Submitted:
03 July 2023
Posted:
03 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Samples and Sample Preparation
2.3. Extraction Method
2.4. Derivatization
2.5. GC-MS Parameters
2.6. Calibration Curve and Controls for GC-MS
2.7. LC-MS/MS Parameters
2.8. Calibration Curve and Controls for LC-MS/MS
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
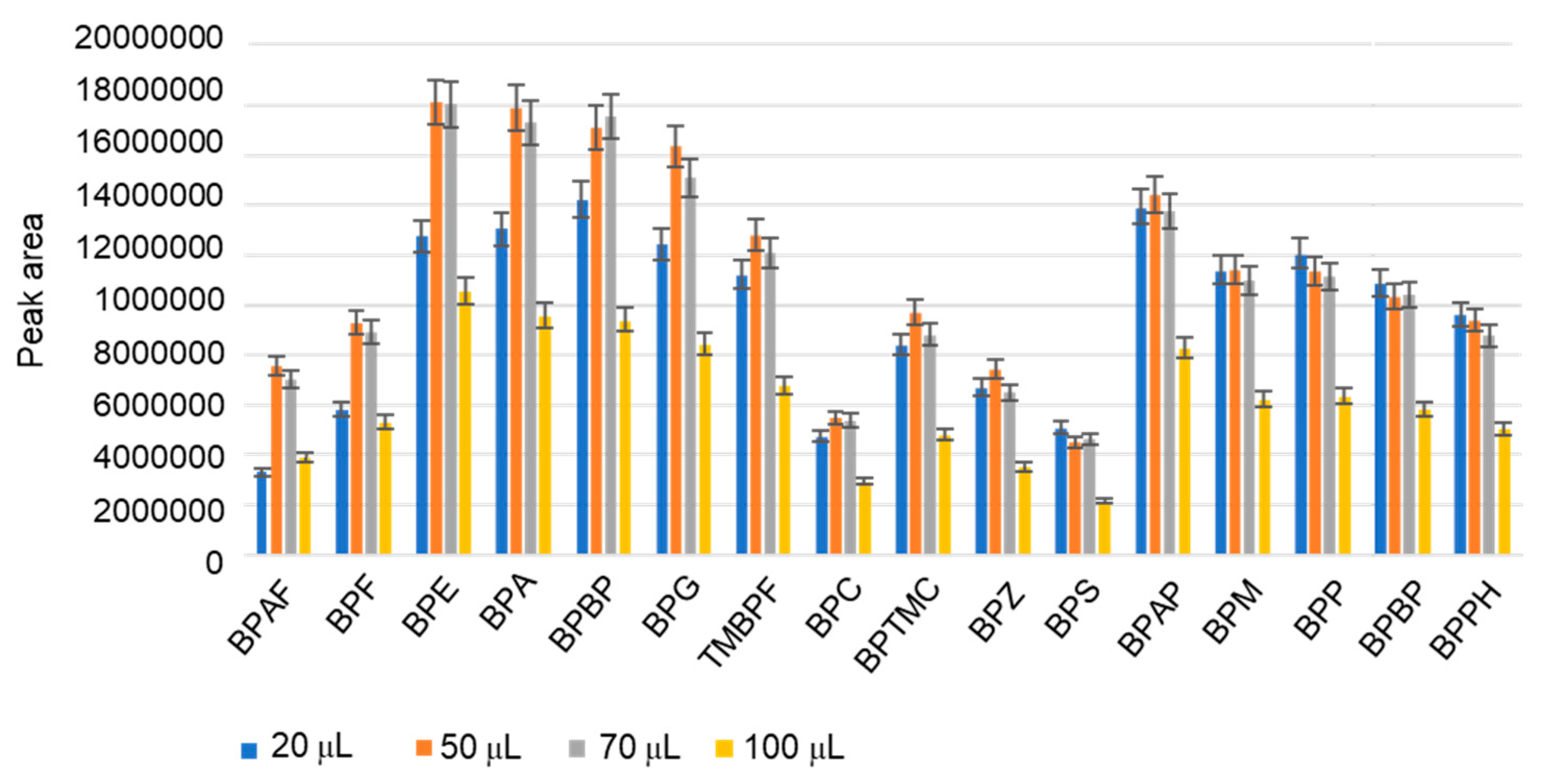
3.1. Optimization of the derivatization
3.2. Statystical validation of the extraction and analytical method
3.3. Quantitative results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pham, H. Q.; Marks, M. J. Epoxy Resins. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; p a09_547.pub2. [CrossRef]
- Serini, V. Polycarbonates. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. Ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2000; 21-207. [CrossRef]
- Bisphenol A market analysis: industry market size, plant capacity, production operating, efficiency, demand & sup-ply, end-user industries, sales channel, regional demand, company share, foreign trade, 2015-2032. Decode the fu-ture of bisphenol A. Last upaded May 2023. Available at https://www.chemanalyst.com/industry-report/bisphenol-a-market-57#:~:text=The%20global%20Bisphenol%20A%20market,the%20forecast%20period%20until%202032 (accessed 9.06.2023).
