Submitted:
30 June 2023
Posted:
03 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study design
2.2. Setting and participants
2.3. Variables and Data sources
2.4. Statistical methods
3. Results
3.1. Participant characteristics
3.2. Biomarker predictive ability in patients with sepsis and a SOFA score ≤6
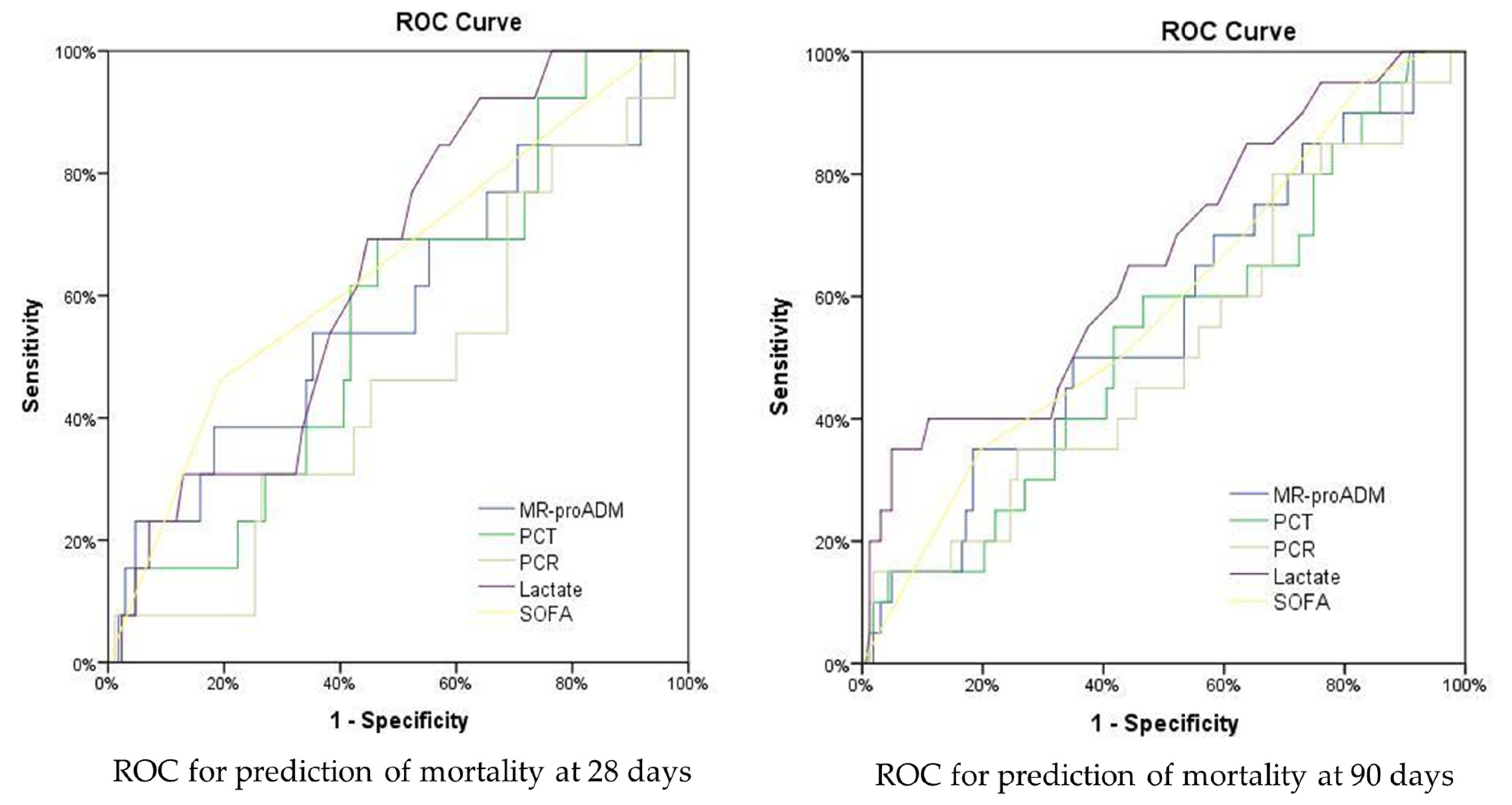
| Analyses | ||||||||
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||||
| Biomarker or clinical score | Patients (N) | AUROC | OR IQR (95% CI) | OR IQR (95% CI) | ||||
| M28d | MR-proADM | 284 | 0.57 [0.45 - 0.69] | 1.08 [0.94 – 1.24] | 1.13 [0.82 – 1.56] | |||
| PCT | 274 | 0.47 [0.35 - 0.59] | 0.99 [0.98 – 1.01] | 0.99 [0.97 – 1.02] | ||||
| CRP | 237 | 0.49 [0.36 - 0.62] | 1.00 [0.99 – 1.01] | 1.01 [0.98 – 1.04] | ||||
| Lactate | 229 | 0.67 [0.55 - 0.79] | 1.13 [0.95 – 1.34] | 0.85 [0.49 – 1.49] | ||||
| SOFA | 284 | 0.63 [0.52 - 0.73] | 1.43 [1.03 – 1.97] | 1.63 [0.69 – 3.84] | ||||
| M90d | MR-proADM | 284 | 0.59 [0.49 - 0.68] | 1.08 [0.96 – 1.21] | 0.93 [0.72 – 1.20] | |||
| PCT | 274 | 0.44 [0.34 - 0.54] | 1.00 [0.99 – 1.00] | 0.99 [0.97 – 1.01] | ||||
| CRP | 237 | 0.54 [0.43 - 0.65] | 1.00 [0.99 – 1.01] | 1.00 [0.98 – 1.03] | ||||
| Lactate | 229 | 0.66 [0.55 - 0.77] | 1.25 [1.07 – 1.46] | 1.50 [0.90 – 2.50] | ||||
| SOFA | 284 | 0.62 [0.54 - 0.71] | 1.40 [1.08 – 1.81] | 1.31 [0.70 – 2.43] | ||||
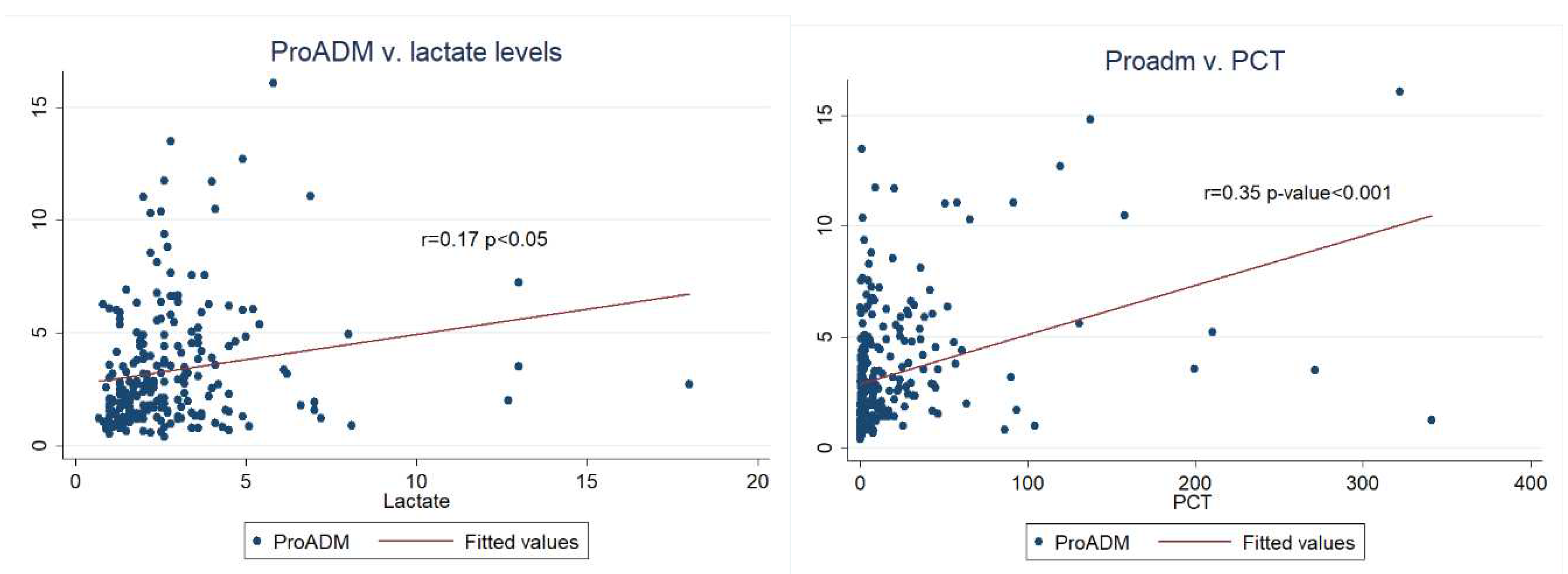
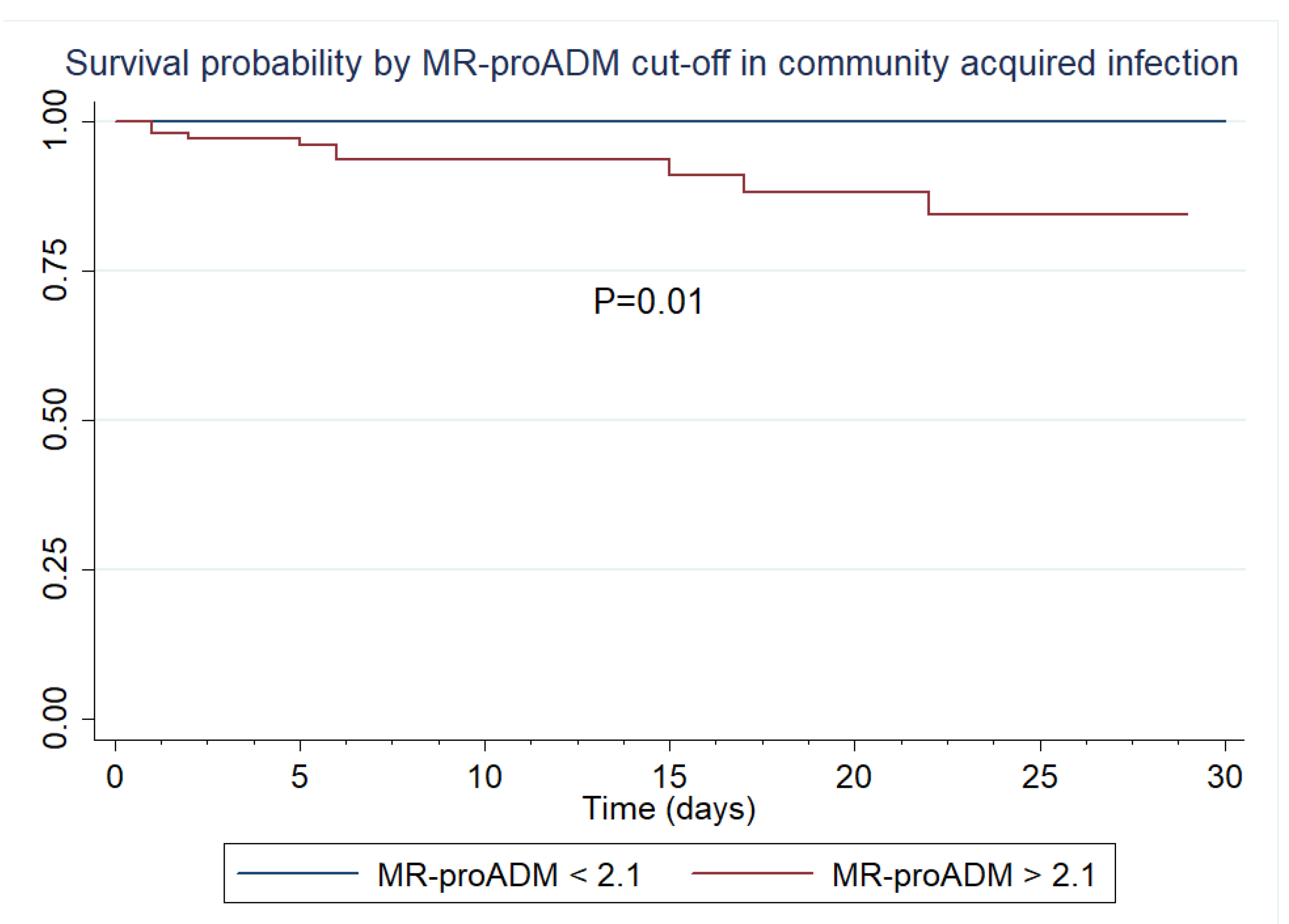
3.3. Inter-biomarker associations and 28-day survival analysis in patients with sepsis and a SOFA score ≤6
4. Discussion
4.1. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yébenes, J.C.; SOCMIC (Catalonian Critical Care Society) Sepsis Working Group; Ruiz-Rodriguez, J.C.; Ferrer, R.; Clèries, M.; Bosch, A.; Lorencio, C.; Rodriguez, A.; Nuvials, X.; Martin-Loeches, I.; et al. Epidemiology of sepsis in Catalonia: analysis of incidence and outcomes in a European setting. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2017, 7, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.-D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, J.-L.; Marshall, J.C.; A Ñamendys-Silva, S.A.; François, B.; Martin-Loeches, I.; Lipman, J.; Reinhart, K.; Antonelli, M.; Pickkers, P.; Njimi, H.; et al. Assessment of the worldwide burden of critical illness: the Intensive Care Over Nations (ICON) audit. Lancet Respir. Med. 2014, 2, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, M.C.; Scherag, A.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Hartog, C.S.; Tsaganos, T.; Schlattmann, P.; Angus, D.C.; Reinhart, K.; International Forum of Acute Care Trialists. Assessment of Global Incidence and Mortality of Hospital-treated Sepsis. Current Estimates and Limitations. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldirà, J.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, J.C.; Wilson, D.C.; Ruiz-Sanmartin, A.; Cortes, A.; Chiscano, L.; Ferrer-Costa, R.; Comas, I.; Larrosa, N.; Fàbrega, A.; et al. Biomarkers and clinical scores to aid the identification of disease severity and intensive care requirement following activation of an in-hospital sepsis code. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.E.; Trzeciak, S.; Kline, J.A. The Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score for predicting outcome in patients with severe sepsis and evidence of hypoperfusion at the time of emergency department presentation*. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 37, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoto, S.; Nobile, E.; Carnà, E.P.R.; Fogolari, M.; Caputo, D.; De Florio, L.; Valeriani, E.; Benvenuto, D.; Costantino, S.; Ciccozzi, M.; et al. Best diagnostic accuracy of sepsis combining SIRS criteria or qSOFA score with Procalcitonin and Mid-Regional pro-Adrenomedullin outside ICU. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.L.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, J.C.; Ferrer, R. Improving knowledge about sepsis 3 definition in critically ill patients: new insights. J. Emerg. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 2, 39–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprung, C.L.; Schein, R.M.H.; Balk, R.A. The new sepsis consensus definitions: the good, the bad and the ugly. Intensiv. Care Med. 2016, 42, 2024–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, J.-L.; de Mendonca, A.; Cantraine, F.; Moreno, R.; Takala, J.; Suter, P.M.; Sprung, C.L.; Colardyn, F.; Blecher, S. Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 26, 1793–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.L.; Bota, D.P.; Bross, A.; Mélot, C.; Vincent, J.-L. Serial Evaluation of the SOFA Score to Predict Outcome in Critically Ill Patients. JAMA 2001, 286, 1754–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; Mcintyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e1063–e1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeletti, S.; Spoto, S.; Fogolari, M.; Cortigiani, M.; Fioravanti, M.; De Florio, L.; Curcio, B.; Cavalieri, D.; Costantino, S.; Dicuonzo, G. Diagnostic and prognostic role of procalcitonin (PCT) and MR-pro-Adrenomedullin (MR-proADM) in bacterial infections. APMIS 2015, 123, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeletti, S.; Dicuonzo, G.; Fioravanti, M.; De Cesaris, M.; Fogolari, M.; Presti, A.L.; Ciccozzi, M.; De Florio, L. Procalcitonin, MR-Proadrenomedullin, and Cytokines Measurement in Sepsis Diagnosis: Advantages from Test Combination. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeletti, S.; Ciccozzi, M.; Fogolari, M.; Spoto, S.; Presti, A.L.; Costantino, S.; Dicuonzo, G. Procalcitonin and MR-proAdrenomedullin combined score in the diagnosis and prognosis of systemic and localized bacterial infections. J. Infect. 