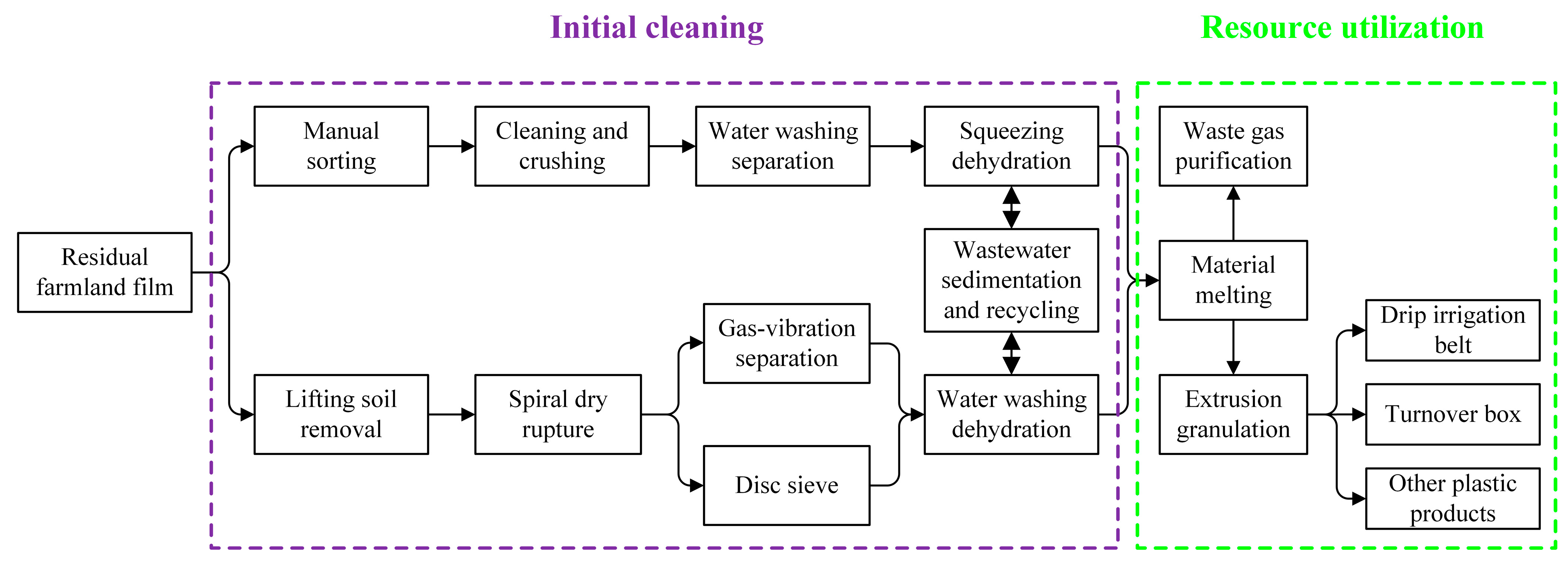
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
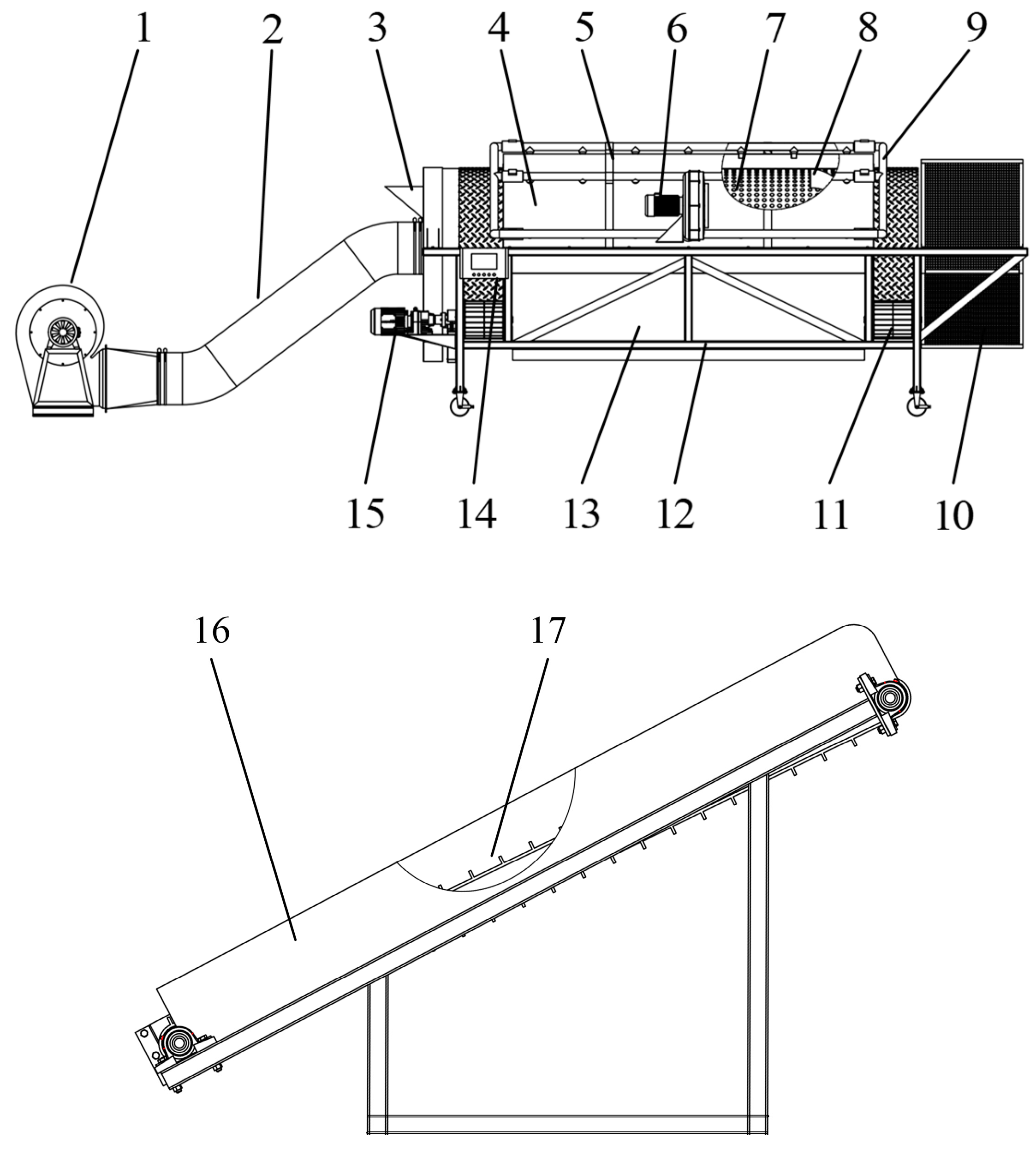
2.1. Overall structure and working principle of the film miscellaneous wind separator
2.1.1. Overall structure
2.1.2. Working principle
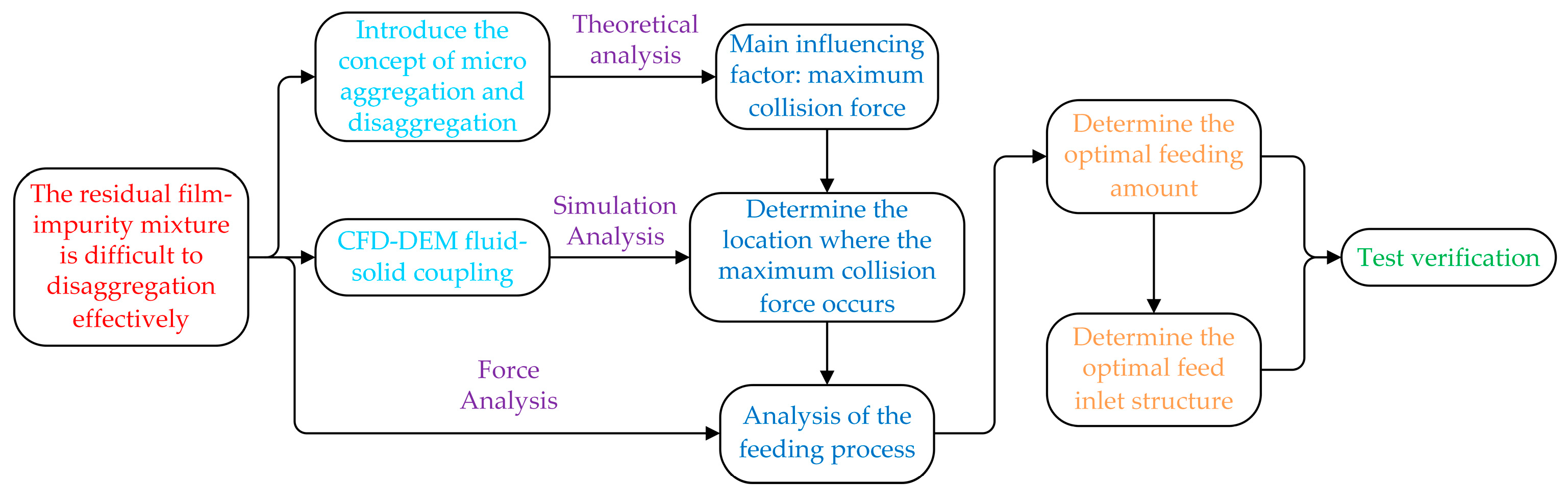
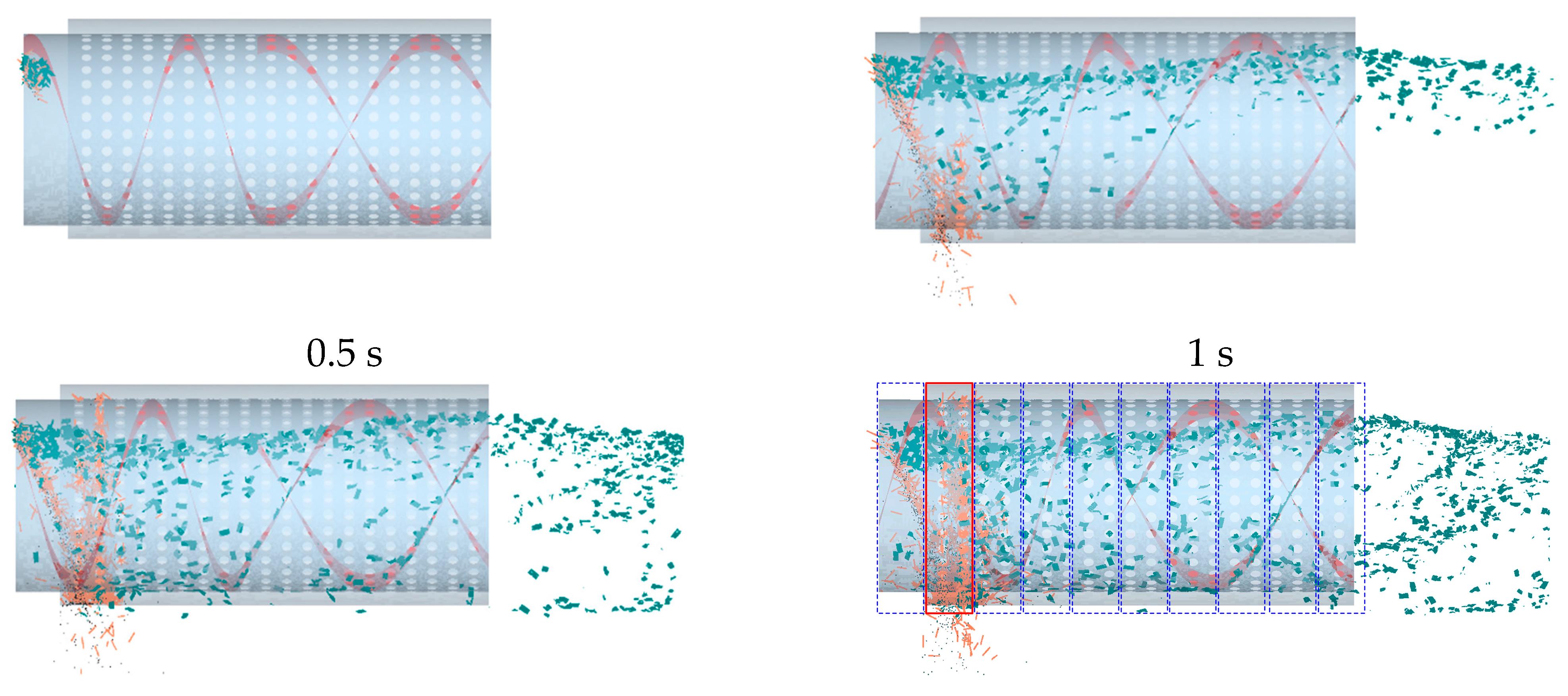
2.2. CFD-DEM fluid-solid coupling simulation analysis
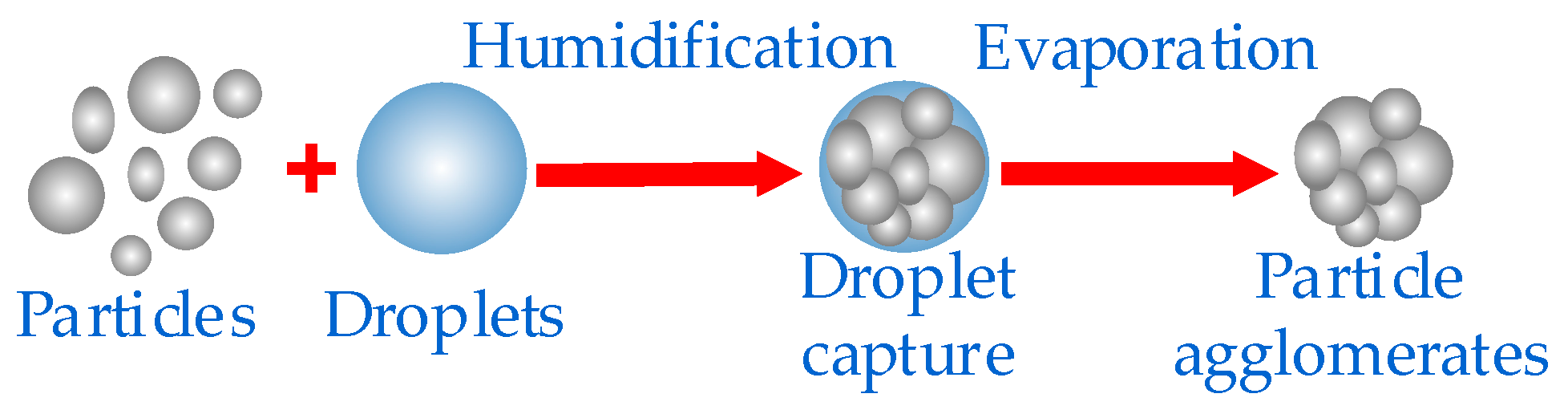
