1. Introduction
Antibiotics are widely used in human medicine worldwide because they treat bacterial infections effectively. Studies conducted since the 1980s have shown that fluoroquinolines are highly effective antibacterial drugs with wide application in both human and veterinary practice [
1]. These compounds have been found to be particularly effective in treating various diseases, such as infections of the skin, respiratory tract, urinary tract, nervous system, as well as bones and joints. The experimental findings have established that fluoroquinolines are an important class of antibiotics, and their effectiveness makes them a valuable treatment option for many bacterial infections. [
2,
3,
4]. Levofloxacin, namely (S)-9-fluoro-2, 3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-1-piperazinyl)-7-oxo-7H-pyrido [1,2,3-de]-1, 4-benzoxazine-6-carboxylic acid is one of the most promising fluoroquinolones, and its antibacterial activity is much higher than the activity of other drugs of the fluoroquinolone family [
5]. Levofloxacin (LEV) directly inhibits bacterial DNA synthesis, and it promotes the breakage of DNA strands by inhibiting DNA-gyrase in susceptible organisms, which inhibits the relaxation of supercoiled DNA [
6]. Considering the importance of these compounds, their prevalence in the environment and aquatic systems [
7], the existence of methods for the control and monitoring of these compounds is of crucial importance. Several different methodological approaches have been developed so far for monitoring the concentration of LEV and they are based on spectrophotometry [
8,
9], high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) [
10,
11] and chemiluminescence [
12]. These methods also have drawbacks such as high cost, extended analysis time, and sample preparation such as derivatization and extraction, while purification is often necessary. Electrochemical methods have been shown to have numerous advantages over traditional methods of analysis, including simplicity of handling, cost-effectiveness, sensitivity, and rapid analysis [
13]. They also offer an easy way to transfer technology and device miniaturization, in vivo and in vitro process monitoring, which are additional parameters that highlight their advantages [
14]. Electrochemical methods are simpler and more reasonable, with excellent reproducibility, short assay time and less in terms of cost compared to other conventional approaches. Additionally, the modification of electrochemical reactions by altering the value of the oxidation and/or reduction potential promotes their existence [
15]. The modification step also allows us to avoid some of the problems of surface contamination [
16,
17].
A proposed study has been put forward which aims to prepare a modified cobalt oxide carbon paste electrode for the purpose of detecting LEV. The key components of this electrode are Co3O4 nanoparticles, which were synthesized via the chemical coprecipitation method. For analyzing the electrochemical properties of LEV at this electrode, the study utilized a range of techniques including cyclic voltammetry, square wave voltammetry, and differential pulse voltammetry. In addition, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, inductively coupled plasma-optical emission spectrometry, transmission and scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction were employed to characterize the synthesized material. The ultimate goal of this study wass to provide a comprehensive understanding of the electrochemical properties of both LEV and the synthesized material, with potential applications in a wide range of fields.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and apparatus
In the study, all reagents used were of analytical grade and were manufactured by Sigma Aldrich. The reagents were used without further purification, including Cobalt (II) chloride hexahydrate (CoCl2∙6H2O), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), paraffin oil, and carbon powder. Britton Robinson buffer solution (BRBS) was used as the supporting electrolyte. To prepare initial pH2, appropriate amounts of boric acid, phosphoric acid, and acetic acid were dissolved in 1 L of ultrapure water (all concentrations were 0.04 M). Other pHs were adjusted using 0.5 M NaOH. For EIS and CV measurements, the Fe2+/3+ redox couple was used, which was prepared from 5 mM potassium hexacyanoferrate(III) (K3[Fe(CN)6]) and potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) trihydrate (K4[Fe(CN)6]∙3H2O) in 0.1M KCl solution. Interference and LEV solutions were prepared freshly on the day of use.
The crystal structure of cobalt oxide nanoparticles was determined using X-ray powder-diffraction (XRD) data measured on dried powders in a high-resolution SmartLab® diffractometer (Rigaku, Japan), equipped with Cu Kα radiation source (λ = 1.5406 Å) under a voltage 40 kV and a 30 mA current. The patterns were collected within the 10-70° 2θ range at a scan rate of 1°/min and 0.02° step size.
Transmission electron microscope Jeol JEM-2100F (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) and scanning electron microscope Jeol JSM-7001F (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) were used to scrutinize the morphological properties of the material. The accelerating voltage of the electron gun was set to the 20 kV required for quantitative EDX analysis.
All electrochemical measurements were performed using a PalmSens4 analyzer (Houten, Utrecht, The Netherlands) running PSTrace voltammetry software (Version 5.8). A three-electrode system was used with an un- or modified CP electrodes, an Ag/AgCl electrode, and a platinum electrode as working, reference, and counter electrode, respectively. Measurements were performed in BRBS at pH 5. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) measurements, Square Wave Voltammetry (SWV) and Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS measurements were done according to the procedures listed in appropriate section.
2.2. Material preparation
The coprecipitation method is an established technique for the synthesis of mixed metal oxides, and has been shown to be effective for the preparation of cobalt oxide. By using this method, we aim to produce a high-quality sample of mixed cobalt oxide that can be used for a variety of applications. This work involves the preparation of mixed cobalt oxide using the coprecipitation method. To achieve this, we will dissolve the appropriate amount of cobalt(II) chloride in water, adjust the pH of the resulting solution to 13 using sodium hydroxide, and heat the solution for 4 hours at 60 °C. The solution will then be washed with water until the reaction is neutral, and the resulting cobalt oxide precipitate will be dried for 16 hours at 100°C and annealed at 700°C for 4 hours.