2015, 72, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela-Sánchez, F.; Valenzuela-Méndez, B.; Rodríguez-Gutiérrez, J.F.; Estella-García. ; González-García, M.. New role of biomarkers: mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin, the biomarker of organ failure. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 329–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elke, G.; the SepNet Critical Care Trials Group; Bloos, F. ; Wilson, D.C.; Meybohm, P. Identification of developing multiple organ failure in sepsis patients with low or moderate SOFA scores. Crit. Care 2018, 22, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hur, M.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Di Somma, S. Circulating Biologically Active Adrenomedullin Predicts Organ Failure and Mortality in Sepsis. Ann. Lab. Med. 2019, 39, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ-Crain, M.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Struck, J.; Harbarth, S.; Bergmann, A.; Müller, B. Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin as a prognostic marker in sepsis: an observational study. Crit. Care 2005, 9, R816–R824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoto, S.; Fogolari, M.; De Florio, L.; Minieri, M.; Vicino, G.; Legramante, J.; Lia, M.S.; Terrinoni, A.; Caputo, D.; Costantino, S.; et al. Procalcitonin and MR-proAdrenomedullin combination in the etiological diagnosis and prognosis of sepsis and septic shock. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer R, Ruiz-Rodriguez JC, Larrosa N, Llaneras J, Molas E, González-López JJ. Sepsis code implementation at Vall d'Hebron University Hospital: rapid diagnostics key to success. ICU Management & Practice. 2017;17(4).
