1. Introduction
In the present fuel consumption of Nepal, traditional, commercial, and renewable hydrocarbon fuels are dominating. As the world knows Electricity and hydrogen are eco-energy carriers. Hydrogen produced from renewable energy resources is an advanced and versatile alternative to electricity and hydrocarbon fuels. The waste biomass to hydrogen conversion technologies present possibilities for the development of modern biohydrogen refineries, prosumer networks, community energy systems, and a circular economy in Nepal based on the emerging financial model of Public-Private-People Partnerships. Nepal, which missed the initial two industrial revolutions, has the opportunity to advance directly into the third-industrial revolution through a focus on hydrogen-powered, renewable sources of energy [
1]. Historically, fuel transition in Nepal from fuelwood to coal, kerosene, LPG, and biogas for domestic and initiation of oil, CNG, methane, and biofuels for industrial and transport applications are preferred based on higher heating values, technical efficiencies, and eco characteristics. Imported fossil fuels adopted in Nepal according to the technologies and infrastructures of the second industrial revolution are not in favour of the environment, economy, and equality in the geopolitical relationships with neighbouring countries of Nepal [
2,
3,
4,
5]. It is necessary to transition the current fuel composition, which is predominantly composed of imported fossil fuels and conventional fuels, to a more optimal mix with a greater proportion of locally sourced, clean renewable energy sources. Nepal with its four rich renewable energy resources – water, biomass, solar, and hydropower, has a possibility to work on the sustainable renewable energy revolution. Hydrogen as a fuel of the third industrial revolution presents a new picture of the world with more powerful, efficient, and zero carbon emission cooktops and geysers in houses, heat and power generators in industries and vehicles on the roads and water, and in the air [
6].
The concept of waste-to-energy is limited in Nepal up to biogas and biomethane and few technologies have been applied to produce these renewable hydrocarbon fuels. The emerging multidisciplinary branches of biotechnology and biohydrogen refinery are presenting a new paradigm of waste-to-hydrogen (Wahh) to produce completely clean hydrogen fuel. Biohydrogen refinery also produces a wide range of bio-based co-products useful in the development of many modern industries. The new technical paradigm of waste-to-hydrogen (Wahh) presents not only new community energy systems to acquire energy independence at local, regional, and national levels but also a modern and rich biohydrogen circular economy to generate jobs for the millions of young people of Nepal and the people need the instant outcome of their investments [
7]. The public-Private-People Partnerships model for the development of biohydrogen systems is a comprehensive model in which people participate from the waste biomass generation to profit sharing with public and private stakeholders. The hydrogen energy system is a multifactor system based on the knowledge of modern sciences and technologies. The hydrogen economy is a complete knowledge economy and Pessimists describe hydrogen energy as a green illusion [
8]. Optimists find two kinds of the future of humanity – (1) Irreversible biosphere catastrophe based on the continuous use of hydrocarbon fuels (2) Development of Hydrogen energy → Hydrogen economy → Hydrogen civilization [
9,
10]. New generations of Nepal can initiate the praxis of hydrogen civilization in the present agrarian civilization of Nepal by developing hydrogen energy and economy.
This paper aims to investigate the compositions, combustion properties, and energy economies of renewable fuels such as fuelwood, biogas, biomethane, and biohydrogen. This paper also covers the concepts of waste-to-hydrogen microgrids, biohydrogen refineries, biohydrogen prosumer networks, biohydrogen circular economy, Public-Private-People Partnerships (4Ps), and hydrogen-centric renewable energy revolution which are taking shape in the industrial countries.
Figure 1.
The current status of SDG in Nepal (D. Paudel et al., 2021).
Figure 1.
The current status of SDG in Nepal (D. Paudel et al., 2021).
2. Description of Biofuels used in Nepal
Biofuels, derived from organic matter, are renewable sources of energy that have the potential to replace conventional fossil fuels. In Nepal, biofuels play a crucial role in providing sustainable energy solutions. The most commonly used biofuels in Nepal are fuelwood, biogas, biomethane, and biohydrogen. Fuelwood is derived from wood and is used as fuel for cooking and heating. Biogas is generated through the anaerobic digestion of organic matter and is primarily used for lighting and cooking. Biomethane is a purified form of biogas that can be used as fuel for transportation. Biohydrogen, produced through the conversion of organic waste, is a clean energy source with zero greenhouse gas emissions during combustion. These biofuels offer a promising alternative to conventional fossil fuels, providing a sustainable energy source for Nepal. (See the further description of these fuels as mentioned in the following section from 2.1 to 2.3)
2.1. Fuelwood: convenient biofuels
Fuelwood is a common form of energy source in Nepal, primarily used for cooking and heating purposes. It is a low-cost and readily available biomass that is widely used in rural areas where grid electricity is not accessible. The fuelwood is collected from forests or purchased from the local market and is often used as an alternative to liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and kerosene. However, the excessive use of fuelwood has resulted in deforestation, decreased soil fertility, and a decline in biodiversity. Despite its negative environmental impacts, the widespread use of fuelwood in Nepal highlights the need for alternative, sustainable energy sources to meet the energy demands of the population [
11].
2.1.1. Composition of Fuelwood
The chemical composition of wood is complex and varies in different species. Mean mass fractions of dry wood composition are primarily carbon (50%) and oxygen (42%), with smaller amounts of hydrogen (6%) and nitrogen (1%). Trace elements such as sodium, calcium, potassium, manganese, magnesium, sulphur, silicon, chlorine, phosphorus, and iron are also present in limited quantities (1%) as shown in
Table 1.
2.1.2. Combustion of Fuelwood
Carbon and hydrogen are the combustible elements in fuelwood that burn and produce heat. Carbon shares 88 % and produces 67 % of the total heat. Hydrogen is relatively more efficient as a heat producer. Hydrogen shares only 12 % and produces 33 % of the total heat. The higher heating values of fuelwoods of different species vary from 13 to 31 MJ/kg. Due to complex structures containing carbon, nitrogen, and other elements, the combustion of fuelwoods emits harmful gases, produces air pollution, and causes many diseases [
12,
13]. People haven’t adopted improved wood-burning stoves successfully in Nepal to increase the efficiency of fuelwood combustion and decrease the emission of harmful gases [
14].
2.1.3. Production and Economy of Fuelwood
Naturally growing wood is the major source of renewable fuel in Nepal. The solid-state of wood has eased people to collect, store and use wood as fuel from the prehistoric period. Distributed infrastructures of fuelwoods mainly based on the self-governed community forestry in Nepal beyond interventions of state and market are evidence of the collective actions of people to manage common-pool resources [
15,
16]. However, the energy economy of fuelwood is subsistent at the cost of increasing forest and environmental degradation [
17]. Growing literacy, living standards, and urbanization of new generations have been replacing fuelwood with imported LPG fuel. After fuelwood, biogas has been used as a renewable fuel in Nepal [
18].
