Submitted:
10 July 2023
Posted:
11 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
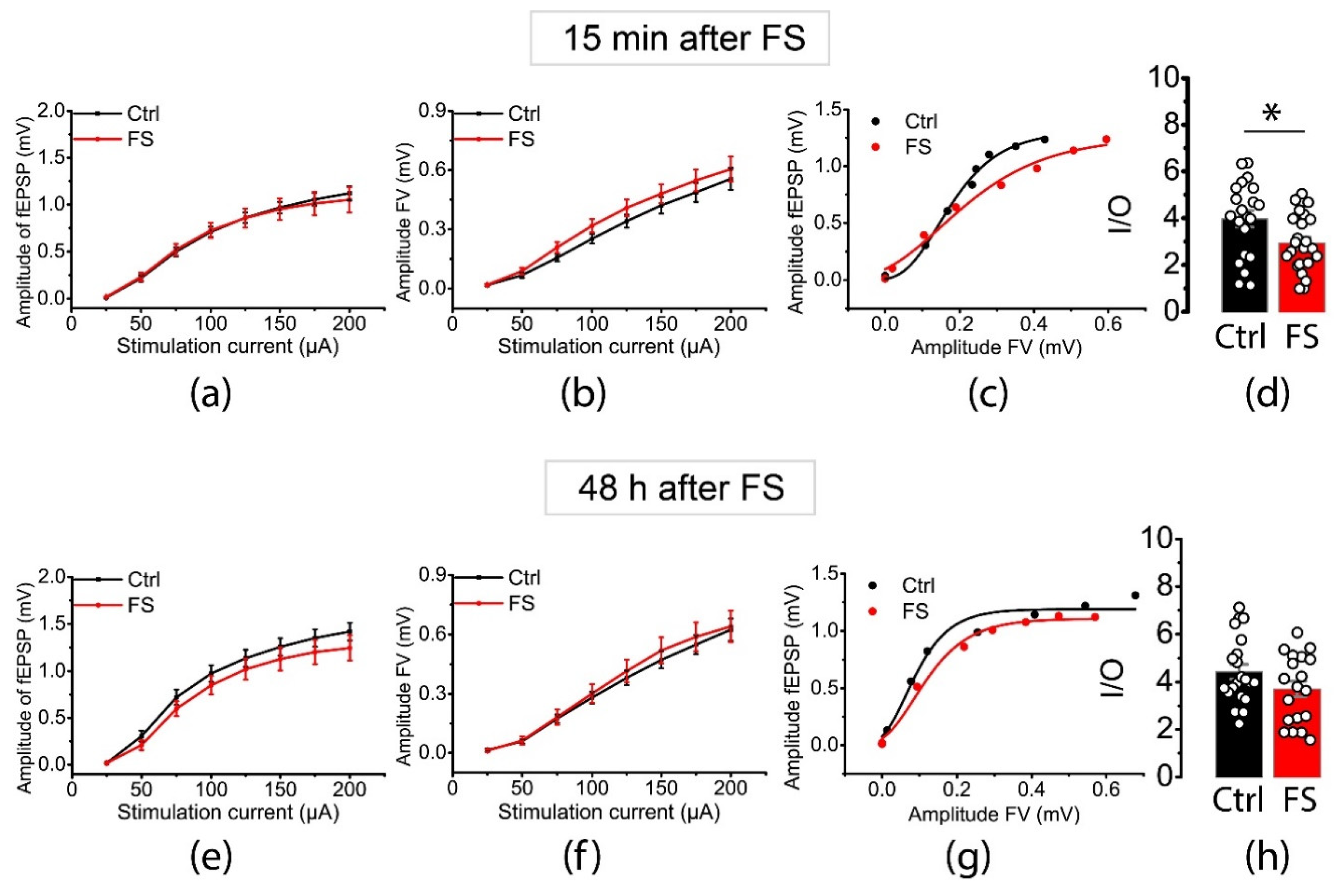
2.1. The Efficacy of Synaptic Neurotransmission at CA3-CA1 is Immediately Reduced after FSs
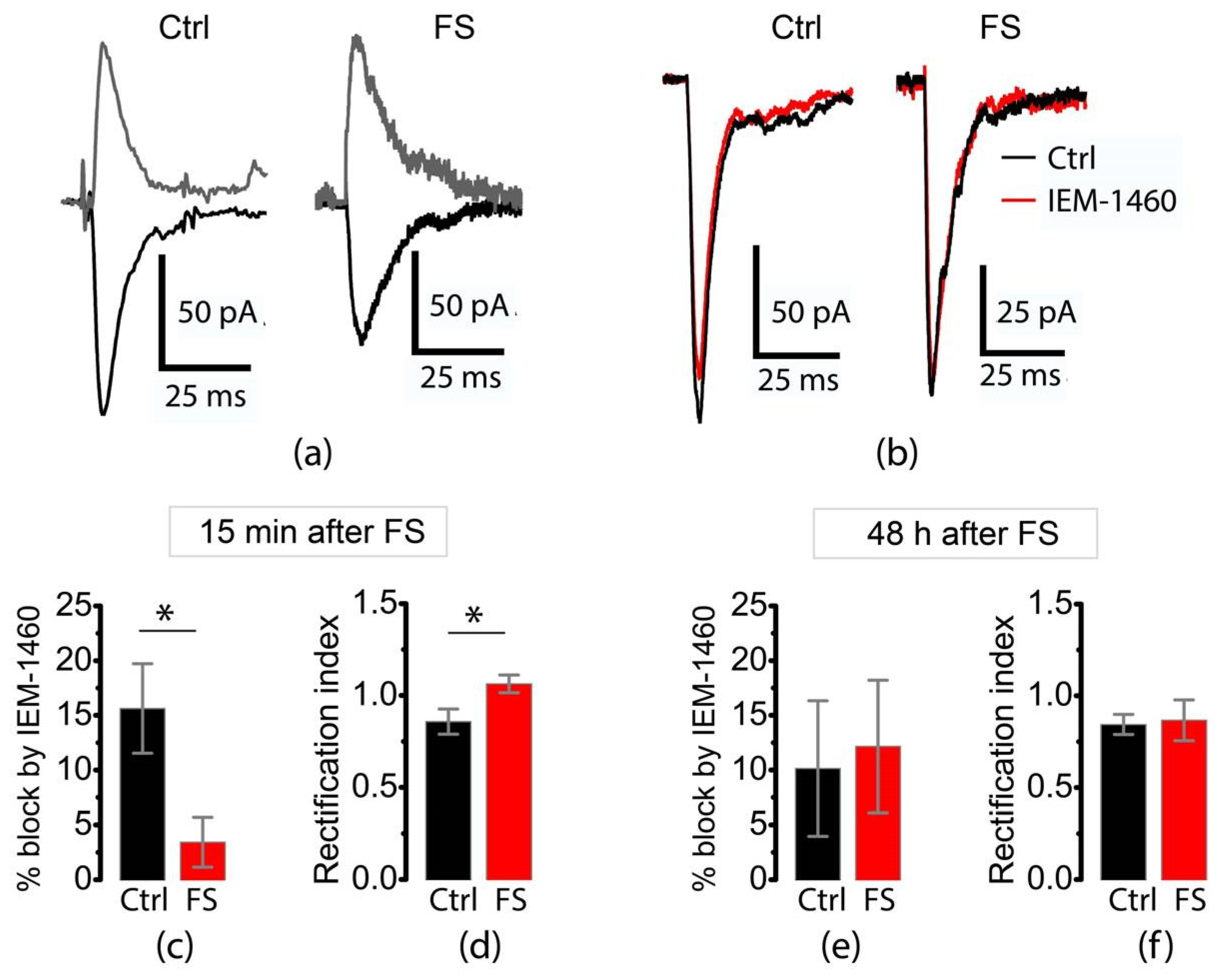
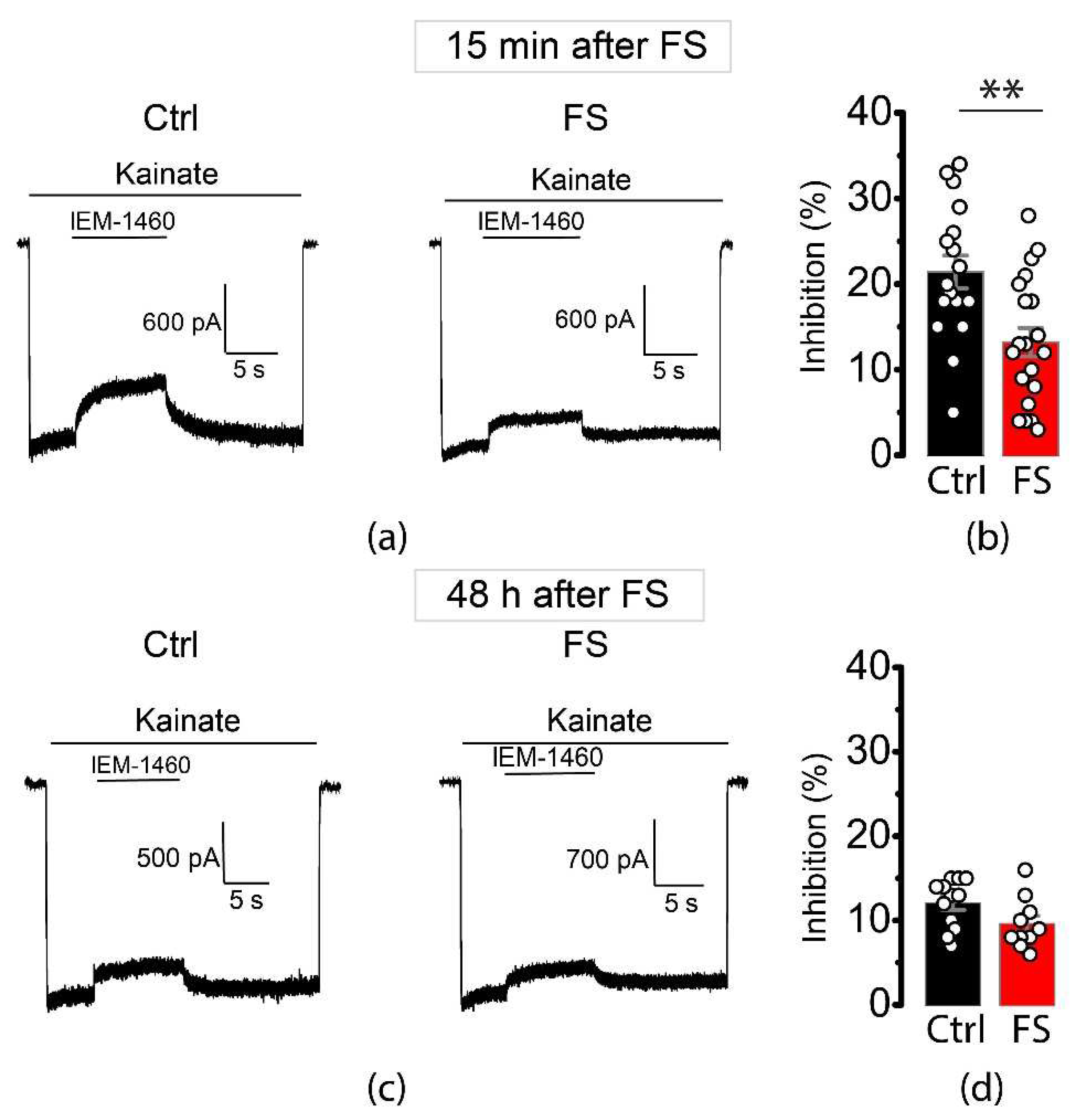
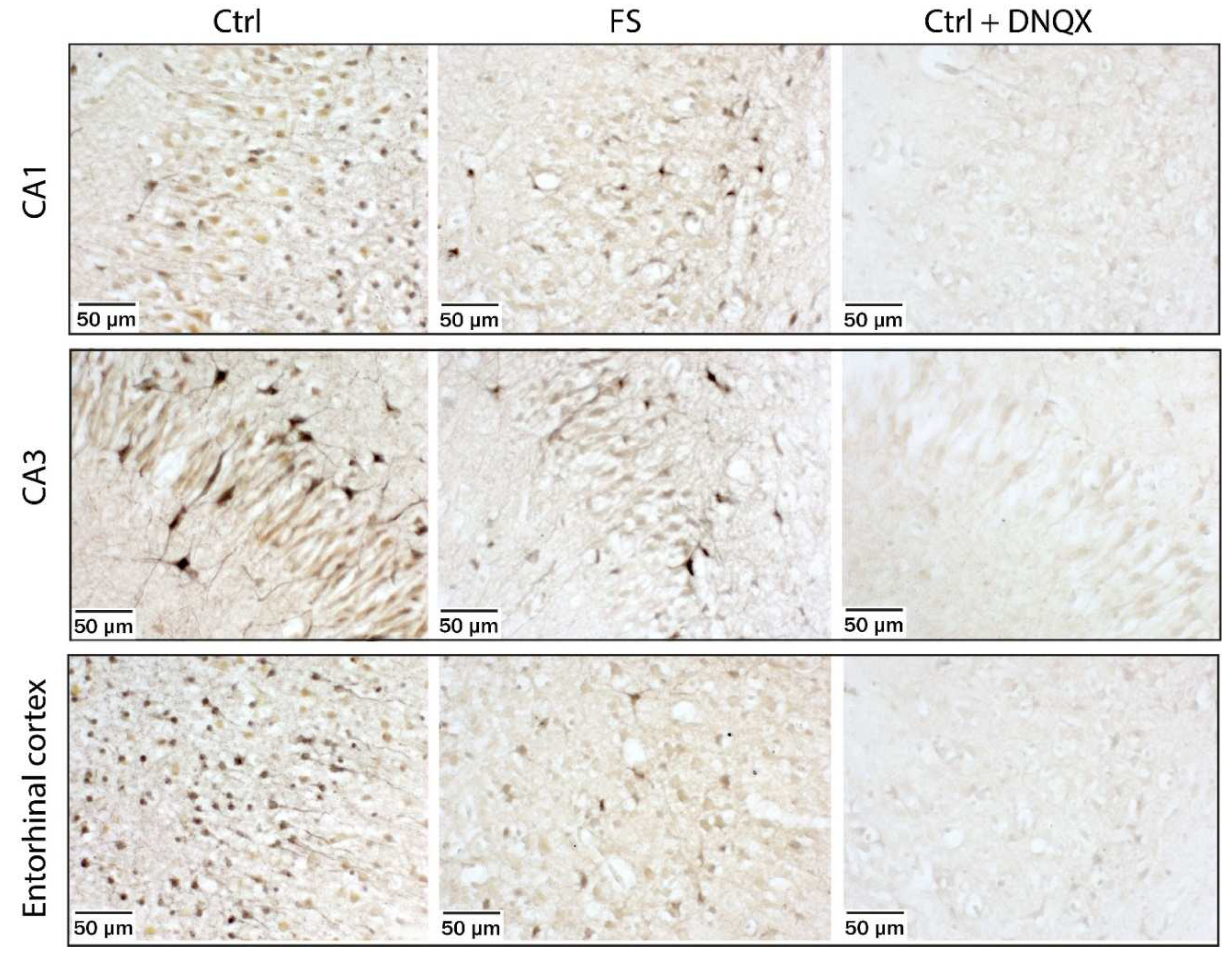
2.2. FSs Cause a Rapid Decrease in the Proportion of CP-AMPA Receptors in the Principal Neurons of the Entorhinal Cortex and Hippocampus
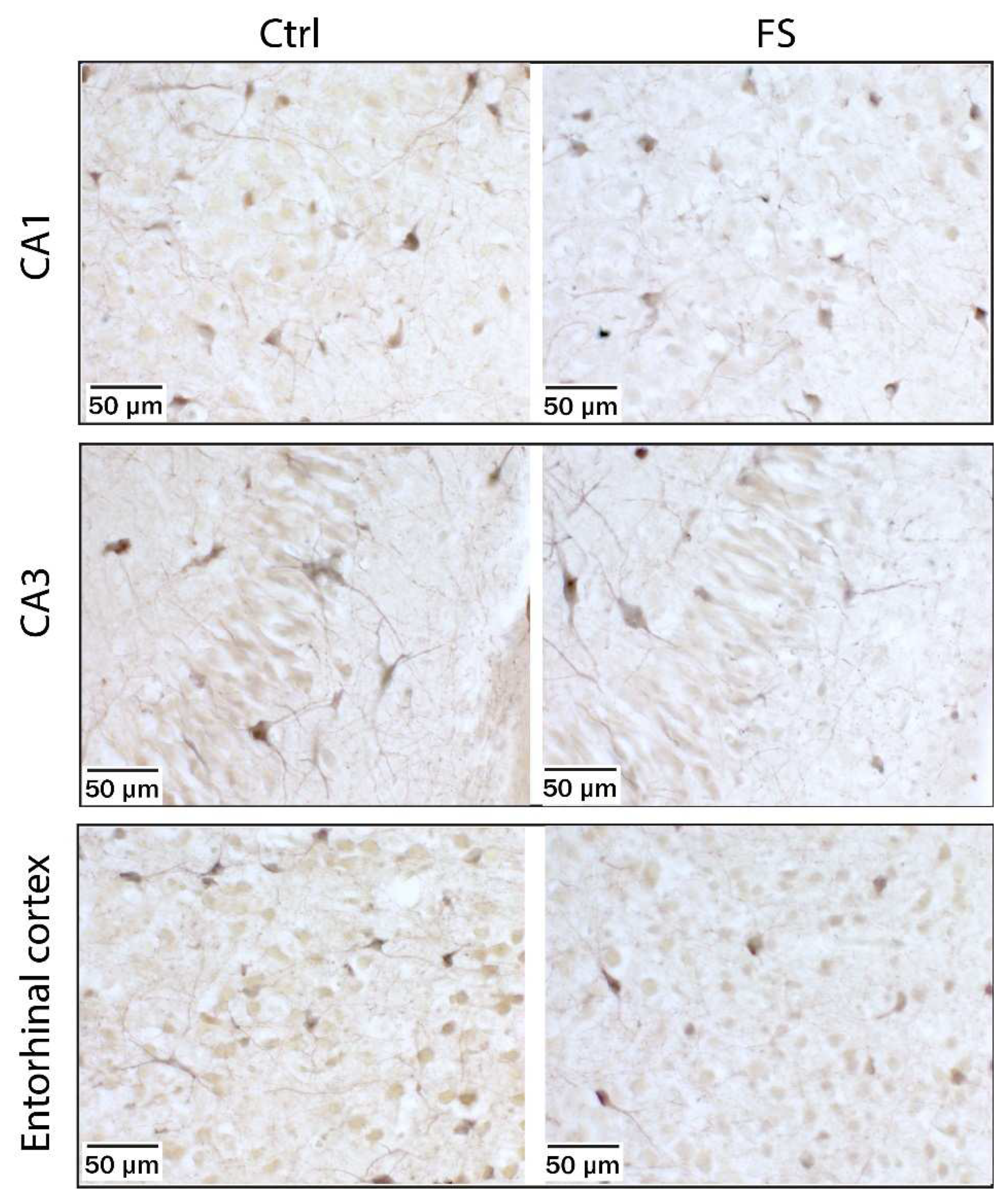
2.4. Kainate-Induced Co2+ Uptake in Hippocampal CA1 and CA3 Areas and in the Entorhinal Cortex is Reduced Immediately after FSs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. FS Model
4.3. Brain Slice Preparation
4.4. Field Potential Recordings
4.5. Whole-Cell Patch-Clamp Recordings from Entorhinal Cortex Pyramidal Neuron Slices
4.6. Patch-Clamp Recordings of Membrane Currents from Isolated CA1 Pyramidal Neurons
4.7. The Kainate-Induced Cobalt Uptake Method
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silverstein, F.S.; Jensen, F.E. Neonatal Seizures. Ann Neurol 2007, 62, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewasingh, L.D.; Chin, R.F.M.; Scott, R.C. Current Understanding of Febrile Seizures and Their Long-Term Outcomes. Dev Med Child Neurol 2020, 62, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, B.; Chen, Z. Generation of Febrile Seizures and Subsequent Epileptogenesis. Neurosci Bull 2016, 32, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waruiru, C.; Appleton, R. Febrile Seizures: An Update. Arch Dis Child 2004, 89, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cendes, F. Febrile Seizures and Mesial Temporal Sclerosis. Curr Opin Neurol 2004, 17, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D. V; Shinnar, S.; Hesdorffer, D.C.; Bagiella, E.; Bello, J.A.; Chan, S.; Xu, Y.; MacFall, J.; Gomes, W.A.; Moshé, S.L.; et al. Hippocampal Sclerosis after Febrile Status Epilepticus: The FEBSTAT Study. Ann Neurol 2014, 75, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, A.; Bender, R.A.; Chen, Y.; Dube, C.; Eghbal-Ahmadi, M.; Baram, T.Z. Developmental