Submitted:
27 June 2023
Posted:
28 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. DNA Amplification by PCR
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
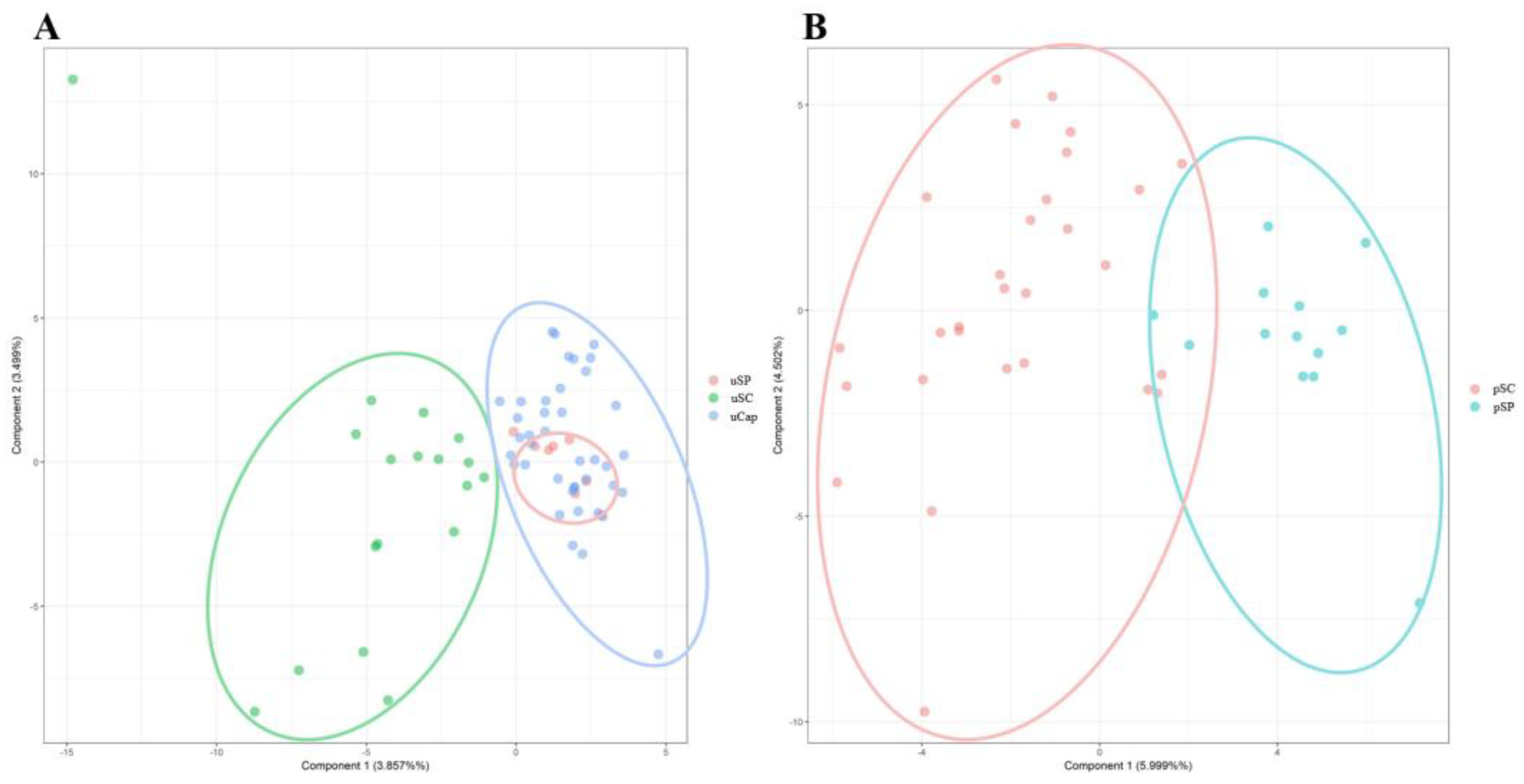
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO, Food and Agriculture Organization. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Brazil, Ministry of Agriculture. Aquicultura tem potencial para crescer mais de 80% em cinco anos. 2020. Available online: https://www.gov.br/casacivil/pt-br/assuntos/noticias/2015/junho/aquicultura-tem-potencial-para-crescer-mais-de-80-em-cinco-anos (accessed on 27 April 2020).