2.2. Biogas and biomethane: a synthetic renewable fuel
Biogas and biomethane are renewable energy sources that are produced from the anaerobic digestion of organic matter, such as animal manure, food waste, and agricultural waste. In Nepal, biogas production has been implemented as a means of managing waste and providing clean energy. Biomethane, on the other hand, is a purified form of biogas that is produced by removing impurities such as carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulphide. Both biogas and biomethane have the potential to significantly contribute to the energy mix in Nepal and provide a sustainable solution for energy generation and waste management. The production of biogas and biomethane is also beneficial for the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions and the improvement of air quality [
19].
2.2.1. Composition of biogas and biomethane
Methane is the main component of biogas. Biogas is a mixture of approximately 60% methane, 35% carbon dioxide, 3-10% water vapour, 1% nitrogen, below 1% hydrogen, and little traces of ammonia, oxygen, and hydrogen sulfide as shown in
Table 2. Mass fractions of methane are 74.87% carbon and 25.13% hydrogen.
2.2.2. Combustion of biogas and biomethane
The mean heating value of raw biogas is 30 MJ/kg. The non-combustible components - carbon dioxide, water vapour, nitrogen, and others present in biogas reduce the heating value of biogas. After purification, biogas with 90% methane has a higher heating value of 45 MJ/kg. The higher heating value of methane is 55.5 MJ/kg. Like fuelwood, carbon and hydrogen are the combustible elements in biogas and methane. Combustion of biogas with impurities emits many harmful greenhouse gases [
21]. Combustion of methane emits carbon dioxide.
2.2.3. Production and Economy of biogas and biomethane
Biogas and biomethane are synthetic renewable fuels. Distributed production of biogas by anaerobic digestion of solid, colloidal, and liquid waste biomass has attracted all sectors – government [
22], non-government [
23], private (HOME - Nepal Biogas Promotion Association (NBPA), n.d.) and people at the household levels. Biomethane is an alternative to all hydrocarbon fossil fuels from the combustion point of view. Medium and large-sized biogas plants at the community levels are economical, efficient, and eco-friendly. However, self-governed community biogas plants and circular economy are not being successfully developed in Nepal due to the lack of industrialization of biogas plants and commercialization of biomethane [
25].
2.3. Biohydrogen: Waste-to-Hydrogen (Wahh)
Biohydrogen, a renewable and sustainable energy source produced through biological processes, has been proposed as a promising alternative to traditional fossil fuels. In Nepal, the use of biohydrogen has been explored as a means to mitigate the country's reliance on imported fossil fuels and address the issue of energy security. Utilizing locally available organic waste materials such as agricultural residues, sewage, and food waste, biohydrogen production can be economically feasible and environmentally sustainable [
26]. The resulting biohydrogen can be used in various applications, including fuel cell vehicles, combined heat and power generation, and industrial processes, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions and contributing to the development of a green economy in Nepal.
2.3.1. Composition of biohydrogen
Carbon-free biohydrogen is a clean fuel in the list of renewable fuels – fuelwood, biogas, biomethane, and other biofuels, and the most suitable alternative to all fossil fuels. Hydrogen mass fractions of fuelwood, water, and methane are 6%, 11.19%, and 25.13% respectively as shown in
Table 3 [
27].
2.3.2. Combustion of biohydrogen
The higher heating value of hydrogen is 142 MJ/kg. Combustion of hydrogen with oxygen produces only water. At high temperatures, the combustion of hydrogen in atmospheric air produces small amounts of harmful oxides of nitrogen.
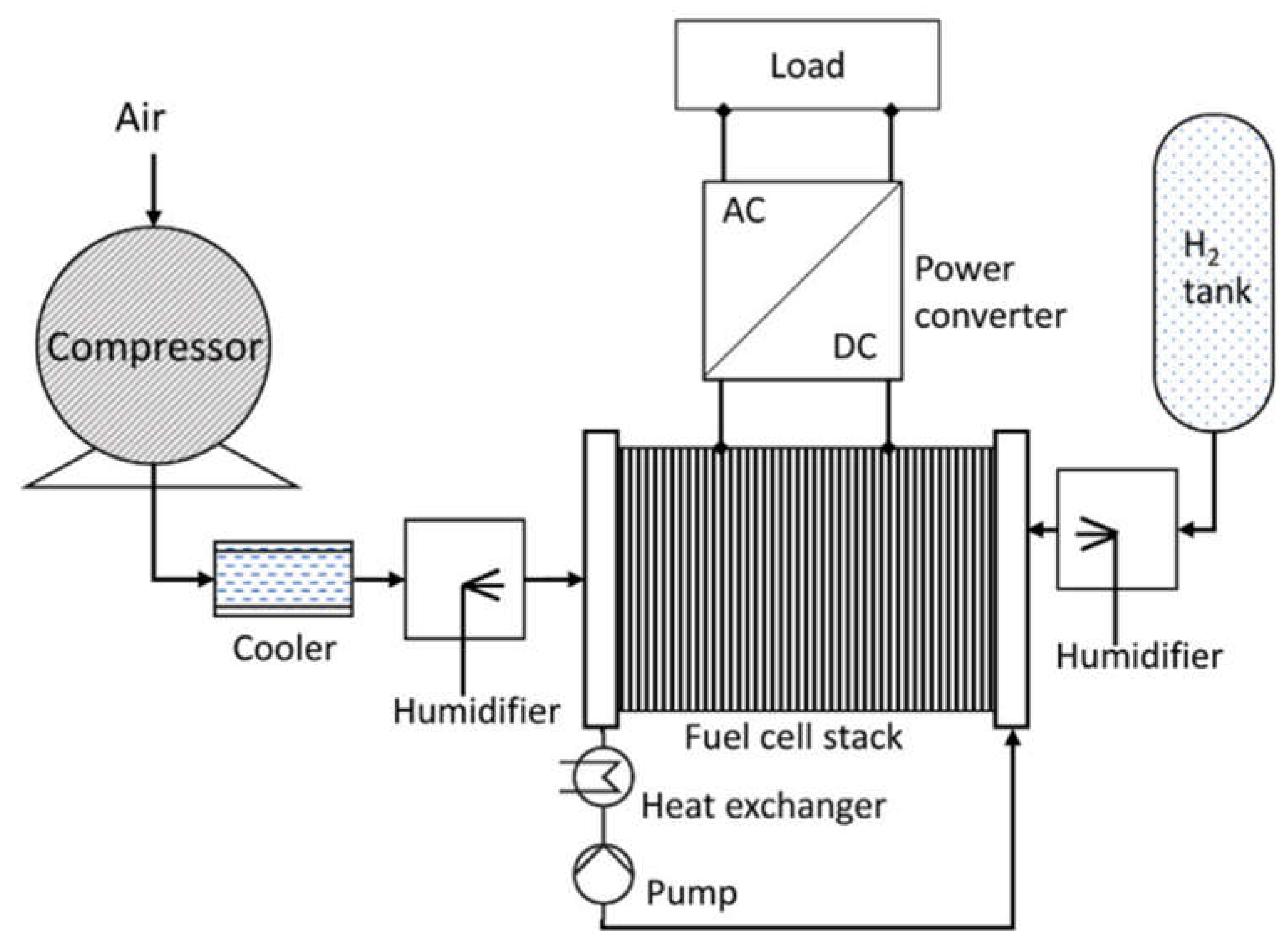
Figure 2.
