1. Introduction
Burn injuries pose significant challenges and have severe consequences for patients' health [
1]. As the body's largest organ, the skin plays a critical role in protection. However, the process of regenerating damaged skin, which consists of specialized layers of fibroblasts and keratinocytes, is complex. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) possess remarkable capabilities for self-renewal and differentiation into various cell types and tissues. They can migrate from their niche to distant tissues, thereby playing a crucial role in wound healing and tissue regeneration [
2]. The human umbilical cord lining (UC) has emerged as a promising source of MSCs. Umbilical cord lining mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) offer several advantages, including non-invasive collection methods for autologous or allogeneic use, lower risk of infection, minimal teratoma formation, versatility, and low immunogenicity with immunosuppressive properties [
3]. Animal studies have demonstrated the diverse roles and beneficial effects of MSCs in promoting wound healing, reducing burn-induced inflammation, and preventing pathological scarring during burn recovery [
1]. Animal studies have demonstrated the diverse roles and beneficial effects of MSCs in promoting wound healing, reducing inflammation caused by burns, and preventing pathological scarring during burn recovery [
1].
The corneal epithelium is a stratified tissue that undergoes rapid regeneration and is crucial for maintaining transparency. Its functionality relies on limbal stem cells located in the basal region of the limbus [
4,
5]. Limbal stem cell deficiency (LSCD) can occur due to various conditions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, chemical burns, cicatricial pemphigoid, and aniridic keratopathy, leading to significant visual impairment [6-8]. Conventional cornea transplantation has limited success in treating LSCD, posing a significant challenge for clinicians. However, the transplantation of adult stem cells, specifically autologous or allogeneic limbal stem cells, has shown promising initial outcomes in addressing these conditions [
9,
10]. Additionally, cultured conjunctival transplantation has emerged as a viable approach for reconstructing the ocular surface and treating various eye diseases [
11,
12]. In cases of bilateral limbal stem cell loss, bioengineered oral mucosal epithelial cell transplantation has been proposed as an alternative solution [13-15]. Unfortunately, transplanted stem cells often experience reduced proliferative capacity over time, leading to graft failure and the need for repeated transplantation [
9].
This study aims to evaluate the isolation and differentiation characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells from the umbilical cord lining membrane and assess the effectiveness of their transplantation in treating experimental thermal burn wounds.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Umbilical cord lining tissue samples
The umbilical cord lining tissues were collected using strict sterile procedures immediately after delivery from consenting pregnant women [
16]. Detailed records of the tissue supply were maintained, including the maternal full name, contact address, consent for tissue donation, and results of prenatal tests or examinations. These records, which encompass both the tissue supply information and screening test results, are securely stored at the Department of Burn Treatment Application Research Laboratory - Vietnam National Institute of Burns. Before collection, the mother's medical history underwent a thorough screening to identify potential human pathogens such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B and C viruses (HBV and HCV), and syphilis.
2.2. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells
Umbilical cord lining mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) were obtained using the explant method, following the protocols described by Freshney and Bich-Phuong et al. [
17,
18].
In cases of natural vaginal childbirth, the umbilical cord tissue was subjected to a Betadine scrub to ensure cleanliness. The cord tissue sample was then dissected to remove the jelly-like substance and blood vessels. Disinfection of the umbilical cord lining was performed using 70% ethanol, followed by rinsing with PBS. Small tissue samples measuring approximately 0.3 cm2 were prepared from the umbilical cord lining and placed in plastic culture flasks containing intermediate mesenchymal stem cell culture medium (Mekostem, Singapore). The seeding density used was 1 tissue sample per 5 cm2. The culture dishes were maintained in a 37°C CO2 incubator with regular medium replacement every 2-3 days. The cultured samples were carefully monitored under an inverted microscope until the emergence of star-shaped or diamond-shaped cells from the tissue samples was observed.
Upon reaching approximately 50% confluence on the culture surface, the cells were detached using the trypsin procedure. Once the cell density reached 8,000 cells/cm2, the cells were transferred to new dishes to facilitate their expansion for 3-4 passages, allowing for further investigation in the development of equivalent tissue scaffolds.
The trypsin/EDTA procedure was employed following the manufacturer's guidelines (Merck, Germany). The culture dishes were cleansed with PBS buffer (0.2 mL/cm2), and a 0.25% Trypsin/EDTA solution (0.1 mL/cm2) was added to the dishes, followed by incubation in a 37°C CO2 incubator for 5-10 minutes. After incubation, fresh culture medium (0.1-0.2 mL/cm2) was added to the dishes, and the cell suspension was collected using centrifuge tubes for cell count determination. The cell tubes were centrifuged at 1,200 rpm for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was discarded. Fresh culture medium was added to the tubes to facilitate further experimentation.
2.3. Transplantation replicates the number of umbilical cord lining mesenchymal stem cells
2.3.1. Evaluation of the ability of cells to create colony
A suspension of individual cells was prepared and introduced into plastic culture dishes with a diameter of 60 mm, at a seeding density of 50 cells per square centimeter. Subsequently, the culture dishes were incubated for a period of 2-3 weeks to observe the formation and development of colonies. Following this incubation period, the cell cultures were fixed using absolute ethanol and stained with Giemsa (Merck, USA). A cluster of cells was recognized as a colony if it consisted of at least 50 cells [
19].
2.3.2. Number and characteristics of cell morphology
Cell quantification was performed using the Neubauer counting chamber [
18]. Cell proliferation and appearance were examined using a phase-contrast microscope. The cellular structure was assessed through Giemsa staining of tissue samples. Tissue morphology was visualized using HE-stained tissue sections. Ultrastructural features were observed using an electron microscope.
2.4. Investigating the expression of HLA antigens of mesenchymal stem cells
Following isolation, mesenchymal stem cells were propagated through third-generation (G3) transplantation [
18]. Subsequently, cells were collected for HLA antigen analysis. HLA types were analyzed using western blot and flow cytometry techniques.
2.4.1. Analysis of the expression of HLA-G and HLA-E
HLA-G and HLA-E expression analysis was performed using western blot techniques at the Laboratory of Cell Research Corporation, National University of Singapore. Umbilical cord lining mesenchymal stem cells were subjected to ultragrinding using ultrasound waves to extract their proteins. Super-crushed proteins (100 μg) were loaded into each well and separated by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis on a 14% acrylamide gel. Following separation, the proteins were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane through electrophoretic transfer in the second direction. The membrane, containing the target antigens, was then blocked with a 2% BSA solution to prevent nonspecific binding. Subsequently, the membrane was incubated with primary antibodies specific to HLA-G or anti-HLA-E. After incubation with an enzyme-conjugated secondary antibody, the antigen-antibody reaction specific to HLA-G or HLA-E was visualized by using a specific substrate to generate a colorimetric signal [
20].