2.3. Electrode preparation
The bare carbon paste electrode was prepared using a standard procedure, mixing 80% glassy carbon powder with 20% silicon oil for 30 minutes. The resulting paste was left overnight before use. A modified carbon paste electrode was also prepared using the same procedure, but with the addition of an appropriate amount of cobalt oxide in percentages of 2, 5, 7, and 15 to the carbon powder. The working electrode was housed in a homemade Teflon body.
3. Results
3.1. Morphology and structure characterization
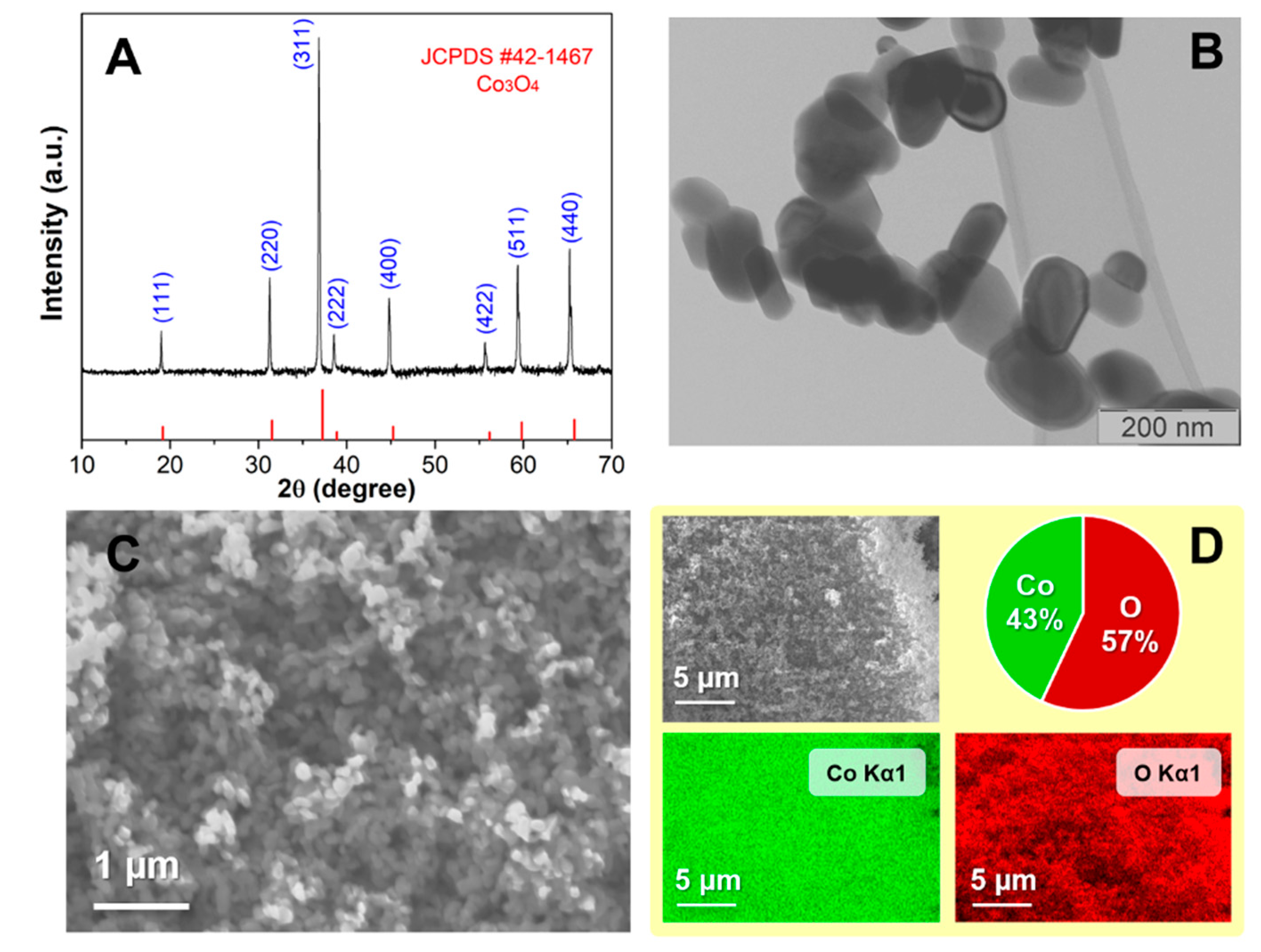
The morphology and the structure of prepared Co
3O
4 nanoparticles were analyzed by X-ray diffraction data (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (
Figure 1).
