Submitted:
27 June 2023
Posted:
27 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Collection and Extract Preparation
2.2. GNPS-based Molecular Networking
2.3. Mass Spectrometry and Compound Annotation
3. Results
3.1. Metabolite Profiling Using HPLC-MS/MS
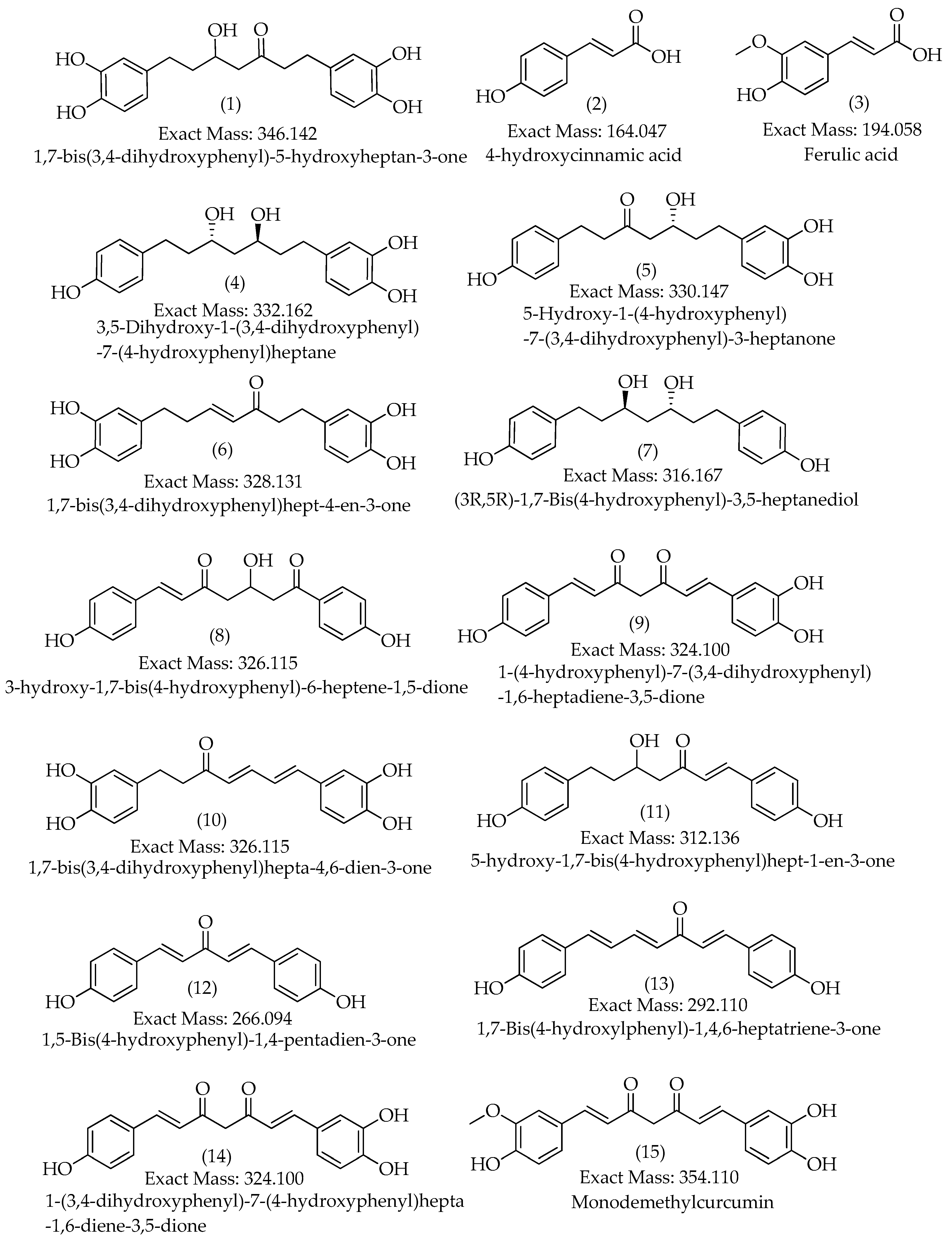
3.2. Characterization of Compounds 1, 4, 5, 6 and 10
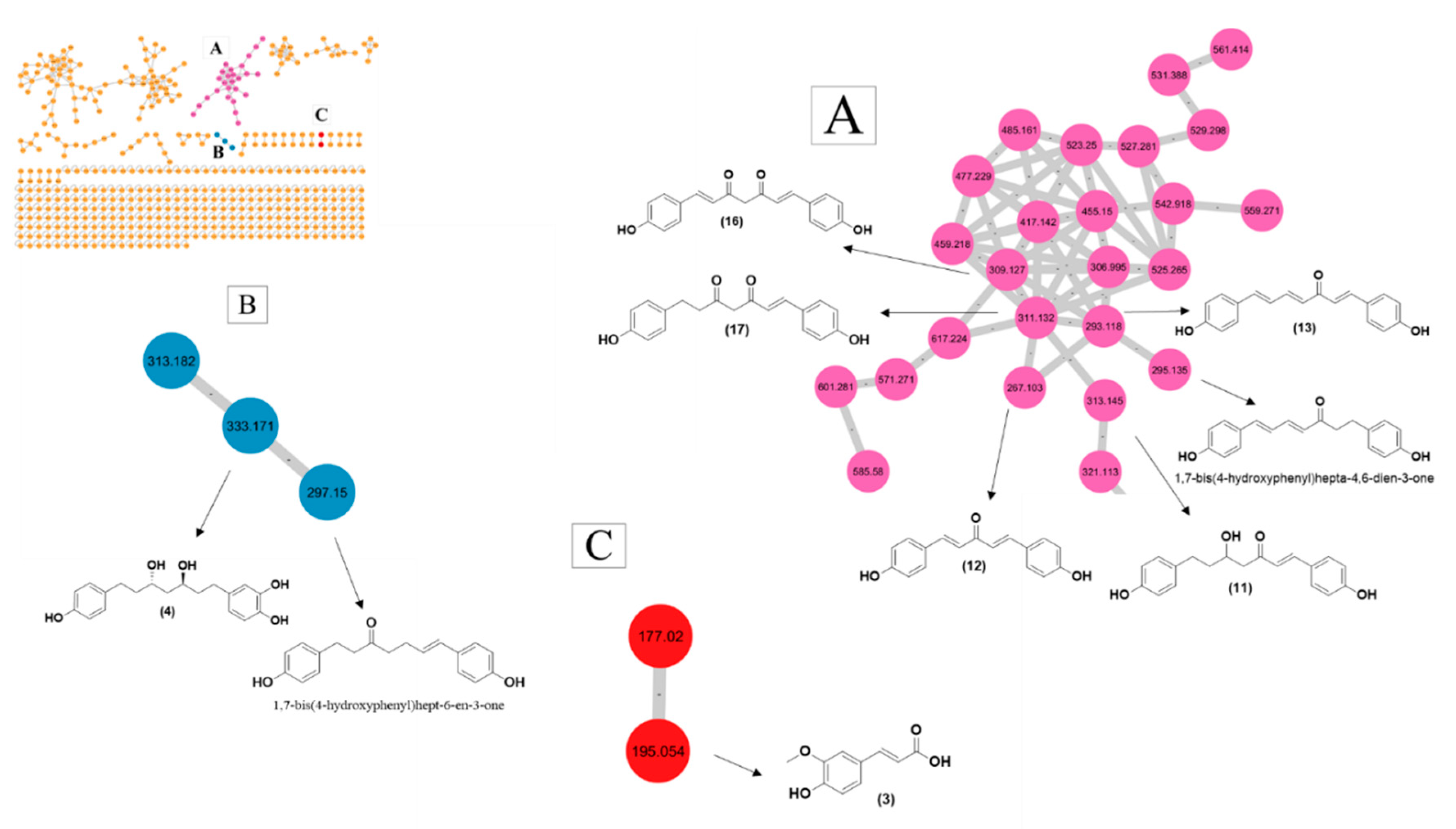
3.3. GNPS-Based Molecular Networking
4. Discussion
4.1. Metabolite Profiling Based on MS1 and MS2 Spectra
4.2. GNPS-Based Metabolite Profiling
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rathaur, P. Turmeric : The Golden Spice Of Life. 2012.