2.4.2. Analysis of the expression of HLA-DR
Flow cytometry techniques were employed to analyze HLA-DR expression in the Stem Cell Laboratory of the University of Natural Sciences, Vietnam National University Ho Chi Minh City. Third-generation mesenchymal stem cells were obtained by treating them with 0.25% trypsin/EDTA. The resulting single-cell suspension was centrifuged at 3,000 rpm for 5 minutes and then adjusted to a density of 10.5 cells/100 μL. The cells were subsequently stained with anti-HLA-DR antibodies. To perform the staining, 100 μL of the cell suspension containing 10.5 cells/100 μL was mixed with 20 μL of the appropriate antibodies and incubated for 30 minutes at room temperature. Following the incubation, a cold FACSflow solution (900 μL) was added to the mixture. All cells in different stained samples were analyzed using the CellQuest Pro software on the FACSCalibur machine (BD Bioscience, USA). Each cell sample was analyzed for a minimum of 10,000 cells [
21].
2.5. Determination of immunogenicity of stem cells
2.5.1. Antigen sample preparation
Cellular samples intended for surface antigen analysis were cultured in 96-well plates until they achieved full confluence. Once accomplished, the supernatant was aspirated, and a single wash with PBS was performed before commencing the ELISA procedure. ELISA assays were conducted by combining the cells with rabbit serum, which was appropriately diluted at various concentrations.
To determine intracellular antigens, the cellular fraction was subjected to sonication to induce cell lysis and disrupt their structural integrity. Protein quantification was carried out using the Bradford method, following the guidelines provided by the manufacturer (BioRad Laboratories, USA). The antigenic proteins, at a concentration of 5 µg/mL, were diluted in a coating buffer solution with a pH of 9.6 and immobilized onto the bottom of the ELISA wells.
Subsequently, the ELISA plates were incubated overnight at a temperature of 4°C. After the incubation, they were washed five times with PBS-T 0.05%. Following the washing steps, the ELISA plates were blocked using a 1% BSA solution for a duration of 2 hours at 37°C, and then washed again five times with PBS-T 0.05%. To preserve their integrity, the plates were hermetically sealed and stored at a temperature of -20°C until the time of the ELISA assay.
2.5.2. Rabbit serum
Rabbit serum was obtained by collecting blood samples from rabbits at four different time points during the stem cell transplantation study: at the start of the study (D0-starting day), and subsequently at the 15th, 30th, and 60th day (D15, D30 and D60). The blood samples were processed to separate the serum component, which was then cryopreserved at -80°C until an adequate sample size was obtained. The serum samples were subsequently analyzed using the ELISA technique.
2.5.3. ELISA immunological analysis method
During the ELISA reaction, rabbit serum was mixed with PBS buffer solution at pH 7.4, using dilution ratios of 1/500, 1/100, 1/50, and 1/10. Each diluted rabbit serum concentration (100 μL) was dispensed into specific wells on the plates. The plates were then incubated at 37°C for 45 minutes, followed by washing the samples 5 times with PBS-T 0.05%. Subsequently, the samples were incubated with HRP-binding antibodies at 37°C for 45 minutes, and washed again 5 times with 0.05% PBS-T. The samples were then exposed to the OPD substrate at a concentration of 0.5 μg/mL and incubated for 5 minutes. The reaction was stopped by adding 2N H2SO4, and the results were read at a wavelength of 450 nm using the DTX880 system (Backman Coulter).
2.6. Differentiation of tissue stem cells into fibroblast cells
2.6.1. Inducing differentiation to generate fibroblasts and mesodermal sheets
The cells were cultured in a mesenchymal stem cell culture medium at a density of 5,000 cells/cm
2. Once the cells firmly adhered to the surface of the plastic plate, fibroblast induction was initiated by supplementing the DMEM medium with 5% FBS and 1% antibiotic. The development and morphological changes of the cells were monitored using a phase-contrast microscope, and assessments were performed after 5 days [
18].
Upon reaching 100% confluency, the fibroblast induction medium was removed. The cells were then maintained in a mixture of DMEM and Ham's F12, mixed in a ratio of 3:1, and supplemented with 10% FBS, 5 ng/mL EGF, 5 μg/mL insulin, 0.4 μg/mL hydrocortisone, 5 μg/mL transferrin, and 1×10-11 M triiodothyronine. The culture medium was replaced three times per week. The cell plates were continuously monitored until the cells exhibited overlapping growth. The cell layers could be allowed to detach naturally or gently scraped using a cell lifter to generate a sheet-like structure resembling mesodermal tissue.
2.6.2. ELISA test for collagen type I in the supernatant of differentiated cells
The first step involved immobilizing a monoclonal antibody onto the bottom of the well. The specimen containing the differentiated cells was added to the well and incubated, followed by washing to remove any non-specifically bound components. Next, a second monoclonal antibody, which was conjugated to the enzyme Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP), was added and incubated for a specified duration as instructed. After the incubation, any nonspecifically bound antibodies were washed away. To generate a luminescent signal, 3,3',5,5'-Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) was added to the mixture and allowed to react. The reaction was subsequently terminated using HCl 2N. The resulting signal was measured using a spectrophotometer at a wavelength of 450 nm. In this test, EGF was employed as a standard. The collagen content in the sample was determined in units of μg/mL.
2.7. Burn induction in rabbit models
The experimental rabbits used in this study were sourced from the Laboratory Animal Breeding Board, Military Medical Academy, Ministry of Defense. Only rabbits within the 10-12 month age range were selected based on specific criteria such as overall health, agility, clear and bright eyes, smooth fur, absence of skin or intestinal diseases, and weighing between 2.0 - 2.5 kg. Prior to the experiment, the rabbits were observed for 2-3 days to ensure their well-being. Throughout the experiment, the rabbits were individually housed in cages, assigned unique identification numbers for monitoring, and provided with a consistent diet comprising rice and fresh vegetables.
The umbilical cord lining mesenchymal stem cell plates used in the study were obtained from the Department of Laboratory Research on Applications in Burn Treatment at Vietnam National Institute of Burns. As a control material, cell-free polyurethane film (tegaderm wound covering) was used. The experimental rabbits were anesthetized with intravenous administration of ketamine at a dosage of 5 mg per 1 kg of body weight. The rabbits were then securely fixed to specialized laboratory tables. Two symmetrical patches of hair were shaved off, creating circular areas with a diameter of approximately 10 cm. This resulted in burn wounds with an area calculated as follows: πr2 = 3.14 × 2.52 = 19.6 cm2. Fourth-degree burns were induced using a specialized instrument containing boiling water at a temperature of 100°C. After the burn was induced, the lesion area appeared milky, and the skin surrounding the burn exhibited a pale pink color. The rabbits regained consciousness within a few minutes after the burn was inflicted and resumed eating within a few hours.