Figure 1A presents the diffraction pattern of synthesized cobalt oxide, pointing to the excellent crystallinity of the sample. Crystal reflections occur at the same position as those for cobalt oxide of spinel structure type, indicating that all the reflections can be indexed to the same space Fdm group and are matching with simulated diffraction data (JCPDS#42-1467) from the literature [
18]. The cobalt oxide nanoparticles are shaped hexagonally elongated in one dimension, as shown in
Figure 1B. The average length of nanoparticles is about (130 ± 30) nm, while the average width is (70 ± 20) nm. The SEM micrographs and EDS elemental mapping of a wider area of the sample are displayed in
Figure 1C,D. SEM figures reveal the homogeneous distribution of the sample while EDS elemental mapping shows that cobalt oxide was formed along the entire sample with the proportion of cobalt and oxygen, 43% and 57% respectively. The prepared cobalt oxide nanoparticles exhibited potential for use as electrochemical sensors due to their small crystallite size and large specific surface area. These properties provide active sites for the accumulation of ions.
Based on the ICP-OES method, the concentration of cobalt in the material used for the electrode preparation was found to be 591.27 mg/g with an RSD of 0.32%. This result is indicative of a high concentration of cobalt in the material, which could potentially have implications for the performance of the electrode. Further investigation may be necessary to fully understand the impact of this concentration on the overall function of the electrode.
3.2. Electrochemical characterization of materials
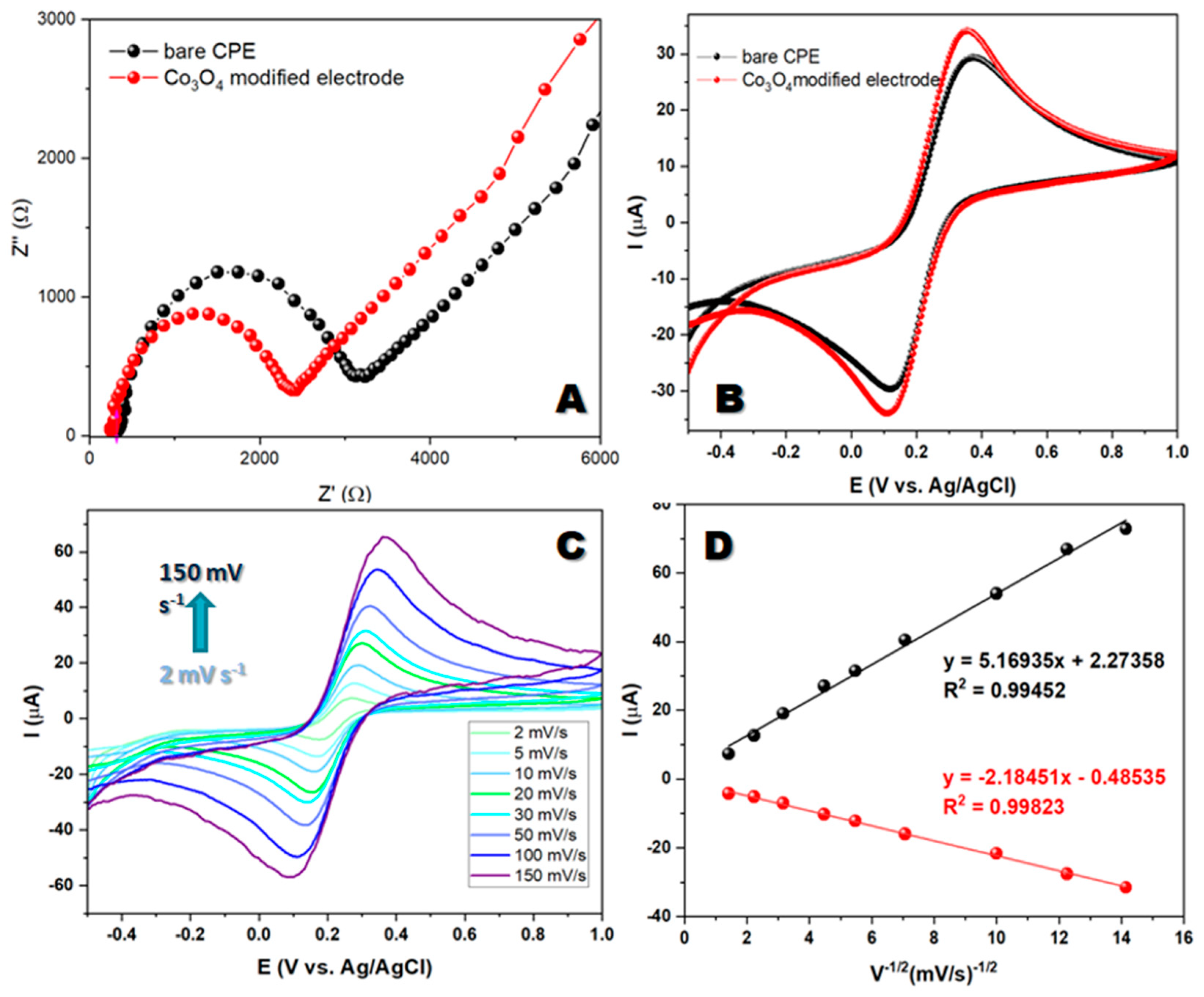
When studying electron transport between the electrolyte and the electrode's active surface, researchers employed electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The resulting EIS spectra consisted of a semicircular high-frequency region and a linear low-frequency region. The semicircle's diameter reflected the resistance to charge transfer, while the linear region indicated mass transfer and the diffusion of electroactive species. These observations provide valuable insights regarding the system's behavior under investigation. EIS measurements were performed in a 5 mM redox system K
3[Fe(CN)
6]/K
4[Fe(CN)
6] and 0.1M KCl as the supporting electrolyte, using electrode modified with synthesized material and unmodified carbon paste electrode. The results obtained by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy show a regular behavior and the obtained spectra consist of two parts: semicircular (high-frequency) and a linear (low-frequency) spectral region.