Febrile Seizures Modulate Hippocampal Gene Expression of Hyperpolarization-Activated Channels in an Isoform- and Cell-Specific Manner. J Neurosci 2002, 22, 4591–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubé, C.M.; Ravizza, T.; Hamamura, M.; Zha, Q.; Keebaugh, A.; Fok, K.; Andres, A.L.; Nalcioglu, O.; Obenaus, A.; Vezzani, A.; et al. Epileptogenesis Provoked by Prolonged Experimental Febrile Seizures: Mechanisms and Biomarkers. J Neurosci 2010, 30, 7484–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhade, S.N.; Zhou, C.; Aujla, P.K.; Fishman, R.; Sucher, N.J.; Jensen, F.E. Early Alterations of AMPA Receptors Mediate Synaptic Potentiation Induced by Neonatal Seizures. The Journal of Neuroscience 2008, 28, 7979–7990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Baram, T.Z.; Soltesz, I. Febrile Seizures in the Developing Brain Result in Persistent Modification of Neuronal Excitability in Limbic Circuits. Nat Med 1999, 5, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, B.J.; Mesches, M.H.; Benke, T.A. A Single Early-Life Seizure Impairs Short-Term Memory but Does Not Alter Spatial Learning, Recognition Memory, or Anxiety. Epilepsy and Behavior 2008, 13, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornejo, B.J.; Mesches, M.H.; Coultrap, S.; Browning, M.D.; Benke, T.A. A Single Episode of Neonatal Seizures Permanently Alters Glutamatergic Synapses. Ann Neurol 2007, 61, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egbenya, D.L.; Hussain, S.; Lai, Y.-C.; Xia, J.; Anderson, A.E.; Davanger, S. Changes in Synaptic AMPA Receptor Concentration and Composition in Chronic Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Mol Cell Neurosci 2018, 92, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekonomou, A.; Smith, A.L.; Angelatou, F. Changes in AMPA Receptor Binding and Subunit Messenger RNA Expression in Hippocampus and Cortex in the Pentylenetetrazole-Induced ‘Kindling’ Model of Epilepsy. Molecular Brain Research 2001, 95, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz Del Angel, Y.; Orfila, J.E.; Herson, P.S.; Brooks-Kayal, A.; González, M.I. Down-Regulation of