- Rivas, L.R. ; Systematic review of the perceived fishes of the Centropomus genus. Copeia 1986, 1, 579–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.G.; Whittington, J.A.; Grier, H.J.; Crabtree, R.E. Age, growth, maturation and protandric sex reversal in common snook, Centropomus undecimalis, from the east and west coasts of South Florida. Fish Bull 2000, 98, 612–624. [Google Scholar]
- Tringali, M.D., Bert. Molecular phylogenetics and ecological diversification of the transisthmian fish genus Centropomus (Perciformes:Centropomidae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 1999, 16, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrona, L.D. Contribution to the biology of "sea bass" Centropomus parallelus (Pisces Centropomidae) of Sud-Est du Brésil: possibilités quacoles. 175 f. Thèse (Doctorat decème Cycle, Sciences et Techniques in Productions Animales) - Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse, France, 1984.
- Mendonça, M.C.F.B. Autoecology of camorim, Centrpomus undecimalis (Bloch, 1792), (Peciformes: Centropomidadae) in hypersaline environment in Galinhos, RN. Brazil. São Carlos. UFSCar. PhD thesis, 145p. 2004.
- Aoki, P. C. M. Thermal tolerance of juveniles of sea bass Centropomus parallelus poey, 1860 (pisces: centropomidae) in freshwater. Dissertation (Master in Biological Sciences) Postgraduate course in Animal Biology, Federal University of Espírito Santo, 1999.
- Barbuio, M. A. T. Comparison of growth and body composition of the seabream Centropomus parallelus (poey, 1860) fed on a commercial diet and dry and semi-moist experimental diets. 57f. Dissertation (Master in Aquaculture) Postgraduate Course in Aquaculture, Federal University of Santa Catarina, Florianópolis. 1999.
- Cerqueira, V.R. Robalo culture: aspects of reproduction, larviculture and fattening. Florianópolis. Ed of the author 2002, 94p.
- Cerqueira, V.R. Cultivation of sea bass, Centropomus parallelus. In Native species for fish farming in Brazil. UFSM: Santa Maria, Brazil, 2005, p.403-431.
- Soligo, T.A. First experiments with breeding, larvae and weaning of sea bass, Centropomus undecimalis in. Brazil. Dissertation, (master's degree) - Federal University of Santa Catarina. Postgraduate Program in Aquaculture, 2007.
- Alvarez-Lajonchère, L.; Tsuzuki, M.Y. A review of methods for Centropomus spp. (snooks) aquaculture and recommendations for the establishment of their culture in Latin America. Aquaculture Research. [CrossRef]
- Adams, A.J.; Hill, J.E.; Kurth, B.N.; Barbour, A.B. Effects of a severe cold event on the subtropical, estuarine-dependent common snook, Centropomus undecimalis. Gulf and Caribbean Research 2010, 24, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, J.T.; Chao, L.; Albieri, R.J.; Giarrizzo, T.; da Silva, F.M.S.; Castro, M.G.; Brick Peres, M.; Villwock de Miranda, L.; Vieira, J.P. Centropomus undecimalis. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, V.R.; Tsuzuki, M.Y. A review of spawning induction, larviculture, and juvenile rearing of the fat snook, Centropomus parallelus. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 2009, 35, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahman, H.; El Hady, M.; Alcivar-Warren, A.; Allen, S.; Al-Tobasei, R.; Bao, L., et al..; et al. Aquaculture genomics, genetics and breeding in the United States: current status, challenges, and priorities for future research. BMC Genomics 2007, 18, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, V.L.; Jones, K.; Cowley, D.E. Genetic Diversity within Fragmented Cutthroat Trout Populations. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 2007, 136, 606–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehner, T.; Pohlmann, K.; Elkin, C.; Monaghan, M.T.; Freyhof, J. Genetic mixing from enhancement stocking in commercially exploited vendace populations. Journal of Applied Ecology 2009, 46, 1340–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegren, H.; Galtier, N. Determinants of genetic diversity. Nature Review Genetics 2016, 17, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futuyma, D.J.; Kirkpatrick, M. Evolution, 4th edition; Sinauer Associates is an imprint of Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sekino, M.; Sugaya, T.; Hara, M.; Taniguchi, N. Relatedness inferred from microsatellite genotypes as a tool for broodstock management of Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture 2004, 233, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Morgan, C.; Shi, J.; Long, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, R.; et al. A comparative linkage map of oilseed rape and its use for QTL analysis of seed oil and erucic acid content. Theor. Appl. Genet 2006, 114, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zou, J.; Tian, E.; Xia, W.; Meng, J. Development of a population for substantial new type Brasscia napus diversified at both A/C genomes. Theor. Appl. Genet 2010, 121, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Ma, B.; Li, H.; Chang, Y.; Han, Y.; Li, J., et al.; et al. Identification, characterization, and utilization of genome-wide simple sequence repeats to identify a QTL of acidity in apple. BMC Genomics 2012, 13, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Mason, A. S.; Fan, H. , et al. Development of gene-based simple sequence repeat markers for association analysis in Cocos nucifera. Mol. Breed.