Figure 2A shows that the Rct value of the modified electrode is lower than the Rct value of the bare electrode. The Rct values indicate that the modified electrode has a low resistance compared with the bare carbon paste electrode. It appears that the low resistance of the Co
3O
4 modified electrode can be attributed to its nanocomposite structure, which possesses superior electronic conductivity and remarkable electrocatalytic activity [
19]. To determine the electron transfer behavior of the bare CPE and Co
3O
4-modified electrode, CV measurements were performed in 5 mM K
3[Fe(CN)
6]
3−/4− in a 0.1 M KCl system. The CV profile of the modified electrode exhibits good redox peaks during forward and backward scans at potentials ranging from -0.5 V to 1 V with a scan rate of 50 mV s
−1 (
Figure 2B).
Figure 2C shows the redox peaks for the Co
3O
4 modified electrode with different scan rates of 2–150 mVs−1 in [Fe(CN)
6]
3−/4−. Increasing the scan rate also expands the anodic and cathodic peak current increasing. The analysis of the current peaks in the electrochemical reaction at the electrode/testing solution interface has revealed an interesting linear correlation between the currents and the square root of the scan rate, as depicted in
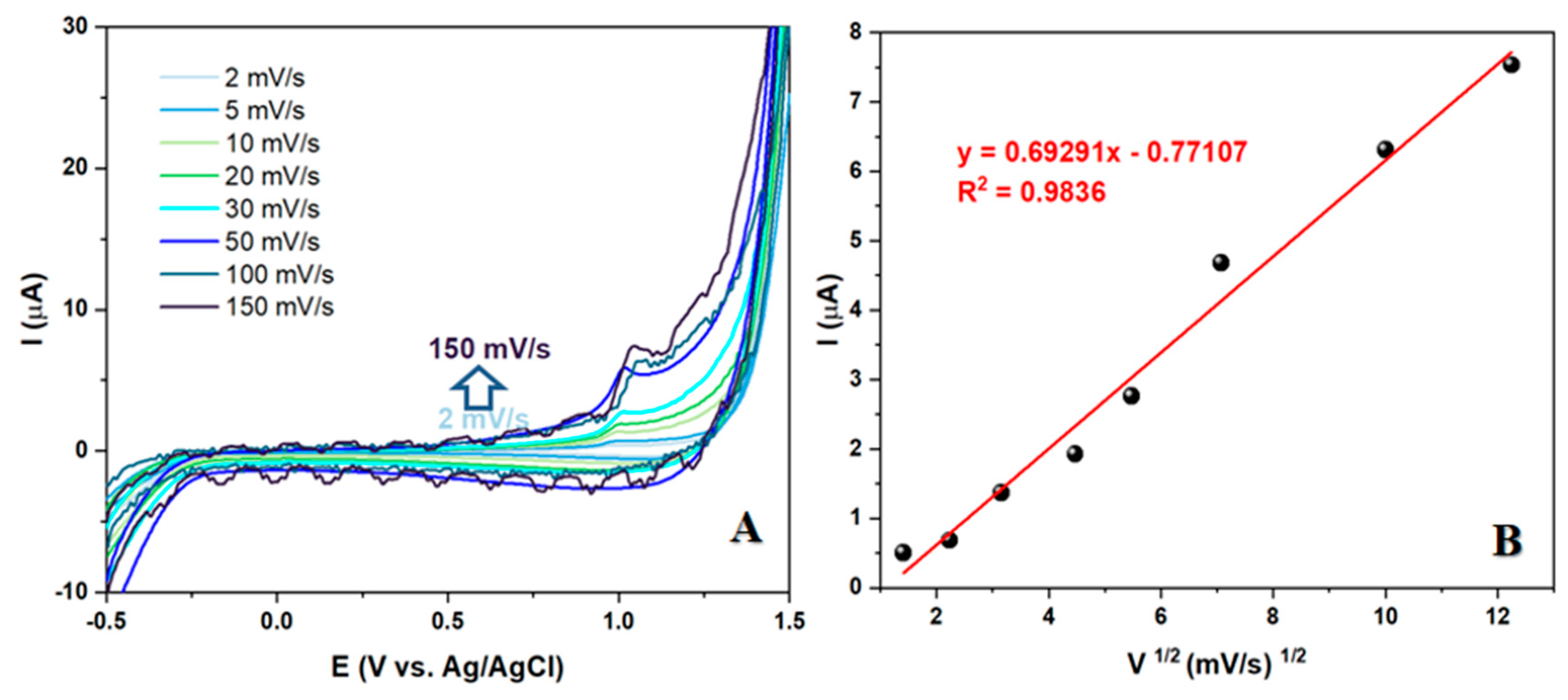
Figure 2D. This correlation suggests that the electrochemical reaction at the interface is diffusion-controlled, which provides valuable insights into the mechanisms of the reaction.