- Li, F.; He, H. Assessing the Accuracy of Diagnostic Tests. Shanghai Arch Psychiatry 2018, 30, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuetz, P.; Albrich, W.; Christ-Crain, M.; Chastre, J.; Mueller, B. Procalcitonin for guidance of antibiotic therapy. Expert Rev. Anti-infective Ther. 2010, 8, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, P.; Aujesky, D.; Müller, C.; Müller, B. Biomarker-guided personalised emergency medicine for all – hope for another hype? Swiss Med Wkly. 2015, 145, w14079–w14079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, P.; Christ-Crain, M.; Thomann, R.; Falconnier, C.; Wolbers, M.; Widmer, I.; Neidert, S.; Fricker, T.; Blum, C.; Schild, U.; et al. Effect of Procalcitonin-Based Guidelines vs Standard Guidelines on Antibiotic Use in Lower Respiratory Tract Infections. JAMA 2009, 302, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuetz, P.; Batschwaroff, M.; Dusemund, F.; Albrich, W.; Bürgi, U.; Maurer, M.; Brutsche, M.; Huber, A.R.; Müller, B. Effectiveness of a procalcitonin algorithm to guide antibiotic therapy in respiratory tract infections outside of study conditions: a post-study survey. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 29, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuetz, P.; Chiappa, V.; Briel, M.; Greenwald, J.L. Procalcitonin Algorithms for Antibiotic Therapy Decisions. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuetz, P.; Wirz, Y.; Sager, R.; Christ-Crain, M.; Stolz, D.; Tamm, M.; Bouadma, L.; E Luyt, C.; Wolff, M.; Chastre, J.; et al. Procalcitonin to initiate or discontinue antibiotics in acute respiratory tract infections. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2019, CD007498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, A.J.; Ng, J.; Thode, H.C.; Spiegel, R.; Weingart, S. Quick SOFA Scores Predict Mortality in Adult Emergency Department Patients With and Without Suspected Infection. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2017, 69, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.Q. New Sepsis Criteria. Chest 2016, 149, 1117–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.Q. SIRS in the Time of Sepsis-3. Chest 2018, 153, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, S.Q.; Q. , S. Diagnosing sepsis: a step forward, and possibly a step back. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 55–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Does, Y.; Limper, M.; Jie, K.E.; Schuit, S.C.; Jansen, H.; Pernot, N.; van Rosmalen, J.; Poley, M.J.; Ramakers, C.; Patka, P.; et al. Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic therapy in patients with fever in a general emergency department population: a multicentre non-inferiority randomized clinical trial (HiTEMP study). Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, K.; del Castillo, J.G.; Backous, C.; Drevet, S.; Ferrer, R.; Gavazzi, G.; Gluck, E.; Jensen, J.-U.; Kanizsai, P.; Ruiz-Rodríguez, J.C.; et al. Hot topics on procalcitonin use in clinical practice, can it help antibiotic stewardship? Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temmesfeld-Wollbrück, B.; Hocke, A.; Suttorp, N.; Hippenstiel, S. Adrenomedullin and endothelial barrier function. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 98, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittard, A.J.; Hawkins, W.J.; Webster, N.R. The role of the microcirculation in the multi-organ dysfunction syndrome. Clin. Intensiv. Care 1994, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, W.-S.; Yin, Y.; Chan, E.C.; Terai, K.; Long, L.M.; Myers, T.G.; Dudek, A.Z.; Druey, K.M. Adrenomedullin surges are linked to acute episodes of the systemic capillary leak syndrome (Clarkson disease). J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 103, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigué, B.; Leblanc, P.-E.; Moati, F.; Pussard, E.; Foufa, H.; Rodrigues, A.; Figueiredo, S.; Harrois, A.; Mazoit, J.-X.; Rafi, H.; et al. Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin (MR-proADM), a marker of positive fluid balance in critically ill patients: results of the ENVOL study. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viaggi, B.; Poole, D.; Tujjar, O.; Marchiani, S.; Ognibene, A.; Finazzi, S. Mid regional pro-adrenomedullin for the prediction of organ failure in infection. Results from a single centre study. PLOS ONE 2018, 13, e0201491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andaluz-Ojeda, D.; Nguyen, H.B.; Meunier-Beillard, N.; Cicuéndez, R.; Quenot, J.-P.; Calvo, D.; Dargent, A.; Zarca, E.; Andrés, C.; Nogales, L.; et al. Superior accuracy of mid-regional proadrenomedullin for mortality prediction in sepsis with varying levels of illness severity. Ann. Intensiv. Care 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Patient population (N =284) |
Survivors (N = 260) |
Non-Survivors (N = 24) |
p-value | |
| Age (years) (mean, S.D.) | 63 (16) | 62 (16) | 70 (9) | 0.001 |
| Female gender (N, %) | 107 (37.7) | 100 (38.5) | 7 (29.2) | 0.36 |
| Definition of sepsis | ||||
| Severe sepsis (N, %) | 184 (64.8) | 170 (65.4) | 14(58.3) | 0.489 |
| Septic shock (N, %) | 100 (35.2) | 90 (34.6) | 10 (41.7) | 0.489 |
| Location of sepsis code activation | ||||
| Emergency Department (N, %) | 138 (48.6) | 127 (48.8) | 11 (45.8) | 0.793 |
| Ward (N, %) | 90 (31.7) | 83 (31.9) | 7 (29.2) | 0.781 |
| ICU (N, %) | 56 (19.7) | 50 (19.2) | 6 (25) | 0.497 |
| Surgical admissions (N, %) | 104 (36.6) | 95 (36.5) | 9 (37.5) | 0.925 |
| Medical admissions (N, %) | 180 (63.4) | 165 (63.5) | 15 (62.5) | 0.925 |
| ICU length of stay (days) (median, IQR) | 4 [2-9] | 3 [2-8] | 11 [5-15] | 0.125 |
| Hospital length of stay (days) (median, IQR) | 13 [6-30] | 14 [7-32] | 7 [3-17] | 0.016 |
| Life-supporting and intensive care therapies | ||||
| Vasopressors (N, %) | 100 (35.2) | 90 (34.6) | 10 (41.7) | 0.489 |
| Renal replacement therapy (N, %) | 11 (8.5) | 9 (7.5) | 2 (20) | 0.172 |
| Mechanical ventilation (N, %) | 51 (18) | 43 (16.5) | 8 (33.3) | 0.04 |
| Mechanical ventilation duration (days) (median, IQR) | 5 [3-12] | 4 [2-8] | 12 [7-16] | 0.02 |
| High Flow Nasal Cannula use (N, %) | 41 (31.5) | 35 (29.2) | 6 (60) | 0.044 |