- Sambrook, J.; Fritschi, E.F.; Maniatis, T. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, 1989.
- Seyoum, S.; Tringali, M. D.; Sullivan, J. Isolation and characterization of 27 polymorphic microsatellite loci for the common snook Centropomus undecimalis. Molecular Ecology Notes 2005, 5, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peakall, R.; Smouse, P.E. GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research--an update. Bioinformatics, 2537. [Google Scholar]
- Jombart, T. Adegenet: a R package for the multivariate analysis of genetic markers. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1403–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 2nd Edition; Springer, New York, 2009.
- Keenan, K.; McGinnity, P.; Cross, T.F.; Crozier, W.W.; Prodöhl, P.A. diveRsity: An R package for the estimation and exploration of population genetics parameters and their associated errors. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 2013, 4, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquette, S.R. PopGenKit: Useful Functions for (Batch) File Conversion and Data Resampling in Microsattelite Datasets. R Package Version 1.0. 2012.
- Ellegren, H. Microsatellites: simple sequences with complex evolution. Nat Rev Genet 2004, 5, 435–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Vidal, U.; Lesher-Gordillo, J.; Contreras-Sánchez, W.M.; Chiappa-Carrara, X. Genetic variability of the common Snook Centropomus undecimalis (Perciformes: Centropomidae) in connected marine and riverine environments. Revista de biologia tropical 2014, 62, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forbes, S.H.; Hogg, J.T.; Buchanan, F.C.; Crawford, A.M.; Allendorf, F.W. Microsatellite evolution in congeneric mammals: domestic and bighorn sheep. Molecular Biology and Evolution 1995, 12, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, D.C.; Milheiriço, C.; Vinga, S.; de Lencastre, H. Assessment of allelic variation in the ccrAB locus in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2006, 58, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frankham, R.; Ballou, J.; Briscoe, D. Introduction to Conservation Genetics, 2nd edition; Cambridge University Press: New York, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Laikre, L.; Palm, S.; Ryman, N. Genetic Population Structure of Fishes: Implications for Coastal Zone Management. Ambio 2005, 34, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S. Evolution and the Genetics of Populations, vol. 4. Variability Within and Among Natural Populations; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, W.R. Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution 1989, 43, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Able, K.W. A re-examination of fish estuarine dependence: Evidence for connectivity between estuarine and ocean habitats. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2005, 64, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvano, R. A. M.; MacCord, P. F. L.; Lima, R.V.; Begossi, A. When does this fish Spawn? Fishermen‟s local knowledge of migration and reproduction of Brazilian coastal fishes. Environmental Biology of Fishes 2006, 76, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aanatro, A.; Pereira, A.N.; Lessa, E. P. Genetic structure of the white croaker, Micropogonias furnieri Desmarest 1823 (Perciformes: Sciaenidae) along Uruguayan coasts: contrasting marine, estuarine, and lacustrine populations. Environmental Biology of Fishes 2011, 91, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Specie | Sample code | Number (n) of samples collected | Collection point | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Federal State | County or region | |||
| C. parallelus | pSC | 29 | Santa Catarina | Balneário de Penha |
| pSP | 13 | São Paulo | Guarujá | |
| C. undecimalis | uCap | 40 | Santa Catarina | Captive* |
| uSC | 18 | Santa Catarina | Balneário de Penha | |
| uSP | 8 | São Paulo | Guarujá | |
| Specie | Parameters | Mean IC | Lower IC | Higher IC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. udecimalis | Fst | 0.0376 | 0.0250 | 0.0532 |
| Fis | -0.0021 | -0.0262 | 0.0202 | |
| C. paralellus | Fst | 0.0592 | 0.0368 | 0.0832 |
| Fis | 0.0020 | -0.0263 | 0.0308 |
| Polpulations | Mean_AR | Lower Bound_AR | Higher Bound_AR | Mean_Fis | Lower Bound_Fis | Higher Bound_Fis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| uSP | 6.58 | 5.2 | 7.9 | -0.1537 | -0.2618 | -0.0992 |
| uSC | 8.9 | 6.7 | 10.6 | -0.0049 | -0.0655 | 0.0455 |
| uCap | 9.9 | 8 | 11.3 | -0.0113 | -0.0388 | 0.0142 |
| pSC | 10.87 | 9.1 | 12.4 | 0.0275 | -0.0086 | 0.0649 |
| pSP | 8.17 | 6.9 | 9.3 | -0.1404 | -0.1949 | -0.1016 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