The configuration of a fuel cell system involves the pressurization and humidification of both hydrogen and air, which then pass through the fuel cell stack. The resulting electrical power generated is subsequently transmitted to a load through the utilization of an AC/DC power converter (Yue et al., 2021).
Figure 2.
The configuration of a fuel cell system involves the pressurization and humidification of both hydrogen and air, which then pass through the fuel cell stack. The resulting electrical power generated is subsequently transmitted to a load through the utilization of an AC/DC power converter (Yue et al., 2021).
2.3.3. Production and Economy of Biohydrogen
The hydrogen content factors of biomethane and other biofuels are more than the hydrogen content factor of water. Biohydrogen production methods present optimum parameters in comparison to other hydrogen production methods [
28]. There are mainly four - biochemical, bioelectrochemical, bio thermochemical, and thermochemical conversion methods of biomass into biohydrogen. Biochemical and bioelectrochemical methods are on the experimental level. Bio thermochemical and thermochemical methods are matured for implementation [
29]. Many companies are working on these methods such as Graforce [
30].
3. The need, purpose, and component of waste-to-hydrogen (Wahh) microgrids
Waste-to-hydrogen (Wahh) microgrids are innovative energy systems that convert organic waste into hydrogen gas, which can then be used as a source of clean and renewable energy. The need for Wahh microgrids in Nepal stems from the country's increasing energy demand, coupled with the growing challenge of waste management and energy security such as open dispersion, collection, and burning of solid waste biomass in the populated municipalities of Nepal produces air pollution. Similarly, sewage disposal into nearby rivulets and rivers produces water and air pollution. Waste biomasses harmful to the environment and the health and aesthetics of human beings are inextricable by-products of human life. In addition, Nepal is located on the southern steep slopes of the central Himalayas with five physiographic regions – 23% High Himalaya, 20% High Mountain, 30% Middle Mountain, 13% Hill and 14% Plain. These all-physiographic regions have their unique climate characteristics. Carbon emissions from fossil fuels consumption for economic growth are adversely affecting the climates of these regions, especially the climate of the mountainous regions [
31]. Nepal has formulated a sound national climate change policy to encourage effective management of hazardous waste and utilization of biodegradable waste, climate-friendly low carbon and zero emission energy efficient technologies to develop industry, transport, and physical infrastructure to minimize and mitigate the adverse effects of global warming [
32]. The purpose of these microgrids is to provide a sustainable and locally available energy source, while also reducing the environmental impact of waste by reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, Wahh microgrids would help address energy poverty and increase access to energy in remote rural areas where grid-based energy is unavailable. Recent developments in the various interdisciplinary branches of biotechnology have enabled to recovery and reform of many valuable ingredients and products from solid and liquid biomasses as co-products of biofuels [
33,
34]. Waste-to-Energy microgrids as part of biorefinery have been developing and commercializing with targets to generate clean biohydrogen fuel and other advanced industrial products in place of biogas, biomethane, and other hydrocarbon biofuels and traditional product like biochar (useful only in the agriculture).
Figure 3.
Component of waste-to-hydrogen (Wahh) microgrids.
Figure 3.
Component of waste-to-hydrogen (Wahh) microgrids.
The Important Component of Wahh [
29]
:
Waste Material: The starting material for waste-to-hydrogen technology is the waste material that will undergo the conversion process. This could include household waste, industrial waste, agricultural waste, or any other form of organic waste.
Waste Pre-processing Unit: This component of waste-to-hydrogen technology is responsible for sorting, shredding, and treating the waste material to ensure that it can be processed effectively.
Gasification Unit: This component converts the waste material into a mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide through a process called gasification. This is achieved by heating the waste material in the absence of oxygen.
Syngas Cleaning Unit: This component removes impurities and contaminants from the syngas generated in the gasification unit, producing a clean, hydrogen-rich syngas stream.
Steam Reformer: This component further purifies the hydrogen from the syngas stream by exposing it to high temperatures and pressure, converting the carbon monoxide into carbon dioxide.
Hydrogen Purification Unit: This component removes the remaining impurities and contaminants from the hydrogen stream, producing a high-purity hydrogen product.
Hydrogen Storage System: This component is used to store the purified hydrogen for later use, which can be transported for use in various applications such as fuel cells, transportation, or energy production [
35].
Control and Monitoring System: This component of waste-to-hydrogen technology is responsible for controlling and monitoring the various processes and systems within the technology, ensuring that they are operating optimally and safely.
4. Wahh in Nepal: A Multifaceted Approach
Waste-to-Hydrogen (Wahh) technology is gaining increasing attention as a way to convert waste into clean and renewable energy, and Nepal is no exception. The implementation of Wahh in Nepal offers significant benefits from both a production and utilization perspective, as well as in its execution and implementation. To make it important the following mentioned component has to work together under the one umbrella of the Nepal government and policymakers. Implementation of Wahh in Nepal has the potential to address the issue of waste management, reduce the country's reliance on non-renewable energy sources, and offer significant benefits for communities and businesses. The development of a supportive regulatory framework, the creation of public-private-people partnerships, and the continued promotion of the technology will be crucial in ensuring that it is implemented effectively and sustainably in Nepal. Therefore, a few other key components are further going to discuss in the following sections.