Each rabbit had two burn wounds created on their back: area A (right wound) for grafting the equivalent mesodermal material plates, and area B (left wound) as control with cell-free tegaderm plates.
At two time points, specifically 5 days (D5) and 10 days (D10) after transplantation, the burn sites on the rabbit's back were examined and recorded. The wounds were evaluated based on various characteristics, including wound condition, wound area, cellular transformation, tissue structure, number of inflammatory cells (neutrophils, macrophages, lymphocytes), number of fibroblasts, and newly regenerated blood vessels.
2.8. Data analysis
The obtained results were imported into Microsoft Excel 2019 software for further processing and analysis. Statistical analysis of the data was conducted using SPSS software version 25.
3. Results
3.1. Cell Growth and Confluence Analysis in Mesenchymal Stem Cell Culture
Cell Growth and Confluence - In the 7th day of culture, only a small proportion of the samples (11.7%) demonstrated cell growth and achieved 50% confluence. However, by the 14th day, there was a significant increase in the number of samples with cell growth and 50% confluence, reaching 58.8%. Subsequently, in the 21st day, the majority of the samples (88.2%) exhibited cell growth and 50% confluence. Finally, at the 28th day, all samples (100%) displayed cell growth and achieved 50% confluence. Upon analyzing the data, it becomes evident that the time required for cell detachment and reaching 50% confluence decreased as the duration of culture increased. The percentage of samples achieving 50% confluence showed a gradual and consistent increase, rising from 0% at 7 days to 94.1% at 28 days. This suggests that the cells initially took longer to detach from the tissue samples and attain 50% confluence, but their efficiency in achieving confluence improved as the culture time extended.
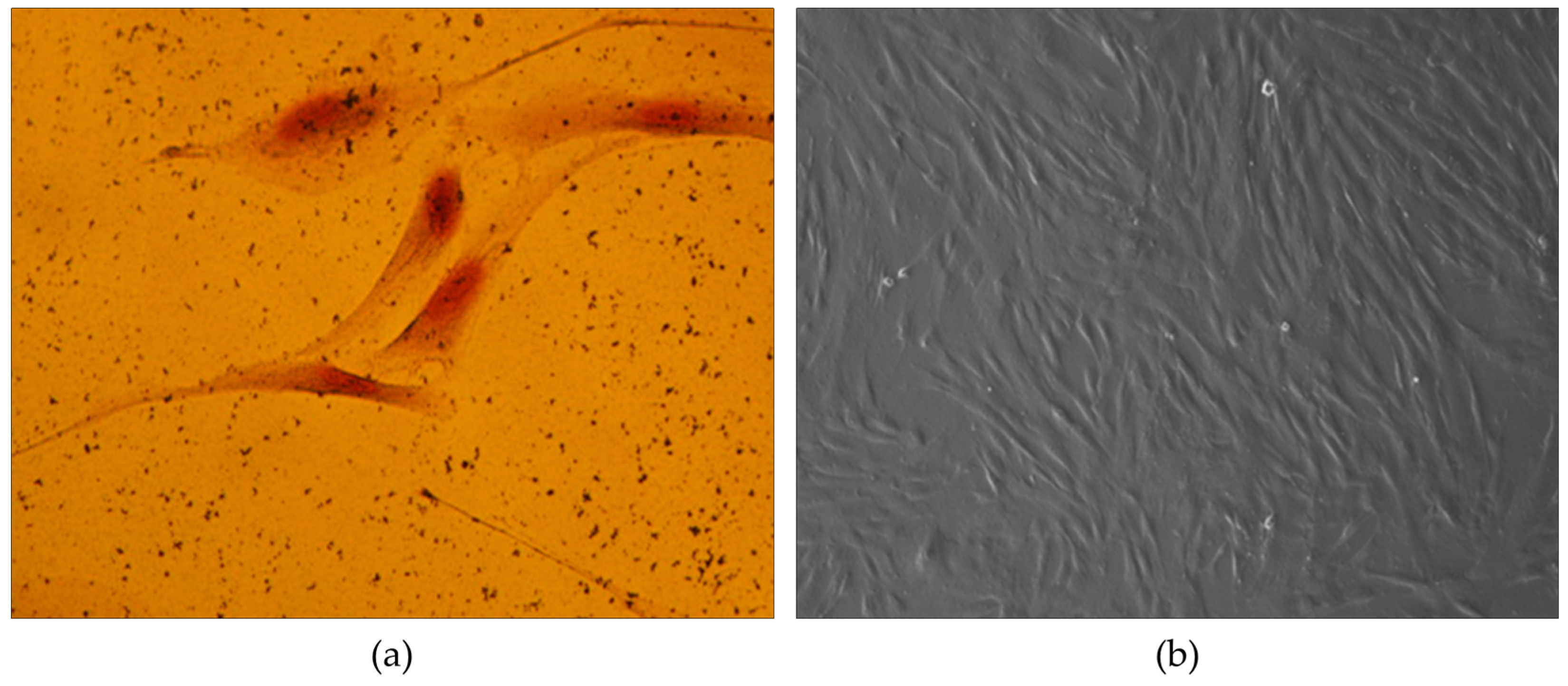
Morphological Characterization - The obtained mesenchymal stem cells from the umbilical cord lining membrane exhibited a distinct morphology characterized by either astrocytes or rhombuses, forming a monolayer without cytoplasmic branch connections (
Figure 1a). Additionally, some oval or polyhedral cells were also observed in the tissue samples; however, their growth was overshadowed by the dominant presence of rhombic cells (
Figure 1b). Furthermore, when the cells were isolated from the tissues, they displayed a remarkable capacity for colony formation. Colonies were visible as early as 5 days into the culture, with the most pronounced colonies observed at 10 days. These colonies were identified as CFU-F (fibroblast colony-forming units).
These findings indicate that a longer culture duration, particularly beyond 21 days, is advantageous for obtaining a higher percentage of samples with cell growth and 50% confluence. Researchers and practitioners can utilize this information to optimize cell culture protocols and carefully plan the desired level of confluence within specific time frames.
