Submitted:
20 July 2023
Posted:
21 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
Material and Method
2.1. Materials
| Oxides | Raw kaolin (wt%) | Washed kaolin (wt%) |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 47.691 | 44.958 |
| Al2O3 | 26.529 | 34.559 |
| Na2O | 1.302 | 1.241 |
| TiO2 | 0.502 | 0.610 |
| Fe2O3 | 1.052 | 1.057 |
| MgO | 0.596 | 0.573 |
| CaO | 5.833 | 2.356 |
| K2O | 0.591 | 0.590 |
| Cl2 | 0.752 | 0 |
| LOI | 15.152 | 14.056 |
2.2. Method
Results and Discussions
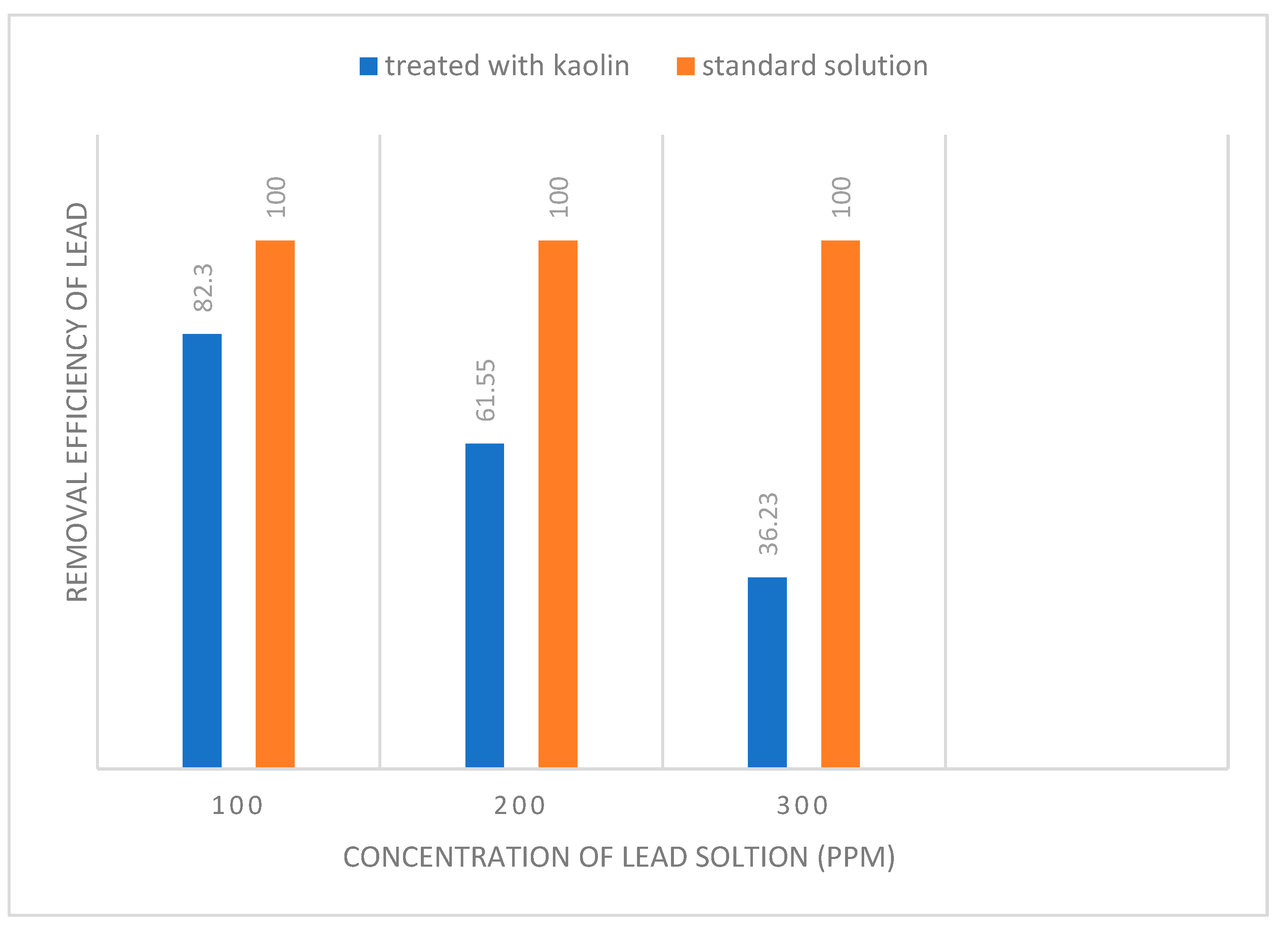
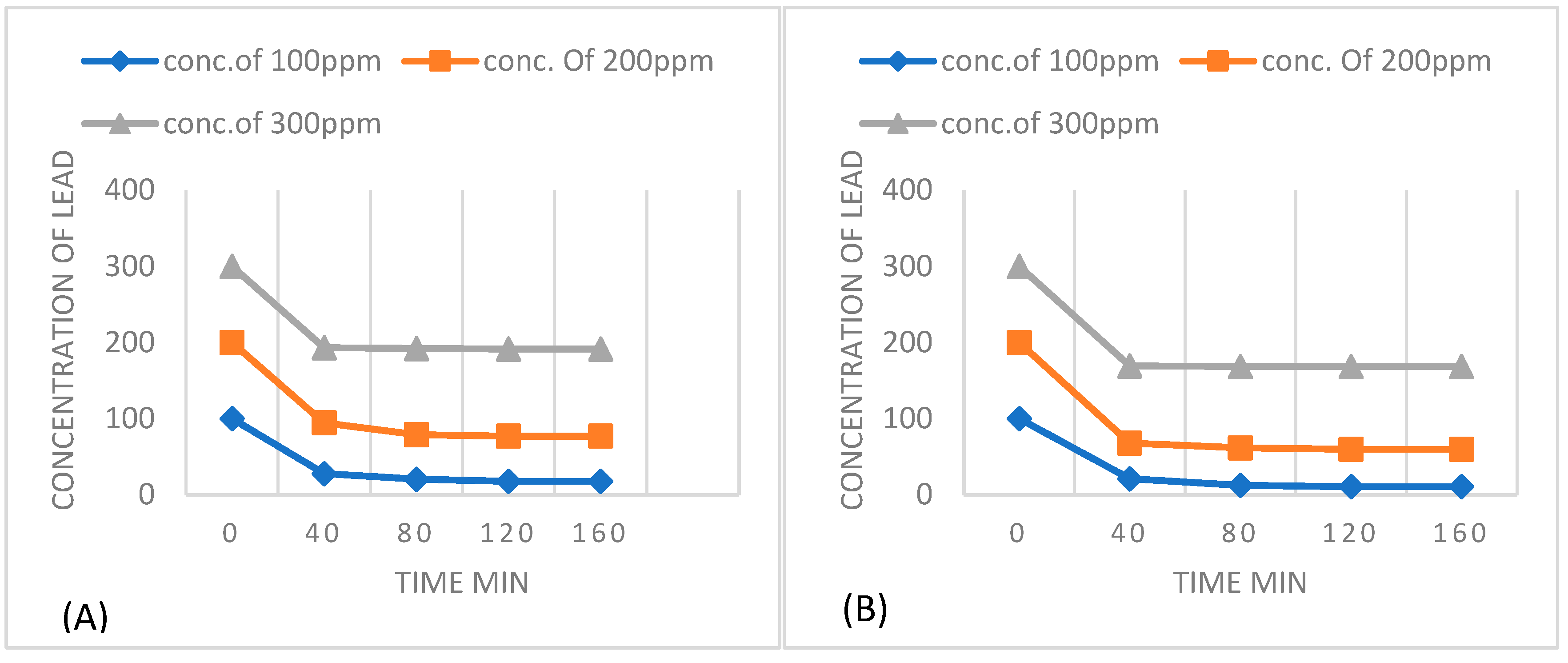
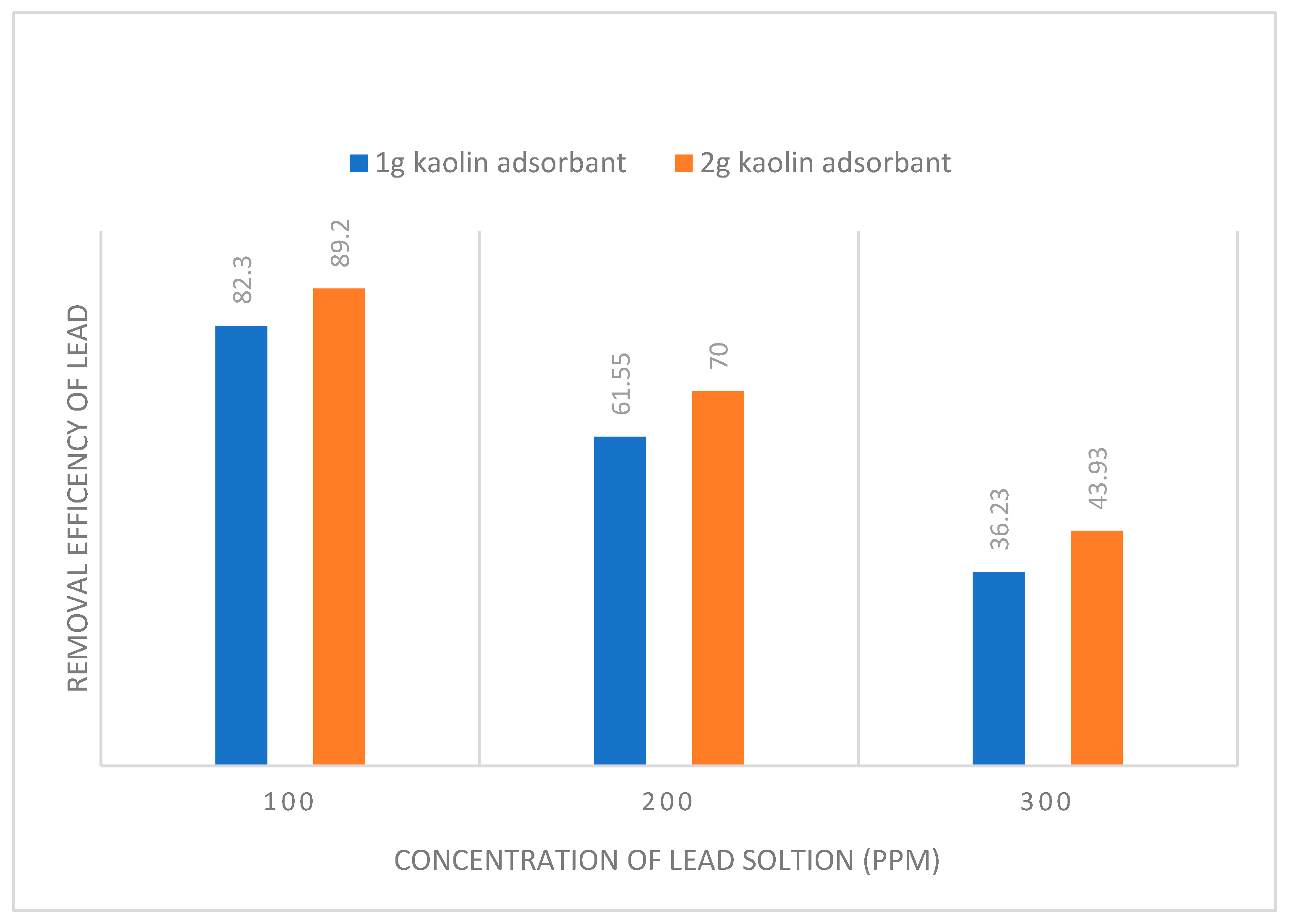
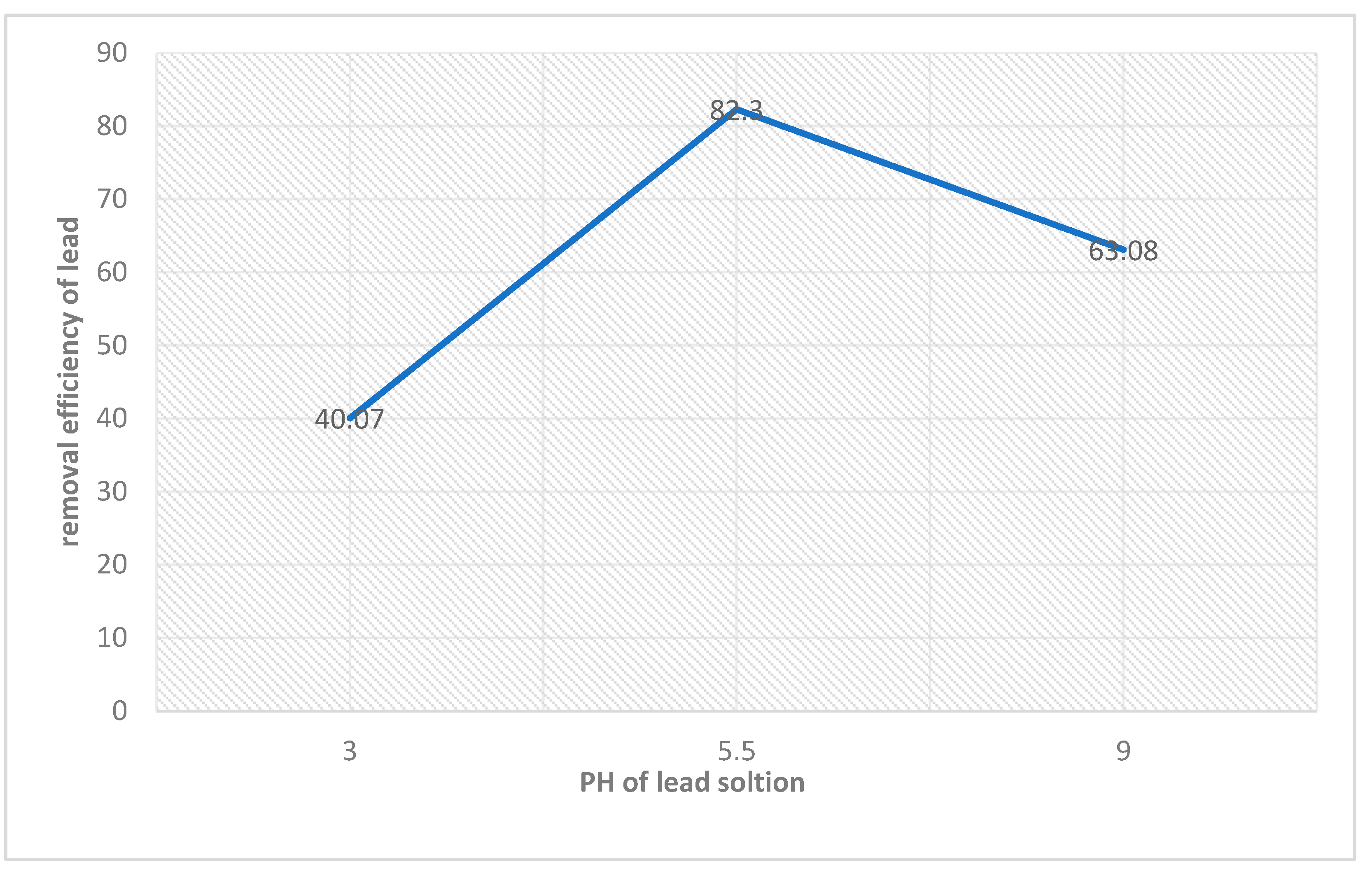
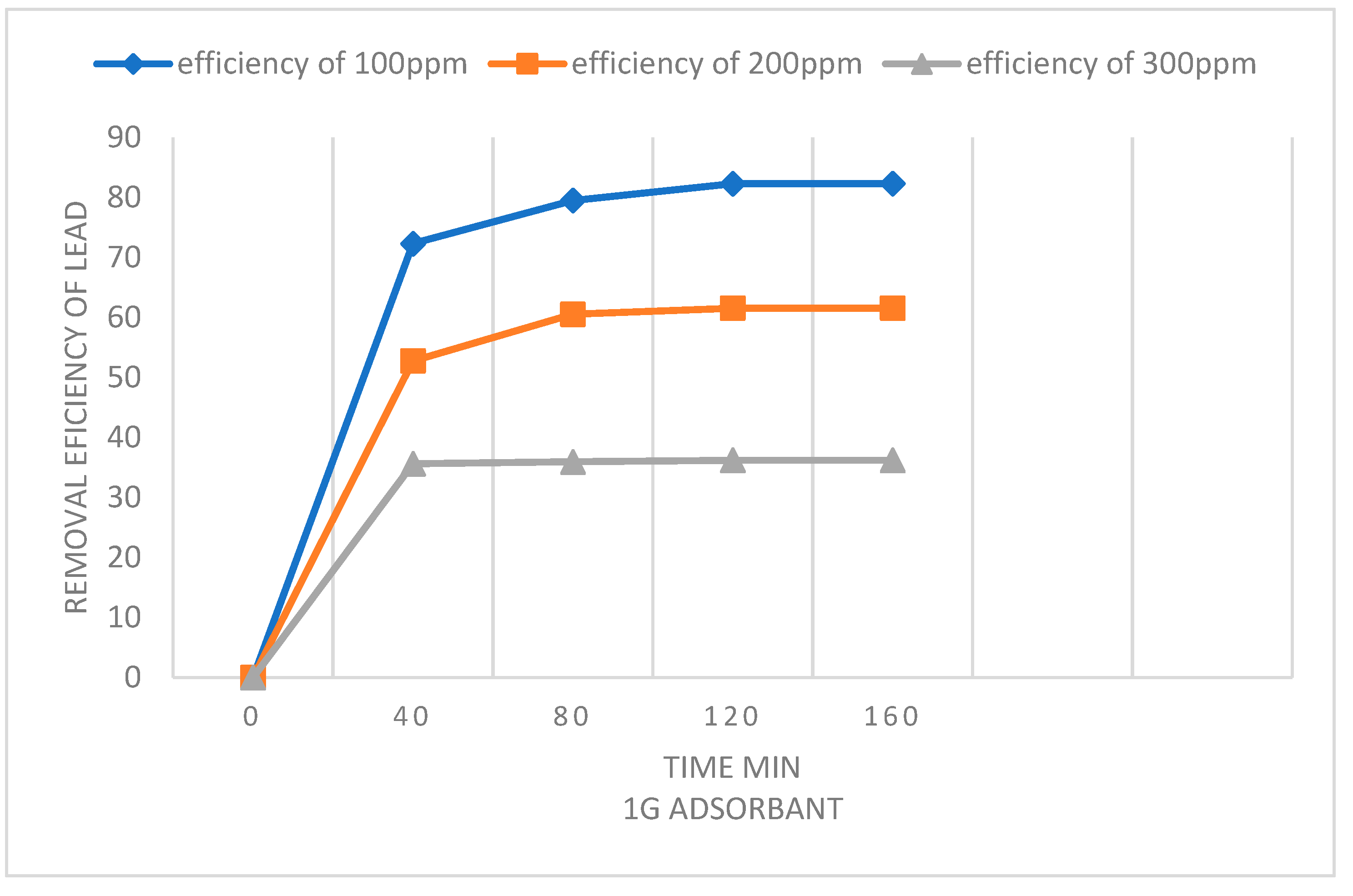
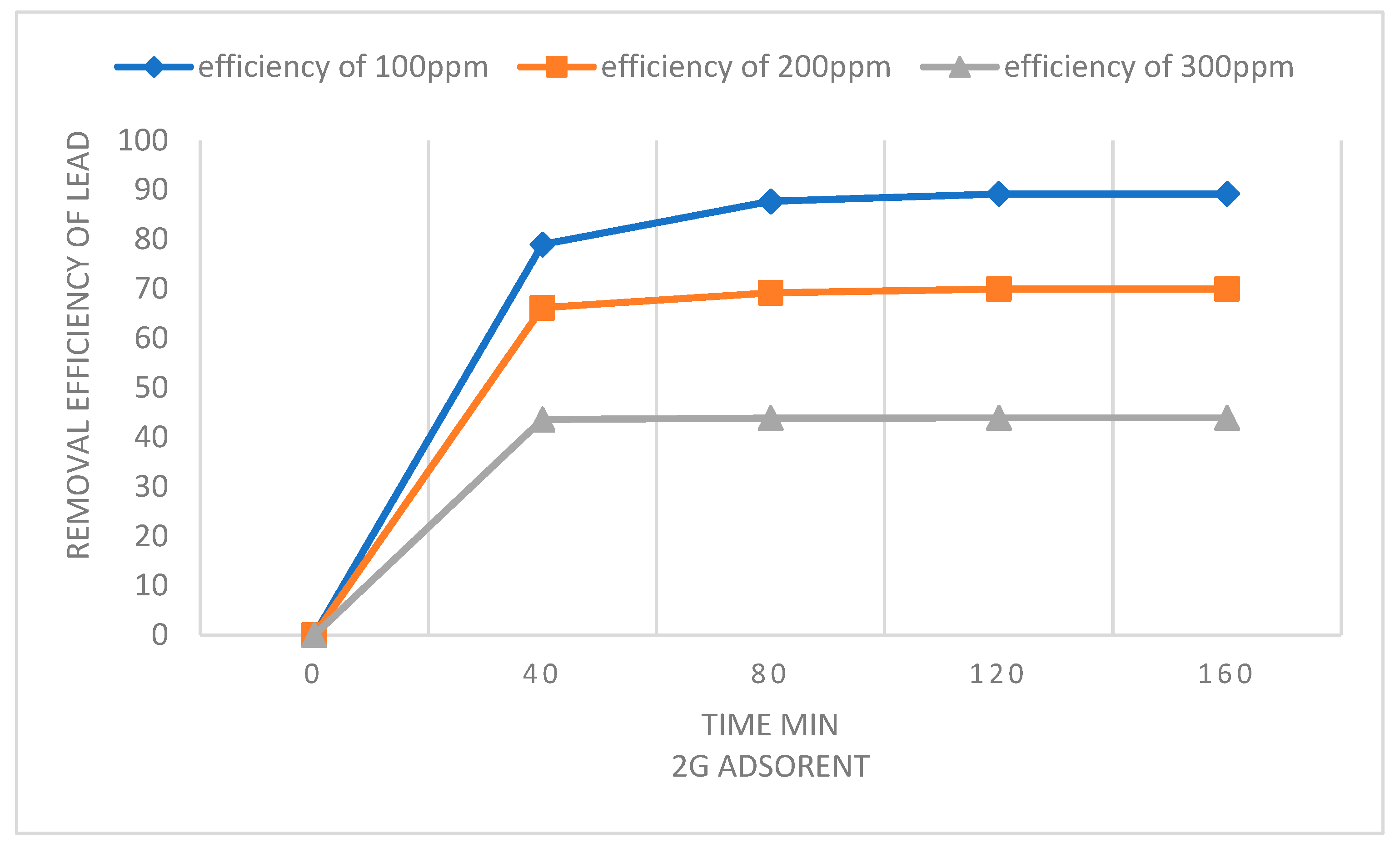
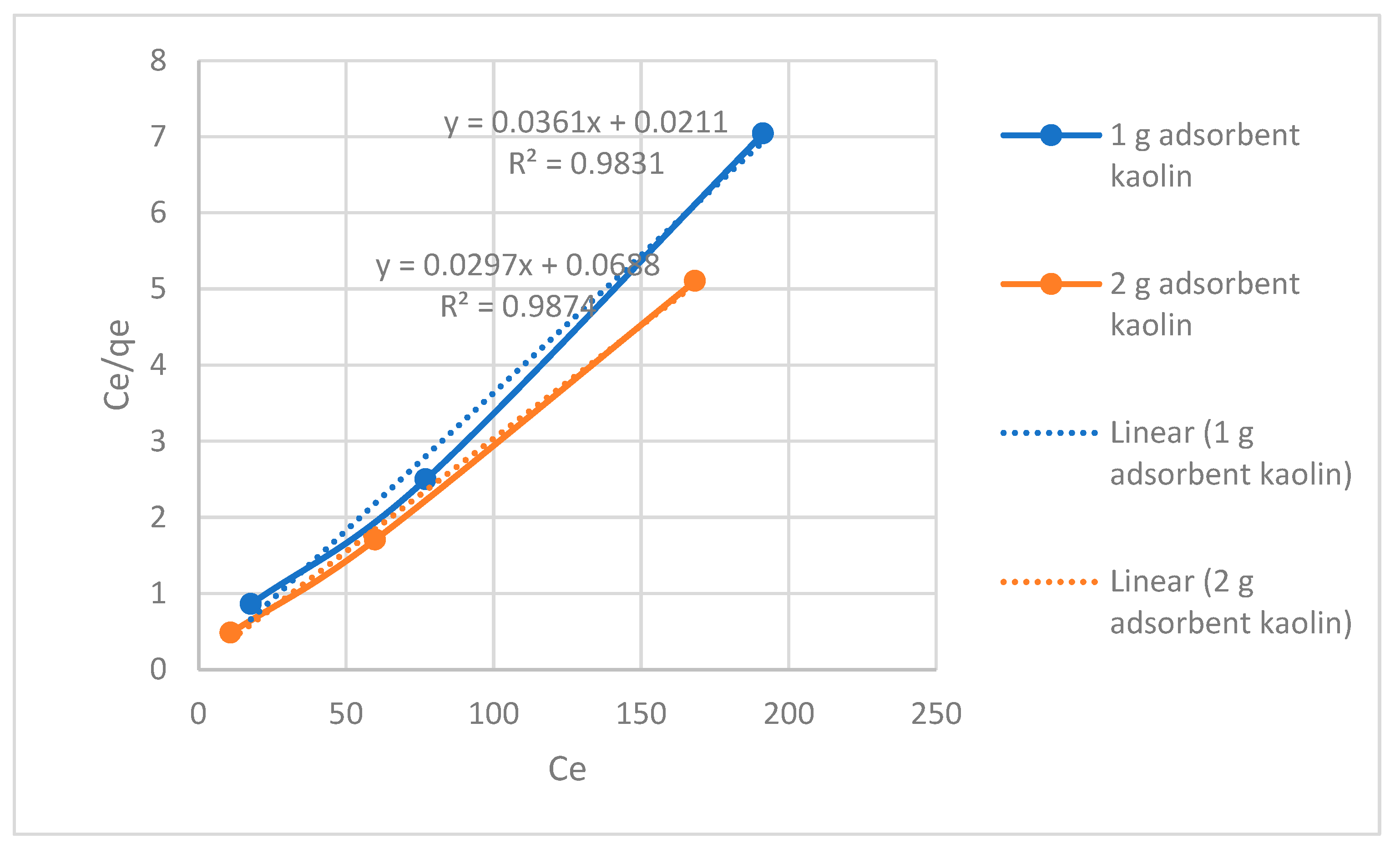
| Adsorbent amount | Langmuir isotherm constants | ||
| Adsorbent /250ml | qmax (mg/g) | b (L/mg) | R2 |
| 1-gram adsorbent | 27.70 | 1.71 | 0.9831 |