2.2.1. Principle of agglomeration and depolymerization of membrane hybrids
2.2.2. Fluid-solid coupling simulation
2.3. Optimal structural form and feeding volume determination
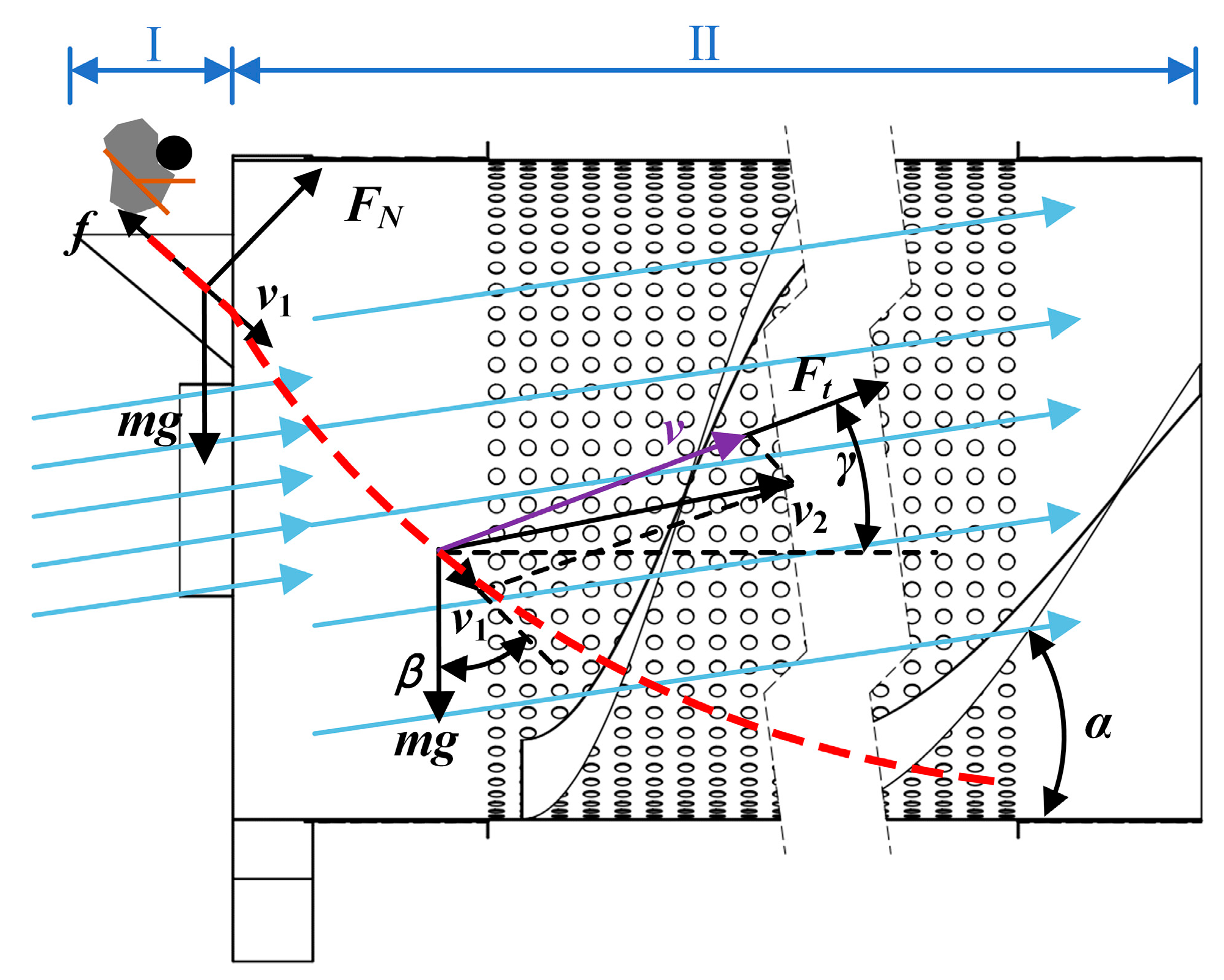
2.3.1. Force analysis of residual film–impurity mixtures
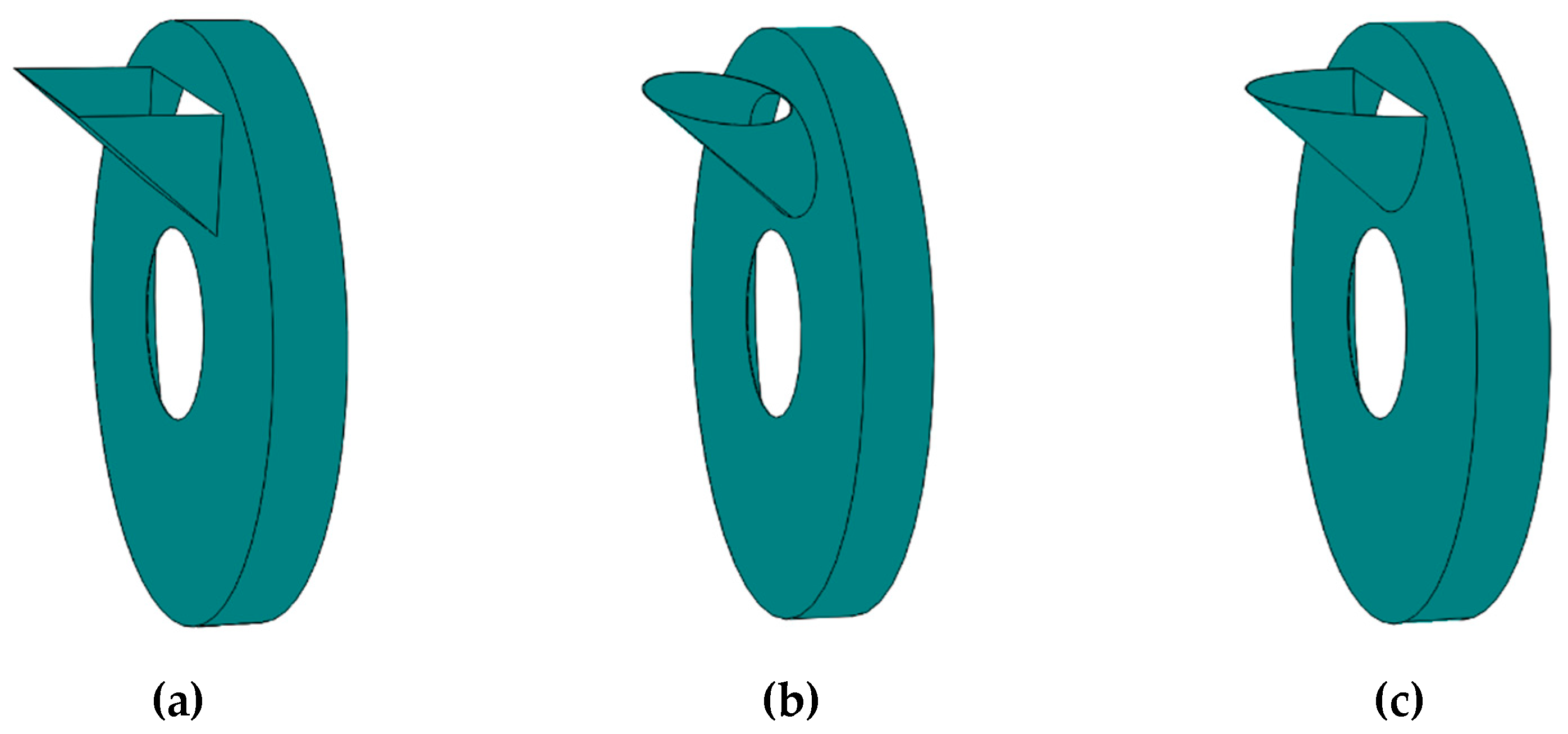
2.3.2. Inlet structure design
2.3.3. Optimal structural form and feeding volume determination
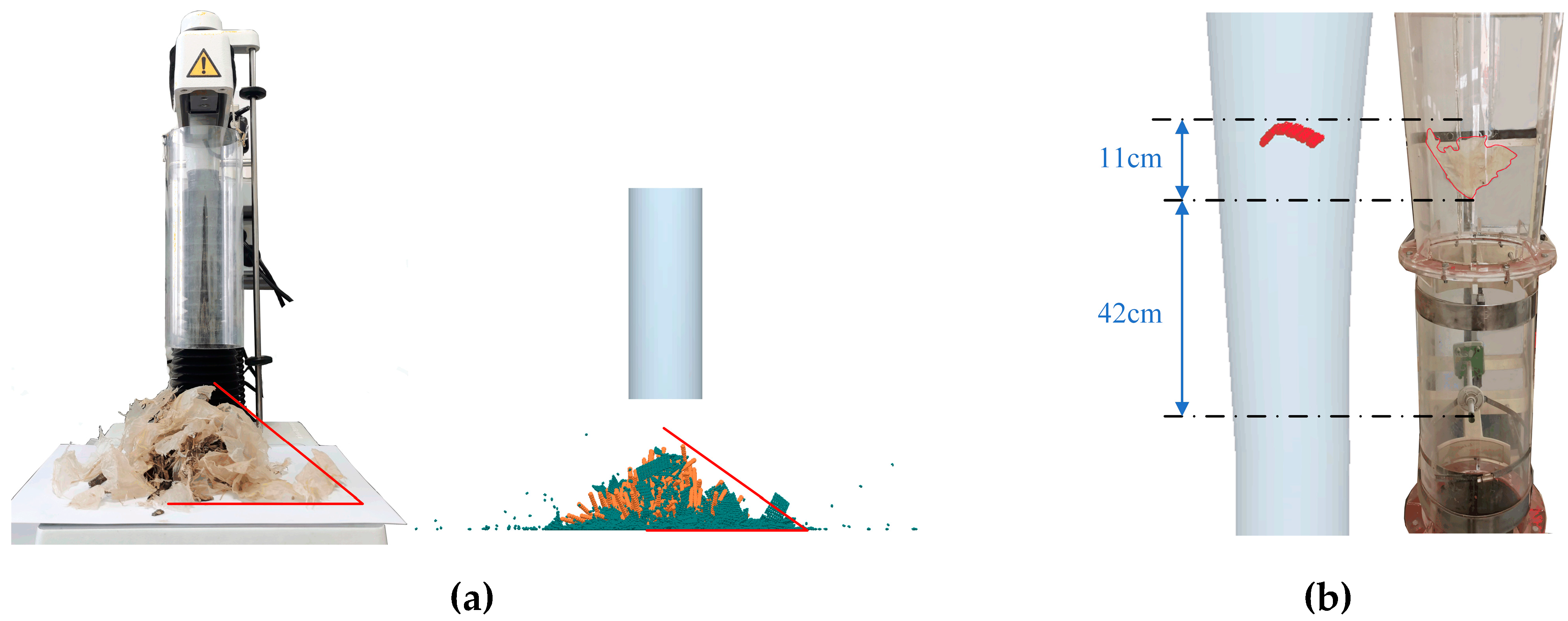
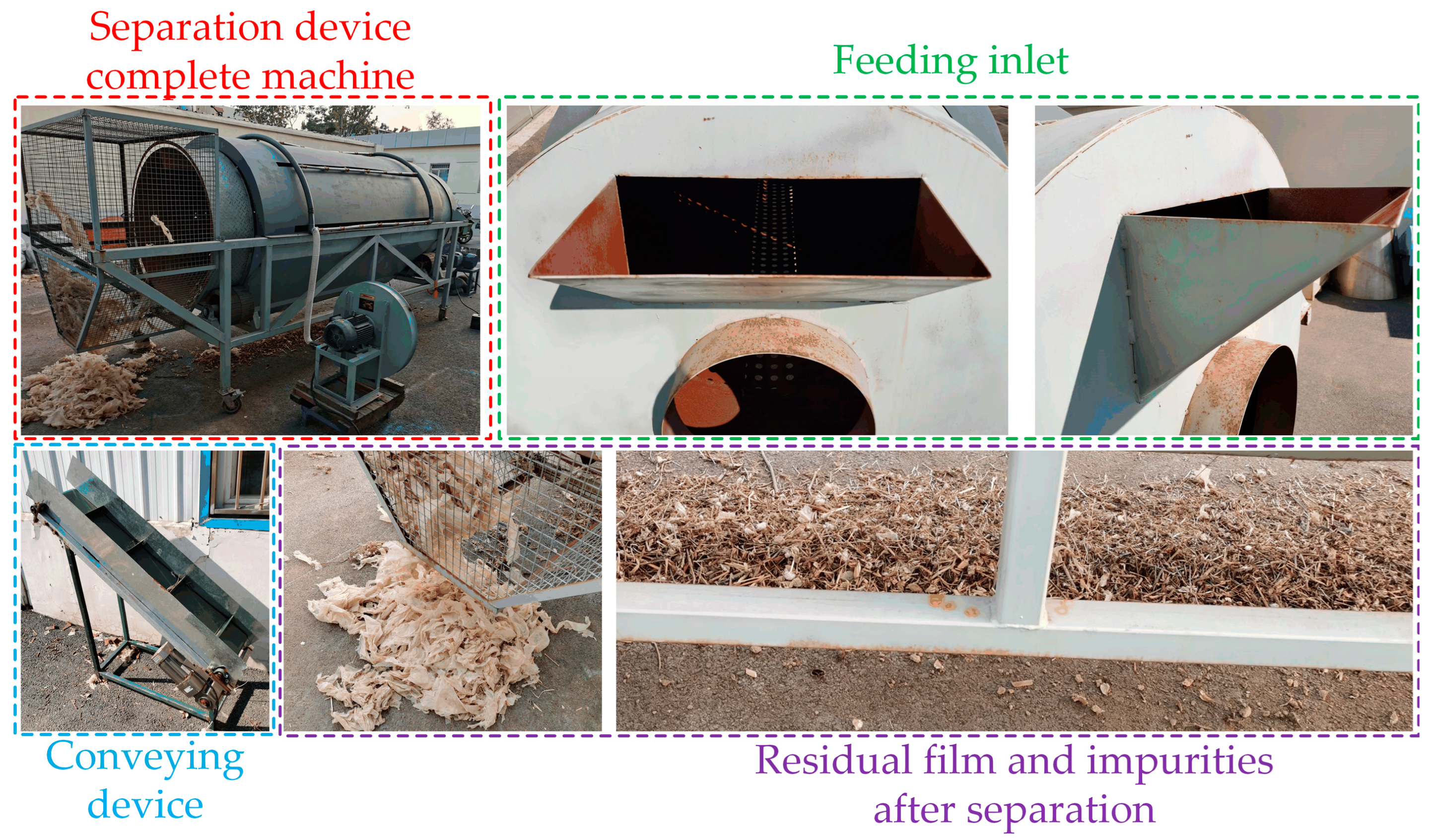