4.1. Biohydrogen refinery
The biohydrogen refinery is a system or process used to produce hydrogen gas from organic waste material, such as agricultural waste or food waste. It uses a series of biochemical and thermochemical processes to convert organic waste into hydrogen. Therefore, It provides a sustainable and environmentally friendly source of hydrogen, reducing the reliance on fossil fuels and contributing to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. It is an important component of the growing hydrogen economy, and its continued development and commercialization will play a crucial role in the transition to a low-carbon energy future. Distributed biorefineries are increasingly becoming popular to produce biofuels and a spectrum of other biobased products to displace the corresponding fossil-fuel-based products with minimum socio-economic and environmental repercussions compared to petroleum refineries [
11]. Production of biohydrogen in the local biorefineries is an advanced alternative to the imports of fossil fuels [
26]. Distributed infrastructures of biorefineries facilitate their life cycle assessment according to the regulations of local hydrogen communities and supply of hydrogen fuel according to the energy mix of integrated community energy systems [
36,
37]. The energy policy of Nepal is focused on the development of hydropower plants with the aim to replace fuelwood and LPG cooking stoves with electric induction stoves, fossil fuel vehicles with electric vehicles, and the export of electricity to neighbouring countries [
38,
39]. Storage and portable use of electricity in the domestic sector is not possible like the easy transportation of hydrogen fuel. Electric vehicles don’t compete with hydrogen vehicles in energy storage, power, mileage, and other parameters. Hydrogen vehicles powered by hydrogen fuel cells and hydrogen engines are suitable for use in the urban as well as difficult rural areas of Nepal.
4.2. Biohydrogen prosumer networks
The biohydrogen prosumer network is a decentralized and distributed network of individuals or communities who produce their hydrogen using local organic waste and then share or exchange it with others in the network [
36,
40]. The benefits of biohydrogen prosumer networks include
i) Local Energy Generation: By producing hydrogen locally, the network can reduce the need for energy transportation and distribution and increase energy security.
ii) Increased Energy Efficiency: The network can use the waste material that would otherwise go to waste and convert it into usable energy, increasing the efficiency and sustainability of energy production.
iii) Decentralized Energy System: The network operates as a decentralized system, reducing the dependence on central authorities and increasing energy independence.
iv) Reduced Emissions: By producing hydrogen from organic waste, the network can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and contribute to a low-carbon energy future.
v) Community Development: The network can help to build local communities and increase social interaction, as well as provide education and training opportunities for individuals and communities [
41].
The calorific value of hydrogen fuel is nearly 2.5 times more than the calorific value of fossil fuels. This is a quantitative distinction between hydrogen and fossil fuels. Hydrogen is a clean fuel in comparison to fossil fuels. This is a qualitative distinction between hydrogen and fossil fuels. Production and distribution of fossil fuels and grid electricity are based on the top-down design. The other qualities of hydrogen fuel are its participatory and sustainable production, distribution, and consumption on the bottom-top design through hydrogen prosumer networks [
42]. Nepal imports 100% of the petroleum needs of its people and employment in the import-based petroleum industries is limited. Biorefineries and hydrogen prosumer networks develop new sources for the incomes of the local communities, governments, and enterprises, and create various types of jobs for the educated new generations [
7].
4.3. Biohydrogen circular economy
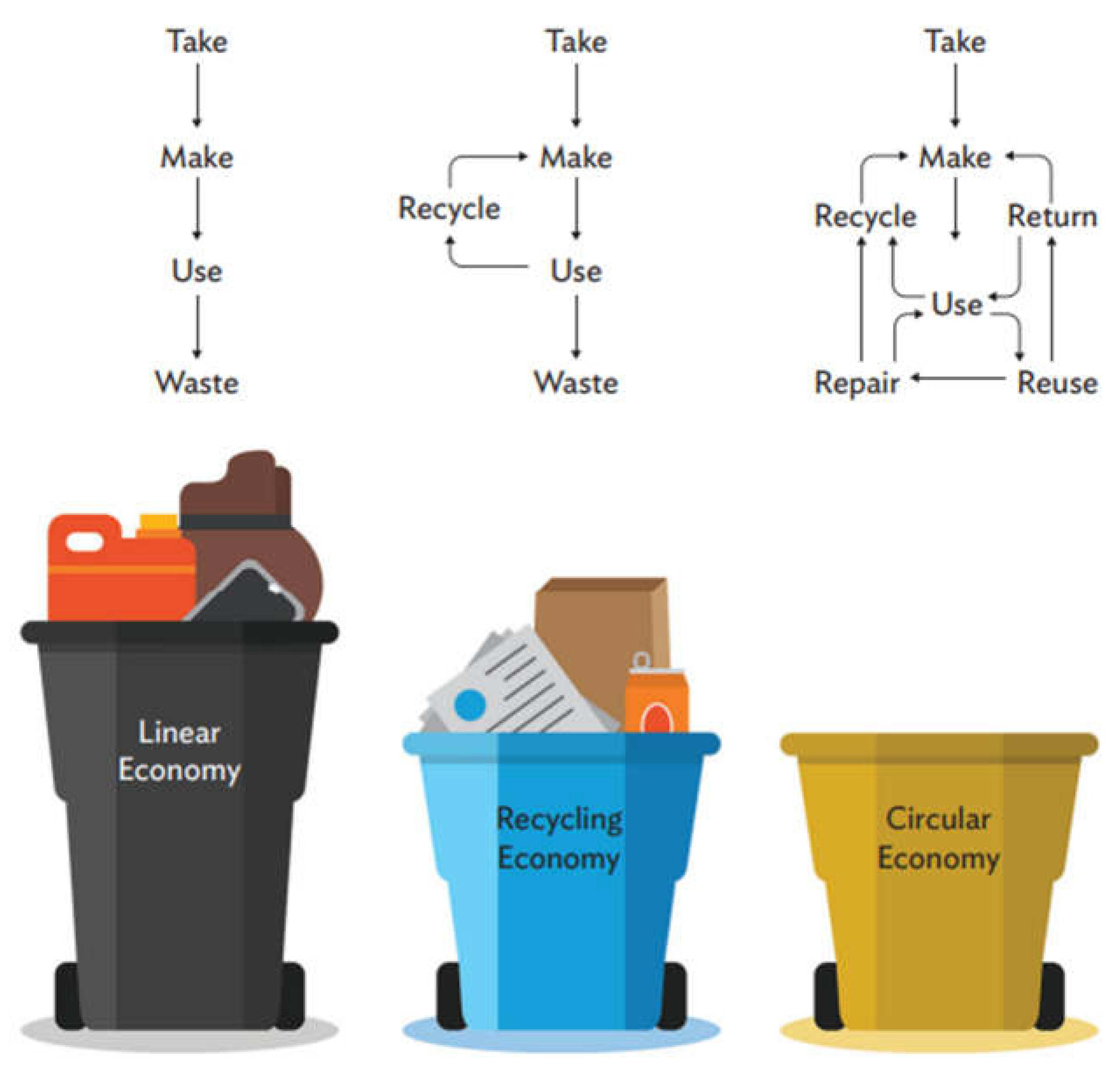
The biohydrogen circular economy refers to a closed-loop system for producing and using hydrogen from organic waste, in a sustainable and environmentally friendly manner. It is a part of the larger circular economy concept, which aims to reduce waste and conserve resources by reusing, repairing refurbishing, and recycling materials and products.