| 2-gram adsorbent | 33.67 | 0.432 | 0.9874 |
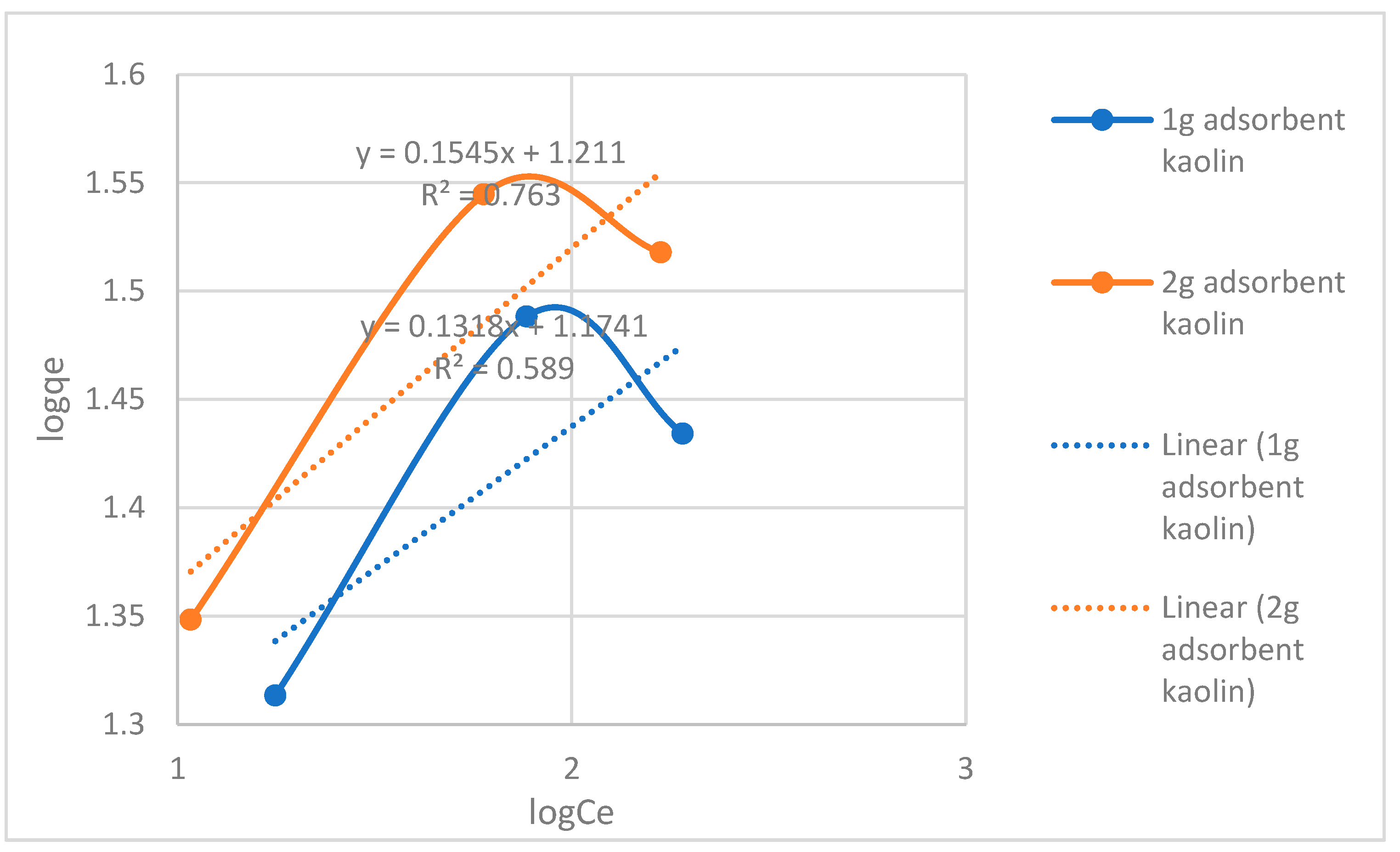
| Adsorbent amount | Freundlich isotherm constants | ||
| Adsorbent /250ml | KF (L/mg) | n | R2 |
| 1-gram adsorbent | 14.93 | 7.587 | 0.589 |
| 2-gram adsorbent | 16.25 | 6.472 | 0.763 |
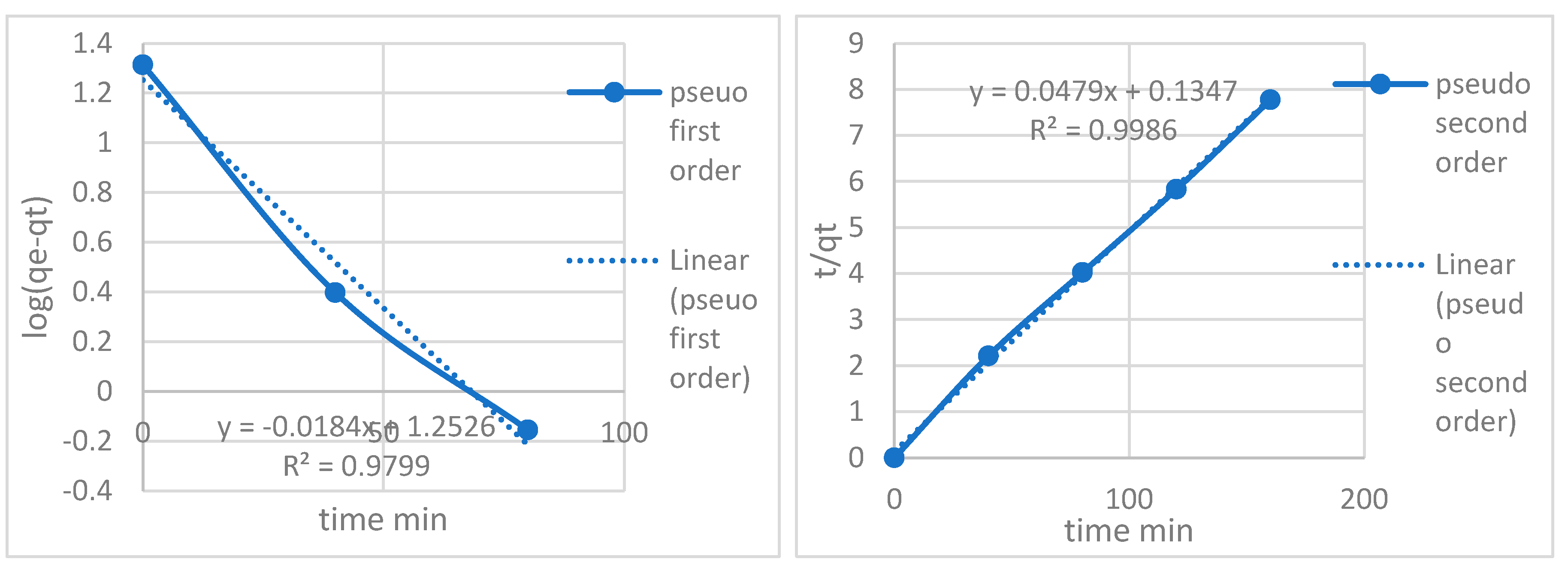
| Pseudo first order constants | |||
| Metal ion | qe (mg/g) | K1 | R2 |
| Pb2+ | 20.575 | 0.0527 | 0.979 |
| Pseudo second order constants | |||