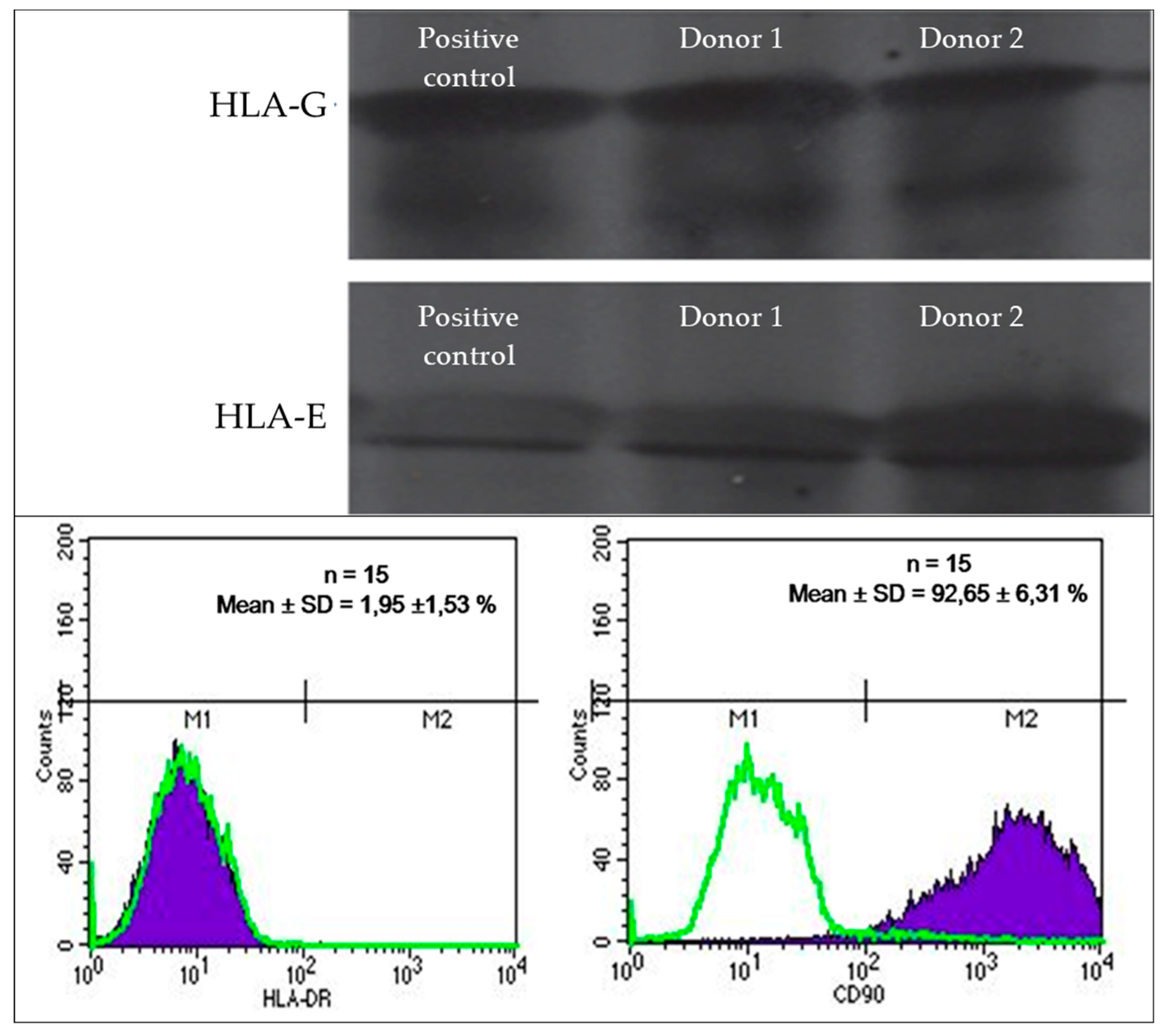
3.2. HLA Expression Profile of Umbilical Cord Lining Mesenchymal Stem Cells
The expression profile of human leukocyte antigen (HLA) markers in the acquired umbilical cord lining mesenchymal stem cells was assessed. The cells displayed a robust expression of the specific CD90 marker, with an average expression level of 92.65% ± 6.3%. Additionally, they exhibited the presence of HLA-E and HLA-G synergistic antigens. Conversely, the expression of HLA-DR was relatively low, accounting for only 1.9% ± 1.53%. These results are visually depicted in
Figure 2.
3.3. Analysis of Cell Differentiation and Cellular Immunogenicity
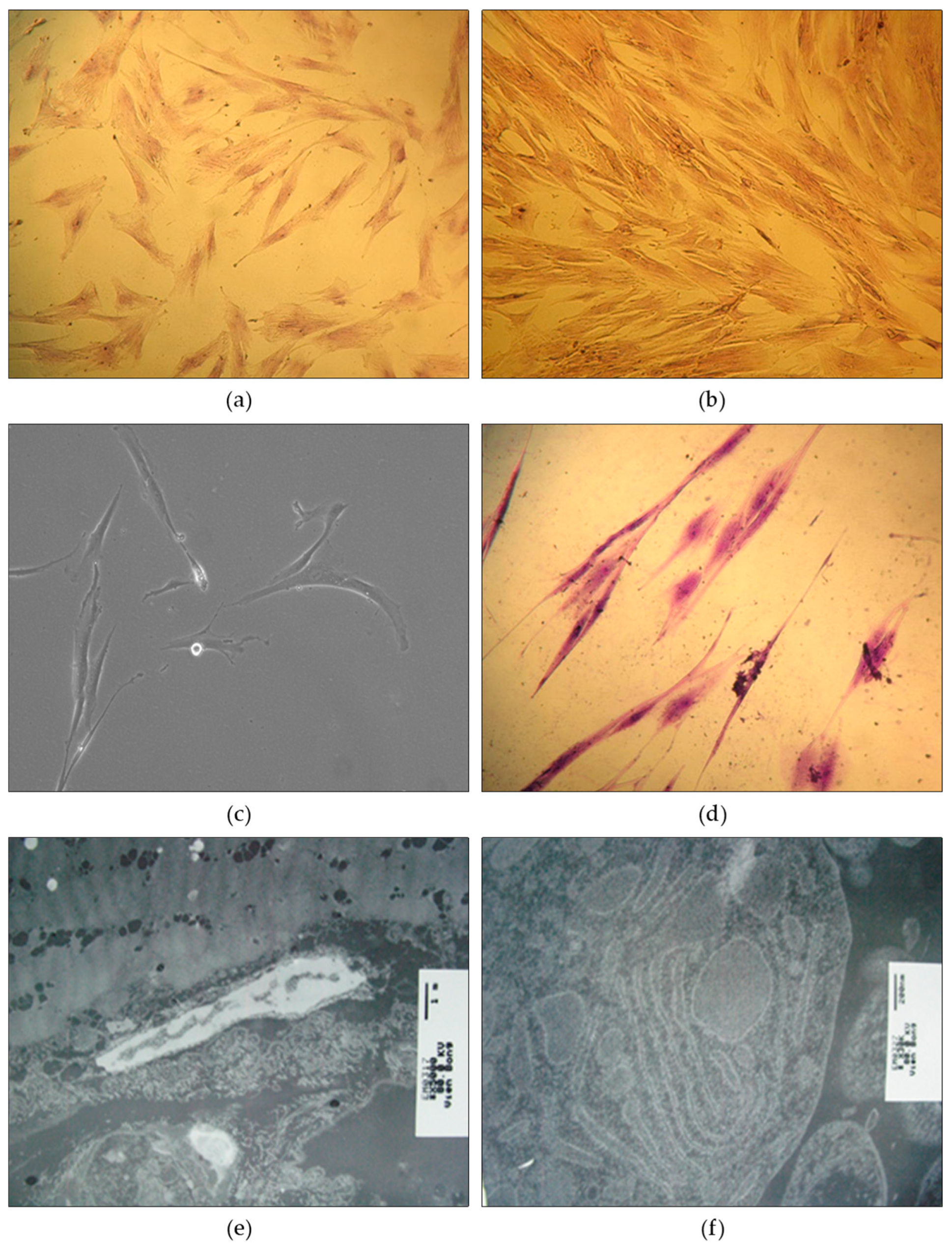
Cell Differentiation - The differentiation of cells was examined across multiple generations. In the 5th generation, the majority of cells displayed an astromorphic shape (69.0%) or a rhombic shape (19.9%), while other cells exhibited oval, polyhedral, or long filamentous forms. As the generations progressed to the 10th and 15th, there was a notable increase in the dominance of rhombic and filamentous cells, accompanied by a decline in astrocyte proportions. Cells in the differentiated generations demonstrated cytoplasmic spreading with plasma branches extending towards the cell poles. Nuclei analysis revealed that circular nuclei were most prevalent (70.7%) in the 5th generation, followed by ovoid nuclei (26.2%). As the generations advanced, the proportion of ovoid nuclei increased while the proportion of circular nuclei decreased. Abnormal monster nuclei were not observed in any of the cell generations. Importantly, the cells maintained their ability to undergo cell division. Detailed results can be found in
Figure 3.
Cellular Immunogenicity - The immunogenicity of supercrushed stem cells and intact cells was evaluated, and both were found to elicit an immune response against stem cells. Notably, supercrushed stem cell antigens demonstrated a higher degree of immunogenicity compared to intact cell antigens. The ELISA test results showed an increase in optical density (OD) values at day 15 after transplantation, followed by a subsequent decrease to normal levels at days 30 and 60 post-transplantation. These fluctuations in OD values indicate that umbilical cord lining membrane stem cells induced a relatively weak and unstable immunogenic response.