The linear economy of Crude oil and natural gas fossil fuels was developed during the first and second industrial revolutions. These were formed underground by anaerobic digestion of the buried biomass over millions of years. The formulation step for the Crude oil and natural gas is “Natural Biomass→ Conversion into Crude Oil and Natural Gas by Natural Anaerobic Digestion→ Extraction→ Refining with Non-Biodegradable Multiproduct→ Use→ Waste.” The linear economic model of fossil fuels and non-biodegradable products are the main causes of the growing global warming and associated climate changes (<i>Global Warming of 1.5 oC —</i>, n.d.).
Concepts of a fossil fuel phase-out and decarbonization by green hydrogen are being promoted as solutions to global warming. Biohydrogen is a concept of third-generation biofuel and the conversion of waste biomass into biohydrogen and biodegradable multiproduct under a circular economic model (closed-loop systems) produces zero waste [
44]. The formulation step for the Biohydrogen is “
Waste Biomass→ Conversion into Biohydrogen by Artificial Anaerobic Digestion and Other Methods with Biodegradable Multiproducts→ Use→ Reuse→ Zero Waste.” This model is more sustainable, reducing the reliance on non-renewable energy sources, reducing waste and emissions, and creating a cleaner and more environmentally friendly energy system. While the linear economy model is not sustainable in the long term and is contributing to environmental degradation and climate change. A comparison of these two models of the economy is given in
Table 4.
Integration of circular economy within the waste management of the municipalities and villages includes the environmental, economic, and social aspects [
45,
46]. Biohydrogen circular economy based on the eco-municipality and eco-village frameworks to acquire energy autonomy and energy justice for the involved communities develops a modern, rich, and sustainable economy of Nepal at the local, regional, and national levels [
47].
The linear economy of fossil fuels is a semi-knowledge economy. The circular economy of biohydrogen is the complete knowledge economy. This is a qualitative distinction between fossil fuels and biohydrogen economies. The Biohydrogen energy potential of Nepal depends on three pillars – (1) the Adoption of the already developed biohydrogen technologies (2) the Development of new biohydrogen technologies and (3) Public-Private-People Partnerships. Among these, the 4Ps pillar is the most important one for economic growth and it is further addressed in the following section.
Figure 4.
Simplified presentation of Circular Economy; Source: Asian Development Bank internal training material.
Figure 4.
Simplified presentation of Circular Economy; Source: Asian Development Bank internal training material.
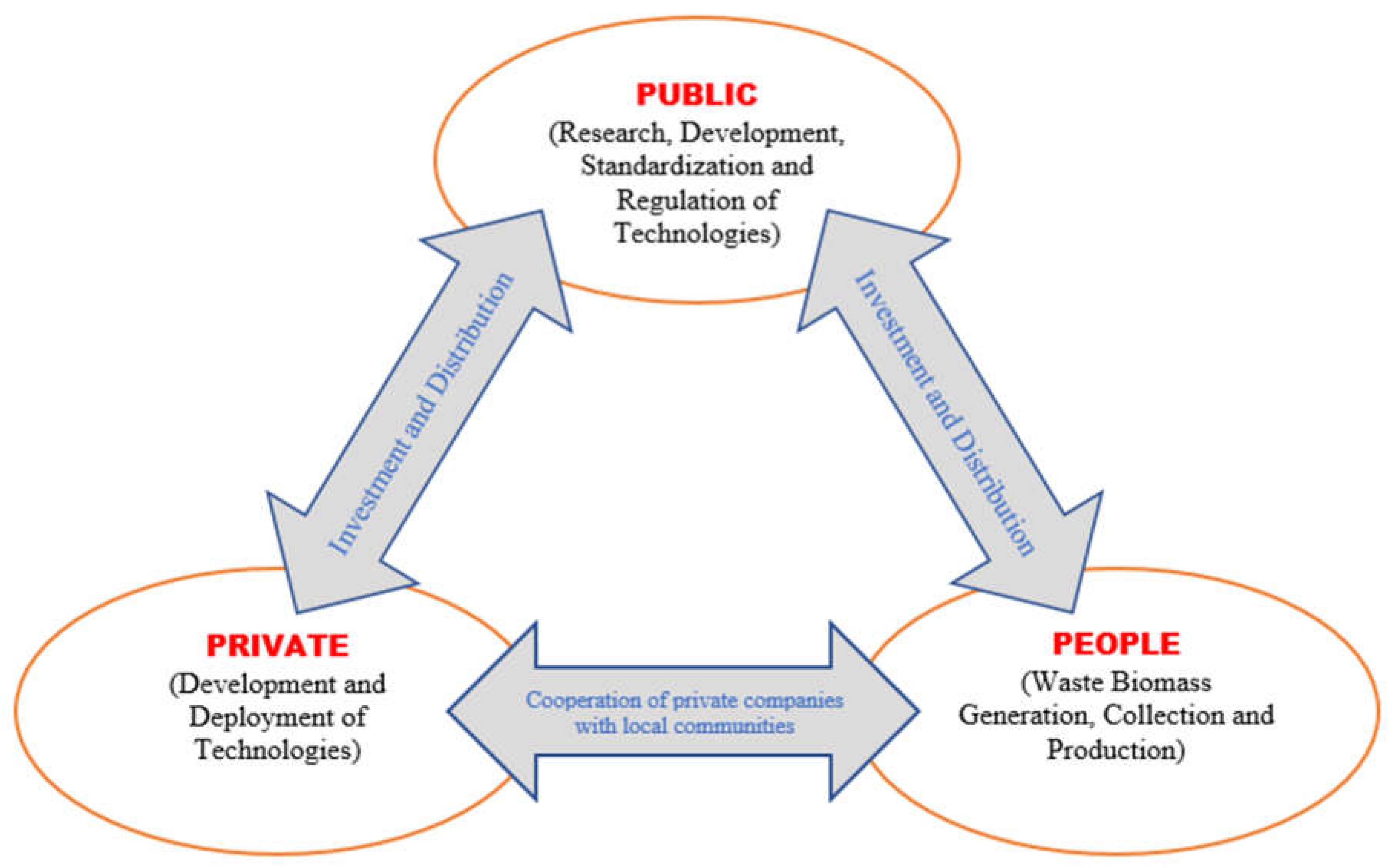
4.4. Public-Private-People Partnerships (4Ps) model of biohydrogen system
The 4Ps model of the biohydrogen system is a collaborative approach to the development and implementation of biohydrogen technology. This model involves the participation and collaboration of the public sector, private sector, and the public (or people) to create a more sustainable and effective biohydrogen system. The public sector provides the necessary regulations, infrastructure, and support for the development and implementation of biohydrogen technology, while the private sector brings the necessary resources, expertise, and innovation to the table. The public, or people, provides support and demand for the adoption of biohydrogen technology and the transition to a low-carbon energy future [
48]. A biohydrogen refinery works on the bottom-top design with its multiple steps - waste biomass generation, collection, production of biohydrogen in the biorefinery, and distribution through the prosumer network. Public, private, and community sectors have different and common roles in the development and management of biohydrogen systems as shown in
Figure 5. The roles of the public sector are to organize research, development, standardization, and regulation of the sciences and technologies of biohydrogen and co-multi products. The roles of the private sector are to cooperate in these works of the public sector, manufacturing types of machinery according to accepted standards and making them available in the markets at reasonable rates [
49]. The roles of the community sector are to follow accepted standards in the waste biomass generation, collection, and production of biohydrogen and co-multi products according to the needs of the community and markets. Public, private, and community sectors have two common works -
(1) Investments in the development of biohydrogen systems and
(2) Distributions of biohydrogen and co-multi products in the markets and share profits according to their investments and works. Public-Private-People Partnerships proposed for the hydropower development in Nepal with the slogan “
Nepal’s Water, the People’s Investment” is only a centralized finance model, not a multidimensional working model. The role of the third sector’s emotions for low-carbon lifestyle as climate change engagement initiatives need concrete objective grounds [
50]. Hydrogen energy is a socially embedded, market-driven public good more than a public utility like the internet. A practical working model of Public-Private-People Partnerships is needed in Nepal for the rapid standardization and regulation of hydrogen as the public goods, diffusion of hydrogen technologies in markets, and development of hydrogen prosumer networks [
51,
52].
