Submitted:
09 July 2023
Posted:
11 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
The Motivation for This Study
Brief Rationale for the Novelty of the Proposed Research
The Objective of This Study
Materials and Methods
Brief Justification for Choosing GSDMM for Text Clustering in This Study
Dictionary Selection Rationale for the Algorithm GSDMM
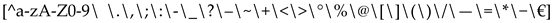 , from the resulting list, you can select the words you want to replace, then use a similar regular expression again to remove unnecessary characters, e.g., ®. I prefer such "manual" tests over the use of commonly available scripts, because I can see exactly what is changed, what is deleted, and the list of substitutions may vary depending on the task, for example, the program being applied may interrupt, considering one or another character unacceptable.
, from the resulting list, you can select the words you want to replace, then use a similar regular expression again to remove unnecessary characters, e.g., ®. I prefer such "manual" tests over the use of commonly available scripts, because I can see exactly what is changed, what is deleted, and the list of substitutions may vary depending on the task, for example, the program being applied may interrupt, considering one or another character unacceptable.Research Results
Preparing the Dictionary for the GSDMM
Results of Text Clustering Using the GSDMM Algorithm
Selection of Publications that Describe the Theme of the Cluster
Description of the Topics of the 9 Clusters, with the Texts of Short Abstracts of the Articles Selected for Each Cluster
Cluster 1. General Focus on Sustainable Energy Issues
Cluster 2. Highlighting Thermal Biomass Processing
Cluster 3. Highlighting the Problems of Specific Regions
Cluster 4. Building Energy Consumption Issues
Cluster 5. Economic Growth, Renewable Energy, and Investment Issues
Cluster 6. Numerical Flow Modeling Issues
Cluster 7. Generation Cost Optimization Planning Models and Generation Deviations
Cluster 8. The Smallest Cluster, Only 31 Entries. Thermal-to-Electrical Energy Conversion Problems
Cluster 9. Weather-Related Risk Issues and False Data Injection Attacks
Remark:
Conclusion
- Assessing the maturity and impact of the energy-based economy, SMART management concepts and social, technological, financial, economic, environmental and communication (S.T.F.E.C.) trends arising from the Industry 4.0 revolution on the competitiveness and creation of modern enterprises. Research priorities are the digitalization of the energy sector and its contribution to climate change mitigation and responsible consumption and production.
- A study to reduce sulphur emissions from the production and use of biomass briquettes. A study to characterize crop residues and determine the most suitable conditions for biomass gasification. A study to minimize the formation of heavy metals and tar when using syngas in internal combustion engines.
- Life cycle assessment of land use requirements for photovoltaic development. Energy policy and cross-sectoral cooperation studies. Issues of renewable energy viability in developing countries, regional integration and electricity demand. Assessment of sustainable development indicators, including biodiversity and mineral depletion.
- Identification of areas suitable for the integration of residential rooftop photovoltaic systems. Study spatial patterns of urban surface heat islands and their relationship to socio-economic, demographic and building characteristics. Development of heat exchangers to reduce temperature differences between indoors and outdoors. Investigation of the role of renewable energy sources in the domestic sphere.
- Study the role of environmental, social and governance factors to attract foreign direct investment in resource exporting countries. Research on the relationship between economic growth and the financing of renewable energy sources. A behavioral intention study on electric vehicles.
- Numerical simulation of mixed convective heat transfer using nanofluids in a heated reservoir. Experimental study of power take-off in a hydraulic system during start-up and long-term operation. Research and design of optical domes for hypersonic aircraft.
- Studies the impact of source load uncertainty on optimal scheduling in integrated power systems using hybrid resolution modelling and instruction cycle scheduling technology. Issues of operational planning and simultaneous operation of RES and HEPS. Modelling strategies for optimizing power flows in distribution networks.
- Study of combined multi-cooling and solar thermal power generation systems for waste heat recovery.