- Lamprea, K.; Bressy, A.; Mirande-Bret, C.; Caupos, E.; Gromaire, M.-C. Alkylphenol and Bisphenol A Contamination of Urban Runoff: An Evaluation of the Emission Potentials of Various Construction Materials and Automotive Sup-plies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25(22), 21887–21900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losada, P. P.; Paz Abuin, S.; Oderiz, L. V.; Lozano, J. S.; Gandara, J. S. Quality Control of Cured Epoxy Resins. J. Chromatogr. A 1991, 585(1), 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- vom Saal, F. S.; Nagel, S. C.; Coe, B. L.; Angle, B. M.; Taylor, J. A. The Estrogenic Endocrine Disrupting hemical Bi-sphenol A (BPA) and Obesity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 354 (1–2), 74–84. [CrossRef]
- Vandenberg, L. N.; Maffini, M. V.; Wadia, P. R.; Sonnenschein, C.; Rubin, B. S.; Soto, A. M. Exposure to Environmen-tally Relevant Doses of the Xenoestrogen Bisphenol-A Alters Development of the Fetal Mouse Mammary Gland. Endocrinology 2007, 148(1), 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarapore, P.; Ying, J.; Ouyang, B.; Burke, B.; Bracken, B.; Ho, S.-M. Exposure to Bisphenol A Correlates with Ear-ly-Onset Prostate Cancer and Promotes Centrosome Amplification and Anchorage-Independent Growth In Vitro. PLoS One 2014, 9(3), e90332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trasande, L.; Attina, T. M.; Blustein, J. Association Between Urinary Bisphenol A Concentration and Obesity Preva-lence in Children and Adolescents. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2012, 308 (11), 1113–1121. [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, V. Y.; Kim, D.; vom Saal, F. S.; Lamb, J. D.; Taylor, J. A.; Bloom, M. S. Serum Unconjugated Bisphenol A Concentrations in Women May Adversely Influence Oocyte Quality during in Vitro Fertilization. Fertil. Steril. 2011, 95(5), 1816–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, A.; Teppala, S. Relationship between Urinary Bisphenol A Levels and Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96(12), 3822–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, M.; Yuan, W.; He, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Gao, E.; Li, G.; Li, D.-K. In Utero Exposure to Bisphenol-A and Ano-genital Distance of Male Offspring. Birth Defects Res. A. Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2011, 91(10), 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Yang, B.-J.; Li, N.; Feng, L.-M.; Shi, X.-Y.; Zhao, W.-H.; Liu, S.-J. Bisphenol A and hormone-associated can-cers: Current progress and perspectives. Medicine 2015, 94, e211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenza, C.J.; Farooq, A.; Shubear, N.S.; Donkor, K.K. A targeted review on fate, occurrence, risk and health impli-cations of bisphenol analogues. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, S.; Raposo, A.; Almeida-González, M.; Carrascosa, C. Bisphenol A: food exposure and impact on human health. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1503–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, N.; Surendranath, A.R.; Pathak, J.L.; Yu, S.; Chung, C.Y. Bisphenol A (BPA) the mighty and the mutagenic. Tox-icol. Rep. 2018, 5, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Kannan, K.; Tan, H.; Zheng, Z.; Feng, Y.-L.; Wu, Y.; Widelka, M. Bisphenol Analogues Other Than BPA: Environmental Occurrence, Human Exposure, and Toxicity—A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50(11), 5438–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochester, J. R.; Bolden, A. L. Bisphenol S and F: A Systematic Review and Comparison of the Hormonal Activity of Bisphenol A Substitutes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123(7), 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Aimuzi, R.; Nian, M.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, K.; Zhang, J. Bisphenol A Substitutes and Sex Hormones in Children and Adolescents. Chemosphere 2021, 278, 130396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Yan, X.; Liao, C.; Jiang, G. Occurrence, fate and risk assessment of BPA and its substituents in wastewater treatment plant: A review. Environ. Res. 2019, 178, 108732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.; Barbato, F.; Mita, D.G.; Grumetto, L. Occurrence of Bisphenol A and its analogues in some foodstuff mar-keted in Europe. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 131, 110575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X. L. Recent Development on Analytical Methods for Determination of Bisphenol A in Food and Biological Samples. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2012, 35, 2795–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.-P.; Li, Y.-Z.; Guo, Z.-Q.; Zhang, X.-X.; Chang, W.-B. A new competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for determination of estrogenic bisphenols. Talanta 2002, 57(6), 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, J.; Xiong, E.; Li, X.; Chen, J. A novel electrochemical aptasensor for bisphenol A assay based on triple-signaling strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 79, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wu, S.; Duan, N.; Wang, Z. Mn2+-doped NaYF 4: Yb/Er upconversion nanoparticle-based electrochemilumi-nescent aptasensor for bisphenol A. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 3823–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Wu, J.; Chu, H.; Mei, Z.; Ye, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Peng, C.; Zheng, L.; Chen, W. Electrochemical aptasensor for the determination of bisphenol A in drinking water. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Yu, Y.; Li, R.; Eda, S.; Chen, J.; Feng, G.; Lawrie, B.; Hu, A. Bisphenol a sensors on polyi-mide fabricated by laser direct writing for onsite river water monitoring at attomolar concentration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8 (28), 17784-17792. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsami.6b 03743. [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, N.; Cunha, S. C.; Ferreira, R.; Fernandes, J. O.; Marques, M.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J. L. Concentrations of Nine Bisphenol Analogues in Food Purchased from Catalonia (Spain): Comparison of Canned and Non-Canned Foodstuffs. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 110992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Yuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Du, X.; Wang, R.; Marwa, P. W.; Petlulu, P.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H. The Ad-verse Health Effects of Bisphenol A and Related Toxicity Mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2019, 176, 108575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benachour, N.; Aris, A. Toxic Effects of Low Doses of Bisphenol-A on Human Placental Cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharma-col. 2009, 241 (3), 322–328. [CrossRef]
- Satoh, K.; Ohyama, K.; Aoki, N.; Iida, M.; Nagai, F. Study on Anti-Androgenic Effects of Bisphenol a Diglycidyl Ether (BADGE), Bisphenol F Diglycidyl Ether (BFDGE) and Their Derivatives Using Cells Stably Transfected with Human Androgen Receptor, AR-EcoScreen. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42(6), 983–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eladak, S.; Grisin, T.; Moison, D.; Guerquin, M.-J.; N’Tumba-Byn, T.; Pozzi-Gaudin, S.; Benachi, A.; Livera, G.; Rouiller-Fabre, V.; Habert, R. A New Chapter in the Bisphenol A Story: Bisphenol S and Bisphenol F Are Not Safe Alternatives to This Compound. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 103(1), 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreman, J.; Lee, O.; Trznadel, M.; David, A.; Kudoh, T.; Tyler, C. R. Acute Toxicity, Teratogenic, and Estrogenic Effects of Bisphenol A and Its Alternative Replacements Bisphenol S, Bisphenol F, and Bisphenol AF in Zebrafish Embryo-Larvae. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51(21), 12796–12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Zhan, H.; Hu, J.; Zhang, T.; Xu, H.; Wong, M.; Xu, B.; Zheng, C. The Occurrence, Potential Toxicity, and Tox-icity Mechanism of Bisphenol S, a Substitute of Bisphenol A: A Critical Review of Recent Progress. Ecotoxicol. Envi-ron. Saf. 2019, 173, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.; Capuozzo, A.; Barbato, F.; Irace, C.; Santamaria, R.; Grumetto, L. Cytotoxicity of Seven Bisphenol Ana-logues Compared to Bisphenol A and Relationships with Membrane Affinity Data. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wang, B.; Han, L.; Wang, L.; Sun, H.; Chen, L. Association of Urinary Concentrations of Bi-sphenols with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Case-Control Study. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M. H.; Woodward, M.; Bao, W.; Liu, B.; Trasande, L. Urinary Bisphenols and Obesity Prevalence Among U. S. Children and Adolescents. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3(9), 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, I. C.; Cohenour, E. R.; Harnett, K. G.; Schuh, S. M. BPA, BPAF and TMBPF Alter Adipogenesis and Fat Ac-cumulation in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells, with Implications for Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22(10), 5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnett, K. G.; Chin, A.; Schuh, S. M. BPA and BPA Alternatives BPS, BPAF, and TMBPF, Induce Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis in Rat and Human Stem Cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 216, 112210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, F.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Geng, C.; Wang, W.; Zhong, L.; Yang, G.; Chen, M. Bisphenol A Induces Oxidative Stress-Associated DNA Damage in INS-1 Cells. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2014, 769, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Liu, X.; Takeda, S.; Choi, K. Genotoxic Potentials and Related Mechanisms of Bisphenol A and Other Bi-sphenol Compounds: A Comparison Study Employing Chicken DT40 Cells. Chemosphere 2013, 93(2), 434–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hercog, K.; Maisanaba, S.; Filipič, M.; Sollner-Dolenc, M.; Kač, L.; Žegura, B. Genotoxic Activity of Bisphenol A and Its Analogues Bisphenol S, Bisphenol F and Bisphenol AF and Their Mixtures in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HepG2) Cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Song, H.; Choi, J.; Sim, S.; Kojima, H.; Park, J.; Iida, M.; Lee, Y. The Mixture Effects of Bisphenol Derivatives on Estrogen Receptor and Androgen Receptor. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Lin, B.; Hu, C.; Zhang, H.; Lin, Z.; Xi, Z. The Combined Toxicological Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparti-cles and Bisphenol A on Zebrafish Embryos. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9(1), 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission regulation (EU). Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 November 2009 on cosmetic products. Official Journal of the European Union.
- Commission directive (EU) No 2011/8/EU of 28 January 2011 Amending Directive 2002/72/EC as Regards the Re-striction of Use of Bisphenol A in Plastic Infant Feeding Bottles. Official Journal of the European Union.
- Commission implementing regulation (EU) No 321/2011 of 1 April 2011 Amending Regulation (EU) No 10/2011 as Regards the Restriction of Use of Bisphenol A in Plastic Infant Feeding Bottles. Official Journal of the European Union.
- Commission regulation (EU) No 10/2011 of 14 January 2011 on Plastic Materials and Articles Intended to Come into Contact with Food. Official Journal of the European Union.
- Commission regulation (EU) No 2018/213 of 12 February 2018 on the Use of Bisphenol A in Varnishes and Coatings Intended to Come into Contact with Food and Amending Regulation (EU) No 10 / 2011 as Regards the Use of That Substance in Plastic Food Contact Materials. Official Journal of the European Union.
- Commission regulation (EU) No 609/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 12 June 2013 on Food Intended for Infants and Young Children, Food for Special Medical Purposes, and Total Diet Replacement for Weight Control and Repealing Council Directive 92/52/EEC, Commission Directives 96/8/EC, 1999/21/EC, 2006/125/EC and 2006/141/EC, Directive 2009/39/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council and Commission Regulations (EC) No 41/2009 and (EC) No 953/2009. Official Journal of the European Union.
- Commission directive (EU) No 2017/898 of 24 May 2017 Amending, for the Purpose of Adopting Specific Limit Val-ues for Chemicals Used in Toys, Appendix C to Annex II to Directive 2009/48/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on the Safety of Toys, as Regards Bisphenol A. Official Journal of the European Union.
- Federal Department of Home Affairs FDHA, Federal Office of Public Health (FOPH). Factsheet BPA-December 2020. Consulted in June 2023.