| Metal ion | qe (mg/g) | K2 | R2 |
| Pb2+ | 20.575 | 0.0088 | 0.998 |
Conclusion
References
- Kim, B.C.; Lee, J.; Um, W.; Kim, J.; Joo, J.; Lee, J.H.; Kwak, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.; Lee, H. Magnetic mesoporous materials for removal of environmental wastes . Journal of hazardous materials. 2011, 192, 1140–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adekunle, A. Effects of industrial effluent on quality of well water within Asa Dam industrial estate, Ilorin, Nigeria. Nature and Science. 2009, 7, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Rafatullah, M.; Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption of methylene blue on low-cost adsorbents: a review. Journal of hazardous materials. 2010, 177, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-W.; Choi, S.-P.; Thiruvenkatachari, R.; Shim, W.-G.; Moon, H. Evaluation of the performance of adsorption and coagulation processes for the maximum removal of reactive dyes. Dyes and pigments. 2006, 69, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Non-conventional low-cost adsorbents for dye removal: a review. Bioresource technology. 2006, 97, 1061–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, M. New trends in removing heavy metals from industrial wastewater. Arabian journal of chemistry. 2011, 4, 361–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Lo, I.M. Synthesis of mesoporous magnetic γ-Fe2O3 and its application to Cr (VI) removal from contaminated water. Water research. 2009, 43, 3727–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.K.; Tiwari, P.N. Removal and recovery of chromium (VI) from industrial waste water. Journal of Chemical Technology & Biotechnology: International Research in Process, Environmental AND Clean Technology 1997, 69, 376–82. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, W.; Al-Itawi, H. Removal of Pb+2 Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption on Kaolinite Clay. American Journal of Applied Sciences 2007, 4, 502–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Fouad, E.; Ahmad, N. Removal of lead from wastewater by adsorption Using Saudi Arabian Clay. International Journal of Chemical and Environmental Engineering. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