AMPA Receptors and Long-Term Potentiation during Early Epileptogenesis. Epilepsy & Behavior 2021, 124, 108320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathern, G.W.; Pretorius, J.K.; Kornblum, H.I.; Mendoza, D.; Lozada, A.; Leite, J.P.; Chimelli, L.M.C.; Fried, I.; Sakamoto, A.C.; Assirati, J.A.; et al. Human Hippocampal AMPA and NMDA MRNA Levels in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Patients. Brain 1997, 120, 1937–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippman-Bell, J.J.; Zhou, C.; Sun, H.; Feske, J.S.; Jensen, F.E. Early-Life Seizures Alter Synaptic Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptor Function and Plasticity. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience 2016, 76, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Shi, Y.; Jackson, A.C.; Bjorgan, K.; During, M.J.; Sprengel, R.; Seeburg, P.H.; Nicoll, R.A. Subunit Composition of Synaptic AMPA Receptors Revealed by a Single-Cell Genetic Approach. Neuron 2009, 62, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingledine, R.; Borges, K.; Bowie, D.; Traynelis, S.F. The Glutamate Receptor Ion Channels. Pharmacol Rev 1999, 51, 7–61. [Google Scholar]
- Henley, J.M.; Wilkinson, K.A. Synaptic AMPA Receptor Composition in Development, Plasticity and Disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2016, 17, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, J.T.R.; Ashby, M.C.; McBain, C.J. The Role of the GluR2 Subunit in AMPA Receptor Function and Synaptic Plasticity. Neuron 2007, 54, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, L.K. Selective Reduction of GluR2 Protein in Adult Hippocampal CA3 Neurons Following Status Epilepticus but Prior to Cell Loss. Hippocampus 1998, 8, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grooms, S.Y. Status Epilepticus Decreases Glutamate Receptor 2 MRNA and Protein Expression in Hippocampal Pyramidal Cells before Neuronal Death. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2000, 97, 3631–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, S.L.; Amakhin, D. V; Veniaminova, E.A.; Kim, K.K.; Zubareva, O.E.; Magazanik, L.G.; Zaitsev, A. V Changes of AMPA Receptor Properties in the Neocortex and Hippocampus Following Pilocarpine-Induced Status Epilepticus in Rats. Neuroscience 2016, 327, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, R.M.; Koh, S.; Rio, C.; Wang, C.; Lamperti, E.D.; Sharma, D.; Corfas, G.; Jensen, F.E. Decreased Glutamate Receptor 2 Expression and Enhanced Epileptogenesis in Immature Rat Hippocampus after Perinatal Hypoxia-Induced Seizures. The Journal of Neuroscience 2001, 21, 8154–8163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, C.; Roth, S.U.; Kiessling, M. Kainate-Induced Epilepsy Alters Protein Expression of AMPA Receptor Subunits GluR1, GluR2 and AMPA Receptor Binding Protein in the Rat Hippocampus. Acta Neuropathol 2001, 101, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakhin, D. V.; Soboleva, E.B.; Ergina, J.L.; Malkin, S.L.; Chizhov, A. V.; Zaitsev, A. V. Seizure-Induced Potentiation of AMPA Receptor-Mediated Synaptic Transmission in the Entorhinal Cortex. Front Cell Neurosci 2018, 12, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini-Giampietro, D.E.; Gorter, J.A.; Bennett, M. V; Zukin, R.S. The GluR2 (GluR-B) Hypothesis: Ca(2+)-Permeable AMPA Receptors in Neurological Disorders. Trends Neurosci 1997, 20, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogawa, Y.; Monokoshi, M.; Silveira, D.C.; Ho Cha, B.; Roberta Cilio, M.; McCabe, B.K.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Holmes, G.L. Timing of Cognitive Deficits Following Neonatal Seizures: Relationship to Histological Changes in the Hippocampus. Developmental Brain Research 2001, 131, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.P. Expression of AMPA Receptor Subunits in Hippocampus after Status Convulsion. Child’s Nervous System 2012, 28, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, I.; Bonini, D.; Via, L. La; Barlati, S.; Barbon, A. AMPA Receptor Properties Are Modulated in the Early Stages Following Pilocarpine-Induced Status Epilepticus. Neuromolecular Med 2013, 15, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.P.; Rai, R.; Gaur, P.; Prasad, S. Development- and Age-Related