| Pre-existing comorbidities | ||||
| Cardiopathy (N, %) | 71 (25) | 65 (25) | 6 (25) | 1.00 |
| Chronic Kidney Disease (N, %) | 50 (17.6) | 47 (18.1) | 3 (12.5) | 0.492 |
| COPD (N, %) | 49 (17.3) | 45 (17.3) | 4 (16.7) | 0.937 |
| Immunosuppression (N, %) | 129 (45.4) | 112 (43.1) | 17 (70.8) | 0.009 |
| Liver cirrhosis (N, %) | 12 (4.2) | 9 (3.5) | 3 (12.5) | 0.035 |
| Microbiology | ||||
| Positive blood culture (N, %) | 108 (38.2) | 99 (38.2) | 9 (37.5) | 0.622 |
| Gram-positive (N, %) | 39 (35.1) | 34 (33.3) | 5 (55.6) | 0.291 |
| Gram-negative (N, %) | 70 (63.1) | 66 (64.7) | 4 (44.4) | 0.343 |
| Fungal (N, %) | 2 (1.8) | 2 (2) | 0 (0) | 0.666 |
| Origin of infection | ||||
| Abdominal (N, %) | 76 (26.8) | 72 (27.7) | 4 (16.7) | 0.243 |
| Bacteria - primary (N, %) | 11 (3.9) | 10 (3.8) | 1 (4.2) | 0.938 |
| Catheter-related (N, %) | 11 (3.9) | 10 (3.8) | 1 (4.2) | 0.938 |
| Central Nervous System (N, %) | 1 (0.4) | 1 (0.4) | 0 (0) | 0.761 |
| Respiratory (N, %) | 68 (23.9) | 57 (21.9) | 11 (45.8) | 0.009 |
| Soft-tissue (N, %) | 18 (6.3) | 16 (6.2) | 2 (8.3) | 0.675 |
| Urinary (N, %) | 84 (29.6) | 79 (30.4) | 5 (20.8) | 0.327 |
| Unknown (N, %) | 8 (2.8) | 8 (3.1) | 0 (0) | 0.383 |
| Other (N, %) | 7 (2.5) | 7 (2.7) | 0 (0) | 0.416 |
| Source control | ||||
| Debridement of infectious foci (N, %) | 15 (5.4) | 14 (5.5 | 1 (4.3) | 0.799 |
| Drainage (N, %) | 40 (14.4) | 38 (14.9) | 2 (8.7) | 0.397 |
| Surgery (N, %) | 35 (12.6) | 33 (12.9) | 2 (8.7) | 0.534 |
| Biomarker and severity scores | ||||
| MR-proADM (nmol/L) (median, IQR) | 2.48 [1.46-4.38] | 2.43 [1.45-4.2] | 2.85 [1.8-4.98] | 0.236 |
| PCT (ng/mL) (median, IQR) | 3.09 [0.7-16,.1] | 3.10 [0.7-17.5] | 3.51[0.7-8.8] | 0.665 |
| Lactate (mmol/L) (mean, SD) | 2.75 (2.09) | 2.70 (2.10) | 3.48 (1.84) | 0.147 |
| CRP (mg/L) (mean, SD) | 56.43 (288.39) | 46.18 (258.14) | 156.57 (494) | 0.312 |
| SOFA (points) (median, IQR) | 4 [3-6] | 4 [3-6] | 5 [4-6] | 0.027 |
| APACHE II (points) (mean, SD) | 19.71 (8.29) | 19.10 (8.11) | 26.50 (7.61) | 0.015 |
| Analyses | ||||||||
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||||
| Biomarker or clinical score | Patients (N) | AUROC | OR IQR (95% CI) | OR IQR (95% CI) | ||||
| Community | MR-proADM | 176 | 0.70 [0.58 – 0.82] | 1.11 [0.91 – 1.35] | 2.11 [0.7 –6.39] | |||
| PCT | 168 | 0.41 [0.30 – 0.52] | 0.92 [0.82 – 1.04] | 0.93 [0.79 –1.11] | ||||
| CRP | 147 | 0.55 [0.32 – 0.78] | 1.01 [1.00 – 1.03] | 1.01 [0.83 –1.25] | ||||
| Lactate | 142 | 0.65 [0.48 – 0.82] | 1.09 [0.75 – 1.56] | 1.31 [0.85 –20.20] | ||||
| SOFA | 176 | 0.69 [0.54 – 0.84] | 1.80 [0.98 – 3.30] | - | ||||
| Hospital | MR-proADM | 108 | 0.48 [0.30 – 0.66] | 1.07 [0.88 – 1.30] | 1.00 [0.69 – 1.46] | |||
| PCT | 106 | 0.53 [0.35 – 0.71] | 1.00 [0.99 – 1.00] | 1.01 [0.96 – 1.06] | ||||
| CRP | 87 | 0.49 [0.32 – 0.66] | 0.99 [0.98 – 1.01] | 1.00 [0.95 – 1.04] | ||||
| Lactate | 93 | 0.70 [0.54 – 0.86] | 1.14 [0.93 – 1.38] | 0.86 [0.44 – 1.65] | ||||
| SOFA | 108 | 0.57 [0.43 – 0.71] | 1.23 [0.85 – 1.77] | 1.18 [0.54 – 2.59] | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