- Lucarini, F.; Krasniqi, T.; Bailat Rosset, G.; Roth, N.; Hopf, N.B.; Broillet, M.-C.; Staedler, D. Exposure to New Emerging Bisphenols Among Young Children in Switzerland. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission (EC). Joint Research Centre. Institute for Health and Consumer Protection. Guidelines for Performance Criteria and Validation Procedures of Analytical Methods Used in Controls of Food Contact Materials; Publications Office: LU, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Vinas, P.; Campillo, N.; Martinez-Castillo, N.; Hernandez-Cordoba, M. Comparison of Two Derivatization-Based Methods for Solid-Phase Microextraction–Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometric Determination of Bisphenol A, Bisphenol S and Biphenol Migrated from Food Cans. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397(1), 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, R.; Horwitz, W. A Heuristic Derivation of the Horwitz Curve. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69(4), 789–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taverniers, I.; Van Bockstaele, E.; De Loose, M. Analytical Method Validation and Quality Assurance. In Pharma-ceutical Sciences Encyclopedia; S.C. Gad (Ed.). John Wiley & Sons, Inc. Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010, 396. [CrossRef]
- Cunha, S. C.; Fernandes, J. O. Assessment of Bisphenol A and Bisphenol B in Canned Vegetables and Fruits by Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry after QuEChERS and Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction. Food Control 2013, 33(2), 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, N.; Cunha, S. C.; Ferreira, R.; Fernandes, J. O.; Marques, M.; Nadal, M.; Domingo, J. L. Concentrations of Nine Bisphenol Analogues in Food Purchased from Catalonia (Spain): Comparison of Canned and Non-Canned Foodstuffs. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 136, 110992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geens, T.; Apelbaum, T. Z.; Goeyens, L.; Neels, H.; Covaci, A. Intake of Bisphenol A from Canned Beverages and Foods on the Belgian Market. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2010, 27(11), 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S. C.; Cunha, C.; Ferreira, A. R.; Fernandes, J. O. Determination of Bisphenol A and Bisphenol B in Canned Seafood Combining QuEChERS Extraction with Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction Followed by Gas Chro-matography–Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404(8), 2453–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Ret. Time (min) | Target Ion (m/z) | Ref. Ions (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BPAF | 18.95 | 411.00 | 480.00, 412.00, 225.00 |
| BPF | 20.285 | 344.00 | 179.00, 345.00, 157.00 |
| BPE | 20.550 | 343.00 | 344.00, 358.00, 193.00 |
| BPA d16 | 20.790 | 368.00 | 369.00, 386.00, 217.00 |
| BPA | 20.860 | 357.00 | 358.00, 372.00, 207.00 |
| BPB | 21.555 | 357.00 | 358.00, 191.00, 221.00 |
| BPG | 21.790 | 441.00 | 442.00, 456.00, 249.00 |
| TMBPF | 22.925 | 385.00 | 400.00, 386.00, 207.00 |