- Issues in the integration of renewable energy into energy systems. A study of the effect of clouds on solar radiation forecasting, predicting wind speed and solar radiation one day in advance. Analysis of cyber-attack detection and mitigation to protect primary and secondary control loops in power grids.
To do
References
- Van Eck NJ, Waltman L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010;84:523–38. [CrossRef]
- Aria M, Cuccurullo C. bibliometrix : An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. Journal of Informetrics 2017;11:959–75. [CrossRef]
- Grootendorst, M. MaartenGr/KeyBERT: BibTeX 2021. [CrossRef]
- Grootendorst, M. BERTopic: Neural topic modeling with a class-based TF-IDF procedure 2022. [CrossRef]
- Wadnare RJ, Sherekar DrSS, Thakare DrVM. Development of Text Clustering Method with K-Means for Analysis of Text Data. IJSRCSEIT 2021:143–51. [CrossRef]
- Duo J, Zhang P, Hao L. A K-means Text Clustering Algorithm Based on Subject Feature Vector. JWE 2021. [CrossRef]
- Uthirapathy SE, Sandanam D. Topic Modelling and Opinion Analysis On Climate Change Twitter Data Using LDA And BERT Model. Procedia Computer Science 2023;218:908–17. [CrossRef]
- Gupta RK, Agarwalla R, Naik BH, Evuri JR, Thapa A, Singh TD. Prediction of research trends using LDA based topic modeling. Global Transitions Proceedings 2022;3:298–304. [CrossRef]
- Mazarura J, De Waal A. A comparison of the performance of latent Dirichlet allocation and the Dirichlet multinomial mixture model on short text. 2016 Pattern Recognition Association of South Africa and Robotics and Mechatronics International Conference (PRASA-RobMech), Stellenbosch, South Africa: IEEE; 2016, p. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Weisser C, Gerloff C, Thielmann A, Python A, Reuter A, Kneib T, et al. Pseudo-document simulation for comparing LDA, GSDMM and GPM topic models on short and sparse text using Twitter data. Comput Stat 2023;38:647–74. [CrossRef]
- Zhao Y, Liang S, Ren Z, Ma J, Yilmaz E, De Rijke M. Explainable User Clustering in Short Text Streams. Proceedings of the 39th International ACM SIGIR conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Pisa Italy: ACM; 2016, p. 155–64. [CrossRef]
- Yin J, Wang J. A Text Clustering Algorithm Using an Online Clustering Scheme for Initialization. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco California USA: ACM; 2016, p. 1995–2004. [CrossRef]
- Campos R, Mangaravite V, Pasquali A, Jorge A, Nunes C, Jatowt A. YAKE! Keyword extraction from single documents using multiple local features. Information Sciences 2020;509:257–89. [CrossRef]
- Krovetz, R. Viewing morphology as an inference process. Proceedings of the 16th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval - SIGIR ’93, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States: ACM Press; 1993, p. 191–202. [CrossRef]
- Yin J, Wang J. A dirichlet multinomial mixture model-based approach for short text clustering. Proceedings of the 20th ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, New York New York USA: ACM; 2014, p. 233–42. [CrossRef]
- Adamik A, Nowicki M, Puksas A. Energy Oriented Concepts and Other SMART WORLD Trends as Game Changers of Co-Production—Reality or Future? Energies 2022;15:4112. [CrossRef]
- Stanisławski, R. Characteristics of Open Innovation among Polish SMEs in the Context of Sustainable Innovative Development Focused on the Rational Use of Resources (Energy). Energies 2022;15:6775. [CrossRef]