2.4. Test equipment
2.5. Test program and evaluation index
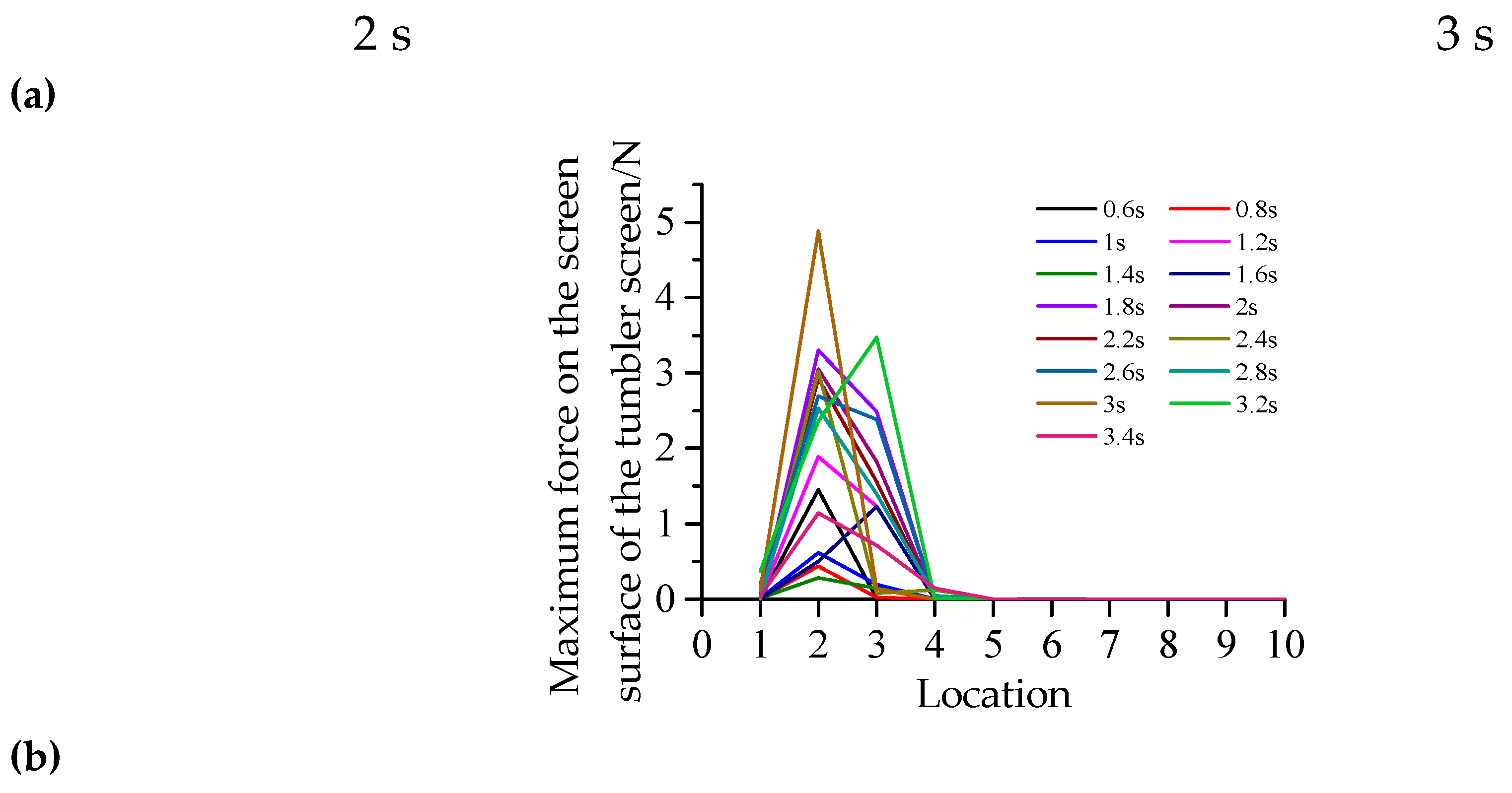
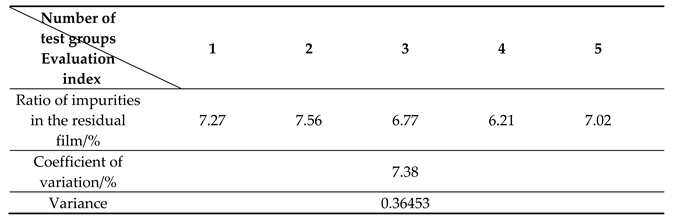
2.5.2. Evaluation indicators
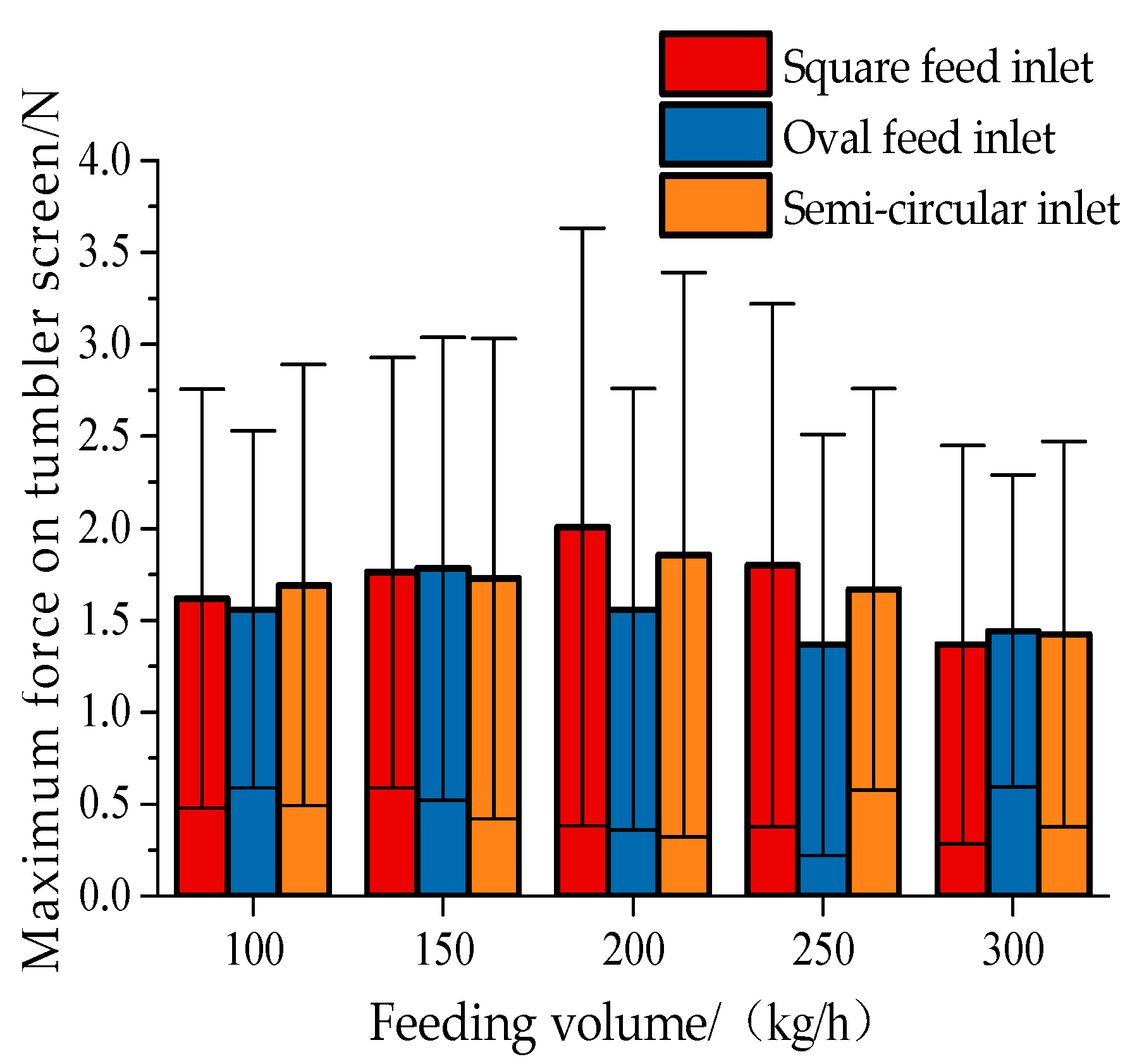
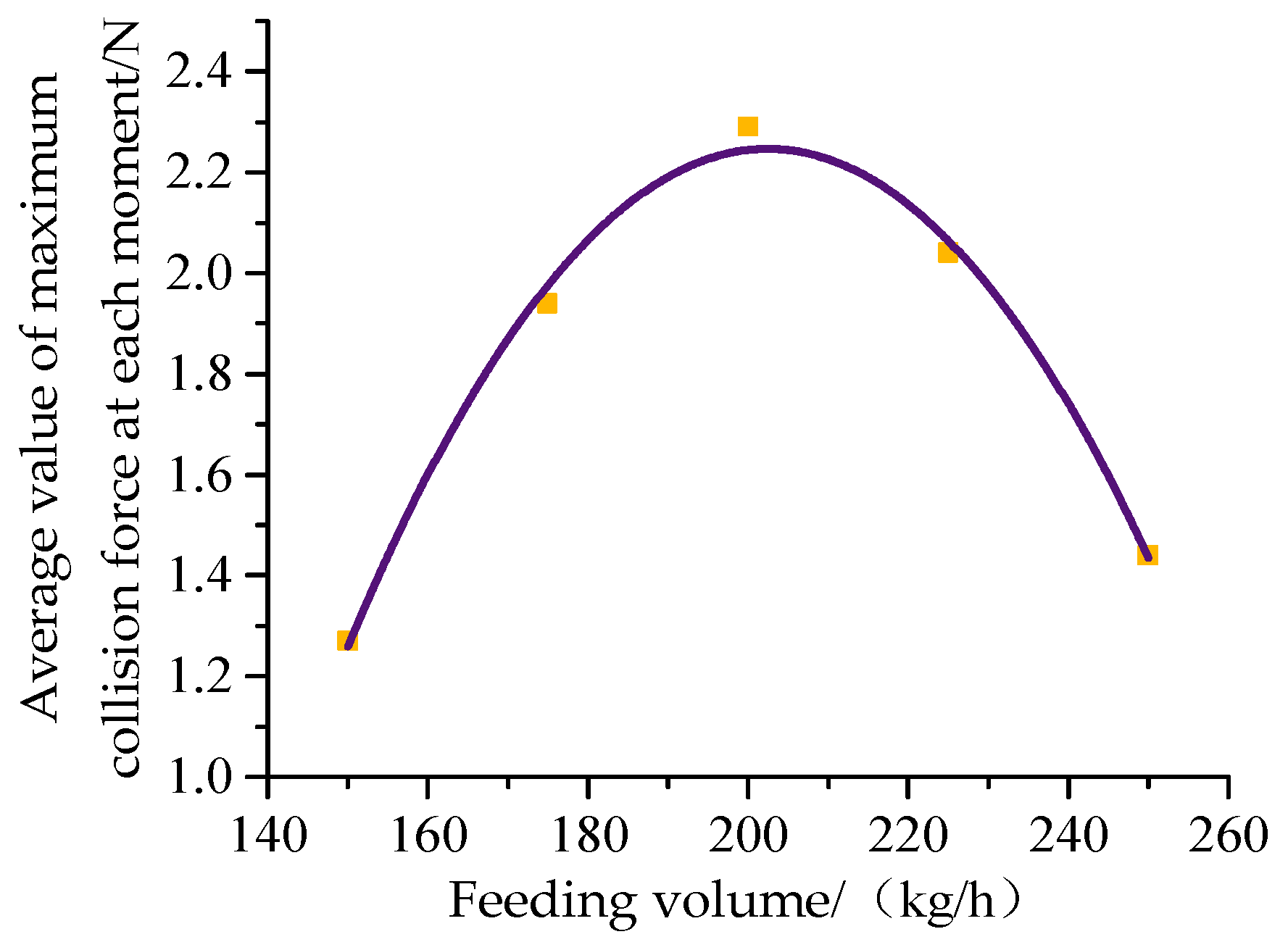
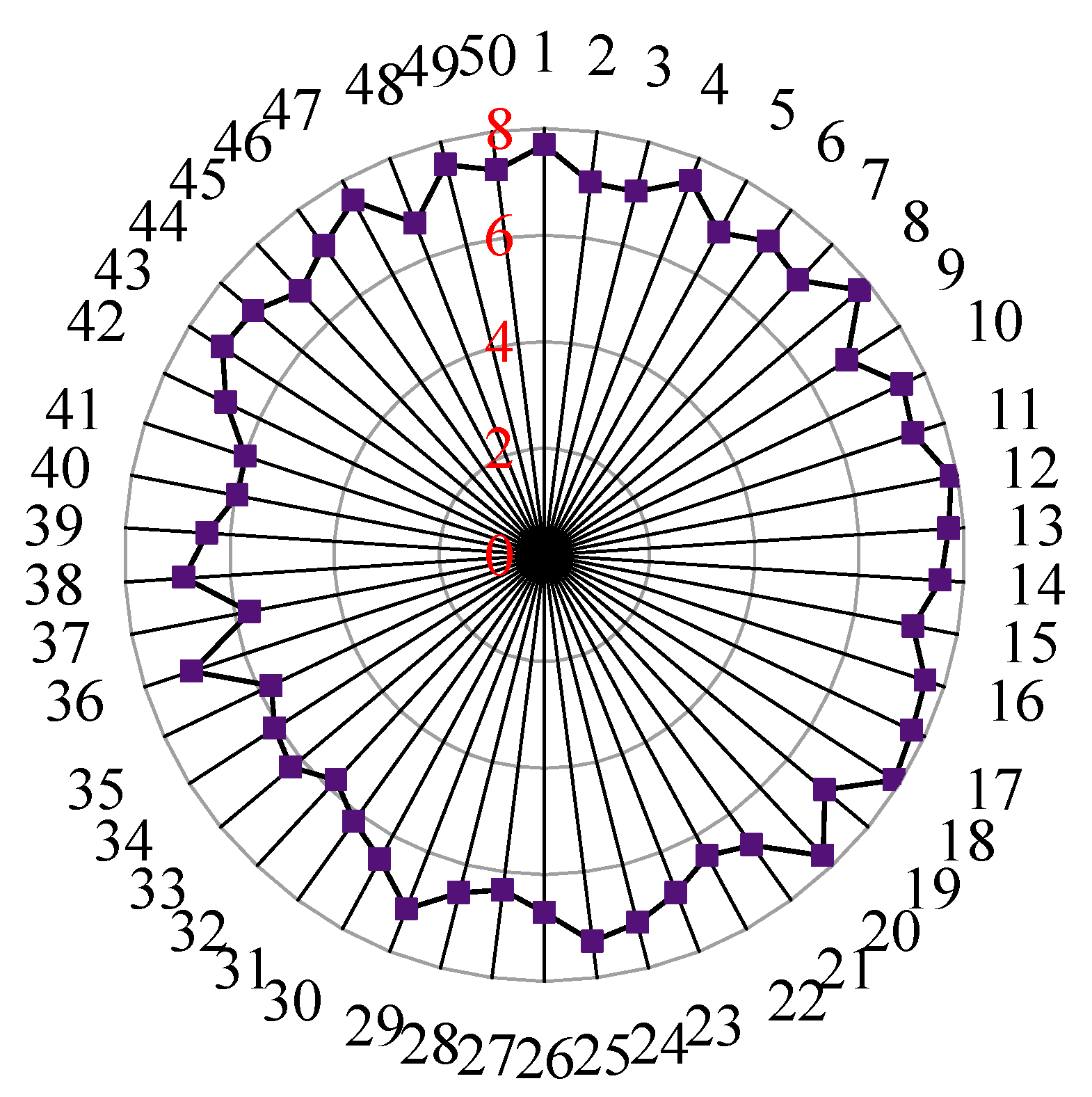
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, D.Q.; Liao, Y.C.; Jia, Z.K. Research progress and development prospects of plastic film covering technology in arid areas Agricultural Research in Arid Areas. 