| BPC | 22.970 | 424.00 | 426.00, 374.00, 354.00 |
| BPZ | 23.950 | 369.00 | 412.00, 370.00, 203.00 |
| Bisphenol TMC | 24.210 | 383.00 | 384.00, 454.00, 397.00 |
| BPS | 24.590 | 394.00 | 379.00, 135.00, 229.00 |
| BPAP | 24.845 | 419.00 | 420.00, 269.00, 434.00 |
| BPM | 26.125 | 475.00 | 476.00, 490.00, 387.00 |
| BPP | 27.400 | 475.00 | 476.00, 490.00, 230.00 |
| BPBP | 28.225 | 419.00 | 420.00 331.00, 496.00 |
| BPPH | 28.395 | 509.00 | 510.00, 542.00, 267.00 |
| Name | Ret. Time (min) | Acquisition segment (min) | Precursor ion (m/z) | Product ion (m/z) |
Collision energy (eV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPS | 7.381 | 3.82-8.32 | 249.2 | 108.1 156.0 |
15 25 |
| BPF | 11.469 | 5.00-12.878 | 199.1 | 93.0 105.0 |
22 22 |
| BPE | 12.578 | 7.00-16.00 | 213.0 | 197.9 118.8 |
12 22 |
| BPA d-16 | 13.378 | 9.915 | 241.1 | 222.9 141.9 |
19 24 |
| BPAF | 15.332 | 11.925-16.925 | 335.0 | 196.9 176.8 |
38 45 |
| BPA | 13.516 | 10.067-15.027 | 226.9 | 211.8 132.9 |
19 26 |
| BPB | 14.705 | 11.28-16.28 | 241.0 | 211.9 225.9 |
18 18 |
| BPC | 15.021 | 11.589-16.589 | 279.0 | 35.0 71.0 |
17 16 |
| BPAP | 15.435 | 12.068-17.068 | 289.0 | 274.0 195.0 |
21 26 |
| BPZ | 16.041 | 12.63-17.63 | 267.2 | 173.0 222.9 |
20 25 |
| BPG | 17.984 | 14.754-19.754 | 311.2 | 295.1 175.1 |
29 25 |
| Bisphenol TMC | 18.172 | 14.866-19.866 | 309.1 | 237.0 200.0 |
33 30 |
| BPBP | 16.989 | 13.665-18.665 | 351.1 | 273.2 258.0 |
27 26 |
| Bisphenol M+P | 18.037 | 14.728-19.728 | 345.0 | 330.0 133.0 |
25 35 |
| Analyte | R2 | Instrumental trueness (%) | LOD | LOQ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPAF | 0.999841 | 95-113 | 0.39 | 1.32 |
| BPF | 0.999998 | 99-105 | 0.04 | 0.15 |
| BPE | 0.999935 | 97-123 | 0.25 | 0.84 |
| BPA | 0.999732 | 94-118 | 0.51 | 1.71 |
| BPB | 0.999990 | 87-102 | 0.10 | 0.33 |
| BPG | 0.999861 | 96-128 | 0.37 | 1.23 |
| TMBPF | 0.999923 | 97-126 | 0.27 | 0.92 |
| BPC | 0.999573 | 93-122 | 0.65 | 2.16 |
| BP-TMC | 0.999658 | 93-119 | 0.58 | 1.93 |
| BPZ | 0.999960 | 89-109 | 0.20 | 0.67 |
| BPS | 0.998243 | 86-105 | 1.66 | 5.55 |
| BPAP | 0.999649 | 93-145 | 0.59 | 1.96 |
| BPM | 0.999750 | 94-112 | 0.5 | 1.65 |
| BPP | 0.999804 | 95-107 | 0.04 | 0.15 |
| BPBP | 0.999913 | 96-104 | 0.03 | 0.10 |
| BPPH | 0.998776 | 74-141 | 0.11 | 0.37 |
| Analyte | Pineapple | Peaches | Soup | Fruit puree | Ravioli | Farce Vol-aux-vent | Tuna | Lemon | Cola light | Beer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BPAF | 91 | 73 | 82 | 79 | 84 | 99 | 100 | 97 | 94 | 103 |
| BPF | 81 | 87 | 79 | 75 | 97 | 80 | 82 | 91 | 96 | 100 |
| BPE | 91 | 98 | 91 | 84 | 85 | 85 | 95 | 100 | 88 | 99 |
| BPA | 97 | 108 | 98 | 92 | 84 | 78 | 94 | 100 | 106 | 99 |
| BPB | 68 | 115 | 97 | 90 | 100 | 70 | 91 | 101 | 96 | 101 |
| BPG | 91 | 92 | 110 | 104 | 84 | 92 | 51 | 87 | 91 | 92 |
| TMBPF | 108 | 118 | 119 | 134 | 98 | 102 | 68 | 100 | 101 | 101 |
| BPC | 103 | 94 | 96 | 88 | 102 | 97 | 71 | 89 | 93 | 103 |
| BPTMC | 110 | 120 | 90 | 82 | 93 | 89 | 123 | 86 | 89 | 95 |
| BPZ | 100 | 101 | 102 | 94 | 105 | 92 | 72 | 92 | 100 | 103 |