- Andriuškevičius K, Štreimikienė D. Energy M&A Market in the Baltic States Analyzed through the Lens of Sustainable Development. Energies 2022;15:7907. [CrossRef]
- Galkovskaya V, Volos M. Economic Efficiency of the Implementation of Digital Technologies in Energy Power. Sustainability 2022;14:15382. [CrossRef]
- Kemeç A, Altınay AT. Sustainable Energy Research Trend: A Bibliometric Analysis Using VOSviewer, RStudio Bibliometrix, and CiteSpace Software Tools. Sustainability 2023;15:3618. [CrossRef]
- Qi J, Li H, Wang Q, Han K. Combustion Characteristics, Kinetics, SO2 and NO Release of Low-Grade Biomass Materials and Briquettes. Energies 2021;14:2655. [CrossRef]
- Qian X, Xue J, Yang Y, Lee SW. Thermal Properties and Combustion-Related Problems Prediction of Agricultural Crop Residues. Energies 2021;14:4619. [CrossRef]
- Vincenti B, Gallucci F, Paris E, Carnevale M, Palma A, Salerno M, et al. Syngas Quality in Fluidized Bed Gasification of Biomass: Comparison between Olivine and K-Feldspar as Bed Materials. Sustainability 2023;15:2600. [CrossRef]
- Sanseverino ER, Cellura M, Luu LQ, Cusenza MA, Nguyen Quang N, Nguyen NH. Life-Cycle Land-Use Requirement for PV in Vietnam. Energies 2021;14:861. [CrossRef]
- Winquist E, Van Galen M, Zielonka S, Rikkonen P, Oudendag D, Zhou L, et al. Expert Views on the Future Development of Biogas Business Branch in Germany, The Netherlands, and Finland until 2030. Sustainability 2021;13:1148. [CrossRef]
- Uhunamure SE, Shale K. A SWOT Analysis Approach for a Sustainable Transition to Renewable Energy in South Africa. Sustainability 2021;13:3933. [CrossRef]
- Ahrens F, Land J, Krumdieck S. Decarbonization of Nitrogen Fertilizer: A Transition Engineering Desk Study for Agriculture in Germany. Sustainability 2022;14:8564. [CrossRef]
- Abdelhafez MHH, Touahmia M, Noaime E, Albaqawy GA, Elkhayat K, Achour B, et al. Integrating Solar Photovoltaics in Residential Buildings: Towards Zero Energy Buildings in Hail City, KSA. Sustainability 2021;13:1845. [CrossRef]
- Sidiqui P, Tariq MAUR, Ng AWM. An Investigation to Identify the Effectiveness of Socioeconomic, Demographic, and Buildings’ Characteristics on Surface Urban Heat Island Patterns. Sustainability 2022;14:2777. [CrossRef]
- Almasri RA, Abu-Hamdeh NH, Alajlan A, Alresheedi Y. Utilizing a Domestic Water Tank to Make the Air Conditioning System in Residential Buildings More Sustainable in Hot Regions. Sustainability 2022;14:15456. [CrossRef]
- Albatayneh A, Albadaineh R, Juaidi A, Abdallah R, Zabalo A, Manzano-Agugliaro F. Enhancing the Energy Efficiency of Buildings by Shading with PV Panels in Semi-Arid Climate Zone. Sustainability 2022;14:17040. [CrossRef]
- Chipalkatti N, Le QV, Rishi M. Sustainability and Society: Do Environmental, Social, and Governance Factors Matter for Foreign Direct Investment? Energies 2021;14:6039. [CrossRef]
- Guan D, Comite U, Sial MS, Salman A, Zhang B, Gunnlaugsson SB, et al. The Impact of Renewable Energy Sources on Financial Development, and Economic Growth: The Empirical Evidence from an Emerging Economy. Energies 2021;14:8033. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X, Chang M. Applying the Extended Technology Acceptance Model to Explore Taiwan’s Generation Z’s Behavioral Intentions toward Using Electric Motorcycles. Sustainability 2023;15:3787. [CrossRef]
- Rajpoot RS, Dhinakaran Shanmugam, Alam MdM. Numerical Analysis of Mixed Convective Heat Transfer from a Square Cylinder Utilizing Nanofluids with Multi-Phase Modelling Approach. Energies 2021;14:5485. [CrossRef]