2005, 23, 208–213. [Google Scholar]
- National Bureau of Statistics. China Statistical Yearbook; Publisher: China Statistical Publishing House, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H.X.; Zhao, Y.C. Theoretical research on the sieving of domestic waste by drum screen Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2007, 1, 124-127.
- Shi, X.; Niu, C.H.; Qiao, Y.Y; Zhang, H.C. ; Wang,X. N. Application of plastic trash sorting technology in separating waste plastic mulch films from impurities Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2016, 32, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Kong, F.C.; Liu, H.S. Discrete element simulation of impact disaggregation for wet granule agglomerate Acta phys. Sin., 2015, 64, 328–337. [Google Scholar]
- Yurij, A.A.; Irina, L.Z.; Ruth, C.; Paula, M. Specific effect of the linear charge density of the acid polysaccharide on thermal aggregation/disaggregation processes in complex carrageenan/lysozyme systems. Food Hydrocolloids, 2017, 70, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q. Numerical simulation of homogenizing humidification and pre-dispersion transport of micro-powder limestone, Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Y.X.; Xiong, X.Y.; Tang, J. Impact disaggregation simulation of wet coal agglomerate using discrete element method. Coal Engineering 2019, 51, 167–171. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.B.; Qi, H.Y.; You, C.F.; Xu, X.C. Mechanical analysis of agglomeration and fragmentation of particles during collisions. J Tsinghua Univ(Sci & Tech) 2022, 12, 1639–1643. [Google Scholar]
- Bellocq, B.; Ruiz, T.; Delaplace, G. Screening efficiency and rolling effects of a rotating screen drum used to process wet soft agglomerates Journal of Food Engineering, 2017, 195, 235-246.