- Issuriya, A.; Kumarnsit, E.; Wattanapiromsakul, C.; Vongvatcharanon, U. Histological Studies of Neuroprotective Effects of Curcuma Longa Linn. on Neuronal Loss Induced by Dexamethasone Treatment in the Rat Hippocampus. Acta Histochemica 2014, 116, 1443–1453. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, G.; Marques, C.; de Oliveira, A.; de Almeida dos Santos, A.; do Amaral, W.; Ineu, R.P.; Leimann, F.V.; Peron, A.P.; Igarashi-Mafra, L.; Mafra, M.R. Extraction of Bioactive Compounds from Curcuma Longa L. Using Deep Eutectic Solvents: In Vitro and in Vivo Biological Activities. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 2021, 70, 102697. [CrossRef]
- Araújo, C. a. C.; Leon, L.L. Biological Activities of Curcuma Longa L. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2001, 96, 723–728. [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.-J.; Zhu, L.-J.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Zhen, Y.-Q.; Zhang, L.; Lin, C.-C.; Chen, L.-X. Diarylheptanoid: A Privileged Structure in Drug Discovery. Fitoterapia 2020, 142, 104490. [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Jaganmohan Rao, L.; Sakariah, K.K. Antioxidant Activities of Curcumin, Demethoxycurcumin and Bisdemethoxycurcumin. Food Chemistry 2006, 98, 720–724. [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Filho, J.G.; de Almeida, M.J.; Sousa, T.L.; dos Santos, D.C.; Egea, M.B. Bioactive Compounds of Turmeric (Curcuma Longa L.). In Bioactive Compounds in Underutilized Vegetables and Legumes; Murthy, H.N., Paek, K.Y., Eds.; Reference Series in Phytochemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2021; pp. 297–318 ISBN 978-3-030-57415-4.
- Tayyem, R.F.; Heath, D.D.; Al-Delaimy, W.K.; Rock, C.L. Curcumin Content of Turmeric and Curry Powders. Nutrition and Cancer 2006, 55, 126–131. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Fu, Y.; Sussman, M.R.; Wu, H. The Effect of Developmental and Environmental Factors on Secondary Metabolites in Medicinal Plants. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2020, 148, 80–89. [CrossRef]
- Shulaev, V. Metabolomics Technology and Bioinformatics. Briefings in Bioinformatics 2006, 7, 128–139. [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Bailey, N.J.C.; Johnson, H.E. Measuring the Metabolome: Current Analytical Technologies. Analyst 2005, 130, 606–625. [CrossRef]
- Dettmer, K.; Aronov, P.A.; Hammock, B.D. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Mass Spectrometry Reviews 2007, 26, 51–78. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Xu, Z.; Dou, J. Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics in Health and Medical Science: A Systematic Review. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 3092–3104. [CrossRef]
- Vincenti, F.; Montesano, C.; Di Ottavio, F.; Gregori, A.; Compagnone, D.; Sergi, M.; Dorrestein, P. Molecular Networking: A Useful Tool for the Identification of New Psychoactive Substances in Seizures by LC–HRMS. Frontiers in Chemistry 2020, 8.
- Saleem, A.; Husheem, M.; Härkönen, P.; Pihlaja, K. Inhibition of Cancer Cell Growth by Crude Extract and the Phenolics of Terminalia Chebula Retz. Fruit. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 2002, 81, 327–336. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, Y.; Lu, D.; Chen, J.; Guo, J.; Liang, J.; Zhang, A.; Yang, Z. Bioassay-Guided Separation and Identification of the Anticancer Composition from Curcuma Longa L. by the Combination Strategy of Methanol Gradient Countercurrent Chromatography and Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Journal of Separation Science 2022, 45, 4478–4490. [CrossRef]
- Segneanu, A.-E.; Vlase, G.; Lukinich-Gruia, A.T.; Herea, D.-D.; Grozescu, I. Untargeted Metabolomic Approach of Curcuma Longa to Neurodegenerative Phytocarrier System Based on Silver Nanoparticles. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2261. [CrossRef]
- Okuda-Hanafusa, C.; Uchio, R.; Fuwa, A.; Kawasaki, K.; Muroyama, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Murosaki, S. Turmeronol A and Turmeronol B from Curcuma Longa Prevent Inflammatory Mediator Production by Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages, Partially via Reduced NF-ΚB Signaling. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5779–5788. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-Q.; Wu, G.-X.; Peng, C.; Fan, Y.-Q.; Li, L.; Liu, F.; Xiong, L. New Bisabolane-Type Sesquiterpenoids from Curcuma Longa and Their Anti-Atherosclerotic Activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 2704. [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Ji, S.; Li, R.; Dong, Y.; Qiao, X.; Hu, H.; Yang, W.; Guo, D.; Tu, P.; Ye, M. Terpecurcumins A–I from the Rhizomes of Curcuma Longa: Absolute Configuration and Cytotoxic Activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 2121–2131. [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, B.; Dai, W. Diarylheptanoids from the Root of Curcuma Aromatica and Their Antioxidative Effects. Phytochemistry Letters 2018, 27, 148–153. [CrossRef]
- Quirós-Fallas, M.I.; Vargas-Huertas, F.; Quesada-Mora, S.; Azofeifa-Cordero, G.; Wilhelm-Romero, K.; Vásquez-Castro, F.; Alvarado-Corella, D.; Sánchez-Kopper, A.; Navarro-Hoyos, M. Polyphenolic HRMS Characterization, Contents and Antioxidant Activity of Curcuma Longa Rhizomes from Costa Rica. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 620. [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Tan, J.; Li, W.; Tembrock, L.R.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, G. The Use of Widely Targeted Metabolomics Profiling to Quantify Differences in Medicinally Important Compounds from Five Curcuma (Zingiberaceae) Species. Industrial Crops and Products 2022, 175, 114289. [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and Community Curation of Mass Spectrometry Data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat Biotechnol 2016, 34, 828–837. [CrossRef]
- Aryal, N.; Chen, J.; Bhattarai, K.; Hennrich, O.; Handayani, I.; Kramer, M.; Straetener, J.; Wommer, T.; Berscheid, A.; Peter, S.; et al. High Plasticity of the Amicetin Biosynthetic Pathway in Streptomyces Sp. SHP 22-7 Led to the Discovery of Streptcytosine P and Cytosaminomycins F and G and Facilitated the Production of 12F-Plicacetin. Journal of Natural Products 2022. [CrossRef]
- Dührkop, K.; Fleischauer, M.; Ludwig, M.; Aksenov, A.A.; Melnik, A.V.; Meusel, M.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Rousu, J.; Böcker, S. SIRIUS 4: A Rapid Tool for Turning Tandem Mass Spectra into Metabolite Structure Information. Nat Methods 2019, 16, 299–302. [CrossRef]
- PubChem PubChem Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Rutz, A.; Sorokina, M.; Galgonek, J.; Mietchen, D.; Willighagen, E.; Gaudry, A.; Graham, J.G.; Stephan, R.; Page, R.; Vondrášek, J.; et al. The LOTUS Initiative for Open Knowledge Management in Natural Products Research. eLife 2022, 11, e70780. [CrossRef]
- ChemSpider | Search and Share Chemistry Available online: http://www.chemspider.com/ (accessed on 26 June 2023).