Alterations in the Expression of AMPA Receptor Subunit GluR2 and Its Trafficking Proteins in the Hippocampus of Male Mouse Brain. Biogerontology 2015, 16, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.S.; Bacci, A.; Kharazia, V.; Huguenard, J.R. A Developmental Switch of AMPA Receptor Subunits in Neocortical Pyramidal Neurons. Journal of Neuroscience 2002, 22, 3005–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toth, Z.; Yan, X.-X.X.; Haftoglou, S.; Ribak, C.E.; Baram, T.Z. Seizure-Induced Neuronal Injury: Vulnerability to Febrile Seizures in an Immature Rat Model. The Journal of Neuroscience 1998, 18, 4285–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, T.; Hara, K.; Shimakawa, S.; Fukui, M.; Tamai, H. Hippocampal Damage after Prolonged Febrile Seizure: One Case in a Consecutive Prospective Series. Epilepsia 2011, 52, 837–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postnikova, T.Y.; Griflyuk, A. V.; Amakhin, D. V.; Kovalenko, A.A.; Soboleva, E.B.; Zubareva, O.E.; Zaitsev, A. V. Early Life Febrile Seizures Impair Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity in Young Rats. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 8218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubareva, O.E.; Kovalenko, A.A.A.; Kalemenev, S. V.; Schwarz, A.P.; Karyakin, V.B.; Zaitsev, A. V. Alterations in MRNA Expression of Glutamate Receptor Subunits and Excitatory Amino Acid Transporters Following Pilocarpine-Induced Seizures in Rats. Neurosci Lett 2018, 686, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, K.; Todorovic, M.; Kapur, J. Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors Are Expressed in a Rodent Model of Status Epilepticus. Ann Neurol 2012, 72, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Rajasekaran, K.; Sun, H.; Williamson, J.; Kapur, J. Enhanced AMPA Receptor-Mediated Neurotransmission on CA1 Pyramidal Neurons during Status Epilepticus. Neurobiol Dis 2017, 103, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippman-Bell, J.J.; Rakhade, S.N.; Klein, P.M.; Obeid, M.; Jackson, M.C.; Joseph, A.; Jensen, F.E. AMPA Receptor Antagonist NBQX Attenuates