Figure 5.
Public-Private-People Partnerships (4Ps) Model of Biohydrogen System.
Figure 5.
Public-Private-People Partnerships (4Ps) Model of Biohydrogen System.
6. Role of biohydrogen in the renewable energy revolution of Nepal
The first and second industrial revolutions based on the centralized coal, oil, and natural gas deposits found in some countries, couldn’t occur simultaneously in all countries. We are living in the middle of the third industrial revolution. After the digital communication revolution, the world is moving towards the renewable energy revolution, the next half of the third industrial revolution. In the first quarter of the 21
st century, all industrial countries have prepared their hydrogen energy roadmaps, systematically developing hydrogen technologies according to their renewable energy resources and applying them to acquire a green hydrogen economy up to 2050. The Third Industrial Revolution offers the prospect that the countries that were left out of both the first and second industrial revolutions, could leapfrog into the new era of the third industrial revolution [
53]. Hydrogen as an energy alternative and water-hydro-hydrogen system [
54]was proposed potential solution for air pollution and fuel autonomy of Kathmandu Valley based on the off-peak grid power [
55] and rural areas of Nepal based on the micro hydropower. Improved water mills extend hydrogen production at the community levels [
56]. Water-solar-hydrogen system extends hydrogen production at the home levels. The drawback of these systems is more electricity consumption per kg hydrogen production in comparison to biomass-hydro/solar-biohydrogen systems, nevertheless, electrolytic hydrogen production by water-hydro/solar-hydrogen systems provides an easy, compact, and carbon-free route.
Water and biomass are raw materials, and solar and hydropower are primary energy sources for the production of hydrogen fuel from water and biomass. Like water, Nepal is rich in biomass. Waste biomass inevitably intertwined with human habitats provide the inexhaustible basis of the biohydrogen system. Nepal has become a nearly open defecation-free country due to the spread of toilets in urban as well as remote rural areas. Modern sanitation facilities can be developed with biohydrogen refineries to keep the communities clean [
57]. Animal husbandry practices in Nepal are traditional with close proximity between human and domestic livestock populations. Open storage and composting of livestock manure contaminate air and water. Integration of livestock manure in the biohydrogen refinery enhances the capacity of the refinery and keeps the communities completely clean. The development of a biohydrogen refinery in the agrarian society of Nepal will transform traditional villages into modern sustainable eco-villages [
58]. The emergence of clean energy technologies and people-oriented eco-city civilization on a global scale with ecological approaches is the main characteristic of the 21
st century’s urban planning [
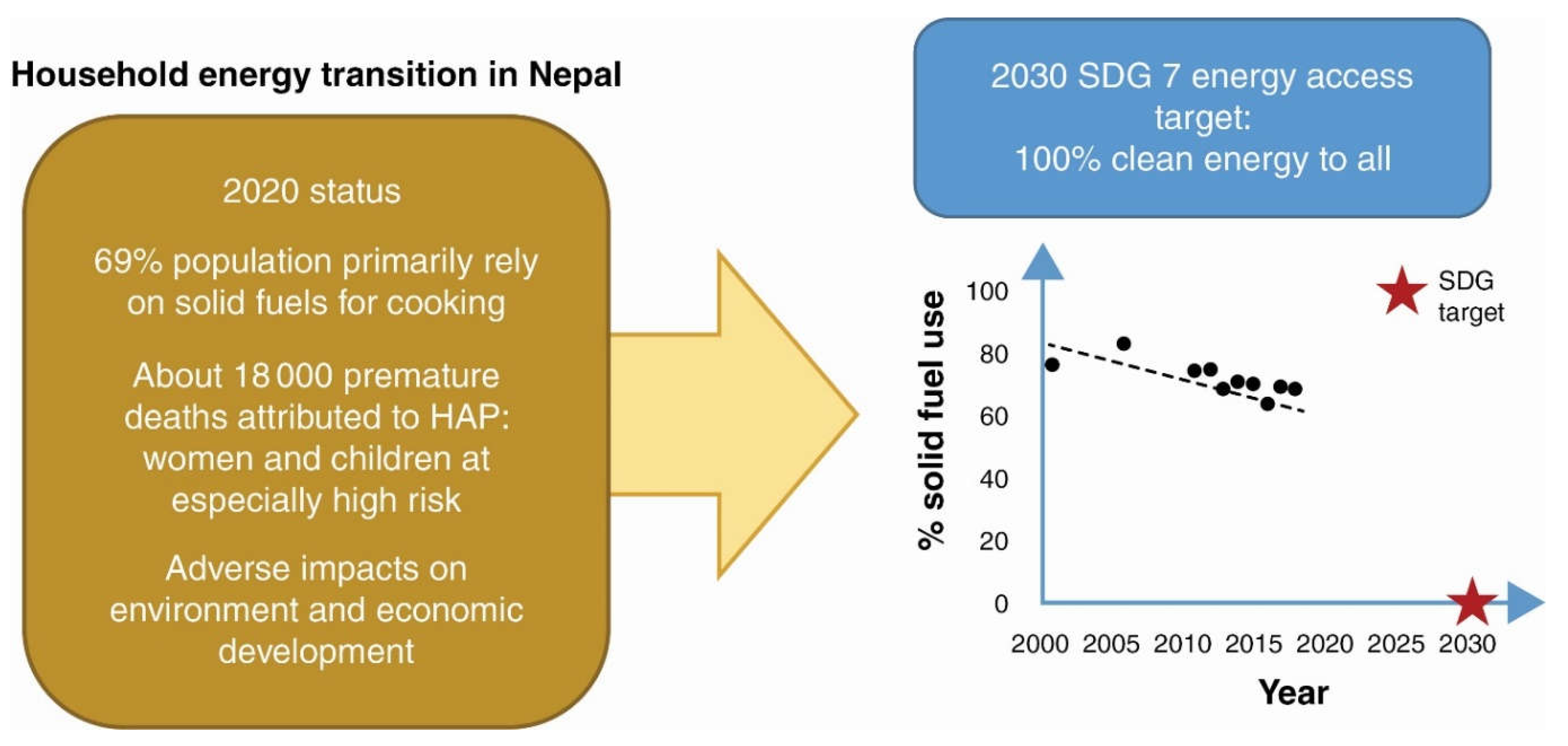
59]. Waste-to-hydrogen technologies are a change in basic assumptions in the field of clean energy technologies. In the total energy consumption in Nepal in the years 2019-20, shares of renewable, commercial, and traditional energy sources were 3.2%, 28.1%, and 68.7% respectively [
59]. Upgradation of waste-to-energy technologies from the present biogas and biomethane production to biohydrogen production will exponentially increase the share of renewable energy, and biohydrogen will play a big role in the renewable energy revolution of Nepal.