- Quinn, R.A.; Nothias, L.-F.; Vining, O.; Meehan, M.; Esquenazi, E.; Dorrestein, P.C. Molecular Networking As a Drug Discovery, Drug Metabolism, and Precision Medicine Strategy. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 2017, 38, 143–154. [CrossRef]
- Ganapathy, G.; Preethi, R.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Diarylheptanoids as Nutraceutical: A Review. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 2019, 19, 101109. [CrossRef]
- Ohshiro, M.; Kuroyanagi, M.; Ueno, A. Structures of Sesquiterpenes from Curcuma Longa. Phytochemistry 1990, 29, 2201–2205. [CrossRef]
- Chao, I.-C.; Wang, C.-M.; Li, S.-P.; Lin, L.-G.; Ye, W.-C.; Zhang, Q.-W. Simultaneous Quantification of Three Curcuminoids and Three Volatile Components of Curcuma Longa Using Pressurized Liquid Extraction and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Molecules 2018, 23, 1568. [CrossRef]
- Alberti, Á.; Riethmüller, E.; Béni, S. Characterization of Diarylheptanoids: An Emerging Class of Bioactive Natural Products. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 2018, 147, 13–34. [CrossRef]
- Kuroyanagi, M.; Shimomae, M.; Nagashima, Y.; Muto, N.; Okuda, T.; Kawahara, N.; Nakane, T.; Sano, T. New Diarylheptanoids from Alnus Japonica and Their Antioxidative Activity. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 2005, 53, 1519–1523. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liao, C.-R.; Wei, J.-Q.; Chen, L.-X.; Zhao, F.; Qiu, F. Diarylheptanoids from Curcuma Kwangsiensis and Their Inhibitory Activity on Nitric Oxide Production in Lipopolysaccharide-Activated Macrophages. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2011, 21, 5363–5369. [CrossRef]
- Riethmüller, E.; Tóth, G.; Alberti, Á.; Végh, K.; Burlini, I.; Könczöl, Á.; Balogh, G.T.; Kéry, Á. First Characterisation of Flavonoid- and Diarylheptanoid-Type Antioxidant Phenolics in Corylus Maxima by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 2015, 107, 159–167. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Ko, H.H.; Seo, S.J.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, M.W.; Myung, S.C.; Bang, H. Diarylheptanoid Hirsutenone Prevents Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Stimulated Production of Inflammatory Mediators in Human Keratinocytes through NF-ΚB Inhibition. International Immunopharmacology 2009, 9, 1097–1104. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Timmermann, B.N.; Gang, D.R. Use of Liquid Chromatography–Electrospray Ionization Tandem Mass Spectrometry to Identify Diarylheptanoids in Turmeric (Curcuma Longa L.) Rhizome. Journal of Chromatography A 2006, 1111, 21–31. [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, S.; Feng, J.; Xiao, Y.; Xue, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, X. Structure Elucidation and NMR Assignments for Curcuminoids from the Rhizomes of Curcuma Longa. Magnetic Resonance in Chemistry 2009, 47, 902–908. [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.W.; Moon, E.; Kwon, O.W.; Lee, S.O.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, S.Z.; Son, M.W.; Lee, K.R. Anti-Neuroinflammatory Diarylheptanoids from the Rhizomes of Dioscorea Nipponica. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2013, 23, 3806–3809. [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Jitoe, A.; Isobe, J.; Nakatani, N.; Yonemori, S. Anti-Oxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Curcumin-Related Phenolics from Rhizomes of Curcuma Domestica. Phytochemistry 1993, 32, 1557–1560. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Kim, D.S.H.L. Discovery of Natural Products from Curcuma Longa That Protect Cells from Beta-Amyloid Insult: A Drug Discovery Effort against Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1227–1231. [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, R.; Tamura, Y.; Yamanaka, H.; Kikuzaki, H.; Nakatani, N. Two Curcuminoid Pigments from Curcuma Domestica. Phytochemistry 1993, 33, 501–502. [CrossRef]
- Park, B.-S.; Kim, J.-G.; Kim, M.-R.; Lee, S.-E.; Takeoka, G.R.; Oh, K.-B.; Kim, J.-H. Curcuma Longa L. Constituents Inhibit Sortase A and Staphylococcus Aureus Cell Adhesion to Fibronectin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9005–9009. [CrossRef]
- Dosoky, N.S.; Setzer, W.N. Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of Essential Oils of Curcuma Species. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1196. [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Ji, S.; Li, R.; Dong, Y.; Qiao, X.; Hu, H.; Yang, W.; Guo, D.; Tu, P.; Ye, M. Terpecurcumins A–I from the Rhizomes of Curcuma Longa: Absolute Configuration and Cytotoxic Activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 2121–2131. [CrossRef]