Later-Life Epileptic Seizures and Autistic-like Social Deficits Following Neonatal Seizures. Epilepsia 2013, 54, 1922–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talos, D.M.; Sun, H.; Zhou, X.; Fitzgerald, E.C.; Jackson, M.C.; Klein, P.M.; Lan, V.J.; Joseph, A.; Jensen, F.E. The Interaction between Early Life Epilepsy and Autistic-Like Behavioral Consequences: A Role for the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (MTOR) Pathway. PLoS One 2012, 7, e35885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, А. V.; Amakhin, D. V.; Dyomina, A. V.; Zakharova, M. V.; Ergina, J.L.; Postnikova, T.Y.; Diespirov, G.P.; Magazanik, L.G. Synaptic Dysfunction in Epilepsy. J Evol Biochem Physiol 2021, 57, 542–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, N.S.; Handy, M.J.; Ito, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Jensen, F.E.; Talos, D.M. Anti-Seizure Efficacy of Perampanel in Two Established Rodent Models of Early-Life Epilepsy. Epilepsy and Behavior 2023, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amakhin, D. V.; Soboleva, E.B.; Chizhov, A. V.; Zaitsev, A. V. Insertion of Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors during Epileptiform Activity In Vitro Modulates Excitability of Principal Neurons in the Rat Entorhinal Cortex. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 12174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Kapur, J. Mechanisms of Status Epilepticus: α-Amino-3-Hydroxy-5-Methyl-4-Isoxazolepropionic Acid Receptor Hypothesis. Epilepsia 2018, 59, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adotevi, N.; Lewczuk, E.; Sun, H.; Joshi, S.; Dabrowska, N.; Shan, S.; Williamson, J.; Kapur, J. α-Amino-3-Hydroxy-5-Methyl-4-Isoxazolepropionic Acid Receptor Plasticity Sustains Severe, Fatal Status Epilepticus. Ann Neurol 2020, 87, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ari, Y. Epilepsies and Neuronal Plasticity: For Better or for Worse? Dialogues Clin Neurosci 2008, 10, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abegg, M.H.; Savic, N.; Ehrengruber, M.U.; McKinney, R.A.; Gähwiler, B.H. Epileptiform Activity in Rat