- Niu Y, Gu X, Yue X, Zheng Y, He P, Chen Q. Research on Thermodynamic Characteristics of Hydraulic Power Take-Off System in Wave Energy Converter. Energies 2022;15:1373. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z, Zhang A, Pan J, Lu W, Sun Y. Fluid-Thermal Interaction Simulation of a Hypersonic Aircraft Optical Dome. Energies 2022;15:8619. [CrossRef]
- Liu Z, Guo F, Liu J, Lin X, Li A, Zhang Z, et al. A Compound Coordinated Optimal Operation Strategy of Day-Ahead-Rolling-Realtime in Integrated Energy System. Energies 2023;16:500. [CrossRef]
- Pareek P, Nguyen HD. State-Aware Stochastic Optimal Power Flow. Sustainability 2021;13:7577. [CrossRef]
- Ali A, Shaaban MF, Sindi HF. Optimal Operational Planning of RES and HESS in Smart Grids Considering Demand Response and DSTATCOM Functionality of the Interfacing Inverters. Sustainability 2022;14:13209. [CrossRef]
- Zheng F, Meng X, Wang L, Zhang N. Power Flow Optimization Strategy of Distribution Network with Source and Load Storage Considering Period Clustering. Sustainability 2023;15:4515. [CrossRef]
- Hammemi R, Elakhdar M, Tashtoush B, Nehdi E. Multi-Objective Optimization of a Solar Combined Power Generation and Multi-Cooling System Using CO2 as a Refrigerant. Energies 2023;16:1585. [CrossRef]
- Öksel C, Koç A. Modeling of a Combined Kalina and Organic Rankine Cycle System for Waste Heat Recovery from Biogas Engine. Sustainability 2022;14:7135. [CrossRef]
- Gao Y, Song Q, Su W, Lin X, Sun Z, Huang Z, et al. Experimentally Identifying the Influences of Key Parameters for an Organic Rankine Cycle Using R123. Sustainability 2023;15:814. [CrossRef]
- Blazakis K, Katsigiannis Y, Stavrakakis G. One-Day-Ahead Solar Irradiation and Windspeed Forecasting with Advanced Deep Learning Techniques. Energies 2022;15:4361. [CrossRef]
- EL-Ebiary A, Mokhtar M, Mansour A, Awad F, Marei M, Attia M. Distributed Mitigation Layers for Voltages and Currents Cyber-Attacks on DC Microgrids Interfacing Converters. Energies 2022;15:9426. [CrossRef]
| keyword | Score | Keyword | Score | Keyword | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | 5.37E-07 | Energy Management | 5.68E-06 | power generation | 1.12E-05 |
| energy system | 1.27E-06 | sustainable energy | 6.48E-06 | energy performance | 1.15E-05 |
| energy | 1.48E-06 | System | 6.55E-06 | energy generation | 1.19E-05 |
| energy consumption | 1.90E-06 | power | 7.68E-06 | Energy Power | 1.22E-05 |
| power system | 2.01E-06 | energy production | 8.40E-06 | energy demand | 1.25E-05 |
| energy storage | 2.38E-06 | energy transition | 8.45E-06 | storage system | 1.26E-05 |
| energy efficiency | 2.77E-06 | wind power | 9.02E-06 | sustainable development | 1.29E-05 |
| energy sources | 3.59E-06 | thermal energy | 9.22E-06 | energy resources | 1.31E-05 |
| solar energy | 3.97E-06 | case study | 9.78E-06 | systems | 1.38E-05 |
| wind energy | 5.01E-06 | Building Energy | 1.04E-05 | power plants | 1.43E-05 |
| Term | Term | Term | Term | Term |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| renewable | demand | electric | wave | economic |
| energy | development | flow | intensity | global |
| system | resources | integrated | future | neural |
| consumption | systems | battery | china | network |
| power | plants | distribution | quality | optimal |
| storage | sector | distributed | fuel | reduce |
| efficiency | hybrid | results | cell | planning |
| sources | green | security | models | research |
| solar | supply | vehicles | market | simulation |
| wind | model | poverty | optimization | operation |