| BPS | 114 | 78 | 105 | 102 | 137 | 156 | 123 | 81 | 106 | 78 |
| BPAP | 100 | 111 | 107 | 97 | 103 | 133 | 46 | 90 | 99 | 94 |
| BPM | 108 | 126 | 104 | 108 | 96 | 83 | 29 | 93 | 100 | 111 |
| BPP | 107 | 105 | 97 | 90 | 93 | 92 | 28 | 97 | 102 | 96 |
| BPBP | 101 | 107 | 85 | 81 | 92 | 87 | 28 | 97 | 93 | 106 |
| BPPH | 103 | 103 | 107 | 101 | 102 | 104 | 25 | 99 | 95 | 111 |
| A. Fruits and vegetable soup: pineapple pulp and canned water (CW), peaches pulp and canned water (CW), and vegetable soup. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analyte | Pineapple- CW | Pineapple Pulp | Peaches- CW | Peaches- Pulp | Soup (1) | Soup (2) | LOD | LOQ | ||||||||||||||
| BPAF | 1.78 | < LOD | <LOD | < LOQ | < LOQ | < LOD | 0.39 | 1.32 | ||||||||||||||
| BPF | <LOD | 0.18 | 0.42 | 0.89 | <LOD | < LOD | 0.04 | 0.15 | ||||||||||||||
| BPE | <LOD | < LOD | < LOQ | 2.62 | 1.24 | < LOD | 0.25 | 0.84 | ||||||||||||||
| BPA | < LOQ | 3.21 | < LOD | < LOQ | < LOD | < LOQ | 0.51 | 1.71 | ||||||||||||||
| BPB | < LOD | 0.60 | < LOD | < LOD | < LOD | < LOD | 0.10 | 0.33 | ||||||||||||||
| B. Fruit purees for children. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analyte | Puree (1) | Puree (2) | Puree (3) | Puree (4) | LOD | LOQ | ||||||||||||||||
| BPE | 1.37 | 0.56 | 0.67 | 0.53 | 0.25 | 0.84 | ||||||||||||||||
| BPA | < LOQ | < LOD | 12.72 | < LOQ | 0.51 | 1.71 | ||||||||||||||||
| BPB | < LOD | < LOD | < LOD | 1.37 | 0.10 | 0.33 | ||||||||||||||||
| BPS | 6.65 | 8.12 | 11.11 | < LOD | 1.66 | 5.55 | ||||||||||||||||
| C. Complex matrices of canned food: ravioli, farce vol-aux vent, and canned tuna. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analyte | Ravioli (1) | Ravioli (2) | Ravioli (3) | Ravioli (4) | Ravioli (5) | Farce Vol-aux-vent (1) | Farce Vol-aux-vent (2) | Tuna | LOD | LOQ | ||||||||||||
| BPAF | < LOD | < LOQ | < LOQ | < LOQ | < LOQ | < LOQ | < LOQ | < LOD | 0.39 | 1.32 | ||||||||||||
| BPE | < LOD | < LOD | < LOD | < LOD | < LOD | < LOD | < LOD | 1.28 | 0.25 | 0.84 | ||||||||||||
| BPA | 21.67 | 26.44 | 36.80 | 26.18 | 22.13 | 40.65 | 37.47 | 10.82 | 0.51 | 1.71 | ||||||||||||
| BPB | 1.12 | 1.79 | 3.91 | 1.92 | 1.83 | 6.90 | 5.11 | < LOD | 0.10 | 0.33 | ||||||||||||
| BPS | 7.42 | 7.13 | 6.74 | 10.44 | 5.58 | < LOD | < LOD | 6.55 | 1.66 | 5.55 | ||||||||||||
| BPM | < LOD | < LOD | < LOD | < LOD | < LOD | < LOD | < LOD | 4.36 | 0.50 | 1.65 | ||||||||||||
| D. Canned beverages: cola light, lemon soft drink, beers | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Analyte | Lemon | Cola light | Beer (1) | Beer (2) | LOD | LOQ | ||||||||||||||||
| BPA | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.51 | 1.71 | ||||||||||||||||
| TMBPF | < LOD | < LOD | 5.62 | 1.02 | 0.27 | 0.92 | ||||||||||||||||
| BPS | < LOD | < LOD | <LOQ | <LOQ | 1.66 | 5.55 | ||||||||||||||||
| Samples | BPA (LC-MS/MS) |
BPA (LC-MS/MS) Recovery (%) | BPA (GC-MS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ravioli (4) | 26.84 | 67 | 26.18 |
| Ravioli (5) | 22.33 | 81 | 22.13 |
| Farce vol-aux-vent (2) | 27.35 | 92 | 37.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