Hippocampus Strengthens Excitatory Synapses. Journal of Physiology 2004, 554, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debanne, D.; Thompson, S.M.; Gähwiler, B.H. A Brief Period of Epileptiform Activity Strengthens Excitatory Synapses in the Rat Hippocampus in Vitro. Epilepsia 2006, 47, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postnikova, T.Y.; Amakhin, D. V.; Trofimova, A.M.; Zaitsev, A. V. Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors Are Essential to the Synaptic Plasticity Induced by Epileptiform Activity in Rat Hippocampal Slices. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2020, 529, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, K.; Pelkey, K.A.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Morita, D.; Terashima, A.; McBain, C.J.; Collingridge, G.L.; Isaac, J.T.R. Transient Incorporation of Native GluR2-Lacking AMPA Receptors during Hippocampal Long-Term Potentiation. Nat Neurosci 2006, 9, 602–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M. AMPA Receptor Trafficking for Postsynaptic Potentiation. Front Cell Neurosci 2018, 12, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Bell, J.J.L.; Sun, H.; Jensen, F.E. Hypoxia-Induced Neonatal Seizures Diminish Silent Synapses and Long-Term Potentiation in Hippocampal CA1 Neurons. Journal of Neuroscience 2011, 31, 18211–18222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippman-Bell, J.J.; Handy, M.; Nieder, C.G.; Getzfread, M.; Jensen, F.E. Altered Hippocampal Dendritic Spine Maturation after Hypoxia-Induced Seizures in Neonatal Rats. Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience 2021, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrar, S.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, W.; Jia, Z. Ca2+ Permeable AMPA Receptor Induced Long-Term Potentiation Requires PI3/MAP Kinases but Not Ca/CaMDependent Kinase II. PLoS One 2009, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullmann, D.M.; Lamsa, K.P. Long-Term Synaptic Plasticity in Hippocampal Interneurons. Nat Rev Neurosci 2007, 8, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Cull-Candy, S.G. Activity-Dependent