3.4. Analysis of Collagen Production and Sheet Material Formation
Collagen Production - In the culture medium group, both the control and experimental groups showed similar soluble collagen content, with values of 0.045 ± 0.002 µg/mL and 0.046 ± 0.001 µg/mL, respectively. The p-value of >0.05 indicates that there is no statistically significant difference between these two groups in terms of soluble collagen production. However, in the floating culture group, a notable difference in soluble collagen content was observed. The control group had a lower value of 0.069 ± 0.003 µg/mL, whereas the experimental group had a significantly higher value of 0.297 ± 0.011 µg/mL. The p-value of <0.01 suggests that the difference in soluble collagen content between these two groups is statistically significant. Overall, the data indicates that differentiated fibroblasts in the experimental group exhibited a higher production of soluble collagen compared to the mesenchymal stem cells in the control group, particularly under the floating culture condition. This finding suggests that the differentiation of fibroblasts may contribute to an increased synthesis of soluble collagen.
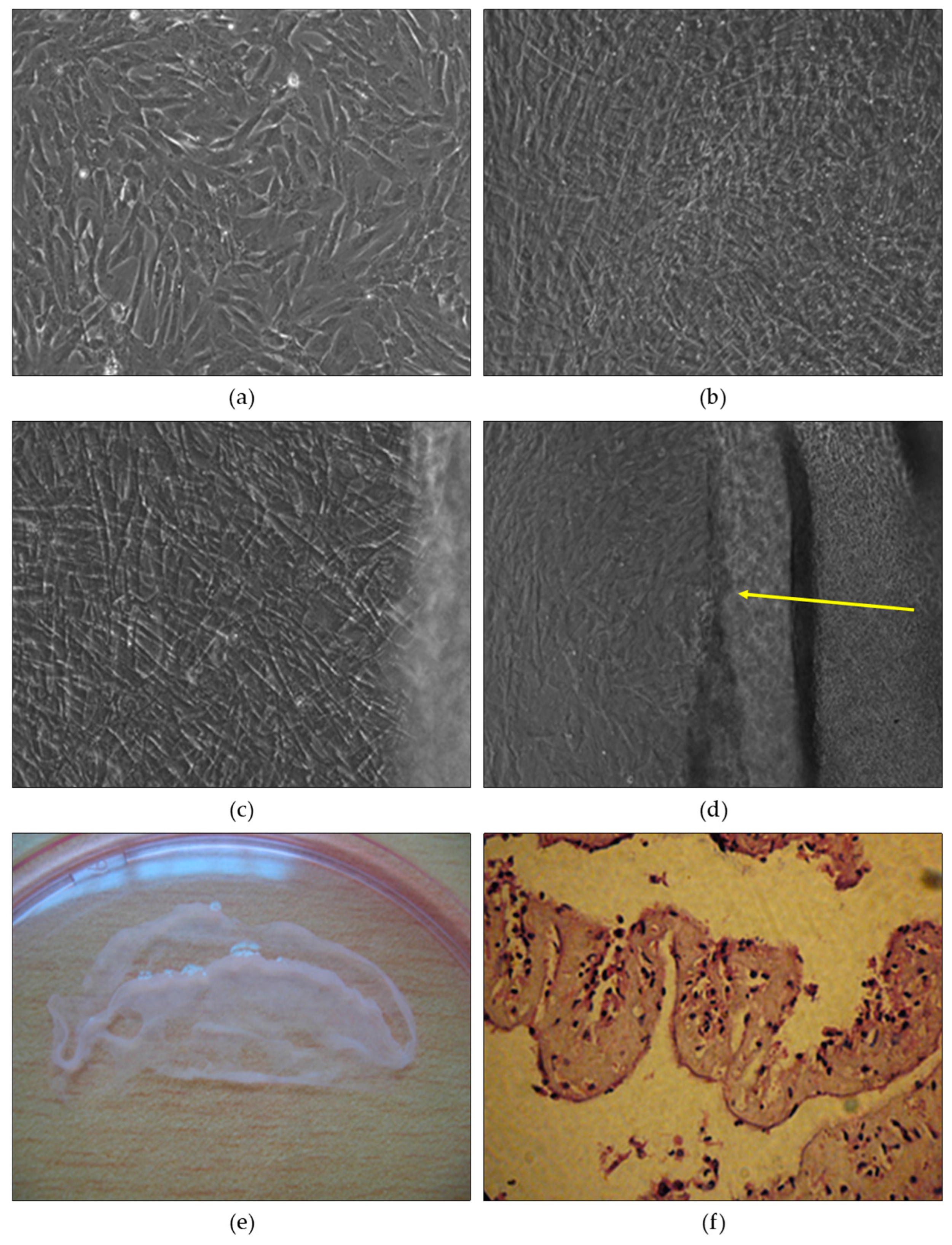
Sheet Material Formation - Following the attainment of full cell coverage, the mesenchymal cells were cultivated under differentiated culture conditions. After two weeks, the culture revealed the presence of long rhombic cells arranged in a crisscross pattern, forming approximately 2-3 layers that interweaved in multiple directions and maintained interconnections (
Figure 4b). In contrast, cells grown under traditional culture conditions displayed no additional structural elements and maintained a monolayered arrangement, with various cell shapes including shorter astrocytes and rhombic cells (
Figure 4a).