- Núñez, N.; Vidal-Casanella, O.; Sentellas, S.; Saurina, J.; Núñez, O. Characterization, Classification and Authentication of Turmeric and Curry Samples by Targeted LC-HRMS Polyphenolic and Curcuminoid Profiling and Chemometrics. Molecules 2020, 25, 2942. [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.-C.; Cherng, C.-Y.; Jeng, J.-F.; Damu, A.G.; Teng, C.-M.; Lee, E.-J.; Wu, T.-S. Isolation of a Natural Antioxidant, Dehydrozingerone from Zingiber Officinale and Synthesis of Its Analogues for Recognition of Effective Antioxidant and Antityrosinase Agents. Arch Pharm Res 2005, 28, 518–528. [CrossRef]
- Imai, S.; Morikiyo, M.; Furihata, K.; Hayakawa, Y.; Seto, H. Turmeronol A and Turmeronol B, New Inhibitors of Soybean Lipoxygenase. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry 1990, 54, 2367–2371. [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.K. Sesquiterpenoids from the Rhizome OfCurcuma Zedoaria. Arch Pharm Res 2001, 24, 424–426. [CrossRef]
- Kuroyanagi, M.; Ueno, A.; Koyama, K.; Natori, S. Structures of Sesquiterpenes of Curcuma Aromatica SALISB. II. : Studies on Minor Sesquiterpenes. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 1990, 38, 55–58. [CrossRef]
- Mohn, T.; Plitzko, I.; Hamburger, M. A Comprehensive Metabolite Profiling of Isatis Tinctoria Leaf Extracts. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 924–934. [CrossRef]
- Su, B.-N.; Park, E.J.; Nikolic, D.; Vigo, J.S.; Graham, J.G.; Cabieses, F.; van Breemen, R.B.; Fong, H.H.S.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Pezzuto, J.M.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Miscellaneous Secondary Metabolites of Deprea Subtriflora. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1089–1093. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, F.; Li, M.Z.; Chen, L.X.; Qiu, F. Diarylheptanoids from the Rhizomes of Curcuma Kwangsiensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1667–1671. [CrossRef]
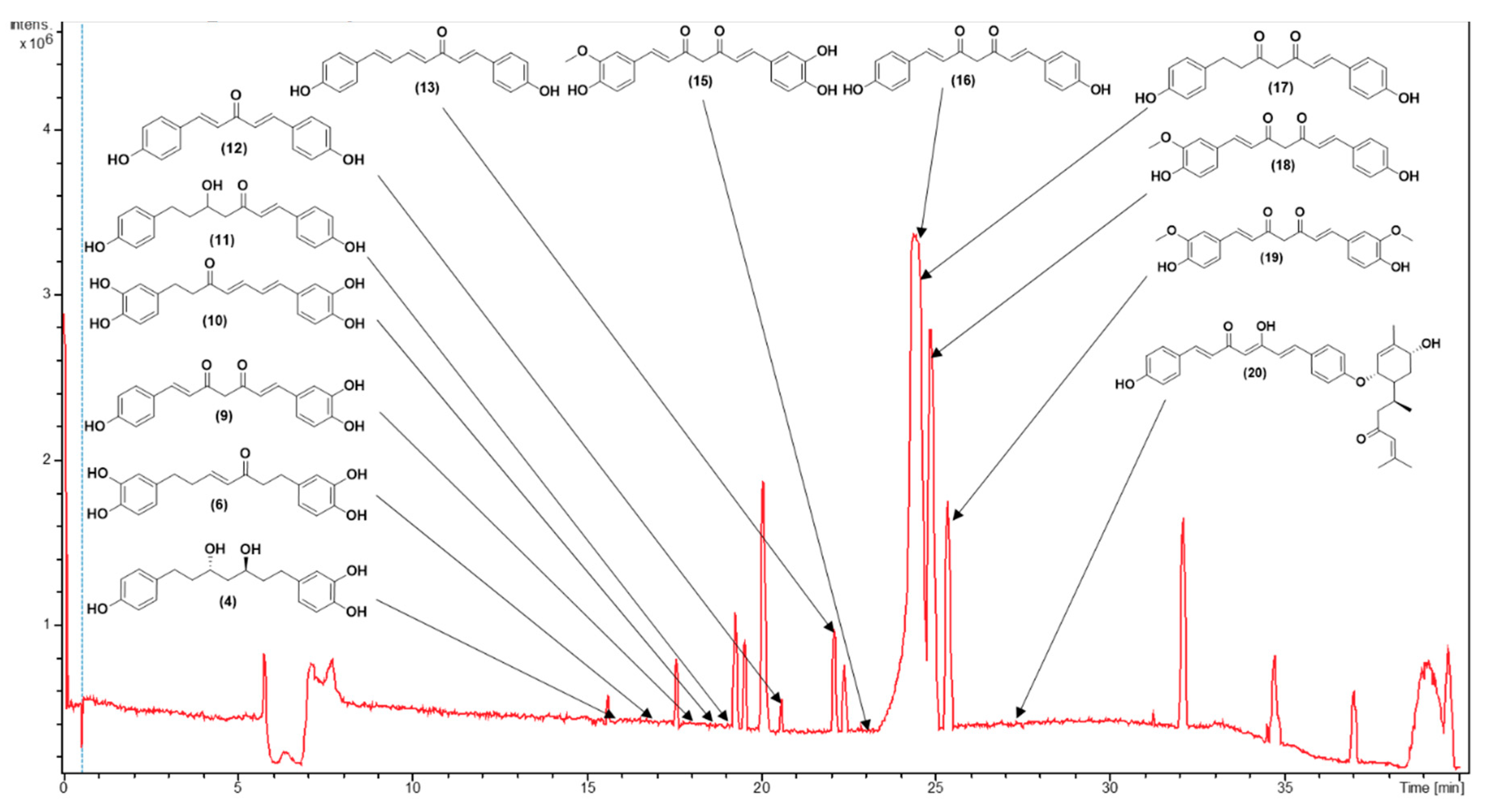
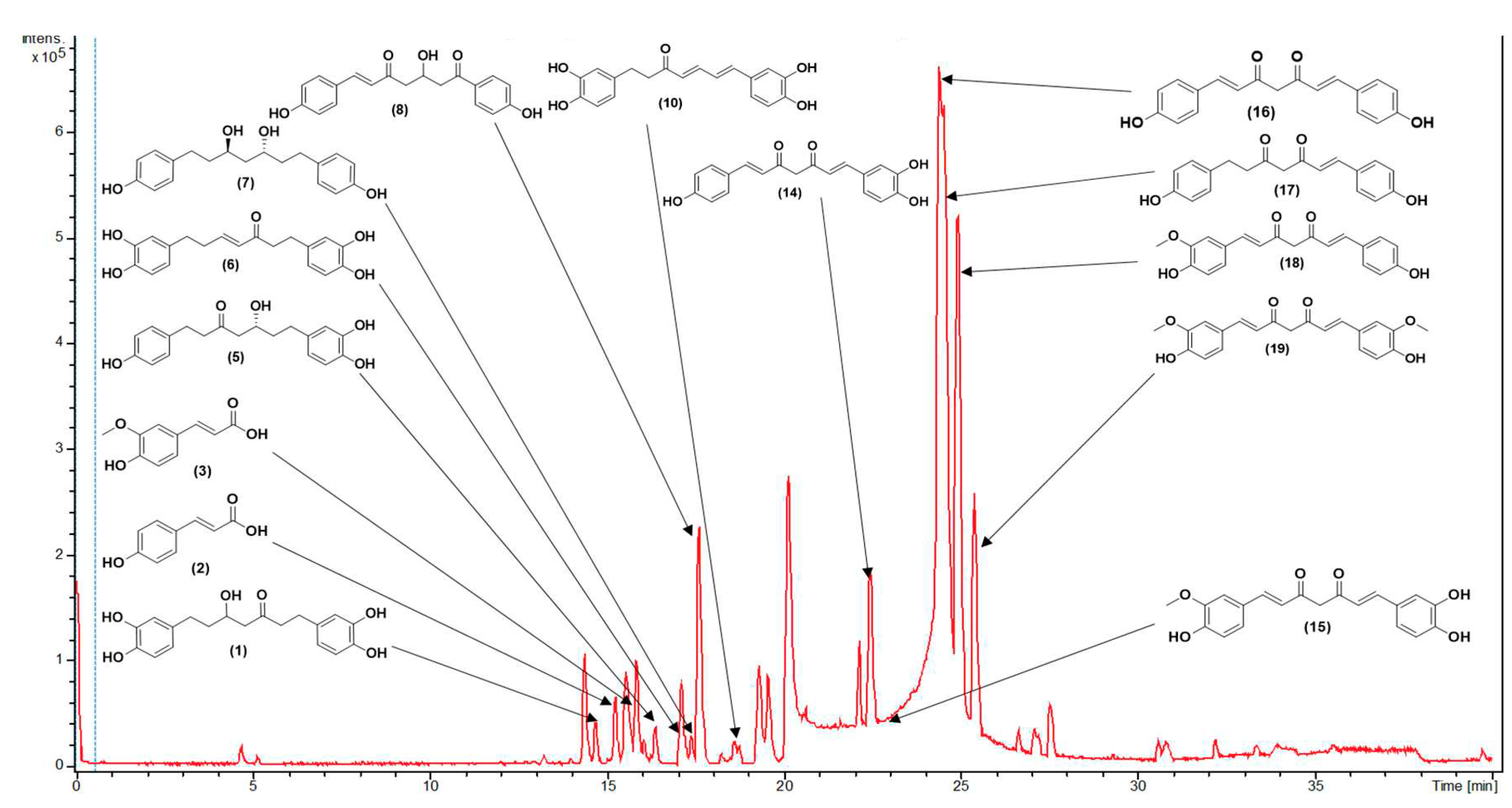
| C.N. | RT(Min) | Detected Ion/adduct | Observed m/z | Calculated m/z |
Error (ppm) |
RDBE | MS2 ion(m/z) | Mol. Formula | Predicted Metabolites | CSI:FingerID score (%) |
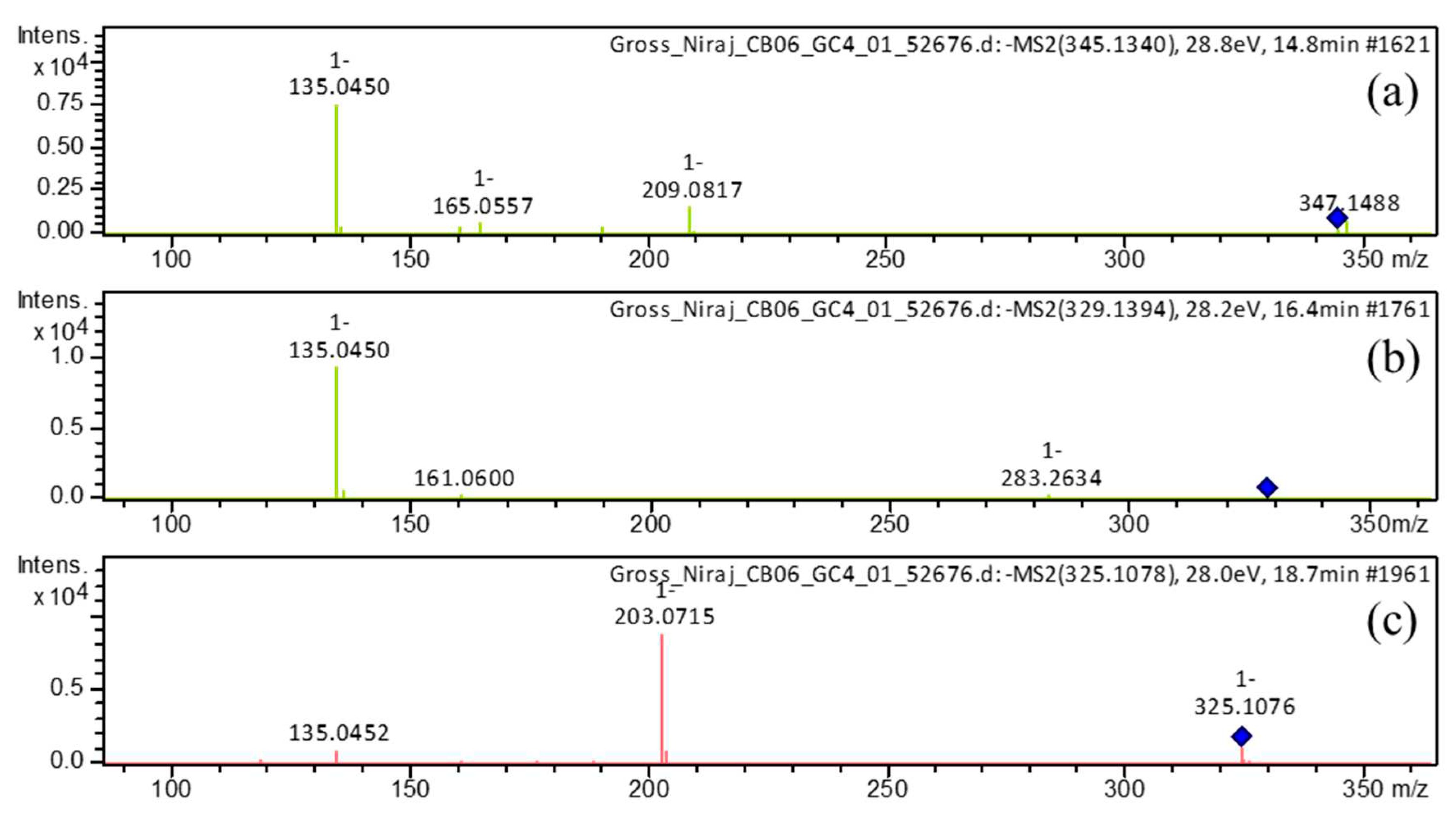
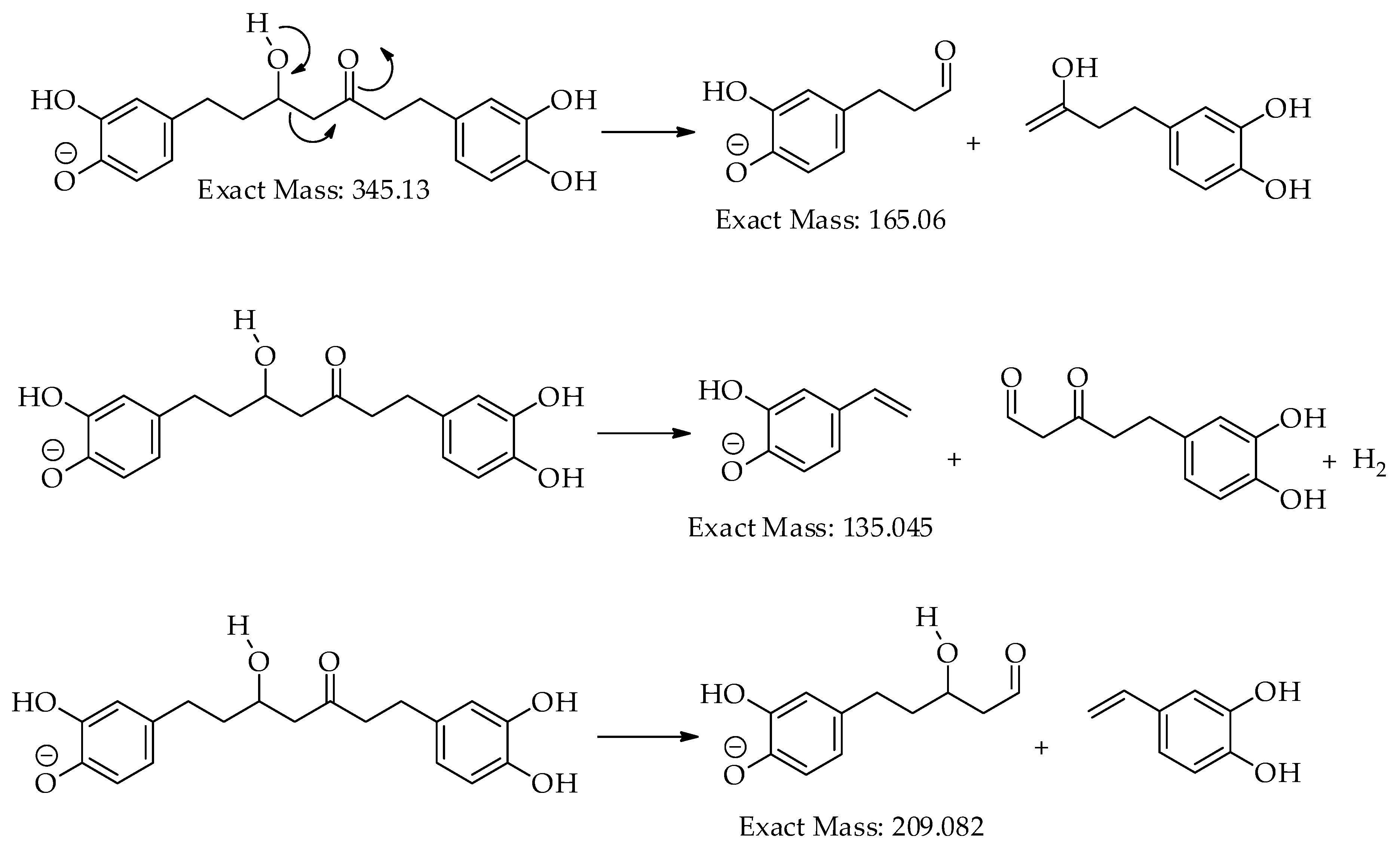
| 1 | 14.7 | [M-H]– | 345.1340 | 345.1344 | 0.9 | 9 | 345, 209, 191, 165, 161, 135 (bp) | C19H22O6 | 1,7-bis(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxyheptan-3-one | 81.08 |