3.3. Detection of LEV
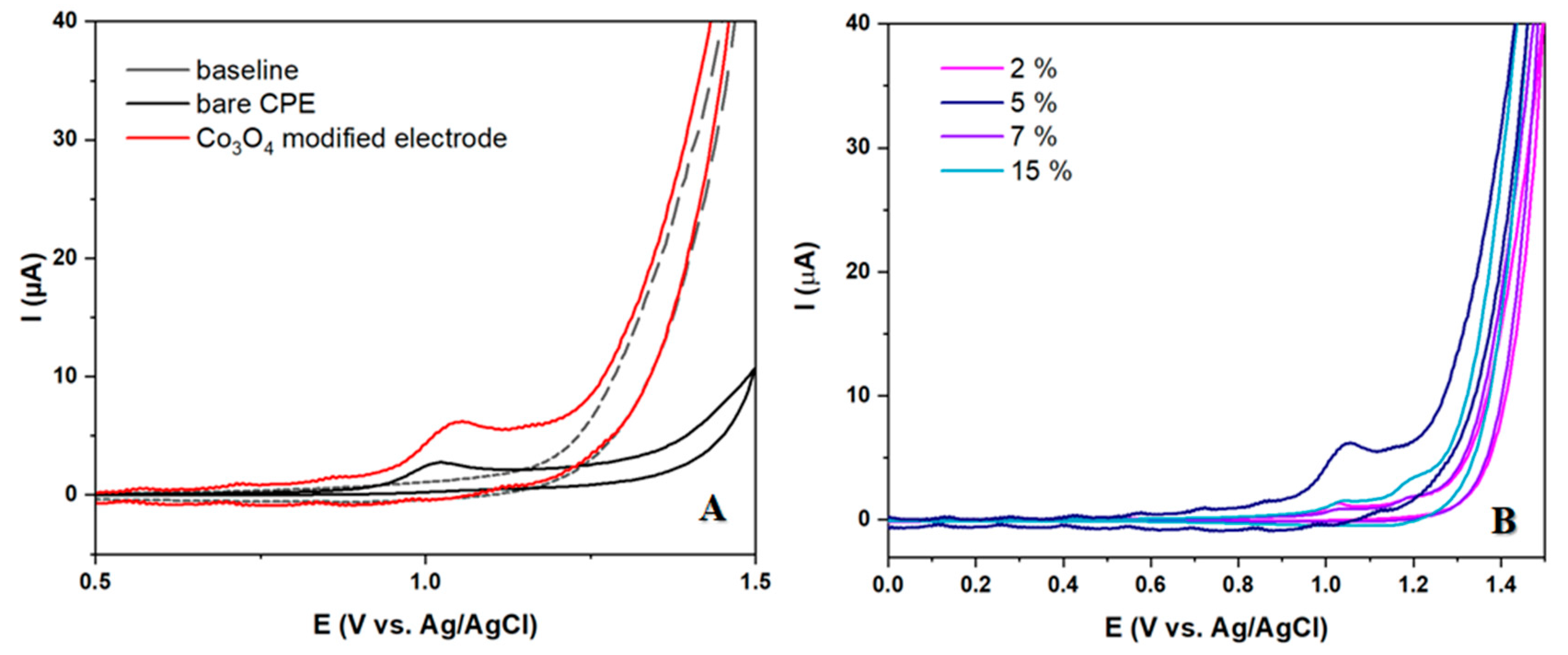
In this section we conducted a thorough investigation on the capability of prepared electrodes to detect 10 μm LEV. The findings revealed a distinct and precise peak resulting from the precipitated analyte at potentials just above 1 V, signifying its oxidation. The modified electrode exhibited a significantly higher peak current in comparison to the unmodified electrode. The impact of various modification percentages on the intensity and shape of the oxidation peak of LEV was thoroughly examined. Following the analysis, the electrode with a 5% modifier was deemed superior and chosen for further research. This electrode was utilized for all additional studies and the development of an analytical procedure for LEV detection.
Figure 3.
CV voltammograms of 50 μM LEV in BRBS at pH 5 for (A) bare and modified CP electrode (B) Modified CP electrodes with different amount of Co3O4 (2, 5, 7 and 15%).
Figure 3.
CV voltammograms of 50 μM LEV in BRBS at pH 5 for (A) bare and modified CP electrode (B) Modified CP electrodes with different amount of Co3O4 (2, 5, 7 and 15%).