| management | based | turbines | sustainability | primary |
| sustainable | analysis | clean | hydrogen | data |
| production | carbon | technologies | high | european |
| transition | emissions | cost | communities | union |
| thermal | photovoltaic | industry | saving | gas |
| case | potential | ghg | smart | paper |
| study | control | show | maximum | environmental |
| building | grid | method | heat | impact |
| generation | policy | recovery | current | conversion |
| performance | electrical | proposed | strategy | total |
| Cl-1 | Cl-2 | Cl-3 | Cl-4 | Cl-5 | Cl-6 | Cl-7 | Cl-8 | Cl-9 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| development | 187 | temperature | 66 | development | 175 | building | 150 | development | 93 | numerical | 124 | load | 104 | temperature | 20 | data | 153 |
| data | 104 | property | 62 | case | 148 | case | 78 | policy | 91 | temperature | 114 | problem | 100 | fluid | 12 | operation | 152 |
| important | 96 | biomass | 58 | plant | 134 | temperature | 61 | data | 82 | characteristic | 83 | operation | 92 | operation | 11 | voltage | 148 |
| case | 92 | material | 57 | policy | 119 | residential | 54 | china | 75 | fluid | 83 | schedule | 72 | net | 10 | load | 137 |
| article | 87 | combustion | 53 | future | 115 | data | 53 | country | 63 | case | 61 | case | 71 | plant | 9 | network | 135 |
| social | 87 | chemical | 51 | photovoltaic | 113 | city | 38 | finding | 63 | mass | 60 | objective | 71 | rankine | 9 | strategy | 109 |
| challenge | 84 | alternative | 48 | scenario | 109 | comfort | 38 | relationship | 59 | distribution | 58 | distribution | 66 | organic | 8 | photovoltaic | 108 |
| policy | 83 | surface | 46 | country | 108 | annual | 35 | growth | 57 | large | 58 | strategy | 66 | recovery | 8 | problem | 102 |
| framework | 79 | engine | 45 | costs | 103 | type | 35 | positive | 52 | turbine | 57 | effectiveness | 64 | refrigeration | 8 | wind | 100 |
| country | 77 | promising | 45 | wind | 103 | material | 34 | empirical | 49 | surface | 56 | network | 62 | turbine | 7 | converter | 95 |
| review | 77 | oil | 44 | fossil | 99 | environment | 33 | panel | 48 | important | 50 | distribute | 60 | configuration | 6 | accuracy | 94 |
| transition | 74 | organic | 43 | data | 95 | strategy | 33 | negative | 47 | development | 47 | wind | 59 | collector | 5 | machine | 93 |
| europe | 70 | solid | 39 | review | 93 | condition | 30 | evidence | 45 | dynamics | 47 | management | 57 | mass | 5 | neural | 86 |
| future | 70 | biodiesel | 38 | sector | 91 | construction | 30 | role | 42 | material | 46 | uncertainty | 54 | mathematics | 5 | controller | 85 |
| finding | 68 | type | 37 | strategy | 90 | load | 28 | green | 41 | data | 44 | voltage | 52 | capture | 4 | case | 83 |
| strategy | 68 | fossil | 34 | resources | 89 | saving | 27 | important | 40 | operation | 43 | battery | 51 | costs | 4 | error | 83 |
| related | 67 | density | 33 | transition | 86 | urban | 27 | industry | 39 | speed | 43 | dispatch | 49 | desalination | 4 | fault | 80 |
| sector | 67 | biofuel | 32 | important | 83 | important | 26 | economy | 35 | behavior | 42 | photovoltaic | 47 | generator | 4 | development | 79 |
| plan | 64 | cell | 31 | plan | 76 | alternative | 25 | regress | 34 | average | 41 | ieee | 46 | location | 4 | learning | 79 |
| literature | 63 | hydrogen | 31 | project | 74 | development | 25 | affect | 33 | wind | 40 | scenario | 45 | parametric | 4 | distribution | 78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