| 2 | 15.3 | [M+H]+ | 165.0551 | 165.0546 | -2.8 | 6 | 147, 119 (bp), 91, 65 | C9H8O3 | 4-hydroxycinnamic acid | 97.08 |
| 15.3 | [M-H]– | 163.0401 | 163.0401 | -0.1 | 6 | 119 (bp), 93 | C9H8O3 | 4-hydroxycinnamic acid | 97.79 | |
| 3 | 15.7 | [M+H]+ | 195.0657 | 195.0652 | -2.7 | 6 | 177, 163, 149, 145 (bp), 134, 117, 106, 89 | C10H10O4 | Ferulic acid | 98.90 |
| 15.7 | [M-H]– | 193.0508 | 193.0506 | -1.0 | 6 | 178, 134 (bp) | C10H10O4 | Ferulic acid | 97.79 | |
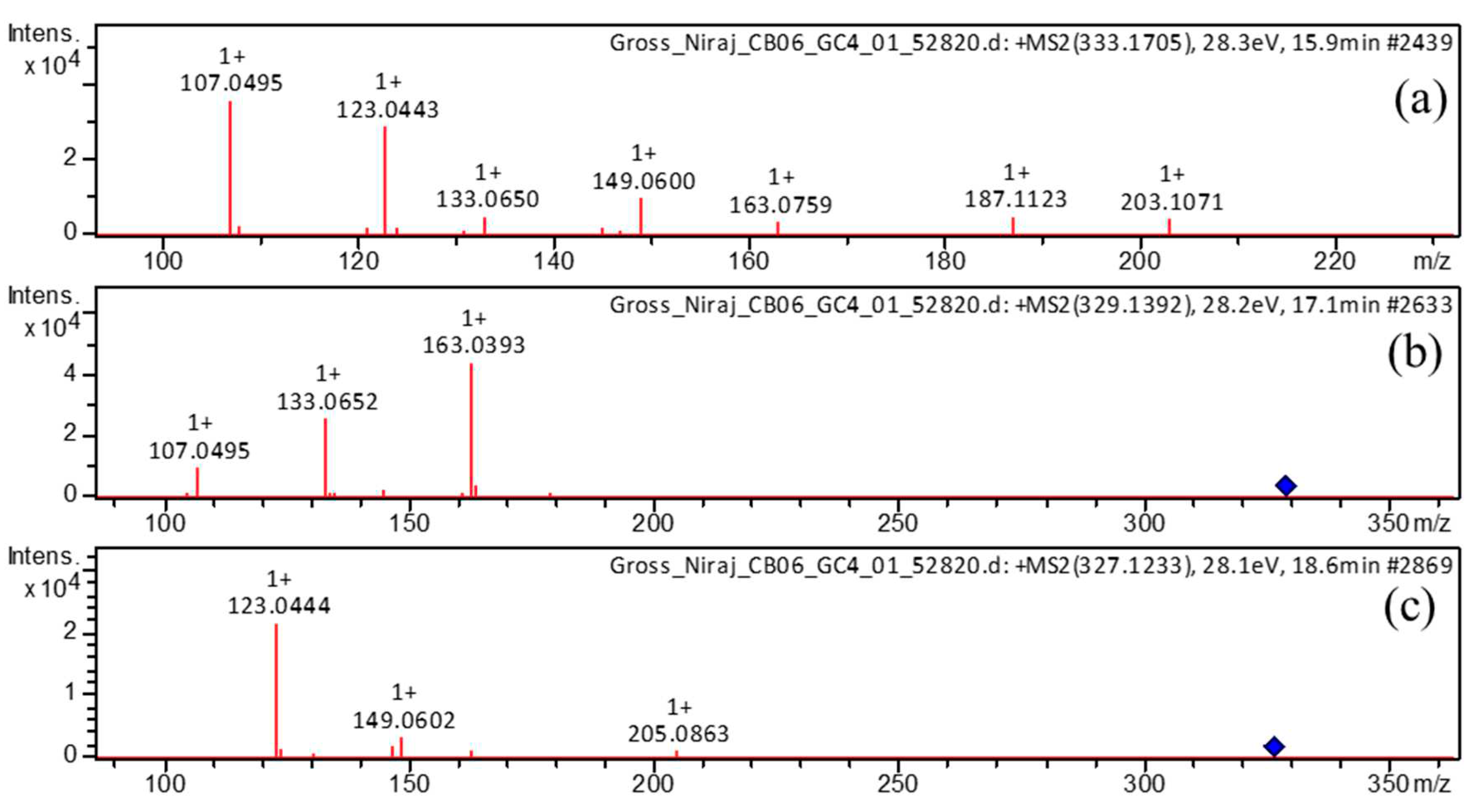
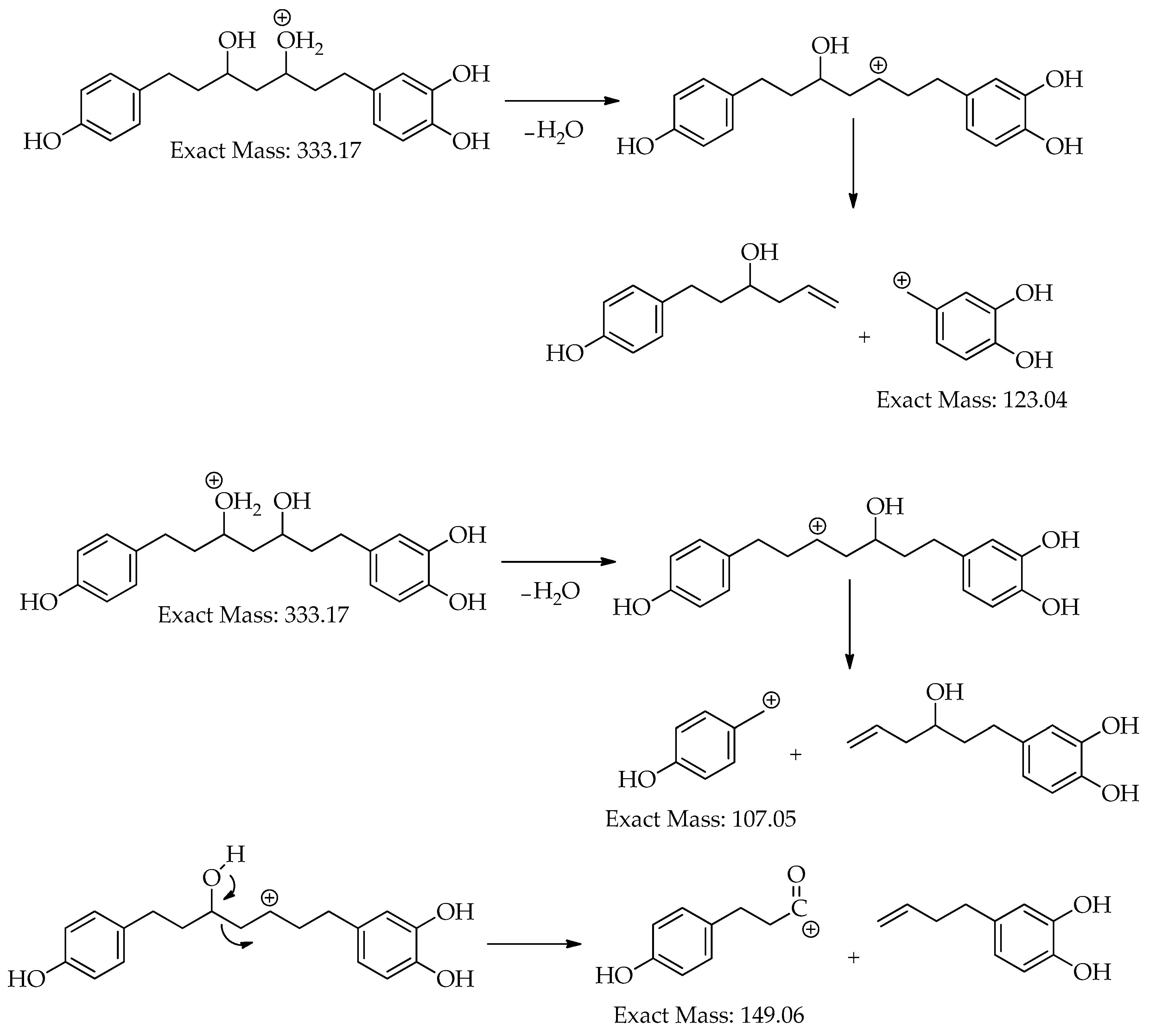
| 4 | 15.8 | [M+H]+ | 333.1705 | 333.1697 | -2.6 | 8 | 203, 187, 163, 149, 133, 123, 107 (bp) | C19H24O5 | 3,5-Dihydroxy-1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptane | 97.35 |
| 15.8 | [M-H]– | 331.1552 | 331.1551 | -0.2 | 8 | 331 (bp) | C19H24O5 | 3,5-Dihydroxy-1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)heptane | 93.65 | |
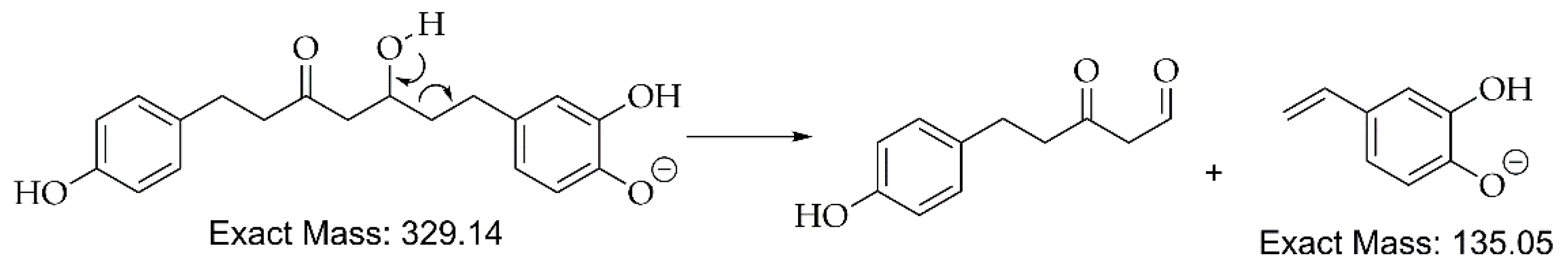
| 5 | 16.4 | [M-H]– | 329.1394 | 329.1394 | 0.0 | 9 | 283, 161, 135 (bp) |
C19H22O5 | 5-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-heptanone | 82.20 |
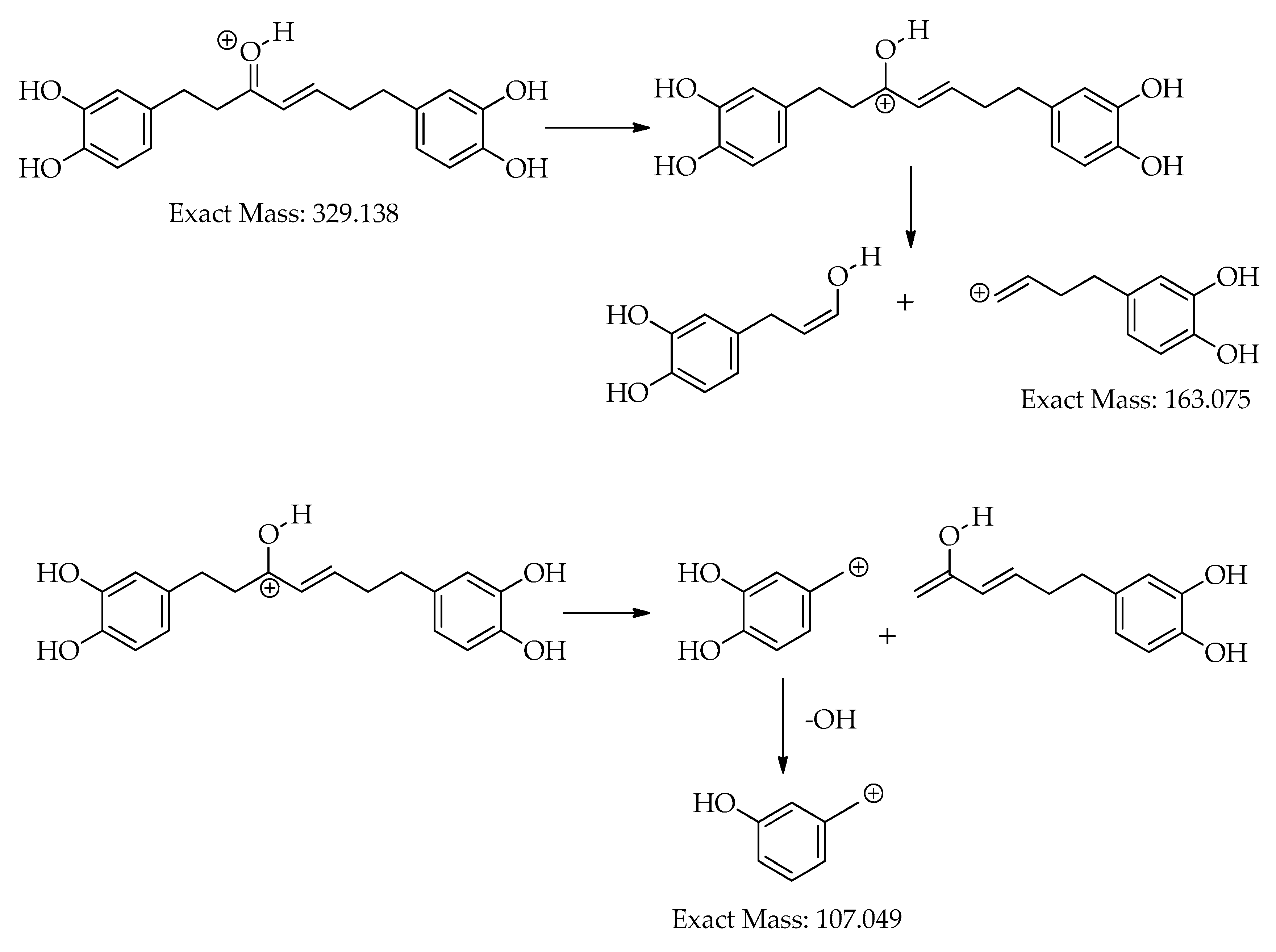
| 6 | 17.1 | [M+H]+ | 329.1392 | 329.1384 | -2.6 | 10 | 215, 179, 163 (bp), 145, 133, 107 | C19H20O5 | 1,7-bis(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)hept-4-en-3-one | 88.14 |
| 17.1 | [M-H]– | 327.1239 | 327.1238 | -0.4 | 10 | 177 (bp), 135 | C19H20O5 | 1,7-bis(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)hept-4-en-3-one | 71.43 | |
| 7 | 17.4 | [M-H]– | 315.1602 | 315.1602 | 0.0 | 8 | 193, 163, 149 (bp), 147, 121, 112, 106, 93 |
C19H24O4 | (3R,5R)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3,5-heptanediol | 95.42 |
| 8 | 17.7 | [M-H]– | 325.1082 | 325.1081 | 0.0 | 11 | 307, 239, 213, 187, 161, 145 (bp), 135, 119, 93, 68 | C19H18O5 | 3-hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-6-heptene-1,5-dione | 73.39 |
| 9 | 18.3 | [M+H]+ | 325.1080 | 325.1071 | -3.0 | 12 | 279, 241, 223, 189, 163, 147 (bp), 131, 107 | C19H16O5 | 1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-1,6-heptadiene-3,5-dione | 61.61 |
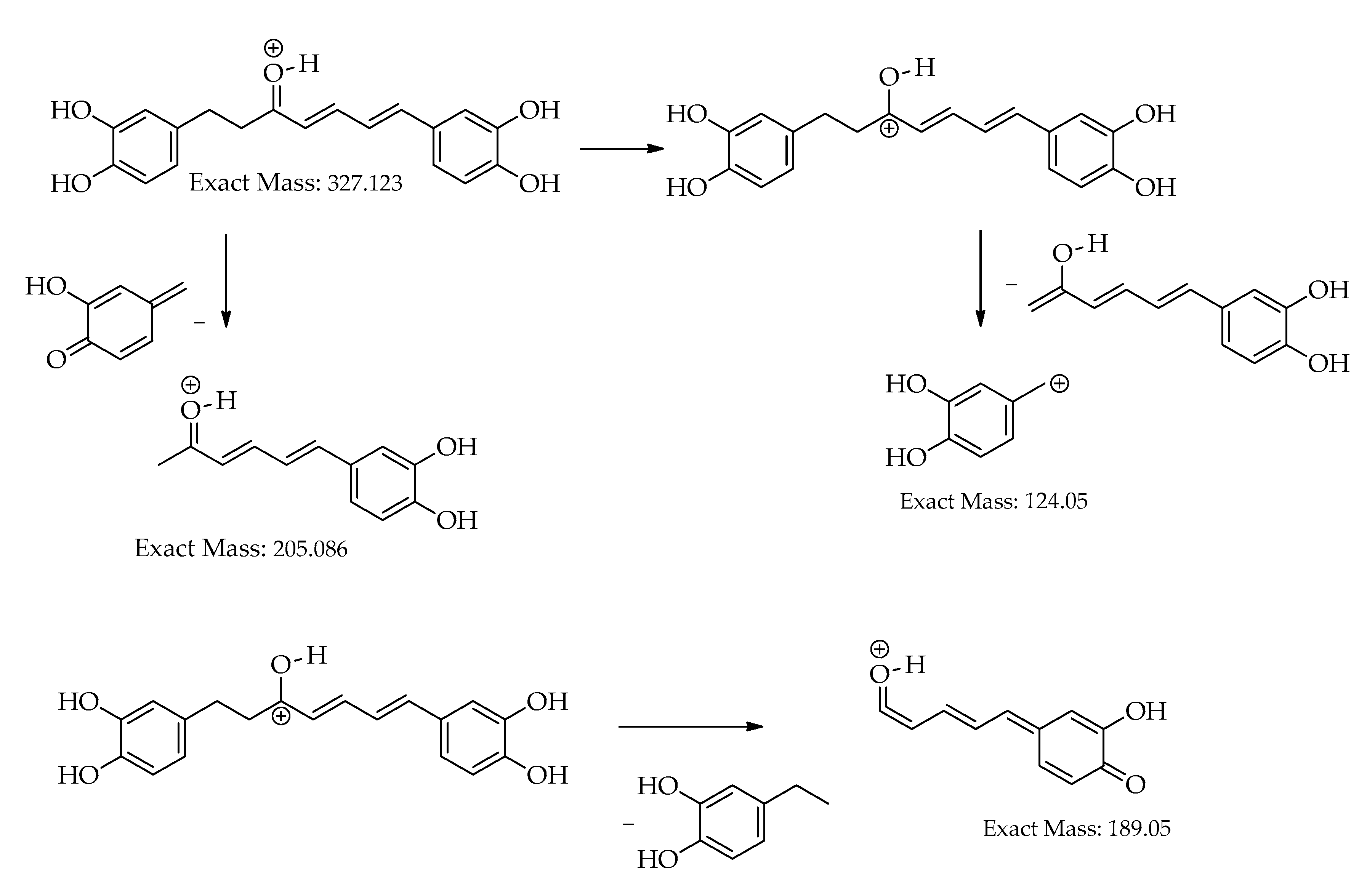
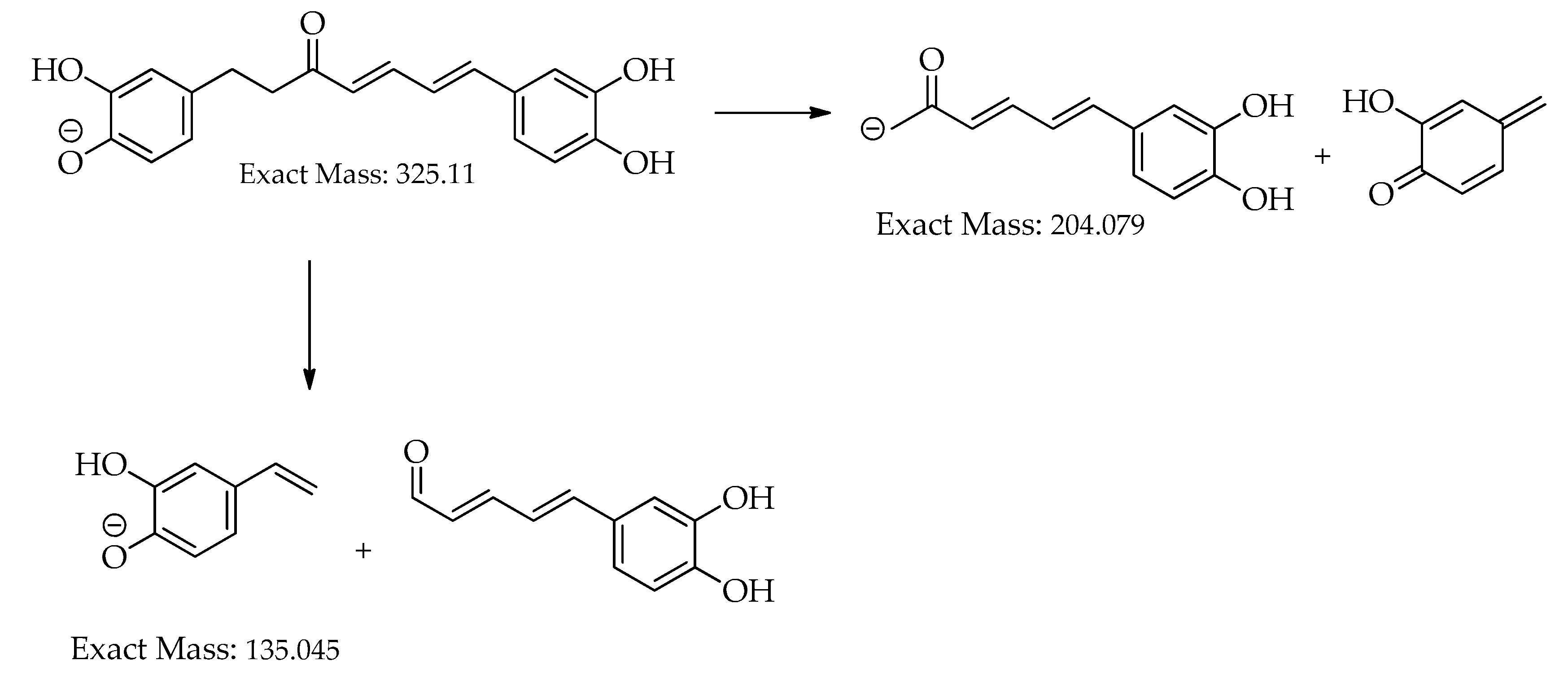
| 10 | 18.6 | [M+H]+ | 327.1233 | 327.1227 | -1.9 | 11 | 257, 205, 189, 163, 149, 131, 123 (bp) | C19H18O5 | 1,7-bis(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)hepta-4,6-dien-3-one | 80.73 |