3.4. Optimization of pH of the supporting electrolyte
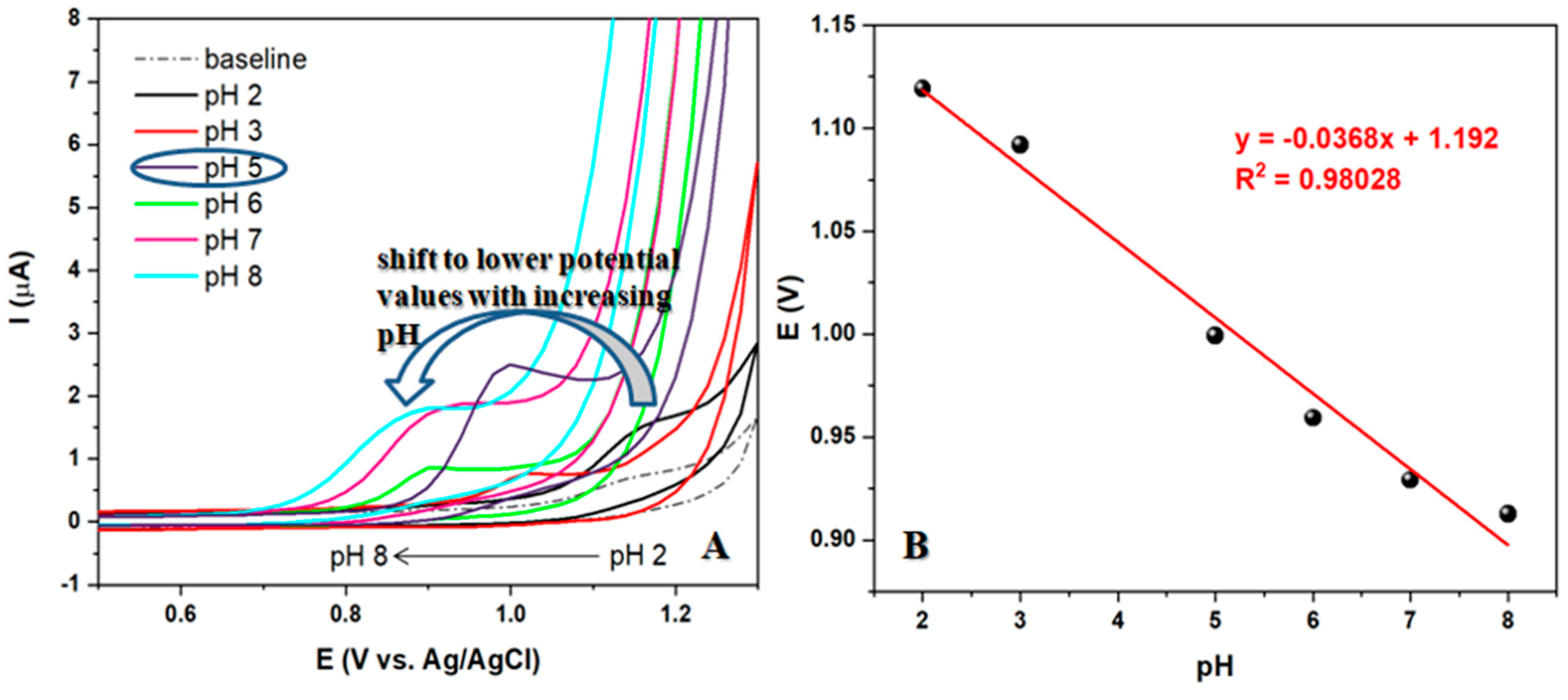
The electrode selected to test the optimal pH value of the supporting electrolyte produced interesting results. As seen in
Figure 4A, when using a scan rate of 50 mV/s in BRBS buffer with a range of pH values from 2 to 10 and a constant concentration of 50 µM of LEV, an increase in pH from 2 to 5 resulted in a double effect of an increase in peak current and a shift of the peak to less positive values. However, a further increase in pH resulted in a peak shift in the same direction, but with a decrease in peak current. It was observed that voltammograms at pH values above 9 did not show a corresponding peak originating from oxidized LEV. Therefore, pH 5 of BRBS buffer was selected for further recordings, which showed a well-defined and oval peak with the most intense current.
The peak potential shifts linearly with the increasing pH of the supporting electrolyte. This correlation can be expressed with the following equation: Ep = 1.19 - 0.037pH. The slope obtained for LEV oxidation process is close to the theoretical one (0.059) which suggested that the same number of protons and electrons are involved in the studied electrochemical reaction. According to the cyclic voltammetry theory for irreversible systems, the number of electrons in the LEV oxidation (n) was determined using the following equation: Ep - Ep1/2 = 47.7 mV/αn, where Ep, Ep1/2, α and n are potential peak, potential peak at half-height, electronic transfer coefficient (0.5), and the number of electrons, respectively. The number of electrons for the oxidation of LEV can be calculated as n = 1.6 ≈ 2 electrons per molecule of LEV.
3.5. Electrochemical behavior of LEV at different scan rates over Co3O4/CPE sensor
The recent study on the electrochemical behavior of LEV has yielded promising results. By examining the kinetics of the electrode reaction at the electrode/test solution interface at different scan rates, it was found that a higher scan speed led to an increase in Faraday and capacitive current. The oxidation current, in particular, displayed a linear dependence on the square root of the scan rate, indicating that the process occurring at the electrode is diffusion-controlled. This finding is significant as it makes the synthesized nanomaterial a strong contender for the development of an electroanalytical method for LEV detection. The study's results suggest that the nanomaterial's diffusion-controlled behavior could be leveraged to create a reliable and efficient method for detecting LEV.
Figure 5.
(A) CV measurements of a 50 μM solution of LEV in BRBS at pH 5 at different scan rates (B) Correlation between peak current and square root of scan rate.
Figure 5.
(A) CV measurements of a 50 μM solution of LEV in BRBS at pH 5 at different scan rates (B) Correlation between peak current and square root of scan rate.