Interestingly, when the umbilical cord lining membrane mesenchymal stem cells were cultured, they exhibited a tendency to form two overlapping layers instead of adopting the coiled structure typically seen in mesodermal fibroblasts. Subsequent observations and medium changes in the differentiated culture revealed a pronounced stacking of cells around days 6-8 (
Figure 4c). By the 10th day, the cell layer began to detach from the surface of the culture plate, and gentle shaking or wiping with a pipette tip resulted in the formation of a distinct cell plate (
Figure 4d). The cell plate occupied a slightly smaller area than the plate's bottom surface, covering approximately two-thirds of the culture plate area (
Figure 4e).
Histological analysis of the sheet material demonstrated that it comprised not only cells but also intercellular cushions. The composition of the sheet material predominantly consisted of fibroblast cells. Based on histological imaging, the cell plate exhibited characteristics akin to mesodermal equivalent material (
Figure 4f).
3.5. Alterations in Rabbit Wounds Following Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation
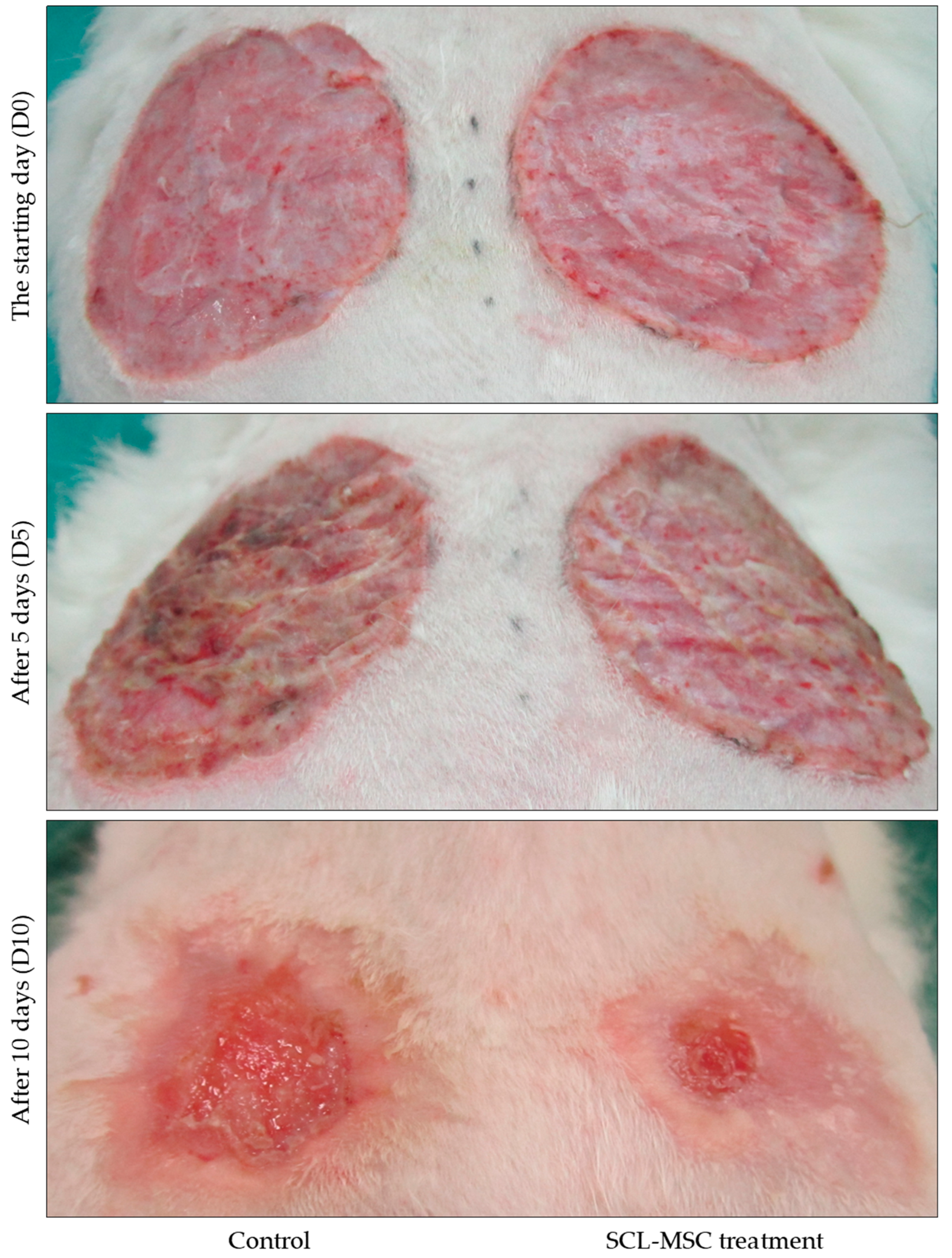
Wound Characteristics and Epithelialization:
Before the transplantation of stem cell material plates, the experimental burn wound exhibited specific characteristics, including a moist wound base, easily peeled pseudomembranous formation, moderate inflammation, and moderate exudation. The wound edges showed slight signs of inflammation. However, after the grafting procedure, notable improvements were observed. The wound area narrowed, the inflammation at the wound edges diminished, and the process of epithelialization towards the center of the wound became more visible. The wound base flattened, without any signs of shrinkage, and after 10 days of transplantation, the presence of an epithelial areola was evident. In contrast, the control area exhibited slow wound shrinkage, a moist wound base, and moderate plateharge. After 10 days of applying the sheet of material without stem cells, the wound base became flat, bloody, and shrunk. These findings are illustrated in
Figure 5.