| 18.7 | [M-H]– | 325.1081 | 325.1081 | 0.0 | 11 | 325,203 (bp),135,119 | C19H18O5 | 1,7-bis(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)hepta-4,6-dien-3-one | 80.77 | |
| 11 | 18.7 | [M+H]+ | 313.1441 | 313.1441 | -2.2 | 10 | 235, 193, 163, 147 (bp), 133, 119, 107 | C19H20O4 | 5-hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hept-1-en-3-one | 63.93 |
| 18.8 | [M-H]– | 311.1288 | 311.1289 | 0.3 | 10 | 311, 190, 174, 161 (bp), 149, 119 | C19H20O4 | 5-hydroxy-1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hept-1-en-3-one | 65.42 | |
| 12 | 20.6 | [M+H]+ | 267.1021 | 267.1016 | -2.1 | 11 | 249, 231, 199, 173, 147 (bp), 119, 107, 91 | C17H14O3 | 1,5-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4-pentadien-3-one |
78.98 |
| 13 | 22.2 | [M+H]+ | 293.1178 | 293.1172 | -2.1 | 12 | 225, 199, 181, 147, 131, 121, 107 (bp) | C19H16O3 | 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4,6-heptatrien-3-one | 69.23 |
| 22.2 | [M-H]– | 291.1029 | 291.1027 | -0.5 | 12 | 291, 249, 223, 211, 197, 185, 171(bp), 145, 119, 93 | C19H16O3 | 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4,6-heptatrien-3-one | 66.48 | |
| 14 | 22.4 | [M-H]– | 323.0928 | 323.0925 | -1.2 | 12 | 159, 143, 135 (bp), 119 | C19H16O5 | 1-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-7-(4-hydroxyphenyl)hepta-1,6-diene-3,5-dione | 59.09 |
| 15 | 22.8 | [M+H]+ | 355.1185 | 355.1176 | -2.5 | 12 | 353, 305, 271 (bp), 253, 239, 211, 177, 163, 145, 119, 68 | C20H18O6 | Monodemethylcurcumin | 75.54 |
| 22.8 | [M-H]– | 353.1034 | 353.1031 | -1.1 | 12 | 307, 217, 187, 173, 158, 145, 135 (bp), 119 | C20H18O6 | Monodemethylcurcumin | 75.56 | |
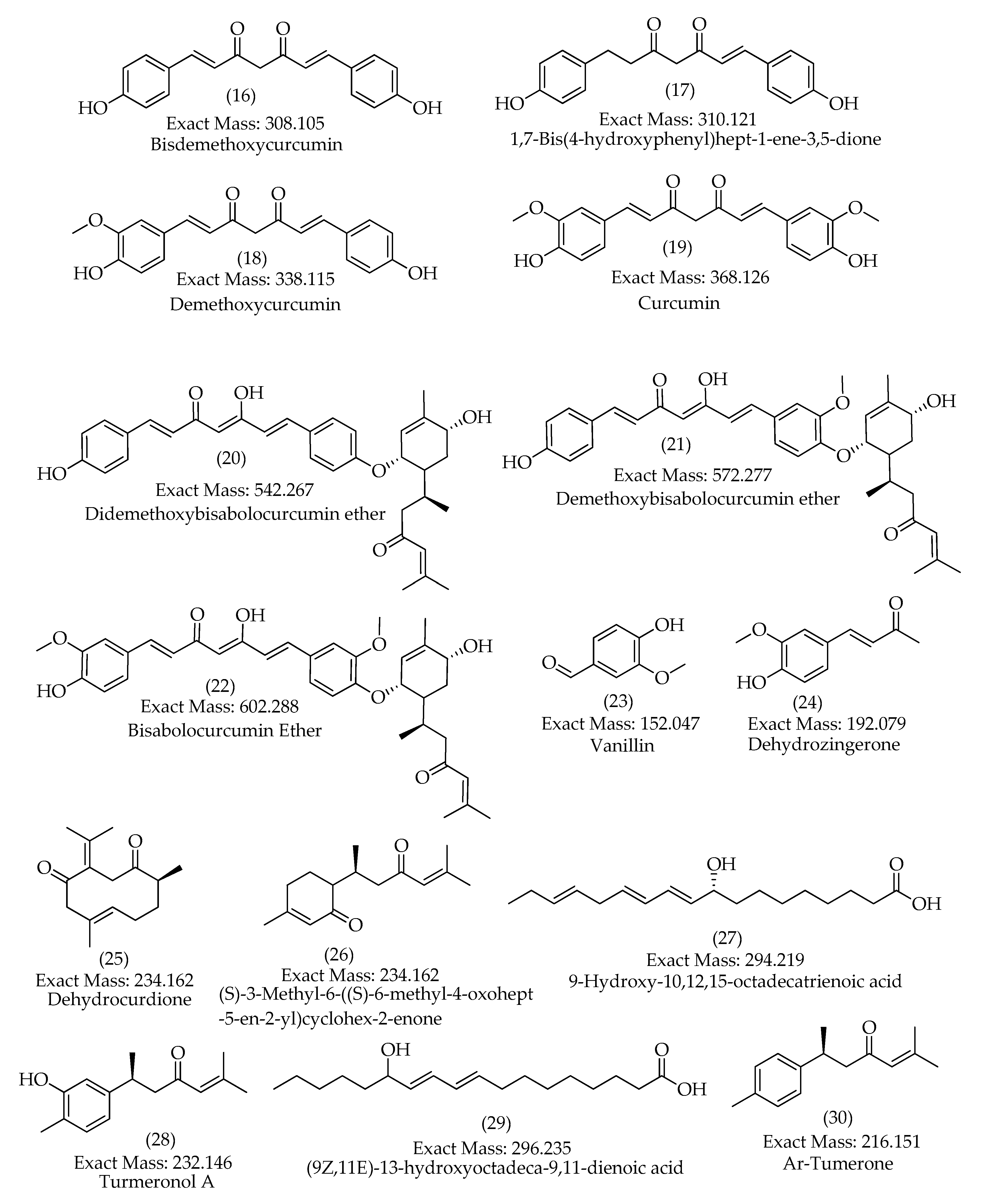
| 16 | 23.9 | [M+H]+ | 309.1127 | 309.1121 | -1.7 | 12 | 225, 205, 189, 147 (bp), 131, 119, 107 | C19H16O4 | Bisdemethoxycurcumin | 93.42 |
| 24.2 | [M-H]– | 307.0979 | 307.0976 | -0.7 | 12 | 187, 143, 119 (bp) | C19H16O4 | Bisdemethoxycurcumin | 96.13 | |
| 17 | 24.2 | [M+H]+ | 311.1280 | 311.1278 | -0.8 | 11 | 225, 205, 189, 147 (bp), 131, 119, 107 | C19H18O4 | 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hept-1-ene-3,5-dione | 75.56 |
| 24.2 | [M-H]– | 309.1132 | 309.1132 | 0.2 | 11 | 189, 187, 161, 145, 143, 119 (bp) | C19H18O4 | 1,7-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hept-1-ene-3,5-dione | 80.43 | |