Change in AMPA Receptor Properties in Cerebellar Stellate Cells. Journal of Neuroscience 2002, 22, 3881–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.J.; Cull-Candy, S.G. Subunit Interaction with PICK and GRIP Controls Ca2+ Permeability of AMPARs at Cerebellar Synapses. Nat Neurosci 2005, 8, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-Q.J.; Cull-Candy, S.G. Synaptic Activity at Calcium-Permeable AMPA Receptors Induces a Switch in Receptor Subtype. Nature 2000, 405, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, G.; Jo, J.; Hogg, E.L.; Piers, T.; Kim, D.H.; Seaton, G.; Seok, H.; Bru-Mercier, G.; Son, G.H.; Regan, P.; et al. Acute Stress Causes Rapid Synaptic Insertion of Ca2+ -Permeable AMPA Receptors to Facilitate Long-Term Potentiation in the Hippocampus. Brain 2013, 136, 3753–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griflyuk, A. V.; Postnikova, T.Y.; Zaitsev, A. V. Prolonged Febrile Seizures Impair Synaptic Plasticity and Alter Developmental Pattern of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP)-Immunoreactive Astrocytes in the Hippocampus of Young Rats. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 12224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notenboom, R.G.E.; Ramakers, G.M.J.J.; Kamal, A.; Spruijt, B.M.; De Graan, P.N.E. Long-Lasting Modulation of Synaptic Plasticity in Rat Hippocampus after Early-Life Complex Febrile Seizures. European Journal of Neuroscience 2010, 32, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postnikova, T.Y.; Amakhin, D. V.; Trofimova, A.M.; Smolensky, I. V.; Zaitsev, A. V. Changes in Functional Properties of Rat Hippocampal Neurons Following Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Status Epilepticus. Neuroscience 2019, 399, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuravin, I.A.; Dubrovskaya, N.M.; Vasilev, D.S.; Postnikova, T.Y.; Zaitsev, A. V. Prenatal Hypoxia Produces Memory Deficits Associated with Impairment of Long-Term Synaptic Plasticity in Young Rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 2019, 164, 107066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