7. Conclusions
In conclusion, this review paper has analyzed the potential of Waste-to-Hydrogen (Wahh) as a solution for both energy generation and waste management. The results of this study have shown that Wahh has significant potential as a clean, renewable energy source that produces zero greenhouse gas emissions during combustion. Furthermore, the review has explored the emerging concepts of waste-to-hydrogen microgrids, biohydrogen refineries, and biohydrogen prosumer networks, as well as the hydrogen-centric renewable energy revolution in the context of industrialized countries. The study presented a comprehensive feasibility analysis of these concepts in Nepal, which will provide valuable insights into the potential for adopting these innovative technologies in the country. In conclusion, the findings of this study suggest that Wahh has the potential to play a critical role in the development of a sustainable and efficient energy system. The significance of these results underscores the importance of continued research in this area to fully realize the potential of Wahh as a solution to meet the world's growing energy demands and environmental challenges.
Author Contributions
AY and PY are working on the day of manuscript Conceptualization, Conceptualization, Writing - Original Draft. VMT, SA, AY, and VR are contributed through Writing - Review & Editing. PY is contributed through manuscript writing, formatting, revision and communicating to yet with all authors for writing and publications. VC is contributed by supervising all authors and writing - reviewing & editing the final manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Ethical Approval and Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Yes, all authors agreed to publish their manuscripts according to journal publication guidelines.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the contributions of individuals and institutions that have assisted in the completion of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
References
- Bhandari, R.; Pandit, S. Electricity as a Cooking Means in Nepal—A Modelling Tool Approach. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- V. Chandra et al., “Recombinant Laccase: A Promising Tool for Industrial Effluent Bioremediation,” Preprint, Jul. 2023. [CrossRef]
- V. Chandra et al., “Comprehensive Overview of Role of Environmental Biotechnology in Reduction of Medical Waste,” International Advance Journal of Engineering, Science and Management, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 112–118, Jun. 2022. [CrossRef]
- V. Chandra, K. Arpita, P. Yadav, V. Raghuvanshi, A. Yadav, and S. Prajapati, “Environmental Biotechnology for Medical Waste Management: A Review of Current Practices and Future Directions,” Preprint, Jun. 2023. [CrossRef]
- V. Chandra, N. Srivastava, A. Kumari, P. Yadav, V. Raghuvanshi, and Rahul, “Recent Development in Production Optimization of Recombinant Laccase Enzymes for Successful Bioremediation of Industrial Effluent: A Review,” International Advance Journal of Engineering, Science and Management, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 68–74, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Gaire and S. Raj Shakya, “Energy and Environmental Implications of Graduating Nepal from Least Developed to Developing Country,” pp. 112–123, 2015.
- Bezdek, R.H. The Hydrogen Economy and Jobs of the Future. ECS Trans. 2020, 96, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehner, “Green Illusions,” Green Illusions, Sep. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Lambert, H.; Pahon, E.; Roche, R.; Jemei, S.; Hissel, D. Hydrogen energy systems: A critical review of technologies, applications, trends and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 146, 111180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, C.Y.; Nousala, S. Emergent-based well-being design for a hydrogen-based community: social acceptance and societal evolution for novel hydrogen technology. Hydrogen Production and Energy Transition 2021, 1, 493–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, R.; Knudsen, M.T.; Dalgaard, T. Multi-criteria assessment of yellow, green, and woody biomasses: pre-screening of potential biomasses as feedstocks for biorefineries. Biofuels, Bioprod. Biorefining 2015, 9, 545–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranabhat, C.L.; Kim, C.-B.; Kim, C.-S.; Ejha, N.; Deepak, K.C.; Connel, F.A. Consequence of Indoor Air Pollution in Rural Area of Nepal: A Simplified Measurement Approach. Front. Public Heal. 2015, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P. Yadav et al., “Interferons for Covid-19: A Literature Review on Their Therapeutic Potential, Clinical Data and Challenges,” Preprint, Jul. 202. [CrossRef]
- Paudel, D.; Jeuland, M.; Lohani, S.P. Cooking-energy transition in Nepal: trend review. Clean Energy 2020, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federation of Community Forestry Users Nepal (FECOFUN). Available online: http://fecofun.org.np/ (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Bharamappanavara, S.C.; Hanisch, M.; Rommel, J. The Effect of Heterogeneity and Freedom of Participation on Collective Action in Rural Self-Help Groups. J. Mix. Methods Res. 2014, 10, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baland, J.; Bardhan, P.; Das, S.; Mookherjee, D.; Sarkar, R. The Environmental Impact of Poverty: Evidence from Firewood Collection in Rural Nepal. Econ. Dev. Cult. Chang. 2010, 59, 23–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- S. Kala and A. Subedi, “Domestic biogas production and use in Nepal : a simple, reliable, clean and cost-effective solution to provide energy security to the rural households : a thesis presented in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Energy Management at Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand,” 2015. Available online: https://mro.massey.ac.nz/handle/10179/8274 (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Government-private sector cooperation stressed for biogas promotion – Radio Nepal. Available online: https://onlineradionepal.gov.np/en/2022/11/08/338668.html (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Pokharel, G.R.; Chettri, A.B. Large-Scale Promotion of Animal Dung-based Domestic Biogas Digesters through Public Private Partnership: A Successful Case of Nepal. Hydro Nepal: J. Water, Energy Environ. 2012, 8, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitázek, J. Klúčik, D. Uhrinová, Z. Mikulová, and M. Mojžiš, Thermodynamics of combustion gases from biogas. Res. Agr. Eng. 2016, 62, S8–S13. Available online: http://agriculturejournals.cz/doi/10.17221/34/2016-RAE.html. [CrossRef]
- “Government of Nepal Ministry of Population and Environment Biomass Energy Strategy 2017,” 2017.