3.6. Quantification of LEV
Our thorough investigation has revealed that square wave voltammetry (SWV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) are the two most efficient techniques for quantitative analysis in voltammetry. Upon conducting a detailed comparison of the voltammograms acquired through DPV and SWV, we have determined that the SWV method provides a superior peak with higher current and resolution. Therefore, we have decided to employ the SWV method for all our subsequent measurements as it offers faster measurement speed, improved detection limits, wider linear working ranges, and better measurement signal processing.
Figure 6.
Signals of 50 μM LEV solution in BRBS at pH 5 obtained by SWV and DPV.
Figure 6.
Signals of 50 μM LEV solution in BRBS at pH 5 obtained by SWV and DPV.
We conducted extensive research to optimize the working parameters for the SWV method, with the goal of improving the method's detection limit and signal discrimination. We used CPE with a 5% Co3O4 modified electrode in BRBS at pH 5, within a potential range of 0 to 1.1 V. To determine the optimal working parameters, we tested various potential increments ranging from 2 mV to 20 mV, as well as varied the frequency value from 10 to 90 Hz and the amplitude from 10 to 90 mV. After conducting these tests, we found that the ideal working parameters for the SWV method were a potential step of 5 mV, amplitude of 70 mV, and a frequency of 5 Hz. These optimized working parameters will significantly enhance the accuracy and precision of the SWV method. By implementing these parameters, we expect to achieve superior results in future experiments and further advance the field of electrochemical analysis.
The positive results obtained on the improvement of the characteristics of the electrode made of carbon paste were confirmed by examining the influence of different concentrations of analyte, using previously optimized parameters.
Figure 7. shows the dependence of the oxidation current on the added amount of standard LEV solution. A linear dependence was obtained for a wide range of concentrations from 1 to 85 μM. The calibration curve can be described by the equation Ap (VμA) = 0.003 + 0.001 × C (μM) with a linear regression coefficient (R) of 0.9975. The limit of detection (LOD) and the limit of quantification (LOQ) were calculated as 3S/b and 10S/b, respectively, where S is the standard deviation of three repeated blank measurements and b is the slope value of the calibration curve. The found values were 0.39 μM for LOD and 1.30 μM for LOQ.
An investigation of the repeatability of the LEV sensor was conducted. This study was carried out using LEV in BRBS pH 5 with 50 μM of analyte. The obtained results revealed that the relative standard deviation (RSD) for five consecutive measurements was 3.5%, indicating excellent repeatability. This data is immensely informative and provides a significant insight into the performance of the LEV sensor. It also highlights the potential applications of this sensor in various fields. Going forward, we aim to continue with our research and testing to further explore the capabilities of the LEV sensor and the potential impact it can make in different areas.
3.7. Interference measurement
To evaluate the selectivity of our method for detecting LEV, we conducted tests by introducing a standard solution of interfering substances to solutions containing 50 μm of LEV. Our findings revealed that the presence of ascorbic acid (AA) and glucose (Glu) did not interfere with the quantification of LEV, resulting in changes in current signal that were less than 3% and 7% respectively. On the other hand, the presence of oxalic acid (OA) and uric acid (UA) caused significant signal reduction, with changes of up to 25%. However, it is important to note that our proposed sensor can still be effectively utilized for determining the concentration of analytes in pharmaceutical formulations where the presence of OA and UA is not expected. Consequently, our results indicate a high degree of accuracy and reliability in our method for detecting LEV.
3.8. Application of a modified electrode for the determination of LEV
In order to test the practical applicability of the method for the quantification of LEV in real-time water samples, three different concentrations of LEV (13.56; 21.67 and 37.96 µM) were added. The results are presented in
Table 1 and demonstrate that the obtained recoveries were in the range of 94-106%. These results indicate that the proposed method is both reliable and reproducible, making it a promising tool for the analysis of LEV in water samples. The RSD values of measurements were below 5%, indicating that the LEV determination at the proposed sensor has good accuracy for real sample analysis. This level of accuracy means that the method can be applied to a range of samples with confidence. Overall, the results of this study highlight the potential of the proposed method for the analysis of LEV in water samples. Further research is certainly recommended to fully explore the capabilities and potential applications of this method. However, the initial findings indicate that this method is a reliable and reproducible tool for the quantification of LEV in real-time water samples.
4. Conclusion
In summary, we created a highly effective method for detecting and measuring Levofloxacin using cobalt oxide (Co3O4) nanomaterial as support for the carbon paste electrode. We meticulously examined the nanomaterial's morphological properties using advanced imaging techniques such as TEM, SEM, and XRD. The detection method we employed, SWV, proved to be exceptional, with a linear correlation concentration/current ranging from 1 to 85 μM, and a detection limit of 0.39 μM. We utilized this optimized method to analyze a real sample and obtained highly satisfactory results. This method can be readily applied in routine research with the use of a calibration line or the standard addition method. Additionally, our method does not require the use of organic solvents, making it significantly more environmentally friendly. Our team's development of energy-efficient and environmentally acceptable sensing methods can serve as a foundation for further research in this field, with the potential to transform this principle into an on-line and distance-controlled application.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.M. and D.S.; methodology D.S., D.M. and Dj.P., formal analysis, F.P., V.V.A.; investigation, T.M., D.S., V.S. and Dj.P.; resources, M.O. and V.S.; data curation, D.M., Dj.P. and F.P.; writing—original draft preparation, T.M., D.S., M.O. and V.S.; writing—review and editing, T.M.,M.O. and V.S.; supervision, M.O. and V.S.