- Peng, Q.J.; Li, C.S.; Kang, J.M.; Shi, G.K.; Zhang, H. Improved design and test on pneumatic cylinder sieve film hybrid separator. Transaction of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51, 126–135. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y.; Zhao, L.L. Study on Aggregation and Disaggregation Mechanism of Wet Fine Coal with Airflow Grading; Publisher: China University of Mining and Technology Press, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, G.; Thornton, C.; Adams, M.J. Discrete particle simulation of agglomerate impact coalescence Chemical engineering science, 1998, 53, 3381-3391.
- Ma, C. Design and experiment of deep fertilization strip tillage device for corn in Northeast China. Master’s Thesis, China Academy of Agricultural Machinery Science, Beijing, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.Q. Simulation analysis of sinking process of particles falling into water based on coupled EDM-CFD. Master’s Thesis, Jilin University, Jilin, 2014.
- Liu, X. Design and experimental research on potato conveying and grading device. Master’s Thesis, Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, Shanxi, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, W.; Zhang, X.J.; Ding, Y.C.; Bai, S.H.; Liu, W.P.; Zhou, X.C. Experiment on suspension separation of residual film and impurity based on EDEM-Fluent coupling. Transaction of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery 2022, 53, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.Y.; Ma, X.; Tan, S.Y.; Chen, L.T.; Zeng, L.C.; An, P. Simulative calibration and experiment on main contact parameters of discrete elements for rice bud seeds. Transaction of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery 2018, 49, 93–99. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Q.C.; Sun, N.; Lu, A.Z.; Cao, Y.S.; Liu, J.; Tian, R.F.; Zhuang, Z.T. Design and experiments of the sequential and continuous feeding system for fresh lotus seeds with low damage. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering 2020, 38, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.S.; Kang, J.M.; Peng, Q.J.; Lin, X.Y.; Hou, J.L. Numerical Simulation and Parameter Optimization of Trommel Screen Type Membrane and Impurity Separation Device. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization 2022, accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.M.; Xie, C.S.; Wang, X.Y.; Chen, Y.K.; Wang, C.W.; Peng, Q.J. Design and test of sieve hole cleating device for trommel sieve type membrane miscellaneous wind separator. Transaction of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery 2022, 53, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.C.; Li, X.Y.; Shi, H.B.; Xu, P.C.; Li, H. Water characteristic curve model for soil with residual plastic film. Transactions of the CSAE 2016, 32, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Wang, Q.J. Photosynthetic and light response characteristics of spring wheat under different irrigation schedules Transaction of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery 2018, 49, 271-277.
- Qi, W.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.Y. Experimental investigation on the impact of drying–wetting cycles on the shrink–swell behavior of clay loam in farmland. Agriculture 2022, 12, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.H.; Gao, X.J.; Zhang, Z.H. Simulation and experiment of seed-filling performance of pneumatic cylinder seed-metering device for Panax notoginseng. Transaction of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery 2016, 47, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y; Wang, R.M.; Li, X.Q.; Wang, M.F.; Li, S.C. Design and test of humidification system for potato ventilated storage. Transaction of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery 2021, 52, 358–366. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.M.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.H.; Du, H.Y.; Peng, Q.J.; Song, Y.M. Aerodynamic characteristics of residual film materials and test of membrane separation device. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization 2020, 41, 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H. Design and experimental study on drum-sieve-based film/impurity separation device. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University of Technology, Shandong, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, C.H.; Shi, X.; Jiang, Y.X.; Yang, H.M.; Qiao, Y.Y. Design and test on type of waste plastic mulch films and impurities winnowing machine. Xinjiang Agricultural Mechanization 2018, 05, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.X. Numerical simulation analysis of membrane stalk separation device based on Fluent. Master’s Thesis, Xinjiang University, Xinjiang, 2017. [Google Scholar]


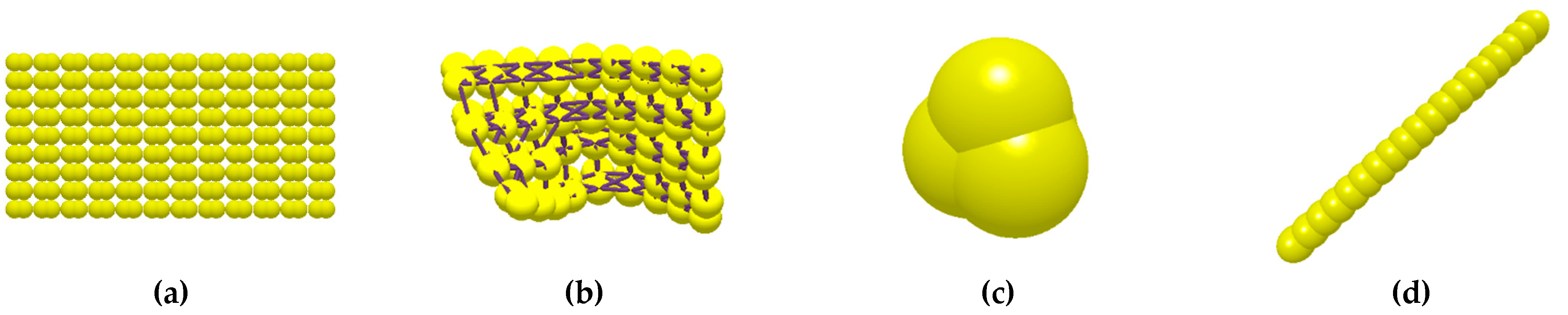

| Materials | Intrinsic parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Residual film | Dimensions (length × width × thickness)/mm × mm × mm | 100×30×0.1 |
| Poisson's ratio | 0.23 | |
| Shear modulus/Pa | 1.2×106 | |
| Density/kg/m3 | 104 | |
| Straw | Dimensions (diameter × length)/mm × mm | 8×80 |
| Poisson's ratio | 0.35 | |
| Shear modulus/Pa | 1.37×108 | |
| Density/kg/m3 | 257.8 | |
| Soil | Equivalent particle size/mm | 2 |
| Poisson's ratio | 0.4 | |
| Shear modulus/Pa | 1.6×108 | |
| Density/kg/m3 | 1430 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