- Biogas Sector Partnership–Nepal-(BSP-Nepal). Available online: https://bspnepal.org.np/ (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- HOME - Nepal Biogas Promotion Association(NBPA). Available online: https://sites.google.com/site/nepalbiogas/about (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- T. Peder and R. L. Araldsen, “Biogas in Nepal : limitations for the expansion of community plants,” 41, Nov. 2016. Available online: https://nmbu.brage.unit.no/nmbu-xmlui/handle/11250/2422464 (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- A. Ghimire, E. Trably, M. Madon, and H. E. D. Van Hullebusch, “Dark fermentative biohydrogen production from organic waste and application of by-products in a biorefinery concept,” http://www.theses.fr, Dec. 2015. Available online: http://www.theses.fr/2015PESC1197.
- Ishaq, H.; Dincer, I.; Crawford, C. A review on hydrogen production and utilization: Challenges and opportunities. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 26238–26264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, C.; Dincer, I. Review and evaluation of hydrogen production options for better environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 218, 835–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Langer, F.; Zech, K.; Rönsch, S.; Oehmichen, K.; Michaelis, J.; Funke, S.; Grasemann, E. Assessment of Selected Concepts for Hydrogen Production Based on Biomass. 2016, 391–416. [CrossRef]
- Production of hydrogen by plasma lysis. Available online: https://www.graforce.com/ (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- C. Engagement and rsvp.crawford@anu.edu.au, “Closing the evidence gap: Energy consumption, real output and pollutant emissions in a developing mountainous economy”. Available online: https://crawford.anu.edu.au/publication/cama-working-paper-series/12084/closing-evidence-gap-energy-consumption-real-output-and (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- National Climate Change Policy, 2076 (2019). | UNEP Law and Environment Assistance Platform. Available online: https://leap.unep.org/countries/np/national-legislation/national-climate-change-policy-2076-2019 (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Das, B.; Bhave, P.V.; Sapkota, A.; Byanju, R.M. Estimating emissions from open burning of municipal solid waste in municipalities of Nepal. Waste Manag. 2018, 79, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, “Community-based waste management strategies in relation to a targeted Nepalese community,” 2015.
- Shakya, N.; Shrestha, R.; Saiju, R.; Thapa, B.S. Hydrogen as a fuel for electrifying transportation sector in Nepal: Opportunities and Challenges. IOP Conf. Series: Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1037, 012064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B. P. Koirala, “Integrated Community Energy Systems,” 2017. [CrossRef]
- Genovese, M.; Fragiacomo, P. Hydrogen refueling station: Overview of the technological status and research enhancement. J. Energy Storage 2023, 61, 106758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. E. I. Shrestha, J. Sartohadi, M. K. Ridwan, and D. R. Hizbaron, “Urban Energy Scenario: the Case of Kathmandu Valley,” Journal of Engineering and Technological Sciences, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 210–224, Jul. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Sartohadi, J.; Ridwan, M.K.; Hizbaron, D.R. Urban Energy Scenario: the Case of Kathmandu Valley. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2017, 49, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirbalouti, R.G.; Dehkordi, M.K.; Mohammadpour, J.; Zarei, E.; Yazdi, M. An advanced framework for leakage risk assessment of hydrogen refueling stations using interval-valued spherical fuzzy sets (IV-SFS). Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 20827–20842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, “THE UTILITY OF THE PARTICIPATORY APPROACH FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT ASSESSMENTS,” 2016. [CrossRef]
- Basnet, A.; Zhong, J. Integrating gas energy storage system in a peer-to-peer community energy market for enhanced operation. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 118, 105789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Warming of 1.5 oC —. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/sr15/ (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Didenko, N.I.; Klochkov, Y.S.; Skripnuk, D.F. Ecological Criteria for Comparing Linear and Circular Economies. Resources 2018, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Z. Shrestha, “The Integration of Circular Economy into the Municipal Solid Waste Management of Kathmandu Metropolitan City in Nepal : Present Sector Challenges & Opportunities for Waste Material (Re)Utilization,” 2018.
- Islar, M.; Brogaard, S.; Lemberg-Pedersen, M. Feasibility of energy justice: Exploring national and local efforts for energy development in Nepal. Energy Policy 2017, 105, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damgaard, C.; McCauley, D.; Long, J. Assessing the energy justice implications of bioenergy development in Nepal. Energy, Sustain. Soc. 2017, 7, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anaerobic Digestion (Large-Scale) | SSWM - Find tools for sustainable sanitation and water management! Available online: https://sswm.info/humanitarian-crises/urban-settings/sanitation/semi-centralised-treatment/anaerobic-digestion-(large-scale) (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Financing Green Infrastructure - Is a Community-Based Public-Private Partnerships (CBP3) Right for You? | US EPA. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/G3/financing-green-infrastructure-community-based-public-private-partnerships-cbp3-right-you (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Lord, A.; Rest, M. Nepal’s Water, the People’s Investment? ETHNOGRAPHIES OF POWER 2021, 81–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAHE | Ministry of Road Transport & Highways, Government of India. Available online: https://morth.nic.in/iahe (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Abad, A.V.; Dodds, P.E. Green hydrogen characterisation initiatives: Definitions, standards, guarantees of origin, and challenges. Energy Policy 2020, 138, 111300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremy. Rifkin, “The third industrial revolution : how lateral power is transforming energy, the economy, and the world,” p. 291.
- Zhou, A.; Zhou, W.; Manandhar, P. A STUDY ON THE PROSPECT OF HYDROPOWER TO HYDROGEN IN NEPAL. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. S. Zaman, A. B. Chhetri, and M. S. Tango, “Feasibility of Hydrogen Production from Micro Hydropower Projects in Nepal”.
- Paudel, S.; Seong, C.Y.; Park, D.R.; Seo, G.T. Anaerobic Hydrogen Fermentation and Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) for Decentralized Sanitation and Reuse-Organic Removal and Resource Recovery. Environ. Eng. Res. 2014, 19, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Keitsch, M.M.; Shrestha, M. Scaling up sustainability: Concepts and practices of the ecovillage approach. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 27, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Singh and S. R. Tiwari, “Eco-city and Other Ecological Approaches in Urban Planning: A Review of the State-of-the-Art,” pp. 253–263, 2016.
- Economic Survey. Available online: https://www.indiabudget.gov.in/budget2020-21/economicsurvey/index.php (accessed on 1 February 2023).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).