Funding
This research has been financially supported by the Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of Republic of Serbia (Contract No: 451-03-47/2023-01/200026 and 451-03-47/2023-01/200168) and Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (agreement No. 075-15-2022-1135) and South Ural State University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The study did not report any data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- M. Rkik, M. Ben Brahim, and Y. Samet. Electrochemical determination of levofloxacin antibiotic in biological samples using boron-doped diamond electrode. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, vol. 794, pp. 175–181, Jun. 2017. [CrossRef]
- C. Siporin, C. L. Heifetz, and J. M. Domagala, Eds., The New generation of quinolones / edited by Clifford Siporin, Carl L. Heifetz, John M. Domagala. in Infectious disease and therapy; V. 5. New York: M. Dekker, 1990.
- J. S. Wolfson and D. C. Hooper, “Fluoroquinolone antimicrobial agents,” Clin Microbiol Rev, vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 378–424, Oct. 1989. [CrossRef]
- G. J. Anderson, “Quinolone Antimicrobial Agents, 3rd Edition,” Emerg Infect Dis, vol. 10, no. 6, pp. 1177a–11177, Jun. 2004. [CrossRef]
- V. L. Tunitskaya, A. R. Khomutov, S. N. Kochetkov, S. K. Kotovskaya, and V. N. Charushin, “Inhibition of DNA gyrase by levofloxacin and related fluorine-containing heterocyclic compounds.”. Acta Naturae 2011, 3, 94–99.
- V. Podder and N. M. Sadiq, Levofloxacin. 2023.
- M. H. Ghanbari, A. Khoshroo, H. Sobati, M. R. Ganjali, M. Rahimi-Nasrabadi, and F. Ahmadi, “An electrochemical sensor based on poly (l-Cysteine)@AuNPs @ reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for determination of levofloxacin,” Microchemical Journal, vol. 147, pp. 198–206, Jun. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Maleque, Md. R. Hasan, F. Hossen, and S. Safi, “Development and validation of a simple UV spectrophotometric method for the determination of levofloxacin both in bulk and marketed dosage formulations,” J Pharm Anal, vol. 2, no. 6, pp. 454–457, Dec. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhan, Y. Zhang, Q. Li, and X. Du, “Selective spectrophotometric determination of paracetamol with sodium nitroprusside in pharmaceutical and biological samples,” Journal of Analytical Chemistry, vol. 66, no. 2, pp. 215–220, Feb. 2011. [CrossRef]
- O. Szerkus et al., “Ultra-high performance liquid chromatographic determination of levofloxacin in human plasma and prostate tissue with use of experimental design optimization procedures,” J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci, vol. 1029–1030, pp. 48–59, Sep. 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. Attimarad, “Simultaneous determination of paracetamol and lornoxicam by RP-HPLC in bulk and tablet formulation,” Pharm Methods, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 61–66, Jan. 2011. [CrossRef]
- X. Shao, Y. Li, Y. Liu, and Z. Song, “Rapid determination of levofloxacin in pharmaceuticals and biological fluids using a new chemiluminescence system,” Journal of Analytical Chemistry, vol. 66, no. 1, pp. 102–107, Jan. 2011. [CrossRef]
- H. Khoshsafar, H. Bagheri, M. Rezaei, A. Shirzadmehr, A. Hajian, and Z. Sepehri, “Magnetic Carbon Paste Electrode Modified with a High Performance Composite Based on Molecularly Imprinted Carbon Nanotubes for Sensitive Determination of Levofloxacin,” J Electrochem Soc, vol. 163, no. 8, pp. B422–B427, 16. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- T. Mutić et al., “The influence of bismuth participation on the morphological and electrochemical characteristics of gallium oxide for the detection of adrenaline,” Anal Bioanal Chem, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. Özcan, F. Hamid, and A. A. Özcan, “Synthesizing of a nanocomposite based on the formation of silver nanoparticles on fumed silica to develop an electrochemical sensor for carbendazim detection,” Talanta, vol. 222, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Özcan and S. Ilkbaş, “Preparation of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanofibers modified pencil graphite electrode and investigation of over-oxidation conditions for the selective and sensitive determination of uric acid in body fluids,” Anal Chim Acta, vol. 891, pp. 312–320, Sep. 2015. [CrossRef]
- A. Özcan and S. Ilkbaş, “Poly(pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid)-modified pencil graphite electrode for the determination of serotonin in biological samples by adsorptive stripping voltammetry,” Sens Actuators B Chem, vol. 215, pp. 518–524, Aug. 2015. [CrossRef]
- K. Thangavelu, K. Parameswari, K. Kuppusamy, and Y. Haldorai, “A simple and facile method to synthesize Co3O4 nanoparticles from metal benzoate dihydrazinate complex as a precursor,” Mater Lett, vol. 65, no. 10, pp. 1482–1484, 11. 20 May. [CrossRef]
- K. Mariappan, saranvignesh Alagarsamy, S.-M. Chen, and S. Subramanian, “Electrochemical Detection of Metronidazole by the Fabricated Composites of Orthorhombic Iron Tungsten Oxide Decorated with Carbon Nanofiber Composites Electrode,” J Electrochem Soc, Mar. 2023. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).