Healing Rate and Inflammatory Response - .
Table 1 presents the comparison of wound changes between the stem cell material plate area (Zone A) and the control area (Zone B). The table includes various monitoring indicators measured at two different time points: Day 5 (D5) and Day 10 (D10) after transplantation. The indicators evaluated include the percentage of wound healing, area of epithelialization, number of inflammatory cells per unit area, number of fibroblasts per unit area, number of neo-vessels per unit area, and the mitotic index.
Percentage of Wound Healing - The data shows that the percentage of wound healing is significantly higher in Zone A compared to Zone B at both D5 (77.44% vs. 68.76%, p < 0.01) and D10 (93.23% vs. 87.36%, p < 0.001). This indicates that the stem cell material plate area promotes faster wound healing compared to the control area.
Area of Epithelialization - The area of epithelialization is larger in Zone A compared to Zone B at both D5 (14.18 cm² vs. 12.52 cm², p < 0.05) and D10 (16.95 cm² vs. 15.74 cm², p < 0.05). This suggests that the stem cell material plate facilitates the growth and coverage of epithelial tissue in the wound area.
Number of Inflammatory Cells - There is no significant difference in the number of inflammatory cells per unit area between Zone A and Zone B at D5 (18.86 vs. 18.01, p = 0.475). However, at D10, Zone A shows a significantly lower number of inflammatory cells compared to Zone B (8.96 vs. 12.5, p = 0.001). This indicates that the stem cell material plate area exhibits reduced inflammation compared to the control area.
Number of Fibroblasts - The number of fibroblasts per unit area is comparable between Zone A and Zone B at both D5 (37.2 vs. 36.56, p = 0.76) and D10 (67.1 vs. 52.73, p < 0.001). This suggests that the presence of the stem cell material plate does not significantly affect the number of fibroblasts in the wound area.
Number of Neo-vessels - There is no significant difference in the number of neo-vessels per unit area between Zone A and Zone B at both D5 (3.50 vs. 3.67, p = 0.484) and D10 (7.23 vs. 4.90, p < 0.001). This indicates that the stem cell material plate area does not significantly impact the formation of new blood vessels in the wound area.
Mitotic Index - The mitotic index, representing the rate of cell division, shows no significant difference between Zone A and Zone B at D5 (1.53 vs. 1.47, p = 0.189). However, at D10, the mitotic index is significantly higher in Zone A compared to Zone B (2.47 vs. 1.86, p < 0.010). This suggests that the stem cell material plate area promotes increased cell division at a later stage of the healing process.
The findings demonstrate that the transplantation of mesenchymal stem cell material plates resulted in improved wound characteristics, enhanced epithelialization, accelerated healing rates, decreased inflammation, and increased fibroblast activity and angiogenesis. These outcomes highlight the potential of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation as a promising approach for promoting wound healing and tissue regeneration in burn injuries.
4. Discussion
The use of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in the treatment of burn wounds has been extensively studied. This study focuses on assessing the developmental characteristics and therapeutic potential of umbilical cord lining-derived MSCs. MSCs possess various properties such as multidirectional differentiation potential, robust proliferation, tissue repair abilities, immune tolerance, and immunomodulation [
1]. The umbilical cord lining is a convenient and painless source of MSCs, which can differentiate into functional cells at the site of the wound. The different layers of the umbilical cord, including Wharton's jelly, veins, arteries, umbilical cord lining, and submeningeal and perivascular regions, can serve as sources for collecting MSCs [
3]. With their versatility, ease of isolation and culture, high spreading potential, and immunosuppressive properties, umbilical cord-derived MSCs hold great promise as a therapeutic tool in regenerative medicine and tissue engineering [
2].
Isolated umbilical cord MSCs exhibit robust colony formation, strong expression of CD90 marker, high expression of HLA-E and HLA-G, and less than 2% expression of HLA-DR factor among total positive cells. HLA-G and HLA-E are class I HLA molecules predominantly expressed in fetal cells, exerting immunosuppressive effects that aid in fetal survival within the maternal body [
3]. On the other hand, HLA-DR is a class II HLA antigen that triggers a strong immune response when transplanted into genetically diverse organisms [
3]. The absence of HLA-DR expression on umbilical cord MSCs, along with low expression of class MHC I molecules and the absence of CD80 and CD86 markers, contributes to their weak immunogenicity and reduced risk of acute graft rejection [
3].
The wound healing process involves a coordinated interplay of different tissues and cellular events, including inflammation, tissue proliferation, and regeneration [
22]. Inflammation, when regulated appropriately, initiates subsequent phases of wound healing. However, excessive inflammation can impede cell proliferation and lead to tissue breakdown. UC-MSC sheets have demonstrated the ability to effectively reduce the number of inflammatory cells in wounds and accelerate wound contraction. Burn wounds treated with UC-MSCs exhibit faster healing rates without excessive shrinkage, which can cause unfavorable scarring and functional impairments. These findings highlight the potential of UC-MSCs in promoting wound healing and scar repair while minimizing aesthetic and functional complications [
23].
UC-MSCs enhance skin wound healing through paracrine activity, which involves the secretion of various factors. These factors contribute to decreased activity of modified growth factor-β 1,3 (TGF-β 1/3) and an increased ratio of basal metalloproteinase to tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (MMP/TIMP) [
23]. The secreted substances from MSCs act on surrounding cells and promote burn repair. Furthermore, combining MSC pretreatment with appropriate dressing materials enhances the therapeutic efficacy of MSCs in burn treatment [
1].
The use of stem cell sheets has been reported as an effective technique for treating burn wounds. Adipose tissue-derived stem cell plates (ASCs) have been shown to effectively reduce burn wound size in mice [
22,
24]. ASC-treated trials exhibited enhanced development of new blood vessels compared to the control group. Neovascular regeneration, facilitated by angiogenesis, plays a crucial role in burn wound healing by ensuring the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to the granulation tissue [
22].