| 18 | 24.8 | [M+H]+ | 339.1229 | 339.1227 | -0.6 | 12 | 289, 255, 195, 177 (bp), 147, 131, 119, 107 | C20H18O5 | Demethoxycurcumin | 99.50 |
| 25.0 | [M-H]– | 337.1085 | 337.1081 | -1.0 | 12 | 217, 202, 187, 173, 158, 149, 119 (bp) | C20H18O5 | Demethoxycurcumin | 98.07 | |
| 19 | 25.3 | [M+H]+ | 369.1337 | 369.1333 | -1.2 | 12 | 285, 268, 225, 177 (bp), 161, 145, 137, 117 | C21H20O6 | Curcumin | 95.00 |
| 25.3 | [M-H]– | 367.1190 | 367.1187 | -0.7 | 12 | 217, 202, 173, 158, 149 (bp), 134, 119 | C21H20O6 | Curcumin | 100 | |
| 20 | 27.0 | [M+H]+ | 543.2747 | 543.2741 | -1.2 | 16 | 349, 309, 229, 189, 147 (bp), 119 | C34H38O6 | Didemethoxybisabolocurcumin ether | 63.29 |
| 21 | 30.1 | [M+Na]+ | 595.2675 | - | - | - | 360, 257 (bp), 239 | C35H40O7 | Demethoxybisabolocurcumin ether | - |
| 22 | 30.7 | [M+Na]+ | 625.2786 | - |
- | - | 301, 294, 257 (bp), 239 | C36H42O8 | Bisabolocurcumin Ether |
- |
| C.N. | RT(Min) | Detected Ion/adduct | Observed m/z | Calculated m/z | Error (ppm) |
RDBE | MS2 ion(m/z) | Mol. Formula | Predicted Metabolites | CSI:FingerID score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23 |
16.0 | [M+H]+ | 153.0547 | 153.0546 | -0.7 | 5 | 125, 111, 93(bp),65 |
C8H8O3 | Vanillin | 98.80 |
| 16.0 | [M-H]– | 151.0339 | 151.0401 | 1.1 | 5 | 136(bp), 108, 92 | C8H8O3 | Vanillin | 92.81 | |
| 24 | 18.2 | [M-H]– | 191.0712 | 191.0714 | 0.7 | 6 | 176(bp), 148, 133 | C11H12O3 | Dehydrozingerone | 98.29 |
| 25 | 24.5 | [M+H]+ | 235.1688 | 235.1693 | 1.8 | 5 | 161, 135, 121, 119(bp), 107, 105, 93, 83 |
C15H22O2 | Dehydrocurdione | 65.84 |
| 26 | 26.4 | [M+H]+ | 235.1697 | 235.1693 | -2.0 | 5 | 231, 213, 198, 175, 158, 147, 133(bp), 107, 97 | C15H22O2 | (6s)-6-methyl-5-(3-oxobutyl)-2-(propan-2-ylidene)cyclohept-4-en-1-one | 63.92 |
| 27 | 28.0 | [M-H]– | 293.2125 | 293.2122 | -1.0 | 4 | 293, 275(bp), 235, 231, 223, 183, 171, 121 | C18H30O3 | 9-Hydroxy-10,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid | 98.76 |
| 28 | 28.5 | [M+H]+ | 233.1534 | 233.1536 | 0.7 | 6 | 145, 135, 131, 120, 119(bp), 117, 91, 83 | C15H20O2 | Turmeronol A | 49.50 |
| 29 | 29.6 | [M-H]– | 295.2282 | 295.2279 | -1.3 | 3 | 295, 277(bp), 195, 183, 171 | C18H32O3 | Coriolic acid | 95.76 |
| 30 | 31.2 | [M+H]+ | 217.1588 | 217.1587 | -0.3 | 6 | 120, 119(bp), 117, 109, 103, 91, 83, 67 | C15H20O | Ar-Tumerone | 93.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