5. Conclusions
Umbilical cord MSCs hold great promise in the field of burn wound healing due to their unique characteristics and therapeutic effects. They possess strong immunomodulatory properties, promote wound healing, and aid in scar repair while minimizing adverse aesthetic and functional consequences. The paracrine activity of MSCs, combined with appropriate pretreatment strategies, can further enhance their efficacy in burn treatment. Additionally, the utilization of stem cell sheets, such as ASCs, has shown promising results in reducing burn wound size and promoting neovascular regeneration. Further research and clinical trials are warranted to explore the full potential of MSC-based therapies in burn wound management.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H.P, N.N.P.T; Data curation, M.H.P, N.N.P.T; Formal analysis, M.H.P, N.N.P.T; Investigation, M.H.P, N.N.P.T, V.H.D ; Methodology, H.H.N, V.H.D; Writing – original draft, M.H.P, N.N.P.T; Writing – review & editing, M.H.P, N.N.P.T, H.H.N, V.H.D.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of VIETNAM NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF BURNS and CAN THO UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY (Code: 22.091.GV/PCT-HDDD).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in this article.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the cooperation and support of outpatients, and collaborators at the Vietnam National Institute of Burns for the time and effort they devoted to the study. We also thank you for the support from Ho Chi Minh city Hospital of Rehabilitation and Occupational Disease and Can Tho University of Medicine and Pharmacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Lei, X.; Tan, J.; Xie, H. Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for burn wound healing. Burns & Trauma 2021, 9, tkab002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, H. Mesenchymal stem cells and skin wound repair and regeneration: possibilities and questions. Cell and Tissue Research 2009, 335, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamura-Inoue, T.; He, H. Umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells: Their advantages and potential clinical utility. World journal of stem cells 2014, 6, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harminder, S.D.; Augusto, A.-B. Autologous limbal transplantation in patients with unilateral corneal stem cell deficiency. British Journal of Ophthalmology 2000, 84, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoft, R.A.; Wiley, L.A.; Sundarraj, N. The multipotential cells of the limbus. Eye 1989, 3, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.C.G. Concept and application of limbal stem cells. Eye 1989, 3, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, L.P.K.; Tan, D.T.H. Ocular surface stem cells and disease: current concepts and clinical applications. Ann Acad Med Singap 2004, 33, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Puangsricharern, V.; Tseng, S.C.G. Cytologlogic Evidence of Corneal Diseases with Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency. Ophthalmology 1995, 102, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Sheha, H.; Li, J.; Tseng, S.C.G. Limbal stem cell transplantation: new progresses and challenges. Eye 2009, 23, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, S.C.; Thomas, P.B.; Nguyen, P. Ocular surface reconstruction: recent advances and future outlook. Current Opinion in Ophthalmology 2007, 18, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, L.P.K.; Tanioka, H.; Kawasaki, S.; Ang, L.P.S.; Yamasaki, K.; Do, T.P.; Thein, Z.M.; Koizumi, N.; Nakamura, T.; Yokoi, N.; et al. Cultivated Human Conjunctival Epithelial Transplantation for Total Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 2010, 51, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.T.H.; Ang, L.P.K.; Beuerman, R.W. Reconstruction of the Ocular Surface by Transplantation of a Serum-Free Derived Cultivated Conjunctival Epithelial Equivalent. Transplantation 2004, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, L.P.K.; Nakamura, T.; Inatomi, T.; Sotozono, C.; Koizumi, N.; Yokoi, N.; Kinoshita, S. Autologous Serum–Derived Cultivated Oral Epithelial Transplants for Severe Ocular Surface Disease. Archives of Ophthalmology 2006, 124, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, K.; Yamato, M.; Hayashida, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Adachi, E.; Nagai, S.; Kikuchi, A.; Maeda, N.; Watanabe, H.; et al. Corneal Reconstruction with Tissue-Engineered Cell Sheets Composed of Autologous Oral Mucosal Epithelium. New England Journal of Medicine 2004, 351, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doan, N.; Huynh, T.Q.; Tran, S.; Wang, G.; Hamlet, S.; Dau, v.; Dao, D.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Doan, J.; et al. Multidisciplinary approach to maximize angiogenesis and wound healing using piezoelectric surgery, concentrated growth factors and photobiomodulation for dental implant placement surgery involving lateral wall sinus lift: two case reports. Vascular Cell 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, H.M.; Ng, B.-Y.; Phan, T.T.; Tan, D.T.H.; Beuerman, R.W.; Ang, L.P.-K. Characterization of a Novel Umbilical Cord Lining Cell with CD227 Positivity and Unique Pattern of P63 Expression and Function. Stem Cell Reviews and Reports 2011, 7, 624–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freshney, R.I. Culture of animal cells: a manual of basic technique and specialized applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.B.P.; Dinh, V.H.; Nguyen, N.T.; Nguyen, N.L.; Nguyen, T.H. In Vitro Assessment of The Effect of Low Level Laser Therapy on the Proliferation and Migration of Fibroblasts Derived from Patients with Chronic Wounds. Vietnam Medical Journal 2023, 525, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secunda, R.; Vennila, R.; Mohanashankar, A.M.; Rajasundari, M.; Jeswanth, S.; Surendran, R. Isolation, expansion and characterisation of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord blood and matrix: a comparative study. Cytotechnology 2015, 67, 793–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre, E.; Rebmann, V.; LeMaoult, J.; Rodriguez, C.; Horn, P.A.; Díaz-Lagares, A.; Echeveste, J.I.; González, A. In vivo identification of an HLA-G complex as ubiquitinated protein circulating in exosomes. European Journal of Immunology 2013, 43, 1933–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.; Choi, W.; Bae, Y.; Kim, M.; Choi, S.; Oh, W.; Jin, H. HLA-A2 Promotes the Therapeutic Effect of Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Hyperoxic Lung Injury. Bioengineering 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busuioc, C.J.; Mogoşanu, G.D.; Popescu, F.C.; Lascăr, I.; Pârvănescu, H.; Mogoantă, L. Phases of the cutaneous angiogenesis process in experimental third-degree skin burns: histological and immunohistochemical study. Romanian journal of morphology and embryology = Revue roumaine de morphologie et embryologie 2013, 54, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Luan, F.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, H.; Liu, J.; Dong, L.; Fu, X.; Han, W. Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium accelerates wound healing with fewer scars. International Wound Journal 2017, 14, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Grahovac, T.; Oh, S.J.; Ieraci, M.; Rubin, J.P.; Marra, K.G. Evaluation of a multi-layer adipose-derived stem cell sheet in a full-thickness wound healing model. Acta Biomaterialia 2013, 9, 5243–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).